Abstract
Acute antiarrhythmics poisoning represents a challenge in the Emergency Department (ED). These patients often develop malignant arrhythmias in need of exceptional therapeutic measures in the ICU. We report a 47-year-old patient admitted to the ED 5 h after the ingestion of a large dose of amiodarone and flecainide in a suicide attempt. During their ED stay, the patient developed signs of cardiotoxicity evidenced by electrocardiogram and ventricular arrhythmias. The toxicological results showed a level of 4.8 mg/L amiodarone and 2.98 mg/L flecainide. He was successfully treated in the ED using a large dose of sodium bicarbonate and lipid emulsion therapy. After hospital admission, he remained stable, with no need for exceptional therapeutic measures such as mechanical circulatory support, cardiac pacing or ECMO. We emphasize the importance of an early start of pharmacological therapies in the ED, which might improve the outcome in antiarrhythmic acute poisoning.
1. Introduction
Antiarrhythmic drugs are widely used in clinical practice. Antiarrhythmic drug therapy carries an understood risk for toxic side effects, even with therapeutic doses. Flecainide induces ventricular tachycardia (VT), which is often resistant to direct current cardioversion because the intense sodium channel blockade increases the voltage threshold for cellular depolarization [1]. Amiodarone prolongs the QT interval, causes conduction disturbances and VT. Amiodarone is also related to exacerbations of VT and an increased defibrillation threshold [2,3]. A combination of these two antiarrhythmics in intentional overdose could lead to dramatic cardiotoxicity.
A review of the literature showed no report of a case with a poisoning including an association of amiodarone and flecainide. We found only two case reports of amiodarone intentional overdose: the first case was of a patient who ingested 8000 mg amiodarone in a suicide attempt, where the blood concentration was 1.1 mg/L, managed with supportive measures; the second case was of a patient with mixed overdose of amiodarone, diltiazem and metoprolol, with a serum level of amiodarone of 2.7 mg/L, in need of intensive care unit (ICU) therapy [4,5]. In flecainide overdose, there is a need for exceptional therapeutic interventions both in the Emergency Department (ED) and ICU [6,7,8,9].
We report the case of a patient who attempted suicide by ingesting a large dose of amiodarone and flecainide, with an electrocardiogram (ECG) depicting signs of cardiotoxicity and ventricular arrhythmias, which was managed successfully in the ED, after hypertonic sodium bicarbonate administration and initiation of lipid emulsion therapy (LET).
After ED admission of a patient with mixed antiarrhythmic drugs poisoning, ECG monitoring, recognition of signs of cardiotoxicity and early initiation of hypertonic sodium bicarbonate and LET may improve the outcome and avoid exceptional therapeutic measures in the ICU.
2. Case Presentation
A 47-year-old patient was admitted to the ED for fatigue, anxiety, headache. The patient declared the ingestion of 2000 mg amiodarone and 5000 mg flecainide in a suicide attempt, 5 h prior to ED arrival. Glasgow Coma Scale score was 12, BP 110/80 mmHg, heart rate 71 bpm.
The patient had an episode of atrial fibrillation converted to sinus rhythm with flecainide two years before, had been subjected to a radiofrequency catheter ablation with the isolation of the pulmonary veins one year earlier for atrial flutter, with successful restoration and maintenance of sinus rhythm, and took amiodarone 100 mg daily since. He had a history of depression, but he had quit the specific therapy for several months. During transportation, the monitor recorded a sinus rhythm of 86/min, a prolonged PR interval 240 msec with a normal QRS complex (Figure 1). He was first admitted to a local hospital, where he received an initial dose of activated charcoal and normal saline solution, then referred to our ED for specific therapy. The ECG recorded upon first medical contact showed an irregular rhythm, a first-degree atrioventricular (AV) block with a wide QRS complex.
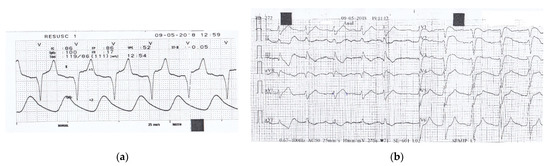
Figure 1.
(a) Monitor recording during transportation to the first hospital shows a sinus rhythm of 86/min, a prolonged PR interval of 240 msec with normal QRS complex of 110 msec.; (b) 12-lead ECG recorded in the local hospital, 3 h after the ingestion of drugs, shows irregular sinus rhythm of 71/min, with a prolonged PR interval of 280 msec, a wide QRS complex of 160 msec, and slightly prolonged QTc interval of 479 msec.
Upon admission to our ED, arterial blood gases (ABG), liver and kidney panel, alkaline phosphatase and LDH were normal, WBC 12.000/mmc, blood glucose 170 mg/dL, and urine toxicological screen negative. Cardiac ultrasound excluded a structural disease. Cardiac biomarkers were within normal range.
Given the large dose of antiarrhythmics ingested, we began sodium bicarbonate 8.4% administration, up to 500 mEq/L (Table 1). A second ABG showed pH 7.53 and a sodium concentration >150 mEq/L. We initially administered 1 g/kg activated charcoal, followed by 25 g every 4 h for 12 h, to reduce the gastrointestinal absorption of flecainide and increase the elimination of amiodarone, which enters in an enteral-hepatic circuit [10,11].

Table 1.
Patient’s evolution during ED admission and therapy provided.
One hour after admission, the ECG changed significantly and VT occurred later (Figure 2). First, we administered MgSO4 2 g over 20 min, then a bolus of 1.5 mL/kg lipid emulsion (Intralipid® 20% IV fat emulsion) was pushed over 2–3 min, which was repeated, followed by 0.25 mL/kg/min infusion over one hour.
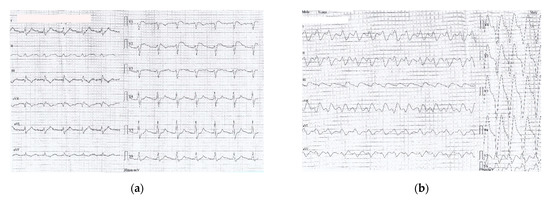
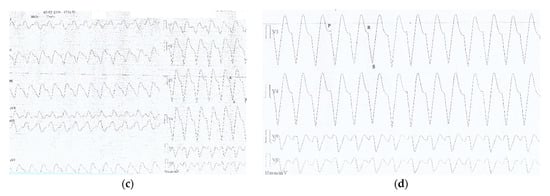
Figure 2.
(a) ECG recorded one hour after ED admission (6 h after drugs ingestion): sinus rhythm 67/min, prolonged PR interval 360 msec, wide QRS complex 200 msec, prolonged QTc 549 msec, negative T wave DIII, aVF, with a coved ST segment elevation in V1-V2; (b) ECG recorded two hours after ED admission (7 h after drug ingestion) showing a slightly irregular rhythm, no visible P waves, sinusoidal pattern, wide LBBB pattern-QRS complexes at a rate of 97/min (c) ECG recorded two and a half hours after ED admission (7 and a half hours after drug ingestion): VT 110/min (wide QRS complex tachycardia, AV dissociation, negative concordance in precordial leads, R to nadir S 160 msec); (d) ECG detail (magnified precordial leads) showing VT criteria: AV dissociation and R to nadir S > 100 msec.
ECG changes showed significant improvement in 20 min after only 100 mL Intralipid® (Figure 3).
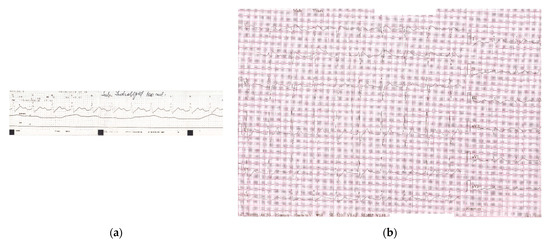
Figure 3.
(a) Monitor recording during first 100 mL Intralipid® solution revealing reversal of ECG changes: sinus rhythm 68/min with distinct visible P waves, prolonged PR interval 320 msec, wide QRS complex 160 msec, QT interval 480 msec; (b)12-lead ECG recorded after administration of the first 100 mL Intralipid®: sinus rhythm 71/min, first degree AV block (PR interval 320 msec), wide QRS complex RBBB-type 180 msec, disappearance of negative T waves in aVF, corrected QTc interval 479 msec.
During his ED stay, the patient remained hemodynamically stable. He was admitted to a medical ward, had no other complications, and was released home 48 h later. The ECG returned completely to normal baseline (Figure 4) and the psychiatric medication was properly re-initiated.
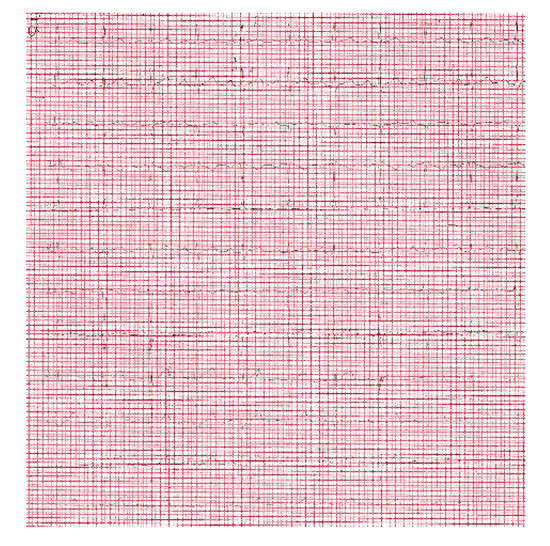
Figure 4.
ECG upon discharge, shows sinus rhythm 90/min, with normal PR, QTc intervals and QRS complex.
The toxicological results, which were not available during ED stay, showed in our patient a level of 4.8 mg/L amiodarone and 2.98 mg/L flecainide from the blood sample obtained upon ED admission (5 h after drug ingestion). These levels were extremely high compared with the usual therapeutic range, which is 1–2.5 mg/L for amiodarone and 0.2–1 mg/L for flecainide [12].
3. Discussion
An extensive search of the literature was performed with the journal search engines Thompson ISI—Web of Science, EMBASE, EBSCO, Scopus and PubMed. We used the MeSH terms suicide, amiodarone, flecainide, AND overdose, intoxication, or poisoning in different permutations. Additionally, we examined the citations of all resulting articles for any additional relevant references. Each article was reviewed, and case reports, which included and pictured a 12-lead ECG performed during intoxication, as well as references to intentionality of the poisoning, time to hospital admission, dosage and/or serum level, therapy administered and setting, were included for analysis. A summary of the details of the included papers is reported in Table 2. The exclusion criteria were: animal and in-vitro studies, forensic and analytical studies, original articles that were not in the English language, as well as comments, editorials, posters, abstracts and letters to the Editor. Those articles reporting flecainide or amiodarone accidental medication errors, and reports with incomplete data were also excluded (Figure 5).

Table 2.
Characteristics and main findings of eligible studies.
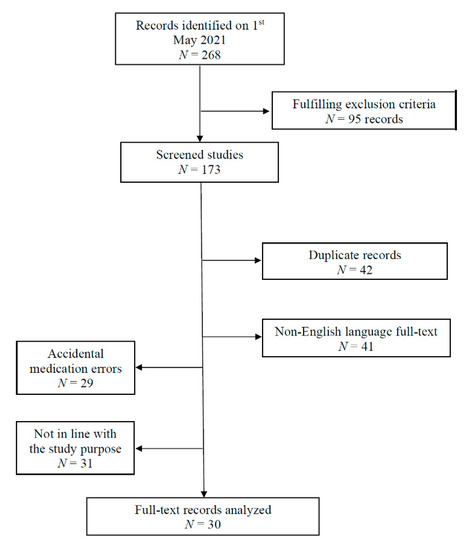
Figure 5.
Flowchart illustrating studies included and excluded in this literature review.
For each article, we analyzed relevant demographic and clinical data from the case. Next, a thorough analysis of each ECG pattern was performed. We also analyzed therapeutic approaches and the department where the treatment was conducted.
To our knowledge, this is the first report of a suicide attempt after intentional ingestion of large doses of amiodarone and flecainide with severe cardiotoxicity and a favorable evolution after LET in the ED. There are reports of accidental overdose in patients treated chronically with flecainide, especially in elders with hepatic or renal comorbidities, that were resolved in the ICU [32,34,37]. There are also reports of flecainide-induced therapy resistant ventricular fibrillation followed by cardiac arrest, successfully treated with cardiopulmonary resuscitation and advanced life support, where amiodarone was used as part of the protocol [19,29,32]. From the studies analyzed, only in one case of accidental flecainide overdose was the patient managed successfully in the ED with Na bicarbonate [36]. All the other reports involved patients in need of exceptional measures, started in the ED and continued in ICU/CCU (Table 2).
In our review, we found two reports of deceased patients, both after ingestion of 10–12 g flecainide. The patients had an unfavorable outcome despite the administration of sodium bicarbonate (250 mL) and ACLS therapies, including ECMO (Table 2) [17,24]. Another patient, with a moderate dose of flecainide ingested in association with other drugs, also had an unfavorable evolution after ED and CCU therapy, which included CPR, administration of MgSO4, electrolyte correction, LET and defibrillation [35].
Flecainide toxicity is rare but potentially fatal; at higher doses, flecainide toxicity can result in hemodynamic collapse, with a mortality rate of up to 22.5% [38]. Amiodarone inhibits several cytochrome P450 pathways, thus increasing serum concentrations of drugs such as statins, calcium channel blocking agents, tacrolimus, quinidine, fentanyl and flecainide. Plasma concentrations >2.5 mg/L have been associated with increased risk of toxicity [39].
Antiarrhythmic drugs’ toxicity can be classified based either on the clinical features, or on ECG changes (Table 3).

Table 3.
Antiarrhythmic drugs toxicity (adapted from [10,11,12]).
Flecainide overdose determines nonspecific symptoms (nausea, vomiting, headache), seizures bradycardia, QRS widening and ventricular arrhythmias [10,11,30,40]. Flecainide is a lipophilic drug that acts by strongly blocking the sodium channels, delaying their reactivation without impeding repolarization. Flecainide binds and opens sodium channels in a dose-dependent manner. In patients without structural heart disease, flecainide slows the conduction and favors reentry, creating areas of functional block, thus producing reentry arrhythmias. Among the class Ic antiarrhythmics, flecainide is the most difficult to detach from the sodium channels, delaying their reactivation [1,11]. The plasmatic peak is 3–4 h after flecainide ingestion. After absorption, 70% of the dose ingested is metabolized in the liver, while 30% is eliminated unchanged by the kidney. In patients with renal impairment, the total clearance of this drug might fall by approximately 40% [41]. The elimination time is dose-dependent, and is increased by urine alkalinization [5,7].
Amiodarone is a class III antiarrhythmic with all the properties of the four Vaughn-Williams antiarrhythmic classes. After oral administration, the maximal plasmatic concentration is reached 3–7 h later [11,40]. Amiodarone affects bioavailability, binding with plasmatic proteins, metabolism by liver cytochromes and kidney elimination of co-administered antiarrhythmics. Thus, amiodarone significantly increases the plasma level of flecainide, leading to severe cardiotoxicity. Amiodarone is likely to cause polymorphic ventricular dysrhythmias and the effect is potentiated by hypokalemia or hyperglycemia [42,43,44].
Large doses of sodium bicarbonate should be administered in flecainide overdose to counteract cardiotoxicity by plasma alkalinization, which decreases the free concentration of the drug, promotes drug dissociation from the sodium channels and increases extracellular concentration of sodium ions that displace the drug from the receptor sites [1,30,45]. The dose of the hypertonic sodium bicarbonate is 1 mEq/kg bolus (range, 0.55–3.0 mEq/kg) followed by infusion of 15 to 20 mEq/h, maintaining a target pH of 7.50 to 7.60 [1].
LET is an adjunctive measure, which will sequestrate both flecainide and amiodarone, decreasing the drug available to block sodium channels [30,45] The mechanism of action of LET is unclear; however, it is postulated that it follows the mechanisms of the “lipid-sink theory” whereby LET acts to sequester lipophilic drugs, such as flecainide, thereby reducing toxic activity on cardiac myocytes [46]. The administration of LET compartmentalizes the offending drug into a lipid phase and away from the target receptors. The drugs with a high lipid solubility favor the lipid partition and leave the serum, thus lower serum concentrations facilitate the removal of the offending agent from tissues by the generation of a concentration gradient [47,48]. The second mechanism suggests that LET exerts a positive inotropic effect with more efficient metabolization of fatty acids [25].
To our knowledge, ten cases have been published in the literature regarding the use of LET as part of a complex therapeutic protocol initiated in the ED, continued in ICU/CCU, for severe cardiotoxicity in flecainide overdose. LET was also used in one case of mixed poisoning including amiodarone, betablockers and calcium-channel blockers. In reviewed cases, LET was associated (in addition to treatment with high doses of sodium bicarbonate) with ACLS measures, CPR, pacing, CVVH and ECMO [6,7,26,28,31,34,35]. In a single case, in which the patient arrived at the ED 90 min after self-poisoning with a lower flecainide dose as compared with our patient, with a serum level of flecainide slightly over the therapeutic range, LET was involved as part of a pharmacological protocol that included atropine, MgSO4, Na bicarbonate for bradycardia, AV block and QTc prolongation. However, this case needed ICU surveillance [25].
Particular to our case was that it was recorded when, in our country, flecainide was not authorized by the National Agency for Medicines and Medical Devices. The use of LET immediately after occurrence of ventricular arrhythmias led to a significant improvement in QRS and QTc duration and the restoration of sinus rhythm, within 20 min, in the ED.
While the evidence base for LET use in acute drug intoxication is evolving, the present evidence and recommendation supports the use of LET in lipophilic cardiotoxin intoxication when there is an immediate threat to life, and other therapies have proven ineffective [49,50].
Patients who do not respond to drug therapy could benefit from cardiac pacing, ECMO, or mechanical circulatory support [30,51]. ECMO is a temporizing measure to allow for cardiac recovery and drug elimination and should be reserved for refractory hemodynamic compromise [52].
Extra-corporeal life support (ECLS) provides respiratory support and also crucially maintains cardiac output, preventing end-organ damage and restoring vital organ perfusion, thereby enabling renal drug elimination, hepatic drug metabolism and drug redistribution. The length of the ECLS support may be determined by serum flecainide level and cardiac stability [26].
The first step in the management of a mixed antiarrhythmic overdose should be recording an ECG to identify QRS widening, QTc prolongation, or atrio-ventricular blocks. The second step should be ABG determination and decontamination measures. Then, pharmacological therapies that proved to be beneficial, such as hypertonic sodium bicarbonate or LET, should be initiated early in the ED, when the first signs of cardiotoxicity occur.
We reported the first case of intentional amiodarone and flecainide poisoning, drugs that interact, both leading to life-threatening cardiotoxicity. The patient was admitted to the ED 5 h after drug ingestion and initially had a nonspecific clinical picture. ECG signs of cardiotoxicity occurred 6 h after ingestion, although immediate measures for decontamination and hypertonic sodium bicarbonate were initiated. Alkalinization with a pH over 7.5 and increased extracellular sodium contribute to flecainide dislocation from cardiomyocytes and decrease serum free flecainide level [45]. LET was given after failure of other therapies, prior to cardiovascular collapse, as the VT occurred. ECG changes in our patient were improved within 20 min of LET. The patient remained hemodynamically stable with an uneventful evolution during the next 48 h of hospitalization.
We undertook the present study with the goal of reviewing the reports of amiodarone and flecainide acute poisoning in humans, with evidence of ED therapies used, their effect, and failure as a treatment for poisoning. We aimed to distinguish which variables might explain failures and successes in either time of administration, substances, or toxic load.
4. Conclusions
With this case and the data reported in the literature, the authors want to point out that: (a) emergency physicians need to proceed to close cardiac monitoring of the patients with mixed antiarrhythmics poisoning; (b) administration of life-saving therapies, such as hypertonic sodium bicarbonate and LET after first cardiotoxicity signs, is feasible in the ED and should help to avoid the need for exceptional measures in the ICU.
Since antiarrhythmics are widely used in clinical practice, further research on pharmacological therapies and antidotes is crucial for taking an important preventive action.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.L. and L.S.; methodology, C.B. and C.L.; software, A.P. and C.L.; validation, V.S., A.P. and C.B.; formal analysis, C.L. and A.P.; writing—original draft preparation, C.L. and C.B., writing—review and editing, A.P., C.L. and L.S.; supervision, C.B. and L.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from the patient whose case is reported in this manuscript.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| ED | Emergency Department |
| ECMO | Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation |
| VT | ventricular tachycardia |
| ICU | intensive care unit |
| ECG | electrocardiogram |
| LET | lipid emulsion therapy |
| AV | atrioventricular |
| ABG | arterial blood gases |
| WBC | white blood cells |
| ACLS | advanced cardiac life support measures |
| GL | gastric lavage |
| AC | activated charcoal |
| CBS | peripheral cardiopulmonary bypass support |
| ECV | electrical cardioversion |
| AF | atrial fibrillation |
| WCT | wide complex tachycardia |
| PEA | pulseless electrical activity |
| CCU | coronary care unit |
| CVVH | continuous veno-venous hemodiafiltration |
| CPR | cardiopulmonary resuscitation |
| VF | ventricular fibrillation |
| STE | ST segment elevation |
| ACS | acute coronary syndrome |
| IABP | intra-aortic balloon pump |
| CTU | cardio-thoracic unit |
| HDI | high-dose-insulin therapy |
| RBBB | right bundle branch block |
| TdP | torsade de pointes |
| ALS | advanced life support |
| ECLS | extra-corporeal life support |
References
- Banavalikar, B.; Shenthar, J.; Padmanabhan, D. Unusual Wide Complex Tachycardia During Rhythm Control for Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2018, 138, 537–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.L.; Hsieh, P.L.; Liu, C.P.; Chiang, H.T.; Tak, T. Ventricular tachycardia after amiodarone: Report of an unusual case. J. Appl. Res. 2003, 3, 159–162. [Google Scholar]
- Forgoros, R.N. Amiodarone-induced refractoriness to cardioversion. Ann. Intern. Med. 1984, 100, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonati, M.; D’Aranno, V.; Galletti, F.; Fortunati, M.T.; Tognoni, G. Acute overdosage of amiodarone in a suicide attempt. J. Toxicol Clin. Toxicol. 1983, 20, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stellpflug, S.J.; Fritzlar, S.J.; Cole, J.B.; Engebretsen, K.M.; Holger, J.S. Cardiotoxic Overdose Treated with Intravenous Fat Emulsion and High-Dose Insulin in the Setting of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. J. Med. Toxicol. 2011, 7, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, J.C.; Judge, B.S. Successful treatment of flecainide-induced cardiac arrest with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in the ED. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2015, 33, 1542.e1–1542.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandawat, A.; McCullough, S.A.; Gilstrap, L.G.; Yeh, R.W. Successful treatment of flecainide overdose with sustained mechanical circulatory support. HeartRhythm Case Rep. 2015, 1, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasui, R.K.; Culclasure, T.F.; Kaufman, D.; Freed, C.R. Flecainide overdose: Is cardiopulmonary support the treatment? Ann. Emerg. Med. 1997, 29, 680–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auzinger, G.M.; Scheinkestel, C.D. Successful extracorporeal life support in a case of severe flecainide intoxication. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 29, 887–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewin, N.A. Antidysrhythmic agents. In Goldfrank’s Toxicologic Emergencies, 7th ed.; Goldfrank, L.R., Flomenbaum, N.E., Lewin, N.A., Howland, M.A., Hoffman, R.S., Nelson, L.S., Eds.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 794–798. [Google Scholar]
- Benowitz, N.L. Antiarrhythmic drugs. In Poisoning & Drug Overdose, 6th ed.; Olson, K.R., Ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 83–86. [Google Scholar]
- Knollmann, B.C.; Roden, D.M. Antiarrhythmic Drugs. In Goodman & Gilman’s: The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 13th ed.; Brunton, L.L., Hilal-Dandan, R., Knollmann, B.C., Eds.; McGraw Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 1996; Available online: https://accessmedicine-mhmedical-com.dbproxy.umfiasi.ro/content.aspx?bookid=2189§ionid=172483385 (accessed on 22 May 2021).
- Winkelmann, B.R.; Leinberger, H. Life-Threatening Flecainide Toxicity. A Pharmacodynamic Approach. Ann. Intern. Med. 1987, 106, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, M.J.; Mowry, J.B.; Kirk, M.A. Sodium bicarbonate to correct QRS in a case of flecainide overdose. J. Emerg. Med. 1997, 15, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, N.A.; Bourke, J.P.; Gascoigne, A.D. Survival in a case of life-threatening flecainide overdose. Intensive Care Med. 1998, 24, 740–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovecchio, F.; Berlin, R.; Brubacher, J.R.; Sholar, J.B. Hypertonic Sodium Bicarbonate in an Acute Flecainide Overdose. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 1998, 16, 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazil, E.; Bodiwala, G.G.; Bouch, D.C. Fatal flecainide intoxication. J. Accid. Emerg. Med. 1998, 15, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Corkeron, M.A.; van Heerden, P.V.; Newman, S.M.; Dusci, L. Extracorporeal circulatory support in near-fatal flecainide overdose. Anaesth. Intensive Care 1999, 27, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegers, A.; Board, P.N. Amiodarone used in successful resuscitation after near-fatal flecainide overdose. Resuscitation 2002, 53, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, C.J.; Whitner, T.E.; Rinaldi, M.J.; Littmann, L. Brugada electrocardiographic pattern elicited by inadvertent flecainide overdose. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2004, 27, 1311–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timperley, J.; Mitchell, A.R.; Brown, P.D.; West, N.E. Flecainide overdose-support using an intra-aortic balloon pump. BMC Emerg. Med. 2005, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Devin, R.; Garrett, P.; Anstey, C. Managing cardiovascular collapse in severe flecainide overdose without recourse to extracorporeal therapy. Emerg. Med. Australas. 2007, 19, 155–159. [Google Scholar]
- Rognoni, A.; Bertolazzi, M.; Peron, M.; Macciò, S.; Ternavasio Cameroni, G.; Gratarola, A.; Rognoni, G. Electrocardiographic changes in a rare case of flecainide poisoning: A case report. Cases J. 2009, 2, 9137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivien, B.; Deye, N.; Mégarbane, B.; Marx, J.S.; Leprince, P.; Bonnet, N.; Roussin, F.; Jacob, L.; Pavie, A.; Baud, F.J.; et al. Extracorporeal life support in a case of fatal flecainide and betaxolol poisoning allowing successful cardiac allograft. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2010, 56, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellsworth, H.; Stellpflug, S.J.; Cole, J.B.; Dolan, J.A.; Harris, C.R. A life-threatening flecainide overdose treated with intravenous fat emulsion. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2013, 36, e87–e89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivalingam, S.K.; Gadiraju, V.T.; Hariharan, M.V.; Atreya, A.R.; Flack, J.E.; Aziz, H. Flecainide toxicity-treatment with intravenous fat emulsion and extra corporeal life support. Acute Card. Care 2013, 15, 90–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Williamson, D.G.; Sinha, A.; Frost, I.; Singh, V.K. Management of persistent wide QRS in flecainide overdose with magnesium sulphate. Emerg. Med. J. 2010, 27, 487–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhtar, O.; Archer, J.R.H.; Dargan, P.I.; Wood, D.M. Acute flecainide overdose and the potential utility of lipid emulsion therapy. Clin. Med. 2015, 15, 301–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.W.; Kwak, J.J.; Namgung, J. Flecainide-Induced Torsade de Pointes Successfully Treated with Intensive Pharmacological Therapy. Int. J. Arrhythmia 2016, 17, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, N.M.; Hill, T.E.; Summers, M.R.; Vranian, M.N.; Faulx, M.D. Management of life-threatening flecainide overdose: A case report and review of the literature. HeartRhythm Case Rep. 2016, 2, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullins, M.E.; Miller, S.N.; Nall, C.E.; Meggs, W.J. Intravenous lipid emulsion therapy for flecainide toxicity. Toxicol. Commun. 2017, 1, 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apfelbaum, J.D.; Gerczynski, J.; Robertson, W.E.; Richey, S. Electrocardiography: Flecainide Toxicity. Emerg. Med. 2018, 50, 124–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodziock, G.; Armstrong, C.; Montgomery, J. Flecainide overdose presenting with long QT and acute Takotsubo cardiomyopathy. J. Electrocardiol. 2019, 52, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heldens, M.; van der Nat, G.A.M.; Melman, P.G. Renal failure, shock, and loss of pacemaker capture: A case of flecainide intoxication. Neth. J. Med. 2019, 77, 189–192. [Google Scholar]
- Gaylor, J.M.; Franco, A.; Manchester, L.; Harrison, R.F. Intentional Flecainide Overdose: A Case Report EMRA. Available online: https://www.emra.org/emresident/article/flecainide-overdose/ (accessed on 5 May 2021).
- Venkataraman, G. Acute Flecainide Toxicity: A Case Report. EP Lab Digest 2020, 20. Available online: https://www.eplabdigest.com/acute-flecainide-toxicity-case-report (accessed on 5 May 2021).
- Donthi, N.; Chandrabhatla, T.; Genovese, L.; de Filippi, C. Fast and furious: Flecainide toxicity presenting as monomorphic ventricular tachycardia. BMJ Case Rep. 2020, 13, e236932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppel, C.; Oberdisse, U.; Heinemeyer, G. Clinical course and outcome in class IC antiarrhythmic overdose. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 1990, 28, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Erven, L.; Schalij, M.J. Amiodarone: An effective antiarrhythmic drug with unusual side effects. Heart 2010, 96, 1593–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, I.T.F.; Man, C.Y. Review on flecainide poisoning. Hong Kong J. Emerg. Med. 2002, 9, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, R.; Dean, R.K.; Chaudhary, A.; Szombathy, T. Flecainide toxicity in renal failure. Bayl. Univ. Med. Cent. Proc. 2018, 31, 328–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krikler, D.M.; McKenna, W.J.; Chamberlain, D.A. Amiodarone and Arrhythmias, 1st ed.; Pergamon Press: New York, NY, USA, 1983; pp. 15–42. [Google Scholar]
- Antonelli, D.; Atar, S.; Freedberg, N.A.; Rosenfeld, T. Torsade de pointes in patients on chronic amiodarone treatment: Contributing factors and drug interactions. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 2005, 7, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Psirropoulos, D.; Lefkos, N.; Boudonas, G.; Efthimiadis, A.; Eklissiarhos, D.; Tsapas, G. Incidence of and predicting factors for torsades de pointes during intravenous administration of amiodarone. Heart Drug 2001, 1, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viland, J.; Langørgen, J.; Wendelbo, Ø. A somnolent woman in her fifties with acute circulatory failure. Tidsskr. Nor. Laegeforen. 2019, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fettiplace, M.R.; Ripper, R.; Lis, K.; Feinstein, D.L.; Rubinstein, I.; Weinberg, G. Rapid cardiotonic effects of lipid emulsion infusion. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 41, e156–e162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fettiplace, M.R.; Lis, K.; Ripper, R.; Kowal, K.; Pichurko, A.; Vitello, D.; Rubinstein, I.; Schwartz, D.; Akpa, B.S.; Weinberg, G. Multimodal contributions to detoxification of acute pharmacotoxicity by a triglyceride micro-emulsion. J. Control. Release 2015, 198, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Heard, K.; Foran, M.; Koyfman, A. Intravenous Lipid Emulsion in the Emergency Department: A Systematic Review of Recent Literature. J. Emerg. Med. 2015, 48, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cave, G.; Harvey, G. Should we consider the infusion of lipid emulsion in the resuscitation of poisoned patients? Crit. Care 2014, 18, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosselin, S.; Hoegberg, L.C.G.; Hoffman, R.S.; Graudins, A.; Stork, C.M.; Thomas, S.H.L.; Stellpflug, S.J.; Hayes, B.D.; Levine, M.; Morris, M.; et al. Evidence-based recommendations on the use of intravenous lipid emulsion therapy in poisoning. Clin. Toxicol. 2016, 54, 899–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newson, J.M.; Santos, S.D.; Walters, B.L.; Todd, B.R. The case of flecainide toxicity: What to look for and how to treat. J. Emerg. Med. 2020, 59, e43–e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentino, M.A.; Panakos, A.; Ragupathi, L.; Williams, J.; Pavri, B.B. Flecainide Toxicity: A Case Report and Systematic Review of its Electrocardiographic Patterns and Management. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2017, 17, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).