Multiplex Assay for Rapid Detection and Analysis of Nucleic Acid Using Barcode Receptor Encoded Particle (BREP)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
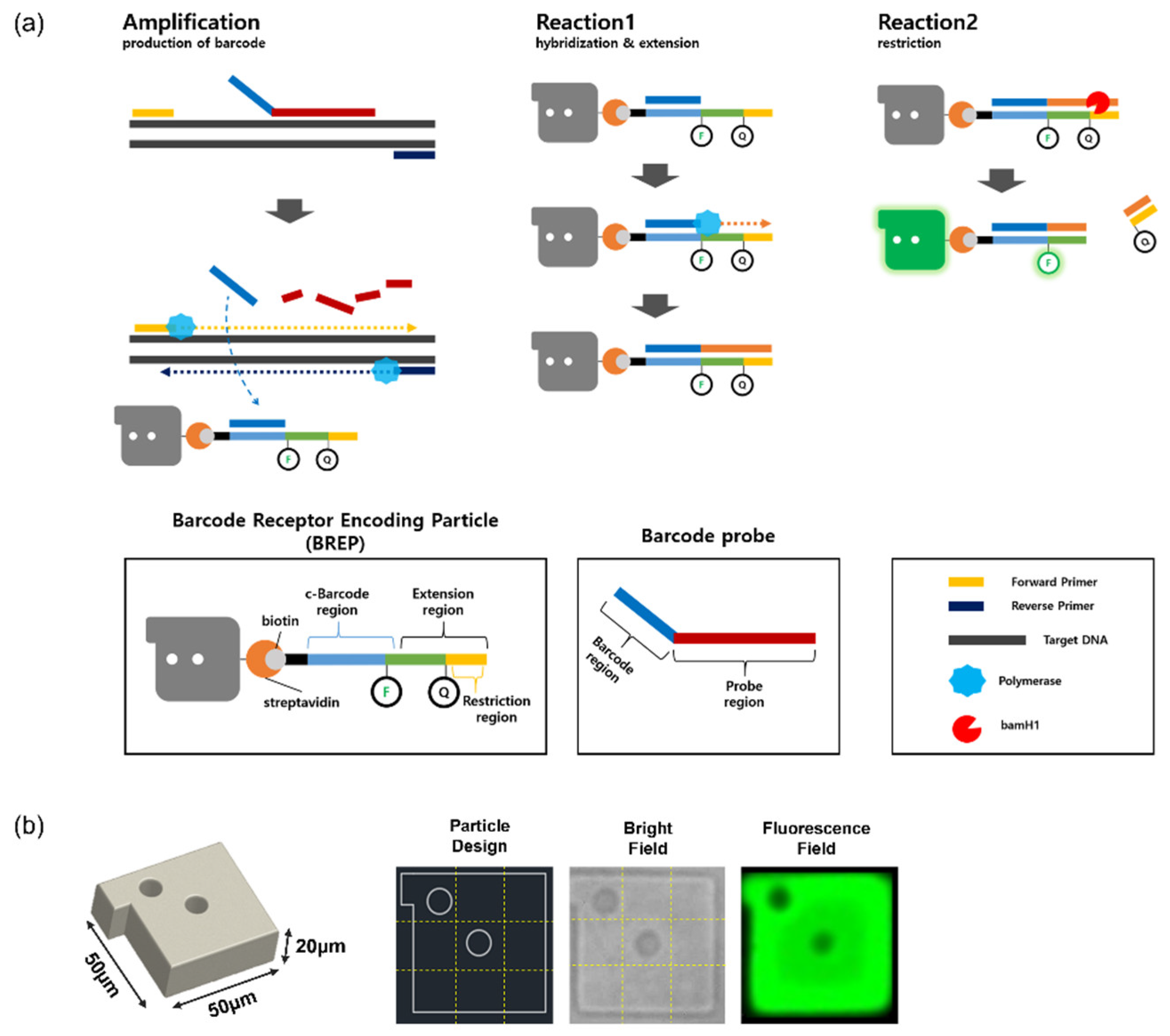
2.2. BREP Assay Design
- (1)
- Amplification: generation of barcode
- (2)
- Reaction 1: hybridization and extension
- (3)
- Reaction 2: restriction
2.3. Hydrogel Particle Synthesis
2.4. Barcode Receptor Immobilization on Streptavidin Functionalized Hydrogel Particles
2.5. BREP Assay
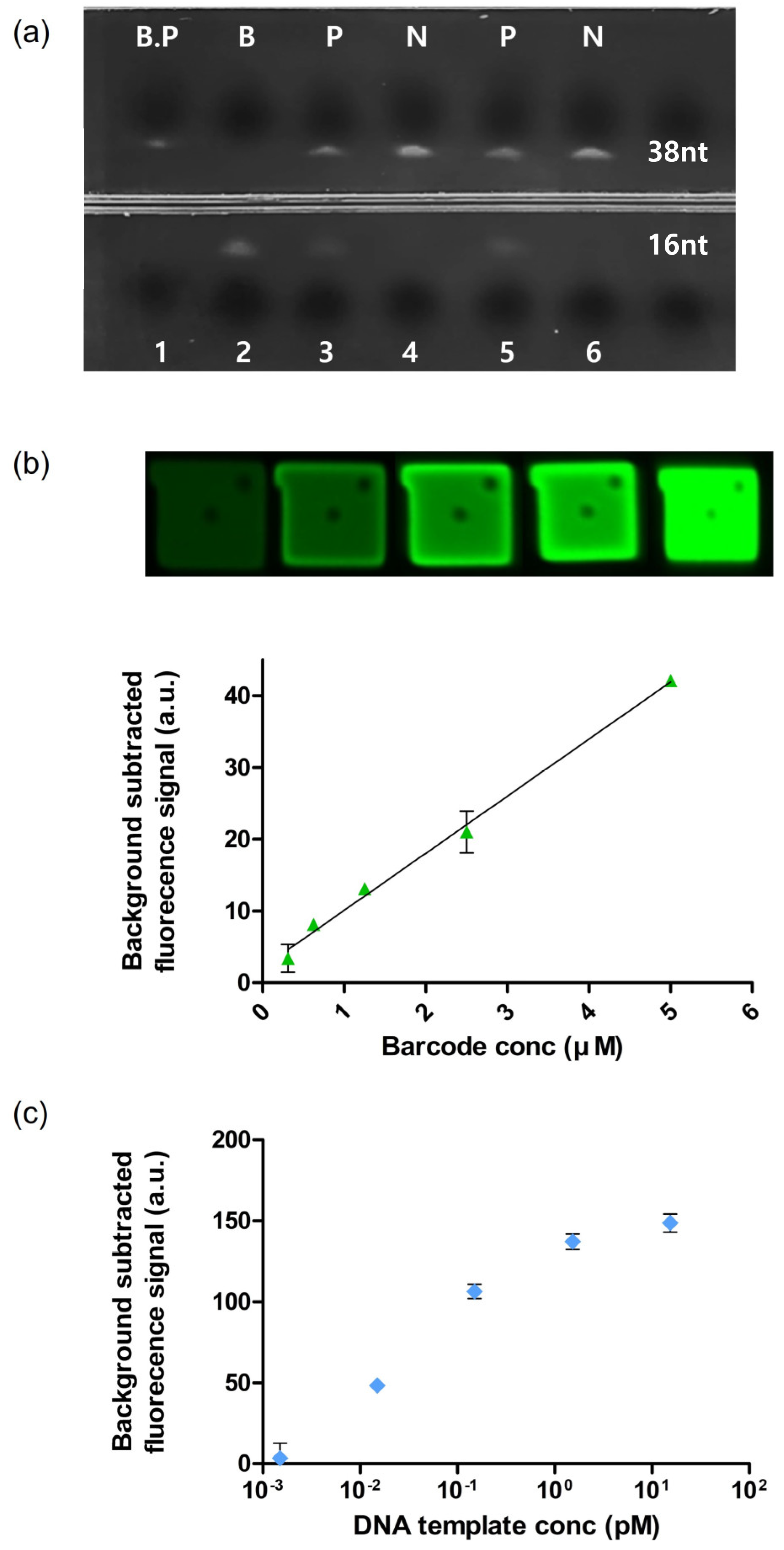
2.6. Validation of Barcode Generation
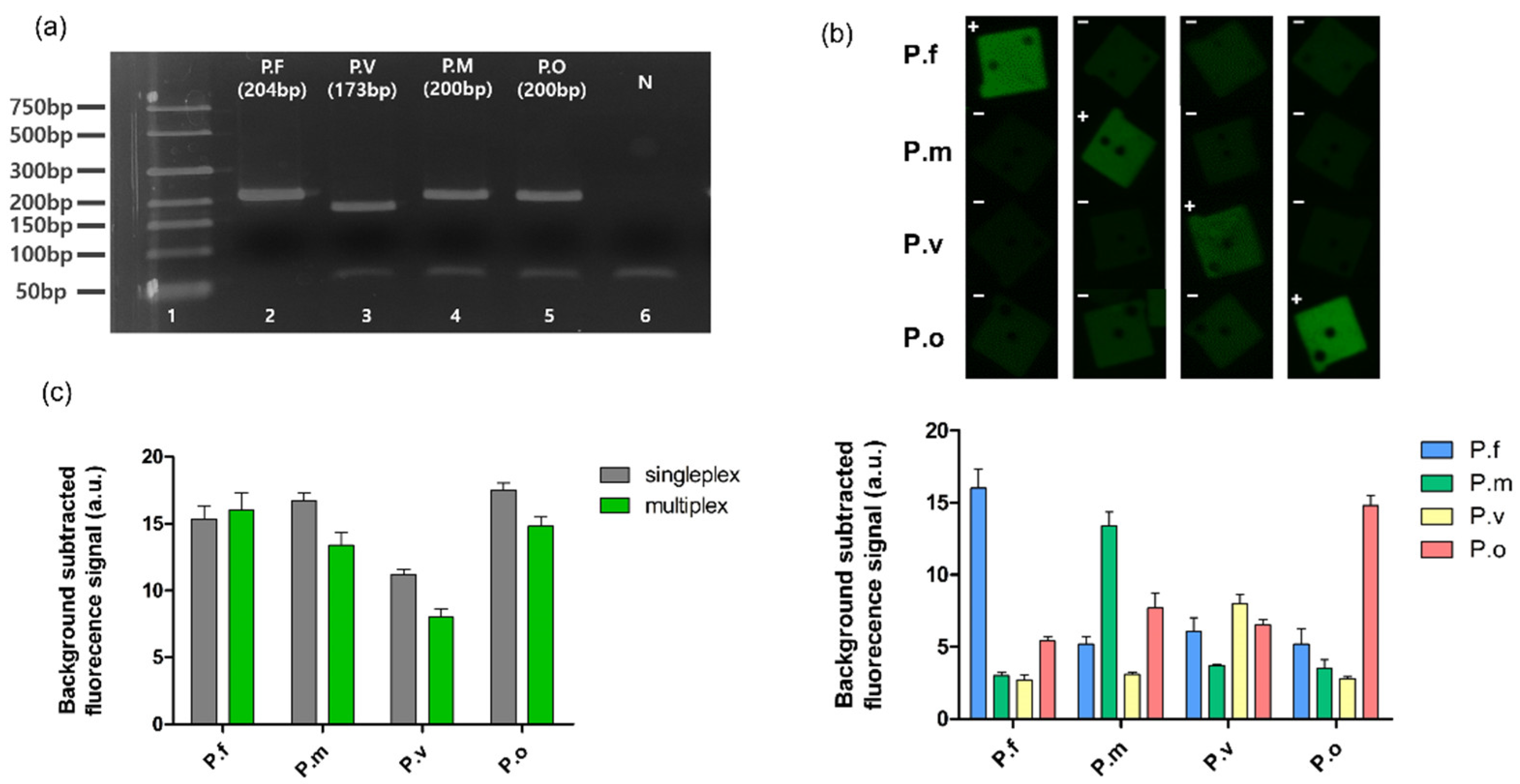
2.7. Multiplexed Detection of Malarial Species
2.8. Analysis of Fluorescence Intensity of BREP
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis of BREP
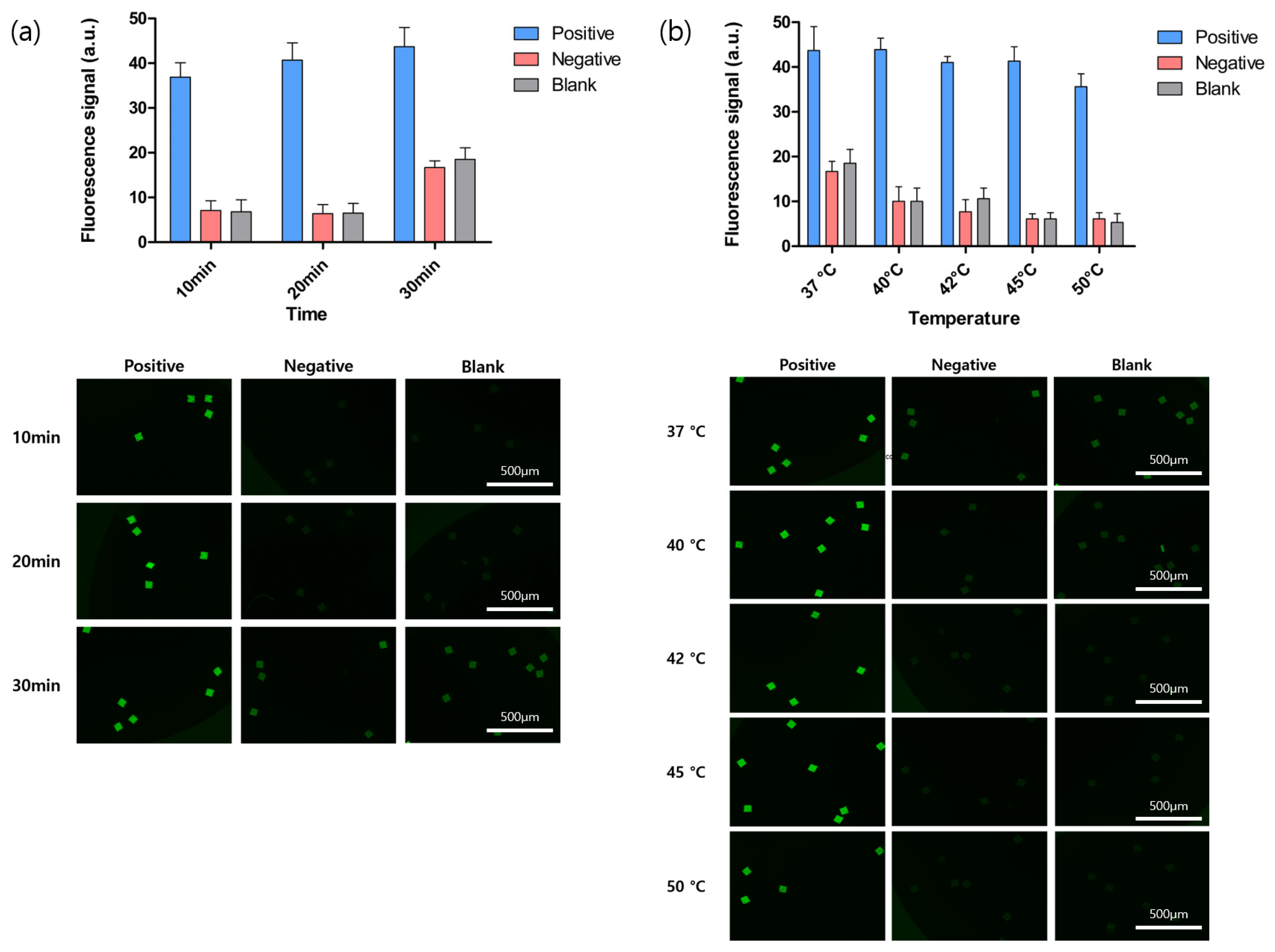
3.2. BREP Assay Optimization
3.3. Validation of BREP Assay
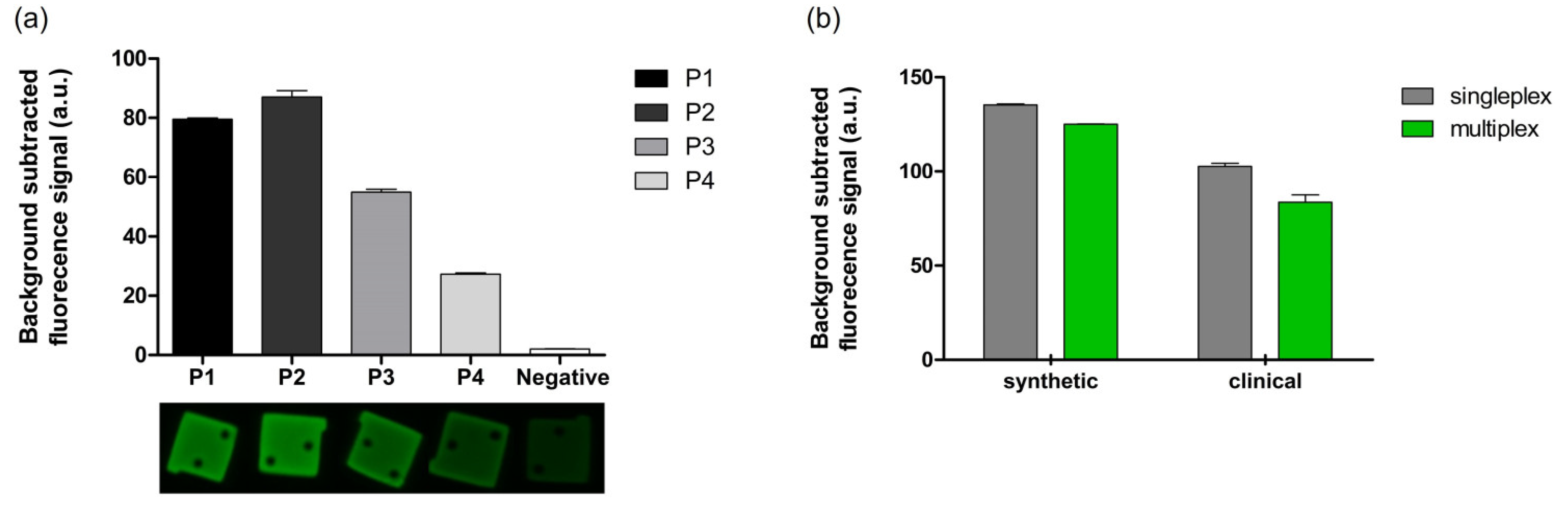
3.4. Multiplexed Detection of Malaria Species
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deshpande, A.; White, P.S. Multiplexed nucleic acid-based assays for molecular diagnostics of human disease. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2012, 12, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, J.P.; Sklar, L.A. Suspension array technology: Evolution of the flat-array paradigm. Trends Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashour, H.M.; Elkhatib, W.F.; Rahman, M.M.; Elshabrawy, H.A. Insights into the recent 2019 novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) in light of past human coronavirus outbreaks. Pathogens 2020, 9, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yao, H.; Xu, X.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, M.; Shao, J.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, H. Limits of Detection of 6 Approved RT–PCR Kits for the Novel SARS-Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2). Clin. Chem. 2020, 66, 977–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontanet, A.; Autran, B.; Lina, B.; Kieny, M.P.; Karim, S.S.A.; Sridhar, D. SARS-CoV-2 variants and ending the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet 2021, 397, 952–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, M.; Shayestehpour, M.; Mirzaei, H. The impact of spike mutated variants of SARS-CoV2 [Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, and Lambda] on the efficacy of subunit recombinant vaccines. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 25, 101606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dikdan, R.J.; Marras, S.A.; Field, A.P.; Brownlee, A.; Cironi, A.; Hill, D.A.; Tyagi, S. Multiplex PCR assays for identifying all major severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 variants. J. Mol. Diagn. 2022, 24, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, A.; Gans, J.; Graves, S.W.; Green, L.; Taylor, L.; Kim, H.B.; Kunde, Y.A.; Leonard, P.M.; Li, P.-E.; Mark, J. A rapid multiplex assay for nucleic acid-based diagnostics. J. Microbiol. Methods 2010, 80, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicewarner-Peña, S.R.; Freeman, R.G.; Reiss, B.D.; He, L.; Peña, D.J.; Walton, I.D.; Cromer, R.; Keating, C.D.; Natan, M.J. Submicrometer Metallic Barcodes. Science 2001, 294, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.; Yoo, S.M.; Yoon, I.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, B. Patterned multiplex pathogen DNA detection by Au particle-on-wire SERS sensor. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 1189–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkel, N.H.; Lou, X.; Wang, C.; He, L. Peer Reviewed: Barcoding the Microworld; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Pregibon, D.C.; Doyle, P.S. Optimization of Encoded Hydrogel Particles for Nucleic Acid Quantification. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 4873–4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braeckmans, K.; De Smedt, S.C.; Leblans, M.; Pauwels, R.; Demeester, J. Encoding microcarriers: Present and future technologies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2002, 1, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadgil, C.; Yeckel, A.; Derby, J.J.; Hu, W.-S. A diffusion–reaction model for DNA microarray assays. J. Biotechnol. 2004, 114, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teles, F.; Fonseca, L. Trends in DNA biosensors. Talanta 2008, 77, 606–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stears, R.L.; Martinsky, T.; Schena, M. Trends in microarray analysis. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schena, M. Genome analysis with gene expression microarrays. Bioessays 1996, 18, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battersby, B.J.; Lawrie, G.A.; Trau, M. Optical encoding of microbeads for gene screening: Alternatives to microarrays. Drug Discov. Today 2001, 6, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Goff, G.C.; Srinivas, R.L.; Hill, W.A.; Doyle, P.S. Hydrogel microparticles for biosensing. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 72, 386–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birtwell, S.; Morgan, H. Microparticle encoding technologies for high-throughput multiplexed suspension assays. Integr. Biol. 2009, 1, 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunbar, S.A. Applications of Luminex® xMAP™ technology for rapid, high-throughput multiplexed nucleic acid detection. Clin. Chim. Acta 2006, 363, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tackett, M.R.; Diwan, I. Using FirePlex(™) Particle Technology for Multiplex MicroRNA Profiling Without RNA Purification. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1654, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fotin, A.V.; Drobyshev, A.L.; Proudnikov, D.Y.; Perov, A.N.; Mirzabekov, A.D. Parallel thermodynamic analysis of duplexes on oligodeoxyribonucleotide microchips. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998, 26, 1515–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wambua, P.; Ivens, J.; Verpoest, I. Natural fibres: Can they replace glass in fibre reinforced plastics? Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dundas, C.M.; Demonte, D.; Park, S. Streptavidin–biotin technology: Improvements and innovations in chemical and biological applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 9343–9353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Zhu, J.; Van Eyk, J.E. Comparison of multiplex immunoassay platforms. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. World Malaria Report 2021; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rubio, J.M.; Benito, A.; Roche, J.; Berzosa, P.J.; García, M.L.; Micó, M.; Edú, M.; Alvar, J. Semi-nested, multiplex polymerase chain reaction for detection of human malaria parasites and evidence of Plasmodium vivax infection in Equatorial Guinea. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1999, 60, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amexo, M.; Tolhurst, R.; Barnish, G.; Bates, I. Malaria misdiagnosis: Effects on the poor and vulnerable. Lancet 2004, 364, 1896–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Cao, X.E.; Finkelstein, J.L.; Cárdenas, W.B.; Erickson, D.; Mehta, S. A two-colour multiplexed lateral flow immunoassay system to differentially detect human malaria species on a single test line. Malar. J. 2019, 18, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for the Treatment of Malaria, 3rd ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Veron, V.; Simon, S.; Carme, B. Multiplex real-time PCR detection of P. falciparum, P. vivax and P. malariae in human blood samples. Exp. Parasitol. 2009, 121, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padley, D.; Moody, A.H.; Chiodini, P.L.; Saldanha, J. Use of a rapid, single-round, multiplex PCR to detect malarial parasites and identify the species present. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 2003, 97, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamau, E.; Tolbert, L.S.; Kortepeter, L.; Pratt, M.; Nyakoe, N.; Muringo, L.; Ogutu, B.; Waitumbi, J.N.; Ockenhouse, C.F. Development of a highly sensitive genus-specific quantitative reverse transcriptase real-time PCR assay for detection and quantitation of plasmodium by amplifying RNA and DNA of the 18S rRNA genes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 2946–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Jung, S.; Byoun, M.S.; Yoo, C.; Sim, S.J.; Lim, C.S.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, S.K. Multiplex real-time PCR using temperature sensitive primer-supplying hydrogel particles and its application for malaria species identification. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, S.; Bong, K.W.; Na, W. Multiplex Assay for Rapid Detection and Analysis of Nucleic Acid Using Barcode Receptor Encoded Particle (BREP). Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3246. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123246
Jung S, Bong KW, Na W. Multiplex Assay for Rapid Detection and Analysis of Nucleic Acid Using Barcode Receptor Encoded Particle (BREP). Biomedicines. 2022; 10(12):3246. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123246
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Semyung, Ki Wan Bong, and Wonhwi Na. 2022. "Multiplex Assay for Rapid Detection and Analysis of Nucleic Acid Using Barcode Receptor Encoded Particle (BREP)" Biomedicines 10, no. 12: 3246. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123246
APA StyleJung, S., Bong, K. W., & Na, W. (2022). Multiplex Assay for Rapid Detection and Analysis of Nucleic Acid Using Barcode Receptor Encoded Particle (BREP). Biomedicines, 10(12), 3246. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123246




