Identification of the Transcriptional Regulatory Role of RUNX2 by Network Analysis in Lung Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
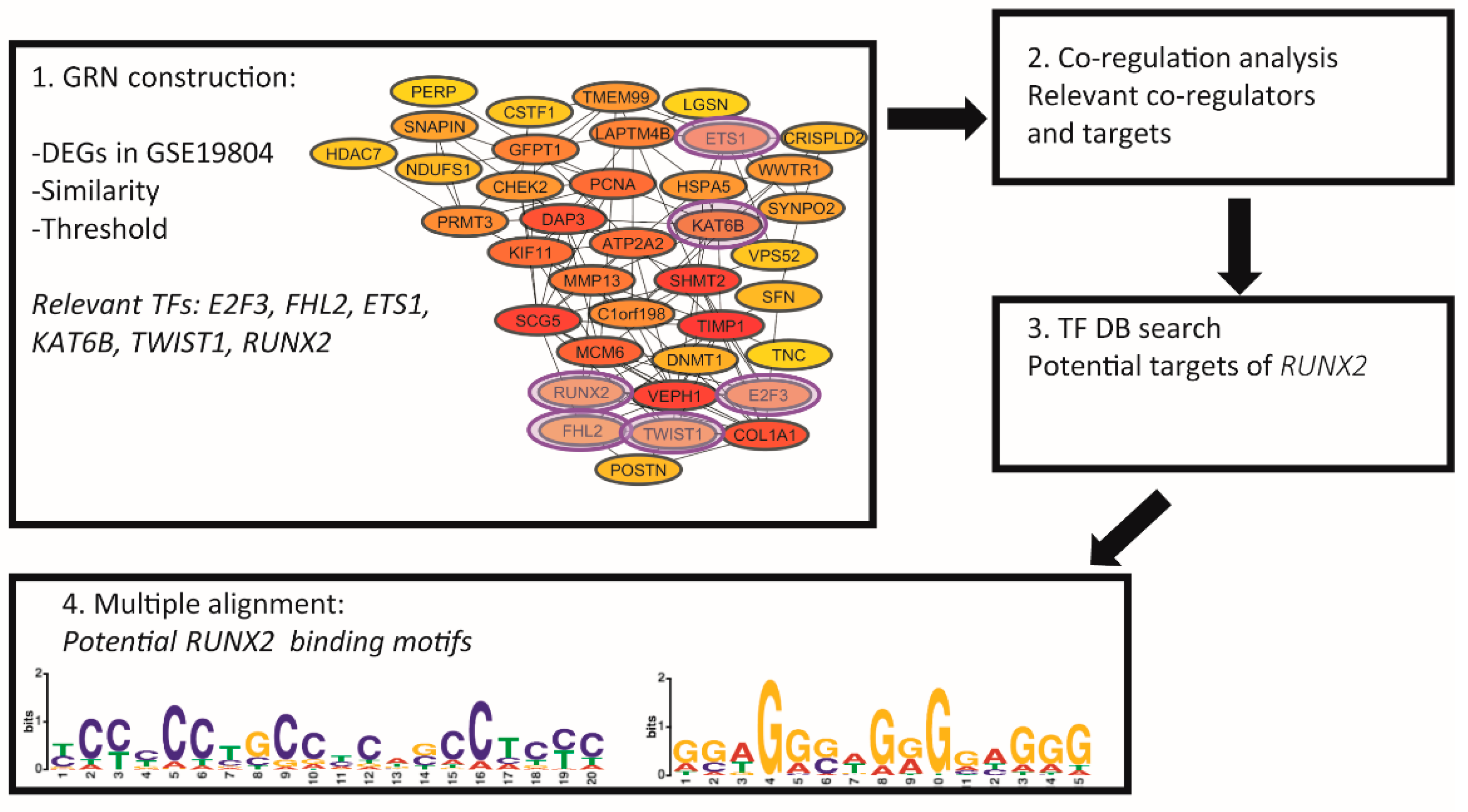
2.1. Gene Regulatory Network Analysis (GRN)
- A list of threshold values to be evaluated is created.
- b.
- For each threshold, a different adjacency matrix is constructed for the similarity matrix S using Equation (1).
- c.
- For each adjacency matrix , the node clustering coefficient is calculated [24]. The expected clustering coefficient for a random graph with the same characteristics is also calculated.
- d.
- The absolute values of the differences between the (under randomness) expected and observed cluster coefficients are calculated and plotted. The threshold is chosen at the point where the difference between the two is the greatest.
- e.
- Finally, the adjacency matrix for the selected threshold is constructed.
2.2. Gene Coregulatory Network Analysis
2.3. Identification of Potential Gene Targets of RUNX2
2.4. Identification of Potential Binding Motifs of RUNX2
3. Results
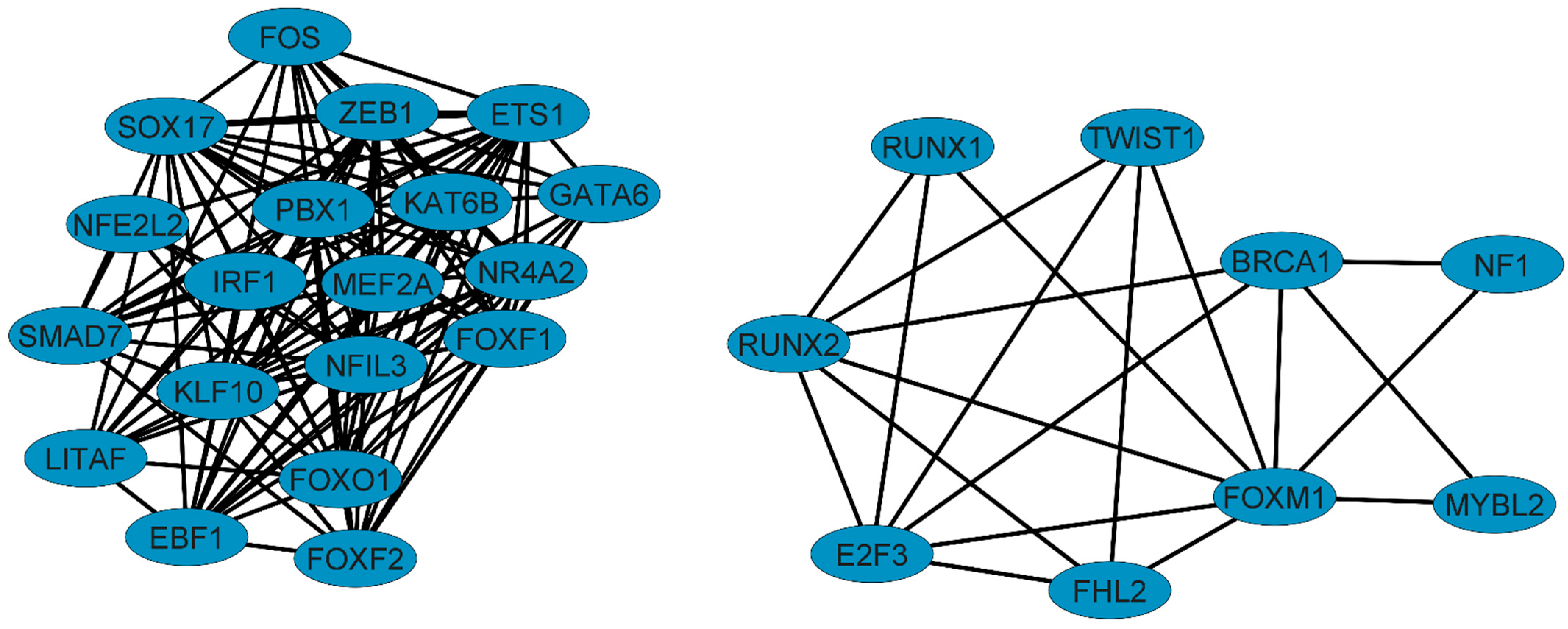
3.1. Six Transcription Factors (E2F3, FHL2, ETS1, KAT6B, TWIST1, and RUNX2) Are Essential Regulators of Gene Expression in NSCLC
3.2. RUNX2 Is an Important Regulator and Coregulator in NSCLC
3.3. Potential Target Genes of RUNX2
3.4. Potential Binding Motifs of RUNX2
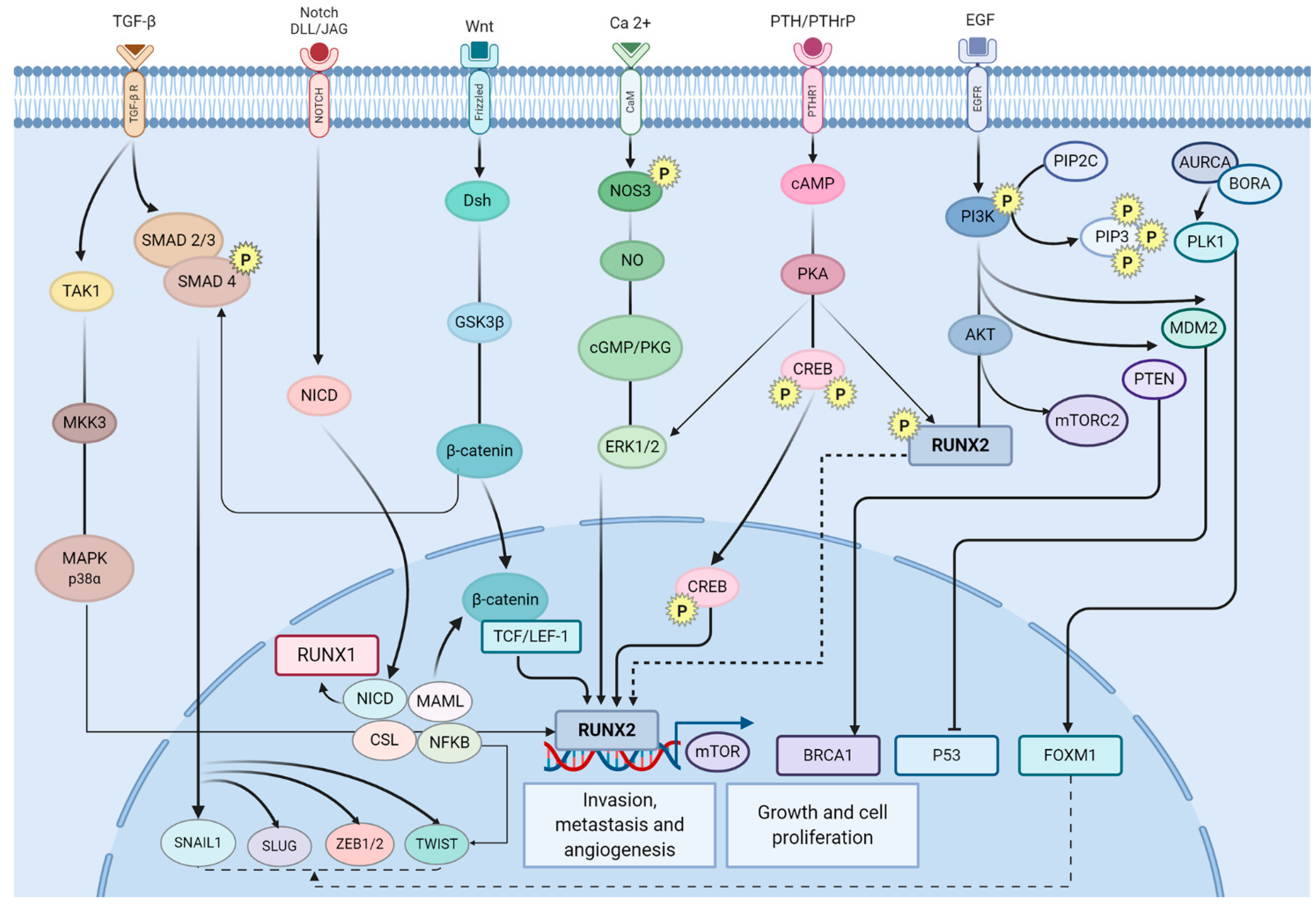
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dela Cruz, C.S.; Tanoue, L.T.; Matthay, R.A. Lung Cancer: Epidemiology, Etiology, and Prevention. Clin. Chest Med. 2011, 32, 605–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gridelli, C.; Rossi, A.; Carbone, D.P.; Guarize, J.; Karachaliou, N.; Mok, T.; Petrella, F.; Spaggiari, L.; Rosell, R. Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primer 2015, 1, 15009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thandra, K.C.; Barsouk, A.; Saginala, K.; Aluru, J.S.; Barsouk, A. Epidemiology of Lung Cancer. Wspolczesna Onkol. 2021, 25, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamel, H.F.M.; Al-Amodi, H.S.A.B. Exploitation of Gene Expression and Cancer Biomarkers in Paving the Path to Era of Personalized Medicine. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics 2017, 15, 220–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soda, M.; Choi, Y.L.; Enomoto, M.; Takada, S.; Yamashita, Y.; Ishikawa, S.; Fujiwara, S.I.; Watanabe, H.; Kurashina, K.; Hatanaka, H.; et al. Identification of the Transforming EML4-ALK Fusion Gene in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Nature 2007, 448, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, A.H.; Niki, M.; Morotti, A.; Taylor, B.S.; Socci, N.D.; Viale, A.; Brennan, C.; Szoke, J.; Motoi, N.; Rothman, P.B.; et al. Identification of DOK Genes as Lung Tumor Suppressors. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchon, F.; Grivaux, M.; Asselain, B.; Lebas, F.X.; Orlando, J.P.; Piquet, J.; Zureik, M. 4-Year Mortality in Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Development and Validation of a Prognostic Index. Lancet Oncol. 2006, 7, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolle, R.; Radvanyi, F.; Elati, M. CoRegNet: Reconstruction and Integrated Analysis of Co-Regulatory Networks. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3066–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henao, J.D. Coexnet: An R Package to Build CO-EXpression NETworks from Microarray Data 2018, 1–13. [Software Version 0.1]. Available online: https://bioconductor.org/packages/coexnet/ (accessed on 11 May 2021).
- Kaczkowski, B.; Tanaka, Y.; Kawaji, H.; Sandelin, A.; Andersson, R.; Itoh, M.; Lassmann, T.; Hayashizaki, Y.; Carninci, P.; Forrest, A.R.R. Transcriptome Analysis of Recurrently Deregulated Genes across Multiple Cancers Identifies New Pan-Cancer Biomarkers. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.H.; Chu, X.Y.; Xue, G.; Xiong, J.H.; Zhang, H.Y. Identifying Cancer Prognostic Modules by Module Network Analysis. BMC Bioinformatics 2019, 20, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otálora-Otálora, B.A.; Florez, M.; López-Kleine, L.; Canas Arboleda, A.; Grajales Urrego, D.M.; Rojas, A. Joint Transcriptomic Analysis of Lung Cancer and Other Lung Diseases. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Jiang, L.; Li, M.; He, D. Statistical Analysis of Gene Regulatory Networks Reconstructed from Gene Expression Data of Lung Cancer. Phys. Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2006, 370, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malysheva, V.; Mendoza-Parra, M.A.; Saleem, M.A.M.; Gronemeyer, H. Reconstruction of Gene Regulatory Networks Reveals Chromatin Remodelers and Key Transcription Factors in Tumorigenesis. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chudasama, D.; Bo, V.; Hall, M.; Anikin, V.; Jeyaneethi, J.; Gregory, J.; Pados, G.; Tucker, A.; Harvey, A.; Pink, R.; et al. Identification of Cancer Biomarkers of Prognostic Value Using Specific Gene Regulatory Networks (GRN): A Novel Role of RAD51AP1 for Ovarian and Lung Cancers. Carcinogenesis 2018, 39, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrbeck, A.; Borlak, J. Cancer Genomics Identifies Regulatory Gene Networks Associated with the Transition from Dysplasia to Advanced Lung Adenocarcinomas Induced by C-Raf-1. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Matos Simoes, R.; Dehmer, M.; Emmert-Streib, F. Interfacing Cellular Networks of S. Cerevisiae and E. Coli: Connecting Dynamic and Genetic Information. BMC Genomics 2013, 14, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolle, R.; Elati, M.; Radvanyi, F. Network Transformation of Gene Expression for Feature Extraction. In Proceedings of the 2012 11th International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications, Boca Raton, FL, USA, 12–15 December 2012; Volume 1, pp. 108–113. [Google Scholar]
- Herreño, A.M.; Ramírez, A.C.; Chaparro, V.P.; Fernandez, M.J.; Cañas, A.; Morantes, C.F.; Moreno, O.M.; Brugés, R.E.; Mejía, J.A.; Bustos, F.J.; et al. Role of RUNX2 Transcription Factor in Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Lung Cancer: Epigenetic Control of the RUNX2 P1 Promoter. Tumor Biol. 2019, 41, 1010428319851014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.P.; Tsai, M.H.; Lee, J.M.; Hsu, C.P.; Chen, P.C.; Lin, C.W.; Shih, J.Y.; Yang, P.C.; Hsiao, C.K.; Lai, L.C.; et al. Identification of a Novel Biomarker, SEMA5A, for Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma in Nonsmoking Women. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2010, 19, 2590–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Kleine, L.; Leal, L.; López, C. Biostatistical Approaches for the Reconstruction of Gene Co-Expression Networks Based on Transcriptomic Data. Brief. Funct. Genomics 2013, 12, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cover, T.M.; Thomas, J.A. Elements of Information Theory; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; Volume 1, ISBN 9780471241959. [Google Scholar]
- Leal Ayala, L.G. Desarrollo de Una Metodología Estadística Aplicada a La Construcción y Comparación de Redes de Coexpresión Génica. Univ. Nac. Colomb. 2013, 1–121. [Google Scholar]
- Elo, L.L.; Järvenpää, H.; Orešič, M.; Lahesmaa, R.; Aittokallio, T. Systematic Construction of Gene Coexpression Networks with Applications to Human T Helper Cell Differentiation Process. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2096–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andy Bunn, M.K. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Found. Stat. Comput. 2017, 10, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Leal, L.G.; López, C.; López-Kleine, L. Construction and Comparison of Gene Co-Expression Networks Shows Complex Plant Immune Responses. PeerJ 2014, 2, e610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, C. Construccion de Redes de Regulacion Genica Usando Datos de Secuenciacion de ARN Construccion de Redes de Regulacion Genica Usando Datos de Secuenciacion de ARN. Univ. Nac. Colomb. 2018, 1–86. [Google Scholar]
- Groeneveld, C.; Robertson, G.; Wang, X.; Fletcher, M.; Markowetz, F.; Meyer, K.; Castro, M. Package RTN: Reconstruction of Transcriptional Regulatory Networks and Analysis of Regulons. [Software Version 2.22.0]. Available online: http://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/RTN.html (accessed on 11 May 2021).
- Sherman, B.T.; Hao, M.; Qiu, J.; Jiao, X.; Baseler, M.W.; Lane, H.C.; Imamichi, T.; Chang, W. DAVID: A Web Server for Functional Enrichment Analysis and Functional Annotation of Gene Lists (2021 Update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W216–W221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, H.; Thomas, P. PANTHER Pathway: An Ontology-Based Pathway Database Coupled with Data Analysis Tools. Methods Mol. Biol. Clifton NJ 2009, 563, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otálora-Otálora, B.A.; Osuna-Garzón, D.A.; Carvajal-Parra, M.S.; Cañas, A.; Montecino, M.; López-Kleine, L.; Rojas, A. Identifying General Tumor and Specific Lung Cancer Biomarkers by Transcriptomic Analysis. Biology 2022, 11, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.-P.; Huang, W.-Y.; Chen, G.; Chen, S.-W.; Yang, J.; He, R.-Q.; Huang, S.-N.; Gan, T.-Q.; Ma, J.; Yang, L.-J.; et al. Clinical Significance of Transcription Factor RUNX2 in Lung Adenocarcinoma and Its Latent Transcriptional Regulating Mechanism. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2020, 89, 107383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.P.; Lu, H.P.; Chen, G.; Yang, J.; Gao, L.; Song, J.H.; Chen, S.W.; Mo, J.X.; Kong, J.L.; Tang, Z.Q.; et al. Integrated Expression Analysis Revealed RUNX2 Upregulation in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma Tissues. IET Syst. Biol. 2020, 14, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, F.; Wienerroither, S.; Stark, A. Combinatorial Function of Transcription Factors and Cofactors. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2017, 43, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, T.; Yoneda, M.; Higashi, M.; Ohkuma, Y.; Ito, T. Enhancer Function Regulated by Combinations of Transcription Factors and Cofactors. Genes Cells Devoted Mol. Cell. Mech. 2018, 23, 808–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, T.M.; Kahler, R.A.; Li, X.; Westendorf, J.J. Histone Deacetylase 3 Interacts with Runx2 to Repress the Osteocalcin Promoter and Regulate Osteoblast Differentiation*. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 41998–42007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullen, D.J.; Yan, C.; Kang, D.S.; Zhou, B.; Borok, Z.; Marconett, C.N.; Farnham, P.J.; Offringa, I.A.; Rhie, S.K. TENET 2.0: Identification of Key Transcriptional Regulators and Enhancers in Lung Adenocarcinoma. PLoS Genet. 2020, 16, e1009023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozo, K.; Kollipara, R.K.; Kelenis, D.P.; Rodarte, K.E.; Zhang, X.; Minna, J.D.; Johnson, J.E. Lineage Transcription Factors Co-Regulate Subtype-Specific Genes Providing a Roadmap for Systematic Identification of Small Cell Lung Cancer Vulnerabilities. bioRxiv 2020, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooten, D.J.; Groves, S.M.; Tyson, D.R.; Liu, Q.; Lim, J.S.; Albert, R.; Lopez, C.F.; Sage, J.; Quaranta, V. Systems-Level Network Modeling of Small Cell Lung Cancer Subtypes Identifies Master Regulators and Destabilizers. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1007343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, L.; Ram, U.; Hari, K.; Jolly, M.K. Topological Signatures in Regulatory Network Enable Phenotypic Heterogeneity in Small Cell Lung Cancer. eLife 2021, 10, e64522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, X.; Wei, K.; Liu, D.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Shi, H. Identification of Key Transcription Factors Associated with Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2017, 23, 172–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Meng, X.; Lu, P.; Bai, H.; Xiao, P.; Fan, Q. Transcriptional Regulatory Networks in Human Lung Adenocarcinoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 6, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wang, W.; Xu, M.; Li, Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, X. A Global View of Regulatory Networks in Lung Cancer: An Approach to Understand Homogeneity and Heterogeneity. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2017, 42, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Li, Z.; Zhao, N.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shang, D.; Qiu, F.; Zhang, R.; Chang, Z.; et al. Functional Analysis of MicroRNA and Transcription Factor Synergistic Regulatory Network Based on Identifying Regulatory Motifs in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. BMC Syst. Biol. 2013, 7, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.-H.; Dreyfuss, J.M.; Ramoni, M.F. A Transcriptional Network Signature Characterizes Lung Cancer Subtypes. Cancer 2011, 117, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Li, M.; Ji, H.; Fang, Z. Landscape of Transcriptional Deregulation in Lung Cancer. BMC Genomics 2018, 19, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Yang, W.; Zhang, J.; Yang, J.Y.; Guan, R.; Yang, M.Q. Transcription Factor and LncRNA Regulatory Networks Identify Key Elements in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Genes 2018, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, J.B.; Javed, A.; Zaidi, S.K.; Lengner, C.; Montecino, M.; van Wijnen, A.J.; Stein, J.L.; Stein, G.S. Regulatory Controls for Osteoblast Growth and Differentiation: Role of Runx/Cbfa/AML Factors. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2004, 14, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitami, K.; Kitami, M.; Kaku, M.; Wang, B.; Komatsu, Y. BRCA1 and BRCA2 Tumor Suppressors in Neural Crest Cells Are Essential for Craniofacial Bone Development. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurkovicova, D.; Magyerkova, M.; Sestakova, Z.; Copakova, L.; Bella, V.; Konecny, M.; Krivjanska, M.; Kulcsar, L.; Chovanec, M. Evaluation of Expression Profiles of MicroRNAs and Two Target Genes, FOXO3a and RUNX2, Effectively Supports Diagnostics and Therapy Predictions in Breast Cancer. Neoplasma 2016, 63, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogachek, M.V.; De Andrade, J.P.; Weigel, R.J. Regulation of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition through Sumoylation of Transcription Factors. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeselsohn, R.; Cornwell, M.; Pun, M.; Buchwalter, G.; Nguyen, M.; Bango, C.; Huang, Y.; Kuang, Y.; Paweletz, C.; Fu, X.; et al. Embryonic Transcription Factor SOX9 Drives Breast Cancer Endocrine Resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E4482–E4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, K.S.; Javed, A.; Drissi, H.; McNeil, S.; Lian, J.B.; Stein, J.L.; van Wijnen, A.J.; Wang, Y.L.; Stein, G.S. Transcription Factors RUNX1/AML1 and RUNX2/Cbfa1 Dynamically Associate with Stationary Subnuclear Domains. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 4167–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidouche, Z.; Haÿ, E.; Vaudin, P.; Charbord, P.; Schüle, R.; Marie, P.J.; Fromigué, O. FHL2 Mediates Dexamethasone-Induced Mesenchymal Cell Differentiation into Osteoblasts by Activating Wnt/Beta-Catenin Signaling-Dependent Runx2 Expression. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2008, 22, 3813–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.; Xu, Y.; He, T.; Qin, C.; Xu, J. Normal and Disease-Related Biological Functions of Twist1 and Underlying Molecular Mechanisms. Cell Res. 2012, 22, 90–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhou, R.-J.; Zhang, G.-Q.; Xu, J.-P. Clinical Significance of RUNX2 Expression in Patients with Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer: A 5-Year Follow-up Study. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodevelopmental Biol. Med. 2013, 34, 1807–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minami, A.; Nakanishi, A.; Ogura, Y.; Kitagishi, Y.; Matsuda, S. Connection between Tumor Suppressor BRCA1 and PTEN in Damaged DNA Repair. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen-Solal, K.A.; Boregowda, R.K.; Lasfar, A. RUNX2 and the PI3K/AKT Axis Reciprocal Activation as a Driving Force for Tumor Progression. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Aguilar, R.; Marchat, L.A.; Ocampo, E.A.; Gariglio, P.; Mena, J.G.; Sepúlveda, N.V.; Castillo, M.M.Í.; López-Camarill, C. Resveratrol Inhibits Cell Cycle Progression by Targeting Aurora Kinase A and Polo-like Kinase 1 in Breast Cancer Cells. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 3696–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Wen, D. The Emerging Role of Polo-like Kinase 1 in Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Tumor Metastasis. Cancers 2017, 9, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roszer, T. Nitric Oxide Signaling and Nitrosative Stress in the Musculoskeletal System. In Systems Biology of Free Radicals and Antioxidants; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 2895–2926. ISBN 9783642300189. [Google Scholar]
- Otálora-Otálora, B.A.; Henríquez, B.; López-Kleine, L.; Rojas, A. RUNX Family: Oncogenes or Tumor Suppressors (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2019, 42, 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Iozzo, R.V.; Sanderson, R.D. Proteoglycans in Cancer Biology, Tumour Microenvironment and Angiogenesis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2011, 15, 1013–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.H.; Hwang, E.S.; McManus, M.T.; Amsterdam, A.; Tian, Y.; Kalmukova, R.; Mueller, E.; Benjamin, T.; Spiegelman, B.M.; Sharp, P.A.; et al. TAZ, a Transcriptional Modulator of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Differentiation. Science 2005, 309, 1074–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusgard, J.L.; Choe, M.; Chumsri, S.; Renoud, K.; MacKerell, A.D.; Sudol, M.; Passaniti, A. RUNX2 and TAZ-Dependent Signaling Pathways Regulate Soluble E-Cadherin Levels and Tumorsphere Formation in Breast Cancer Cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 28132–28150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, S.K.; Sullivan, A.J.; Medina, R.; Ito, Y.; Van Wijnen, A.J.; Stein, J.L.; Lian, J.B.; Stein, G.S. Tyrosine Phosphorylation Controls Runx2-Mediated Subnuclear Targeting of YAP to Repress Transcription. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 790–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, R.; Wang, X.; Drissi, H.; Liu, F.; O’Keefe, R.J.; Chen, D. Cyclin D1-Cdk4 Induce Runx2 Ubiquitination and Degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 16347–16353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, N.; Liu, H.; Qu, F.; Fan, J.; Mao, K.; Yin, Y.; Liu, J.; Geng, Z.; Wang, Y. Hypoxia Inhibits the Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells into Osteoblasts by Activation of Notch Signaling. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2013, 94, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, A.J.; Dickey-Sims, C.; Ransick, A.; Rupp, D.E.; McCarthy, J.J.; Coffman, J.A. CBFβ Is a Facultative Runx Partner in the Sea Urchin Embryo. BMC Biol. 2006, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, T.; Wu, D.; Sugimoto, H.; Nagase, H.; Nakagawara, A. Runt-Related Transcription Factor 2 (RUNX2) Inhibits P53-Dependent Apoptosis through the Collaboration with HDAC6 in Response to DNA Damage. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.M.; Lee, E.H. Transcriptional Regulatory Cascades in Runx2-Dependent Bone Development. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2013, 19, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, B.-G.; Lee, S.-J.; Lee, H.-K.; Lee, S.-H.; Ryoo, H.-M.; Cho, J.-Y. The Suppressive Effect of Myeloid Elf-1-like Factor (MEF) in Osteogenic Differentiation. J. Cell. Physiol. 2007, 211, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Qi, T.; Yang, D.; Qi, M.; Li, D.; Xiang, X.; Huang, K.; Tong, Q. MicroRNA-9 Suppresses the Proliferation, Invasion and Metastasis of Gastric Cancer Cells through Targeting Cyclin D1 and Ets1. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Xie, Y.; Lei, Y.; Kuang, Z.; Liu, X. The MicroRNA-130a-5p/RUNX2/STK32A Network Modulates Tumor Invasive and Metastatic Potential in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzotti, G.; Torricelli, F.; Donati, B.; Sancisi, V.; Gugnoni, M.; Ciarrocchi, A. HDACs Control RUNX2 Expression in Cancer Cells through Redundant and Cell Context-Dependent Mechanisms. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Matsumoto, Y.; Asano, Y.; Yamamura, Y.; Katsuyama, T.; La Rose, J.; Tomonobu, N.; Komalasari, N.L.G.Y.; Sakaguchi, M.; Rottapel, R.; et al. RUNX2 Phosphorylation by Tyrosine Kinase ABL Promotes Breast Cancer Invasion. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 665273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Meng, L.; Sun, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Hua, S. MicroRNA-196b Inhibits Cell Growth and Metastasis of Lung Cancer Cells by Targeting Runx2. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.-W.; Zhou, Y.-L.; You, Q.-J.; Shou, F.; Pang, Q.-F.; Chen, J.-L. WWOX Inhibits the Invasion of Lung Cancer Cells by Downregulating RUNX2. Cancer Gene Ther. 2016, 23, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, G.S.; Lian, J.B.; van Wijnen, A.J.; Stein, J.L.; Montecino, M.; Javed, A.; Zaidi, S.K.; Young, D.W.; Choi, J.-Y.; Pockwinse, S.M. Runx2 Control of Organization, Assembly and Activity of the Regulatory Machinery for Skeletal Gene Expression. Oncogene 2004, 23, 4315–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tandon, M.; Gokul, K.; Ali, S.A.; Chen, Z.; Lian, J.; Stein, G.S.; Pratap, J. Runx2 Mediates Epigenetic Silencing of the Bone Morphogenetic Protein-3B (BMP-3B/GDF10) in Lung Cancer Cells. Mol. Cancer 2012, 11, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasim, M.T.; Ogo, T.; Ahmed, M.; Randall, R.; Chowdhury, H.M.; Snape, K.M.; Bradshaw, T.Y.; Southgate, L.; Lee, G.J.; Jackson, I.; et al. Molecular Genetic Characterization of SMAD Signaling Molecules in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Hum. Mutat. 2011, 32, 1385–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trembath, R.C.; Thomson, J.R.; Machado, R.D.; Morgan, N.V.; Atkinson, C.; Winship, I.; Simonneau, G.; Galie, N.; Loyd, J.E.; Humbert, M.; et al. Clinical and Molecular Genetic Features of Pulmonary Hypertension in Patients with Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrell, N.W. Pulmonary Hypertension Due to BMPR2 Mutation: A New Paradigm for Tissue Remodeling? Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2006, 3, 680–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, E.R.; Neil, J.C. The Runx Genes: Lineage-Specific Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors. Oncogene 2004, 23, 4308–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aronson, B.D.; Fisher, A.L.; Blechman, K.; Caudy, M.; Gergen, J.P. Groucho-Dependent and -Independent Repression Activities of Runt Domain Proteins. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1997, 17, 5581–5587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagata, T.; Maki, K.; Mitani, K. Runx1/AML1 in Normal and Abnormal Hematopoiesis. Int. J. Hematol. 2005, 82, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blyth, K.; Terry, A.; Mackay, N.; Vaillant, F.; Bell, M.; Cameron, E.R.; Neil, J.C.; Stewart, M. Runx2: A Novel Oncogenic Effector Revealed by in Vivo Complementation and Retroviral Tagging. Oncogene 2001, 20, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blyth, K.; Cameron, E.R.; Neil, J.C. The RUNX Genes: Gain or Loss of Function in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Transcription Factor | LD | LD CCPs | LC CCPs | LCI | LCII | NSCLC-GRN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E2F3 | - | BRCA1 | FOXM1 | RUNX1 | RUNX1 | RUNX2, FHL2, TWIST1 |
| FHL2 | - | - | FOXM1 | - | - | RUNX2, TWIST1 |
| ETS1 | - | IRF1, NR4A2, ZEB1 | SOX17, FOS, FOXO1, KLF10, SMAD7 LATIF, NR4A2, ZEB1, EBF1 | GATA6, FOXF2, FOXF1, NFIL3, NFE2L2, PBX1, MEF2A, EBF1 | KAT6B | |
| KAT6B | - | NR4A2, ZEB1 | SOX17, FOXO1, KLF10, SMAD7 | FOXF1, FOXF2, GATA6, PBX1 | EST1 | |
| TWIST1 | IPF PAH | - | FOXM1 | - | - | RUNX2, FHL2, E2F3 |
| RUNX2 | PAH | BRCA1 | FOXM1 | RUNX1 | RUNX1 | E2F3, FHL2, TWIST1 |
| RUNX2 Targets | Dysregulation | Signaling Pathways |
|---|---|---|
| ALYREF | NSCLC | RNA Polymerase II Transcription, TAP/NFX1 pathway |
| C1orf198 | LC | Cell-mediated immune response pathway |
| DFNB59 | SCLC | Afferent auditory pathway |
| ELANE | NSCLC | Extracellular matrix organization, Innate Immune System |
| ERP27 | SCLC | Photodynamic therapy-induced unfolded protein response |
| ESR1 | SCLC | ERBB4, RNA Polymerase II Transcription, estrogen signaling pathway |
| ETS1 | LC | PDGF, RAS, VEGF, MAPK signaling pathway |
| HDAC5 | SCLC | RNA Polymerase II Transcription, Notch singling pathway |
| HES1 | SCLC | RNA Polymerase II Transcription, angiogenesis, Notch singling pathway |
| HNRPU | SCLC | mRNA Splicing, lncRNA in canonical Wnt signaling pathway |
| KIAA1107 | SCLC | - |
| LRP5 | LC | Negative regulation of TCF, lncRNA in canonical Wnt, Wnt signaling pathway |
| MYST4 | SCLC | HATs acetylate histones, chromatin organization, P53 signaling pathway |
| NAGK | SCLC | Synthesis of substrates in N-glycan biosynthesis, metabolism of proteins |
| NR0B2 | SCLC | RNA Polymerase II Transcription, nuclear receptor transcription pathway |
| PRUNE | SCLC | - |
| R3HDML | NSCLC | - |
| REM2 | SCLC | - |
| RNF145 | LC | NFκB signaling pathway |
| SNAPIN | NSCLC | Trans-Golgi Network Vesicle Budding, vesicle-mediated transport |
| SYNPO2 | NSCLC | Nuclear import pathway |
| TLE1 | SCLC | TCF-dependent, Hedgehog, Notch, Wnt signaling pathway |
| TMEM99 | NSCLC | - |
| VEPH1 | LC | TGF-beta, Wnt signaling pathway |
| YAP1 | SCLC | ERBB4, RNA Polymerase II Transcription, transcriptional regulation by RUNX2 |
| ZNF436 | LC | RNA Polymerase II Transcription, gene expression (transcription) |
| ZNF585A | SCLC | RNA Polymerase II Transcription, gene expression (transcription) |
| TF | Targets | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Upregulated | Downregulated | ||
| RUNX2 | 308 | 124 | 432 |
| BRCA1 | 465 | 65 | 530 |
| FOXM1 | 1559 | 938 | 2497 |
| RUNX1 | 1725 | 912 | 2637 |
| E2F3 | 548 | 287 | 835 |
| FHL2 | 362 | 296 | 658 |
| TWIST1 | 256 | 85 | 341 |
| Article Title | Lung Cancer | Highlighted Genes |
|---|---|---|
| Topological signatures in regulatory network enable phenotypic heterogeneity in small cell lung cancer (2021). | SCLC | TP53, RB1, ASCL1, NEUROD1, YAP1, and POU2F3 |
| A global view of regulatory networks in lung cancer: An approach to understand homogeneity and heterogeneity (2016). | LAD SCC LCC SCLC | HLTF, FOXM1, ARNTL2, LAU, ZNF187, HNRPK, C1orf107, GRLF1, HMGA1, E2F6, IRF1, TFDP1, SUV39H1, RBL1, STAT5A, and HNRPD |
| A Transcriptional Network Signature Characterizes Lung Cancer Subtypes (2011). | LAC SCC | ABCC3, CLDN3, DPP4, MUC3B, MUC5B, NTRK2, SPINK1, and TJP3 KRT6A, KRT6B, KRT6C, KRT17, RHCG, SPRR1A, and VSNL1 |
| Landscape of transcriptional deregulation in lung cancer (2018). | LAC SCC | TP63/SOX2/DMRT3 LEF1/MSC |
| Transcriptional regulatory networks in human lung adenocarcinoma (2012). | LAC | PPARG, CEBPB, ETV4, FLI1, TAL1, and NFκB1 |
| Transcription Factor and lncRNA Regulatory Networks Identify Key Elements in Lung Adenocarcinoma (2018). | LAC | TP53, SMAD4, SOX9, NFE2L2, MGA, ETV6, GATA3, and RUNX1 |
| Lineage transcription factors co-regulate subtype-specific genes providing a roadmap for systematic identification of small cell lung cancer vulnerabilities (2020). | SCLC | NKX2-1, PROX1, ASCL1, HES1, JAG2, TGFB2, FOXA2, ID2, INSM1, and PROX1. |
| Identification of Key Transcription Factors Associated with Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma (2017). | LUSC | NFIC, BRCA1, NFATC2, IRF1, NR2F1, FOXF1, NR4A2, HOXA5, EGR1, EGR2, ZEB1, YY1, BRCA1, E2F3, and MEF2A. |
| Functional analysis of microRNA and transcription factor synergistic regulatory network based on identifying regulatory motifs in non-small cell lung cancer (2013). | NSCLC | E2F1, ESR1, STAT1, RB1, MYC, NFKB1, miR-590, and miR-570 |
| TENET 2.0: Identification of key transcriptional regulators and enhancers in lung adenocarcinoma (2020). | LAC | NKX2-1, CENPA, FOXM1, and MYBL2 |
| Systems-level network modeling of Small Cell Lung Cancer subtypes identifies master regulators and destabilizers (2019). | SCLC | ELF3 and NR0B1 as master regulators, and TCF3 as a master destabilizer. STAT6, and EBF1. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Otálora-Otálora, B.A.; González Prieto, C.; Guerrero, L.; Bernal-Forigua, C.; Montecino, M.; Cañas, A.; López-Kleine, L.; Rojas, A. Identification of the Transcriptional Regulatory Role of RUNX2 by Network Analysis in Lung Cancer Cells. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3122. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123122
Otálora-Otálora BA, González Prieto C, Guerrero L, Bernal-Forigua C, Montecino M, Cañas A, López-Kleine L, Rojas A. Identification of the Transcriptional Regulatory Role of RUNX2 by Network Analysis in Lung Cancer Cells. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(12):3122. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123122
Chicago/Turabian StyleOtálora-Otálora, Beatriz Andrea, Cristian González Prieto, Lucia Guerrero, Camila Bernal-Forigua, Martin Montecino, Alejandra Cañas, Liliana López-Kleine, and Adriana Rojas. 2022. "Identification of the Transcriptional Regulatory Role of RUNX2 by Network Analysis in Lung Cancer Cells" Biomedicines 10, no. 12: 3122. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123122
APA StyleOtálora-Otálora, B. A., González Prieto, C., Guerrero, L., Bernal-Forigua, C., Montecino, M., Cañas, A., López-Kleine, L., & Rojas, A. (2022). Identification of the Transcriptional Regulatory Role of RUNX2 by Network Analysis in Lung Cancer Cells. Biomedicines, 10(12), 3122. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123122






