Adalimumab Originator vs. Biosimilar in Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A Multicentric Retrospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
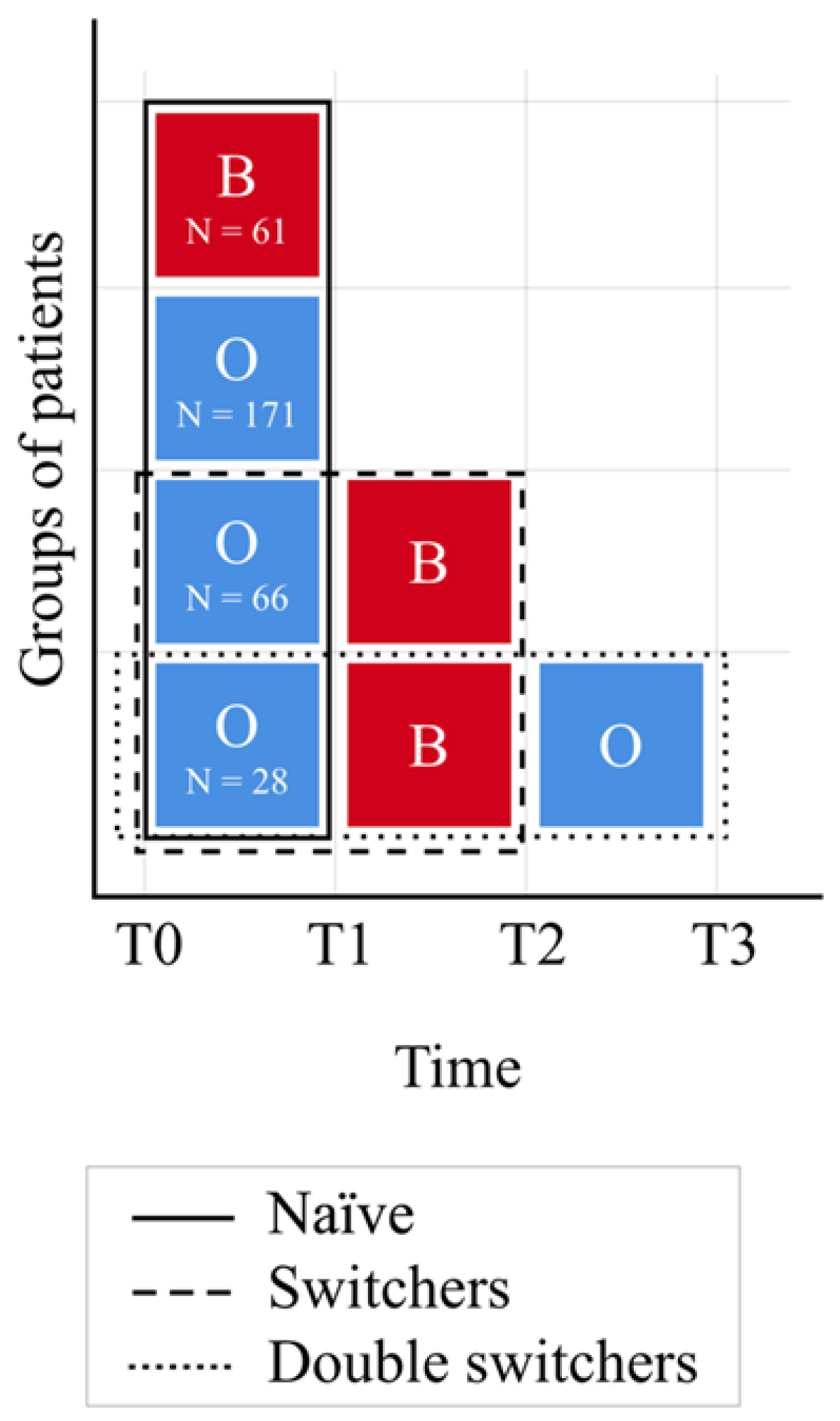
2.2. Timeline
2.3. Statistical Analyses
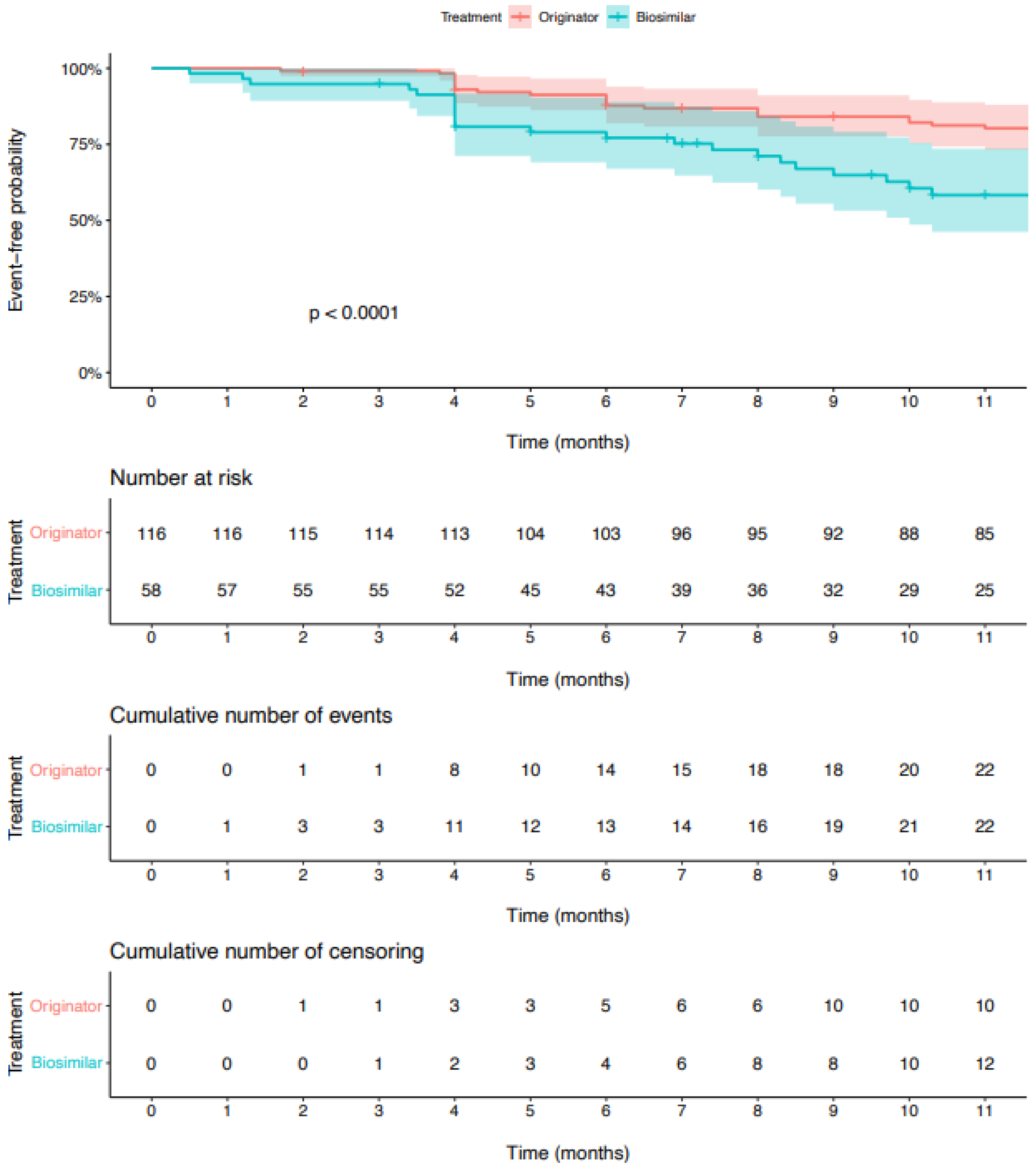
3. Results
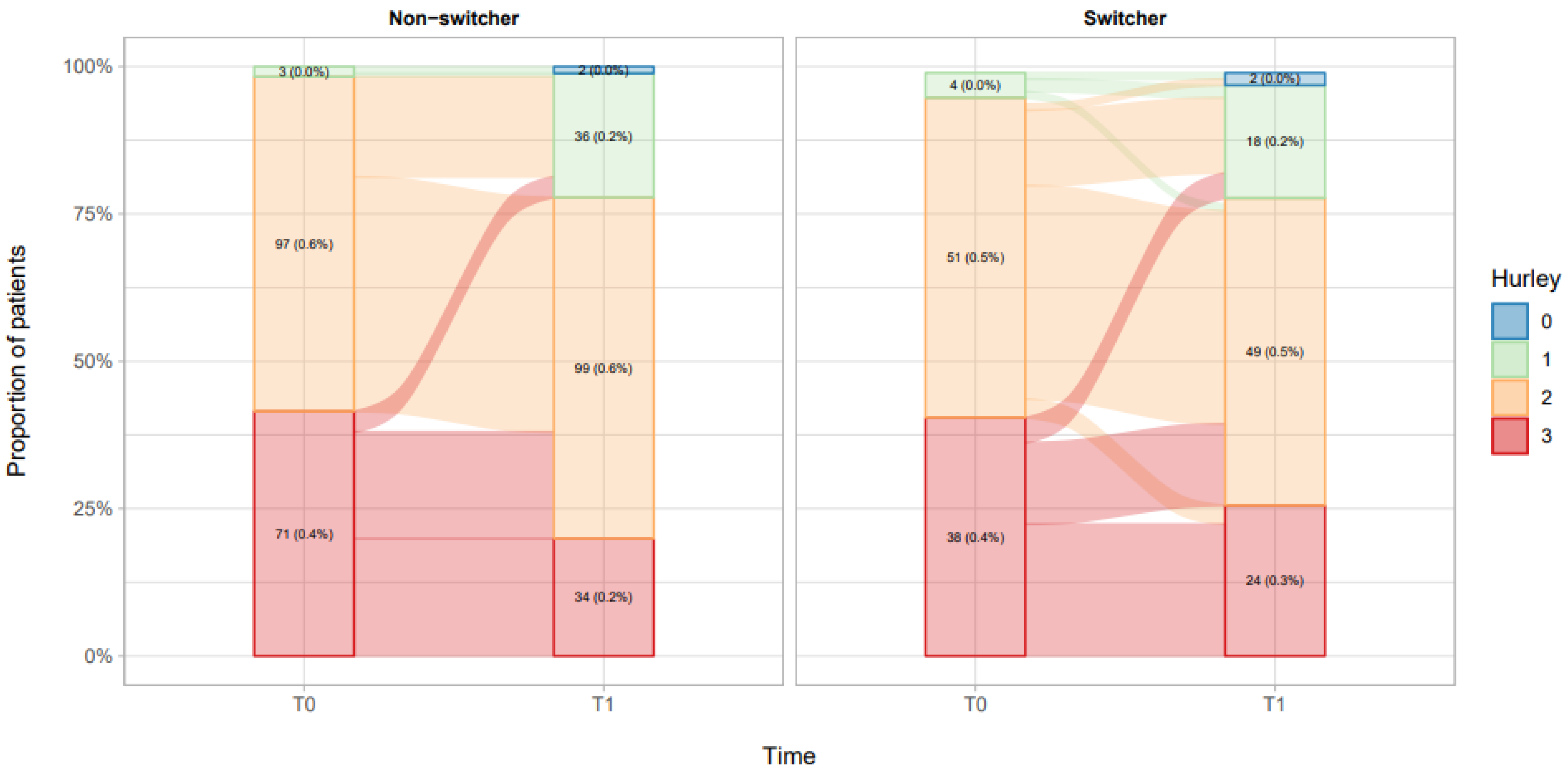
3.1. Non-Switcher Analysis
3.2. Switcher Analysis
3.3. Final Model
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saunte, D.M.L.; Jemec, G.B.E. Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Advances in Diagnosis and Treatment. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2017, 318, 2019–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alikhan, A. Hidradenitis Suppurativa. JAMA Dermatol. 2016, 152, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingram, J.R. The epidemiology of hidradenitis suppurativa. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 183, 990–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchero, H.; Herlin, C.; Bekara, F.; Fluieraru, S.; Teot, L. Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Therapeutic Interventions. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2019, 85, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veraldi, S.; Guanziroli, E.; Benzecry, V.; Nazzaro, G. Multidisciplinary approach for hidradenitis suppurativa patients. G Ital. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018, 153, 18–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulliver, W.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Prens, E.; Jemec, G.B.E.; Tzellos, T. Evidence-based approach to the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa/acne inversa, based on the European guidelines for hidradenitis suppurativa. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2016, 17, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touhouche, A.T.; Chaput, B.; Rouquet, R.M.; Montastier, E.; Caron, P.; Gall, Y.; Aquilina, C.; Boulinguez, S.; Marguery, M.C.; Giordano-Labadie, F.; et al. Integrated multidisciplinary approach to hidradenitis suppurativa in clinical practice. Int. J. Womens Dermatol. 2020, 6, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimball, A.B.; Okun, M.M.; Williams, D.A.; Gottlieb, A.B.; Papp, K.A.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Armstrong, A.W.; Kerdel, F.; Gold, M.H.; Forman, S.B.; et al. Two Phase 3 Trials of Adalimumab for Hidradenitis Suppurativa. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Cernea, M.; Abramovits, W.; Vincent, K.D. Adalimumab (Humira) for Hidradenitis Suppurativa. Skinmed 2016, 14, 291–294. [Google Scholar]
- Gellad, W.F.; Good, C.B. Adalimumab and the Challenges for Biosimilars. JAMA 2019, 322, 2171–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, P. Humira: The impending patent battles over adalimumab biosimilars. Pharm. Pat. Anal. 2016, 5, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricceri, F.; Rosi, E.; Di Cesare, A.; Pescitelli, L.; Fastame, M.T.; Prignano, F. Clinical experience with adalimumab biosimilar imraldi in hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e14387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, S. Low-dose adalimumab biosimilar (ZRC-3197) in the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2018, 84, 745–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynne, C.; Altendorfer, M.; Sonderegger, I.; Gheyle, L.; Ellis-Pegler, R.; Buschke, S.; Lang, B.; Assudani, D.; Athalye, S.; Czeloth, N. Bioequivalence, safety and immunogenicity of BI 695501, an adalimumab biosimilar candidate, compared with the reference biologic in a randomized, double-blind, active comparator phase I clinical study (VOLTAIRE®-PK) in healthy subjects. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2016, 12, 1361–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno-Gracia, M.; Gargallo-Puyuelo, C.J.; Gomollón, F. Bioequivalence studies with anti-TNF biosimilars. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2019, 10, 1031–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero-Vilchez, T.; Cuenca-Barrales, C.; Rodriguez-Tejero, A.; Martinez-Lopez, A.; Arias-Santiago, S.; Molina-Leyva, A. Switching from Adalimumab Originator to Biosimilar: Clinical Experience in Patients with Hidradenitis Suppurativa. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurly, H. Axillary hyperhidrosis, apocrine bromhidrosis, hidradenitis suppurativa, and familial benign pemphigus: Surgical approach. In Dermatologic Surgery: Principles and Practice; Roenigk, R.K., Roenigk, H.H., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 729–739. [Google Scholar]
- Ingram, J.R. Refining the hidradenitis suppurativa Hurley staging system for mild, moderate and severe disease. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 180, 991–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 17 August 2022).
- Ho, D.E.; Imai, K.; King, G.; Stuart, E.A. MatchIt: Nonparametric Preprocessing for Parametric Causal Inference. J. Stat. Softw. 2011, 42, 1–28. Available online: http://www.jstatsoft.org/v42/i08/ (accessed on 17 August 2022). [CrossRef]
- Murdaca, G.; Negrini, S.; Greco, M.; Schiavi, C.; Giusti, F.; Borro, M.; Puppo, F. Immunogenicity of infliximab and adalimumab. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2019, 18, 343–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Degner, J.; Davis, J.W.; Idler, K.B.; Nader, A.; Mostafa, N.M.; Waring, J.F. Identification of HLA-DRB1 association to adalimumab immunogenicity. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frampton, J.E. SB5, An Adalimumab Biosimilar. BioDrugs 2018, 32, 507–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraev, K.; Geneva-Popova, M.; Popova, V.; Popova, S.; Maneva, A.; Batalov, A.; Stankova, T.; Delcheva, G.; Stefanova, K. Drug-neutralizing Antibodies against TNF-alpha blockers as Biomarkers of Therapy Effect Evaluation. Folia Med. 2020, 62, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartelds, G.M.; Krieckaert, C.L.; Nurmohamed, M.T.; van Schouwenburg, P.A.; Lems, W.F.; Twisk, J.W.; Dijkmans, B.A.; Aarden, L.; Wolbink, G.J. Development of antidrug antibodies against adalimumab and association with disease activity and treatment failure during long-term follow-up. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2011, 305, 1460–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorlacius, L.; Garg, A.; Riis, P.T.; Nielsen, S.M.; Bettoli, V.; Ingram, J.; Del Marmol, V.; Matusiak, L.; Pascual, J.; Revuz, J.; et al. Inter-rater agreement and reliability of outcome measurement instruments and staging systems used in hidradenitis suppurativa. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 181, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Overall N = 174 | Originator N = 116 | Biosimilar N = 58 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), Mean (SD) | 33.26 (12.13) | 33.16 (12.59) | 33.45 (11.25) | 0.885 |
| Female sex, N (%) | 84 (48.3) | 56 (48.3) | 28 (48.3) | 0.999 |
| BMI, Mean (SD) | 27.22 (4.66) | 27.25 (4.68) | 27.16 (4.66) | 0.910 |
| Current smoker, N (%) | 129 (74.1) | 87 (75.0) | 42 (72.4) | 0.854 |
| Disease duration (years), Median [IQR] | 10 [5, 19] | 10 [5, 19] | 10 [5, 19] | 0.634 |
| HS localization, N (%) | ||||
| Armpits | 78 (44.8) | 53 (45.7) | 25 (43.1) | 0.872 |
| Groin | 82 (47.1) | 53 (45.7) | 29 (50.0) | 0.707 |
| Perineum | 21 (12.1) | 13 (11.2) | 8 (13.8) | 0.805 |
| Others/Unavailable | 74 (42.5) | 50 (43.1) | 24 (41.4) | 0.957 |
| Hurley score, Mean (SD) Median [IQR] | 2.37 (0.52) 2 [2, 3] | 2.37 (0.52) 2 [2, 3] | 2.36 (0.52) 2 [2, 3] | 0.915 |
| Hurley Score Worsened, N (%) | Stable Hurley Score, N (%) | Hurley Score Improved, N (%) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1—Challenge (originator) | 1 (3.6) | 18 (64.3) | 9 (32.1) | 0.001 |
| T2—De-challenge (biosimilar) * | 6 (21.4) | 22 (78.6) | 0 (0.0) | |
| T3—Re-challenge (originator) | 0 (0.0) | 23 (82.1) | 5 (17.9) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Burlando, M.; Fabbrocini, G.; Marasca, C.; Dapavo, P.; Chiricozzi, A.; Malvaso, D.; Dini, V.; Campanati, A.; Offidani, A.; Dattola, A.; et al. Adalimumab Originator vs. Biosimilar in Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A Multicentric Retrospective Study. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2522. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102522
Burlando M, Fabbrocini G, Marasca C, Dapavo P, Chiricozzi A, Malvaso D, Dini V, Campanati A, Offidani A, Dattola A, et al. Adalimumab Originator vs. Biosimilar in Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A Multicentric Retrospective Study. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(10):2522. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102522
Chicago/Turabian StyleBurlando, Martina, Gabriella Fabbrocini, Claudio Marasca, Paolo Dapavo, Andrea Chiricozzi, Dalma Malvaso, Valentina Dini, Anna Campanati, Annamaria Offidani, Annunziata Dattola, and et al. 2022. "Adalimumab Originator vs. Biosimilar in Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A Multicentric Retrospective Study" Biomedicines 10, no. 10: 2522. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102522
APA StyleBurlando, M., Fabbrocini, G., Marasca, C., Dapavo, P., Chiricozzi, A., Malvaso, D., Dini, V., Campanati, A., Offidani, A., Dattola, A., Caro, R. D. C., Bianchi, L., Venturini, M., Gisondi, P., Guarneri, C., Malara, G., Trifirò, C., Malagoli, P., Fargnoli, M. C., ... Parodi, A. (2022). Adalimumab Originator vs. Biosimilar in Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A Multicentric Retrospective Study. Biomedicines, 10(10), 2522. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102522









