From Altered Metabolic and Anthropometric Parameters to Metabolic Syndrome: A Cross-Sectional Survey on the Effectiveness and Safety of Neo-Policaptil® Gel Retard
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Product
2.2. Survey Design
2.3. Statistical Analysis
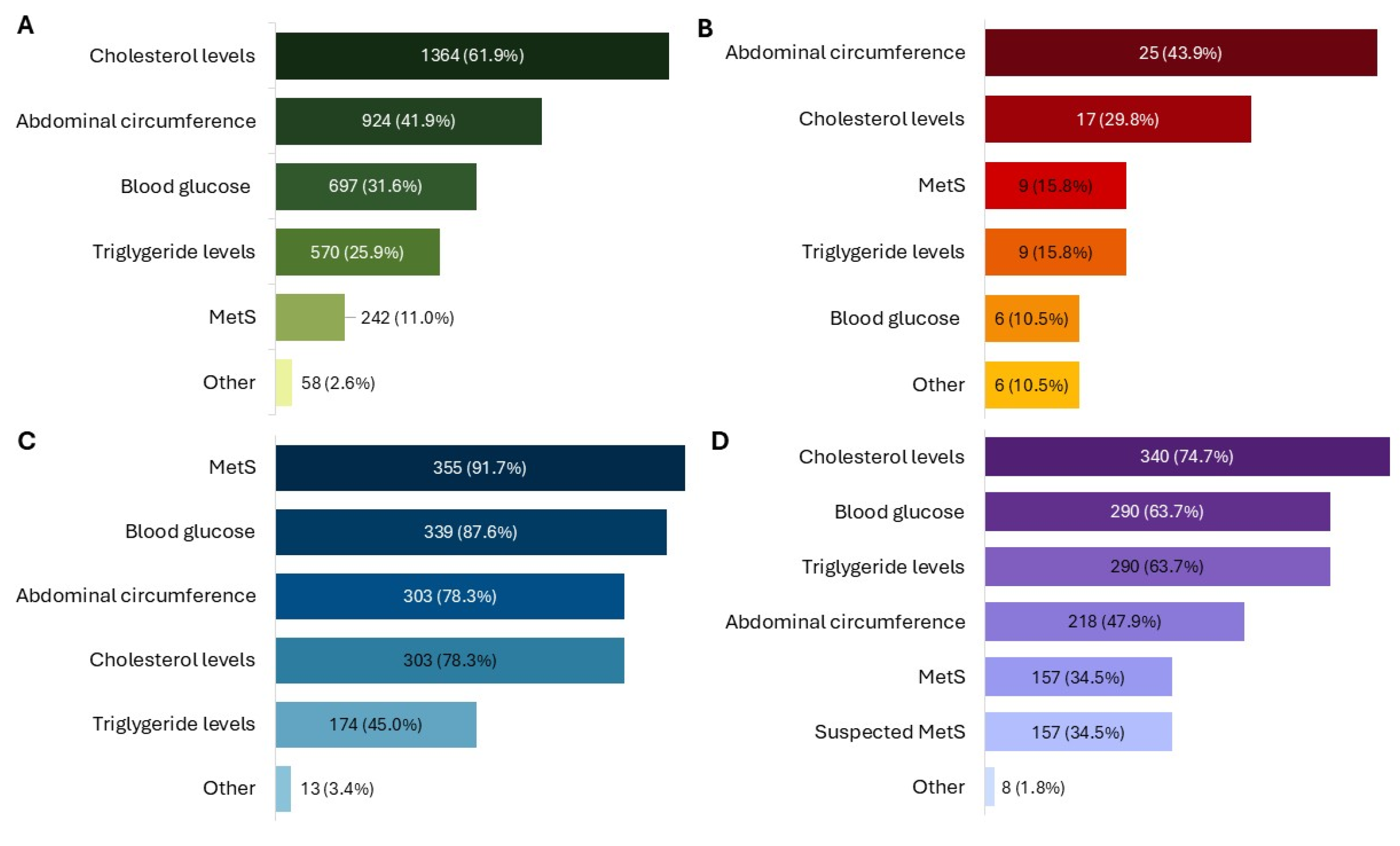
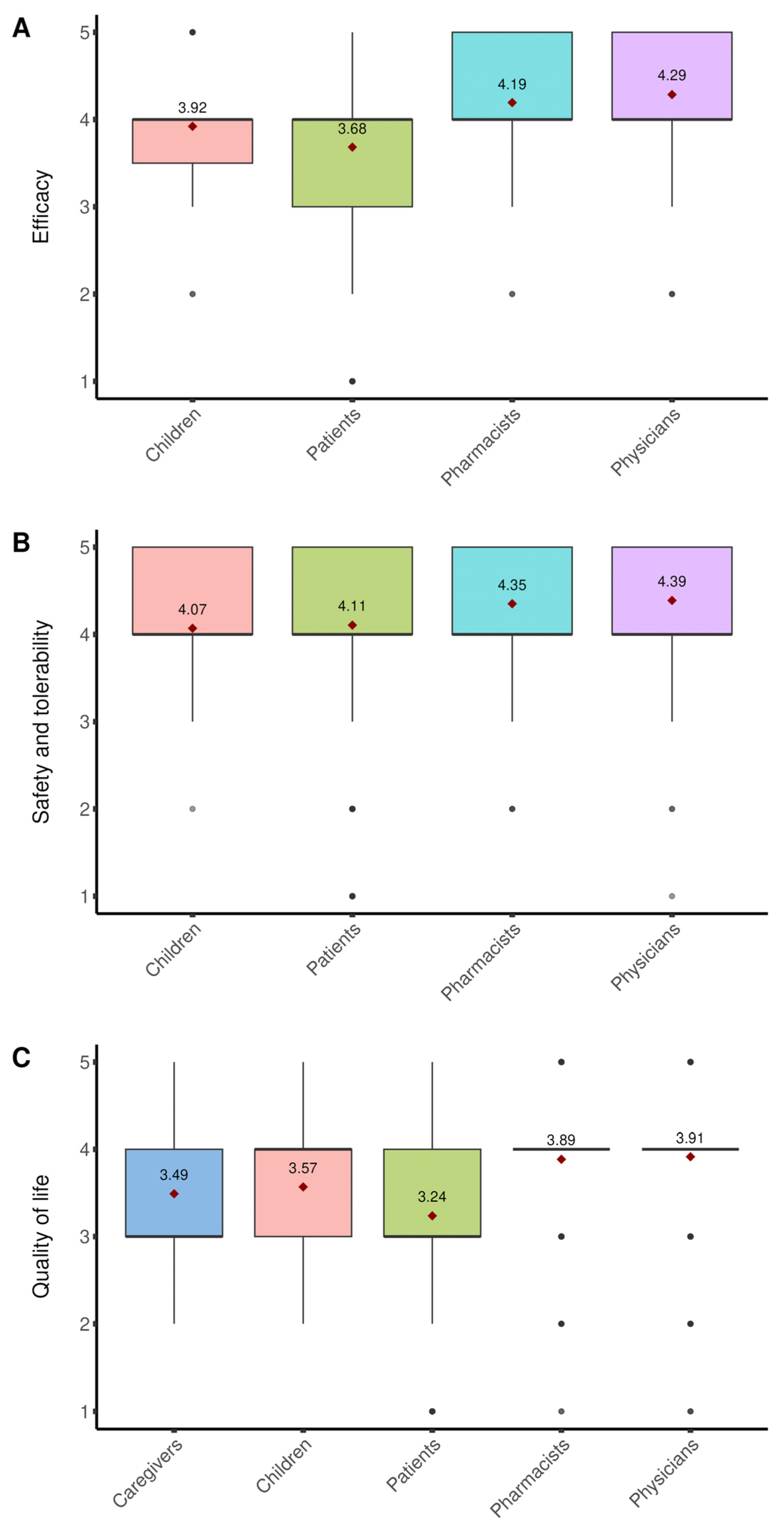
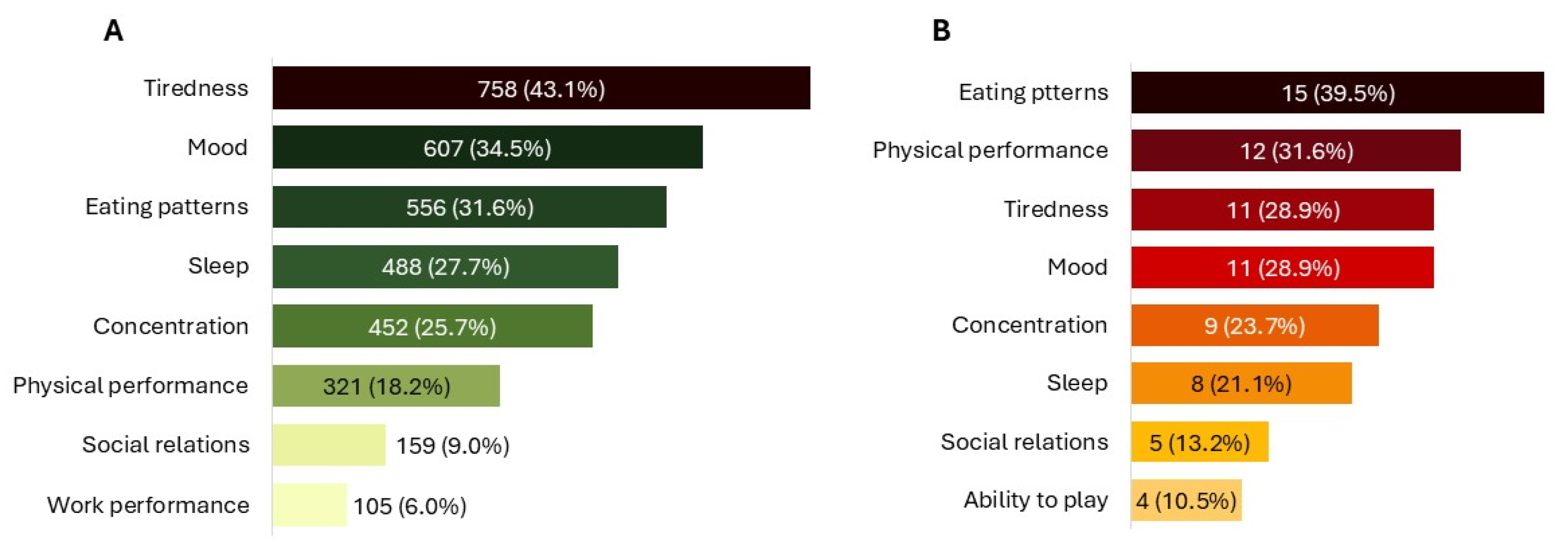
3. Results
3.1. Patients/Child Caregivers
3.1.1. Direct Use
3.1.2. Child Administration
3.2. Physicians
3.3. Pharmacists
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MetS | Metabolic syndrome |
| QoL | Quality of life |
| HCPs | Healthcare professionals |
| TG | Triglycerides |
| HDL-C | High-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| IFG | Impaired fasting glucose |
| IGT | Impaired glucose tolerance |
| MTF | Metformin |
| SBMD | Substance-based medical device |
| NPGR | Neo-Policaptil® Gel Retard |
| RWD | Real world data |
| PGR | Policaptil Gel Retard® |
| GPs | General practitioners |
| GLP-1 | Glucagon-like peptide-1 |
| USEs | Unusual serious events |
| RWE | Real-world evidence |
| MAFLD | Metabolic non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
References
- Alberti, K.G.M.M.; Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Cleeman, J.I.; Donato, K.A.; Fruchart, J.-C.; James, W.P.T.; Loria, C.M.; Smith, S.C. Harmonizing the Metabolic Syndrome: A Joint Interim Statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation 2009, 120, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmet, P.; Alberti, K.G.M.; Kaufman, F.; Tajima, N.; Silink, M.; Arslanian, S.; Wong, G.; Bennett, P.; Shaw, J.; Caprio, S.; et al. The Metabolic Syndrome in Children and Adolescents? An IDF Consensus Report. Pediatr. Diabetes 2007, 8, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nsiah, K.; Shang, V.O.; Boateng, K.; Mensah, F. Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients. Int. J. Appl. Basic Med. Res. 2015, 5, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, M.; Varghese, T.P.; Sharma, R.; Chand, S. Association Between Metabolic Syndrome and Diabetes Mellitus According to International Diabetic Federation and National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III Criteria: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2020, 19, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgert, T.S.; Taksali, S.E.; Dziura, J.; Goodman, T.R.; Yeckel, C.W.; Papademetris, X.; Constable, R.T.; Weiss, R.; Tamborlane, W.V.; Savoye, M.; et al. Alanine Aminotransferase Levels and Fatty Liver in Childhood Obesity: Associations with Insulin Resistance, Adiponectin, and Visceral Fat. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 4287–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBoer, M.D. Assessing and Managing the Metabolic Syndrome in Children and Adolescents. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, J.A.; Friedman, L.A.; Wang, P.; Glueck, C.J. Metabolic Syndrome in Childhood Predicts Adult Metabolic Syndrome and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus 25 to 30 Years Later. J. Pediatr. 2008, 152, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntner, P.; Menke, A.; Srinivasan, S.; Patel, D.A.; Chen, W.; Berenson, G. Impact of Childhood Metabolic Syndrome Components on the Risk of Elevated Uric Acid in Adulthood: The Bogalusa Heart Study. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2008, 335, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirode, G.; Wong, R.J. Trends in the Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in the United States, 2011–2016. JAMA 2020, 323, 2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forouzanfar, M.H.; Afshin, A.; Alexander, L.T.; Anderson, H.R.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Biryukov, S.; Brauer, M.; Burnett, R.; Cercy, K.; Charlson, F.J.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Comparative Risk Assessment of 79 Behavioural, Environmental and Occupational, and Metabolic Risks or Clusters of Risks, 1990–2015: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 2016, 388, 1659–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The GBD 2015 Obesity Collaborators. Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity in 195 Countries over 25 Years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 13–27. [CrossRef]
- Gepstein, V.; Weiss, R. Obesity as the Main Risk Factor for Metabolic Syndrome in Children. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swinburn, B.A.; Kraak, V.I.; Allender, S.; Atkins, V.J.; Baker, P.I.; Bogard, J.R.; Brinsden, H.; Calvillo, A.; De Schutter, O.; Devarajan, R.; et al. The Global Syndemic of Obesity, Undernutrition, and Climate Change: The Lancet Commission Report. Lancet 2019, 393, 791–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinehr, T.; de Sousa, G.; Toschke, A.M.; Andler, W. Comparison of Metabolic Syndrome Prevalence Using Eight Different Definitions: A Critical Approach. Arch. Dis. Child. 2007, 92, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelin, A.-M.; Mătăsaru, S. Metabolic Syndrome in Obese Children and Adolescents. Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat. Iasi 2012, 116, 957–961. [Google Scholar]
- Taskinen, M.-R.; Packard, C.J.; Borén, J. Dietary Fructose and the Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortera, R.R.; Bains, Y.; Gugliucci, A. Fructose at the Crossroads of the Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity Epidemics. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2019, 24, 186–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhupathiraju, S.N.; Hu, F.B. Epidemiology of Obesity and Diabetes and Their Cardiovascular Complications. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 1723–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaquero Alvarez, M.; Aparicio-Martinez, P.; Fonseca Pozo, F.J.; Valle Alonso, J.; Blancas Sánchez, I.M.; Romero-Saldaña, M. A Sustainable Approach to the Metabolic Syndrome in Children and Its Economic Burden. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancia, G.; Bombelli, M.; Facchetti, R.; Casati, A.; Ronchi, I.; Quarti-Trevano, F.; Arenare, F.; Grassi, G.; Sega, R. Impact of Different Definitions of the Metabolic Syndrome on the Prevalence of Organ Damage, Cardiometabolic Risk and Cardiovascular Events. J. Hypertens. 2010, 28, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberger, J.; Daniels, S.R.; Eckel, R.H.; Hayman, L.; Lustig, R.H.; McCrindle, B.; Mietus-Snyder, M.L. Progress and Challenges in Metabolic Syndrome in Children and Adolescents: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association Atherosclerosis, Hypertension, and Obesity in the Young Committee of the Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young; Council on Cardiovascular Nursing; and Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism. Circulation 2009, 119, 628–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, K.F.; Sweat, V.; Yau, P.L.; Turchiano, M.M.; Convit, A. Impact of Metabolic Syndrome on Cognition and Brain: A Selected Review of the Literature. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 2060–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.M.Y.; Huxley, R.R.; Wildman, R.P.; Woodward, M. Indices of Abdominal Obesity Are Better Discriminators of Cardiovascular Risk Factors than BMI: A Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2008, 61, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, H.J.; Glaesmer, H.; Klotsche, J.; Böhler, S.; Lehnert, H.; Zeiher, A.M.; März, W.; Pittrow, D.; Stalla, G.K.; Wittchen, H.-U.; et al. Accuracy of Anthropometric Indicators of Obesity to Predict Cardiovascular Risk. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arumugam, V.; Lee, J.-S.; Nowak, J.K.; Pohle, R.J.; Nyrop, J.E.; Leddy, J.J.; Pelkman, C.L. A High-Glycemic Meal Pattern Elicited Increased Subjective Appetite Sensations in Overweight and Obese Women. Appetite 2008, 50, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabák, A.G.; Herder, C.; Rathmann, W.; Brunner, E.J.; Kivimäki, M. Prediabetes: A High-Risk State for Diabetes Development. Lancet 2012, 379, 2279–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ference, B.A.; Ginsberg, H.N.; Graham, I.; Ray, K.K.; Packard, C.J.; Bruckert, E.; Hegele, R.A.; Krauss, R.M.; Raal, F.J.; Schunkert, H.; et al. Low-Density Lipoproteins Cause Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. 1. Evidence from Genetic, Epidemiologic, and Clinical Studies. A Consensus Statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 2459–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Onis, M. Development of a WHO Growth Reference for School-Aged Children and Adolescents. Bull. World Health Organ. 2007, 85, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnussen, C.G.; Koskinen, J.; Chen, W.; Thomson, R.; Schmidt, M.D.; Srinivasan, S.R.; Kivimäki, M.; Mattsson, N.; Kähönen, M.; Laitinen, T.; et al. Pediatric Metabolic Syndrome Predicts Adulthood Metabolic Syndrome, Subclinical Atherosclerosis, and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus but Is No Better Than Body Mass Index Alone: The Bogalusa Heart Study and the Cardiovascular Risk in Young Finns Study. Circulation 2010, 122, 1604–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, S.M.; Shalaby, M.A.; El-Shiekh, R.A.; El-Banna, H.A.; Emam, S.R.; Bakr, A.F. Metabolic Syndrome: Risk Factors, Diagnosis, Pathogenesis, and Management with Natural Approaches. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 3, 100335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.; Sanders, R.A. Metabolic Syndrome. Pediatr. Rev. 2012, 33, 459–466; quiz 467–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caranti, D.A.; de Mello, M.T.; Prado, W.L.; Tock, L.; Siqueira, K.O.; de Piano, A.; Lofrano, M.C.; Cristofalo, D.M.J.; Lederman, H.; Tufik, S.; et al. Short- and Long-Term Beneficial Effects of a Multidisciplinary Therapy for the Control of Metabolic Syndrome in Obese Adolescents. Metabolism 2007, 56, 1293–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowler, W.C.; Barrett-Connor, E.; Fowler, S.E.; Hamman, R.F.; Lachin, J.M.; Walker, E.A.; Nathan, D.M. Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group Reduction in the Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes with Lifestyle Intervention or Metformin. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.X.; Gurka, M.J.; Deboer, M.D. Metabolic Syndrome Severity and Lifestyle Factors among Adolescents. Minerva Pediatr. 2018, 70, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rask Larsen, J.; Dima, L.; Correll, C.U.; Manu, P. The Pharmacological Management of Metabolic Syndrome. Expert. Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 11, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornari, E.; Maffeis, C. Treatment of Metabolic Syndrome in Children. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Palomo, F.; Moreno-Cabañas, A.; Ramirez-Jimenez, M.; Alvarez-Jimenez, L.; Valenzuela, P.L.; Lucia, A.; Ortega, J.F.; Mora-Rodriguez, R. Exercise Reduces Medication for Metabolic Syndrome Management: A 5-Year Follow-Up Study. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2021, 53, 1319–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khera, R.; Murad, M.H.; Chandar, A.K.; Dulai, P.S.; Wang, Z.; Prokop, L.J.; Loomba, R.; Camilleri, M.; Singh, S. Association of Pharmacological Treatments for Obesity with Weight Loss and Adverse Events: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA 2016, 315, 2424–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weihe, P.; Weihrauch-Blüher, S. Metabolic Syndrome in Children and Adolescents: Diagnostic Criteria, Therapeutic Options and Perspectives. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2019, 8, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, M.B. Metformin Should Not Be Used to Treat Prediabetes. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 1983–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, E.; Atkinson, G.; Richter, B.; Metzendorf, M.-I.; Baur, L.; Finer, N.; Corpeleijn, E.; O’Malley, C.; Ells, L.J. Drug Interventions for the Treatment of Obesity in Children and Adolescents. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 11, CD012436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboca. Available online: https://www.aboca.com/product/metarecod/ (accessed on 15 November 2025).
- Guarino, G.; Strollo, F.; Della-Corte, T.; Satta, E.; Romano, C.; Alfarone, C.; Corigliano, G.; Corigliano, M.; Cozzolino, G.; Brancario, C.; et al. Comparison between Policaptil Gel Retard and Metformin by Testing of Temporal Changes in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome and Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetology 2022, 3, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, G.; Strollo, F.; Malfertheiner, P.; Della Corte, T.; Stagi, S.; Masarone, M.; Gentile, S. Efficacy and Safety of a Polysaccharide-Based Natural Substance Complex in the Treatment of Obesity and Other Metabolic Syndrome Components: A Systematic Review. Front. Drug Saf. Regul. 2022, 2, 844256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centorame, G.; Baldassarre, M.P.A.; Di Dalmazi, G.; Gambacorta, F.; Febo, F.; Consoli, A.; Formoso, G. Policaptil Gel Retard® Reduces Body Weight and Improves Insulin Sensitivity in Obese Subjects. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2022, 34, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stagi, S.; Papacciuoli, V.; Ciofi, D.; Piccini, B.; Farello, G.; Toni, S.; Ferrari, M.; Chiarelli, F. Retrospective Evaluation on the Use of a New Polysaccharide Complex in Managing Paediatric Type 1 Diabetes with Metabolic Syndrome (MetS). Nutrients 2021, 13, 3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, G.; Strollo, F.; Della Corte, T.; Satta, E.; Gentile, S. Effect of Neo-Policaptil Gel Retard on Liver Fat Content and Fibrosis in Adults with Metabolic Syndrome and Type 2 Diabetes: A Non-Invasive Approach to MAFLD. Diabetes Ther. 2023, 14, 2089–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornari, E.; Morandi, A.; Piona, C.; Tommasi, M.; Corradi, M.; Maffeis, C. Policaptil Gel Retard Intake Reduces Postprandial Triglycerides, Ghrelin and Appetite in Obese Children: A Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deehan, E.C.; Mocanu, V.; Madsen, K.L. Effects of Dietary Fibre on Metabolic Health and Obesity. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 21, 301–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papathanasopoulos, A.; Camilleri, M. Dietary Fiber Supplements: Effects in Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome and Relationship to Gastrointestinal Functions. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 65–72.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercati, V.; Marini, F.; Aboca SpA Societa Agricola. New System with Emerging Properties for Use in the Treatment of Metabolic Syndrome. US Patent US20230354869A1, 9 November 2023. [Google Scholar]
- European Union. Regulation (EU) 2017/745 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 5 April 2017 on Medical Devices, Amending Directive 2001/83/EC, Regulation (EC) No 178/2002 and Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 and Repealing Council Directives 90/385/EEC and 93/42/EEC (Text with EEA Relevance); European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cioeta, R.; Cossu, A.; Giovagnoni, E.; Rigoni, M.; Muti, P. A New Platform for Post-Marketing Surveillance and Real-World Evidence Data Collection for Substance-Based Medical Devices. Front. Drug Saf. Regul. 2022, 2, 992359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundell, S.; Toots, A.; Sönnerfors, P.; Halvarsson, A.; Wadell, K. Participatory Methods in a Digital Setting: Experiences from the Co-Creation of an eHealth Tool for People with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2022, 22, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RAOSOFT. Sample Size Calculator. Available online: http://www.raosoft.com/samplesize.html (accessed on 9 December 2025).
- Jaksa, A.; Arena, P.J.; Hanisch, M.; Marsico, M. Use of Real-World Evidence in Health Technology Reassessments Across 6 Health Technology Assessment Agencies. Value Health 2025, 28, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, M.; Tang, S.; Zhang, F.; Fu, S.; Ding, H.; Cha, Y.; Ma, X.; Shi, Y.; Cai, Y. Chemical Exposure in Females of Childbearing Age Associated with Sex Hormones: Evidence from an Untargeted Exposomic Approach. Environ. Int. 2025, 197, 109362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cioeta, R.; Muti, P.; Rigoni, M.; Morlando, L.; Siragusa, F.; Cossu, A.; Giovagnoni, E. Effectiveness and Tolerability of Poliprotect, a Natural Mucosal Protective Agent for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease and Dyspepsia: Surveys from Patients, Physicians, and Pharmacists. Front. Drug Saf. Regul. 2022, 2, 969831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogacci, F.; ALGhasab, N.S.; Di Micoli, V.; Giovannini, M.; Cicero, A.F.G. Cholesterol-Lowering Bioactive Foods and Nutraceuticals in Pediatrics: Clinical Evidence of Efficacy and Safety. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghavami, A.; Ziaei, R.; Talebi, S.; Barghchi, H.; Nattagh-Eshtivani, E.; Moradi, S.; Rahbarinejad, P.; Mohammadi, H.; Ghasemi-Tehrani, H.; Marx, W.; et al. Soluble Fiber Supplementation and Serum Lipid Profile: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Adv. Nutr. 2023, 14, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachos, D.; Malisova, S.; Lindberg, F.A.; Karaniki, G. Glycemic Index (GI) or Glycemic Load (GL) and Dietary Interventions for Optimizing Postprandial Hyperglycemia in Patients with T2 Diabetes: A Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmari, L.A. Dietary Fiber Influence on Overall Health, with an Emphasis on CVD, Diabetes, Obesity, Colon Cancer, and Inflammation. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1510564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Baek, Y.; Lee, S. Consumption of Dietary Fiber and APOA5 Genetic Variants in Metabolic Syndrome: Baseline Data from the Korean Medicine Daejeon Citizen Cohort Study. Nutr. Metab. 2024, 21, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veluvali, A.; Snyder, M. Dietary Fiber Deficiency in Individuals with Metabolic Syndrome: A Review. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2023, 26, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, C.M.; Garetto, S.; Montellier, E.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Baldi, P.; Sassone-Corsi, P.; Lucci, J. A Non-Pharmacological Therapeutic Approach in the Gut Triggers Distal Metabolic Rewiring Capable of Ameliorating Diet-Induced Dysfunctions Encompassed by Metabolic Syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRorie, J.W. Evidence-Based Approach to Fiber Supplements and Clinically Meaningful Health Benefits, Part 1: What to Look for and How to Recommend an Effective Fiber Therapy. Nutr. Today 2015, 50, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, G.; Della Corte, T.; Strollo, F.; Gentile, S. Policaptil Gel Retard in Adult Subjects with the Metabolic Syndrome: Efficacy, Safety, and Tolerability Compared to Metformin. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2021, 15, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holscher, H.D. Dietary Fiber and Prebiotics and the Gastrointestinal Microbiota. Gut Microbes 2017, 8, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proietti, G.; Burico, M.; Quintiero, C.M.; Giovagnoni, E.; Mercati, V.; Gianni, M.; Mattoli, L. Ready Biodegradability Study and Insights with Ultra-high-performance Liquid Chromatograph Coupled to a Quadrupole Time of Flight of a Metformin-based Drug and of Metarecod, a Natural Substance-Based Medical Device. J. Mass Spectrom. 2023, 58, e4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gabriele, E.; Cioeta, R.; Muti, P.; Rigoni, M.; La Salvia, R.; Cossu, A.; Giovagnoni, E. From Altered Metabolic and Anthropometric Parameters to Metabolic Syndrome: A Cross-Sectional Survey on the Effectiveness and Safety of Neo-Policaptil® Gel Retard. Healthcare 2025, 13, 3293. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13243293
Gabriele E, Cioeta R, Muti P, Rigoni M, La Salvia R, Cossu A, Giovagnoni E. From Altered Metabolic and Anthropometric Parameters to Metabolic Syndrome: A Cross-Sectional Survey on the Effectiveness and Safety of Neo-Policaptil® Gel Retard. Healthcare. 2025; 13(24):3293. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13243293
Chicago/Turabian StyleGabriele, Elena, Roberto Cioeta, Paola Muti, Marta Rigoni, Roberta La Salvia, Andrea Cossu, and Emiliano Giovagnoni. 2025. "From Altered Metabolic and Anthropometric Parameters to Metabolic Syndrome: A Cross-Sectional Survey on the Effectiveness and Safety of Neo-Policaptil® Gel Retard" Healthcare 13, no. 24: 3293. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13243293
APA StyleGabriele, E., Cioeta, R., Muti, P., Rigoni, M., La Salvia, R., Cossu, A., & Giovagnoni, E. (2025). From Altered Metabolic and Anthropometric Parameters to Metabolic Syndrome: A Cross-Sectional Survey on the Effectiveness and Safety of Neo-Policaptil® Gel Retard. Healthcare, 13(24), 3293. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13243293





