A Subset Screen of the Compounds Australia Scaffold Library Identifies 7-Acylaminodibenzoxazepinones as Potent and Selective Hits for Anti-Giardia Drug Discovery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Cultivation
2.2. Compounds
2.3. Primary Giardia Screen Compounds
2.4. Giardia Dose Response Assays
2.5. Mammalian Cell Cytotoxicity Assays
2.6. Anti-Bacterial Activity Assays
2.7. Minimum Lethal Concentration Assessments
2.8. Combination Studies
2.9. In Vivo Tolerability Assessments
3. Results
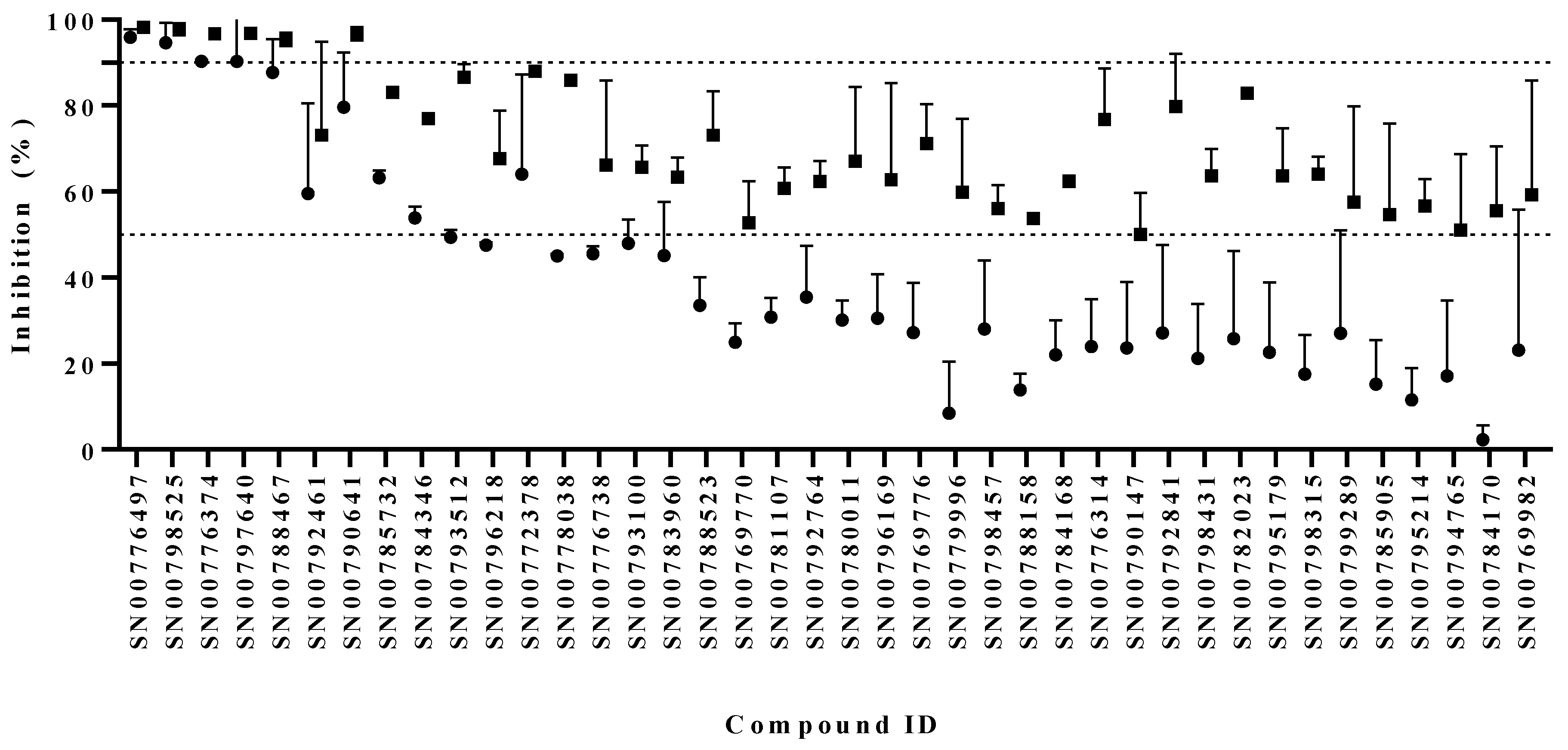
3.1. Identification of Compounds with Anti-Giardia Activity
3.2. Activity Assessments with Selected Scaffold Sets
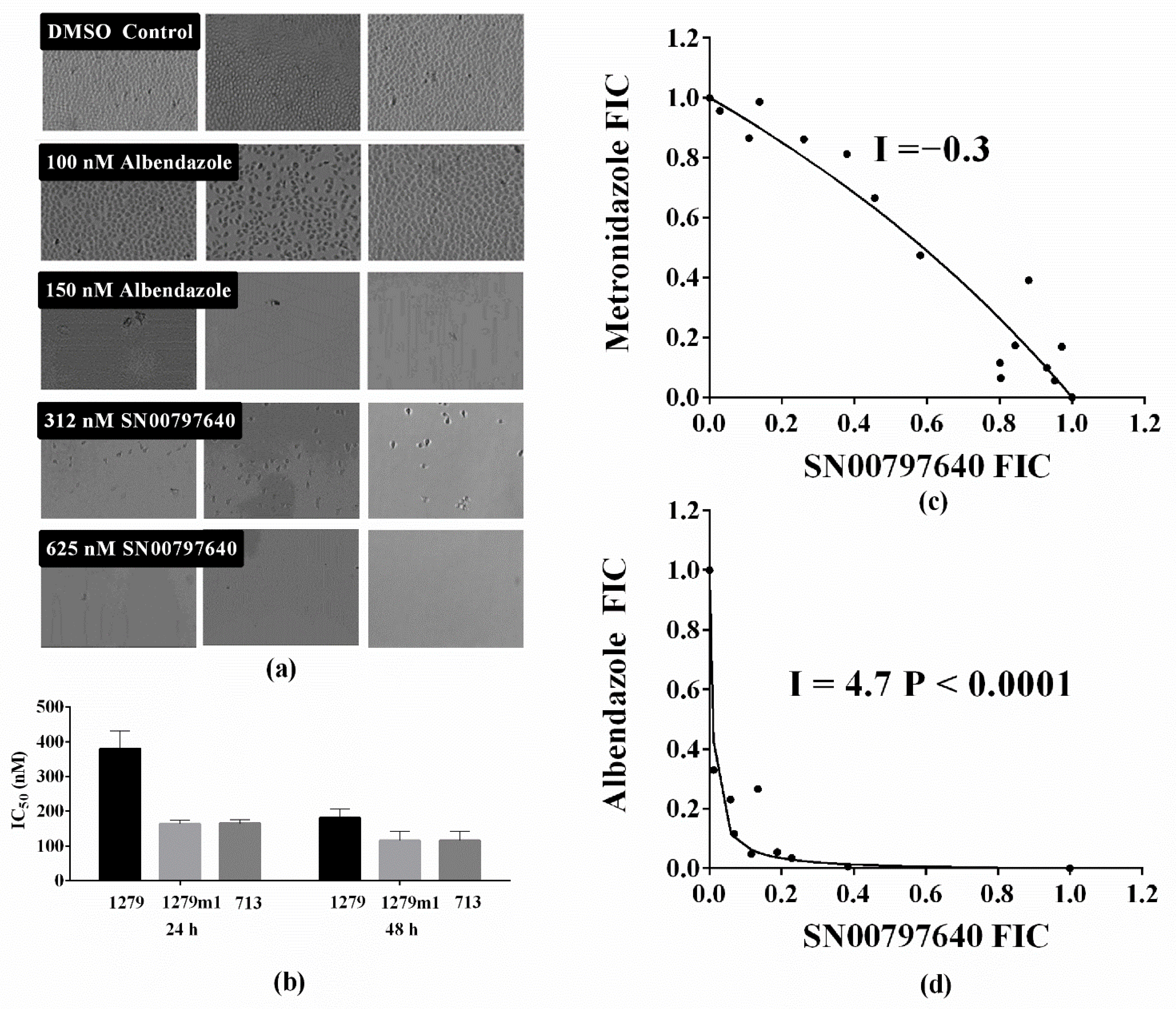
3.3. Follow-Up Activity Studies with CL9406 Scaffold Compound SN00797640
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Riches, A.; Hart, C.J.S.; Trenholme, K.R.; Skinner-Adams, T.S. Anti-Giardia Drug Discovery: Current Status and Gut Feelings. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 13330–13354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simsek, Z.; Zeyrek, F.Y.; Kurcer, M.A. Effect of Giardia infection on growth and psychomotor development of children aged 0-5 years. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2004, 50, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ajjampur, S.S.; Koshy, B.; Venkataramani, M.; Sarkar, R.; Joseph, A.A.; Jacob, K.S.; Ward, H.; Kang, G. Effect of cryptosporidial and giardial diarrhoea on social maturity, intelligence and physical growth in children in a semi-urban slum in south India. Ann. Trop. Paediatr. 2011, 31, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanevik, K.; Wensaas, K.A.; Rortveit, G.; Eide, G.E.; Morch, K.; Langeland, N. Irritable bowel syndrome and chronic fatigue 6 years after Giardia infection: A controlled prospective cohort study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 59, 1394–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanevik, K.; Dizdar, V.; Langeland, N.; Hausken, T. Development of functional gastrointestinal disorders after Giardia lamblia infection. BMC Gastroenterol. 2009, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litleskare, S.; Rortveit, G.; Eide, G.E.; Hanevik, K.; Langeland, N.; Wensaas, K.A. Prevalence of Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Chronic Fatigue 10 Years After Giardia Infection. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 1064–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šlapeta, J.; Dowd, S.E.; Alanazi, A.D.; Westman, M.E.; Brown, G.K. Differences in the faecal microbiome of non-diarrhoeic clinically healthy dogs and cats associated with Giardia duodenalis infection: Impact of hookworms and coccidia. Int. J. Parasitol. 2015, 45, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, S.M.; Nash, T.E. The role of normal flora in Giardia lamblia infections in mice. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 181, 1510–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.F.; Uetanabaro, A.P.T.; Costa, A.F.; Alves, C.A.; Farias, L.M.; Bambirra, E.A.; Penna, F.J.; Vieira, E.C.; Nicoli, J.R. Influence of bacteria from the duodenal microbiota of patients with symptomatic giardiasis on the pathogenicity of Giardia duodenalis in gnotoxenic mice. J. Med. Microbiol. 2000, 49, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalle, M.; Hanevik, K. Treatment-refractory giardiasis: Challenges and solutions. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 1921–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pélissier, M.A.; Vasquez, N.; Balamurugan, R.; Pereira, E.; Dossou-Yovo, F.; Suau, A.; Pochart, P.; Magne, F. Metronidazole effects on microbiota and mucus layer thickness in the rat gut. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2010, 73, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, C.W.; Jarrad, A.M.; Cooper, M.A.; Blaskovich, M.A.T. Nitroimidazoles: Molecular Fireworks That Combat a Broad Spectrum of Infectious Diseases. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 7636–7657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivancos, V.; Gonzalez-Alvarez, I.; Bermejo, M.; Gonzalez-Alvarez, M. Giardiasis: Characteristics, Pathogenesis and New Insights About Treatment. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 1287–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, T.B.; Hill, D.R. Treatment of giardiasis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2001, 14, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, M.; Poulsen, S.A. An overview of Australia’s compound management facility: The Queensland Compound Library. ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upcroft, J.A.; Boreham, P.F.; Campbell, R.W.; Shepherd, R.W.; Upcroft, P. Biological and genetic analysis of a longitudinal collection of Giardia samples derived from humans. Acta Trop. 1995, 60, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capon, A.G.; Upcroft, J.A.; Boreham, P.F.; Cottis, L.E.; Bundesen, P.G. Similarities of Giardia antigens derived from human and animal sources. Int. J. Parasitol. 1989, 19, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keister, D.B. Axenic culture of Giardia lamblia in TYI-S-33 medium supplemented with bile. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1983, 77, 487–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meloni, B.P.; Thompson, R.C.; Reynoldson, J.A.; Seville, P. Albendazole: A more effective antigiardial agent in vitro than metronidazole or tinidazole. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1990, 84, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejman-Yarden, N.; Miyamoto, Y.; Leitsch, D.; Santini, J.; Debnath, A.; Gut, J.; McKerrow, J.H.; Reed, S.L.; Eckmann, L. A reprofiled drug, auranofin, is effective against metronidazole-resistant Giardia lamblia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 2029–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frei, A.; Zuegg, J.; Elliott, A.G.; Baker, M.; Braese, S.; Brown, C.; Chen, F.; Dowson, C.G.; Dujardin, G.; Jung, N.; et al. Metal complexes as a promising source for new antibiotics. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 2627–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riches, A.G.H.C.; Schmit, M.; Debele, E.; Tiash, S.; Clapper, E.; Skinner-Adams, T.; Ryan, J.H. Structural reassignment of a dibenz[b,f][1,4]oxazepin-11(10H)-one with potent antigiardial activity. Aust. J. Chem. 2022, 75, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, C.J.; Munro, T.; Andrews, K.T.; Ryan, J.H.; Riches, A.G.; Skinner-Adams, T.S. A novel in vitro image-based assay identifies new drug leads for giardiasis. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2017, 7, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.H.; Chung, T.D.; Oldenburg, K.R. A Simple Statistical Parameter for Use in Evaluation and Validation of High Throughput Screening Assays. J. Biomol. Screen. 1999, 4, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, W.; Koella, J.C. A comparison of three methods of estimating EC50 in studies of drug resistance of malaria parasites. Acta Trop. 1993, 55, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, J.A.; Jones, A.J.; Avery, V.M.; Sumanadasa, S.D.; Ng, S.S.; Fairlie, D.P.; Skinner-Adams, T.S.; Andrews, K.T. Profiling the anti-protozoal activity of anti-cancer HDAC inhibitors against Plasmodium and Trypanosoma parasites. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2015, 5, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfield, C.J.; Pudney, M.; Gutteridge, W.E. Interactions of atovaquone with other antimalarial drugs against Plasmodium falciparum in vitro. Exp. Parasitol. 1995, 80, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner-Adams, T.; Davis, T.M. Synergistic in vitro antimalarial activity of omeprazole and quinine. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1999, 43, 1304–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedillo-Rivera, R.; Munoz, O. In-vitro susceptibility of Giardia lamblia to albendazole, mebendazole and other chemotherapeutic agents. J. Med. Microbiol. 1992, 37, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.J.; Wu, Y.T.; Yang, S.T.; Lo, K.H.; Chen, S.K.; Chen, Y.H.; Huang, W.I.; Yuan, C.H.; Guo, C.W.; Huang, L.Y.; et al. High-throughput identification of antibacterials against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and the transglycosylase. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 8512–8529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, T.; Nakamura, T.; Misawa, K.; Sakamoto, S.; Onoda, H. New Adenosine A2A Receptor Antagonists. JP2005126374, 24 October 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, T.; Shiohara, H.; Terao, Y.; Nakayama, S.; Miyazawa, K.; Ohnota, H. Novel Benzofuran Derivative, Medicinal Composition Containing the Same, and Uses of These. WO2005073210, 21 January 2005. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Liu, S.; Menon, A.; Stanford, S.; Oppong, E.; Gunawan, A.M.; Wu, L.; Wu, D.J.; Barrios, A.M.; Bottini, N.; et al. A potent and selective small-molecule inhibitor for the lymphoid-specific tyrosine phosphatase (LYP), a target associated with autoimmune diseases. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 4990–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.N.; Stewart, G.; Rideau, E.; Westwood, N.J.; Smith, T.K. A Class of 5-Nitro-2-furancarboxylamides with Potent Trypanocidal Activity against Trypanosoma brucei in Vitro. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 796–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escobedo, A.A.; Lalle, M.; Hrastnik, N.I.; Rodríguez-Morales, A.J.; Castro-Sánchez, E.; Cimerman, S.; Almirall, P.; Jones, J. Combination therapy in the management of giardiasis: What laboratory and clinical studies tell us, so far. Acta Trop. 2016, 162, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwa, M.S.; Veenstra, J.G.; Van Dijk, M.; Roos, M.H. Beta-tubulin genes from the parasitic nematode Haemonchus contortus modulate drug resistance in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Mol. Biol. 1995, 246, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oxberry, M.E.; Thompson, R.C.; Reynoldson, J.A. Evaluation of the effects of albendazole and metronidazole on the ultrastructure of Giardia duodenalis, Trichomonas vaginalis and Spironucleus muris using transmission electron microscopy. Int. J. Parasitol. 1994, 24, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Espinosa, R.; Arguello-Garcia, R.; Saavedra, E.; Ortega-Pierres, G. Albendazole induces oxidative stress and DNA damage in the parasitic protozoan Giardia duodenalis. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compound (Scaffold) | Structure | IC50 (µM; Mean ± SD) | Selectivity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Giardia (48 h) | NFF | |||
| SN00776497 (SC003542) | 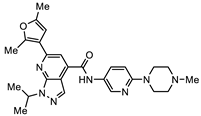 | 0.08 + 0.09 | 8.1 2 | 101 |
| SN00776477 (SC003542) | 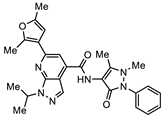 | >10.0 | Not tested | Not tested |
| SN00788467 (CL3439) | 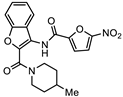 | 0.06 + 0.06 | >10.0 | >166 |
| SN00785329 (CL3439) | 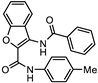 | >10.0 | Not tested | Not tested |
| SN00797640 (CL9406) | 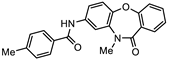 | 0.18 + 0.02 | >10.0 | >55 |
| SN00797660 (CL9406) |  | >10.0 | Not tested | Not tested |
| Metronidazole 1 | 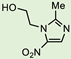 | 2.7 ± 0.7 | >75 | >27 |
| Albendazole 1 | 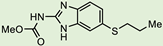 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 1.1 ± 0.5 | 27 |
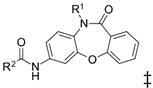
| Compound | R1 | R2 | IC50 (µM; Mean ± SD) | Selectivity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Giardia (48 h) | NFF | ||||
| SN00797638 | Me |  | >10 | Not determined | Not determined |
| SN00797644 | Me |  | >10 | Not determined | Not determined |
| SN00797647 | Me | 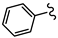 | >10 | Not determined | Not determined |
| SN00797642 | Me | 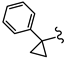 | >10 | Not determined | Not determined |
| SN00797645 | Me | 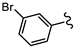 | >10 | Not determined | Not determined |
| SN00797639 | Me | 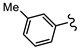 | >10 | Not determined | Not determined |
| SN00797640 | Me | 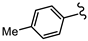 | 0.18 + 0.02 | 21.8 + 0.57 | 121 |
| SN00797643 | Me | 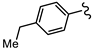 | 0.47 + 0.08 | >10 | >20 |
| SN00797641 | Me | 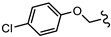 | >10 | Not determined | Not determined |
| SN00797646 | Me |  | >8.6 * | Not determined | Not determined |
| SN00797635 | Me | 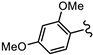 | >10 | Not determined | Not determined |
| SN00797637 | Me | 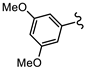 | 5.0 + 0.7 | Not determined | Not determined |
| SN00797636 | Me | 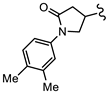 | >10 | Not determined | Not determined |
| SN00797648 | Me | 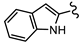 | 1.7 + 0.4 | >20 | >11 |
| SN00797649 | Me |  | >10 | Not determined | Not determined |
| SN00797659 | Me2CH | 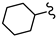 | >10 | Not determined | Not determined |
| SN00797661 | Me2CH | 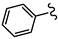 | >10 | Not determined | Not determined |
| SN00797658 | Me2CH | 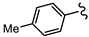 | >10 | Not determined | Not determined |
| SN00797656 | Me2CH | 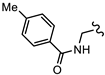 | >10 | Not determined | Not determined |
| SN00797660 | Me2CH | 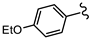 | >10 | Not determined | Not determined |
| SN00797650 | Me2CH | 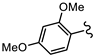 | >10 | Not determined | Not determined |
| SN00797651 | Me2CH | 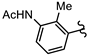 | >10 | Not determined | Not determined |
| SN00797652 | Me2CH | 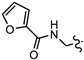 | >10 | Not determined | Not determined |
| SN00797655 | Me2CH | 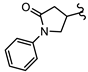 | >10 | Not determined | Not determined |
| SN00797654 | Me2CH | 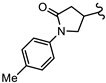 | >10 | Not determined | Not determined |
| SN00797653 | Me2CH | 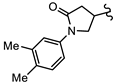 | >10 | Not determined | Not determined |
| SN00797663 | Me2CH | 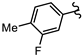 | >10 | Not determined | Not determined |
| SN00797657 | Me2CH | 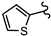 | >10 | Not determined | Not determined |
| SN00797662 | Me2CH | 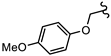 | >10 | Not determined | Not determined |
| SN00797664 | Me2CH | 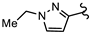 | >10 | Not determined | Not determined |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hart, C.J.S.; Riches, A.G.; Tiash, S.; Clapper, E.; Ramu, S.; Zuegg, J.; Ryan, J.H.; Skinner-Adams, T.S. A Subset Screen of the Compounds Australia Scaffold Library Identifies 7-Acylaminodibenzoxazepinones as Potent and Selective Hits for Anti-Giardia Drug Discovery. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3182. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123182
Hart CJS, Riches AG, Tiash S, Clapper E, Ramu S, Zuegg J, Ryan JH, Skinner-Adams TS. A Subset Screen of the Compounds Australia Scaffold Library Identifies 7-Acylaminodibenzoxazepinones as Potent and Selective Hits for Anti-Giardia Drug Discovery. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(12):3182. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123182
Chicago/Turabian StyleHart, Christopher J. S., Andrew G. Riches, Snigdha Tiash, Erin Clapper, Soumya Ramu, Johannes Zuegg, John H. Ryan, and Tina S. Skinner-Adams. 2022. "A Subset Screen of the Compounds Australia Scaffold Library Identifies 7-Acylaminodibenzoxazepinones as Potent and Selective Hits for Anti-Giardia Drug Discovery" Biomedicines 10, no. 12: 3182. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123182
APA StyleHart, C. J. S., Riches, A. G., Tiash, S., Clapper, E., Ramu, S., Zuegg, J., Ryan, J. H., & Skinner-Adams, T. S. (2022). A Subset Screen of the Compounds Australia Scaffold Library Identifies 7-Acylaminodibenzoxazepinones as Potent and Selective Hits for Anti-Giardia Drug Discovery. Biomedicines, 10(12), 3182. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123182





