Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in the Treatment of Crohn’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lavy, A.; Weisz, G.; Adir, Y.; Ramon, Y.; Melamed, Y.; Eidelman, S. Hyperbaric oxygen for perianal Crohn’s disease. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 1994, 19, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.L.; Shaffer, V.O. Modern Management of Perianal Crohn’s Disease: A Review. Am. Surg. 2021, 87, 1361–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petagna, L.; Antonelli, A.; Ganini, C.; Bellato, V.; Campanelli, M.; Divizia, A.; Efrati, C.; Franceschilli, M.; Guida, A.M.; Ingallinella, S.; et al. Pathophysiology of Crohn’s disease inflammation and recurrence. Biol. Direct 2020, 15, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgart, D.C.; Carding, S.R. Inflammatory bowel disease: Cause and immunobiology. Lancet 2007, 369, 1627–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cushing, K.; Higgins, P.D.R. Management of Crohn Disease: A Review. JAMA 2021, 325, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftus, E.V., Jr. Crohn’s Disease: Etiology, Complications, Assessment, Therapy, and Management. Gastroenterol. Clin. North Am. 2017, 46, xiii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, H.; Fichera, A.; Hurst, R.D.; Michelassi, F. Crohn’s Disease. In Maingot’s Abdominal Operations, 13th ed.; Zinner, M.J., Ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Beaugerie, L.; Langholz, E.; Nyboe-Andersen, N.; Pigneur, B.; Soko, H. Differences in epidemiological features between ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease: The early life-programmed versus late dysbiosis hypothesis. Med. Hypotheses 2018, 115, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovde, Ø.; Moum, B.A. Epidemiology and clinical course of Crohn’s disease: Results from observational studies. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 1723–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gravina, A.G.; Panarese, I.; Trotta, M.C.; D’Amico, M.; Pellegrino, R.; Ferraraccio, F.; Galdiero, M.; Alfano, R.; Grieco, P.; Federico, A. Melanocortin 3,5 receptors immunohistochemical expression in colonic mucosa of inflammatory bowel disease patients: A matter of disease activity? World J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 30, 1132–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravina, A.G.; Pellegrino, R.; Durante, T.; Palladino, G.; Imperio, G.; D’amico, G.; Trotta, M.C.; Dallio, M.; Romeo, M.; D’amico, M.; et al. The Melanocortin System in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Insights into Its Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potentials. Cells 2023, 12, 1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Chu, J.; Feng, S.; Guo, C.; Xue, B.; He, K.; Li, L. Immunological mechanisms of inflammatory diseases caused by gut microbiota dysbiosis: A review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 164, 114985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummins, E.P.; Crean, D. Hypoxia and inflammatory bowel disease. Microbes Infect. 2017, 19, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eltzschig, H.K.; Carmeliet, P. Hypoxia and inflammation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gren, S.T.; Grip, O. Role of Monocytes and Intestinal Macrophages in Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2016, 22, 1992–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alemany-Cosme, E.; Sáez-González, E.; Moret, I.; Mateos, B.; Iborra, M.; Nos, P.; Sandoval, J.; Beltrán, B. Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis of Crohn’s Disease and the Interconnection with Immunological Response, Microbiota, External Environmental Factors, and Epigenetics. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J. Pathomechanisms of Oxidative Stress in Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Potential Antioxidant Therapies. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 4535194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzoghaibi, M.A. Concepts of oxidative stress and antioxidant defense in Crohn’s disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 6540–6547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisham, M.B. Oxidants and free radicals in inflammatory bowel disease. Lancet 1994, 344, 859–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iborra, M.; Moret, I.; Rausell, F.; Bastida, G.; Aguas, M.; Cerrillo, E.; Nos, P.; Beltrán, B. Role of oxidative stress and antioxidant enzymes in Crohn’s disease. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2011, 39, 1102–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidemann, J.; Domschke, W.; Kucharzik, T.; Maaser, C. Intestinal microvascular endothelium and innate immunity in inflammatory bowel disease: A second line of defense? Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 5425–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moret-Tatay, I.; Iborra, M.; Cerrillo, E.; Tortosa, L.; Nos, P.; Beltrán, B. Possible Biomarkers in Blood for Crohn’s Disease: Oxidative Stress and MicroRNAs-Current Evidences and Further Aspects to Unravel. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 2325162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, S.; Qi, C.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, R.; Xiang, L.; Chen, L.; Zhu, Y.; Tang, C.; et al. Oxidative stress gene expression, DNA methylation, and gut microbiota interaction trigger Crohn’s disease: A multi-omics Mendelian randomization study. BMC Med. 2023, 21, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soufli, I.; Hablal, A.; Bessaad, S.; Amri, M.; Labsi, M.; Boussa, R.S.; Ameur, F.; Belguendouz, H.; Younes, S.A.; Idris, N.S.; et al. Nitric Oxide, Neutrophil/Lymphocyte, and Platelet/Lymphocyte Ratios as Promising Inflammatory Biomarkers in Complicated Crohn’s Disease: Outcomes of Corticosteroids and Anti-TNF-α Therapies. Inflammation 2023, 46, 1091–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messaris, E.; Dassopoulos, T. Concepts in inflammatory bowel disease management. In Shackelford’s Surgery of the Alimentary tract, 8th ed.; Yeo, C.J., Ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 1888–1918. [Google Scholar]
- Worsey, M.J.; Hull, T.; Ryland, L.; Fazio, V. Strictureplasty is an effective option in the operative management of duodenal Crohn’s disease. Dis. Colon Rectum 1999, 42, 596–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taschieri, A.M.; Cristaldi, M.; Elli, M.; Danelli, P.G.; Molteni, B.; Rovati, M.; Porro, G.B. Description of new “bowel-sparing” techniques for long strictures of Crohn’s disease. Am. J. Surg. 1997, 173, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boscá, M.M.; Alós, R.; Maroto, N.; Gisbert, J.P.; Beltrán, B.; Chaparro, M.; Nos, P.; Mínguez, M.; Hinojosa, J. Recommendations of the Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis Spanish Working Group (GETECCU) for the treatment of perianal fistulas of Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 43, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Cheon, J.H. Updates on conventional therapies for inflammatory bowel diseases: 5-aminosalicylates, corticosteroids, immunomodulators, and anti-TNF-α. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2022, 37, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alenazi, N.; Alsaeed, H.; Alsulami, A.; Alanzi, T. A Review of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 7099–7105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossignol, D.A. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment for inflammatory bowel disease: A systematic review and analysis. Med. Gas. Res. 2012, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lansdorp, C.A.; Buskens, C.J.; Gecse, K.B.; D’haens, G.R.; Van Hulst, R. Wound healing of metastatic perineal Crohn’s disease using hyperbaric oxygen therapy: A case series. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2020, 8, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, C.E.; Cooley, B.J.; Davis, J.C. Healing of severe perineal and cutaneous Crohn’s disease with hyperbaric oxygen. Gastroenterology 1989, 97, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, E.W., Jr.; Bright, D.E.; Villar, L.F. Closure of refractory perineal Crohn’s lesion. Integration of hyperbaric oxygen into case management. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1990, 35, 1561–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dulai, P.S.; Gleeson, M.W.; Taylor, D.; Holubar, S.D.; Buckey, J.C.; Siegel, C.A. Systematic review: The safety and efficacy of hyperbaric oxygen therapy for inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 1266–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakutis, F.S.; Nishitokukado, I.; dos Santos, F.M.; Ortiz-Agostinho, C.L.; de Alencar, D.T.; Achtschin, C.G.; Nunes, V.S.; Leite, A.Z.A.; Sipahi, A.M. Evaluation of oxidative stress in an experimental model of Crohn’s disease treated with hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Clinics 2023, 78, 100305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feitosa, M.R.; Parra, R.S.; Machado, V.F.; Vilar, G.N.; Aquino, J.C.; Rocha, J.J.R.; Kotze, P.G.; Féres, O. Adjunctive Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Refractory Crohn’s Disease: An Observational Study. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2021, 2021, 6628142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lansdorp, C.A.; Gecse, K.B.; Buskens, C.J.; Löwenberg, M.; Stoker, J.; Bemelman, W.A.; D’haens, G.R.; van Hulst, R.A. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for the treatment of perianal fistulas in 20 patients with Crohn’s disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 53, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansdorp, C.A.; Buskens, C.J.; Gecse, K.B.; Löwenberg, M.; Stoker, J.; Bemelman, W.A.; D’haens, G.R.A.M.; van Hulst, R.A. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for the treatment of perianal fistulas in 20 patients with Crohn’s disease: Results of the HOT-TOPIC trial after 1-year follow-up. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2022, 10, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bafutto, M.; Oliveira, E.C.; Bafutto, A.A.F.; Filho, C.A.X. Use of vedolizumab combined with hyperbaric oxygen therapy to treat enteric fistula in Crohn’s disease. Med. Gas. Res. 2023, 14, 133–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, G.; Borody, T.; Turner, R.; Leis, S.; Campbell, J. Combining infliximab, anti-MAP and hyperbaric oxygen therapy for resistant fistulizing Crohn’s disease. Future Sci. OA 2015, 1, FSO77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, H.C.M. MH Hyperbaric Information for Physicians and Clinicians [Internet]. Bara-Med. 2014. Available online: https://bara-medhyperbaric.com/hyperbaric-oxygen-therapy-resources/hbot-clinicians-and-physicians/physicians-faq/ (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- Ortega, M.A.; Fraile-Martinez, O.; García-Montero, C.; Callejón-Peláez, E.; Sáez, M.A.; Álvarez-Mon, M.A.; García-Honduvilla, N.; Monserrat, J.; Álvarez-Mon, M.; Bujan, J.; et al. A General Overview on the Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: Applications, Mechanisms and Translational Opportunities. Medicina 2021, 57, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thom, S.R. Hyperbaric oxygen: Its mechanisms and efficacy. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2011, 127 (Suppl. S1), 131S–141S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibbles, P.M.; Edelsberg, J.S. Hyperbaric-oxygen therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 1642–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuBose, K.J.; Cooper, J.S. Hyperbaric Patient Selection [Internet]. StatPearls—NCBI Bookshelf. 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499820/ (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Liang, Y.; Zhu, F.; Zhou, G. The new insights of hyperbaric oxygen therapy: Focus on inflammatory bowel disease. Precis. Clin. Med. 2024, 7, pbae001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liang, T.Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, G. The role of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in inflammatory bowel disease: A narrative review. Med. Gas. Res. 2021, 11, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravina, A.G.; Pellegrino, R.; Durante, T.; Palladino, G.; D’onofrio, R.; Mammone, S.; Arboretto, G.; Auletta, S.; Imperio, G.; Ventura, A.; et al. Inflammatory bowel diseases patients suffer from significant low levels and barriers to physical activity: The “BE-FIT-IBD” study. World J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 29, 5668–5682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gravina, A.G.; Pellegrino, R.; Palladino, G.; Imperio, G.; Ventura, A.; Cipullo, M.; Coppola, A.; Federico, A. Profiling the patient with inflammatory bowel disease in the relationship between physical activity and partner/social network status: A post hoc patient-tailored analysis of the “BE-FIT-IBD” study. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambiru, S.; Furuyama, N.; Kimura, F.; Shimizu, H.; Yoshidome, H.; Miyazaki, M.; Shimada, H.; Ochiai, T. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy as a prophylactic and treatment against ileus and recurrent intestinal obstructionsoon after surgery to relieve adhesive intestinal obstruction. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23, e379–e383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myren, J. Introductory remarks on Crohn’s disease. Observations from the OMGE studies. Ann. Gastroenterol. D’hepatol. 1985, 21, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Harmer, M. Crohn’s disease—A misnomer? Bristol Med. Chir. J. 1988, 103, 9–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, T.; Watanabe, T. Surgery for luminal Crohn’s disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funayama, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Sasaki, I. Surgical management in intestinal Crohn’s disease. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


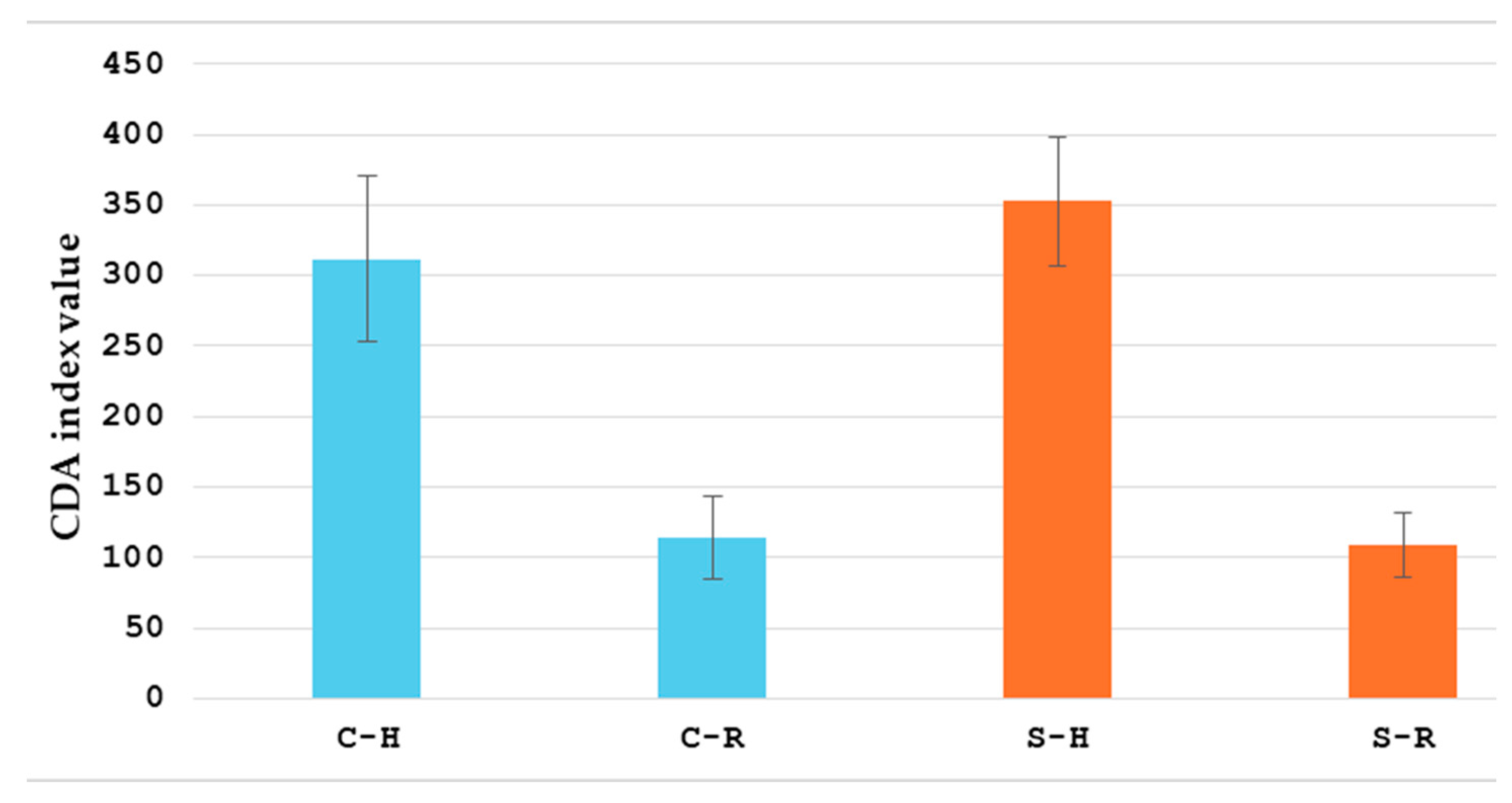
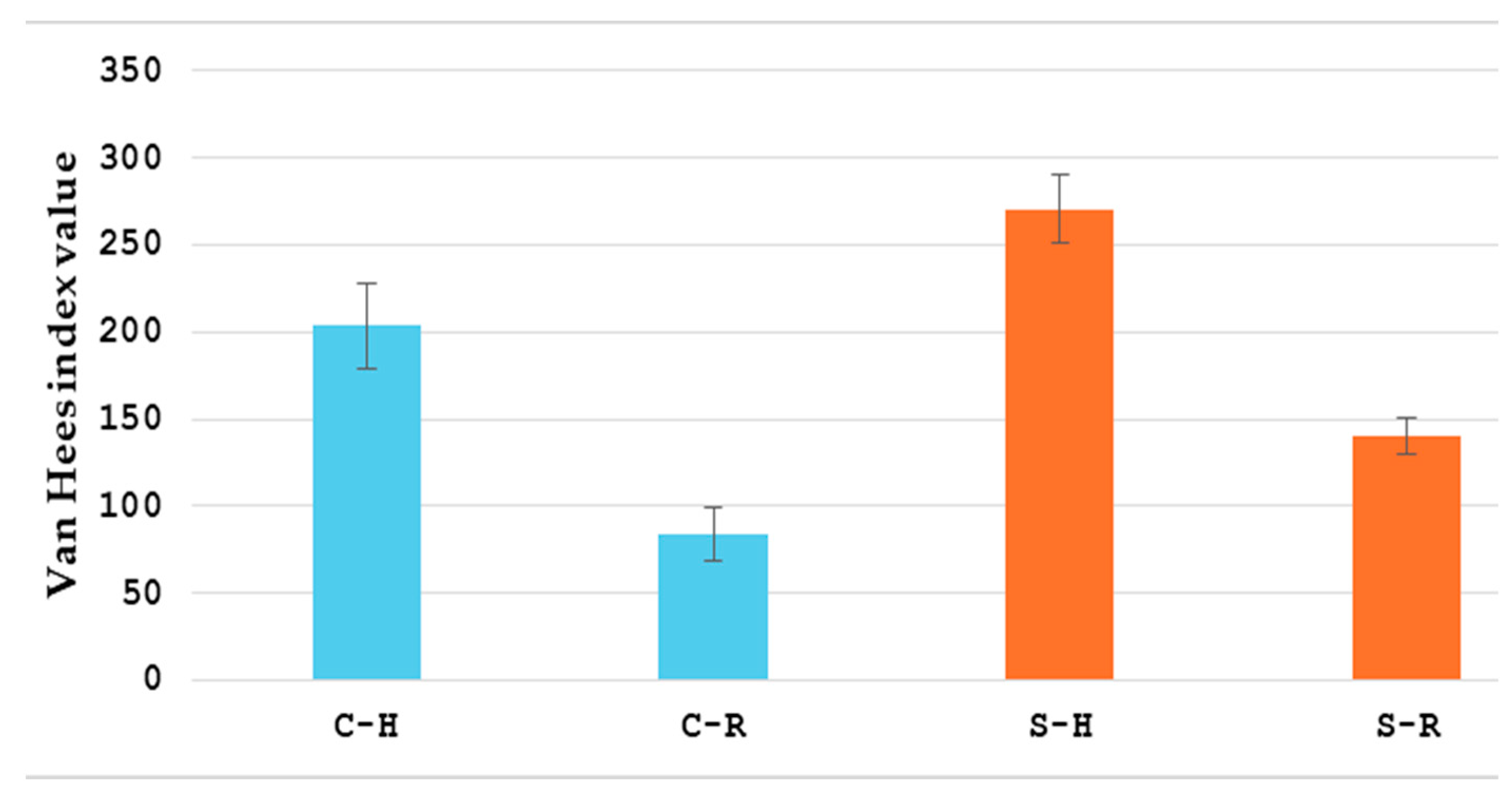
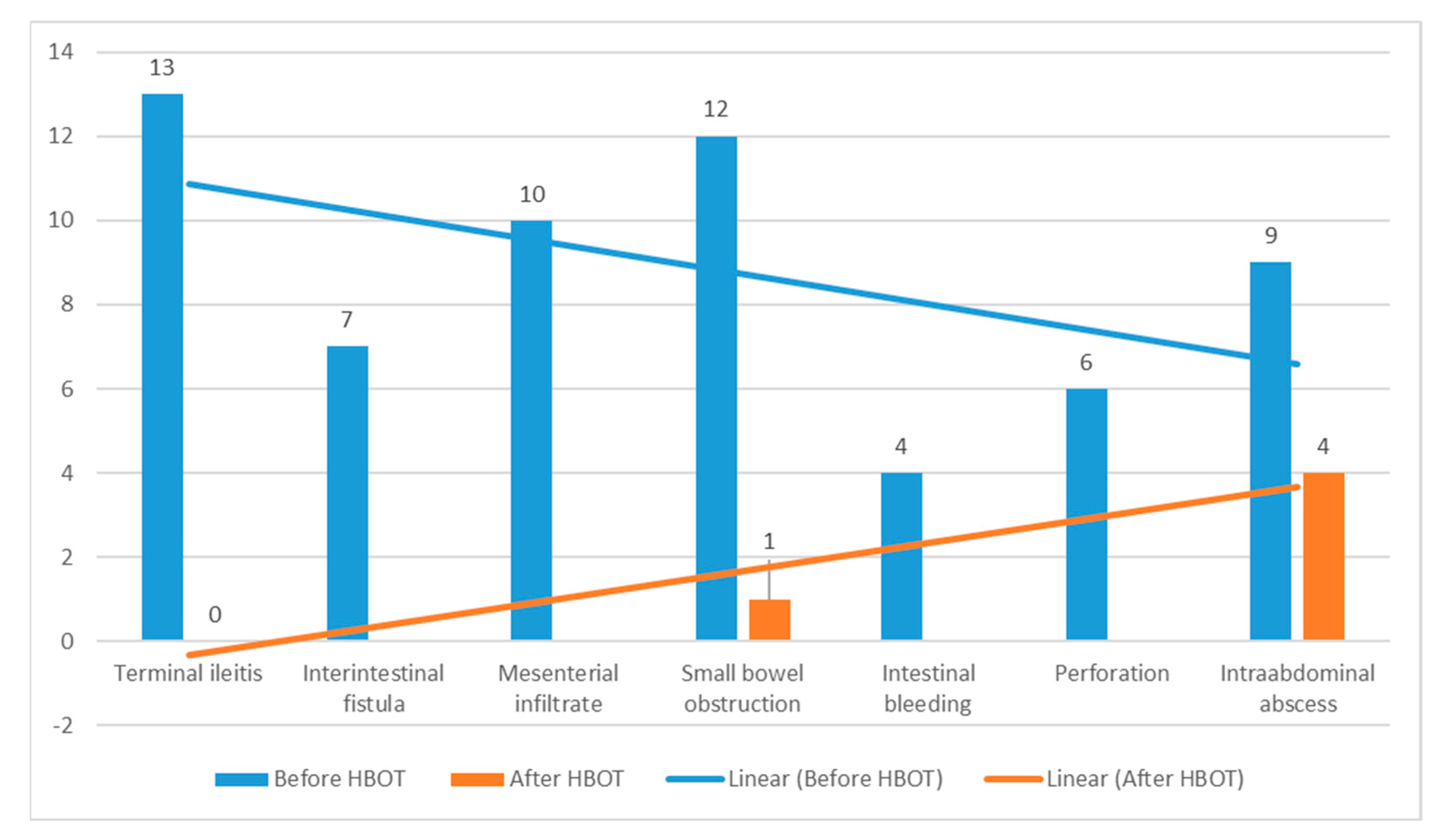
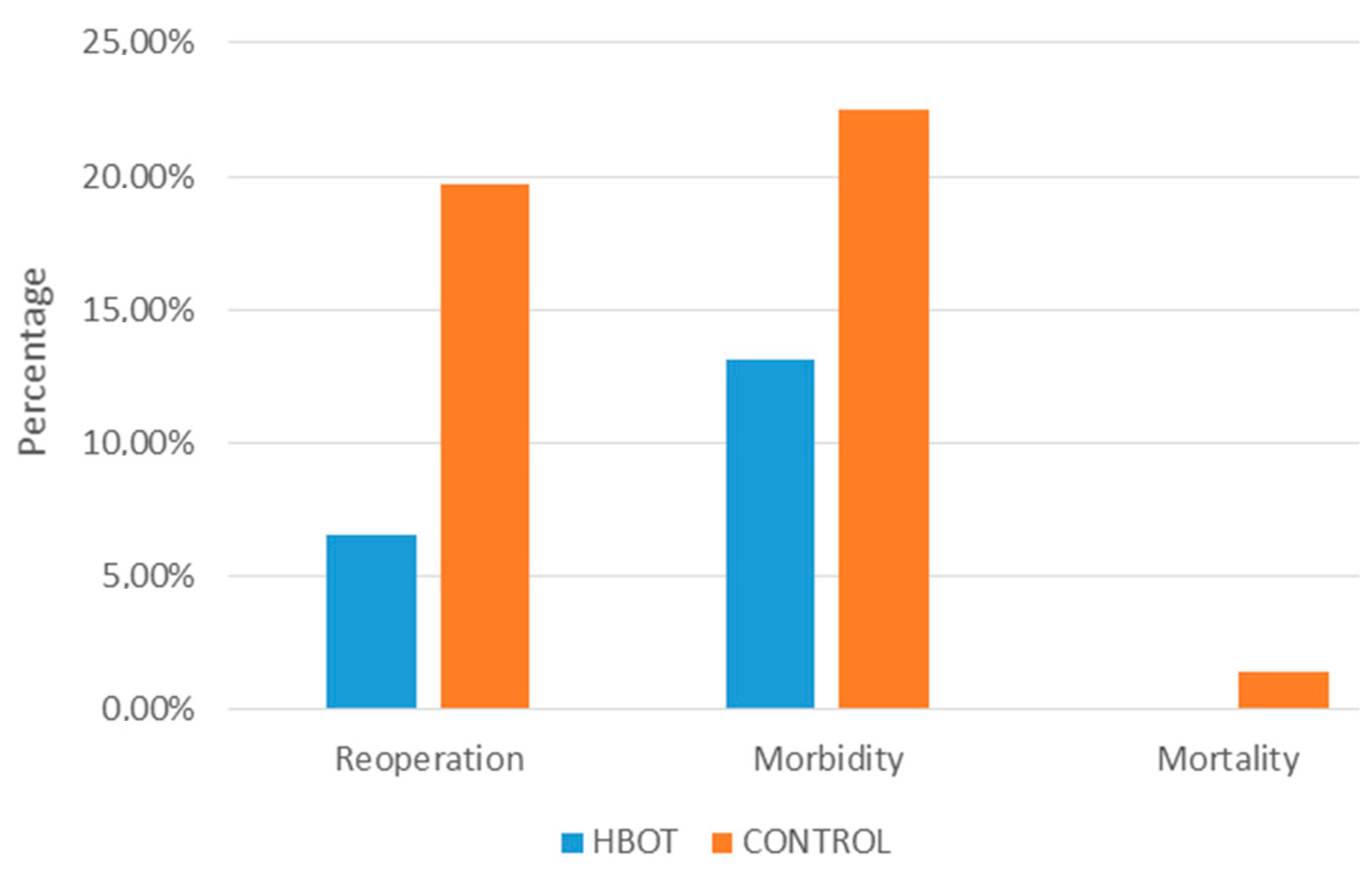
| Category | Total (n = 61) | Conservative (n = 34) | Surgical (n = 27) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean (±SD) | 32.7 ± 2.3 | 31.6 ± 2.7 | 33.2 ± 2.9 | 0.86 |
| Male sex (n, %) | 28 (45.9) | 15 (44.1) | 13 (44.8) | 0.69 |
| BMI, kg/m2, mean (±SD) | 23.7 ± 4.8 | 23.9 ± 5.8 | 23.6 ± 4.2 | 0.92 |
| Disease type (Greenstein classification) | <0.005 | |||
| Perforating | 18 (29.5%) | 6 (17.6%) | 12 (44.4%) | |
| Non-perforating | 43 (70.5%) | 28 (82.4%) | 15 (55.6%) | |
| Previous surgeries | 0.90 | |||
| Yes | 9 (14.7%) | 4 (11.7%) | 5 (18.5%) | |
| No | 52 (85.2%) | 30 (88.3%) | 22 (81.5%) | |
| ASA score | 0.92 | |||
| I–II | 55 (90.2%) | 32 (94.1%) | 23 (85.1%) | |
| III | 6 (9.8%) | 2 (5.9%) | 4 (14.9%) | |
| Crohn’s disease complications as a major cause of patient hospitalization | - | |||
| Terminal ileitis (moderate to severe) | 13 | 12 | 1 | |
| Interintestinal fistula | 7 | 5 | 2 | |
| Mesenteric infiltration | 10 | 8 | 2 | |
| Small bowel obstruction | 12 | 4 | 8 | |
| Intestinal bleeding | 4 | 1 | 3 | |
| Perforation | 6 | 0 | 6 | |
| Intra-abdominal abscess | 9 | 4 | 5 |
| Category | Conservative n = 34 | Surgical n = 27 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hospitalization, median (range) | 9 (3–25) | 12 (6–42) | 0.014 |
| Morbidity, n (%) | 3 (8.8%) | 5 (14.8%) | 0.31 |
| Mortality, n (%) | 0 | 0 | - |
| Time to bowel movements, median (range) | 2 (1–5) | 3 (1–8) | 0.56 |
| Need for surgery after HBOT, n (%) | 2 (5.8) | 2 (7.4) | 0.9 |
| Category | HBOT (n = 61) | Without HBOT (n = 76) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean (±SD) | 32.7 ± 2.3 | 31.3 ± 2.6 | 0.81 |
| Male sex (n, %) | 28 (45.9) | 37 (48.8) | 0.72 |
| Surgical patients | 27 | 29 | 0.47 |
| Conservative patients | 35 | 47 | 0.73 |
| BMI, kg/m2, mean (±SD) | 23.7 ± 4.8 | 24.2 ± 4.4 | 0.54 |
| Type of disease (according to Greenstein) | |||
| Perforating | 18 | 28 | |
| Non-perforating | 43 | 48 | 0.36 |
| ASA score | |||
| I–II | 55 | 64 | 0.82 |
| III | 6 | 12 | 0.73 |
| CRP (mg/L), mean (±SD) | 67 ± 32.2 | 94 ± 53 | <0.05 |
| Mortality | 0 | 1 | - |
| Need for (re)operation, n (%) | 4 (6.5) | 14 (18.4) | 0.04 |
| Duration of hospitalization, median (range) | 11 (3–42) | 16 (6–62) | <0.05 |
| Morbidity (>3a) | 8 (13.1%) | 16 (21.0%) | 0.22 |
| Time to the restoration of intestinal passage | 2 (1–8) | 4 (2–11) | <0.05 |
| Average reduction in CDAI | 63 ± 32 | 51 ± 24 | <0.05 |
| Average reduction in van Hees index | 112 ± 41 | 97 ± 39 | <0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krstulović, J.; Augustin, G.; Romić, I.; Tavra, A.; Batinović, F.; Hrgović, Z. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in the Treatment of Crohn’s Disease. Healthcare 2025, 13, 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13020128
Krstulović J, Augustin G, Romić I, Tavra A, Batinović F, Hrgović Z. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in the Treatment of Crohn’s Disease. Healthcare. 2025; 13(2):128. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13020128
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrstulović, Jure, Goran Augustin, Ivan Romić, Ante Tavra, Franko Batinović, and Zrinka Hrgović. 2025. "Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in the Treatment of Crohn’s Disease" Healthcare 13, no. 2: 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13020128
APA StyleKrstulović, J., Augustin, G., Romić, I., Tavra, A., Batinović, F., & Hrgović, Z. (2025). Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in the Treatment of Crohn’s Disease. Healthcare, 13(2), 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13020128








