Abstract
The low operating temperature of nanowire gas sensors along with their high surface-to-volume ratio are two factors that make gas sensors more practical. In this paper, the growth of ZnO nanowires on a vertically aligned CNT forest is reported. The utilized method for ZnO growth was a rapid microwave-assisted hydrothermal route, which facilitates low-temperature and ultra-fast fabrication. Organic vapor sensing properties of fabricated samples were studied in response to different alcoholic vapors at a wide operating temperature range of 25 to 300 °C. Enhancement of the gas response was observed with increasing operating temperature. Moreover, the effect of the ZnO nanowire length on organic vapor sensing properties of CNT-ZnO samples was investigated. Results proved that CNT-ZnO samples with long ZnO wires exhibit higher sensitivity to examined analytes. Different length ZnO nanowires were attained via variation of the microwave exposure time and power. Fabrication parameters were selected based on numerous runs. The length of ZnO synthesized at each distinct run was calculated based on SEM micrographs of the samples.
1. Introduction
Today, the detection and quantification of different gases are very important. One of the best technologies for the detection of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) vapor is semiconductor gas sensors [1]. These sensors show resistive variation in contact with different gases depending on the type of gas. This is due to the adsorption and desorption of gas molecules, which results in different electrical resistance of the surface. This mechanism is used to identify the presence of gas [2]. Semiconducting metal oxides, due to their low cost, easy processing and treating, high gas response, good electrical properties, and regular structure at the nanoscale, are appropriate for sensor fabrication [1,3,4]. In recent years, the use of oxide nanostructures has attracted much attention [5,6]. Zinc oxide (ZnO) is known as one of the semiconductors that have a wide application range. It can be used in industrial optics [7,8], sensors [9,10], solar cells [8], and biological sciences [11,12]. ZnO as a gas sensor is used either as a part of composite material [13] or individually [14]. In addition, doping of ZnO is an effective way to enhance its gas sensing properties [15,16,17].
The performance of the metal oxide gas sensor is greatly affected by the surface morphology of the sensor. However, one of the major challenges for gas sensors is that they need high temperatures to work [2]. However, the improvement of the structure and orientation of materials, such as using a regular nanostructure, would overcome this limitation [5,18].
Another way to reduce the operating temperature of metal oxide gas sensors is to use them in a composite structure [19,20,21]. Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) have been adopted extensively as composite materials for metal oxide gas sensors due to their unique morphology and properties [19]. The reinforcement of ZnO with CNT has developed advanced multifunctional gas sensors with improved properties. Many reports show that the CNT-ZnO composite is a better gas sensor as compared to bare ZnO and CNT [22,23,24]. So far, the effect of the different morphological structures of the zinc oxide microstructure in ZnO hybrid compounds has not been investigated.
In this paper, we used a fast microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis method to grow ZnO nanowire. To increase the organic vapor sensing properties and lower the working temperature of the sensor, ZnO has been grown on a Carbon Nanotube (CNT). The method used for CNT growth was Plasma-Enhancement-Chemical-Vapor-Deposition (PECVD). Therefore, the sensor temperature is reduced, and the CNT tubes are considered a very good place for ZnO seeding.
This paper investigated whether ZnO nanowire length has positive effects on the organic vapor sensing parameters of the CNT-ZnO sensor.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. CNT Growth
A PECVD method for growing CNTs on glass substrates was used in this work [25]. To achieve aligned CNTs, two-stage plasma was used. In this method, dividing the growth area into two zones provided low-temperature conditions. A 10 nm nickel deposited on the glass substrate was placed in the second zone to provide low-temperature criteria. Ni played the role of the catalyst. Hydrogen (H2) and acetylene (C2H2) were used as gas feeds. The sample was heated to 250 °C at 22 mbar while 100 sccm H2 flowed in the chamber. This is followed by the ignition of a 100 W DC plasma, and the temperature was kept constant. After 5 min, 25 sccm of C2H2 was added for the specific growth time. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of the surface and the cross-section of the bare CNT on the glass substrate can be viewed in Figure 1a,b, respectively.
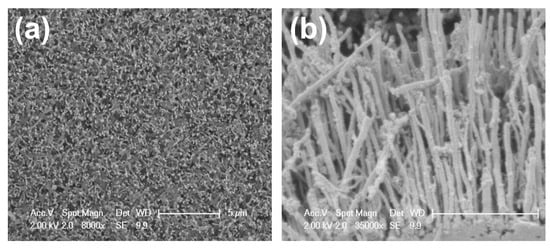
Figure 1.
(a) Top-view and (b) cross-sectional SEM images of the bare fabricated CNTs.
2.2. ZnO Nanowire Growth
CNT was used as a substrate for ZnO growth. Before the final ZnO coating, to provide nanowires with growth areas, a seed layer was coated on the CNTs.
First of all, zinc oxide nanoparticles with diameters of about 10 nm were spin-coated on CNT films grown on substrates to achieve a layer with ~100 nm thickness called the seed layer. These nanoparticles act as the seed layer for growing ZnO nanowires. The applied solution was created by mixing zinc acetate dihydrate (Zn(CH3COO)2·2H2O) and acetone to achieve a 5 milli molar solution. One to five droplets of this solution were applied to the spinning substrates (3000 rpm and 30 s duration). This was repeated 1 to 5 times to increase the number of ZnO particles on the CNT surface. Then, samples were annealed in air at 350 °C for 30 min, which led to the dissociation of zinc acetate and the formation of nanometer ZnO particles.
The solution used for ZnO growth was a mixture of the following materials: 5.6 g of ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH), 0.35 g of hexamethylenimine ((CH2)6N4), 0.8 g of polyethylenimine (end-capped, molecular weight 800 g/mol LS), and 1.48 g of zinc nitrate hexahydrate (Zn(NO3)2·6H2O), added to 200 mL of deionized water.
All materials used for the growth of ZnO were from the Merck company.
After growing ZnO seeds on CNT, the samples were inserted into a hydrothermal solution in a neutral (glass) container. Then, the container was placed in boiling water, which was warmed by a microwave. It was set for 20–60 min, with 180–850 watts of power to achieve different lengths of ZnO nanowire. The selected conditions were chosen based on the experimental works reported in Ref. [26]. The schematic of the 3-step production method is shown in Figure 2.
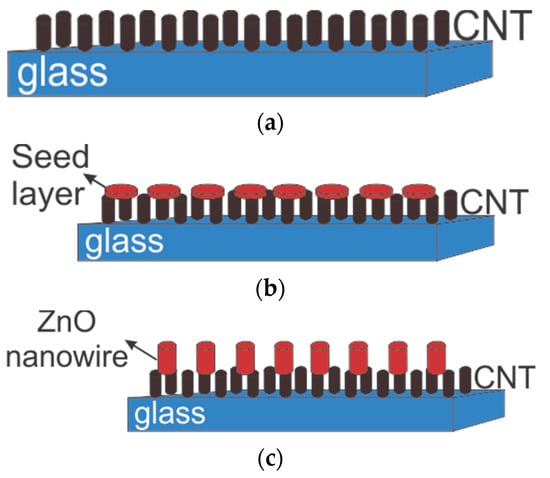
Figure 2.
Three steps of zinc oxide nanowire growth on CNT: (a) CNT substrate, (b) ZnO seed layer on CNT, and (c) ZnO grown on CNT.
The physical structure of samples was investigated using SEM images. The morphology and length of nanowire structures were feasible via the hydrothermal growth of oxide on such processed samples. SEM was performed (in a CAMSCAN2300 unit) at an electron accelerating voltage of 25 kV. Figure 3 shows the SEM image of the ZnO nanowire grown using the fast method at different microwave powers. This power variation was applied to the samples with the same growth solution. As illustrated in Figure 3, in these SEM micrographs, samples were tilted at a certain angle in order to highlight specimens’ features. By considering tilt angles, the length of the ZnO nanowire for the 600 watts, 450 watts, and 180 watts of microwave power was estimated to be 1500 nm, 1000 nm, and 500 nm, respectively. This measurement was performed by averaging the length of nanowires.
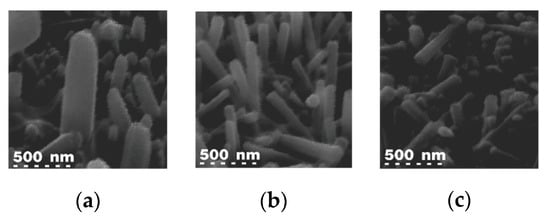
Figure 3.
SEM image of the ZnO nanowire grown on CNT substrates at different microwave power: (a) 600 watts, (b) 450 watts, and (c) 180 watts for 30 min.
To prove the presence of ZnO and CNT in the obtained CNT-ZnO sample, X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD) was employed. The XRD patterns of the as-prepared sample are presented in Figure 4. In the XRD patterns of the CNT-ZnO composite, the location and intensity of the diffraction peaks that are present at 31.84°, 34.52°, 36.33°, 47.63°, 56.71°, 62.96°, 66.43°, 68.13°, and 69.18° can be indexed into (100), (002), (101), (102), (110), (103), (200), (112), and (201) crystal planes of wurtzite-type hexagonal ZnO (JCPDS No. 65-3411) [27]. Figure 4b illustrates the magnified spectrum of the CNT-ZnO sample before 2 Theta = 30°. This spectrum shows carbon peaks at 12.9°, 23.98°, and 27.9°. These observations indicate that the hexagonal crystalline wurtzite phase of ZnO remains unchanged in the CNT-ZnO sample [28], while peaks related to the planes of graphitic carbon are observed simultaneously in the spectrum [29].
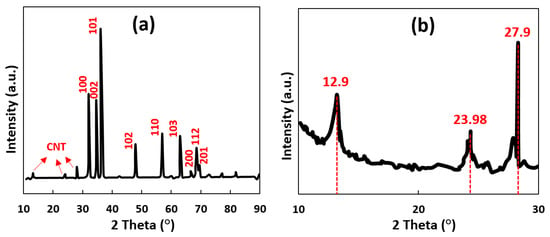
Figure 4.
XRD pattern of (a) CNT-ZnO sample and (b) magnified peaks in the carbon portion (2 Theta = [10, 30]) of the XRD pattern of the CNT-ZnO sample.
2.3. Measurement Method
To extract the organic vapor sensing properties of the fabricated samples, the resistance of samples in clean air and in the vicinity of vapors was measured. The fabricated sensors with dimensions of 5 × 5 mm were entered into a gas chamber with a specified volume of an analyte. Sample resistance variation is reported as the target gas enters the chamber. The Keithley 2400 source meter (one Chanel, from 0.2 Ω to 200 MΩ, from ±1 μA to ±1 A, from ±200 mV to ±200 V, 20 W) was used for electrical resistance measurements.
Equation (1) shows the defined relation for the Response of sensors:
In which Rg is the sensor resistance in the gas and Ra is the sensor resistance in clean air.
3. Results and Discussion
Figure 5 illustrates the investigating and extracting process of the organic vapor response of fabricated sensors. A micro-heater at the button of the sensors had been placed to control the temperature of samples. The surface temperature of the fabricated sensors was read by an S-type thermocouple. By changing the heater current, the sample surface temperature was set at the beginning of each test and kept constant until the end of the test. ITO electrodes were deposited on top of the samples for electrical measurement (two parallel strip lines on two opposite edges of samples with 1 mm width). Fabricated samples were placed in a chamber that could measure the organic vapor concentration. Resistance changes in the presence of vapor and clean air were recorded continuously. According to the effect of humidity on the gas response of metal oxide gas sensors, the humidity was kept constant in all experiments (35% relative humidity).
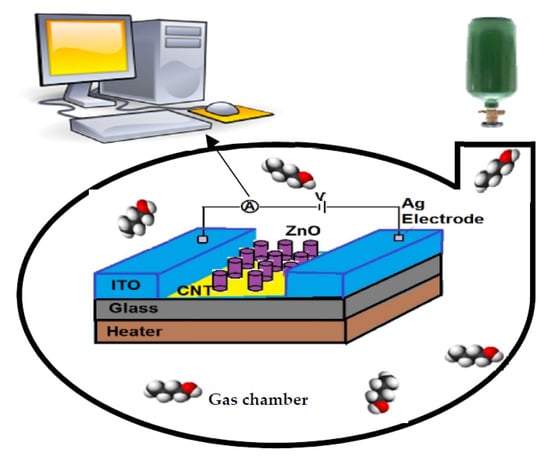
Figure 5.
The schematic diagram of fabricated CNT-ZnO samples and measurement systems.
As relative humidity depends on both the pressure and temperature together in the chamber, for all humidity sensing, the temperature has been kept constant for the correct comparison. A commercial humidity meter (Samwon) measures the ambient humidity. The number of humidity changes at specified percentages, which were provided by calibration, was created by a commercial ultrasonic humidifier JR model JRG while the temperature was kept constant. A 1.6 MHz oscillator with 100 V output voltage was designed for the humidifier.
To eliminate the bias voltage effect on organic vapor sensing properties of the samples, the electrical behavior of the sensor should be clarified. Therefore, the I–V characteristic of the samples was extracted.
As Figure 6a illustrates, this sample shows ohmic behavior. This ohmic behavior at higher temperatures was confirmed. The ohmic behavior of contacts ensures that each surface resistance change is due to gas changing. In addition, the base resistance of the samples did not change after the voltage was applied in the I–V measurement.
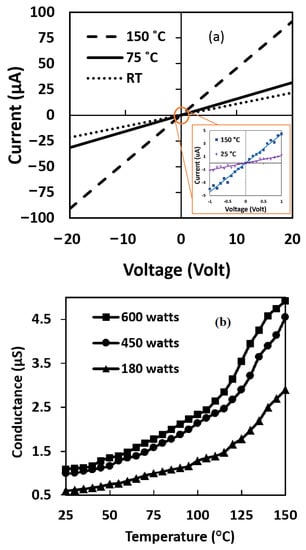
Figure 6.
(a) I–V curve recorded for CNT-ZnO sample at junction point at different temperatures. (b) Conductance–temperature relationship of the CNT-ZnO samples with different microwave powers at zero pressure.
In addition, electrical resistance was measured for all three fabricated samples with different ZnO lengths at zero pressure and room temperature. The measured resistance (Rair) for samples with 600 watts, 450 watts, and 180 watts of microwave power were 0.91 M, 1.01 M, and 1.64 M ohm, respectively. Increasing the length of the nanowires (with increasing microwave power), as shown in Figure 3, causes uniformity of the nanowires and consequently reduces the potential barrier between the grain boundaries. Figure 6b shows the effect of temperature on the electrical conductance of the sensors at no applied pressure and room temperature. Higher microwave power leads to lower electrical resistance. The effect of ZnO nanowire length is increased at lower temperatures. As Figure 6b shows, the sample with higher ZnO lengths gives lower electrical resistance, but the effect of temperature variation in all three samples has a similar trend. Increasing the temperature increases the electrical conductance. CNT-ZnO is a hybrid sample. As in the semiconductors [30], the observed conductance temperature relationship shows an increase in the conductivity of the samples under the effect of temperature, which is due to the increase in the concentration of charge carriers.
Figure 7 presents the results of resistance measurement as a function of relative humidity at a fixed room temperature. This figure shows that increasing the RH results in a reduction in the electrical resistance of all sensors. This is mainly due to the homogenous morphology and size of ZnO nanowires and the higher specific surface area. Thus, the ZnO nanowires absorb moisture easily and uniformly. The ZnO nanowire sensor usually shows high humidity sensitivity [31], but in the CNT-ZnO samples, due to the presence of p-type CNT substrate, less sensitivity was observed. As humidity acts as a reducing gas on p-type sensors, such as CNT-ZnO, an increase in RH causes an increase in the electron transfer between the surface of ZnO nanowires and H2O molecules. Meanwhile. some of these electrons recombine via holes in CNT. Therefore, the impact of humidity in CNT-ZnO is lower compared to ZnO sensors.
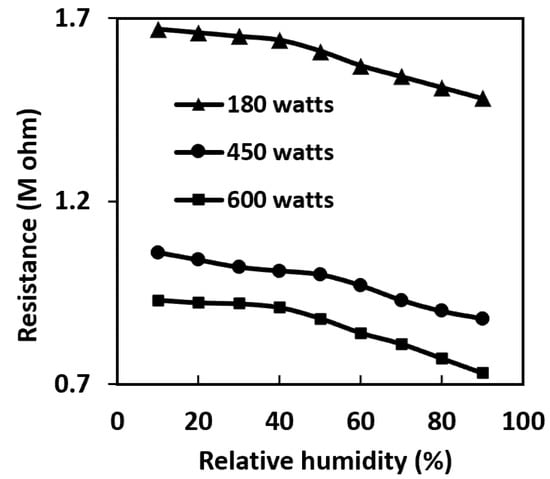
Figure 7.
Relative humidity vs. dc resistance plots at room temperature for CNT-ZnO samples with different microwave powers at zero pressure.
Although the effect of humidity on this hybrid sensor is less than the intrinsic ZnO nanowire sensor [32], according to Figure 7, at relative humidity above 50%, the effect of humidity cannot be ignored.
The sensing mechanism of the CNT-ZnO organic vapor sensors is mostly based on the p-type CNT gas sensor property at room temperature. In general, their electrical resistance is modified by the electron transfer between the surface of CNT-ZnO samples and oxidizing or reducing gas molecules adsorbed on the sample’s surface. If the p-type semiconducting CNT-ZnO at room temperature adsorbs the reducing gas molecules, the electric resistance of the samples increases with the enhancement of the density of adsorbed gas molecules [33,34].
The CNT-ZnO heterojunction affects the type of semiconductor composite. The CNT-ZnO sample shows p-type behavior at low temperatures, while it shows n-type behavior at high temperatures, as shown in Figure 8. At temperatures higher than ~90 °C, CNT-ZnO samples showed n-type behavior in response to reducing gases, which means that in the presence of reducing gas, the resistance of samples was reduced. This occurrence was completely reversible and shows the dominance of ZnO behavior over CNT at temperatures higher than ~90 °C. In this sensory mechanism, an electrical change can occur due to the electron exchange between the surface and conduction band, resulting from oxidation or reduction reactions when encountering gas molecules. ZnO growth not only increases the adsorption surface for gas but also increases the grain boundary, which results in forming a native oxide on the surface. Therefore, in the presence of a reduction gas, the interaction between the adsorbed oxygen increases the sensory performance. Temperature also improves this mechanism. This effect of changing the amount of charge carrier in the semiconductor changes the mechanism of conductance. In addition, nitrogen contaminants on the sample surface at room temperature are important to the number of carriers. Nitrogen molecules adsorb the electron from the surface due to their electron-acceptor nature and shift energy levels toward higher energies.
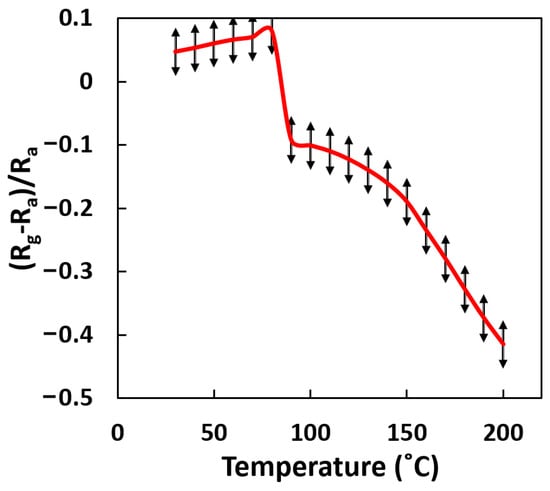
Figure 8.
A typical curve of sensor response () vs. operating temperature in CNT-ZnO samples. As shown in the figure, increasing the operating temperature changes the sign of response level calculated (curve obtained in the presence of 3000 ppm of butanol (Rg) and in clean air (Ra)).
Reducing gases such as acetone, ethanol, and butanol vapor were studied in this paper because they have short- and long-term adverse health effects [35,36,37,38]. Additionally, it is important to improve the performance of a gas sensor that could be used in reducing gas detection.
As shown in Figure 9, organic vapor sensing properties of fabricated hybrid structures were investigated in response to different vapors at different temperature levels and several concentrations. The level of response at each organic vapor was calculated using Equation (1). The concentration of target vapors was 3000 ppm, close to the saturation concentration. The sample resistance increased when exposed to target reducing vapors because the CNT-ZnO samples grown are p-type. The fabricated sensors show a good response to target organic vapors at room temperature and also show an increased response due to increased temperature.
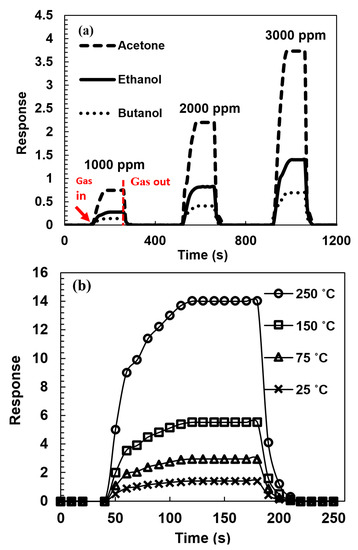
Figure 9.
(a) Response of the CNT-ZnO samples organic vapor sensor in different concentrations of acetone, ethanol, and butanol at room temperature and (b) absolute response of the CNT-ZnO sample organic vapor sensor in 3000 ppm concentration ethanol at several temperatures.
Different VOC gas molecules interact with the adsorbed oxygen and release carriers, which leads to a change in the depletion layer. This reduction in the depletion layer depends on the reaction rate and the number of released carriers. Because the reaction rate and the number of released carriers are different in various types of gases, the sensitivity to each type of VOC gas is different.
Changing the response in different lengths of ZnO nanowire is shown in Figure 10. 3000 ppm of ethanol vapor was selected to show the length effect. The variation of sensitivity is related to the shape and size of ZnO nanowires. As shown in Figure 10a, increasing the length increased the sensitivity and response. To ensure the validity of this claim, the process was evaluated at different temperatures. As shown in Figure 10a, the effect of increased ZnO nanowires length on the sensor response is similar at different temperatures. It was found that increasing the ZnO nanowires from 0.5 um to 1.5 um led to an increase of approximately 30% in the response. As shown in Figure 10b, the highest sensitivity was observed at 230 °C temperature for all samples. At this temperature, sensors have the highest response to the analyte, independent of the gas concentration [3]. As Figure 10b illustrates, with different lengths of the nanowires, this temperature value does not change.
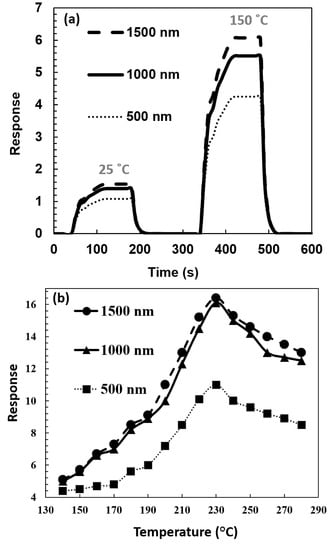
Figure 10.
Response of the different lengths of ZnO nanowires CNT-ZnO samples to organic vapor sensor in 3000 ppm concentration of ethanol (a) at room temperature and 150 °C (b) versus operating temperature.
When the temperature is increased, a thermally activated reaction leads to a steep increase in the rate of detection reactions at the pore walls, so the gas response will increase. After the optimum temperature, gas molecules cover the outermost regions of the sensing surface. In this range, an increasing temperature is associated with a low penetration depth, so the deeper-lying parts of the gas sensor remain unaffected by the gas molecules, and a decrease in the gas response results [39].
Figure 11 shows response changes to ZnO nanowire lengths with different organic vapors. Moreover, changing the target organic vapor clearly proves this claim. The five potential types of sites for adsorption on CNT-ZnO are (I) the parts of their external surfaces that are decorated with metal, (II) internal (endohedral) sites, (III) interstitial channels, (IV) external groove sites, or (V) external surfaces [40]. It can be seen that increasing the length of ZnO nanowires improves the gas sensitivity of the CNT-ZnO sensors via adsorption site effects. The oxygen molecules are adsorbed on the ZnO nanowires. In addition, the formation of oxygen ions (O2−, O−, O2−) occurs on the surface due to the extraction of carriers (electrons) from the conduction band of ZnO, leading to a decrease in the conductivity of ZnO. Moreover, the adsorbed oxygen ions are highly dependent on the working temperature [41]. These ions interact with gas molecules and change the electrical conductivity of the samples. An increase in adsorption sites in samples will increase oxygen trapped at the surface of the sensor. As a result, the reaction of these oxygen molecules with the reducing gas molecules increases. On the other hand, increasing the lengths of a nanowire, (I) provides a higher surface-to-volume ratio, (II) causes nanowires to form in a forest-like shape, and (III) increases the density of wires.
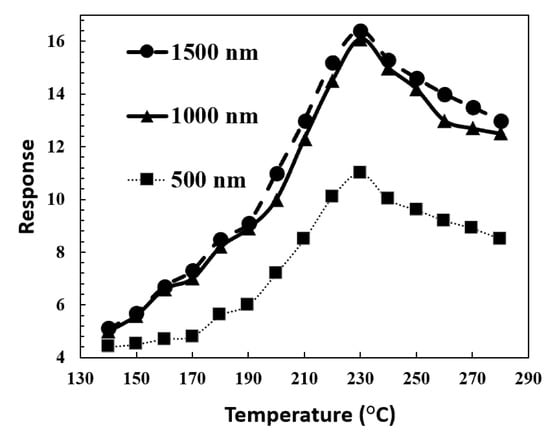
Figure 11.
Response of the different lengths of ZnO nanowires CNT-ZnO samples to organic vapor sensor in 3000 ppm concentration of acetone, ethanol, and butanol at different operating temperatures.
Based on the information obtained in this research, various morphologies of zinc oxide according to growth parameters, as well as other metal oxides in hybrid structures with carbon nanotubes, could be the subject of new research.
4. Conclusions
In summary, we reported a fast microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis method to grow ZnO nanowire on multi-walled aligned CNT. In addition, the adsorption mechanism of multi-length nanowires on CNT-ZnO surfaces and the fabrication of MWCNTs and ZnO nanowires-based reducing gas sensors were investigated. A hybrid CNT-ZnO organic vapor sensor was developed herein with high sensitivity and favorable response properties in detecting acetone, ethanol, and butanol vapor at different temperatures. It was found that we could significantly enhance the device sensitivities by changing the length of ZnO nanowires. Increasing the ZnO nanowire’s length occur with changing the microwave power. Increasing the nanowires’ length increased the response by up to 30%. Moreover, the results of the theory of the potential barrier and the carrier’s transport, as well as the morphology of the sensing layer, confirm this increase in the sensitivity of the sensor. Chemical and physical studies of semiconductor types considering the temperature variation in the composite structure of ZnO with organic materials can be further investigated.
Author Contributions
M.S. (conceptualization, methodology, software, data curation, writing—original draft preparation, visualization, investigation, validation, and writing—reviewing and editing). S.P. (validation, and writing—reviewing and editing). S.R. (methodology, validation, and supervision). H.G. (supervision). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mirzaei, A.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, S.S.; Neri, G. Nanostructured semiconducting metal oxide gas sensors for acetaldehyde detection. Chemosensors 2019, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.-J.; Lee, J.-H. Highly sensitive and selective gas sensors using p-type oxide semiconductors: Overview. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 192, 607–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yin, L.; Zhang, L.; Xiang, D.; Gao, R. Metal oxide gas sensors: Sensitivity and influencing factors. Sensors 2010, 10, 2088–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shooshtari, M.; Salehi, A.; Vollebregt, S. Effect of temperature and humidity on the sensing performance of TiO2 nanowire-based ethanol vapor sensors. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 325501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arafat, M.M.; Dinan, B.; Akbar, S.A.; Haseeb, A.S.M.A. Gas sensors based on one dimensional nanostructured metal-oxides: A review. Sensors 2012, 12, 7207–7258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shooshtari, M.; Salehi, A. Ammonia room-temperature gas sensor using different TiO2 nanostructures. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Yan, H.; Mao, S.; Russo, R.; Johnson, J.; Saykally, R.; Morris, N.; Pham, J.; He, R.; Choi, H.J. Controlled growth of ZnO nanowires and their optical properties. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2002, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazzazi, F.; Young, A.; O’Loughlin, C.; Daniels-Race, T. Fabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles deposited on (3-Aminopropyl) triethoxysilane-treated silicon substrates by an optimized voltage-controlled electrophoretic deposition and their application as fluorescence-based sensors. Chemosensors 2020, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carotta, M.; Cervi, A.; di Natale, V.; Gherardi, S.; Giberti, A.; Guidi, V.; Puzzovio, D.; Vendemiati, B.; Martinelli, G.; Sacerdoti, M.; et al. ZnO gas sensors: A comparison between nanoparticles and nanotetrapods-based thick films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 137, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, M.W.; Park, K.S.; Heo, J.H.; Park, J.G.; Kim, D.W.; Choi, K.J.; Lee, J.H.; Hong, S.H. Gas sensing properties of defect-controlled ZnO-nanowire gas sensor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 263103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmavathy, N.; Vijayaraghavan, R. Enhanced bioactivity of ZnO nanoparticles—An antimicrobial study. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2008, 9, 035004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Fandi, M.G.; Alshraiedeh, N.H.; Oweis, R.J.; Hayajneh, R.H.; Alhamdan, I.R.; Alabed, R.A.; Alrawi, O.F.A. Direct electrochemical bacterial sensor using ZnO nanorods disposable electrode. Sens. Rev. 2018, 38, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, G.B.; Aval, L.F.; Esmaili, P. Performance of gas nanosensor in 1-4 per cent hydrogen concentration. Sens. Rev. 2019, 39, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, N.; Akhtar, K. High performance room temperature gas sensor based on novel morphology of zinc oxide nanostructures. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2019, 29, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Yang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Dong, G. Metal-organic frameworks-derived hollow zinc oxide/cobalt oxide nanoheterostructure for highly sensitive acetone sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 283, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wu, J.; Li, P.; Cao, Y.; Yang, Z. Hierarchical nanoheterostructure of tungsten disulfide nanoflowers doped with zinc oxide hollow spheres: Benzene gas sensing properties and first-principles study. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 31245–31256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Yang, Z.; Li, P.; Zhou, X. Ozone gas sensing properties of metal-organic frameworks-derived In2O3 hollow microtubes decorated with ZnO nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 301, 127081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, S.; Li, F.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, X.; Wang, C.; Zhu, J. Porous spheres-like ZnO nanostructure as sensitive gas sensors for acetone detection. Mater. Lett. 2013, 100, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shooshtari, M.; Salehi, A. An electronic nose based on carbon nanotube-titanium dioxide hybrid nanostructures for detection and discrimination of volatile organic compounds. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 13, 131418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Pan, G.; Sun, C.; He, P.; Cao, G.; Luo, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, H. Enhanced photoelectric responses induced by visible light of acetone gas sensors based on CuO-ZnO nanocomposites at about room temperature. Sens. Rev. 2018, 38, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.Y.; Hsu, M.C.; Su, P.G.; Lin, H.M.; Wu, R.J.; Lai, H.J. A novel SnO2 gas sensor doped with carbon nanotubes operating at room temperature. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2004, 101, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, M.; Neogi, S.; Mahapatra, R.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Ghosh, R. Material dependent and temperature driven adsorption switching (p-to n-type) using CNT/ZnO composite-based chemiresistive methanol gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 336, 129729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Singhal, A.; Divan, R.; Stan, L.; Liu, Y.; Paprotny, I. Selective volatile organic compound gas sensor based on carbon nanotubes functionalized with ZnO nanoparticles. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 2021, 39, 042803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthwal, S.; Singh, B.; Barthwal, S.; Singh, N.B. ZnO-CNT nanocomposite based gas sensors—An overview. Sens. Lett. 2017, 15, 955–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaei, M.; Fard, H.G.; Koohsorkhi, J. Low-temperature growth of vertically aligned carbon nanotubes on a glass substrate using low power PECVD. J. Nano Res. 2014, 27, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahpeykar, S.; Koohsorkhi, J.; Ghafoori-Fard, H. Ultra-fast microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of long vertically aligned ZnO nanowires for dye-sensitized solar cell application. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 165602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, H.; Girot, E.; Mozet, K.; Alem, H.; Medjahdi, G.; Schneider, R. ZnO rods/reduced graphene oxide composites prepared via a solvothermal reaction for efficient sunlight-driven photocatalysis. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 185, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondamareddy, K.K.; Bin, H.; Lu, D.; Kumar, P.; Dwivedi, R.K.; Pelenovich, V.O.; Zhao, X.Z.; Gao, W.; Fu, D. Enhanced visible light photodegradation activity of RhB/MB from aqueous solution using nanosized novel Fe-Cd co-modified ZnO. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10691. [Google Scholar]
- Madhusudhana Reddy, M.; Ramanjaneya Reddy, G.; Chennakesavulu, K.; Sundaravadivel, E.; Prasath, S.S.; Rabel, A.M.; Sreeramulu, J. Synthesis of zinc oxide and carbon nanotube composites by CVD method: Photocatalytic studies. J. Porous Mater. 2017, 24, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.S.; Elkady, M.F. Semiconductor nanomaterials for gas sensor applications. In Environmental Nanotechnology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; Volume 3, pp. 305–355. [Google Scholar]
- Kiasari, N.M.; Soltanian, S.; Gholamkhass, B.; Servati, P. Room temperature ultra-sensitive resistive humidity sensor based on single zinc oxide nanowire. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2012, 182, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.S.; Mamat, M.H.; Rusop, M. Humidity sensor—A review of nanostructured zinc oxide (ZnO)-based humidity sensor. Adv. Mater. Res. 2015, 1109, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, M.M.; Ibrahim, D.S.; Asyraf, M.M.; Jarin, S.; Tomal, A. A review on recent advances of CNTs as gas sensors. Sens. Rev. 2017, 37, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidry, A.A.; Fatima, Q.; Mehmood, A.; Shahzad, A.; Ji, Y.; Saruhan, B. Adsorption Kinetics of NO2 Gas on Pt/Cr-TiO2/Pt-Based Sensors. Chemosensors 2021, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shooshtari, M.; Salehi, A.; Vollebregt, S. Effect of humidity on gas sensing performance of carbon nanotube gas sensors operated at room temperature. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 21, 5763–5770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Xu, H.; Yu, X.; Li, L.; Gao, Y.; Sun, P.; Lu, G. Detection of low concentration acetone utilizing semiconductor gas sensor. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 5478–5484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wu, Z.; Zong, X. Metal-organic frameworks-derived zinc oxide nanopolyhedra/S, N: Graphene quantum dots/polyaniline ternary nanohybrid for high-performance acetone sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 288, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shooshtari, M.; Sacco, L.N.; Van Ginkel, J.; Vollebregt, S.; Salehi, A. Enhancement of Room Temperature Ethanol Sensing by Optimizing the Density of Vertically Aligned Carbon Nanofibers Decorated with Gold Nanoparticles. Materials 2022, 15, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, G.; Baik, N.S.; Miura, N.; Yamazoe, N. Gas sensing properties of tin oxide thin films fabricated from hydrothermally treated nanoparticles: Dependence of CO and H2 response on film thickness. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2001, 77, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Choi, W.C.; Song, W.; Kwon, Y.T.; Shrestha, S.P.; Park, C.-Y. Preparation and field emission properties of Er-decorated multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Carbon 2010, 48, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zeng, W. Room-temperature gas sensing of ZnO-based gas sensor: A review. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2017, 267, 242–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).