Plasma Metabolic Disturbances in Parkinson’s Disease Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Clinical Samples
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. Derivatization
2.5. Gas Chromatography-Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (GC-TOFMS) Analysis
2.6. Data Analysis
2.7. Statistics and Bioinformatics
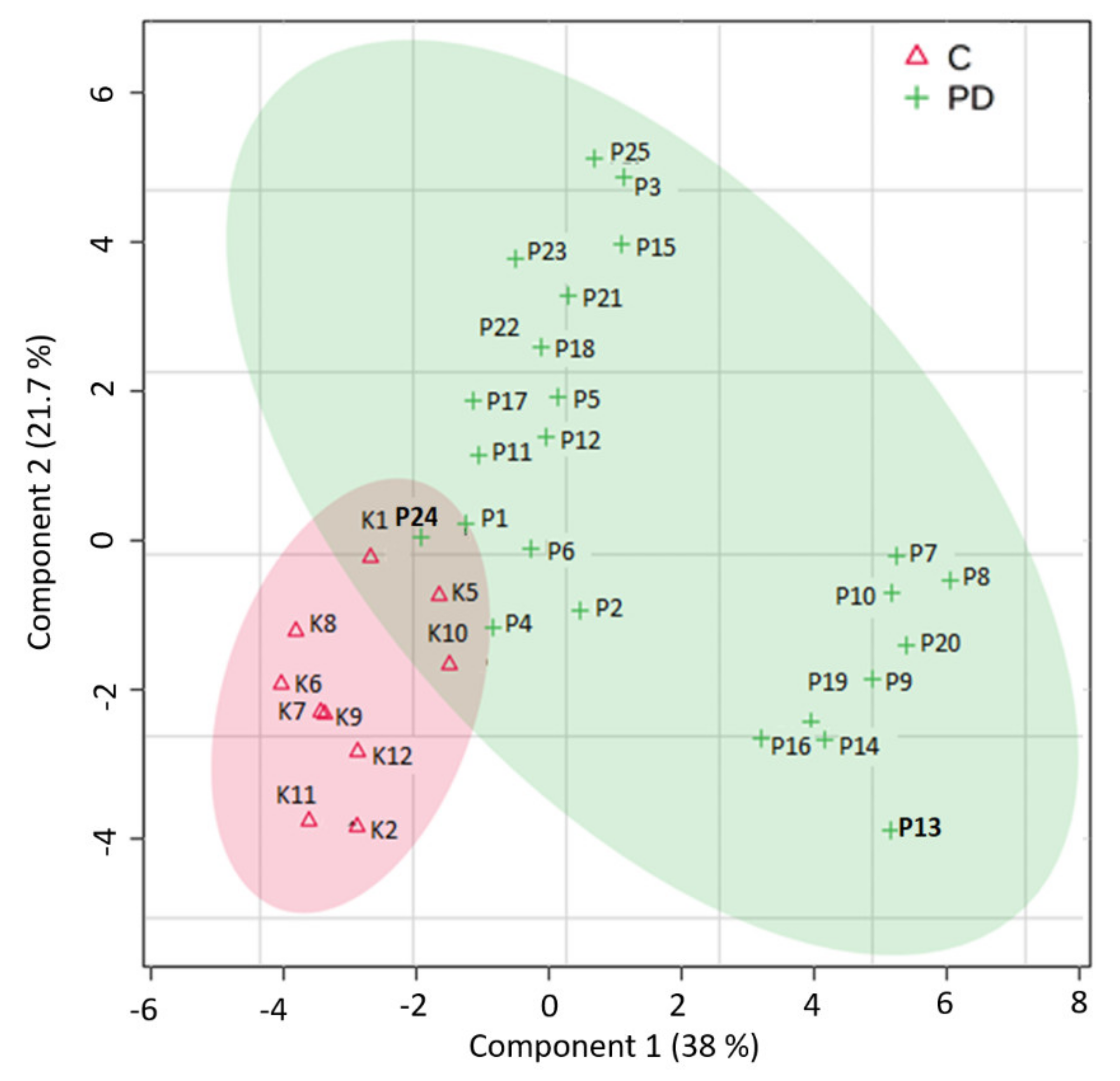
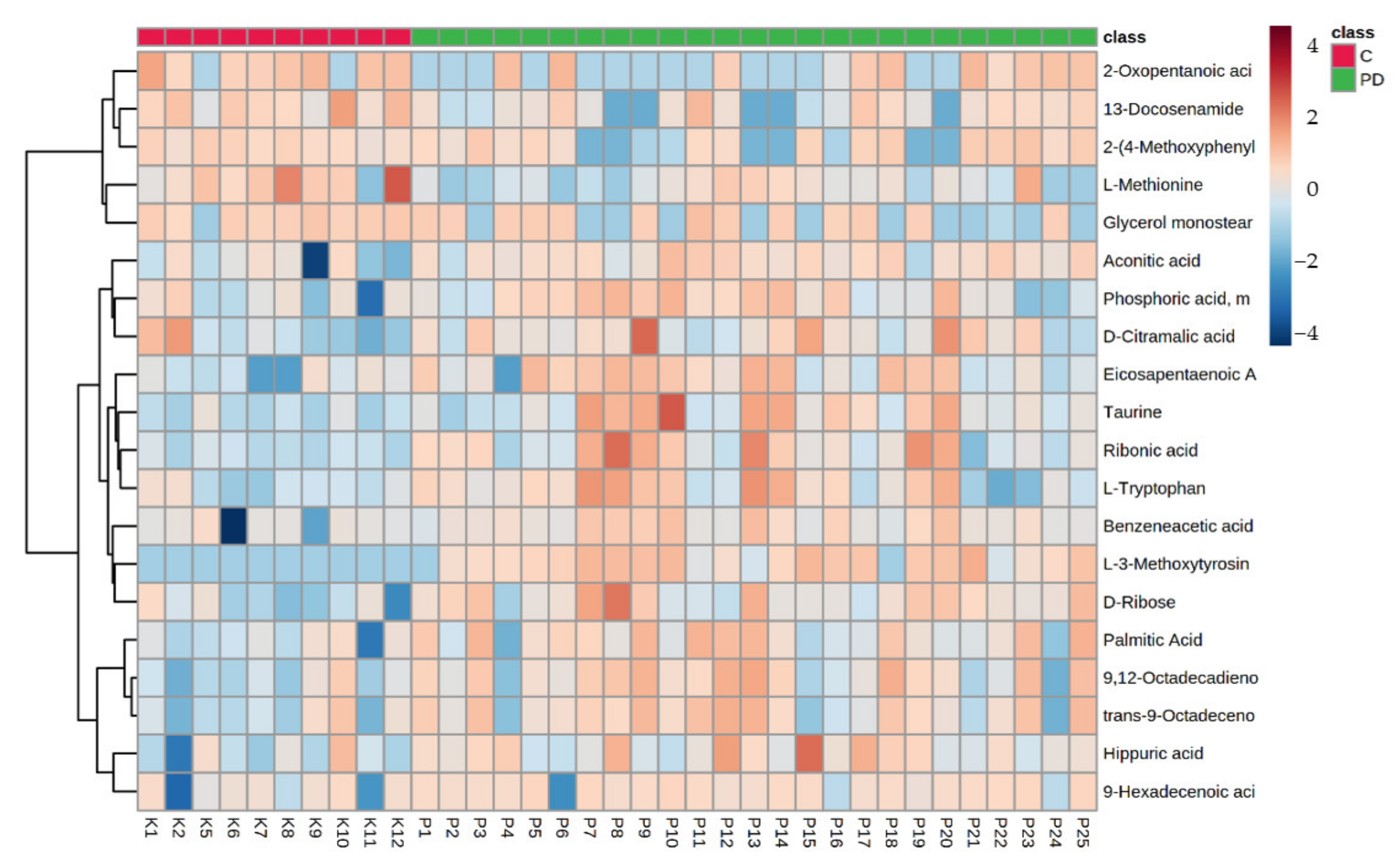
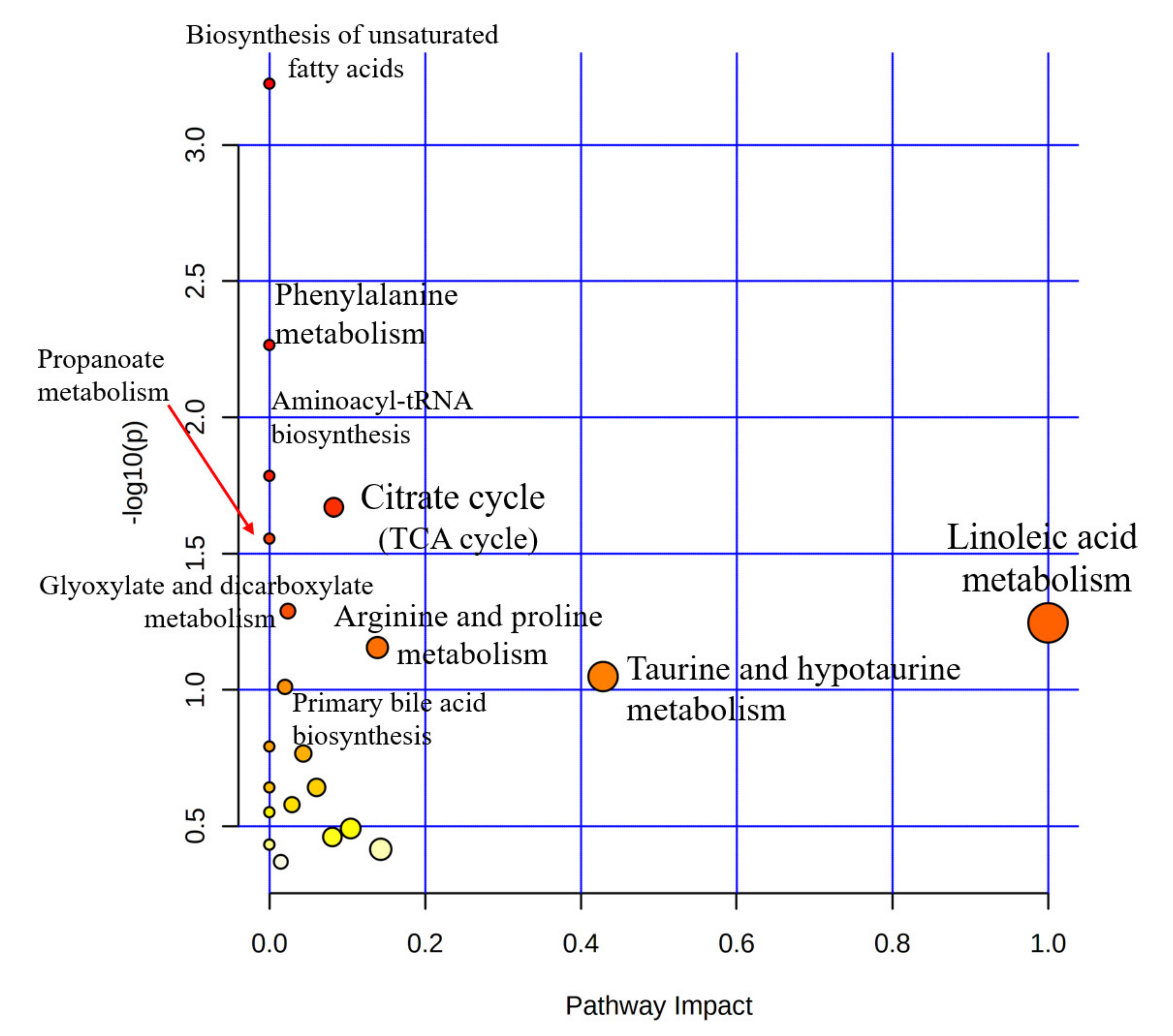
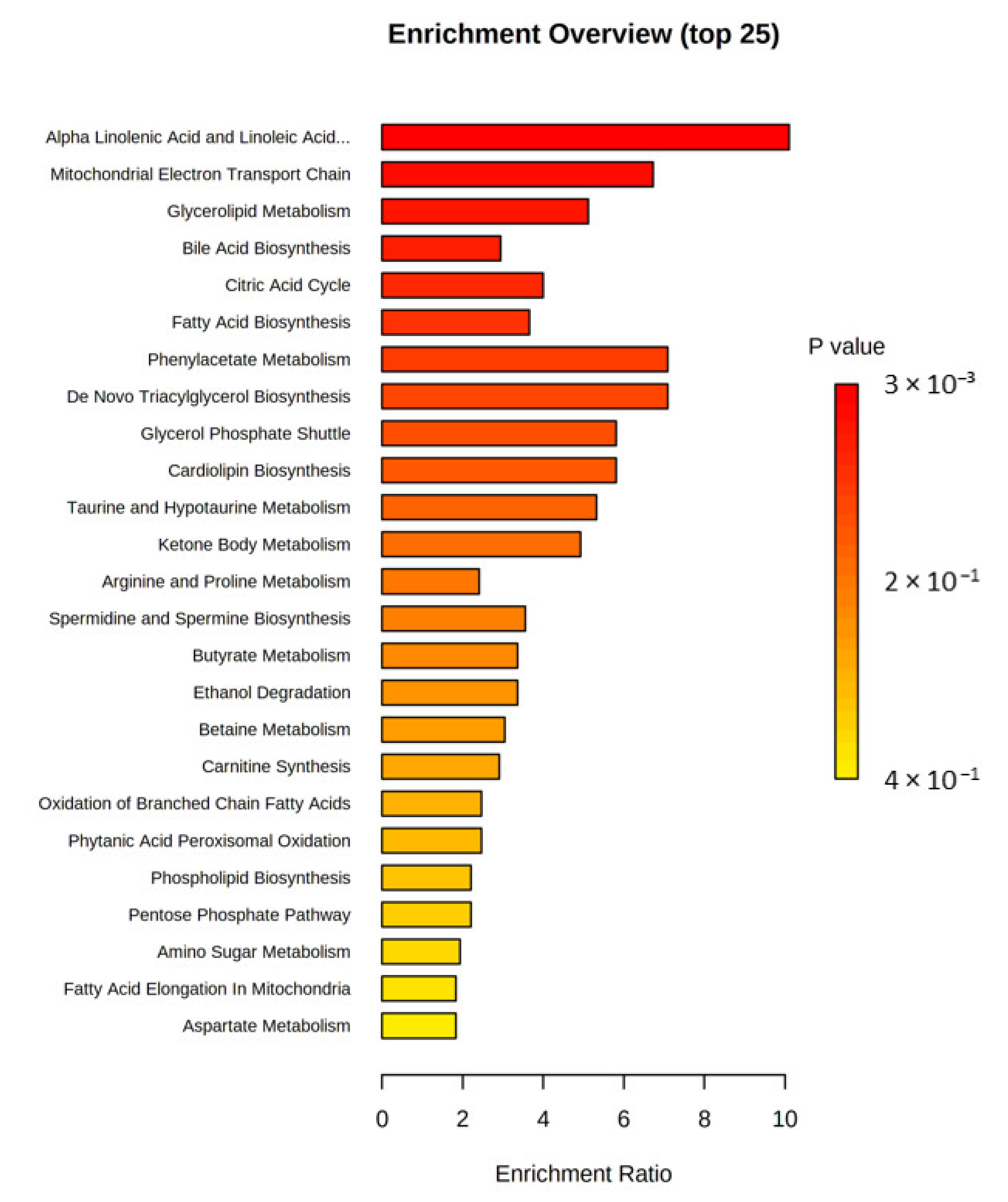
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, X.; Xie, X.; Sun, L.; Ding, J.; Cai, H. Longitudinal Metabolomics Profiling of Parkinson’s Disease-Related α-Synuclein A53T Transgenic Mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gątareka, P.; Pawełczyk, M.; Jastrzębski, K.; Głąbiński, A.; Kałużna-Czaplińska, J. Analytical methods used in the study of Parkinson’s disease. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Riano, C.; Saiz, J.; Barbas, C.; Bergareche, A.; Huerta, J.M.; Ardanaz, E.; Konjevod, M.; Mondragon, E.; Erro, E.M.; Chirlaque, M.D.; et al. Prognostic biomarkers of Parkinson’s disease in the Spanish EPIC cohort: A multiplatform metabolomics approach. NPJ Park. Dis. 2021, 7, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamelak, M. Parkinson’s Disease, the Dopaminergic Neuron and Gammahydroxybutyrate. Neurol 2018, 7, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Fan, X.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y. Review of Metabolomics-Based Biomarker Research for Parkinson’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 1041–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfil, M.; Kamel, S.; Kandil, M.; Koo, B.K.; Schaefer, S.M. Implications of the Gut Microbiome in Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2020, 35, 921–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metta, V.; Leta, V.; Mrudula, K.R.; Prashanth, L.K.; Goyal, V.; Borgohain, R.; Chung-Faye, G.; Chaudhuri, K.R. Gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease: Molecular pathology and implications of gut microbiome, probiotics, and fecal microbiota transplantation. J. Neurol. 2022, 269, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Li, C.; Gong, J.; Zhu, W.; Gu, L.; Li, N. The risk of Parkinson’s disease in inflammatory bowel disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoehn, M.M.; Yahr, M.D. Parkinsonism: Onset, progression and mortality. Neurology 1967, 17, 427–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Postuma, R.B.; Berg, D.; Stern, M.; Poewe, W.; Olanow, C.W.; Oertel, W.; Obeso, J.; Marek, K.; Litvan, I.; Lang, A.E.; et al. MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiehn, O. Metabolomics by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry: The combination of targeted and untargeted profiling. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2016, 114, 30.4.1–30.4.32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chong, J.; Wishart, D.S.; Xia, J. Using MetaboAnalyst 4.0 for Comprehensive and Integrative Metabolomics Data Analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 68, e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, L.; Johansson, E.; Kettaneh-Wold, N.; Wold, S. Introduction to Multi- and Megavariate Data Analysis Using Projection Methods (PCA & PLS); Umetrics: Umeå, Sweden, 1999; pp. 213–225. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Y.; Li, T.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Li, S.; Xu, G.; Le, W. Comprehensive metabolic profiling of Parkinson’s disease by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Mol. Neurodegener. 2021, 16, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figura, M.; Kuśmierska, K.; Bucior, E.; Szlufik, S.; Koziorowski, D.; Jamrozik, Z.; Janik, P. Serum amino acid profile in patients with Parkinson’s disease. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirayama, M.; Tsunoda, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Tsuda, T.; Ohno, K. Serum Tyrosine-to-Phenylalanine Ratio is Low in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Park. Dis. 2016, 6, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Qian, Y.; Xu, S.; Mo, C.; Yan, Z.; Yang, X.; Xiao, Q. Plasma branched-chain and aromatic amino acids correlate with the gut microbiota and severity of Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Park. Dis. 2022, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kori, M.; Aydın, B.; Unal, S.; Arga, K.Y.; Kazan, D. Metabolic Biomarkers and Neurodegeneration: A Pathway Enrichment Analysis of Alzheimer’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease, and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. OMICS 2016, 20, 645–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picca, A.; Calvani, R.; Landi, G.; Marini, F.; Biancolillo, A.; Gervasoni, J.; Persichilli, S.; Primiano, A.; Urbani, A.; Bossola, M.; et al. Circulating amino acid signature in older people with Parkinson’s disease: A metabolic complement to the EXosomes in PArkiNson Disease (EXPAND) study. Exp. Gerontol. 2019, 128, 110766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mally, J.; Szalai, G.; Stone, T.W. Changes in the concentration of amino acids in serum and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 1997, 151, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meoni, G.; Tenori, L.; Schade, S.; Licari, C.; Pirazzini, C.; Bacalini, M.G.; Garagnani, P.; Turano, P.; PROPAG-AGEING Consortium; Trenkwalder, C.; et al. Metabolite and lipoprotein profiles reveal sex-related oxidative stress imbalance in de novo drug-naive Parkinson’s disease patients. npj Park. Dis. 2022, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trupp, M.; Jonsson, P.; Ohrfelt, A.; Zetterberg, H.; Obudulu, O.; Malm, L.; Wuolikainen, A.; Linder, J.; Moritz, T.; Blennow, K.; et al. Metabolite and peptide levels in plasma and CSF differentiating healthy controls from patients with newly diagnosed Parkinson’s disease. J. Park. Dis. 2014, 4, 549–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, K.; Vowinckel, J.; Keller, M.A.; Ralser, M. Methionine Metabolism Alters Oxidative Stress. Resistance via the Pentose Phosphate Pathway. Antioxid. Redox. Signal 2016, 24, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Postuma, R.B.; Lang, A.E. Homocysteine and levodopa: Should Parkinson disease patients receive preventative therapy? Neurology 2004, 63, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozycka, A.; Jagodzinski, P.P.; Kozubski, W.; Lianeri, M.; Dorszewska, J. Homocysteine level and mechanisms of injury in Parkinson’s disease as related to MTHFR, MTR, and MTHFD1 genes polymorphisms and L-dopa treatment. Curr. Genom. 2013, 14, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barichella, M.; Severgnini, M.; Cilia, R.; Cassani, E.; Bolliri, C.; Caronni, S.; Ferri, V.; Cancello, R.; Ceccarani, C.; Faierman, S.; et al. Unraveling gut microbiota in Parkinson’s disease and atypical parkinsonism. Mov. Disord. 2019, 34, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrucci, D.; Cerroni, R.; Unida, V.; Farcomeni, A.; Pierantozzi, M.; Mercuri, N.B.; Biocca, S.; Stefani, A.; Desideri, A. Dysbiosis of gut microbiota in a selected population of Parkinson’s patients. Park. Relat. Disord. 2019, 65, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, H.; Liu, L.-F.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Chua, K.-K.; Song, J.-X.; Mok, V.C.T.; Li, M.; Cai, Z. Comprehensive urinary metabolomic profiling and identification of potential noninvasive marker for idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molina, J.A.; Jiménez-Jiménez, J.; Gomez, P.; Vargas, C.; Navarro, J.A.; Ortí-Pareja, M.; Gasalla, T.; Benito-León, J.; Bermejo, F.; Arenas, J. Decreased cerebrospinal fluid levels of neutral and basic amino acids in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 1997, 150, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilman, P.L.; Wang, E.W.; Lewis, M.M.; Krzyzanowski, S.; Capan, C.D.; Burmeister, A.R.; Du, G.; Galvis, M.L.E.; Brundin, P.; Huang, X.; et al. Tryptophan Metabolites Are Associated with Symptoms and Nigral Pathology in Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2020, 35, 2028–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, N.; Kincses, Z.T.; Toldi, J.; Vécsei, L. Altered tryptophan metabolism in Parkinson’s disease: A possible novel therapeutic approach. J. Neurol. Sci. 2011, 310, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, S.M.; Hernán, M.A.; Willett, W.C.; Ascherio, A. Weight loss in Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 2003, 53, 676–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, A.; Visanji, N.P.; Liu, L.W.C.; Lang, A.E.; Pfeiffer, R.F. Gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, I.; Gibson, G.; Heinken, A.; Scott, K.; Swann, J.; Thiele, I.; Tuohy, K. Gut microbiota functions: Metabolism of nutrients and other food components. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Havelund, J.F.; Heegaard, N.H.H.; Færgeman, N.J.K.; Gramsbergen, J.B. Biomarker research in Parkinson’s disease using metabolite profiling. Metabolites 2017, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, Y.; Le, W. Recent advances and perspectives of metabolomics-based investigations in Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Wuolikainen, A.; Trupp, M.; Jonsson, P.; Marklund, S.L.; Andersen, P.M.; Forsgren, L.; Öhman, A. NMR analysis of the CSF and plasma metabolome of rigorously matched amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease and control subjects. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willkommen, D.; Lucio, M.; Moritz, F.; Forcisi, S.; Kanawati, B.; Smirnov, K.S.; Schroeter, M.; Sigaroudi, A.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P.; Michalke, B. Metabolomic investigations in cerebrospinal fluid of Parkinson’s disease. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e02087522018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pathan, M.; Wu, J.; Lakso, H.-Å.; Forsgren, L.; Öhman, A. Plasma Metabolite Markers of Parkinson’s Disease and Atypical Parkinsonism. Metabolites 2021, 11, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Kumaran, S.S.; Goyal, V.; Sharma, R.K.; Sinha, N.; Dwivedi, S.N.; Srivastava, A.K.; Jagannathan, N.R. Identification of potential urine biomarkers in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease using NMR. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 510, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, R.M.; Wang, Z.; Brown, J.M.; Engen, P.A.; Naqib, A.; Goetz, C.G.; Hall, D.A.; Metman, L.V.; Shaikh, M.; Forsyth, C.B.; et al. Gut microbial metabolites in Parkinson’s disease: Association with lifestyle, disease characteristics, and treatment status. Neurobiol. Dis. 2022, 170, 105780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.J.; Chen, C.C.; Liao, H.-Y.; Wu, Y.-W.; Liou, J.-M.; Wu, M.-S.; Kuo, C.-H.; Lin, C.-H. Alteration of Gut Microbial Metabolites in the Systemic Circulation of Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. J. Park. Dis. 2022, 12, 1219–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosario, D.; Bidkhori, G.; Lee, S.; Bedarf, J.; Hildebrand, F.; Le Chatelier, E.; Uhlen, M.; Ehrlich, S.D.; Proctor, G.; Wüllner, U.; et al. Systematic analysis of gut microbiome reveals the role of bacterial folate and homocysteine metabolism in Parkinson’s disease. Cell Rep. 2021, 34, 108807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, D.K.; Sinclair, E.; Xu, Y.; Sarkar, D.; Walton-Doyle, C.; Liscio, C.; Banks, P.; Milne, J.; Silverdale, M.; Kunath, T.; et al. Discovery of Volatile Biomarkers of Parkinson’s Disease from Sebum. ACS Cent. Sci. 2019, 5, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gall, W.E.; Beebe, K.; Lawton, K.A.; Adam, K.P.; Mitchell, M.W.; Nakhle, P.J.; Ryals, J.A.; Milburn, M.V.; Nannipieri, M.; Camastra, S.; et al. alpha-hydroxybutyrate is an early biomarker of insulin resistance and glucose intolerance in a nondiabetic population. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wuolikainen, A.; Jonsson, P.; Ahnlund, M.; Antti, H.; Marklund, S.L.; Moritz, T.; Forsgren, L.; Andersen, P.M.; Trupp, M. Multi-platform mass spectrometry analysis of the CSF and plasma metabolomes of rigorously matched amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease and control subjects. Mol. Biosyst. 2016, 12, 1287–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahata, I.; Bousset, L.; Melki, R.; Fukunaga, K. Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 3 is Critical for α-Synuclein Uptake and MPP+-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Cultured Dopaminergic Neurons. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, H.; Gerhold, K.; Mayers, J.R.; Wiest, M.M.; Watkins, S.M.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Identification of a lipokine, a lipid hormone linking adipose tissue to systemic metabolism. Cell 2008, 134, 933–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hertel, J.; Harms, A.C.; Heinken, A.; Baldini, F.; Thinnes, C.; Glaab, E.; Vasco, D.A.; Pietzner, M.; Stewart, I.D.; Wareham, N.J.; et al. Integrated Analyses of Microbiome and Longitudinal Metabolome Data Reveal Microbial-Host Interactions on Sulfur Metabolism in Parkinson’s Disease. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 1767–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graham, S.F.; Rey, N.L.; Yilmaz, A.; Kumar, P.; Madaj, Z.; Maddens, M.; Bahado-Singh, R.O.; Becker, K.; Schulz, E.; Meyerdirk, L.K. Biochemical Profiling of the Brain and Blood Metabolome in a Mouse Model of Prodromal Parkinson’s Disease Reveals Distinct Metabolic Profiles. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 2460–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Goyal, V.; Kumaran, S.S.; Dwivedi, S.N.; Srivastava, A.; Jagannathan, N.R. Quantitative metabolomics of saliva using proton NMR spectroscopy in patients with Parkinson’s disease and healthy controls. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 41, 1201–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, L.; Allen, G.F.; Mamais, A.; Ling, H.; Li, A.; Duberley, K.E.; Hargreaves, I.P.; Pope, S.; Holton, J.L.; Lees, A.; et al. Dysregulation of glucose metabolism is an early event in sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 1111–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Camandola, S.; Mattson, M.P. Brain metabolism in health, aging, and neurodegeneration. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 1474–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, D.; Gao, Y.; Yang, R.; Guan, T.; Hong, J.-S.; Gao, H.-M. The pentose phosphate pathway regulates chronic neuroinflammation and dopaminergic neurodegeneration. J. Neuroinflammation 2019, 16, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barupal, D.K.; Fiehn, O. Generating the Blood Exposome Database Using a Comprehensive Text Mining and Database Fusion Approach. Environ. Health Perspect. 2019, 127, 97008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Sun, F.; Ma, Y.; Deng, L.; Lü, J.; Li, T.; Wang, C. Serum metabolomics analysis on benign prostate hyperplasia in mice based on liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Se Pu 2014, 32, 1301–1305. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Metz, C.E. Basic principles of ROC analysis. Semin. Nucl. Med. 1978, 8, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Study Population | PD | Control |
|---|---|---|
| Participants | 25 | 12 |
| Gender | ||
| Female | 8 | 5 |
| Male | 17 | 7 |
| Age (years) | 68.7 ± 7.0 | 56.2 ± 18.3 |
| BMI | 26.7 ± 3.6 | 30.5 ± 9.1 |
| Disease duration (years) | 5.5 ± 4.1 | - |
| Hoehn and Yahr scale | 2.4 ± 1.1 | - |
| H–Y1 | 7 (28%) | - |
| H–Y2 | 4 (16%) | |
| H–Y3 | 8 (32%) | |
| H–Y4 | 6 (24%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gątarek, P.; Sekulska-Nalewajko, J.; Bobrowska-Korczaka, B.; Pawełczyk, M.; Jastrzębski, K.; Głąbiński, A.; Kałużna-Czaplińska, J. Plasma Metabolic Disturbances in Parkinson’s Disease Patients. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3005. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123005
Gątarek P, Sekulska-Nalewajko J, Bobrowska-Korczaka B, Pawełczyk M, Jastrzębski K, Głąbiński A, Kałużna-Czaplińska J. Plasma Metabolic Disturbances in Parkinson’s Disease Patients. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(12):3005. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123005
Chicago/Turabian StyleGątarek, Paulina, Joanna Sekulska-Nalewajko, Barbara Bobrowska-Korczaka, Małgorzata Pawełczyk, Karol Jastrzębski, Andrzej Głąbiński, and Joanna Kałużna-Czaplińska. 2022. "Plasma Metabolic Disturbances in Parkinson’s Disease Patients" Biomedicines 10, no. 12: 3005. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123005
APA StyleGątarek, P., Sekulska-Nalewajko, J., Bobrowska-Korczaka, B., Pawełczyk, M., Jastrzębski, K., Głąbiński, A., & Kałużna-Czaplińska, J. (2022). Plasma Metabolic Disturbances in Parkinson’s Disease Patients. Biomedicines, 10(12), 3005. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123005