Abstract
A solid state electrochemiluminescence (ECL) sensor based on Ru(bpy)32+-encapsulated silica nanoparticles (RuNP) covalently immobilised on a screen printed carbon electrode has been developed and characterised. RuNPs were synthesised using water-in-oil microemulsion method, amino groups were introduced on their surface, and they were characterised by transmission electron microscopy. Aminated RuNPs were covalently immobilised on activate screen-printed carbon electrodes to form a solid state ECL biosensor. The biosensor surfaces were characterised using electrochemistry and scanning electron microscopy, which showed that aminated nanoparticles formed dense 3D layers on the electrode surface thus allowing immobilisation of high amount of Ru(bpy)32+. The developed sensor was used for ECL detection of biogenic polyamines, namely spermine, spermidine, cadaverine and putrescine. The sensor exhibited high sensitivity and stability.
1. Introduction
Electrogenerated chemiluminescence or electrochemiluminescence (ECL) is an analytical technique based on light emission at the surface of an electrode from compounds that have reached the excited state via electrochemical reactions [1,2,3,4].
ECL can be classified as a spectro-electrochemical method. The main advantages of ECL over fluorescence are simplicity, as there is no need for an external excitation source as well as low background due to the absence of background scattering. Furthermore, ECL has high spatial control of electrochemical methods as the reactions take place at the surface of an electrode.
The most common ECL luminophore is probably the tris(2,2’bipyridyl)ruthenium(II) (Ru(bpy)32+), which is a red crystalline polypyridyl compound. Although many other transition metal polypyridyl complexes generate ECL, the high stability of Ru(bpy)32+ in aqueous solutions and in the presence of oxygen, its high quantum yield and capability to reach excited state in the reaction with a number of important molecules make it a highly exploited ECL luminophore in assays and sensors [5,6].
ECL of Ru(bpy)32+ can be generated through two main mechanisms: (i) ion annihilation ECL is generated by reaction of oxidised and reduced form of Ru(bpy)32+, and (ii) coreactant ECL, in which the coreactant, upon electrochemical oxidation or reduction forms a high energy intermediate capable to further react with the luminophore to produce excited states [2,7]. The coreactant type ECL is more commonly used due to the simplicity of the system: the signal can be generated in a single oxidation or reduction step, while in annihilation generation the rapid generation of both oxidised and reduced luminophore species is necessary [2,7]. The low reduction potential of Ru(bpy)32+ poses further challenges for the generation of reduced species in aqueous solution, which is the required environment for any practical ECL applications.
Ru(bpy)32+ and its derivatives have been used as labels in immunoassays and DNA analysis over two decades [8,9]. In assays, the ECL signal is typically generated by oxidative coreactant mechanism using tripropylamine (TPA) as a coreactant, which is the most widely used coreactant in assays and commercial applications [10,11].
Many important analytes can act as coreactants with Ru(bpy)32+, such as proline [12], guanine [13], codeine [14], nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) [15], hydrogen peroxide [16], thus making ECL a very important technique for rapid and simple detection. Often these small molecules lack fluorescence, do not absorb in the UV-Vis region, and demonstrate weak electroactivity, which makes their detection challenging and derivatisation is frequently necessary. With ECL, the direct, simple and rapid detection of non-derivatised molecules is possible.
When ECL is used for coreactant detection, it is important to immobilise high concentration of dye at the surface of an electrode for maximum sensitivity, as the ECL reaction involves the ruthenium complex localised at the surface of an electrode; this means that the electrochemiluminescent layer at higher distance from the electrode is wasted. Furthermore, Ru(bpy)32+ can effectively be regenerated during the ECL generation, thus catalysing the detection itself [7]. The attempts to immobilise the ECL luminophore at the surface of an electrode include but are not limited to the use of Nafion as an ion exchange matrix for Ru(bpy)32+ cation [17,18], synthesis and drop casting of electrochemiluminescent metallopolymers on electrodes [19], electropolymerisation of an electrochemiluminescent compound on the electrode [20], electrografting of diazotised ruthenium complexes directly on the electrode [21], immobilisation of Ru(bpy)32+ on indium tin oxide electrode via citrate-capped gold nanoparticles [22], as well as incapsulation of Ru(bpy)32+ into ultrathin Langmuir-Shaefer [23] and Langmuir-Blodget [24] Nafion films.
Great efforts have been undertaken to enhance the quantum yield of ECL and to generate brighter labels. One of the most promising approaches is encapsulation of Ru(bpy)32+ dye into silicate matrix, e.g., to effectively form dye encapsulated silica nanoparticles [25,26]. As the Ru(bpy)32+ is positively charged, it interacts electrostatically with negatively charged silica. Extremely sensitive immunoassay detection down to sub pg/mL levels has been reported [27].
In this contribution we report on the development of solid state ECL sensors based on the immobilisation of Ru(bpy)32+ on silica nanoparticles deposited on screen printed carbon electrodes.
The sensors were tested for the detection of four biogenic polyamines: putrescine (NH2(CH2)4NH2), cadaverine (NH2(CH2)5NH2), spermine (NH2(CH2)3NH(CH2)4NH(CH2)3NH2) and spermidine (NH2(CH2)4NH(CH2)3NH2). Putrescine and cadaverine are diamines each containing two primary amino groups, while spermine and spermidine have two and one secondary amino groups, respectively.
There are two main reasons for the determination of biogenic amines in food: (i) their potential toxicity; and (ii) the possibility to use them as food quality markers [28]. Biogenic polyamines are good indicators of food ripening or spoilage: during storage of fish, biogenic amines might form due to the degradation of proteins and amino acids [28,29]. In particular, the levels of putrescine, cadaverine and histamine have been established as good indicators of bacterial spoilage of meat and fish [29]. Changes in putrescine and cadaverine levels in saliva are correlated with cell growth and proliferation, as well as tumour growth in oral cancer [30]. Putrescine is also used to monitor chemotherapy effect on oral cancer cells [30]. The levels of spermine and putrescine in plasma have also been associated with chronic renal failure [31]. Thus, effective monitoring of these analytes is important in food and health care industries.
Most commonly biogenic amines are detected using chromatographic methods; pre- or post-column derivatisation is frequently performed as polyamines do not contain optically active or fluorescent groups. This is both costly and time consuming [28]. Previously, ECL determination of biogenic amines with Ru(bpy)32+ solution combined with capillary electrophoresis has been reported [32].
We report solid state ECL biosensor based on covalent immobilisation of Ru(bpy)32+-encapsulated silica nanoparticles on screen printed carbon surface. The sensors were used for the direct detection of biogenic amines, which were shown to act as coreactants in ECL generation.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
Tetraethoxylortosilicate (TEOS), tris(2,2-bipyridyl)ruthenium(II) hexahydrate (Ru(bpy)3Cl2∙6H2O), 1-hexanol, cyclohexane, sodium tetraborate, spermine, spermidine, cadaverine dihydrochloride, putrescine, Triton X-100 (TX-100), 1-ethyl-3-(dimethylaminopropyl)-carbodiimide (EDC), (3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane (APTES), N-Hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) and all usual chemicals were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich, Spain. Screen printed carbon electrodes with working electrode diameter 3 mm, were obtained from DropSens, Spain. Aqueous solutions were prepared with Milli-Q water Millipore (18 mΩ∙cm) and all reagents were used as received.
2.2. Instrumentation and Methods
Electrochemical measurements were done by Palmsense potentiostat, the Netherlands, controlled by PSTrace software. Cyclic voltammetry was performed on screen-printed electrodes, which incorporated silver/silver chloride reference and carbon counter electrodes. The electrodes were electrochemically pretreated by cyclic voltammetry by sweeping potential ten times from +0.2 to +1.3 V vs. Ag/AgCl reference electrode on the chip at scan rate of 100 mV/s in 0.5 M KOH solution. The ECL signal was recorded via an optical fibre connected to the photomultiplier tube Hamamatsu H10682-01 controlled by a lab-written Labview program, which collected points at the frequency of 10 Hz. Nanoparticles were characterised using transmission electron microscope TEM (JEOL JEM–1011), while modified surface was characterised using scanning electron microscope—SEM (QUANTA 600) and electrochemistry.
2.3. Nanoparticles Synthesis
Synthesis of Ru(bpy)32+-encapsulated silica nanoparticles (RuNPs) was done according to the previously published micro emulsion method [25,26,27]. The water-in-oil micro emulsion was prepared by mixing 1.77 mL of TX-100, 7.5 mL of cyclohexane and 1.8 mL of 1-hexane. Then, 80 µL of 0.1 M aqueous solution of Ru(bpy)32+ was added into the mixture in the presence of 100 µL TEOS. The polymerization reaction was initiated by addition of 60 µL of 28 % NH4OH solution. The reaction was allowed to proceed for 2 h in dark. The nanoparticles were precipitated by addition of 20 mL of acetone and centrifugation for 15 min at the rotation speed of 4000 rpm. Finally, particles were washed several times with absolute ethanol and finally with water to remove any free surfactant or dye and allowed to dry at 60 °C in oven.
2.4. Nanoparticles Surface Modification
The surface of the nanoparticles was modified to contain amino functional groups. Amino groups were introduced by treating 1 mg of nanoparticles with 600 µL of APTES dissolved in 2 mL of ethanol for 1 h. Then, nanoparticles were centrifuged at 4000 rpm for 15 min, the supernantant was discarded and the particles were subsequently washed three times with ethanol and water and dried at 60 °C in an oven.
2.5. Immobilization
After the electrochemical pretreatment of the electrodes (Section 2.2), the COOH groups present on the electrode surface were converted into the reactive succinimidyl esters by covering the surface for 30 min with freshly prepared 0.2 M EDC/0.1 M NHS solution prepared in 0.1 M MES buffer, pH 5.0. After washing and drying of the electrode surface with nitrogen, a droplet containing 1 mg/mL of aminated RuNPs was pipetted onto the surface in order to form a covalent bond between the nanoparticle surface amino group and the newly formed succinimidyl ester at the carbon surface. RuNPs were allowed to react for 2 h with the carbon surface groups. The electrodes were then washed with water to remove all non-covalently bound particles and free dye, and were dried with nitrogen. At the end, the surface of the working electrode was visibly yellow.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Electrochemical and ECL Behaviour of Biogenic Amines
First, the ECL efficiency of the biogenic amines was investigated at pH values 7.5 and 9.2, in 0.1 M phosphate and 0.05 M tetraborate buffer, respectively. These pH values were chosen as it is known that pH strongly influences ECL efficiency. This is because ECL generation typically involves formation of high-energy intermediates, which is a strongly pH dependent process [12,33]. Table 1 shows the obtained signal to background ratio for the four biogenic polyamines at different pH values. The signal corresponds to the ECL signal in the presence of the analyte, and background corresponds to the ECL generated in the absence of analyte, in 5 mM Ru(bpy)32+ solution.

Table 1.
Comparison of signal to background ratios of 10 µM analyte in the presence of 5 mM Ru(bpy)32+ at pH 7.5 (0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer) and pH 9.2 (0.05 M sodium tetraborate buffer).
| Biogenic Amine | S/N at pH 7.5 | S/N pH 9.2 |
|---|---|---|
| Spermine | 320 | 85 |
| Spermidine | 355 | 91 |
| Putrescine | 15 | 25 |
| Cadaverine | 5 | 18 |
As can be seen from Table 1, spermine and spermidine generate significantly higher ECL signal than putrescine and cadaverine. This is expected, as these molecules contain secondary amine groups, while putrescine and cadaverine contain both two primary amine groups. Spermine and spermidine generated considerably higher ECL signal at pH 7.5, and thus this pH was used for their measurement, while putrescine and cadaverine had higher signal at pH 9.2. The difference was most significant for cadaverine, which exhibited overall the lowest signal of the four analytes. Neutral pH is generally optimal for the detection of secondary and tertiary amines, however, for primary amines high pH values are typically required [33]. Unfortunately, high pH value also contributes to the high background ECL, as OH. radicals can also act as ECL coreactants. Therefore, pH 9.2 was chosen as a higher pH detection buffer to compromise between high ECL signal and low background.
Next, the electrochemical behaviour of biogenic amines was investigated. In a typical ECL reaction, in the presence of Ru(bpy)32+, the electrochemical oxidation of the analyte interacts with the oxidation of Ru(bpy)32+ leading to the enhanced or catalytical current. Figure 1 shows the cyclic voltammograms of Ru(bpy)32+ measured in tetraborate buffer, pH 9.2, in the absence and presence of putrescine and cadaverine. Inset shows cyclic voltammograms of the polyamines in buffer.
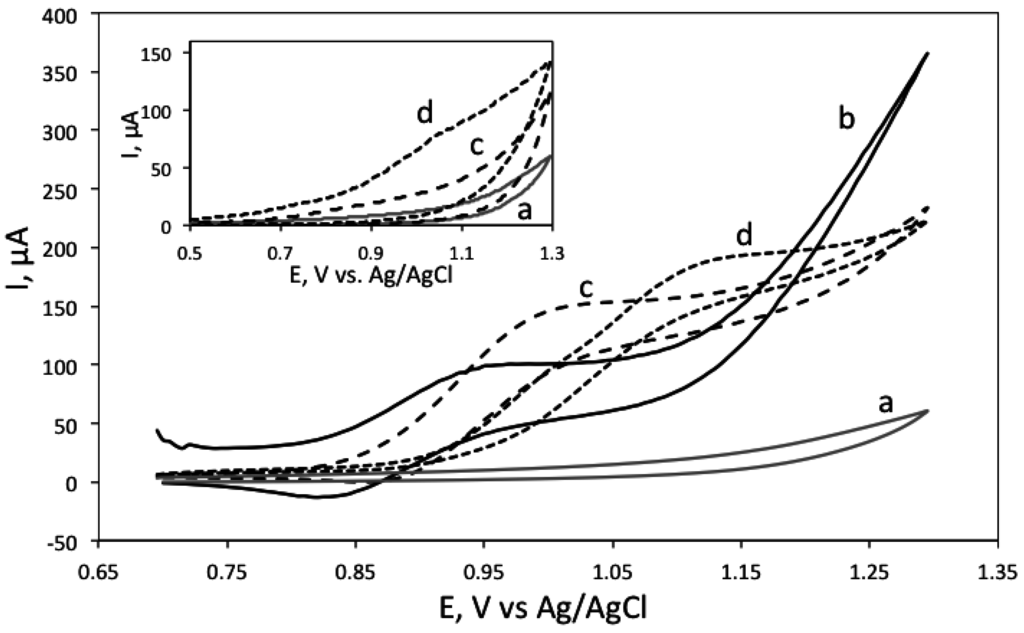
Figure 1.
Cyclic voltammogram of 5 mM Ru(bpy)32 solution alone (solid line, marked with b), in the presence of 100 μM cadaverine (dashed line, c), and in the presence of 100 μM putrescine (dotted line, d). Background (grey line, a) corresponds to 0.05 M tetraborate buffer, pH 9.2. Inset shows cyclic voltammograms of 100 mM cadaverine (dashed line, c) and putrescine (dotted line, d) in tetraborate buffer, pH 9.2 as well as buffer background (grey line, a).
Figure 1.
Cyclic voltammogram of 5 mM Ru(bpy)32 solution alone (solid line, marked with b), in the presence of 100 μM cadaverine (dashed line, c), and in the presence of 100 μM putrescine (dotted line, d). Background (grey line, a) corresponds to 0.05 M tetraborate buffer, pH 9.2. Inset shows cyclic voltammograms of 100 mM cadaverine (dashed line, c) and putrescine (dotted line, d) in tetraborate buffer, pH 9.2 as well as buffer background (grey line, a).
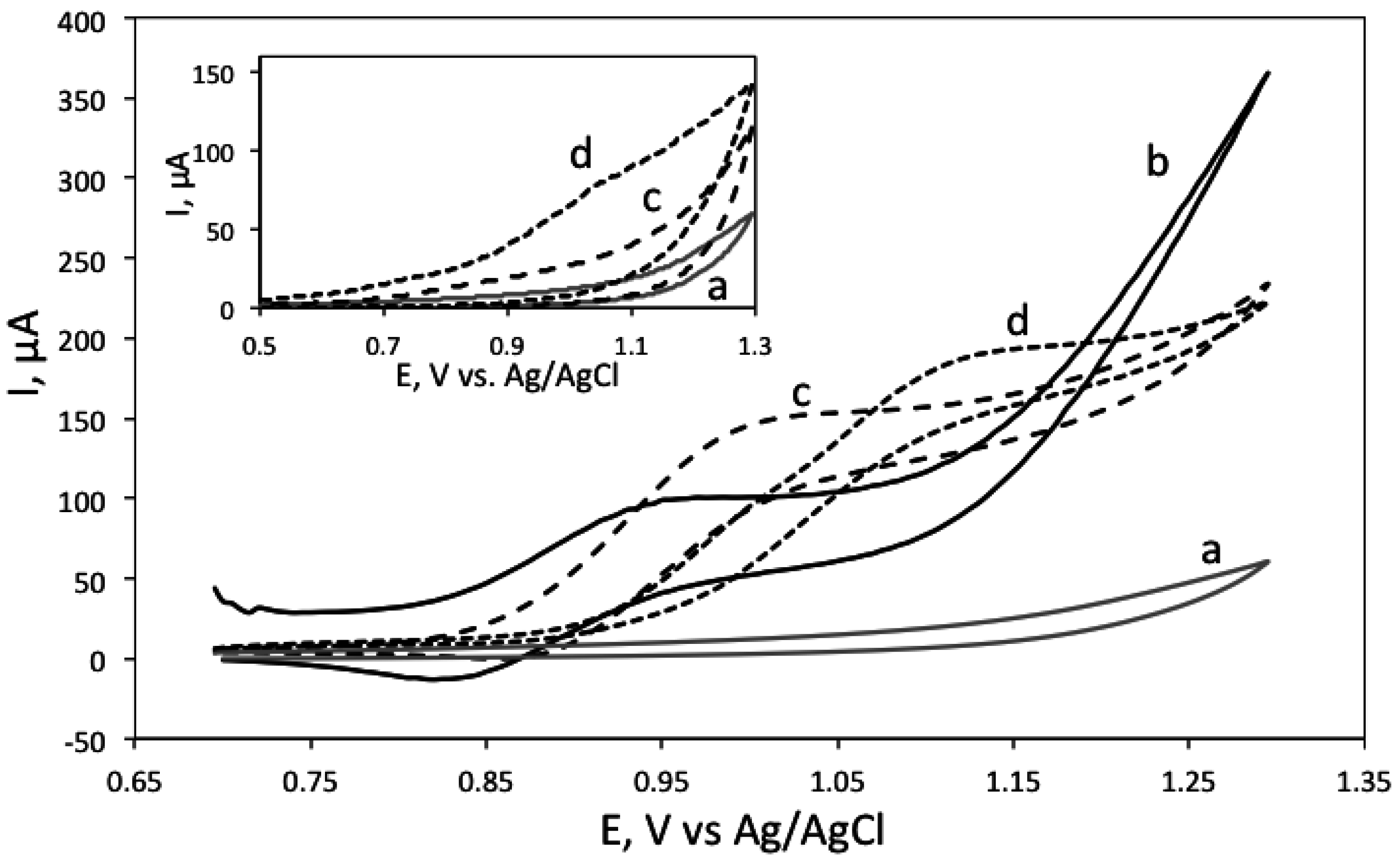
Figure 2 shows the voltammograms of Ru(bpy)32+ in phosphate buffer, pH 7.5, in the presence and absence of spermine and spermidine and the inset shows cyclic voltammograms of spermine and spermidine in the absence of Ru(bpy)32+.
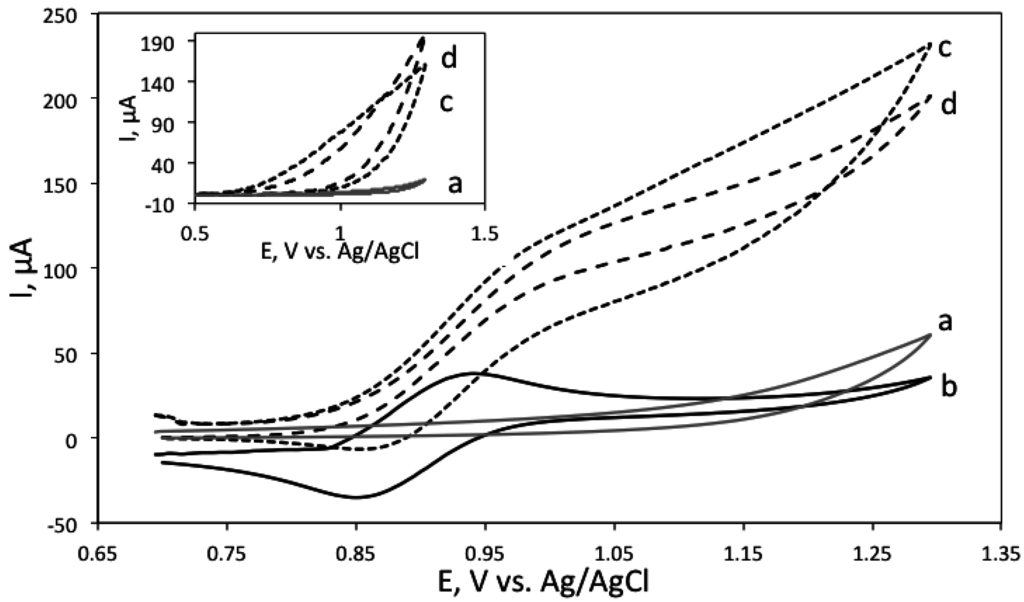
Figure 2.
Cyclic voltammogram of 5 mM Ru(bpy)32 in 100 mM phosphate buffer, pH 7.5 (solid line, b), in the presence of 10 μM spermine (dotted line, c) and in the presence of 10 μM spermidine (dashed line, d). Inset shows cyclic voltammograms of 100 mM spermine (dotted line, c) and spermidine (dashed line, d) in phosphate buffer, pH 7.5. The background (grey line, b) corresponds to 100 mM phosphate buffer, pH 7.5.
Figure 2.
Cyclic voltammogram of 5 mM Ru(bpy)32 in 100 mM phosphate buffer, pH 7.5 (solid line, b), in the presence of 10 μM spermine (dotted line, c) and in the presence of 10 μM spermidine (dashed line, d). Inset shows cyclic voltammograms of 100 mM spermine (dotted line, c) and spermidine (dashed line, d) in phosphate buffer, pH 7.5. The background (grey line, b) corresponds to 100 mM phosphate buffer, pH 7.5.
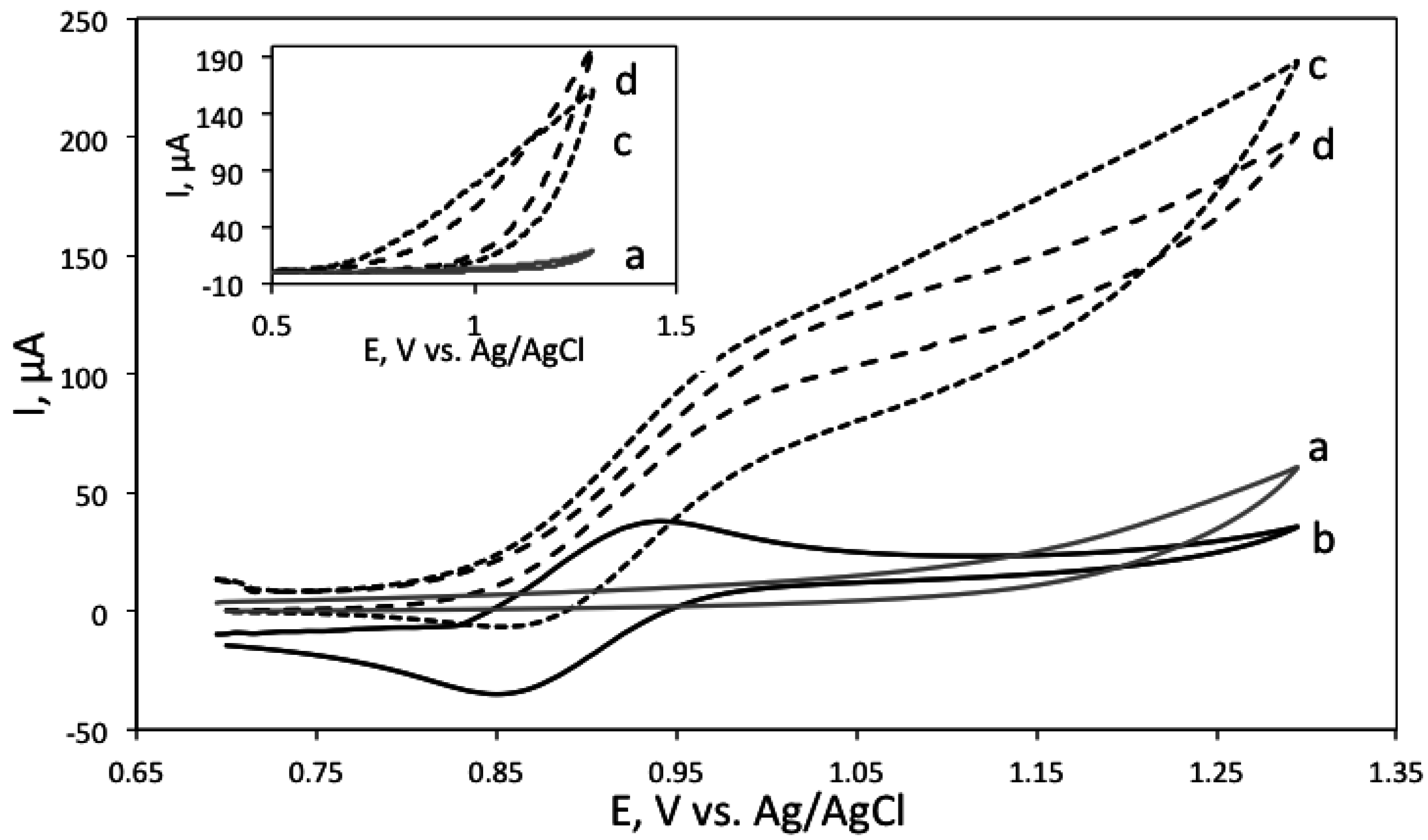
As can be seen from Figure 1 and Figure 2, the polyamines alone showed very little electrochemical activity, with a small, irreversible oxidation peak occurring around 0.9 V vs. an Ag/AgCl reference electrode. It is interesting to note that in the presence of the analytes, the voltammetric pattern turns from peak-shaped to sigmoidally shaped, accompanied by a concomitant current enhancement, which is consistent with an electrocatalytic process [34].
3.2. Characterisation of Silica Nanoparticles
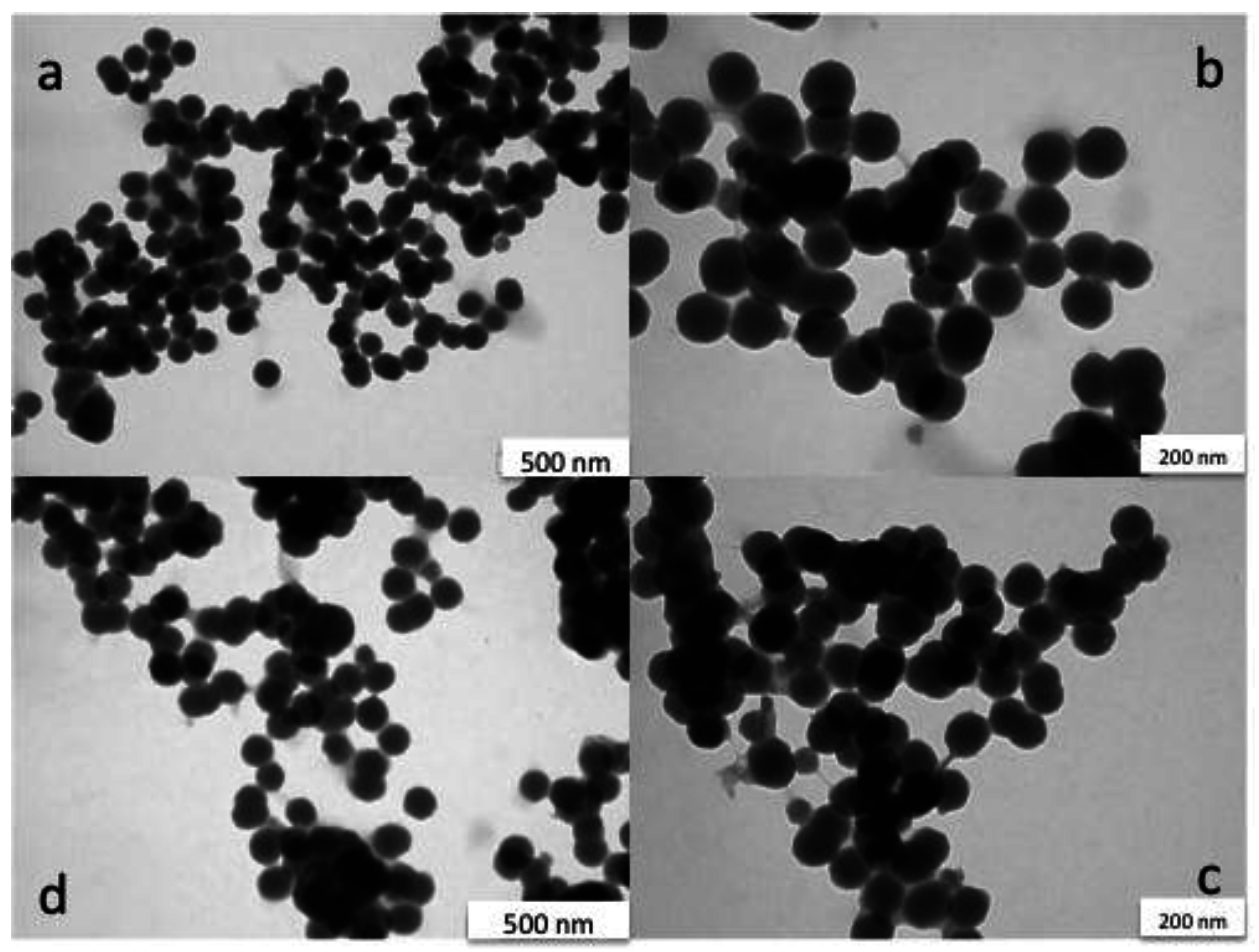
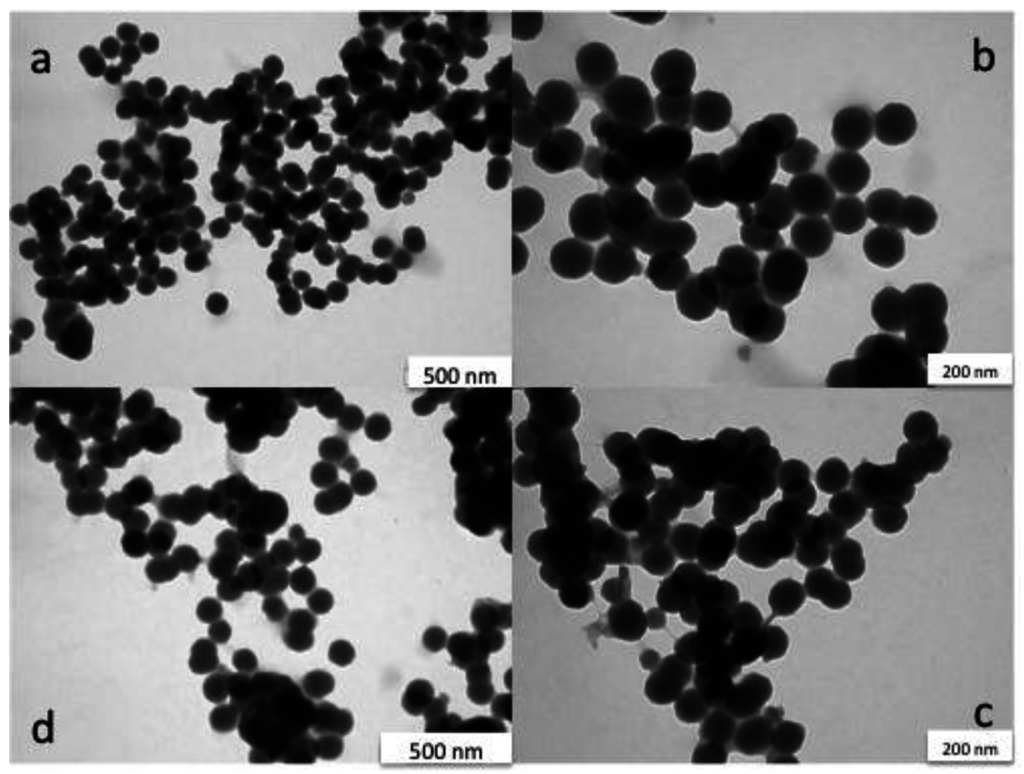
The synthesized nanoparticles were characterized by TEM (Figure 3) before and after the surface modification and immobilisation on the electrode. As can be seen from Figure 3, the nanoparticles are spherical in shape and the size of the particles is on average 103 ± 8 nm. Introduction of the amino groups on the surface did not influence the particle size.
3.3. Characterisation of the Modified Carbon Surface
Figure 4 shows SEM image of modified carbon surface. As can be seen, nanoparticles are clustered together in a tight network forming 3-dimentional structure on the surface and thus allowing immobilisation of high amount of Ru(bpy)32+ on the electrode surface.
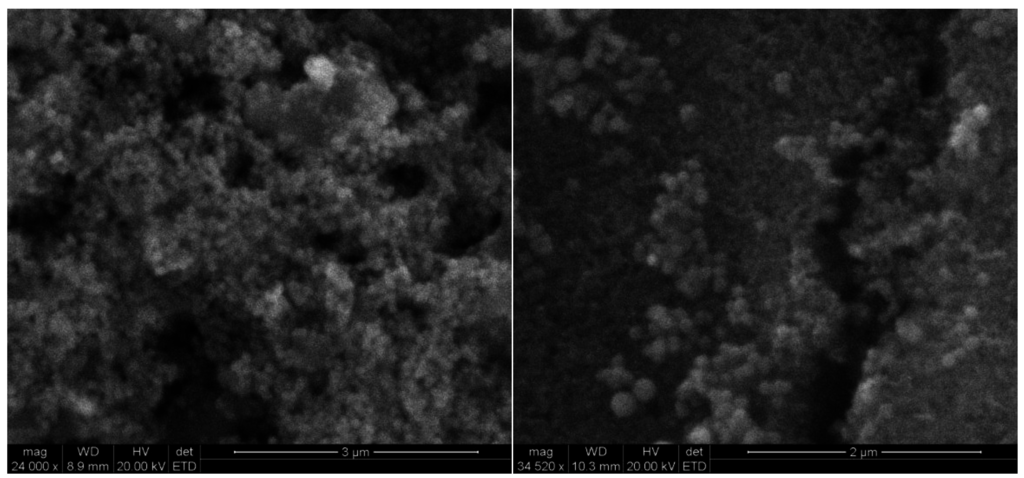
Figure 4.
SEM image of the RuNPs modified sensor surface. The nanoparticles appeared to form 3D structures on the electrode surface, thus allowing for immobilization of a high amount of dye. The scale bar is 3 µm (left) and 2 µm (right).
Figure 4.
SEM image of the RuNPs modified sensor surface. The nanoparticles appeared to form 3D structures on the electrode surface, thus allowing for immobilization of a high amount of dye. The scale bar is 3 µm (left) and 2 µm (right).
The electrochemical behaviour of the formed sensor was also investigated. Figure 5 shows the cyclic voltammogram recorded with the RuNPs modified electrode in 0.1 M phosphate buffer, pH 7.5. A rather broad oxidation peak was detected at 0.880 V vs. Ag/AgCl which corresponds to the one-electron oxidation of Ru(bpy)32+. The relatively low resolution of this peak from the background is related to the fact that Ru(bpy)32+ is not directly in contact with the electrode surface, but it is incorporated on the silica layer deposited on the electrode. Anyhow this CV confirms that even when incorporated in silica, the ruthenium complex is still electroactive.
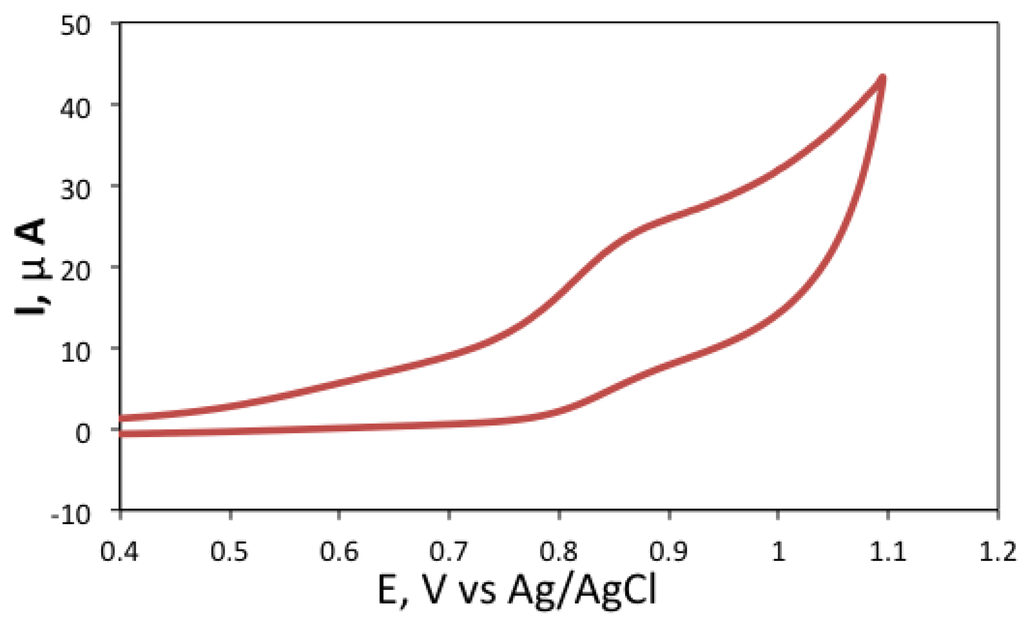
Figure 5.
Cyclic voltammogram of RuNP modified screen-printed carbon electrode surface in 0.1 M phosphate buffer, pH 7.5. Conditions: potential was swept at 0.01 mV/s.
Figure 5.
Cyclic voltammogram of RuNP modified screen-printed carbon electrode surface in 0.1 M phosphate buffer, pH 7.5. Conditions: potential was swept at 0.01 mV/s.
As the silicate layer is porous, small molecules like biogenic amines can easily penetrate into the nanoparticles and interact with the oxidised luminophore.
3.4. ECL Detection of the Biogenic Amines
Finally, the sensors were used for detection of biogenic amines. Figure 6 shows the calibration curve obtained for spermine and spermidine. Both compounds contain secondary amino groups in addition to two primary amino groups and act as highly efficient coreactants, which allowed their detection at low nanomolar level.
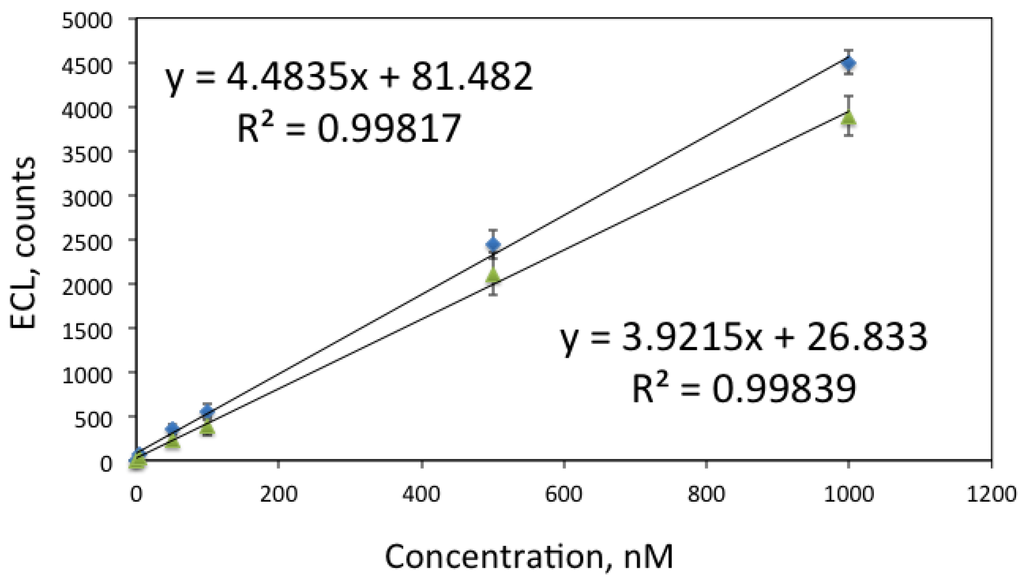
Figure 6.
Calibration curves for spermine (diamonds) and spermidine (triangles), measured in 0.1 M phosphate buffer, pH 7.5. Conditions: ECL signal was generated by sweeping potential from 0.8 to 1.3 V vs. an Ag/AgCl reference electrode and recorded with PMT via an optical fibre. Each measurement was done in triplicate with intermediate washing of the sensor.
Figure 6.
Calibration curves for spermine (diamonds) and spermidine (triangles), measured in 0.1 M phosphate buffer, pH 7.5. Conditions: ECL signal was generated by sweeping potential from 0.8 to 1.3 V vs. an Ag/AgCl reference electrode and recorded with PMT via an optical fibre. Each measurement was done in triplicate with intermediate washing of the sensor.
Figure 7 shows the calibration curves obtained for cadaverine and putrescine. Although these diamines have very similar structure, the only difference being that cadaverine has five carbon atoms while putrescine has four, considerably better signal was obtained for putrescine.
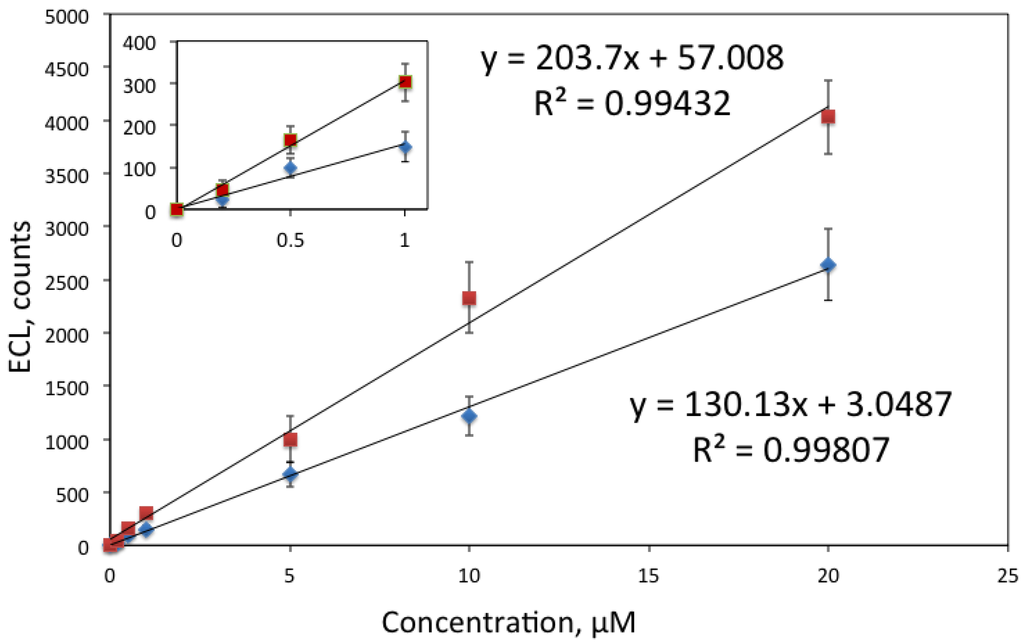
Figure 7.
Calibration curves for putrescine (quadrates) and cadaverine (diamonds), measured in 0.05 M tetraborate buffer, pH 9.2. Conditions: ECL signal was generated by sweeping potential from 0.8 to 1.3 V vs. an Ag/AgCl reference electrode and recorded with PMT via an optical fibre. The inset shows the calibration plot at low concentrations (≤ 1 μM).
Figure 7.
Calibration curves for putrescine (quadrates) and cadaverine (diamonds), measured in 0.05 M tetraborate buffer, pH 9.2. Conditions: ECL signal was generated by sweeping potential from 0.8 to 1.3 V vs. an Ag/AgCl reference electrode and recorded with PMT via an optical fibre. The inset shows the calibration plot at low concentrations (≤ 1 μM).
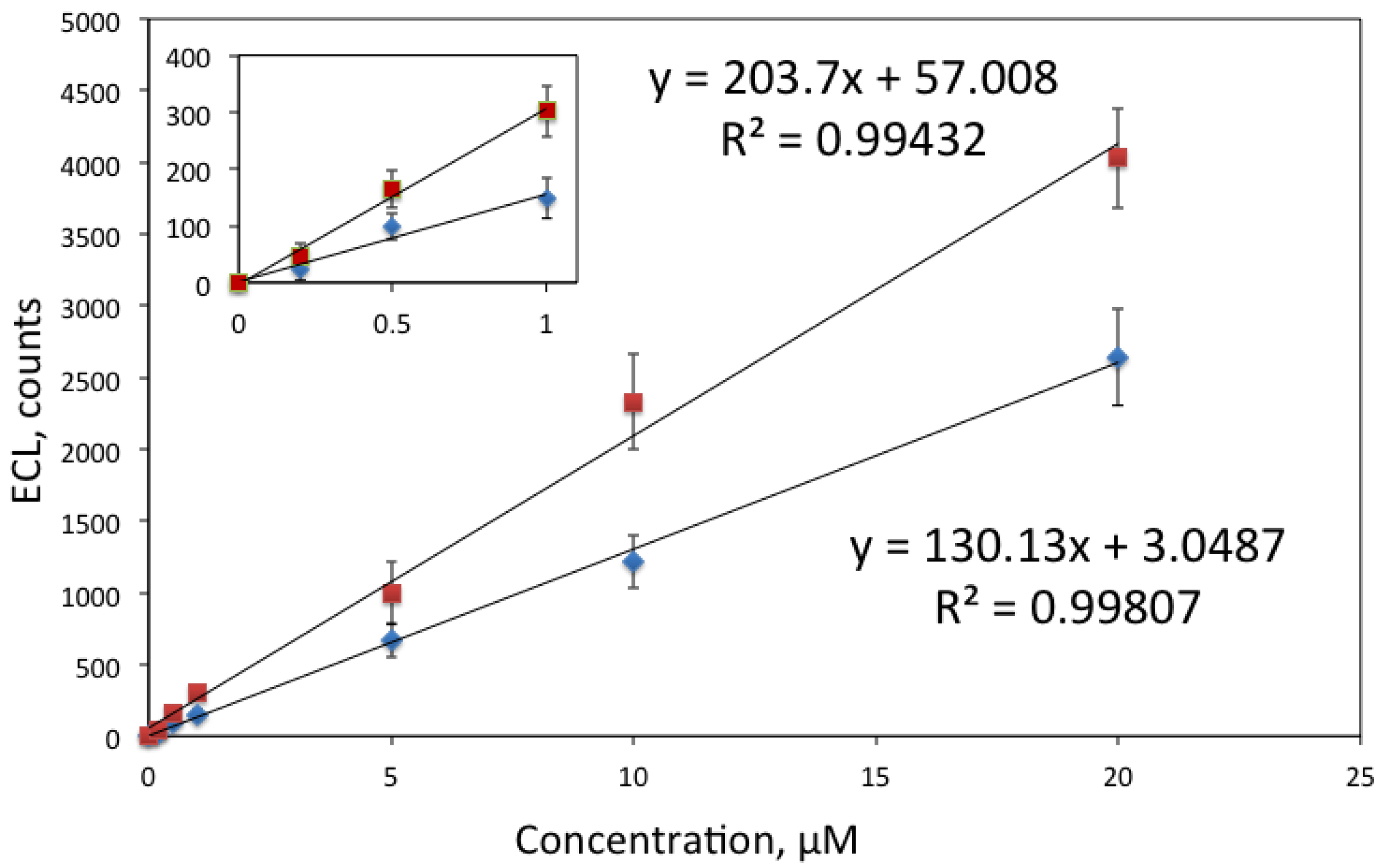
The obtained LODs, defined as three times standard deviation of the blank, were 5 nM for spermine and spermidine, 90 nM for putrescine and 120 nM for cadaverine. This is an improvement for previously reported measurements reported where LOD for spermine and spermidine were reported to be 7.6 nM and for cadaverine and putrescine 170 nM [32]. It should be however noted that the measurement conditions [32] were considerably different: detection was performed in solution after capillary electrophoresis detection, and the detection pH was 11. In our case solid-state sensor was used. Simultaneous detection of analytes was not attempted; in the future integration of the ECL sensor with a separation method could be envisaged.
4. Conclusions
In this contribution we have described fabrication of a solid state ECL sensor, based on covalent immobilization of Ru(bpy)32+-encapsulated silica nanoparticles on screen printed carbon electrode. The sensor was found stable upon multiple washings and measurements. The sensor was used for detection of biogenic polyamines (spermine, spermidine, cadaverine and putrescine), which are important markers of food quality and spoilage. LOD obtained for spermine and spermidine was 5 nM, for putrescine 90 nM and for cadaverine 120 nM. Thus, this sensor is potentially useful as a portable biosensor for food and clinical studies, as well as a detector integrated with a separation method, such as capillary electrophoresis.
Author Contributions
The experimental work and writing was mainly carried out by first two authors. The data analysis and final article formulation has been carried out by all authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Su, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, Z.; Lv, Y. Recent advances in Chemiluminescence. Appl. Spectros. Rev. 2007, 42, 139–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, M.M. Electrochemiluminescence (ECL). Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 3003–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, W. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence and its biorelated applications. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2506–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoncello, P.; Forster, R.J.; Keyes, T.E. Nanostructured materials for electrochemiluminescence (ECL)-based detection methods: Recent advances and future perspectives. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 3191–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Wang, E. Electrochemiluminescence of tris(2,2'-bipyridyl)ruthenium and its applications in bioanalysis: A review. Luminescence 2011, 26, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzyka, K. Current trends in the development of the electrochemicaluminescent immunosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 54, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Wang, E.K. Solid-state electrochemiluminescence of tris(2,2'-bipyridyl) ruthenium. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2008, 27, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, G.F.; Shah, H.P.; Kenten, J.H.; Leland, J.; Kamin, R.A.; Link, J.; Peterman, J.; Powell, M.J.; Shah, A.; Talley, D.B. Electrochemiluminescence detection for development of immunoassays and DNA probe assays for clinical diagnostics. Clin. Chem. 1991, 37, 1534–1539. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spehar-Délèze, A.; Schmidt, L.; Neier, R.; Kulmala, S.; de Rooij, N.; Koudelka-Hep, M. Electrochemiluminescent hybridization chip with electric field aided discrimination. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 22, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leland, J.K.; Powell, M.J. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence: an oxidative-reduction type ECL reaction sequence using tripropyl amine. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1990, 137, 3127–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, W.; Choi, J.-P.; Bard, A.J. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence 69: The tris(2,2'-bipyridine)ruthenium(II)/tri-n-propylamine (TPrA) system revisited—A new route involving TPrA cation radicals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 14478–14485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.; Jia, J.; Yang, X.; Dong, S.; Wang, E. Capillary electrophoresis with solid-state electrochemiluminescence detector. Electrophoresis 2002, 23, 3692–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennany, L.; Foster, R.J.; Rusling, J.F. Simultaneous Direct Electrochemiluminescence and Catalytic Voltammetry Detection of DNA in Ultrathin Films. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 5213–5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenway, G.M.; Nelstrop, L.J.; Port, S.N. Tris(2,2-bipyridyl)ruthenium(II) chemiluminescence in a microflow injection system for codeine determination. Anal. Chim. Acta 2000, 405, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eunsook, S.J.; Norris, B.J.; Puntano, P. An electrogenerated chemiluminescence imaging fiber electrode chemical sensor for NADH. Electroanalysis 2001, 13, 1287–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-P.; Bard, A.J. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence (ECL) 79. Reductive-oxidation ECL of tris(2,2'-bipyridine)ruthenium(II) using hydrogen peroxide as a coreactant in pH 7.5 phosphate buffer solution. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 541, 143–150. [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein, I.; Bard, A.J. Polymer Films on Electrodes. 5. Electrochemistry and Chemiluminescence at Nafion-Coated Electrodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1981, 103, 5007–5013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Liu, S. Solid state electrochemiluminescence analysis with coreactant of the immobilized tris(2,2'-bipyridyl) ruthenium. Anal. Biochem. 2010, 402, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devadoss, A.; Dennany, L.; Dickinson, C.; Keyes, T.E.; Forster, R.J. Enhanced Electrochemiluminescence and Charge Transport through Films of Metallopolymer-Gold Nanoparticle Composites. Electrochem. Comm. 2012, 19, 43–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatanarayanan, A.; Spehar-Délèze, A.; Dennany, L.; Pellegrin, Y.; Keyes, T.E.; Forster, R.J. Ruthenium Amino-phenanthroline Films Deposited from an Ionic Liquid: Deposition, Electrochemical and Photonic Properties. Langmuir 2008, 24, 11233–11238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piper, D.J.E.; Barbante, G.J.; Brack, N.; Pigram, P.J.; Hogan, C.F. Highly Stable ECL Active Films Formed by the Electrografting of a Diazotized Ruthenium Complex Generated in situ from the Amine. Langmuir 2011, 27, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.P.; Du, Y.; Dong, S.J.; Wang, E.K. Method for effective immobilization of Ru(bpy)32+ on an electrode surface for solid-state electrochemiluminescence detection. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 8166–8169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoncello, P.; Dennany, L.; Forster, R.J.; Unwin, P.R. Nafion-Tris(2–2'-bipyridyl)ruthenium(II) Ultrathin Langmuir-Schaefer Films: Redox Catalysis and Electrochemiluminescent Properties. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 7549–7553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moretto, L.M.; Kohls, T.; Badocco, D.; Pastore, P.; Sojic, N.; Ugo, P. Electrochemiluminescence of Ru(bpy)32+ loaded in Nafion Langmuir-Blodget films: Role of the interfacial ultrathin film. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2010, 1–2, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, L.; Yang, X.R. One-step synthesis of Ru(2,2'-bipyridine)3Cl2-immobilized silica nanoparticles for use in electrogenerated chemiluminescence detection. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 1353–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.H.; Dong, S.J. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence sensors using Ru(bpy)32+ doped in silica nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 5119–5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardesai, N.P.; Barron, J.; Rusling, J.F. Carbon nanotube microwell array for sensitive electrochemiluminescent detection of cancer biomarker proteins. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 6698–6703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Önal, A. A review: Current analytical methods for the determination of biogenic amines in food. Food Chem. 2007, 103, 1475–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombelli, S.; Mascini, M. Electrochemical biosensors for biogenic amines: A comparison between different approaches. Anal. Chim. Acta 1998, 358, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, M.; Wong, D.T.; Hirayama, A.; Soga, T.; Tomita, M. Capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry based saliva metabolomics identifies oral, breast and pancreatic cancer-specific profiles. Metabolomics 2010, 6, 78–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igarachi, K.; Ueda, S.; Yoshida, K.; Kashiwagi, K. Polyamines in renal failure. Amino Acids 2006, 31, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, E. Direct tris(2,2'-bipyridyl)ruthenium(II) electrochemiluminescence detection of polyamines separated by capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2003, 24, 3131–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, A.W.; Greenway, G.M. Relationship between structural attributes and observed electrogenerated chemiluminescence (ECL) activity of tertiary amines as potential analytes for the tris(2,2-bipyridine)ruthenium(II) ECL reaction. A review. Analyst 1996, 121, 101R–106R. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 501–503. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).