Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) Treatment in Patients with Complications of Kidney and Peripheral Vascular Diseases in Indonesia
Abstract
1. Introduction
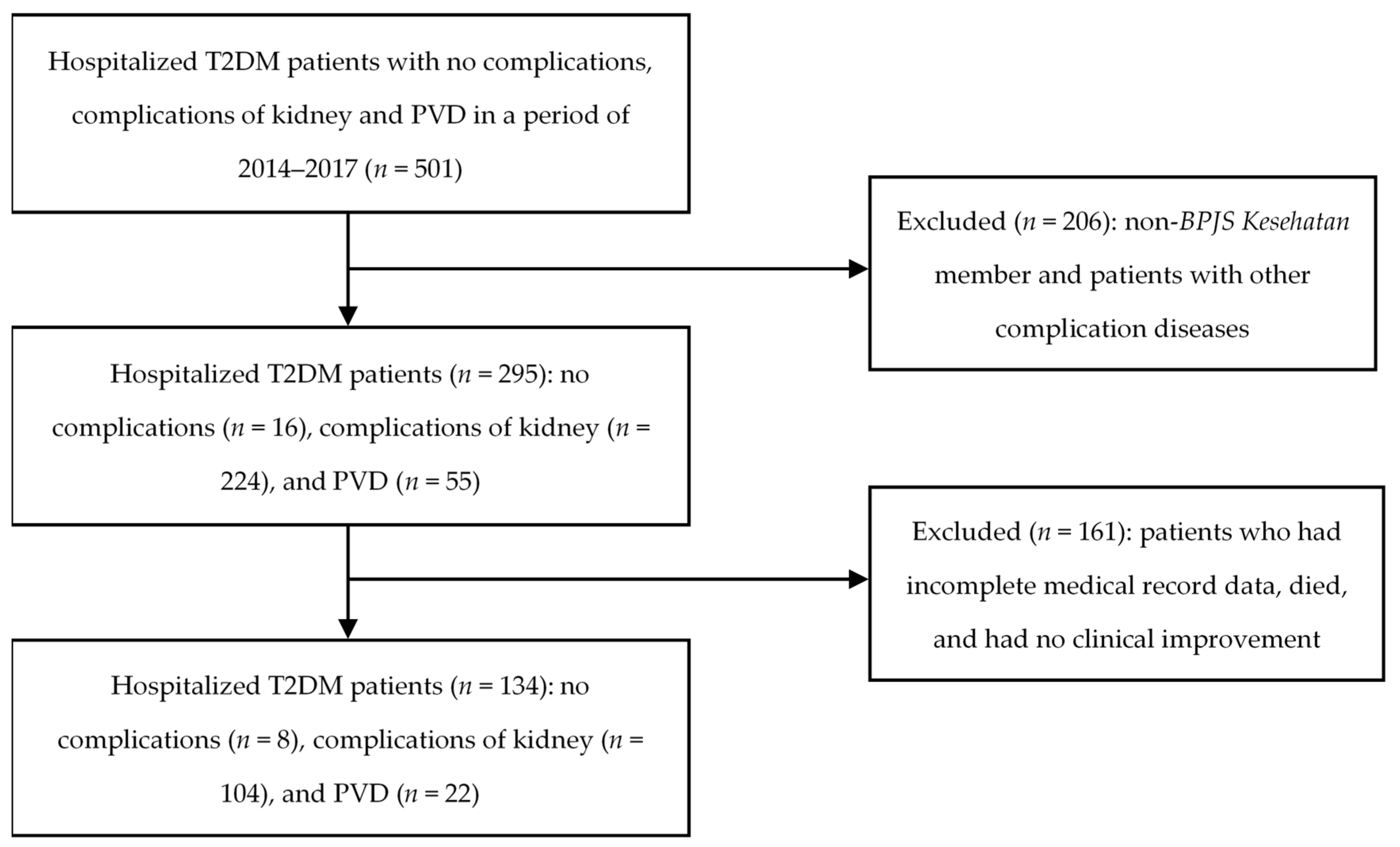
2. Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saeedi, P.; Petersohn, I.; Salpea, P.; Malanda, B.; Karuranga, S.; Unwin, N.; Colagiuri, S.; Guariguata, L.; Motala, A.A.; Ogurtsova, K.; et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 157, 107843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soelistijo, S.A.; Novida, H.; Rudijanto, A.; Soewondo, P.; Suastika, K.; Manaf, A. Management and Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Indonesia 2015; PB Perkeni: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sinuraya, R.K.; Oktrina, A.; Handayani, N.K.; Destiani, D.P.; Puspitasari, I.M. Clinical Pharmacy Services Improve Blood Sugar Control of Diabetes Mellitus Patients. Indones. J. Clin. Pharm. 2019, 8, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IDF. IDF Diabetes Atlas Ninth Edition (9th) 2019. Available online: https://www.diabetesatlas.org/upload/resources/2019/IDF_Atlas_9th_Edition_2019.pdf (accessed on 5 September 2020).
- Basic Health Research. Badan Penelitian dan Pengembangan Kesehatan, Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia; Basic Health Research: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- ADA. Standards of medical care in diabetes-2015 abridged for primary care providers. Clin. Diabetes 2015, 33, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ADA. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care 2010, 33 (Suppl. 1), S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ADA. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2013, 36 (Suppl. 1), S67–S74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ADA. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2013, 36 (Suppl. 1), S8. [Google Scholar]
- Flint, A.; Arslanian, S. Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes in Youth. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, S177–S183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inzucchi, S.E.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Buse, J.B.; Diamant, M.; Ferrannini, E.; Nauck, M.; Peters, A.L.; Tsapas, A.; Wender, R.; Matthews, D.R. Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes: A Patient-Centered Approach: Position Statement of the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 1364–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roden, M.; Shulman, G.I. The integrative biology of type 2 diabetes. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 576, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casqueiro, J.; Casqueiro, J.; Alves, C. Infections in patients with diabetes mellitus: A review of pathogenesis. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 16 (Suppl. 1), S27–S36. [Google Scholar]
- Pecoits-Filho, R.; Abensur, H.; Betônico, C.C.R.; Machado, A.D.; Parente, E.B.; Queiroz, M.; Salles, J.E.N.; Titan, S.; Vencio, S. Interactions between kidney disease and diabetes: Dangerous liaisons. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2016, 8, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallon, V.; Komers, R. Pathophysiology of the Diabetic Kidney. Compr. Physiol. 2011, 1, 1175–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourghasem, M.; Shafi, H.; Babazadeh, Z. Histological changes of kidney in diabetic nephropathy. Casp. J. Intern. Med. 2015, 6, 120–127. [Google Scholar]
- Hidayati, T.; Adiningrat, A.; Akrom, A. Clinical conditions and history of illness among terminal chronic kidney disease patients. Int. J. Public Health Sci. 2019, 8, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdanpanah, L.; Shahbazian, H.; Nazari, I.; Arti, H.R.; Ahmadi, F.; Mohammadianinejad, S.E.; Cheraghian, B.; Hesam, S. Incidence and Risk Factors of Diabetic Foot Ulcer: A Population-Based Diabetic Foot Cohort (ADFC Study)—Two-Year Follow-Up Study. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 2018, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulton, A.J.M.; Kirsner, R.S.; Vileikyte, L. Neuropathic Diabetic Foot Ulcers. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pemayun, T.G.D.; Naibaho, R.M. Clinical profile and outcome of diabetic foot ulcer, a view from tertiary care hospital in Semarang, Indonesia. Diabet. Foot Ankle 2017, 8, 1312974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelstein, E.A.; Chay, J.; Bajpai, S. The Economic Burden of Self-Reported and Undiagnosed Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes on Indonesian Households. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmawati, R.S.; Ng, N.; Prabandari, Y.S.; Nichter, M. Smoking among diabetes patients in Yogyakarta, Indonesia: Cessation efforts are urgently needed. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2009, 14, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wild, S.; Roglic, G.; Green, A.; Sicree, R.; King, H. Global prevalence of diabetes: Estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligita, T.; Wicking, K.; Francis, K.; Harvey, N.; Nurjannah, I. How people living with diabetes in Indonesia learn about their disease: A grounded theory study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, R.; Dennis, S.; Hasan, I.; Slewa, J.; Chen, W.; Tian, D.; Bobba, S.; Zwar, N. A systematic review of chronic disease management interventions in primary care. BMC Fam. Pr. 2018, 19, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdford, D.A. Pharmacoeconomics: From Theory to Practice. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2010, 74, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodrogi, J.; Kaló, Z. Principles of pharmacoeconomics and their impact on strategic imperatives of pharmaceutical research and development. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 159, 1367–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Suwantika, A.; Postma, M.J. Effect of breastfeeding promotion interventions on cost-effectiveness of rotavirus immunization in Indonesia. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statistics of West Java Province, Indonesia. Total Population in West Java Province, Indonesia. Available online: https://jabar.bps.go.id/dynamictable/2020/02/11/212/-jumlah-penduduk-dan-jenis-kelamin-menurut-kabupaten-kota-di-provinsi-jawa-barat-2019.html (accessed on 15 January 2020).
- West Java Province. In 2040, Approximately 642 Million People in the World Will Suffer Diabetes. Available online: https://jabarprov.go.id/index.php/news/26203/2040_Sebanyak_642_Juta_Penduduk_Dunia_Akan_Mengalami_Diabetes (accessed on 15 January 2020).
- Kalyani, R.R.; Egan, J.M. Diabetes and Altered Glucose Metabolism with Aging. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 42, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia Chee, W.; Egan Josephine, M.; Ferrucci, L. Age-Related Changes in Glucose Metabolism, Hyperglycemia, and Cardiovascular Risk. Circ. Res. 2018, 123, 886–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comino, E.J.; Harris, M.F.; Islam, M.D.F.; Tran, D.T.; Jalaludin, B.; Jorm, L.; Flack, J.; Haas, M. Impact of diabetes on hospital admission and length of stay among a general population aged 45 year or more: A record linkage study. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2015, 15, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allende-Vigo, M.Z.; González-Rosario, R.A.; González, L.; Sánchez, V.; Vega, M.A.; Alvarado, M.; Ramón, R.O. Inpatient Management of Diabets Mellitus among Noncritically Ill Patients at the University Hospital of Puerto Rico. Endocr. Pr. 2014, 20, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, H.; Kawai, K.; Kobayashi, M.; on behalf of the Japan Diabetes Clinical Data Management Study Group. Microalbuminuria Is Common in Japanese Type 2 Diabetic Patients: A nationwide survey from the Japan Diabetes Clinical Data Management Study Group (JDDM 10). Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 989–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retnakaran, R.; Cull, C.A.; Thorne, K.I.; Adler, A.I.; Holman, R.R.; for the UKPDS Study Group. Risk Factors for Renal Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes: U.K. Prospective Diabetes Study 74. Diabetes 2006, 55, 1832–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andayani, T.M.; Ibrahim, M.I.M.; Asdie, A.H. Assessing the Impact of Complications on the Direct Medical Costs of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Outpatients. Int. J. Curr. Pharm. Res. 2010, 2, 32–35. [Google Scholar]
- Soewondo, P.; Ferrario, A.; Tahapary, D.L. Challenges in diabetes management in Indonesia: A literature review. Glob. Health 2013, 9, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suwantika, A.A.; Zakiyah, N.; Lestari, K.; Postma, M.J. Accelerating the introduction of rotavirus immunization in Indonesia. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2014, 13, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gonçalves, A.C.O.; Cazarim, M.D.S.; Sanches, C.; Pereira, L.R.L.; Camargos, A.M.T.; Aquino, J.A.; Baldoni, A.O. Cost-effectiveness analysis of a pharmacotherapeutic empowerment strategy for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2019, 7, e000647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, K.R.; Ali, M.K.; Zhou, X.; Ng, B.P.; Jawanda, S.; Proia, K.; Zhang, X.; Gregg, E.W.; Albright, A.L.; Zhang, P. Cost-effectiveness of Interventions to Manage Diabetes: Has the Evidence Changed Since 2008? Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 1557–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, B.; Farzadfar, F.; Ghaderi, H.; Hadian, M. Cost effectiveness of type 2 diabetes screening: A systematic review. Med. J. Islam. Repub. Iran 2016, 30, 326. [Google Scholar]
- Piatt, G.; Ye, W.; Kuo, S.; Sinco, B.R.; Herman, W.H.; Spencer, M.S.; Palmisano, G.; Heisler, M.; Kieffer, E.C. Cost-Effectiveness of Diabetes Self-Management Education and Support in the Community—Projections from a Randomized Controlled Trial. Diabetes 2018, 67, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.C.; Driver, V.R.; Wrobel, J.S.; Armstrong, D.G. Foot ulcers in the diabetic patient, prevention and treatment. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2007, 3, 65–76. [Google Scholar]
| Category | Sub-Category | Total | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 58 | 43.28% |
| Female | 76 | 56.72% | |
| Ages (years) | 18–44 | 10 | 7.46% |
| 45–64 | 93 | 69.40% | |
| ≥65 | 31 | 23.14% | |
| Length of stay (days) | 1–3 | 14 | 10.45% |
| 4–10 | 73 | 54.48% | |
| >10 | 47 | 35.07% | |
| Types of T2DM complications | Without complication | 8 | 5.97% |
| Kidney disease | 104 | 77.61% | |
| PVD | 22 | 16.42% |
| Types of T2DM Complication | Year | Cost * | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hospital Room | Doctors’ Fee | Medicines | Laboratory Tests | Blood Transfusion | Medical Services | Total Cost | ||
| Without complication | 2014 | 2,647,000 | 500,000 | 2,456,500 | 1,439,500 | - | 345,940 | 7,388,940 |
| 2015 | 2,864,887 | 486,812 | 547,225 | 880,825 | - | 1,315,689 | 6,095,439 | |
| 2016 | 4,825,000 | 800,000 | 843,000 | 680,376 | - | 1,983,500 | 9,131,876 | |
| 2017 | 7,711,548 | 1,076,358 | 1,192,141 | 754,391 | 297,056 | 871,972 | 11,903,465 | |
| Average | 4,512,109 | 715,792 | 1,258,716 | 938,773 | 74,264 | 1,129,275 | 8,629,930 | |
| Complication of kidney disease | 2014 | 1,606,250 | 237,813 | 1,657,331 | 1,634,793 | 223,750 | 2,577,721 | 7,937,657 |
| 2015 | 1,948,082 | 288,436 | 2,047,165 | 1,834,698 | 151,364 | 2,277,201 | 8,546,946 | |
| 2016 | 2,424,766 | 509,571 | 2,716,532 | 2,651,687 | 856,325 | 3,364,893 | 12,523,774 | |
| 2017 | 4,048,111 | 451,043 | 3,106,726 | 2,556,657 | 455,057 | 3,873,361 | 14,490,955 | |
| Average | 2,506,802 | 371,716 | 2,381,939 | 2,169,459 | 421,624 | 3,023,294 | 10,874,833 | |
| Complication of PVD | 2014 | 7,055,200 | 1,427,500 | 10,563,515 | 3,629,325 | 618,300 | 9,194,600 | 32,488,440 |
| 2015 | 9,746,297 | 1,888,830 | 11,592,904 | 3,214,702 | 1,301,086 | 10,942,231 | 38,686,049 | |
| 2016 | 4,576,995 | 792,428 | 5,751,749 | 3,781,058 | 407,443 | 7,439,602 | 22,749,276 | |
| 2017 | 5,180,618 | 878,947 | 13,208,775 | 3,846,804 | 1,148,742 | 7,700,424 | 31,964,311 | |
| Average | 6,639,778 | 1,246,926 | 10,279,236 | 3,617,972 | 868,893 | 8,819,214 | 31,472,019 | |
| Types of T2DM Complication | Year | Cost * | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hospital Room | Doctors’ Fee | Medicines | Laboratory Tests | Blood Transfusion | Medical Services | Total Cost | ||
| Without complication | 2014 | 35.82% | 6.77% | 33.25% | 19.48% | 0.00% | 4.68% | 100.00% |
| 2015 | 47.00% | 7.99% | 8.98% | 14.45% | 0.00% | 21.58% | 100.00% | |
| 2016 | 52.84% | 8.76% | 9.23% | 7.45% | 0.00% | 21.72% | 100.00% | |
| 2017 | 64.78% | 9.04% | 10.02% | 6.34% | 2.50% | 7.33% | 100.00% | |
| Average | 50.11% | 8.14% | 15.37% | 11.93% | 0.62% | 13.83% | 100.00% | |
| Complication of kidney disease | 2014 | 20.24% | 3.00% | 20.88% | 20.60% | 2.82% | 32.47% | 100.00% |
| 2015 | 22.79% | 3.37% | 23.95% | 21.47% | 1.77% | 26.64% | 100.00% | |
| 2016 | 19.36% | 4.07% | 21.69% | 21.17% | 6.84% | 26.87% | 100.00% | |
| 2017 | 27.94% | 3.11% | 21.44% | 17.64% | 3.14% | 26.73% | 100.00% | |
| Average | 22.58% | 3.39% | 21.99% | 20.22% | 3.64% | 28.18% | 100.00% | |
| Complication of PVD | 2014 | 21.72% | 4.39% | 32.51% | 11.17% | 1.90% | 28.30% | 100.00% |
| 2015 | 25.19% | 4.88% | 29.97% | 8.31% | 3.36% | 28.28% | 100.00% | |
| 2016 | 20.12% | 3.48% | 25.28% | 16.62% | 1.79% | 32.70% | 100.00% | |
| 2017 | 16.21% | 2.75% | 41.32% | 12.03% | 3.59% | 24.09% | 100.00% | |
| Average | 20.81% | 3.88% | 32.27% | 12.03% | 2.66% | 28.34% | 100.00% | |
| Year | Types of T2DM Complication | Total Cost (IDR) | Blood Glucose Reduction (mg/dL) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | Without complication | 11,330,400 | 95 | 0.01639 * |
| Complication of kidney disease | 15,064,238 | 98 | ||
| Complication of PVD | 21,475,940 | 65 | ||
| 2015 | Without complication | 11,031,545 | 121 | 0.01747 * |
| Complication of kidney disease | 14,813,909 | 84 | ||
| Complication of PVD | 21,377,659 | 169 | ||
| 2016 | Without complication | 6,094,319 | 54 | 0.02735 * |
| Complication of kidney disease | 9,663,898 | 93 | ||
| Complication of PVD | 14,614,062 | 87 | ||
| 2017 | Without complication | 9,832,741 | 15 | 0.00227 * |
| Complication of kidney disease | 10,396,008 | 64 | ||
| Complication of PVD | 12,256,473 | 98 | ||
| Average | Without complication | 9,572,251 | 71 | 0.01453 * |
| Complication of kidney disease | 12,484,513 | 85 | ||
| Complication of PVD | 17,431,034 | 105 | ||
| ICER ** | Complication of kidney disease | IDR 215,723 | ||
| per 1 mg/dL blood glucose reduction | ||||
| Complication of PVD | IDR 234,591 | |||
| per 1 mg/dL blood glucose reduction | ||||
| Year | Types of T2DM Complication | Total Cost (IDR) | Blood Glucose Reduction (mg/dL) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | Without complication | 7,388,940 | 95 | 0.097 |
| Complication of kidney disease | 7,937,657 | 98 | ||
| Complication of PVD | 32,488,440 | 65 | ||
| 2015 | Without complication | 6,095,439 | 121 | 0.11595 |
| Complication of kidney disease | 8,546,946 | 84 | ||
| Complication of PVD | 38,686,049 | 169 | ||
| 2016 | Without complication | 9,131,875 | 54 | 0.03434 * |
| Complication of kidney disease | 12,523,774 | 93 | ||
| Complication of PVD | 22,749,276 | 87 | ||
| 2017 | Without complication | 11,903,465 | 15 | 0.04541 * |
| Complication of kidney disease | 14,490,955 | 64 | ||
| Complication of PVD | 31,964,311 | 98 | ||
| Average | Without complication | 8,629,930 | 71 | 0.07219 |
| Complication of kidney disease | 10,874,833 | 85 | ||
| Complication of PVD | 31,472,019 | 105 | ||
| ICER ** | Complication of kidney disease | IDR 166,289 | ||
| per 1 mg/dL blood glucose reduction | ||||
| Complication of PVD | IDR 681,853 | |||
| per 1 mg/dL blood glucose reduction | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Priyadi, A.; Permana, H.; Muhtadi, A.; Sumiwi, S.A.; Sinuraya, R.K.; Suwantika, A.A. Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) Treatment in Patients with Complications of Kidney and Peripheral Vascular Diseases in Indonesia. Healthcare 2021, 9, 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9020211
Priyadi A, Permana H, Muhtadi A, Sumiwi SA, Sinuraya RK, Suwantika AA. Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) Treatment in Patients with Complications of Kidney and Peripheral Vascular Diseases in Indonesia. Healthcare. 2021; 9(2):211. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9020211
Chicago/Turabian StylePriyadi, Akhmad, Hikmat Permana, Ahmad Muhtadi, Sri A. Sumiwi, Rano K. Sinuraya, and Auliya A. Suwantika. 2021. "Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) Treatment in Patients with Complications of Kidney and Peripheral Vascular Diseases in Indonesia" Healthcare 9, no. 2: 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9020211
APA StylePriyadi, A., Permana, H., Muhtadi, A., Sumiwi, S. A., Sinuraya, R. K., & Suwantika, A. A. (2021). Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) Treatment in Patients with Complications of Kidney and Peripheral Vascular Diseases in Indonesia. Healthcare, 9(2), 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9020211






