Abstract
The development of sensing systems that can detect ultra-trace amounts of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) remains a key challenge in biological and biomedical fields. In the present study, we introduce a simple and highly sensitive enzymeless H2O2 biosensor based on a three-dimensional open pore nickel (Ni) foam electrode functionalized with hemoglobin (Hb). Our findings revealed that the Hb maintained its biological functions and effective electronic connection even after immobilization process. The exceptional physical and intrinsic catalytic properties of the Ni foam combined with the bio-functionality and electron transport facility of the Hb robustly construct a H2O2 biosensor. The enzymeless H2O2 biosensor showed high selectivity, a quick response time, high sensitivity, a wide linear range and a low limit of detection (0.83 μM at a signal-to-noise ratio of three). Such an electrode composition with safe immobilization processes offers viability for engineering new biosensors.
1. Introduction
There is a growing demand worldwide to develop efficient sensing systems with high flexibility and low capital cost for control recognition and real-time monitoring of toxic analytes and biological molecules at very low concentrations [1]. The design of a high-performance sensing system for environmental screening has therefore attracted considerable attention [2]. Porous materials have attracted much attention because of their high porosity, stability, mechanical strength, relatively low toxicity and mass transfer ability [3]. They are promising candidates in a plethora of technologically important disciplines, including environmental capture, sensor design, nanofiltration and fuel cells [4]. Porous metallic materials possessing high specific surface areas and an open-pore architecture, namely metallic foams, offer unique physical and chemical characteristics to interact with atoms, ions and molecules along the porous network [5]. These attractive features of metallic foam make it a suitable material for a wide range of potential applications, such as catalysts [6], separation systems [7], chemical sensors [8] and electrochemical applications (water electrolyzers, alkaline fuel cells, electrochemical supercapacitors, electrochromic devices and alkaline batteries) [9].
H2O2 is a very simple compound in nature, but with great significance in pharmaceutical, clinical, environmental, mining, textile and food manufacturing applications [10]. In addition to its cytotoxic effects in living organisms, H2O2 also plays a key role as a signaling molecule in regulating diverse biological processes, such as immune cell activation, stomatal closure and root growth [11]. The design of a simple, accurate, rapid and low-cost H2O2 sensor for biology, medicine, environmental and food industries has therefore attracted considerable attention. Many conventional techniques for H2O2 determination, such as fluorometry [12], spectrofluorometry [13], chemiluminescence [14], fluorescence spectrophotometry [15] and electrochemical analysis [16], have been applied to determine H2O2. Electrochemical sensors/bio-sensors presently hold a leading position in many sensing applications, including clinical, healthcare, environmental, food and national defense detection, due to their simplicity, speed, high sensitivity and selectivity [17]. The H2O2 detection industry is dominated by using enzymatic electrodes in which the enzyme, horseradish peroxidase, is predominantly used [18]. It is a highly selective enzyme and works at a wide range of pHs, but it bears poor long-term stability, poor tolerance in experimental conditions and high cost [19]. Therefore, the development of non-enzymatic detection of H2O2 selectively and sensitively by an electrochemical method has received continuous interest, due to the simple fabrication of electrode materials, direct data correlation and being more cost effective than conventional methods [20].
To develop an advanced sensing system, the roles of the electrode material and architecture are indispensable. To date, metal oxides, such as copper oxide [21] and nickel oxide [22], have been extensively applied in the construction of non-enzymatic H2O2 sensors. However, poor stability and the toxic nature of copper oxide has limited it from commercialization. Nickel foam (Ni foam), as a commercial material, could be the electrode substrate material of choice, because of its high mechanical strength, inertness, relatively low toxicity and low cost. The above-mentioned physical characteristics and corrosion stability in aqueous alkaline solution make it a suitable material for specialized electrochemical applications, such as fuel cells, electrochemical sensors and supercapacitors [23].
The performance of an electrochemical sensor is mainly determined by the electrochemical activity and kinetics of the electrodes [24]. Therefore, to improve the energy density of an electrochemical sensor at high rates, it is critical to enhance the kinetics of ion and electron transport in electrodes and at the electrode-electrolyte interface and to engage sufficient electro-active species exposed on the surface for the faradaic redox reaction. The high surface area, as well as the tunable and three-dimensional (3D) open pore architecture cause Ni foam materials to become versatile hosts for numerous guest molecules, such as proteins, drugs and small biomolecules [25]. The safe immobilization of the proteins onto Ni foam, while maintaining their full biological activity, as well as the effective electronic connection between their redox-active sites and the electrode surface, remains a key challenge for designing electrochemical sensors and biosensors. The most attractive features of the hemeproteins are not only their stability over a wide pH range, but they also have significant functioning in the design of a biosensor as a biological electron-transport chain [26] and peroxidase-like activity [27]. Recently, we reported a nano-magnet selective adsorbent for hemeproteins without changing their chemical or physical functionality [28]. In this induced-fit separation model, in addition to the heme group distributions and protein-carrier binding energy, the morphology and magnetic properties of Ni-based materials had a key function in broadening the controlled immobilization affinity and selectivity of hemeproteins.
In this study, we report the simple fabrication of an amperometric biosensor for H2O2 using a Hb-modified 3D open-pore Ni-foam electrode (Scheme 1). The emerging functionality of the 3D porous Ni foam network and heme activity have key advantages for enhancing the electrochemical performance of the electrode toward the non-enzymatic H2O2 sensor. The results show the promising utilization of the Hb-modified Ni foam electrode for the detection of H2O2 with high sensitivity, excellent selectivity, a wide working range and a lower detection limit.
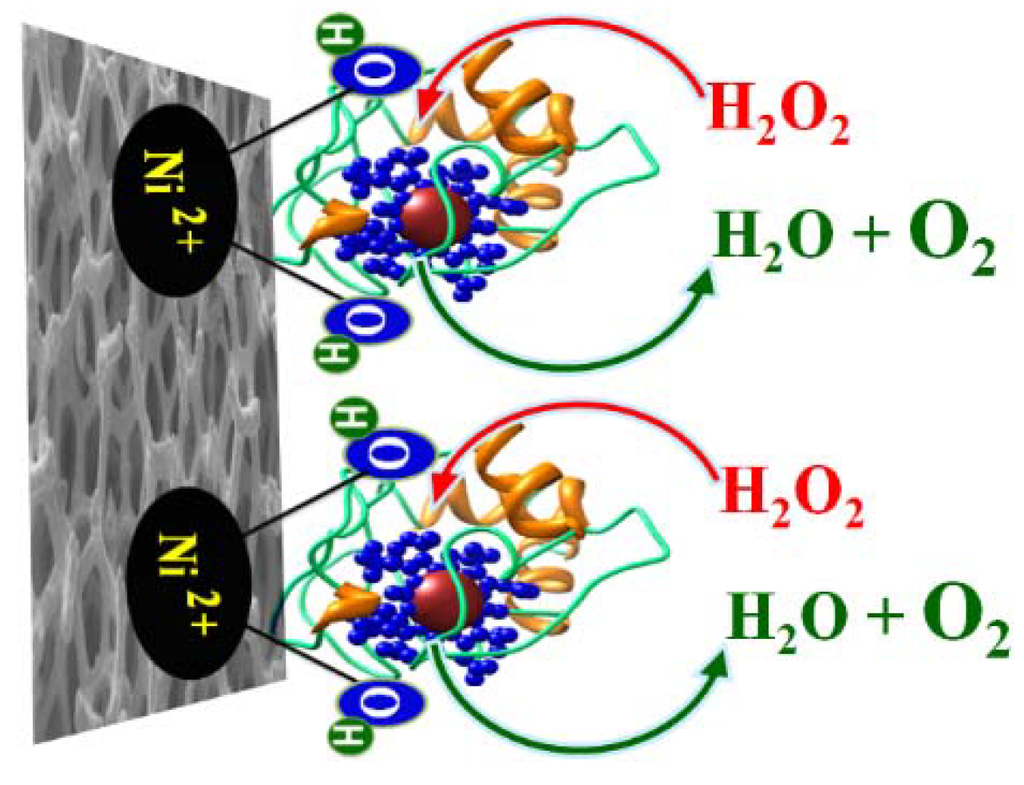
Scheme 1.
Electro-catalytic oxidation of H2O2 over Ni foam decorated by Hb.
Scheme 1.
Electro-catalytic oxidation of H2O2 over Ni foam decorated by Hb.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Chemicals
All chemicals were of analytical grade and used without further purification. H2O2 aqueous solution (30% v/v), Hb, uric acid (UA), hydrochloric acid (HCl) and phosphate buffer saline (PBS) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Company Ltd., (Saint Louis, MO, USA). Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and L(+)-ascorbic acid (AA) were obtained from Wako Company Ltd., Osaka, Japan. The commercial 3D porous Ni foam was purchased from Nilaco Corporation Tokyo. Green tea was obtained from a local supermarket (Tsukuba, Japan). Green tea contains green tea extract, sucrose, honey, ascorbic acid, citrate and water with pH 5.3.
2.2. Preparation of the Hb-Modified Ni Foam Electrode
The Hb-modified electrode was fabricated simply by the immobilization of Hb onto the Ni foam electrode in the following way. In the first step, Ni foam was carefully cleaned with a concentrated HCl solution (2 M) in an ultrasound bath for 5 min to remove the surface NiO layer. Deionized water and absolute ethanol were then used for 5 min each to ensure that the surface of the Ni foam was completely clean. The second step was the immobilization of a specific amount of Hb onto the surface of the Ni foam electrode. The third step was drying the resulting electrode based on Hb-modified Ni foam at 60 °C overnight prior to electrochemical analysis.
2.3. Instrumentation
A Zennium/ZAHNER-Elektrik instrument, controlled by Thales Z 2.0 software at room temperature, was used for the electrochemical measurements. A conventional three electrode system, consisting of a Ni foam/Hb-modified Ni foam (1 mm × 1 cm × 2 cm) working electrode, a platinum wire counter electrode and a Ag/AgCl (3 M NaCl) reference electrode, was used.
2.4. Materials Characterization
The morphology of the Ni foam and Hb-modified Ni foam was investigated via field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM, JEOL model 6500). The scanning electron microscope was operated at 15 keV in order to record better SEM micrographs of the Ni foam and Hb-modified Ni foam. Before being placed in the chamber, the Ni foam was secured on a specimen stub using a double-sided carbon tape. Then, a 10-nm Pt film was coated via anion sputtering (Hitachi E-1030) at room temperature to obtain high-resolution micrographs. Before sputtering deposition, the Pt target (0.1 m in diameter, purity 99.95%) was sputter cleaned in pure Ar. The sputtering deposition system used for the experiments consists of a stainless steel chamber, evacuated down to 8 × 10−5 Pa with a turbo molecular pump backed up by a rotary pump. The Ar working pressure (2.8 × 10−1 Pa), the power supply (100 W) and the deposition rate were kept constant throughout these investigations. The chemical composition was analyzed by energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) microanalysis incorporated in the FE-SEM instrument.
The interfacial properties of the Ni foam and Hb-modified Ni foam were characterized through static water contact angles (WCAs). WCAs on the surfaces of the bare Ni foam and Hb-modified Ni foam electrode were measured at room temperature with contact angle analysis equipment (VCA Optima, Ast Products, Inc., Billerica, MA, USA) using the sessile drop method with 100-µL water droplets. WCAs values were recorded after 3 s from droplet deposition.
2.5. Determination of H2O2 in a Real Sample
The real sample analysis was performed in a commercially available green tea. Before the determination of H2O2 in the green tea sample, the standard titration method (KMnO4) was employed to confirm whether the samples contained the endogenous H2O2. For the determination of the H2O2 concentration in the green tea sample, standard concentrations of H2O2 were injected into the test solution, and the mixed samples were analyzed using the Hb-modified Ni foam. The response current was recorded when the steady state was reached. The difference between the baseline and the steady-state current was used to calculate the concentration of H2O2.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Features of Hb-Modified Ni Foam
A key approach to boosting the electrochemical activity of the Ni foam-based electrode is its morphological and/or chemical composition, as well as suitable pore sizes for the [OH−] electrolytes to penetrate into the active site of the 3D porous network matrix. In the current work, 3D porous Ni foam was used as a substrate for the immobilization of Hb to improve the energy density of the electrochemical sensor at high rates. This successful immobilization of Hb onto 3D Ni foam might easily enhance the kinetics of ion and electron transport in the Ni foam electrode, at the electrode-electrolyte interface and to engage sufficient electro-active species exposed on the surface for the faradaic redox reaction, as evidenced by the SEM profile, EDX and WCAs analyses.
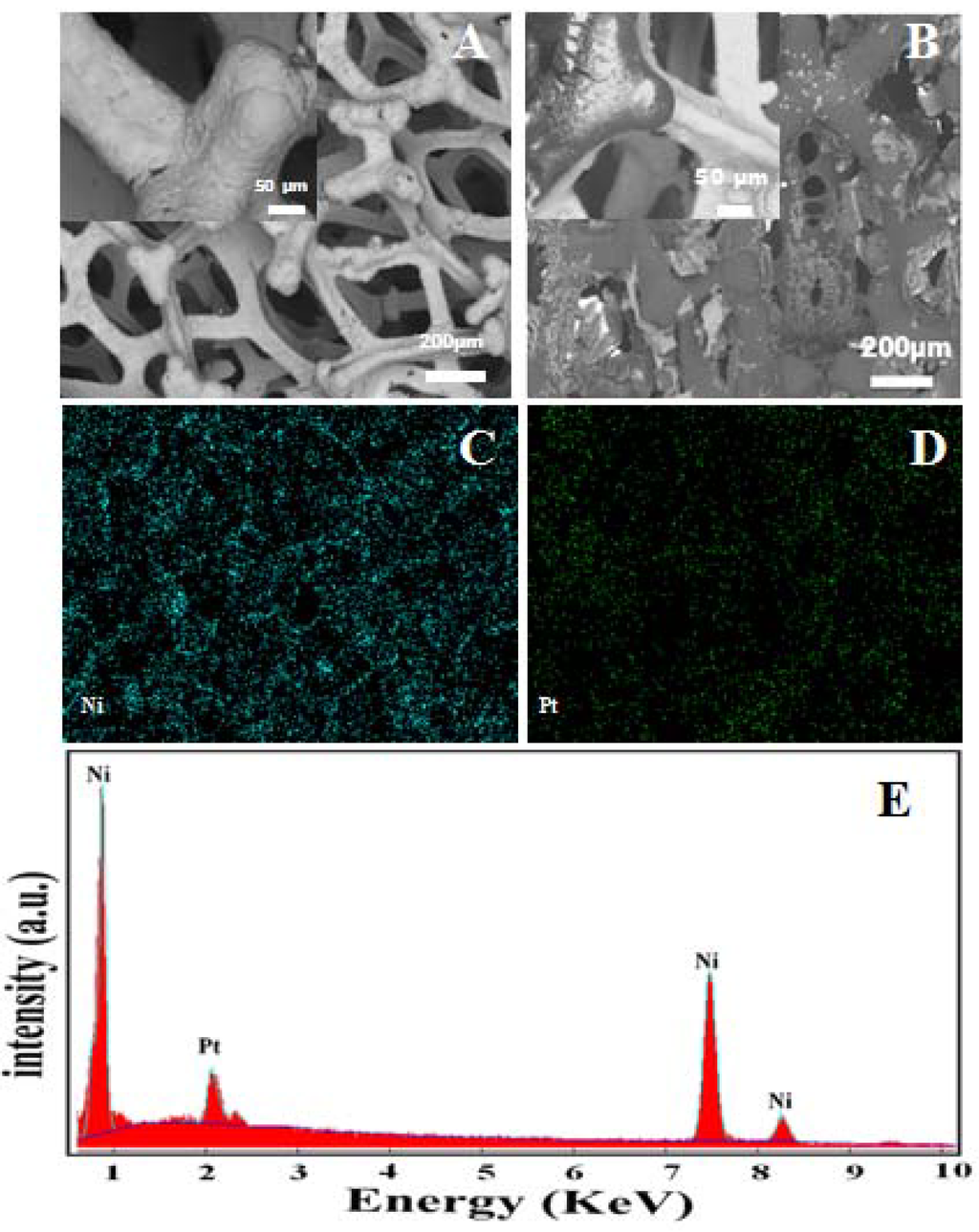
Figure 1.
(A) SEM image of bare Ni foam; (B) Hb-modified Ni foam. The insets of (A) and (B) show the highly magnified image of bare Ni foam and hemoglobin-modified Ni foam with covered and non-covered surfaces. (C) EDX mapping of the Ni and (D) Pt atoms. (E) EDX spectrum of the Ni foam.
Figure 1.
(A) SEM image of bare Ni foam; (B) Hb-modified Ni foam. The insets of (A) and (B) show the highly magnified image of bare Ni foam and hemoglobin-modified Ni foam with covered and non-covered surfaces. (C) EDX mapping of the Ni and (D) Pt atoms. (E) EDX spectrum of the Ni foam.
Figure 1 shows the typical SEM micrographs of the Ni foam before and after modification with Hb. The Ni foam exhibits a 3D cross-linked structure with a pore size of a few hundred micrometers (Figure 1A). The high-magnification SEM image reveals the compact structure of the interconnected grain-like vertebrae with narrow grain boundaries inserted in (Figure 1A). The modification of the porous 3D-Ni foam with Hb (Figure 1B) results in the formation of a film over the surface of the Ni foam, because of the high binding interactions between the Ni foam and the Hb [28]. The inset in Figure 1B shows the high-magnification SEM image of the Hb covered and non-covered Ni foam electrode surface. The safe immobilization of Hb into the 3D porous architecture of Ni foam provides high accessibility and enables rapid ion transport of electrons and ions. The chemical composition of the Ni foam electrode was characterized using SEM-EDS analysis. Figure 1C,D shows the mapping of Ni and Pt atoms. The Pt atoms were originally from the sputtering deposition process. Figure 1E shows the energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectrum of the Ni foam coated with Pt film. The EDX analysis shows that the Ni foam was in pure metallic form, and there is no sub-layer of oxides.
3.2. Electrochemical Mechanism of the Working Electrode
The electrochemical performance of an electrode material is generally characterized using cyclic voltammetry (CV) profiles. To investigate the effect of the formation type of redox species on the electrode surface, we examined the CV response of the bare Ni foam and Hb-modified Ni foam in an alkaline solution containing 2 mM of H2O2 at a scan rate of 100 mV/s (Figure 2). The unsymmetrical nature of the redox peaks of both electrodes indicates the quasi-reversible redox process. Anodic oxidation of the Ni foam is related to the Ni/Ni(OH)2 and Ni(OH)2/NiOOH redox reaction onto our working electrode, as previously reported [29]. Our findings reveal that the weak anodic peak at 0.40 and the strong anodic peak at 0.78 V (vs. Ag/AgCl) correspond to the oxidation of Ni to Ni(OH)2 and of Ni(OH)2 to NiOOH species, respectively. Whereas in the cathodic sweep-based process, the strong peak at 0.63 V was due to the reduction of NiOOH to Ni(OH)2 [30]. It is important to note that the Ni(OH)2 can exist in two crystallographic forms, namely the hydrous α-Ni(OH)2 and the anhydrous β-Ni(OH)2 [31]. Therefore, the strong anodic (0.78 V) and cathodic peak (0.63 V) can be related to the formation of the Ni(OH)2/NiOOH redox couple. In turn, because of the instability of the α-Ni(OH)2 phase and the transformation tendency to change to the β-phase in alkali solution (i.e., 0.1 M NaOH), the weak anodic peak centered at 0.40 V may be attributed to the conversion of hydrous α-Ni(OH)2 to anhydrous β-Ni(OH)2 [32]. The peak-to-peak separation value (ΔEp) of the CV assay using the bare Ni foam and Hb-modified Ni foam electrodes showed a relatively small ΔEp value by applying theHb-modified Ni foam electrode. This finding indicated that the Hb-modified Ni foam electrode exhibited significantly improved electro-catalytic activity for H2O2 in terms of the reversibility and fast electron transfer rate compared with the sensing system of bare Ni foam. In addition, the Hb-modified Ni electrode possesses a higher current response than the Ni foam electrode. This finding indicates the following two key components:
(i) Hb enhanced the surface activation, the electron-transfer reaction and does not impede the diffusion of hydroxide ions through the 3D porous network [33]. Surface activation of Hb is attributed to the heme cofactor. The heme group is composed of a ring of conjugated double bonds that surround an iron atom. The iron atom contains narrowly-spaced energy levels. Double bonds and iron atoms can acquire and transfer electrons easily, because they have narrowly spaced energy levels that facilitate small energy transitions. These small energy transitions prevent the loss of energy as heat; instead, it can convert energy into small processes, such as the pumping of protons across a membrane or the reduction of metals.
(ii) Based on the 3D structure of Hb, the hydrophobic amino acid cluster is buried inside the molecule, while the hydrophilic residues are located toward the surface of the molecule [34]. This configuration structure increases the hydrophilicity of the electrode surface and increases the number of active sites compared with bare Ni foam electrode (Scheme 1).
To confirm the wettability, the interfacial properties of both electrodes were characterized through contact angle measurements (Figure 3). The WCAs of the bare Ni foam (Figure 3A) and Hb-modified (Figure 3B) electrodes are 120.45° and 109.45°, respectively. In addition, the surface energies and surface tensions of the bare Ni foam and Hb-modified Ni foam were also calculated using Girifalco–Good–Fowkes–Young equation (Equation (1)) [35], which indicate that the surface energy and surface tension of the bare Ni foam increased after modification with Hb (Table 1).
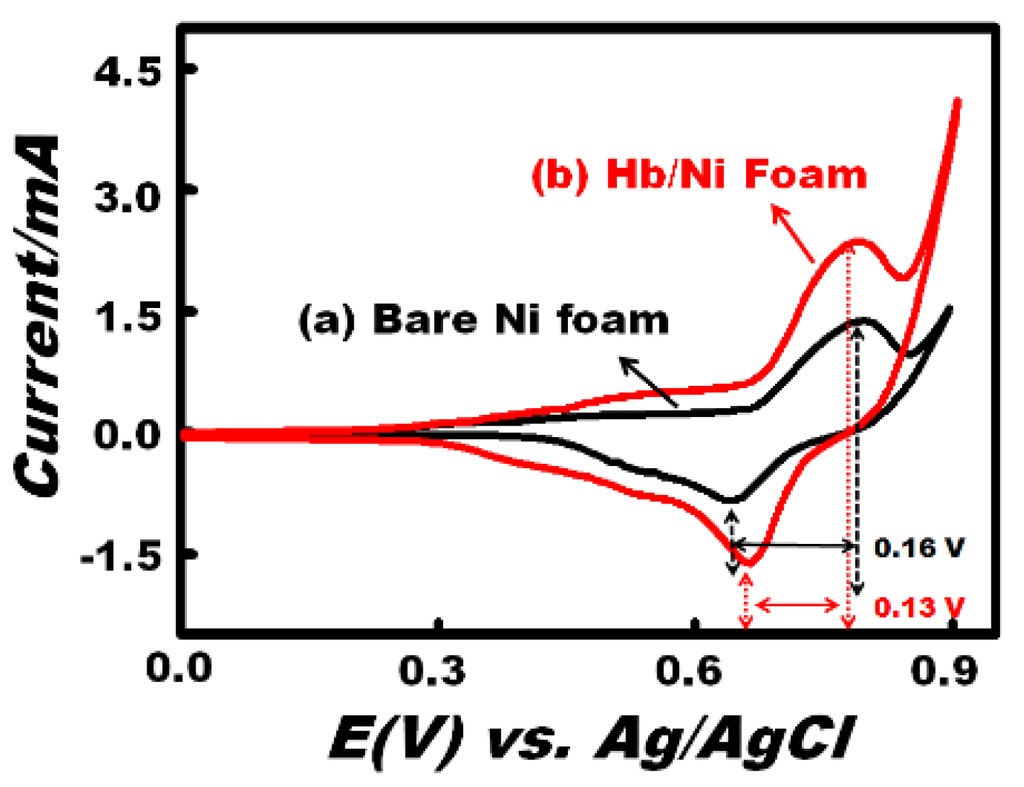
Figure 2.
Typical cyclic voltammetry (CV) curve of the (a) bare Ni foam and (b) Hb-modified Ni foam electrodes in the presence of H2O2 (2 mM) at a scan rate of 100 mV/s.
Figure 2.
Typical cyclic voltammetry (CV) curve of the (a) bare Ni foam and (b) Hb-modified Ni foam electrodes in the presence of H2O2 (2 mM) at a scan rate of 100 mV/s.
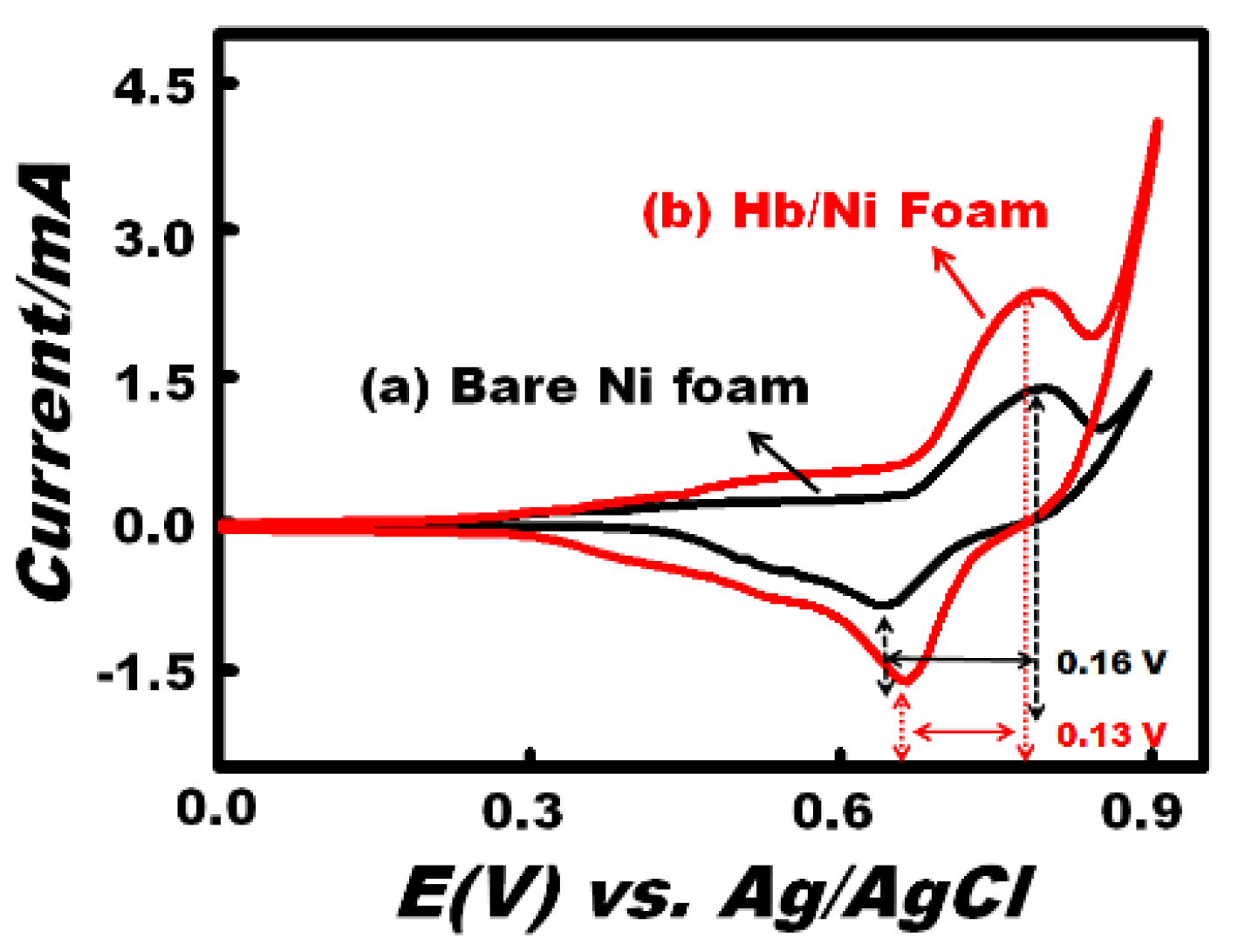
Figure 3.
Optical images of a water droplet on the surface of the (A) bare Ni foam and (B) Hb-modified Ni foam electrodes.
Figure 3.
Optical images of a water droplet on the surface of the (A) bare Ni foam and (B) Hb-modified Ni foam electrodes.
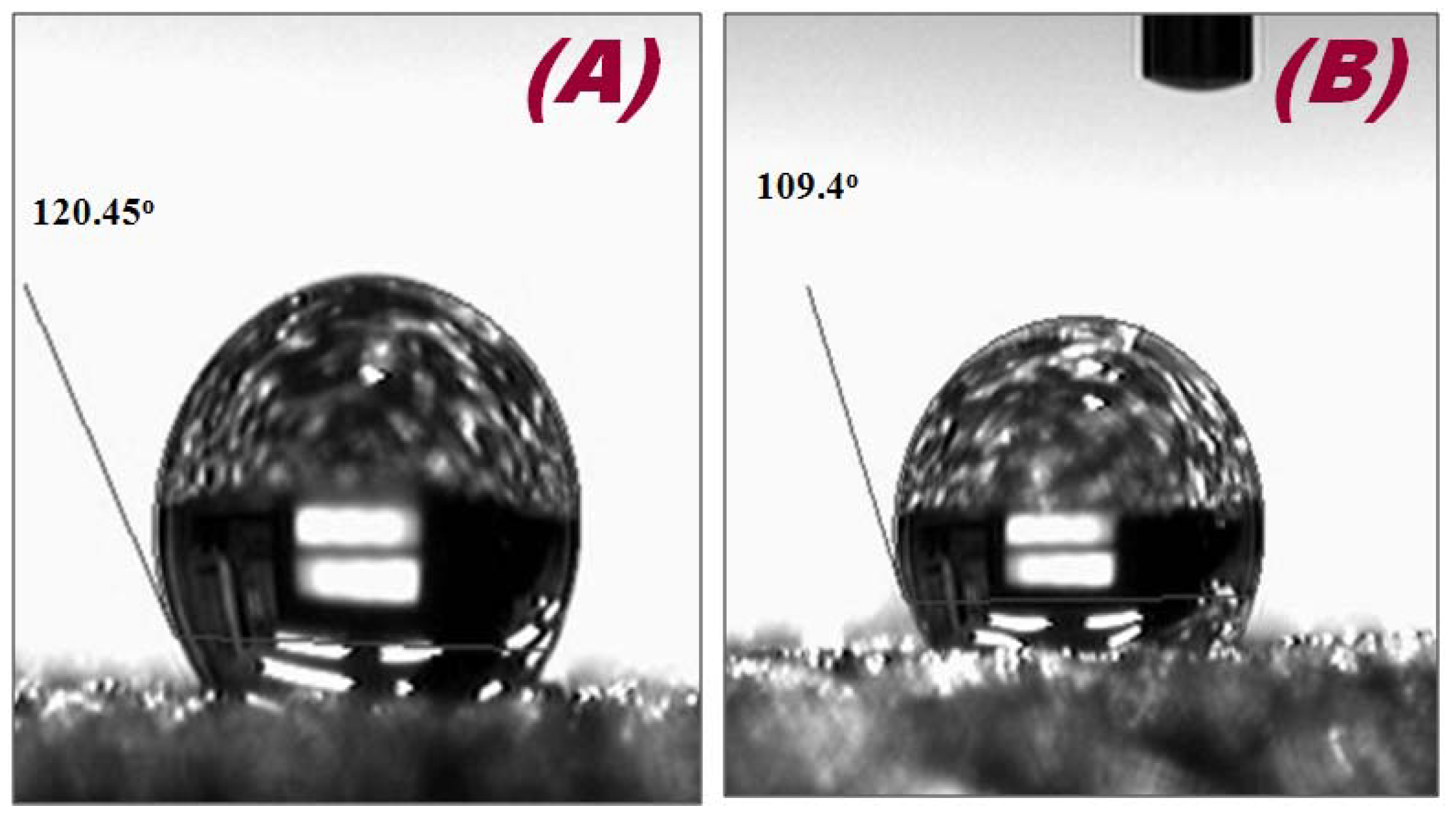

Table 1.
Contact angle, surface energy and surface tension of the bare Ni foam and Hb-modified Ni foam.
| Sensor | Contact Angle | Surface Energy (m·Jm−2) | Surface Tension (N/m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ni foam | 120.45° | 4.40 | 14.40 |
| Hb/Ni foam | 109.45° | 8.06 | 19.71 |
The effect of H2O2 concentration on the cyclic voltammetric response of the Hb-modified electrode workability was investigated at a scan rate of 100 mV/s (Figure 4). Results enabled quantitative determination of the specific detection range (DR) of the H2O2 (0.5–9.0 mM) by monitoring the CV signaling change with the addition of the H2O2 analyte (Figure 4A). Among all concentrations used, Figure 4A shows that the anodic peak centered at 0.78 V of NiOOH species disappeared at a higher concentration (9 mM) of H2O2. This finding indicated that at low H2O2 concentrations, the NiOOH could be produced and could act as the major electro-catalytic species. It is also important to mention that the major electro-catalytic species (i.e., β-Ni(OH)2) centered at 0.40 V were produced with the addition of low and high doses of H2O2. Therefore, the anodic peak centered at 0.40 V and the cathodic peak at 0.63 V can be attributed to the formation of couple Ni(OH)2/NiOOH redox species, as previously reported by Sanli et al. [37]. The change of the electrochemical behavior at low and high doses of additive H2O2 suggested that the high concentration of H2O2 may indicate the complete coverage of the entire anhydrous β-Ni(OH)2 layer-supported Hb-modified Ni foam electrode surfaces, leading to the formation of hydrous intermediate α-Ni(OH)2. This α-Ni(OH)2 intermediate undergoes electrochemical oxidation to form H+-Ni(OH)2-H+ along with O2. The H+-Ni(OH)2-H+ reacts with OH− ions to produce H2O and to regenerate the Ni(OH)2 species. However, by using a lower concentration of H2O2, partial coverage of anhydrous β-Ni(OH)2 layer-supported Hb-modified Ni foam electrode surfaces may occur, thereby leading to the electro-oxidation of β-Ni(OH)2 to form NiOOH at a relatively high potential E(V) ≥ 0.78 [38]. The formation of an active surface layer of Ni(OH)2 enabled sensitive detection over a wide range of concentrations of H2O2 by using the Hb-modified Ni foam electrode under our sensing conditions.
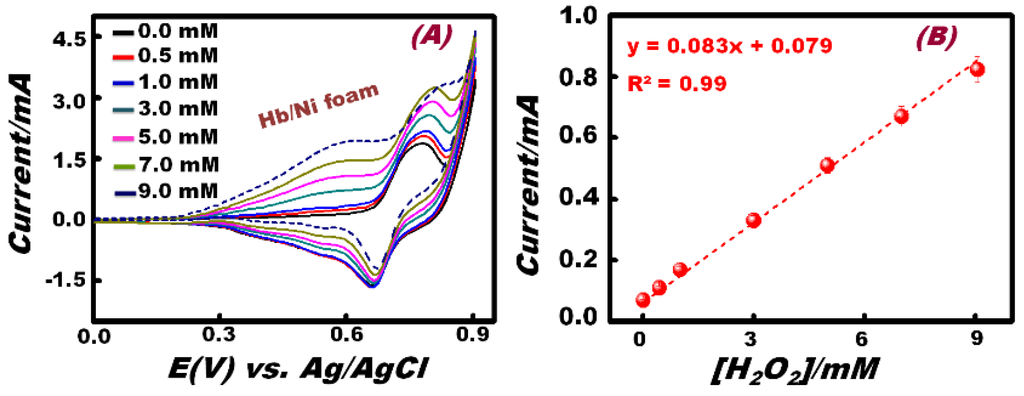
Figure 4.
(A) Typical CV patterns of successive H2O2 addition in the Hb-modified Ni foam electrode in 0.1 M NaOH solution at a scan rate of 100 mV/s; (B) effect of H2O2 concentration on the response of the H2O2 sensor based on the Hb-modified Ni foam electrode.
Figure 4.
(A) Typical CV patterns of successive H2O2 addition in the Hb-modified Ni foam electrode in 0.1 M NaOH solution at a scan rate of 100 mV/s; (B) effect of H2O2 concentration on the response of the H2O2 sensor based on the Hb-modified Ni foam electrode.
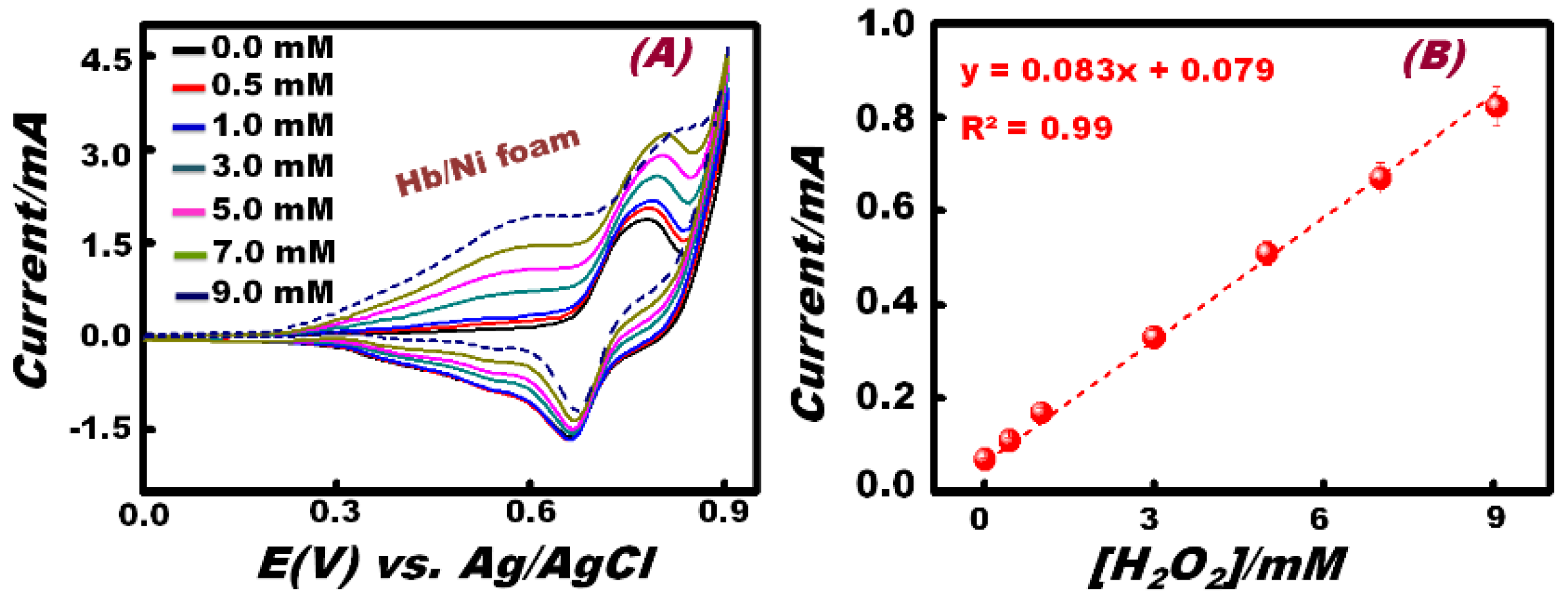
To demonstrate the linear relationship between the anodic peak current and H2O2 concentration, a calibration curve was constructed (Figure 4B). The linear response was observed from 0.5 to 9 mM (I(A) = 0.083 × 10−6 A/M [H2O2] + 0.79 × 10−7 A; with R2 = 0.99). The limit of detection (LOD) of H2O2 using the Hb-modified Ni foam electrode was estimated from the linear part of the response curve. The LOD was found to be 5.03 × 10−3 M (based on 3σ).
3.3. Sensitivity of the Working Electrode
The application of amperometric measurements as a simple electrochemical tool to detect low concentrations of H2O2 was explored. Figure 5 compares the amperometric response of the bare Ni foam and Hb-modified Ni foam electrode to consecutive increments of 5 × 10−5 M in the H2O2 concentration, in 0.1 M NaOH solution under constant stirring conditions at a fixed applied potential of 0.40 V (vs. Ag/AgCl). The Hb-modified Ni foam electrode clearly exhibits a fast response time (~3 s) and good and stable steady-state current with a dramatically enhanced current value compared with the bare Ni foam electrode. High sensitivity and repeatability result from the excellent electron-transfer hydrophilic surfaces that enhance the diffusion of the electrolyte to the active sites. Analysis of the limiting current (IL) for Ni foam and Hb-modified Ni foam electrodes as a function of H2O2 concentrations is depicted in Figure 4B.
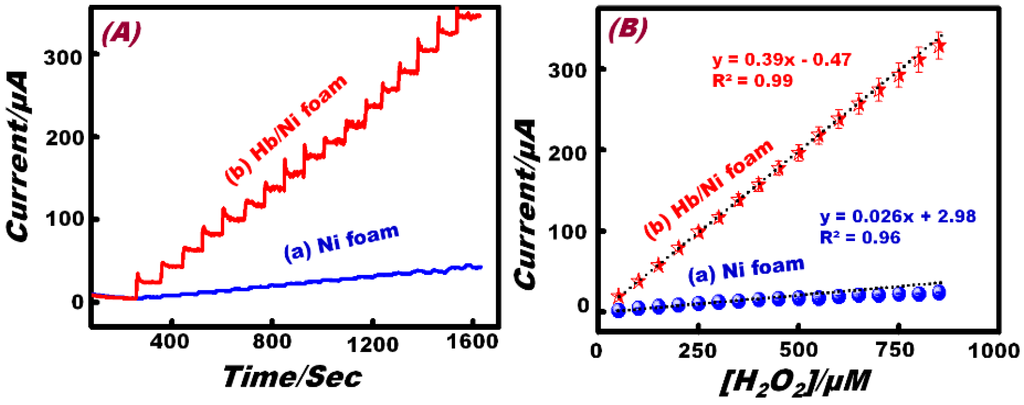
Figure 5.
(A) The amperometric response of the (a) Ni foam and (b) Hb/Ni foam electrodes to the successive addition of 50 μM H2O2 in 0.1 M NaOH solution at 0.40 V vs. Ag/AgCl. (B) The standard calibration graph derived from the current-time plot.
Figure 5.
(A) The amperometric response of the (a) Ni foam and (b) Hb/Ni foam electrodes to the successive addition of 50 μM H2O2 in 0.1 M NaOH solution at 0.40 V vs. Ag/AgCl. (B) The standard calibration graph derived from the current-time plot.
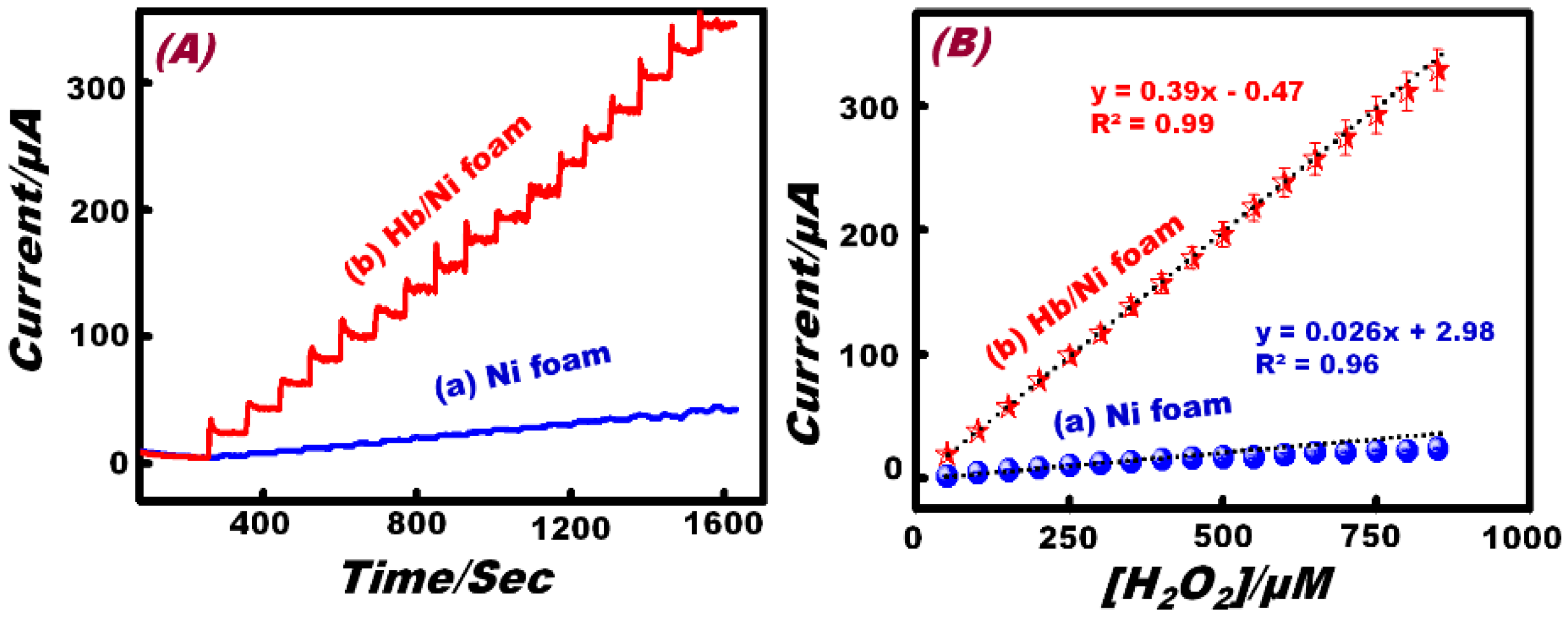
The Ni foam electrode shows a linear region over the range of 50 μM to 500 μM (IL (A) = 0.026 A/M [H2O2] + 2.98 × 10−6 A; R2 = 0.96; N = 5). Based on the linear region, the limit of detection (S/N = 3) was found to be 35.21 μM. However, the Hb-modified Ni foam electrode shows a linear region in the wide concentration range of 50 μM to 850 μM (IL (A) = 0.39 A/M [H2O2] − 0.04 × 10−6 A; R2 = 0.99; N = 5). The corresponding detection limit was found to be 6.85 μM. The sensitivity of the Hb-modified Ni foam (0.39 μA·mM−1) was found to be higher than that of the Ni foam (0.02 µA·mM−1) by almost 20 times. These interesting results demonstrate that the Hb-modified commercial Ni foam electrode has high applicability and sensitivity compared to the Ni foam electrode.
In order to measure the detection limit, a lower concentration of H2O2 was detected by amperometric experiment under the same conditions using the Hb-modified Ni foam electrode. Figure 6A displays the amperometric responses resulting from the successive additions of H2O2 (2 μM) into the solution containing 0.1 M NaOH. The Hb-modified Ni foam electrode shows a stable and repeatable amperometric signal, even at a lower concentration of H2O2. Analysis of the limiting current (IL) as a function of H2O2 concentration is presented in Figure 6B, which reveals a linear range of up to 18 μM (IL (A) = 0.48 A/M [H2O2] + 4.48 × 10−6 A; R2 = 0.99; N = 5). According to this linear range, the detection limit was calculated to be 0.83 μM. Results reveal that the Hb effectively functions as a perfect mediator and enhances the kinetics of ions and electron transport in the Ni foam electrode (at the electrode electrolyte interface) and has high applicability as compared to other non-enzymatic hydrogen peroxide sensors (Table 2).
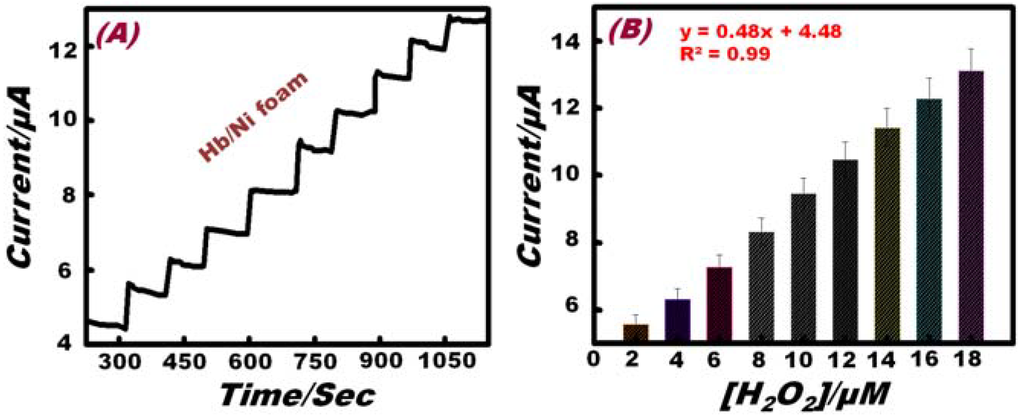
Figure 6.
(A) The amperometric response of the Hb/Ni foam electrode to the successive addition of 2 μM H2O2 to 0.1 M NaOH solution at 0.40 V (vs. Ag/AgCl). (B) The standard calibration graph derived from the current-time plot.
Figure 6.
(A) The amperometric response of the Hb/Ni foam electrode to the successive addition of 2 μM H2O2 to 0.1 M NaOH solution at 0.40 V (vs. Ag/AgCl). (B) The standard calibration graph derived from the current-time plot.

Table 2.
Comparison of the Hb-modified Ni foam-based hydrogen peroxide sensor with other non-enzymatic hydrogen peroxide sensors.
| Sensing Material | Electrolyte | Linear Range (M) | Limit of Detection (M) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PdNPs/PEDOT * | PBS | 2.5 × 10−6~1.0 × 10−3 | 2.84 × 10−6 | [39] |
| nano-CuO/Nf-coated Pt | 0.1 M NaOH | 1.5 × 10−7~9 × 10−3 | 0.6 × 10−7 | [40] |
| NiO/CPE* | 0.1 M NaOH | 0.6~6 × 10−3 | 0.34 × 10−3 | [41] |
| NiO-NPs/cMWCNT/PANI* | PBS | 3 × 10−6~7 × 10−3 | 0.2 × 10−6 | [42] |
| Hb/Ni foam | 0.1 M NaOH | 5 × 10−6~9 × 10−3 | 0.41 × 10−6 | Present study |
PEDOT = poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene), CPE = carbon paste electrode, cMWCNT/PANI = carboxylated multiwalled carbon nanotubes/polyaniline
3.4. Selectivity of the Working Electrode
A selective sensor is an exceptionally promising strategy for water treatment and environmental management [43,44]. A major advantage of the Hb-modified Ni foam electrode is its selectivity toward the electro-oxidation of H2O2 ions. The analytical performance of the Hb-modified Ni foam composite electrode is carried out under the same conditions of amperometric measurements in the presence of UA and AA as potential interfering agents. Figure 7 indicates the amperometric response of the Hb-modified Ni foam composite working electrode at an applied potential of 0.40 V in 0.1 M NaOH. After the successive addition of 25 μM H2O2, 0.5 mM UA, 0.5 mM AA and 25 μM H2O2, no significant interference changes in the limiting current were observed. Ascorbic acid shows some very low, unstable current responses, which may be attributed to the inhibition function of the Hb mediator [45]. In addition, high selectivity of the Hb-modified electrode can be attributed to the strong binding efficiency (~Eads = 211.45 kcal·mol−1) of the porous Ni foam with the Hb [46] that enhances the faradic redox process of the Hb-modified Ni foam electrode toward H2O2 compared with the interferences, such as AA and UA.
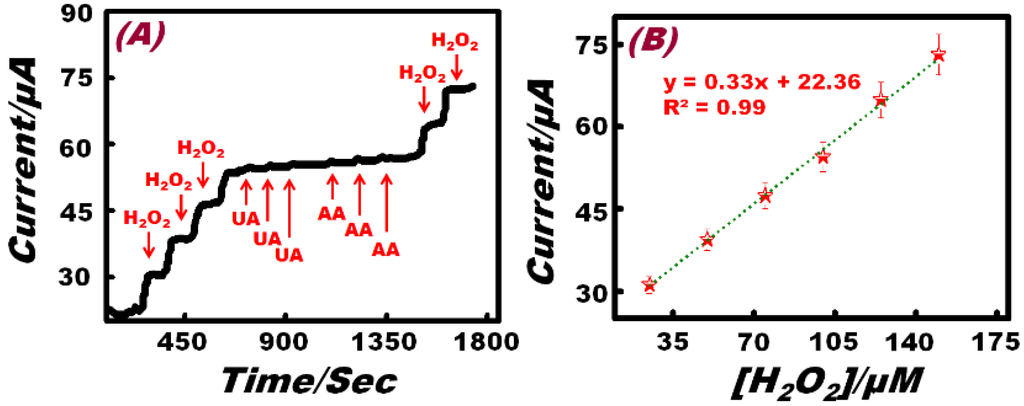
Figure 7.
(A) Amperometric selective signal of Hb-modified Ni foam to successive addition of 25 μM H2O2, 0.5 mM UA, 0.5 mM AA and 25 μM H2O2, respectively, at 0.40 V (vs. Ag/AgCl) in 0.1 M NaOH solution. (B) The standard calibration graph derived from the current-time plot.
Figure 7.
(A) Amperometric selective signal of Hb-modified Ni foam to successive addition of 25 μM H2O2, 0.5 mM UA, 0.5 mM AA and 25 μM H2O2, respectively, at 0.40 V (vs. Ag/AgCl) in 0.1 M NaOH solution. (B) The standard calibration graph derived from the current-time plot.
3.5. Reproducibility and Long-Term Stability of the Working Electrode
A reproducibility experiment of multiple (≥5) Hb-modified Ni foam electrodes was explored using a fixed concentration of H2O2 (500 µM) at an applied potential of 100 mV/s via the amperometric response. The relative standard deviation of the five amperometric response assays were in the range of 1.80%–2.1%, as evidenced by the fitting plot of the response current graph (Figure 8A).
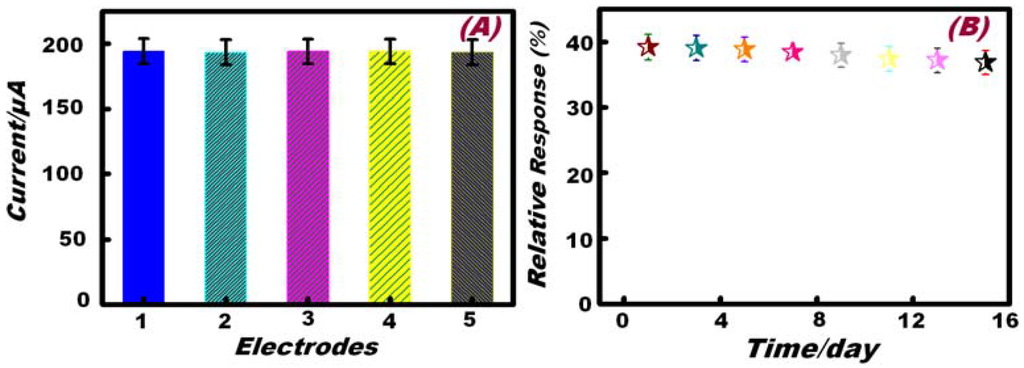
Figure 8.
(A) Amperometric current response of 5 different Hb/Ni foam electrodes to 500 µM H2O2 at 0.40 V (vs. Ag/AgCl). (B) Long-term stability of Hb/Ni foam electrode for continuous H2O2 detection for 15 days at 0.40 V (vs. Ag/AgCl).
Figure 8.
(A) Amperometric current response of 5 different Hb/Ni foam electrodes to 500 µM H2O2 at 0.40 V (vs. Ag/AgCl). (B) Long-term stability of Hb/Ni foam electrode for continuous H2O2 detection for 15 days at 0.40 V (vs. Ag/AgCl).
The long-term stability of the developed electrode is a critical factor in practical detection applications. To evaluate the stability of this H2O2 sensor, the Hb-modified Ni foam electrode was stored at 4 °C in a sealed system for 14 days. The stability was examined by amperometric measurements of the sensor response to 100 µM H2O2 in a NaOH (0.1 M) solution at a scan rate of 100 mV/s. The variation of the sensing response efficiency at the Hb-modified Ni foam electrode decreases to about 98% of its initial response current on the seventh day and about 94% on the 15th day (Figure 8B).
3.6. Determination of H2O2 in a Real Sample
The utilization of the proposed sensor for the measurement of H2O2 was studied by analyzing a commercially available green tea (green tea extract, sucrose, honey, ascorbic acid, citrate and water) containing a known amount of H2O2. Green tea was filtered before the measurement in order to prevent electrode fouling. The sample was diluted 1:1 with 0.1 M NaOH and then was detected. Figure 9A depicts the typical amperometric response resulting from the addition of 25 µM H2O2 at an applied potential of 0.40 V in 0.1 M NaOH electrolyte. Analysis of the current versus H2O2 concentration is depicted in Figure 9B, where a linear response was observed (I(A) = 0.33 A/M [H2O2] + 0.15 × 10−6 A; R= 0.99; N = 5). The very small difference in amperometric current response and sensitivity between the experimental and real sample is due to the latter being diluted by a factor of 50.
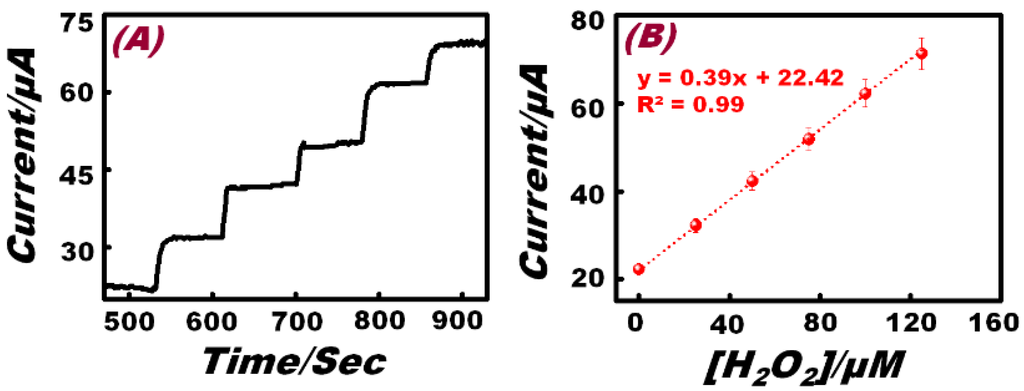
Figure 9.
(A) The amperometric response of the Hb-modified Ni foam electrode to the successive addition of 25 μM H2O2 in commercially available green tea and 0.1 M NaOH solution with a 1:1 ratio at 0.40 V vs. Ag/AgCl. (B) Standard calibration graph derived from the current-time plot.
Figure 9.
(A) The amperometric response of the Hb-modified Ni foam electrode to the successive addition of 25 μM H2O2 in commercially available green tea and 0.1 M NaOH solution with a 1:1 ratio at 0.40 V vs. Ag/AgCl. (B) Standard calibration graph derived from the current-time plot.
4. Conclusions
A simple enzymeless H2O2 sensor within a concentration range from 0.5 to 9 mM is reported based on the immobilization of Hb on 3D porous Ni foam. The electro-catalytic activity of Ni foam toward H2O2 was observed before and after the modification with heme proteins. The successful immobilization of Hb onto the 3D Ni foam enhanced the kinetics of ion and electron transport in the Ni foam electrode, at the electrode-electrolyte interface, and engaged sufficient electro-active species exposed on the surface for the faradic redox reaction. These findings can be attributed to the catalytic and electron transport biological functionality of the Hb-modified Ni foam electrode. This bio-functionality enhances the surface activation and the electrochemical reactivity of the Ni foam electrode. Such results demonstrate that the immobilization of Hb onto the Ni foam electrode is a promising non-enzymatic H2O2 sensor. The specific utility of this sensor design was interesting for its application as molecular and ion species sensing tools in environmental samples and physiological fluids [47,48,49,50,51].
Author Contributions
The present work is designed to pursuit Prof. Sherif' Lab goals. This research work introduces the idea of Prof. Sherif; however, the other authors effectively achieved the experimental facts towards goal attainment. All Authors are shared in discussion, writing down the texture body of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The present findings of research impacts show the real degree of variety among all presented work reported by the Authors and other groups. We here declare that there is no confliction of interests in this research work.
References
- El-Safty, S.A.; Shenashen, M.A.; Ismael, M.; Khairy, M. Mesocylindrical Aluminosilica Monolith Biocaptors for Size-Selective Macromolecule Cargos. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 3013–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Safty, S.A.; Ismail, A.A.; Matsunaga, H.; Hanaoka, T.; Mizukami, F. Optical Nanoscale Pool-on-Surface Design for Control Sensing Recognition of Multiple Cations. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 1485–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Safty, S.A.; Shenashen, M.A.; Ismael, M.; Khairy, M.; Awual, M.R. Mesoporous aluminosilica sensors for the visual removal and detection of Pd(II) and Cu(II) ions. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 166, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Safty, S.A. Designs for Size-Exclusion Separation of Macromolecules by Densely Engineered Mesofilters. Trends Anal. Chem. 2011, 30, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Yang, L.; Hou, L.; Shen, L.; Zhang, X.; (David) Lou, X.W. Growth of ultrathin mesoporous Co3O4 nanosheet arrays on Ni foam for high-performance electrochemical capacitors. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 7883–7887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; El-Safty, S.A. Development of Mesoscopically Assembled Sulfated Zirconia Nanoparticles as Promising Heterogeneous and Recyclable Biodiesel Catalysts. ChemCatChem 2013, 5, 3050–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairy, M.; El-Safty, S.A.; Ismael, M.; Kawarada, H. Mesoporous NiO nanomagnets as catalysts and separators of chemical agents. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 127, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaji, T.; El-Safty, S.A.; Matsunaga, H.; Hanaoka, T.; Mizukami, F. Optical Sensors Based on Nanostructured Cage Materials for the Detection of Toxic Metal Ions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 7202–7208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairy, M.; El-Safty, S. Mesoporous NiO nanoarchitectures for electrochemical energy storage: Influence of size, porosity, and morphology. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 23801–23809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veal, E.A.; Day, A.M.; Morgan, B.A. Hydrogen Peroxide Sensing and Signaling. Mol. Cell 2007, 26, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, E. A novel hydrogen peroxide sensor based on horseradish peroxidase immobilized on colloidal Au modified ITO electrode. Electrochem. Commun. 2004, 6, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Diwu, Z.; Panchuk-Voloshina, N.; Haugland, R.P. A Stable Nonfluorescent Derivative of Resorufin for the Fluorometric Determination of Trace Hydrogen Peroxide: Applications in Detecting the Activity of Phagocyte NADPH Oxidase and Other Oxidases. Anal. Biochem. 1997, 253, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirata-Ozturk, B.; Ozen, G.; Filik, H.; Tor, I.; Afsar, H. Spectrofluorometric Determination of Hydrogen Peroxide. J. Fluoresc. 1998, 8, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.H.; Jang, J.; Kim, B.K.; Choi, H.N.; Lee, W. Detection of hydrogen peroxide with luminol electrogenerated chemiluminescence at mesoporous platinum electrode in neutral aqueous solution. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2011, 660, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, P.A.; Wong, A.Y.S. Spectrophotometric determination of hydrogen peroxide in rainwater. Anal. Chim. Acta 1998, 370, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Li, X.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Xue, L.; Li, X.; Gu, J.; Wang, M.; Jiang, L. Non-enzymatic electrochemical sensors for the detection of hydrogen peroxide based on Cu2O/Cu nanocomposites. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 1114–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yuan, R.; Chai, Y.; Li, W.; Ling, S. A Novel Nonenzymatic Hydrogen Peroxide Sensor Based on a Polypyrrole Nanowire-Copper Nanocomposite Modified Gold Electrode. Sensors 2008, 8, 5141–5152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, A.A.; Solanki, P.R.; Malhotra, B.D. Nanostructured metal oxides based enzymatic electrochemical biosensors. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 142, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.J.; Li, J.; Dong, S.J. Hemin functionalized graphene nanosheets based dual biosensor platforms for hydrogen peroxide and glucose. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 160, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighi, B.; Nikzad, R. Prussian blue modified carbon ionic liquid electrode: Electrochemical characterization and its application for hydrogen peroxide and glucose measurements. Electroanalysis 2009, 16, 1862–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.J.; Hwang, S.W.; Whang, D. Non-enzymatic electrochemical CuO nanoflowers sensor for hydrogen peroxide detection. Talanta 2010, 80, 1648–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, A.; Wang, G.; Gu, J.; Zhang, X.; Fang, B. An unusual H2O2 electrochemical sensor based on Ni(OH)2 nanoplates grown on Cu substrate. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 7182–7187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairy, M.; El-Safty, S. Hemoproteins-nickel foam hybrids as effective supercapacitors. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 1356–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairy, M.; El-Safty, S.A. Nanosized rambutan-like nickel oxides as electrochemical sensor and pseudocapacitor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 193, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Safty, S.A.; Shenashen, M.A.; Khairy, M. Bioadsorption of proteins on large mesocage-shaped mesoporous alumina monoliths. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 103, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, G.R.; Williams, R.J.P. Nuclear-Magnetic-Resonance Studies of Ferrocytochrome C, pH and Temperature Dependence. Eur. J. Biochem. 1980, 103, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlereth, D.; Mantele, W. Redox-induced conformational changes in myoglobin and hemoglobin: Electrochemistry and ultraviolet visible and fourier transform infrared difference spectroscopy at surface modified gold electrodes in an ultra thin layer spectroelectrochemical cell. Biochemistry 1992, 31, 7494–7502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khairy, M.; El-Safty, S.; Ismael, M. Mesoporous nanomagnet supercaptors for selective heme proteins from human cells. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 10832–10834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Xiao, X.; Li, Z.; Xu, F.; Tan, H.; Sun, L.; Wang, L. A novel nonenzymatic hydrogen peroxide sensor based on three-dimensional porous Ni foam modified with a Pt electrocatalyst. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Peng, H.; Chen, X.; Hou, H.; Liu, C. Nickel hydroxide modified silicon nanowires electrode for hydrogen peroxide sensor applications. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 61, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann, M.; Korinek, K.; Pletcher, D. The oxidation of organic compounds at a nickel anode in alkaline solution. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1971, 31, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Cheng, K.; Xue, X.; Yin, J.; Wang, G.; Cao, D. Three-dimensional porous Ni film electrodeposited on Ni foam: High performance and low-cost catalytic electrode for H2O2 electrooxidation in KOH solution. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 107, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunea, A.; Pavel, I.; David, S.; Gaspar, S. Modification with hemeproteins increases the diffusive movement of nanorods in dilute hydrogen peroxide solutions. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 8803–8805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, K.; Suzuki, M.; Nakamura, N.; Ohno, H. Direct evidence of electron flow via the heme c group for the direct electron transfer reaction of fructose dehydrogenase using a silver nanoparticle-modified electrode. Electrochem. Commun. 2009, 11, 1623–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oss, C.J. A Review of: “Wettability”; Berg, J.C., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 717–718. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Chang, H.; Kim, M.S.; Leem, J.; Ballato, J.; Kim, S. Low-temperature growth of multiple-stack high-density ZnO nanoflowers/nanorods on plastic substrates. Nanotechnology 2012, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanli, A.E.; Aytac, A. Response to disselkamp direct peroxide/peroxide fuel cell as a novel type fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epee, N.S.; Palacìn, M.R.; Delahaye-Vidal, A.; Chabre, Y.; Tarâscon, J.M. Evidence for direct γ-NiOOH ↔ β-Ni(OH)2 transitions during electrochemical cycling of the nickel hydroxide electrode. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1998, 145, 1434–1441. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, F.; Yue, R.; Du, Y.; Xu, J.; Yang, P. A one-pot “green” synthesis of pd-decorated PEDOT nanospheres for nonenzymatic hydrogen peroxide sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 44, 127–131. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, X.; Yuan, R.; Chai, Y.; Shi, Y.; Yuan, Y. Direct electrocatalytic reduction of hydrogen peroxide based on nafion and copper oxide nanoparticles modified pt electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2008, 612, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojani, R.; Raoof, J.B.; Norouzi, B. An Efficient Sensor for Determination of Concentrated Hydrogen Peroxide Based on Nickel Oxide Modified Carbon Paste Electrod. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 1852–1863. [Google Scholar]
- Lata, S.; Batra, B.; Karwasra, N.; Pundir, C.S. An amperometric H2O2 biosensor based on cytochrome c immobilized onto nickel oxide nanoparticles/carboxylated multiwalled carbon nanotubes/polyaniline modified gold electrode. Process Biochem. 2012, 47, 992–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Safty, S.A.; Hoa, N.D.; Shenashen, M.A. Topical Developments of Nanoporous Membrane Filters for Ultrafine Noble Metal Nanoparticles. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 33, 5439–5450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairy, M.; El-Safty, S.A.; Shenashen, M. Environmental Remediation and Monitoring of Cadmium. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 62, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zweier, J.L. A real-time electrochemical technique for measurement of cellular hydrogen peroxide generation and consumption: Evaluation in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2001, 31, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Safty, S.A.; Shenashen, M.A. Mercury-Ion Optical Sensors. Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 48, 98–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairy, M.; El-Safty, S.A.; Shenashen, M.A.; Elshehy, E.A. Simultaneous Detection and Removal of Cadmium Ions from Different Environmental Matrices. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2014, 10, 126–141. [Google Scholar]
- Shenashen, M.A.; El-Safty, S.A.; Elshehy, E.A. Synthesis, Morphological Control, and Properties of Silver Nanoparticles in Potential Applications. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2014, 31, 293–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Safty, S.A.; Abdellatef, S.; Ismael, M.; Shahat, A. Optical Nanosphere Sensor Based on Shell-by-Shell Fabrication for Removal of Toxic Metals from Human Blood. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2013, 2, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Safty, S.A.; Shenashen, M.A. Optical Mesosensor for Capturing of Fe(III) and Hg(II) Ions from Water and Physiological fluids. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2013, 183, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshehy, E.A.; El-Safty, S.A.; Shenashen, M.A. Reproducible Design for the Optical Screening and Sensing of Hg(II) Ions. Chemosensors 2014, 2, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
