Prognostic Role of Androgen Receptor Expression in HER2+ Breast Carcinoma Subtypes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Immunohistochemistry
2.2. Baseline Data
2.3. Statistical Analysis
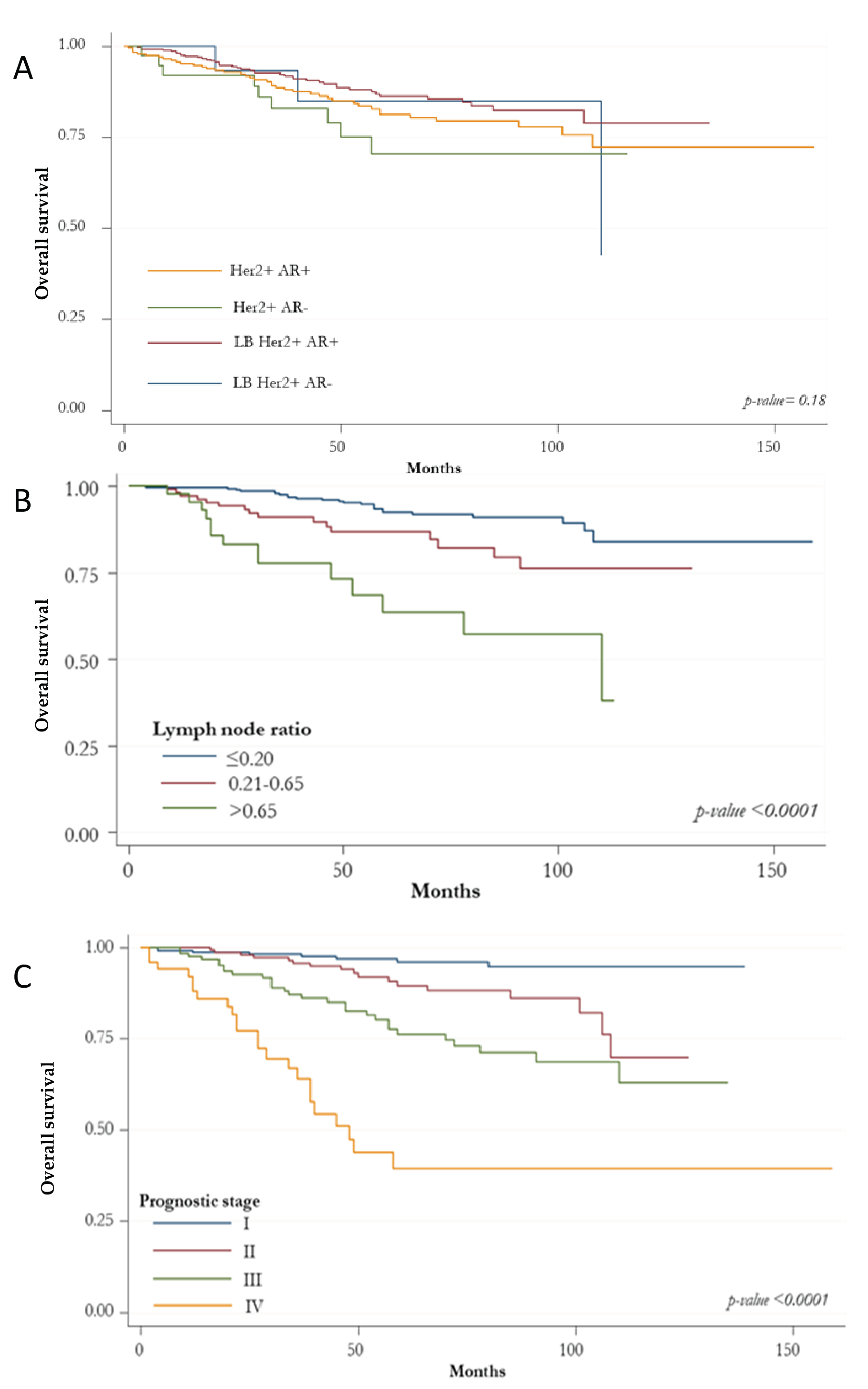
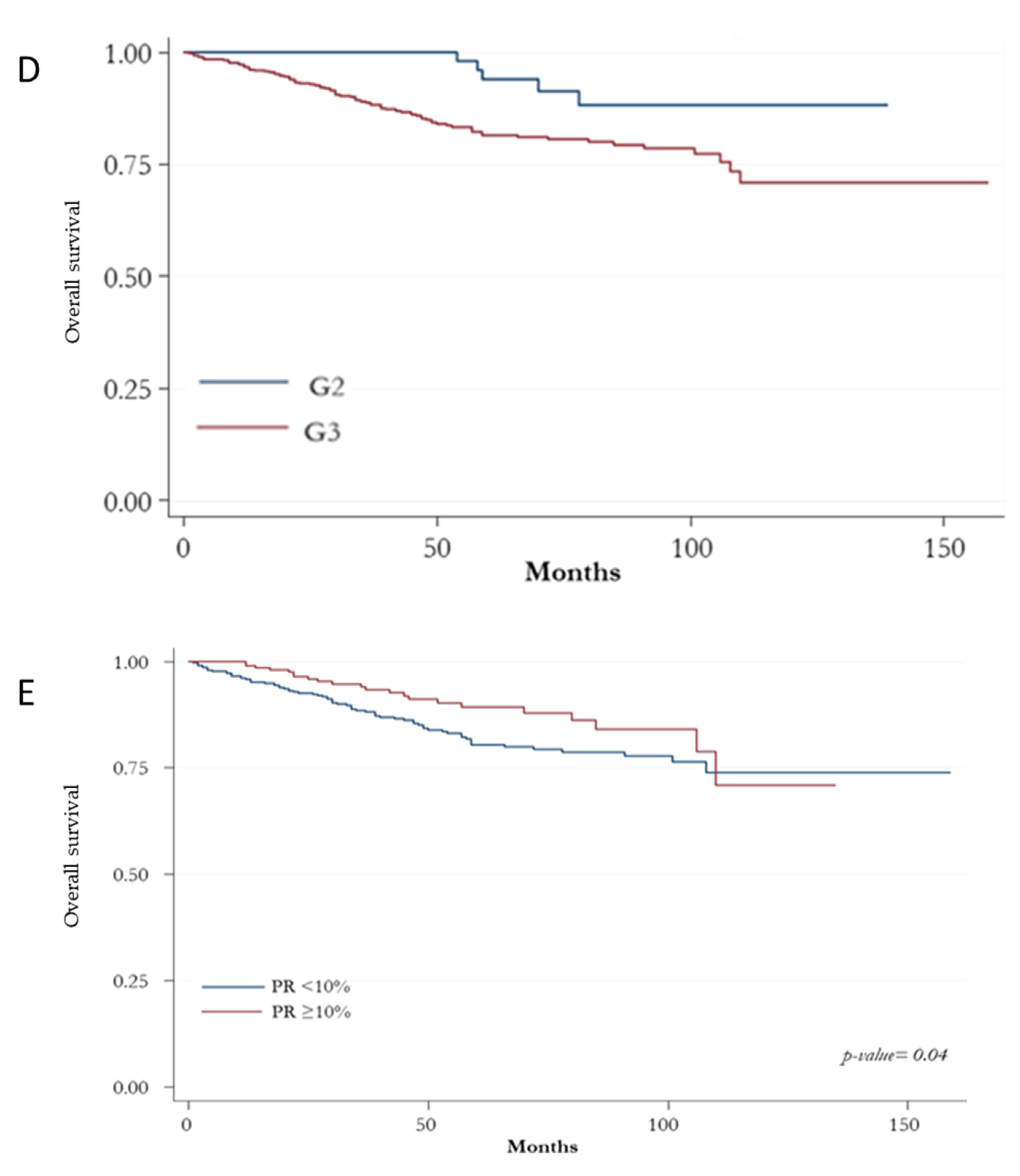
3. Results
Prognostic Indicators according to HER2+ BC Subtypes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sanges, F.; Floris, M.; Cossu-Rocca, P.; Muroni, M.R.; Pira, G.; Urru, S.A.M.; Barrocu, R.; Gallus, S.; Bosetti, C.; D’Incalci, M.; et al. Histologic subtyping affecting outcome of triple negative breast cancer: A large Sardinian population-based analysis. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uva, P.; Cossu-Rocca, P.; Loi, F.; Pira, G.; Murgia, L.; Orrù, S.; Floris, M.; Muroni, M.R.; Sanges, F.; Carru, C.; et al. miRNA-135b Contributes to Triple Negative Breast Cancer Molecular Heterogeneity: Different Expression Profile in Basal-like Versus non-Basal-like Phenotypes. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 15, 536–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Su, K.; Zeng, J. Clinicopathological classification and traditional prognostic indicators of breast cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 8500–8505. [Google Scholar]
- Boyle, P. Triple-negative breast cancer: Epidemiological considerations and recommendations. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2012, 23 (Suppl. 6), vi7–vi12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakha, E.A.; Allison, K.H.; Ellis, I.O.; Horii, R.; Masuda, S.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Tsuda, H.; Vincent-Salomon, A. Invasive breast carcinoma: General overview. In WHO Classification of Tumours, 5th ed.; WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board, Ed.; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2019; pp. 82–101. [Google Scholar]
- Wolff, A.C.; Hammond, M.E.H.; Hicks, D.G.; Dowsett, M.; McShane, L.M.; Allison, K.H.; Allred, D.C.; Bartlett, J.M.S.; Bilous, M.; Fitzgibbons, P.; et al. Recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists clinical practice guideline update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3997–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittrich, A.; Gautrey, H.; Browell, D.; Tyson-Capper, A. The HER2 Signaling Network in Breast Cancer—Like a Spider in its Web. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 2014, 19, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burstein, H.J.; Curigliano, G.; Loibl, S.; Dubsky, P.; Gnant, M.; Poortmans, P.; Colleoni, M.; Denkert, C.; Piccart-Gebhart, M.; Regan, M.; et al. Estimating the benefits of therapy for early-stage breast cancer: The St. Gallen International Consensus Guidelines for the primary therapy of early breast cancer 2019. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1541–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Deng, S.; Chen, J.; Xu, X.; Hu, X.; Kong, D.; Liang, G.; Yuan, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. The Synergistic Effects of Pyrotinib Combined With Adriamycin on HER2-Positive Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, C.; Cobleigh, M.A.; Tripathy, D.; Gutheil, J.C.; Harris, L.N.; Fehrenbacher, L.; Slamon, D.J.; Murphy, M.; Novotny, W.F.; Burchmore, M.; et al. First-line, single-agent Herceptin® (trastuzumab) in metastatic breast cancer: A preliminary report. Eur. J. Cancer 2001, 37, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gijsen, M.; King, P.; Perera, T.; Parker, P.J.; Harris, A.L.; Larijani, B.; Kong, A. HER2 Phosphorylation Is Maintained by a PKB Negative Feedback Loop in Response to Anti-HER2 Herceptin in Breast Cancer. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scaltriti, M.; Rojo, F.; Ocaña, A.; Anido, J.; Guzman, M.; Cortes, J.; Di Cosimo, S.; Matias-Guiu, X.; Ramon y Cajal, S.; Arribas, J.; et al. Expression of p95HER2, a truncated form of the HER2 receptor, and response to anti-HER2 therapies in breast cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2007, 99, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagata, Y.; Lan, K.H.; Zhou, X.; Tan, M.; Esteva, F.J.; Sahin, A.A.; Klos, K.S.; Li, P.; Monia, B.P.; Nguyen, N.T.; et al. PTEN activation contributes to tumor inhibition by trastuzumab, and loss of PTEN predicts trastuzumab resistance in patients. Cancer Cell 2004, 6, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Zi, X.; Pollak, M. Molecular mechanisms underlying IGF-I-induced attenuation of the growth-inhibitory activity of trastuzumab (Herceptin) on SKBR3 breast cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 108, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, G.; Brantley-Sieders, D.M.; Vaught, D.; Yu, J.; Xie, L.; Wells, S.; Jackson, D.; Muraoka-Cook, R.; Arteaga, C.; Chen, J. Elevation of receptor tyrosine kinase EphA2 mediates resistance to trastuzumab therapy. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moinfar, F.; Okcu, M.; Tsybrovskyy, O.; Regitnig, P.; Lax, S.F.; Weybora, W.; Ratschek, M.; Tavassoli, F.A.; Denk, H. Androgen receptors frequently are expressed in breast carcinomas: Potential relevance to new therapeutic strategies. Cancer 2003, 98, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Koo, J.; Park, H.S.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, S.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Park, B.W.; Lee, K.S. Expression of androgen receptors in primary breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2010, 21, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemeier, L.A.; Dabbs, D.J.; Beriwal, S.; Striebel, J.M.; Bhargava, R. Androgen receptor in breast cancer: Expression in estrogen receptor-positive tumors and in estrogen receptor-negative tumors with apocrine differentiation. Mod. Pathol. 2010, 23, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kensler, K.H.; Regan, M.M.; Heng, Y.J.; Baker, G.M.; Pyle, M.E.; Schnitt, S.J.; Hazra, A.; Kammler, R.; Thürlimann, B.; Colleoni, M.; et al. Prognostic and predictive value of androgen receptor expression in postmenopausal women with estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer: Results from the Breast International Group Trial 1-98. Breast Cancer Res. 2019, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collins, L.C.; Cole, K.S.; Marotti, J.D.; Hu, R.; Schnitt, S.J.; Tamimi, R.M. Androgen receptor expression in breast cancer in relation to molecular phenotype: Results from the Nurses’ Health Study. Mod. Pathol. 2011, 24, 924–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Q.; Niu, Y.; Liu, N.; Zhang, J.Z.; Liu, T.J.; Zhang, R.J.; Wang, S.L.; Ding, X.M.; Xiao, X.Q. Expression of androgen receptor in breast cancer and its significance as a prognostic factor. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2011, 22, 1288–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.S.; Kuang, X.Y.; Sun, W.L.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, Y.Z.; Liu, Y.R.; Lang, G.T.; Qiao, F.; Hu, X.; Shao, Z.M. Androgen receptor expression predicts different clinical outcomes for breast cancer patients stratified by hormone receptor status. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 41285–41293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bozovic-Spasojevic, I.; Zardavas, D.; Brohee, S.; Ameye, L.; Fumagalli, D.; Ades, F.; De Azambuja, E.; Bareche, Y.; Piccart, M.; Paesmans, M.; et al. The Prognostic Role of Androgen Receptor in Patients with Early-Stage Breast Cancer: A Meta-analysis of Clinical and Gene Expression Data. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 2702–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Amicis, F.; Thirugnansampanthan, J.; Cui, Y.; Selever, J.; Beyer, A.; Parra, I.; Weigel, N.L.; Herynk, M.H.; Tsimelzon, A.; Lewis, M.T.; et al. Androgen receptor overexpression induces tamoxifen resistance in human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 121, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rechoum, Y.; Rovito, D.; Iacopetta, D.; Barone, I.; Andò, S.; Weigel, N.L.; O’Malley, B.W.; Brown, P.H.; Fuqua, S.A.W. AR collaborates with ERα in aromatase inhibitor-resistant breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 147, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amato, N.C.; Gordon, M.A.; Babbs, B.; Spoelstra, N.S.; Butterfield, K.T.C.; Torkko, K.C.; Phan, V.T.; Barton, V.N.; Rogers, T.J.; Sartorius, C.A.; et al. Cooperative Dynamics of AR and ER Activity in Breast Cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2016, 14, 1054–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerratana, L.; Basile, D.; Buono, G.; De Placido, S.; Giuliano, M.; Minichillo, S.; Coinu, A.; Martorana, F.; De Santo, I.; Del Mastro, L.; et al. Androgen receptor in triple negative breast cancer: A potential target for the targetless subtype. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018, 68, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricciardelli, C.; Bianco-Miotto, T.; Jindal, S.; Butler, L.M.; Leung, S.; McNeil, C.M.; O’Toole, S.A.; Ebrahimie, E.; Millar, E.K.A.; Sakko, A.J.; et al. The Magnitude of Androgen Receptor Positivity in Breast Cancer Is Critical for Reliable Prediction of Disease Outcome. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 2328–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Micello, D.; Marando, A.; Sahnane, N.; Riva, C.; Capella, C.; Sessa, F. Androgen receptor is frequently expressed in HER2-positive, ER/PR-negative breast cancers. Virchows Arch. 2010, 457, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isola, J.J. Immunohistochemical demonstration of androgen receptor in breast cancer and its relationship to other prognostic factors. J. Pathol. 1993, 170, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farmer, P.; Bonnefoi, H.; Becette, V.; Tubiana-Hulin, M.; Fumoleau, P.; Larsimont, D.; MacGrogan, G.; Bergh, J.; Cameron, D.; Goldstein, D.; et al. Identification of molecular apocrine breast tumours by microarray analysis. Oncogene 2005, 24, 4660–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ni, M.; Chen, Y.; Lim, E.; Wimberly, H.; Bailey, S.T.; Imai, Y.; Rimm, D.L.; Shirley Liu, X.; Brown, M. Targeting Androgen Receptor in Estrogen Receptor-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Mattos Lima Lin, F.; Pincerato, K.M.; Bacchi, C.E.; Baracat, E.C.; Carvalho, F.M. Coordinated expression of oestrogen and androgen receptors in HER2-positive breast carcinomas: Impact on proliferative activity. J. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 65, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Bi, X.; Huang, Z.; Huang, J.; Xia, W.; Shi, W.; Yuan, Z. The prognostic value of androgen receptor (AR) in HER2-enriched metastatic breast cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2020, 27, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urru, S.A.M.; Gallus, S.; Bosetti, C.; Moi, T.; Medda, R.; Sollai, E.; Murgia, A.; Sanges, F.; Pira, G.; Manca, A.; et al. Clinical and pathological factors influencing survival in a large cohort of triple-negative breast cancer patients. BMC Cancer 2018, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elston, C.W.; Ellis, I.O. Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. I. The value of histological grade in breast cancer: Experience from a large study with long-term follow-up. Histopathology 2002, 41, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edge, S.B.; Compton, C.C. The american joint committee on cancer: The 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging manual and the future of TNM. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 17, 1471–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinh-Hung, V.; Verkooijen, H.M.; Fioretta, G.; Neyroud-Caspar, I.; Rapiti, E.; Vlastos, G.; Deglise, C.; Usel, M.; Lutz, J.M.; Bouchardy, C. Lymph node ratio as an alternative to pN staging in node-positive breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1062–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Staaf, J.; Jönsson, G.; Ringnér, M.; Vallon-Christersson, J.; Grabau, D.; Arason, A.; Gunnarsson, H.; Agnarsson, B.A.; Malmström, P.O.; Johannsson, O.T.; et al. High-resolution genomic and expression analyses of copy number alterations in HER2-amplified breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2010, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicolás Díaz-Chico, B.; Germán Rodríguez, F.; González, A.; Ramírez, R.; Bilbao, C.; Cabrera de León, A.; Aguirre Jaime, A.; Chirino, R.; Navarro, D.; Díaz-Chico, J.C. Androgens and androgen receptors in breast cancer. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 105, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, M.J.; Wolff, A.C. The androgen receptor in breast cancer: Learning from the past. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 124, 619–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietri, E.; Conteduca, V.; Andreis, D.; Massa, I.; Melegari, E.; Sarti, S.; Cecconetto, L.; Schirone, A.; Bravaccini, S.; Serra, P.; et al. Androgen receptor signaling pathways as a target for breast cancer treatment. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2016, 23, R485–R498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nahleh, Z. Androgen receptor as a target for the treatment of hormone receptor-negative breast cancer: An unchartered territory. Future Oncol. 2008, 4, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Niu, F.; Shen, H.; Liu, X.; Chen, L.; Niu, Y. Androgen receptor and metastasis-associated protein-1 are frequently expressed in estrogen receptor negative/HER2 positive breast cancer. Virchows Arch. 2016, 468, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucukzeybek, B.B.; Bayoglu, I.V.; Kucukzeybek, Y.; Yıldız, Y.; Oflazoglu, U.; Atahan, M.K.; Taskaynatan, H.; Alacacıoglu, A.; Yigit, S.; Tarhan, M.O. Prognostic significance of androgen receptor expression in HER2-positive and triple-negative breast cancer. Pol. J. Pathol. 2018, 69, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akashi, M.; Yamaguchi, R.; Kusano, H.; Ogasawara, S.; Abe, E.; Obara, H.; Yamaguchi, M.; Akiba, J.; Kakuma, T.; Tanaka, M.; et al. Androgen receptor expression is useful to predict the therapeutic effect in HER2-positive breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 184, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajković-Molek, K.; Mustać, E.; Avirović, M.; Georgev, P.; Demaria, M.; Aničić, J.; Ban, J.; Babarović, E. The expression of calpain-1 and androgen receptor in breast cancer and their correlation with clinicopathological characteristics: An immunohistochemical retrospective study. Pathol.-Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 153068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Tapias, P.; Rubiano, W.; Rondón-Lagos, M.; Villegas, V.-E.; Rangel, N. Intrinsic Subtypes and Androgen Receptor Gene Expression in Primary Breast Cancer. A Meta-Analysis. Biology 2021, 10, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liegl, B.; Horn, L.C.; Moinfar, F. Androgen receptors are frequently expressed in mammary and extramammary Paget’s disease. Mod. Pathol. 2005, 18, 1283–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barton, V.N.; D’Amato, N.C.; Gordon, M.A.; Christenson, J.L.; Elias, A.; Richer, J.K. Androgen Receptor Biology in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: A Case for Classification as AR+ or Quadruple Negative Disease. Horm. Cancer 2015, 6, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peters, A.A.; Buchanan, G.; Ricciardelli, C.; Bianco-Miotto, T.; Centenera, M.M.; Harris, J.M.; Jindal, S.; Segara, D.; Jia, L.; Moore, N.L.; et al. Androgen Receptor Inhibits Estrogen Receptor-α Activity and Is Prognostic in Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 6131–6140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rich, J.N. Cancer Stem Cells in Radiation Resistance. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 8980–8984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turashvili, G.; Bouchal, J.; Burkadze, G.; Kolar, Z. Wnt signaling pathway in mammary gland development and carcinogenesis. Pathobiology 2006, 73, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, M.; Chen, Y.; Fei, T.; Li, D.; Lim, E.; Liu, X.S.; Brown, M. Amplitude modulation of androgen signaling by c-MYC. Genes Dev. 2013, 27, 734–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chia, K.M.; Liu, J.; Francis, G.D.; Naderi, A. A feedback loop between androgen receptor and ERK signaling in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer. Neoplasia 2011, 13, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, L.; Du, Z.; Xiong, X.; Ma, H.; Zhu, Z.; Gao, H.; Cao, J.; Li, T.; Li, H.; Yang, K.; et al. Targeting Androgen Receptor in Treating HER2 Positive Breast Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bryś, M.; Wójcik, M.; Romanowicz-Makowska, H.; Krajewska, W.M. Androgen receptor status in female breast cancer: RT-PCR and Western blot studies. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 128, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
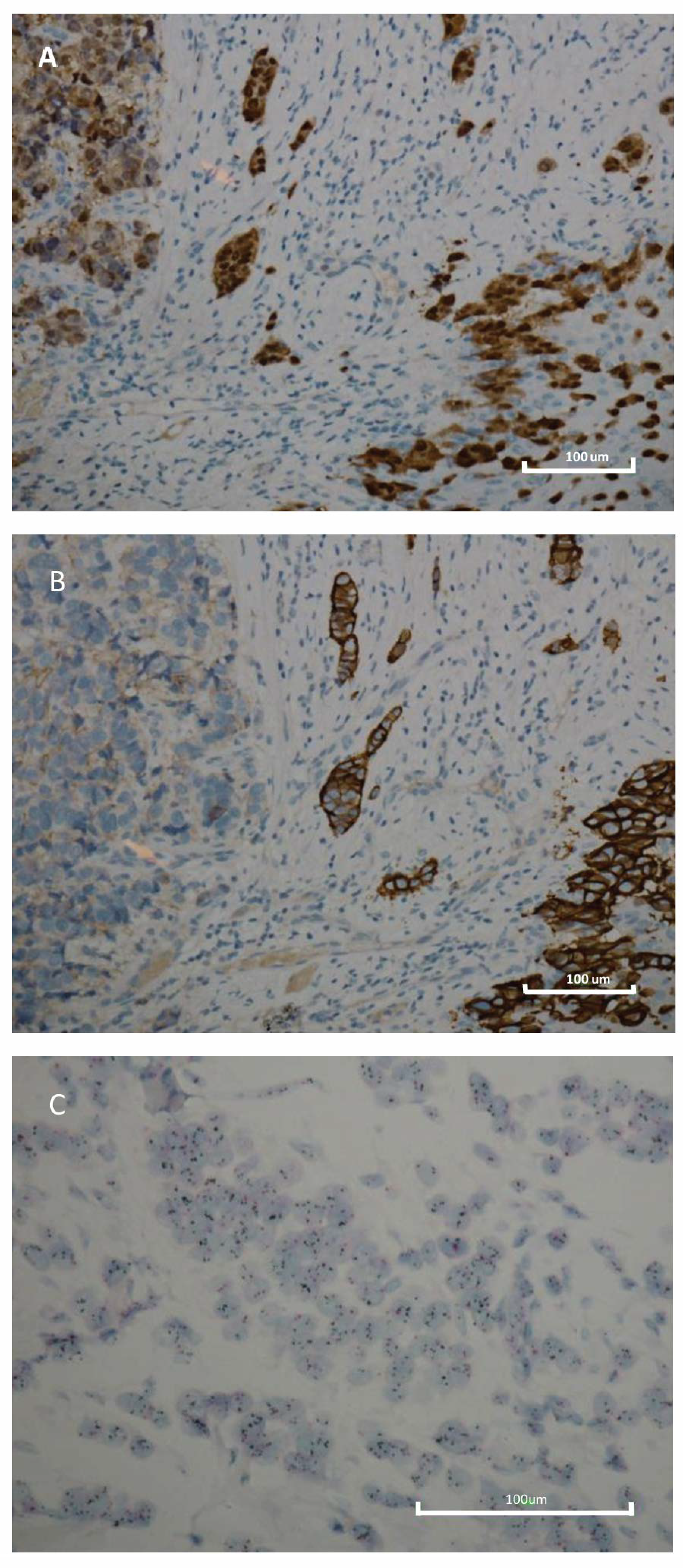
| IHC BC Subtypes | Number | % | HER2 IHC Intensity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2+ | 3+ | |||
| Luminal B HER2 + AR+ | 396 | 57.0 | 126 | 270 |
| Luminal B HER2 + AR− | 18 | 2.6 | 6 | 12 |
| HER2 + AR+ | 241 | 34.7 | 22 | 219 |
| HER2 + AR− | 40 | 5.7 | 5 | 35 |
| Variables | n = 695 | |
|---|---|---|
| Median (IQR) age, years | 58 (49–68) | |
| Age (year), n (%) | <58 | 332 (47.8) |
| ≥58 | 363 (52.2) | |
| Site, n (%) | Left | 396 (57.2) |
| Right | 296 (42.8) | |
| Histologic type, n (%) | Ductal | 590 (85.0) |
| Apocrine | 39 (5.6) | |
| Lobular | 30 (4.3) | |
| Micropapillary/papillary | 15 (2.2) | |
| Mixed (ductal + lobular) | 13 (1.9) | |
| Mucinous | 7 (1.0) | |
| Histologic grade, n (%) | G2 | 112 (16.3) |
| G3 | 575 (83.7) | |
| Pathological tumor size, n (%) | pT0 * | 53 (8.5) |
| pT1 | 203 (32.6) | |
| pT2 | 288 (46.2) | |
| pT3 | 27 (4.3) | |
| pT4 | 52 (8.4) | |
| Pathological lymph node status, n (%) | pN0 | 321 (55.9) |
| pN1 | 134 (23.3) | |
| pN2 | 73 (12.7) | |
| pN3 | 46 (8.0) | |
| Lymph node ratio, n (%) | ≤0.20 | 400 (72.3) |
| 0.21–0.65 | 106 (19.2) | |
| >0.65 | 47 (8.5) | |
| Prognostic stage, n (%) | I | 249 (40.8) |
| II | 174 (28.5) | |
| III | 134 (21.9) | |
| IV | 54 (8.8) | |
| Metastasis, n (%) | 54 (7.8) | |
| Proliferation index (Ki-67), n (%) | <14% | 9 (1.3) |
| ≥14% | 686 (98.7) | |
| PR expression, n (%) | <10% | 455 (65.5) |
| ≥10% | 240 (34.5) | |
| ER expression, n (%) | <10% | 281 (40.4) |
| ≥10% | 414 (59.6) | |
| AR expression, n (%) | <10% | 59 (8.5) |
| ≥10% | 636 (91.5) | |
| HER2 expression, n (%) | 2+ | 159 (22.9) |
| 3+ | 536 (77.1) | |
| Mortality, n (%) | 99 (14.2) | |
| AR− (n = 58) | AR+ (n = 637) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median (IQR) age, years | 55 (44–68) | 59 (49–68) | 0.045 | |
| Age (year), n (%) | <50 | 23 (39.7) | 161 (25.3) | 0.020 |
| ≥50 | 35 (60.3) | 476 (74.7) | ||
| Site, n (%) | Left | 32 (55.2) | 364 (57.4) | 0.740 |
| Right | 26 (44.8) | 270 (42.3) | ||
| Histologic type, n (%) | CDI | 52 (89.7) | 538 (84.6) | 0.770 |
| CLI | 1 (1.7) | 29 (4.6) | ||
| CDI + CLI | 0 (0.0) | 13 (2.0) | ||
| Apocrine | 3 (5.2) | 36 (5.7) | ||
| Micropapillary + papillary | 1 (1.7) | 14 (2.2) | ||
| Mucinous | 1 (1.7) | 6 (0.9) | ||
| Histologic grade, n (%) | G2 | 3 (5.2) | 109 (17.3) | 0.020 |
| G3 | 55 (94.8) | 520 (82.7) | ||
| Pathological tumor size, n (%) | pT0 * | 4 (7.6) | 49 (8.6) | 0.020 |
| pT1 | 11 (20.8) | 192 (33.7) | ||
| pT2 | 25 (47.2) | 263 (46.2) | ||
| pT3 | 7 (13.2) | 20 (3.5) | ||
| pT4 | 6 (11.3) | 45 (7.9) | ||
| Pathological lymph node status, n (%) | pN0 | 20 (46.5) | 301 (56.7) | 0.430 |
| pN1 | 14 (32.6) | 120 (22.6) | ||
| pN2 | 5 (11.6) | 68 (12.8) | ||
| pN3 | 4 (9.3) | 42 (7.9) | ||
| Lymph node ratio, n (%) | ≤0.20 | 26 (65.0) | 374 (72.9) | 0.470 |
| 0.21–0.65 | 10 (25.0) | 96 (18.7) | ||
| >0.65 | 4 (10.0) | 43 (8.4) | ||
| Prognostic stage, n (%) | I | 8 (16.3) | 241 (42.8) | 0.001 |
| II | 22 (44.9) | 152 (27.0) | ||
| III | 13 (26.5) | 122 (21.7) | ||
| IV | 6 (12.2) | 48 (8.5) | ||
| Metastasis, n (%) | 6 (10.3) | 48 (7.5) | 0.440 | |
| Proliferation index (Ki-67), n (%) | <14% | 0 (0.0) | 9 (1.4) | 1.000 |
| ≥14% | 58 (100.0) | 627 (98.6) | ||
| ER expression, n (%) | <10% | 40 (69.0) | 241 (37.8) | <0.0001 |
| ≥10% | 18 (31.0) | 396 (62.2) | ||
| PR expression, n (%) | <10% | 51 (87.9) | 404 (63.4) | <0.0001 |
| ≥10% | 7 (12.1) | 233 (36.6) | ||
| AR expression, n (%) | <10% | 57 (98.3) | 2 (0.3) | <0.0001 |
| ≥10% | 1 (1.7) | 635 (99.7) | ||
| HER2 expression, n (%) | 2+ | 11 (19.0) | 148 (23.2) | 0.680 |
| 3+ | 48 (81.0) | 489 (76.8) | ||
| Mortality, n (%) | 12 (20.7) | 87 (13.7) | 0.140 | |
| LB HER2+ AR− (n = 18) | LB HER2+ AR+ (n = 396) | HER2+ AR− (n = 40) | HER2+ AR+ (n = 241) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median (IQR) age, years | 53.5 (41–62) | 59 (48–69) | 55 (45–70) | 59 (50–68) | 0.160 | |
| Age (year), n (%) | <50 | 8 (44.4) | 110 (27.8) | 15 (37.5) | 51 (21.2) | 0.030 |
| ≥50 | 10 (55.6) | 286 (72.2) | 25 (62.5) | 190 (78.8) | ||
| Site, n (%) | Left | 11 (61.1) | 230 (58.4) | 21 (52.5) | 134 (55.8) | 0.870 |
| Right | 7 (38.9) | 164 (41.6) | 19 (47.5) | 106 (44.2) | ||
| Histologic type, n (%) | CDI | 16 (88.9) | 338 (85.4) | 36 (90.0) | 200 (83.3) | <0.0001 |
| CLI | 1 (5.6) | 25 (6.3) | 0 (0.0) | 4 (1.7) | ||
| CDI + CLI | 0 (0.0) | 10 (2.5) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (1.3) | ||
| Apocrine | 1 (5.6) | 8 (2.0) | 2 (5.0) | 28 (11.7) | ||
| Micropapillary + papillary | 0 (0.0) | 11 (2.7) | 1 (2.5) | 3 (1.3) | ||
| Mucinous | 0 (0.0) | 4 (1.0) | 1 (2.5) | 2 (0.8) | ||
| Histologic grade, n (%) | G2 | 1 (5.6) | 100 (25.5) | 2 (5.0) | 9 (3.8) | <0.0001 |
| G3 | 17 (94.4) | 292 (74.5) | 38 (95.0) | 228 (96.2) | ||
| Pathological tumor size, n (%) | pT0 * | 2 (12.5) | 20 (5.7) | 2 (5.4) | 29 (13.2) | 0.007 |
| pT1 | 4 (25.0) | 127 (36.3) | 7 (18.9) | 65 (29.6) | ||
| pT2 | 6 (37.5) | 162 (46.3) | 19 (51.4) | 101 (45.9) | ||
| pT3 | 2 (12.5) | 15 (4.3) | 5 (13.5) | 5 (2.3) | ||
| pT4 | 2 (12.5) | 26 (7.4) | 4 (10.8) | 20 (9.1) | ||
| Pathological lymph node status, n (%) | pN0 | 6 (40.0) | 182 (55.8) | 14 (50.0) | 119 (58.1) | 0.570 |
| pN1 | 4 (26.7) | 75 (23.0) | 10 (35.7) | 45 (22.0) | ||
| pN2 | 3 (20.0) | 46 (14.1) | 2 (7.1) | 22 (10.7) | ||
| pN3 | 2 (13.3) | 23 (7.1) | 2 (7.1) | 19 (9.3) | ||
| Lymph node ratio, n (%) | ≤0.20 | 7 (50.0) | 227 (70.9) | 19 (73.1) | 147 (76.2) | 0.300 |
| 0.21–0.65 | 6 (42.9) | 64 (20.0) | 4 (15.4) | 32 (16.6) | ||
| >0.65 | 1 (7.1) | 29 (9.1) | 3 (11.5) | 14 (7.3) | ||
| Prognostic stage, n (%) | I | 6 (35.3) | 193 (55.5) | 2 (6.3) | 48 (22.3) | <0.0001 |
| II | 4 (23.5) | 64 (18.4) | 18 (56.3) | 88 (40.9) | ||
| III | 4 (23.5) | 60 (17.2) | 9 (28.1) | 62 (28.8) | ||
| IV | 3 (17.7) | 31 (8.9) | 3 (9.4) | 17 (7.9) | ||
| Metastasis, n (%) | 3 (16.7) | 32 (8.1) | 3 (7.5) | 16 (6.6) | 0.400 | |
| Proliferation index (Ki-67), n (%) | <20% | 1 (5.6) | 30 (7.6) | 0 (0.0) | 11 (5.0) | 0.180 |
| ≥20% | 17 (94.4) | 366 (92.4) | 40 (100.0) | 229 (95.0) | ||
| <14% | 0 (0.0) | 6 (1.5) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (1.2) | 1.000 | |
| ≥14% | 18 (100.0) | 390 (98.5) | 40 (100.0) | 238 (98.8) | ||
| ER expression, n (%) | <10% | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 40 (100.0) | 241 (100.0) | <0.0001 |
| ≥10% | 18 (100.0) | 396 (100.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| PR expression, n (%) | <10% | 11 (61.1) | 166 (41.9) | 40 (100.0) | 238 (98.8) | <0.0001 |
| ≥10% | 7 (38.9) | 230 (58.1) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (1.2) | ||
| AR expression, n (%) | <10% | 17 (94.4) | 0 (0.0) | 40 (100.0) | 2 (0.8) | <0.0001 |
| ≥10% | 1 (5.6) | 396 (100.0) | 0 (0.0) | 239 (99.2) | ||
| HER2 expression, n (%) | 2+ | 6 (33.3) | 126 (31.8) | 5 (12.5) | 22 9.1) | <0.0001 |
| 3+ | 12 (66.7) | 270 (68.1) | 35 (87.5) | 219 (90.9) | ||
| Mortality, n (%) | 3 (16.7) | 45 (11.4) | 9 (22.5) | 42 (17.4) | 0.060 | |
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p-Value | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | ||
| LB HER2 + AR− | 1.21 (0.34–4.26) | 0.770 | - | - | |
| LB HER2 + AR+ | 0.58 (0.38–0.89) | 0.010 | 4.17 (0.29–59.39) | 0.290 | |
| HER2 + AR− | 1.82 (0.84–3.96) | 0.130 | - | - | |
| HER2 + AR+ | 1.47 (0.95–2.27) | 0.080 | - | - | |
| Age, years | 1.03 (1.01–1.05) | <0.0001 | 1.02 (0.99–1.04) | 0.200 | |
| Age ≥ 50 years | 1.50 (0.89–2.53) | 0.130 | - | - | |
| Histologic type, CDI VS. others | 0.49 (0.29–0.81) | 0.006 | 0.36 (0.18–0.75) | 0.006 | |
| Histologic grade G3 VS. G2 | 4.08 (1.62–10.27) | 0.003 | 2.21 (0.68–7.18) | 0.190 | |
| Tumor size, from pT0 to pT4 | 2.49 (1.96–3.17) | <0.0001 | - | - | |
| Pathological tumor size | pT0 * | Ref. | - | - | |
| pT1 | 1.05 (0.22–5.08) | 0.960 | 1.31 (0.24–7.11) | 0.750 | |
| pT2 | 3.99 (0.93–17.07) | 0.060 | 2.51 (0.53–11.87) | 0.240 | |
| pT3 | 4.44 (0.76–25.97) | 0.100 | 2.56 (0.34–19.48) | 0.360 | |
| pT4 | 23.61 (5.20–107.30) | <0.0001 | 5.25 (0.87–31.47) | 0.070 | |
| Pathological lymph node status, from pN0 to pN3 | 2.12 (1.65–2.71) | <0.0001 | - | - | |
| Pathological lymph node status | pN0 | Ref. | Ref. | - | - |
| pN1 | 2.40 (1.15–5.01) | 0.020 | 1.20 (0.47–3.11) | 0.700 | |
| pN2 | 4.13 (1.89–9.03) | <0.0001 | 2.11 (0.49–9.15) | 0.320 | |
| pN3 | 10.17 (4.62–22.36) | <0.0001 | 3.17 (0.57–17.69) | 0.190 | |
| Lymph node ratio | 8.47 (3.76–19.10) | <0.0001 | - | - | |
| Lymph node ratio | ≤0.20 | Ref. | Ref. | - | - |
| 0.21–0.65 | 2.67 (1.37–5.20) | 0.004 | 1.06 (0.35–3.21) | 0.910 | |
| >0.65 | 6.36 (3.02–13.40) | <0.0001 | 1.60 (0.45–5.88) | 0.480 | |
| Prognostic stage, from I to IV | 2.89 (2.22–3.76) | <0.0001 | - | - | |
| Prognostic stage | I | Ref. | Ref. | - | - |
| II | 3.26 (1.38–7.74) | 0.007 | 1.43 (0.47–4.42) | 0.530 | |
| III | 8.61 (3.82–19.40) | <0.0001 | 1.96 (0.45–8.52) | 0.370 | |
| IV | 25.97 (10.72–62.89) | <0.0001 | 1.79 (0.23–14.14) | 0.580 | |
| Metastasis | 7.23 (4.02–12.99) | <0.0001 | - | - | |
| Proliferation index, % | 1.02 (1.01–1.03) | 0.002 | 1.02 (0.99–1.04) | 0.150 | |
| Proliferation index (Ki-67) ≥14% | - | - | - | - | |
| ER expression, % | 0.99 (0.99–1.00) | 0.008 | - | - | |
| ER expression ≥10% | 0.59 (0.39–0.91) | 0.020 | 0.17 (0.02–2.42) | 0.190 | |
| PR expression, % | 0.99 (0.99–1.00) | 0.070 | - | - | |
| PR expression ≥10% | 0.53 (0.32–0.87) | 0.010 | 1.28 (0.47–3.44) | 0.630 | |
| AR expression, % | 0.99 (0.98–0.99) | 0.008 | 0.99 (0.98–1.00) | 0.050 | |
| AR expression ≥10% | 0.62 (0.32–1.22) | 0.170 | - | - | |
| HER2, % | 1.00 (0.99–1.01) | 0.480 | - | - | |
| HER2 expression 3 + VS. 2+ | 1.20 (0.71–2.03) | 0.490 | - | - | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Orrù, S.; Pascariello, E.; Sotgiu, G.; Piras, D.; Saderi, L.; Muroni, M.R.; Carru, C.; Arru, C.; Mocci, C.; Pinna, G.; et al. Prognostic Role of Androgen Receptor Expression in HER2+ Breast Carcinoma Subtypes. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10010164
Orrù S, Pascariello E, Sotgiu G, Piras D, Saderi L, Muroni MR, Carru C, Arru C, Mocci C, Pinna G, et al. Prognostic Role of Androgen Receptor Expression in HER2+ Breast Carcinoma Subtypes. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(1):164. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10010164
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrrù, Sandra, Emanuele Pascariello, Giovanni Sotgiu, Daniela Piras, Laura Saderi, Maria Rosaria Muroni, Ciriaco Carru, Caterina Arru, Cristina Mocci, Giampietro Pinna, and et al. 2022. "Prognostic Role of Androgen Receptor Expression in HER2+ Breast Carcinoma Subtypes" Biomedicines 10, no. 1: 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10010164
APA StyleOrrù, S., Pascariello, E., Sotgiu, G., Piras, D., Saderi, L., Muroni, M. R., Carru, C., Arru, C., Mocci, C., Pinna, G., Barbara, R., Cossu-Rocca, P., & De Miglio, M. R. (2022). Prognostic Role of Androgen Receptor Expression in HER2+ Breast Carcinoma Subtypes. Biomedicines, 10(1), 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10010164









