Abstract
This work deals with the development of screen-printed carbon electrodes modified with L-glutamic acid via two different approaches: electropolymerization (SPCE/PGA) and aryl diazonium electrochemical grafting (SPCE/EGA). SPCE/PGA and SPCE/EGA were analytically compared in the determination of hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) by differential pulse voltammetry. Both electrochemical characterization and analytical performance indicate that SPCE/EGA is a much better sensor for HCTZ. The detection and quantification limits were at the level of μmol L−1 with a very good linearity in the studied concentration range. In addition, the proposed SPCE/EGA was successfully applied for the determination of HCTZ in an anti-hypertensive drug with high reproducibility and good trueness.
1. Introduction
Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ), 6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide, is a drug widely used around the world for hypertension treatment, either alone or in combination with other anti-hypertensive drugs. HCTZ acts on the kidneys inhibiting sodium and chloride ions reabsorption into nephron-contoured tubules, and also preventing water reabsorption, which results in a decrease in blood pressure. Moreover, HCTZ is also used in the treatment of renal tubular acidosis, diabetes insipidus, edema, and the prevention of kidney stones [1,2].
The determination of HCTZ in different matrices is currently carried out by means of different analytical techniques. Prominent among them is the high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with UV-VIS detection [3,4,5], which is the analytical technique recommended by the United States Pharmacopeia [6]. Although HPLC/tandem MS [7] or capillary electrophoresis [8,9] are also considered. Methods for the individual determination of HCTZ are also described. Thus, Youssef [10] describes the use of an optical sensor for the fluorimetric determination of this compound. In [11,12] chemiluminescence was considered. Nevertheless, these techniques have some disadvantages, such as high initial investment (equipment), the need for sample pre-treatments, time-consuming procedures, required expertise, and the high cost of consumables. In this sense, electroanalytical methods play a fundamental role and are stated as a very notable alternative for the determination of this anti-hypertensive drug [13,14,15,16,17,18]. In particular, voltammetric techniques provide excellent detection and quantification limits, high sensitivity and selectivity, with relatively low economic cost. Taking into account that the performance of voltammetry is strongly influenced by the working electrode used, the design of this electrode is an area of major concern.
In the last decade, electrode modification through the immobilization of different species on the electrode surface has caused great interest in the development of new electrochemical sensors for the detection and quantification of different analytes in solution [19,20,21]. Thus, an essential aspect in the design of these new sensors is the molecule immobilization procedure. In this sense, one of the widely used electrode modification approaches is the electropolymerization, where through consecutive voltammetry sweeps it is possible to generate a polymer layer on the electrode surface, which also enables to study the charge transfer kinetics [22]. However, another suitable strategy for molecule immobilization that has aroused interest in recent years is based on aryl diazonioum salt monolayers anchored on the electrode surface [23,24,25]. This approach allows the incorporation of a wide range of functional groups to the electrode surface [26] and leads to the development of a recognition device with high repeatability, reproducibility, and stability in the measurements reported [27,28,29,30,31].
Glutamic acid is one of the 20 most common amino acids that can be easily immobilized on the electrode surface, linked through an amino bond between α-amino and β-carboxylic acid groups [32,33]. In the literature there are many works based on the application of electrochemical sensors modified with glutamic acid by electropolymerization for the determination of different analytes, including caffeic acid [34], hydrazine [35], ascorbic acid [36,37], and hydrochlorotiazide [38] among others, which provide good detection and quantification limits. Nevertheless, from the best of our knowledge studies on the application of glutamic acid modified electrodes via electrografting have not yet been attempted.
Regardless of the modification approach, it can be applied to different types of carbon surfaces such as graphite, glassy carbon, diamond, carbon nanomaterials and screen-printed carbon ink, among others. In this sense, in the last years, screen-printed carbon electrodes (SPCE) have generated great interest as a support for electrode modification. The screen-printing technology allows the mass production of reproducible, disposable, and relatively economical devices that usually include a three-electrode configuration printed on the same strip. Other important characteristics of these screen-printed electrodes (SPEs) are related with their miniaturized size and their capability to be connected to portable instrumentation, which makes them especially suitable for on-site analysis [39,40,41].
In this work, both electropolymerization and electrografting modification approaches have been considered for the first time in the development of a glutamic acid modified electrode using a screen-printed carbon electrode as a support. Glutamic acid screen-printed carbon electrodes modified by both approaches electropolymerization (SPCE/PGA) and electrochemical grafting (SPCE/EGA) will be compared in terms of their electrochemical characterization and their analytical performance in the determination of hydrochlorothiazide. Moreover, the applicability of SPCE/EGA as a better sensor will be tested through its determination in a commercial anti-hypertensive drug.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
L-glutamic acid (≥ 99%), 4-aminobenzoic acid (ABA), N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide (sulfo-NHS), N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-N’-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC), potassium dihydrogen phosphate, sodium monophosphate, ethanol and sodium nitrite were provided from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Potassium ferrocyanide K4[Fe(CN)6]·3H2O, hydrochloride acid, 2-(N-morpholino)-ethanesulfonic acid (MES) and sodium hydroxide were supplied by Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). Potassium ferricyanide K3[Fe(CN)6] was purchased from Panreac (Barcelona, Spain). All reagents were of analytical grade. Hydrochlorothiazide (Pure) was provided by Laboratorio Chile® (Lab Chile®, Santiago, Chile). Commercial capsules of HCTZ (Hidroronol) from ITF-Labomed® (Santiago, Chile, capsules declared 50 mg hydrochlorothiazide per tablet) were commercially obtained.
Deionized and ultrapure water (Milli-Q plus 185 system, Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA) was used in all experiments.
2.2. Instrumentation
Cyclic voltammetric (CV) and differential pulse voltammetric (DPV) measurements were performed using an Autolab System PGSTAT12 (Eco Chemie BV, Utrecht, The Netherlands) attached to a Metrohm 663 VA Stand (Metrohm, Herisau, Switzerland). The acquisition and treatment of data were carried out by means of a personal computer with GPES software, version 4.9 (Eco Chemie).
A traditional electrochemical cell based on a three-electrode system was used in all the experiments: (i) an Ag/AgCl in saturated KCl (Ag/AgCl/KClsat, CH-Instruments, Austin, TX, USA) electrode was used in aqueous media as a reference electrode; (ii) a platinum wire (CH-Instruments, USA) was used as a counter electrode; and (iii) the working electrode was a screen-printed carbon electrode modified with L-glutamic acid via both electropolymerization (SPCE/PGA) and electrografting (SPCE/EGA) procedures. SPCE/PGA and SPCE/EGA were prepared using a commercial screen-printed carbon disk electrode of 4 mm of diameter (reference DRP-110, DS SPE) supplied by DropSens (Oviedo, Spain). SPEs were connected to the Autolab System by means of a flexible cable (reference CAC, DropSens).
For pH measurements, a Crison micro pH 2000 pH-meter was used, and all electrochemical measurements were carried out in a glass cell at room temperature (20 °C) without oxygen removal.
2.3. Procedures
2.3.1. Preparation of Modified SPCEs by Electropolymerization with L-Glutamic Acid (SPCE/PGA)
Before starting the preparation of the L-glutamic acid modified screen-printed carbon electrode, the main parameters affecting the electropolymerization approach were optimized. Thus, both the number of voltammetric cycles and the scan rate applied between −0.2 to +2.8 V vs. Ag/AgCl/KClsat were studied. The optimization was performed considering the oxidation current peak response of 100.0 µmol L−1 HCTZ in 0.01 mol L−1 HCl by DPV. Figure 1 shows the results of a two-factor central composite design (9 experiments) for the screening of a wide range of cycles (1–60) and scan rates (1–200 mV s−1). The fitting of a quadratic second order polynomial model allowed us to draw a rough estimate of the response surface (the mesh in Figure 1), which exhibits the highest peak currents in the region corresponding to a small number of voltammetric cycles (between 0 and 10) and high scan rates (between 150 and 200 mV s−1). A new set of measurements carried out inside this restricted area (not shown) produced the optimum response for the combination of five cycles and 180 mV s−1. Therefore, according to these results, the unmodified SPCEs were immersed in L-glutamic acid 0.02 mol L−1 prepared in hydrochloric acid 0.04 mol L−1 solution, and five voltammetric cycles were applied between −0.2 and +2.8 V with a scan rate of 180 mV s−1. The obtained SPCE/PGA was rinsed with ultrapure water and dried at room temperature.
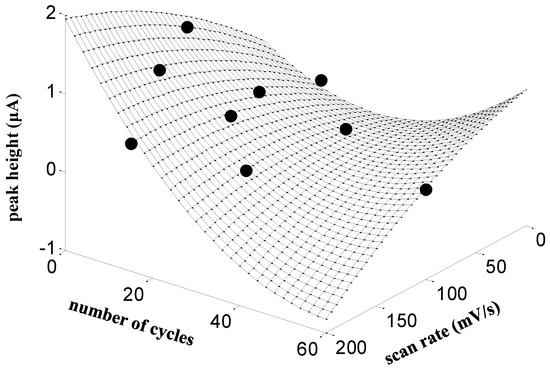
Figure 1.
Effect of the number of voltammetric cycles and scan rate on the peak height of HCTZ on SPCE/PGA. Conditions: 100.0 µmol L−1 of HCTZ in 0.01 mol L−1 HCl by DPV. Black points indicate experimental values according to a central composite design, whereas the mesh surface has been obtained by the fitting of a quadratic second order polynomial model to the experimental values.
2.3.2. Preparation of Modified SPCEs by Electrografting with L-Glutamic Acid (SPCE/EGA)
SPCE/EGA electrodes were prepared according to a two-step procedure previously described in the literature [29,30] with minor changes.
Diazonium Salt Electrografting
The aryl diazonium salt was obtained in-situ by adding 2 mmol L−1 of sodium nitrite to a cooled acidic solution (1 mol L−1 aqueous HCl) of 73 mmol L−1 4-aminobenzoic acid. The resulting solution was stirred for 30 min in an ice bath before the electrochemical grafting process [42] was performed. Then, the SPCE was immersed in 20 mL of the diazonium salt solution and 15 CV cycles between 0 V and −1 V at scan rate of 0.2 V s−1 were performed. Finally, the functionalized SPCE were carefully rinsed with Milli-Q water and methanol to remove any physisorbed compounds on the electrode surface.
Covalent Immobilization of L-Glutamic Acid via Carbodiimide Coupling
Carboxyl groups generated during the electrografting process on SPCE surface were activated by dropping 10 μL of 26 mmol L−1 N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-N’-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC) and 35 mmol L−1 of N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide (sulfo-NHS) in 100 mmol L−1 MES buffer (pH 4.5) onto the electrode surface for about one hour, then the electrodes were rinsed with Milli-Q water and dried at room temperature. The activated carboxyl groups reacted overnight at 4 °C with amine groups of L-glutamic acid by placing 10 µL of 2.9 mg/100 μL of L-glutamic acid solution prepared in 90:10 of 0.1 mol L−1 MES buffer (pH 4.5) and ethanol, respectively.
2.3.3. Voltammetric Measurements
For differential pulse voltammetric measurements of hydrochlorothiazide using both SPCE/PGA and SPCE/EGA, the experimental conditions were a pulse amplitude of 5 mV, a pulse width of 0.0050 s, a scan rate of 5 mV s−1 scanning the potential from 0.70 to 1.60 V vs. Ag/AgCl/KClsat.
Linear calibration plots were obtained by increasing HCTZ concentration in hydrochloric acid 0.01 mol L−1 solution, according to previous studies [38,43].
The assay of HCTZ tablets was performed according to the Razak protocol [44]: three tablets were crushed and homogenized, and the amount equivalent to one tablet was dissolved in 50 mL 0.02 mol L−1 NaOH and sonicated for 10 min. Then, a volume of the sample in 0.01 mol L−1 hydrochloric acid solution was placed in the cell and the scan was recorded. Calibration was performed by the standard addition method: four aliquots of HCTZ standard solutions were further added and the respective curves were recorded.
In both linear calibration plots and analysis of the tablet samples, to improve the repeatability of both electrodes SPCE/PGA and SPCE/EGA, a conditioning step was performed before each measurement by applying a conditioning potential (Econd) of 0.7 V for 30 s in the same measuring solution. In all cases, peak currents were calculated considering the background current.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Electrochemical Characterization
Electrochemical characterization of both SPCE/ PGA and SPCE/EGA was performed at each functionalization step by CV using 2 mmol L−1 K4[Fe(CN)6]·3H2O/K3[Fe(CN)6] as redox probe prepared in 100 mmol L−1 phosphate buffer at pH 7.4. The potential window was set between –0.4 and 0.8 V at a 100 mV s−1 scan rate. As it can be seen in Figure 2, for SPCE/EGA after electrografting a current decrease, in comparison to bare SPCE, is observed, which can be attributed to the formation of a blocking layer [45]. For both SPCE/PGA and SPCE/EGA, the immobilization of L-glutamic acid via electropolymerization and covalent binding, respectively, resulted in both, higher current peaks in comparison with bare SPCE and a better reversibility of the couple Fe(II)/Fe(III), due to their enhanced surface area. This increase is more remarkable in the electrografting approach than in the electropolymerization one, resulting in a sensor with better chemical and mechanical stability.
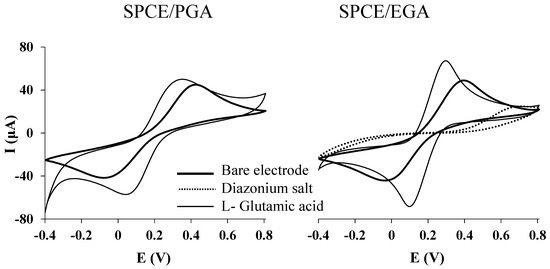
Figure 2.
CVs plots recorded at each functionalization step for SPCE/PGA and SPCE/EGA. Measurements were performed in a 2 mmol L−1 ferrocyanide/ferricyanide solution in phosphate buffer at pH 7.4 by using a scan rate of 100 mV s−1.
3.2. Repeatability and Reproducibility
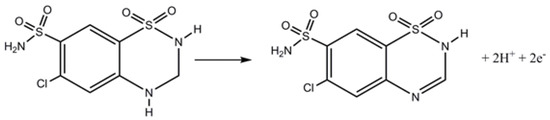
Scheme 1.
Proposed mechanism for oxidation of HCTZ.
The electrochemical parameters applied for the detection of HCTZ (see Section 2.3.3) were optimized in a previous work [38].
Figure 3 shows a comparison of the analytical performance of SPCE/PGA (dotted line), SPCE/EGA (solid line), and bare SPCE (dashed line) for the determination of a solution containing 60.0 µmol L−1 HCTZ. A well-defined peak can be observed for HCTZ with all electrodes. However, a more intense peak is obtained using screen-printed electrodes modified with L-glutamic acid, particularly by electrografting modification procedure.
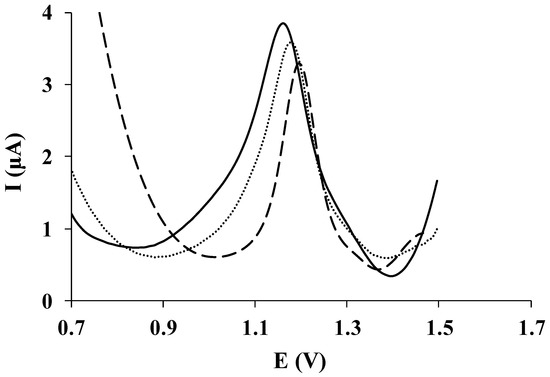
Figure 3.
DP voltammetric measurements of 60.0 µmol L−1 HCTZ in HCl 0.01 mol L−1 recorded on SPCE/PGA (dotted line), SPCE/EGA (solid line), and bare SPCE (dashed line).
Repeatability and reproducibility of both SPCE/PGA and SPCE/EGA were determined by measuring a solution of 100.0 µmol L−1 HCTZ prepared in HCl 0.01 mol L−1. The estimated repeatability, which was calculated using each L-glutamic acid-modified electrode, using the same unit for five repetitive measurements, produced a relative standard deviation (RSD) of 3.3% and 3.2% for SPCE/PGA and SPCE/EGA, respectively. The reproducibility calculated from three different L-glutamic acid-modified units for both electrodes within a series of five repetitive measurements yielded an RSD of 4.8% and 3.6% for SPCE/PGA and SPCE/EGA, accordingly.
The reproducibility value achieved for SPCE/PGA is similar to that reported for a glassy carbon electrode modified also with L-glutamic acid via electropolymerization (3.61%) [38], whereas the obtained repeatability value is much better than that achieved using the L-glutamic acid glassy carbon electrode modified by electropolymerization (10.7%) [38]. Concerning the repeatability and reproducibility values attained for SPCE/EGA, these are of the same order of those reported for glutathione modified screen-printed carbon nanofiber electrode [30], glassy carbon modified with penicillamine [29] or epoxy graphite modified with crown ethers [28], which were modified using the same strategy (repeatability between 1.6% and 7.6%; and reproducibility between 2.1% and 8.9%).
3.3. Calibration Data
The analytical response of both SPCE/PGA and SPCE/EGA was compared under the above-mentioned experimental conditions. For this reason, calibration plots of HCTZ by DPV ranging from 10.0 to 500.0 µmol L−1 for SPCE/PGA and 1.0 to 500.0 µmol L−1 for SPCE/EGA were constructed. Table 1 summarizes the analytical parameters obtained using a SPCE/PGA and a SPCE/EGA. The limit of detection (LOD) was evaluated as three times the standard deviation of the intercept over the slope of the calibration curve of the target ions. The limit of quantification (LOQ) was calculated by considering 10 times the previous relation and it was established as the lowest value of the linear calibration curves. The linearity was maintained up to a maximum concentration level of 300.0 and 200.0 µmol L−1 for SPCE/PGA and SPCE/EGA, respectively. Figure 4 shows the evolution of DPV signals of HCTZ using both SPCE/PGA (Figure 4a) and SPCE/EGA (Figure 4b) when the concentration of HCTZ increases. In both cases, well-defined peaks close to 1.2 V can be observed over the selected concentration range. The corresponding sensitivities (μA µmol−1 L) and the correlation coefficients for both SPCE/PGA and SPCE/EGA are presented in Table 1, being the SPCE/EGA more sensitive to the HCTZ determination than the SPCE/PGA.

Table 1.
Calibration data for the determination of HCTZ by DPV on SPCE/PGA and SPCE/ EGA in the presence of 0.01 mol L−1 hydrochloric acid.
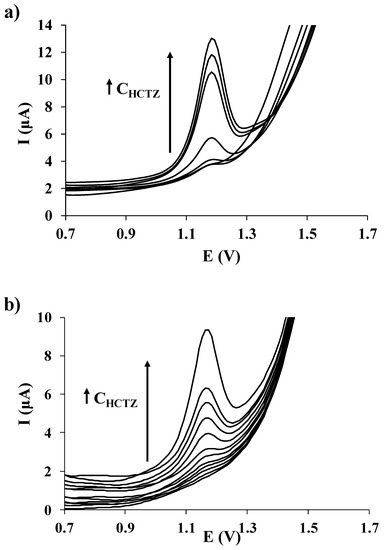
Figure 4.
DP voltammetric measurements of increasing concentrations of HCTZ in HCl 0.01 mol L−1 recorded on (a) SPCE/PGA (from 10.0 to 300.0 µmol L−1); and (b) SPCE/EGA (from 1.0 to 200.0 µmol L−1).
As summarized in Table 1, both LOD and LOQ were at the level of μmol L−1, being those achieved using SPCE/EGA lower than for SPCE/PGA. Table 2 presents a comparison of the results obtained from SPCE/PGA and SPCE/EGA and those from other electrodes used in the determination of HCTZ, e.g., glassy carbon electrode [47], boron-doped diamond electrode [18], modified graphene oxide sheet paste electrode [48], or modified carbon paste electrodes [49,50]. In comparison with the summarized results, the LOD and LOQ values reached in this work for HCTZ determination are similar or even slightly lower depending on both the electrode and method considered. Regarding the determination of HCTZ with other glutamic acid-modified electrodes, the LOD and LOQ values obtained in this work for both SPCE/PGA and SPCE/EGA are much better than earlier results achieved using a glassy carbon electrode modified by electropolymerization with L-glutamic acid (LOD and LOQ values of 19.6 µmol L−1 and 65.0 µmol L−1, respectively) [38]. This improvement could be attributed to the much larger effective surface area that present the SPCEs in comparison to the conventional glassy carbon electrode, which allows immobilizing more selective ligands. Moreover, it must be highlighted that unlike glassy carbon, SPEs do not require any polishing prior to glutamic acid immobilization that, together with the good reproducibility, the disposable character and the low-cost commercial availability of the SPEs (which are the basis of both SPCE/PGA and SPCE/EGA) ensures an accessible and cheap methodology.

Table 2.
Comparison of the analytical parameters of some electrodes used in the determination of HCTZ.
Finally, if we compare the analytical performance of both developed electrodes SPCE/PGA and SPCE/EGA, from the reported calibration data (Table 1) coupled with the better repeatability and reproducibility previously observed, we can conclude that the immobilization of glutamic acid via electrochemical grafting is a much better approach for HCTZ determination. In addition, the durability of the glutamic acid immobilized via electrografting on each screen-printed device (about 15 measurements without loss of sensitivity) is much higher than that shown for the glutamic acid screen-printed carbon electrodes modified by the electropolymerization approach (about seven measurements without loss of sensitivity).
3.4. Application to the Analysis of an Anti-Hypertensive Drug
Considering the analytical performance and the reproducibility of both glutamic acid modified screen-printed electrodes, SPCE/EGA was considered for the determination of HCTZ in drugs and its applicability was tested by measuring a commercial anti-hypertensive drug (Hidroronol capsules, from ITF-Labomed®, which contain 50 mg HCTZ per tablet).
HCTZ determination was performed by means of the standard addition method. DPV measurements were performed under the above-mentioned conditions, including four HCTZ additions. Representative voltammograms acquired in the analysis of the antihypertensive drug using SPCE/EGA are shown in Figure 5a. Well-defined peaks that behave equally to the calibration data were obtained and, as it is illustrated in Figure 5b, a good correlation of the representative DPV measurements carried out with SPCE/EGA was also obtained for HCTZ.
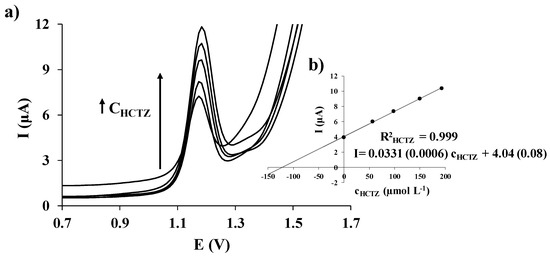
Figure 5.
DP voltammograms measured with SPCE/EGA in HCl 0.01 mol L−1 for an anti-hypertensive drug sample before and after four successive additions of a standard solution of HCTZ (a); and the corresponding HCTZ standard addition plot (b), including in parenthesis the standard deviations of the slope and the intercept.
Three replicates of the DPV determination of the anti-hypertensive drug using SPCE/EGA were performed. The obtained HCTZ concentration data are summarized in Table 3. Good agreement between the three replicates, as well as with the HCTZ value reported by ITF-LABOMED Laboratory was obtained.

Table 3.
Total concentration of HCTZ determined in three replicates of an anti-hypertensive drug by DPV on SPCE/EGA using standard addition calibration method in the presence of 0.01 mol L−1 hydrochloric acid. Relative standard deviation (RSD) and relative error are also shown.
These successful results confirm the applicability of SPCE/EGA for the determination of HCTZ in drugs being, therefore, a valuable and interesting option to the most conventional electrodes for the determination of HCTZ.
4. Conclusions
The developed sensors for the determination of HCTZ are the first approach on glutamic acid-based screen-printed electrodes. Two different modification approaches, electropolymerization and electrochemical grafting, were considered for the immobilization of the glutamic acid on the SPCE surface. Thus, in this work the analytical performance of both SPCE/PGA and SPCE/EGA were compared, concluding that the SPCE/EGA has an enhanced chemical and mechanical stability with respect to SPCE/PGA and also performs much better for HCTZ determination. In comparison with the unique existing glutamic acid-based electrode for HCTZ determination, the repeatability, the reproducibility, as well as the calibration data obtained in this study for both developed sensors are much better than those achieved by the preceding glutamic acid glassy carbon electrode modified via electropolymerization [38]. Moreover, the developed sensors present all the addition advantages provided by the use of low-cost commercially available SPCE as a support which, unlike glassy carbon substrate, does not require polishing of the surface of the carbon screen-printed prior to glutamic acid immobilization.
The applicability of SPCE/EGA, as the best-developed sensor, for the determination of HCTZ by DPV was demonstrated using a commercial anti-hypertensive drug with a good trueness and a high reproducibility inferred by the relative error (%) and the RSD (%), respectively.
Thus, the above presented results suggest that the SPCE/EGA can be very appropriate for the determination of HCTZ at μmol L−1 levels in drug samples. It could be also applicable to biological samples like plasma or urine, but this would require a careful study about the possible interferences that could be present in such complex media.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the Generalitat of Catalonia (Project 2014SGR269) and FONDECYT GRANT 1170352 (Chile). Camilo González-Vargas acknowledges PhD fellowship N° 21130071 awarded.
Author Contributions
C. González-Vargas, N. Serrano, C. Ariño and J.M. Díaz-Cruz conceived, designed the experiments, discussed the results and made a first draft of the paper. C. González-Vargas and N. Serrano performed the experiments and the data treatment. M. Esteban and R. Salazar revised the writing of the paper from the first draft to the definitive version.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Schoenberger, J.A. Losartan with hydrochlorothiazide in the treatment of hypertension. J. Hypertens. Suppl. 1995, 13, S43–S47. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ramsay, L.E.; Yeo, W.W. Double-blind comparison of losartan, lisinopril and hydrochlorothiazide in hypertensive patients with a previous angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor-associated cough. J. Hypertens. Suppl. 1995, 13, S73–S76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlucci, G.; Palumbo, G.; Mazzeo, P.; Quaglia, M.G. Simultaneous determination of losartan and hydrochlorothiazide in tablets by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2000, 23, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, L.R.; Godge, R.K.; Vora, A.T.; Damle, M.C. Validated RP-HPLC method for simultaneous determination of telmisartan and hydrochlorothiazide in pharmaceutical formulation. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Rel. Technol. 2007, 30, 3059–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashru, R.C.; Sutariya, V.B.; Thakker, A.J. High performance liquid chromatographic method for simultaneous determination of fosinopril sodium and hydrochlorothiazide in tablets formulation. Ars Pharm. 2006, 47, 375–383. [Google Scholar]
- United States Pharmacopoeia. United States Pharmacopoeial Convention; United States Pharmacopoeia: Rockville, MD, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, L.; Gu, J. A liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous quantification of valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide in human plasma. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2007, 852, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillaert, S.; Van den Bossche, W. Simultaneous determination of hydrochlorothiazide and several angiotensin-II-receptor antagonists by capillary electrophoresis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2003, 31, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balesteros, M.R.; Faria, A.F.; de Oliveira, M.A.L. Determination of losartan associated with chlorthalidone or hydrochlorothiazide in capsules by capillary zone electrophoresis. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2007, 18, 554–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, A.O. Spectrofluorimetric assessment of hydrochlorothiazide using optical sensor nano-composite terbium ion doped in sol-gel matrix. J. Fluoresc. 2012, 22, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murillo Pulgarín, J.A.; Alañón Molina, A.; Pérez-Olivares Nieto, G. Determination of hydrochlorothiazide in pharmaceutical preparations by time resolved chemiluminescence. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 518, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Baeyens, W.R.G.; Delanghe, J.; Van der Weken, G.; Calokerinos, A.C. Cerium (IV)-based chemiluminescence analysis of hydrochlorothiazide. Talanta 1998, 46, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajik, S.; Taher, M.A.; Beitollahi, H. First report for simultaneous determination of methyldopa and hydrochlorothiazide using a nanostructured based electrochemical sensor. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2013, 704, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beitollahi, H.; Ghorbani, F. Benzoylferrocene-modified carbon nanotubes paste electrode as a voltammetric sensor for determination of hydrochlorothiazide in pharmaceutical and biological samples. Ionics 2013, 19, 1673–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardenal Santos, M.C.; Teixeira Tarley, C.R.; Dall’Antonia, L.H.; Sartori, E.R. Evaluation of boron-doped diamond electrode for simultaneous voltammetric determination of hydrochlorothiazide and losartan in pharmaceutical formulations. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 188, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machini, W.B.S.; David-Parra, D.N.; Teixeira, M.F.S. Electrochemical investigation of the voltammetric determination of hydrochlorothiazide using a nickel hydroxide modified nickel electrode. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 57, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaei, B.; Damiri, S. Multiwalled carbon nanotubes modified electrode as a sensor for adsorptive stripping voltammetric determination of hydrochlorothiazide. IEEE Sens. J. 2008, 9, 1523–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires Eisele, A.P.; Mansano, G.R.; de Oliveira, F.M.; Casarin, J.; Teixeira Tarley, C.R.; Romão Sartori, E. Simultaneous determination of hydrochlorothiazide and valsartan in combined dosage forms: Electroanalytical performance of cathodically pretreated boron-doped diamond electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2014, 732, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Sun, H.; Fu, H.-F.; Tan, Z.-C. Sensitive simultaneous determination of nitrophenol isomers at poly(p-aminobenzene sulfonic acid) film modified graphite electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 156, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezi, N.; Kokkinos, C.; Economou, A.; Prodromidis, M.I. Voltammetric determination of trace Tl(I) at disposable screen-printed electrodes modified with bismuth precursor compounds. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2013, 182, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Xi, J.; Hou, F.; Han, L.; Li, G.; Gong, S.; Chen, C.; Sun, W. Application of three-dimensional reduced graphene oxide-gold composite modified electrode for direct electrochemistry and electrocatalysis of myoglobin. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 58, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira Santos, D.; Boldrin Zanoni, M.V.; Bergamini, M.F.; Chiorcea-Paquim, A.-M.; Diculescu, V.C.; Oliveira Brett, A.-M. Poly(glutamic acid) nanofibre modified glassy carbon electrode: Characterization by atomic force microscopy, voltammetry and electrochemical impedance. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 3991–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooding, J.J. Advances in interfacial design for electrochemical biosensors and sensors: Aryl diazonium salts for modifying carbon and metal electrodes. Electroanalysis 2008, 20, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delamar, M.; Hitmi, R.; Pinson, J.; Saveant, J.M. Covalent modification of carbon surfaces by grafting of functionalized aryl radicals produced from electrochemical reduction of diazonium salts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 5883–5884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranton, S.; Bélanger, D. Electrochemical derivatization of carbon surface by reduction of in situ generated diazonium cations. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2005, 109, 24401–24410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Chow, E.; Böcking, T.; Hibbert, D.B.; Gooding, J.J. Study of factors affecting the performance of voltammetric copper sensors based on Gly-Gly-His modified glassy carbon and gold electrodes. Electroanalysis 2006, 18, 1141–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, N.; Prieto-Simón, B.; Cetó, X.; del Valle, M. Array of peptide-modified electrodes for the simultaneous determination of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Zn(II). Talanta 2014, 125, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, N.; González-Calabuig, A.; del Valle, M. Crown ether-modified electrodes for the simultaneous stripping voltammetric determination of Cd(II), Pb(II) and Cu(II). Talanta 2015, 138, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Ràfols, C.; Serrano, N.; Díaz-Cruz, J.M.; Ariño, C.; Esteban, M. Penicillamine-modified sensor for the voltammetric determination of Cd(II) and Pb(II) ions in natural samples. Talanta 2015, 144, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Ràfols, C.; Serrano, N.; Díaz-Cruz, J.M.; Ariño, C.; Esteban, M. Glutathione modified screen-printed carbon nanofiber electrode for the voltammetric determination of metal ions in natural samples. Talanta 2016, 155, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Calabuig, A.; Guerrero, D.; Serrano, N.; del Valle, M. Simultaneous voltammetric determination of heavy metals by use of crown ether-modified electrodes and chemometrics. Electroanalysis 2016, 28, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Luo, L.; Ding, Y.; Ye, D. Poly-glutamic acid modified carbon nanotube-doped carbon paste electrode for sensitive detection of L-tryptophan. Bioelectrochemistry 2011, 82, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagasawa, M.; Holtzer, A. The helix-coil transition in solutions of polyglutamic acid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1964, 86, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.P.; Bergamini, M.F.; Fogg, A.G.; Zanoni, M.V.B. Application of a glassy carbon electrode modified with poly(glutamic acid) in caffeic acid determination. Microchim. Acta 2005, 151, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, A.-M.; Chen, H.-Y. Electrocatalytic oxidation of hydrazine at the poly(glutamic acid) chemically modified electrode and its amperometric determination. Anal. Lett. 1997, 30, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, A.-M.; Chen, H.-Y. Electrocatalytic oxidation and determination of ascorbic acid at poly(glutamic acid) chemically modified electrode. Anal. Chim. Acta 1997, 344, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lin, X. Covalent modification of glassy carbon electrode with glutamic acid for simultaneous determination of uric acid and ascorbic acid. Analyst 2001, 126, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Vargas, C.; Garcia, C.; Celis, F.; Salazar, R. Differential pulse voltammetry determination of anti-hypertensive drug hydrochlorothiazide in pharmaceuticals using glassy-carbon electrode modified by electropolymerization with l- and d-glutamic acids. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2017. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Taleat, Z.; Khoshroo, A.; Mazloum-Ardakani, M. Screen-printed electrodes for biosensing: A review (2008–2013). Microchim. Acta 2014, 181, 865–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, J.; González-García, M.B.; Hernández-Santos, D.; Fanjul-Bolado, P.; Ribotti, A.; McCaul, M.; Diamond, D.; Magni, P. Screen-printed electrodes for environmental monitoring of heavy metal ions: A review. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, A.; Marty, J.L. Disposable screen printed electrochemical sensors: Tools for environmental monitoring. Sensors 2014, 14, 10432–10453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bélanger, D.; Pinson, J. Electrografting: A powerful method for surface modification. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 3995–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salamanca-Neto, C.A.R.; Pires Eisele, A.P.; Gouveia Resta, V.; Scremin, J.; Romão Sartori, E. Differential pulse voltammetric method for the individual and simultaneous determination of antihypertensive drug metoprolol and its association with hydrochlorothiazide in pharmaceutical dosage forms. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 230, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razak, O.A. Electrochemical study of hydrochlorothiazide and its determination in urine and tablets. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2004, 34, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlberg, E.; Helgée, B.; Parker, V.D. The reaction of aryl radicals with metallic electrodes. Acta Chem. Scand. B 1980, 34, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourencao, B.C.; Silva, T.A.; Fatibello-Filho, O.; Swain, G.M. Voltammetric studies of propranolol and hydrochlorothiazide oxidation in standard and synthetic biological fluids using anitrogen-containing tetrahedral amorphous carbon (ta-C:N) electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 143, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, A.F. Electrochemical oxidation behavior of hydrochlorothiazide on a glassy carbon electrode and its voltammetric determination in pharmaceutical formulations and biological fluids. J. Food Drug Anal. 2014, 22, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beitollahi, H.; Hamzavi, M.; Torkzadeh-Mahani, M. Electrochemical determination of hydrochlorothiazide and folic acid in real samples using a modified graphene oxide sheet paste electrode. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 52, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heli, H.; Pishahang, J.; Barzegar Amiri, H.; Sattarahmady, N. Synthesis of nickel nanowrinkles and its application for the electrocatalytic oxidation and sensitive detection of hydrochlorothiazide. Microchem. J. 2017, 130, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi-Maleh, H.; Ganjali, M.R.; Norouzi, P.; Bananezhad, A. Amplified nanostructure electrochemical sensor for simultaneous determination of captopril, acetaminophen, tyrosine and hydrochlorothiazide. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 73, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).