Neonatal Factors Associated with Mortality Among Preterm Infants Admitted to Neonatal Intensive Care in a Peruvian National Hospital
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. Population and Sample
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Variables
2.5. Data Analysis
2.6. Ethical Considerations
2.7. Data Availability and Use of Generative AI
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Analysis of Results
3.2. Bivariate Analysis
3.3. Multivariate Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mihretu, E.; Genie, Y.D.; Adugnaw, E.; Shibabaw, A.T. Survival Status and Predictors of Mortality among Preterm Neonates Admitted in Bench Sheko Zone, Sheka Zone and Keffa Zone Governmental Hospitals, Southwest Ethiopia (2021): Prospective Follow-up Study. BMJ Open 2024, 14, e083897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Born Too Soon: Decade of Action on Preterm Birth. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240073890 (accessed on 12 September 2025).
- Cao, G.; Liu, J.; Liu, M. Global, Regional, and National Incidence and Mortality of Neonatal Preterm Birth, 1990-2019. JAMA Pediatr. 2022, 176, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukosha, M.; Kaonga, P.; Kapembwa, K.M.; Musonda, P.; Vwalika, B.; Lubeya, M.K.; Jacobs, C. Modelling Mortality within 28 Days among Preterm Infants at a Tertiary Hospital in Lusaka, Zambia: A Retrospective Review of Hospital-Based Records. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2021, 39, 69. [Google Scholar]
- Khasawneh, W.; Khriesat, W. Assessment and Comparison of Mortality and Short-Term Outcomes among Premature Infants before and after 32-Week Gestation: A Cross-Sectional Analysis. Ann. Med. Surg. 2020, 60, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Bank Open Data. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Goal 3|Department of Economic and Social Affairs. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal3 (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Saleem, S.; Tikmani, S.S.; Goudar, S.S.; Hwang, K.; Dhaded, S.; Guruprasad, G.; Nadig, N.G.; Kusagur, V.B.; Patil, L.G.C.; Siddartha, E.S.; et al. Neonatal Mortality among Preterm Infants Admitted to Neonatal Intensive Care Units in India and Pakistan: A Prospective Study. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2023, 130 (Suppl. S3), 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steurer, M.A.; Baer, R.J.; Chambers, C.D.; Costello, J.; Franck, L.S.; McKenzie-Sampson, S.; Pacheco-Werner, T.L.; Rajagopal, S.; Rogers, E.E.; Rand, L.; et al. Mortality and Major Neonatal Morbidity in Preterm Infants with Serious Congenital Heart Disease. J. Pediatr. 2021, 239, 110–116.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesan, T.; Rees, P.; Gardiner, J.; Battersby, C.; Purkayastha, M.; Gale, C.; Sutcliffe, A.G. National Trends in Preterm Infant Mortality in the United States by Race and Socioeconomic Status, 1995–2020. JAMA Pediatr. 2023, 177, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Womack, L.S.; Rossen, L.M.; Hirai, A.H. Urban-Rural Infant Mortality Disparities by Race and Ethnicity and Cause of Death. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2020, 58, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.N.; Vuong, A.D.B.; Pham, X.T.T. Neonatal Outcomes in the Surgical Management of Placenta Accreta Spectrum Disorders: A Retrospective Single-Center Observational Study from 468 Vietnamese Pregnancies beyond 28 Weeks of Gestation. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2024, 24, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmatpour, S.; Moradi, G.; Zokaie, M.; Karimi, Z.; Moradi, Y.; Noori, E. Risk Factors Associated with Neonatal Mortality and Their Status: A Matched Case-Control Study in Kurdistan. Med. J. Islam. Repub. Iran 2024, 38, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josfeld, L.; Huebner, J. Development and Analysis of Quality Assessment Tools for Different Types of Patient Information—Websites, Decision Aids, Question Prompt Lists, and Videos. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2023, 23, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakariya, Y.F. Cronbach’s Alpha in Mathematics Education Research: Its Appropriateness, Overuse, and Alternatives in Estimating Scale Reliability. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 1074430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wubetu, A.D.; Amare, Y.E.; Haile, A.B.; Degu, M.W. Newborn Birth Weight and Associated Factors Among Mother-Neonate Pairs in Public Hospitals, North Wollo, Ethiopia. Pediatr. Health Med. Ther. 2021, 12, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mense, L.; Nögel, S.; Kaufmann, M.; Küster, H.; Braun, N.; Simma, B.; Rüdiger, M. Assessing the Postnatal Condition: The Predictive Value of Single Items of the Apgar Score. BMC Pediatr. 2025, 25, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariniotaki, C.; Thomou, C.; Gkentzi, D.; Panteris, E.; Dimitriou, G.; Hatzidaki, E. Neonatal Sepsis: A Comprehensive Review. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, M.G.; Reed, K.L.; Brown, R.N.; Newborn Brain Society Guidelines and Publications Committee. Perinatal Asphyxia from the Obstetric Standpoint. Semin. Fetal. Neonatal Med. 2021, 26, 101259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, R.; Patel, A.I.; Weng, Y.; Schroeder, A.R.; Lee, H.C.; Aby, J.; Frymoyer, A. Incidence of Neonatal Hypothermia in the Newborn Nursery and Associated Factors. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2331011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Geest, B.A.M.; de Mol, M.J.S.; Barendse, I.S.A.; de Graaf, J.P.; Bertens, L.C.M.; Poley, M.J.; Ista, E.; Kornelisse, R.F.; Reiss, I.K.M.; Steegers, E.A.P.; et al. Assessment, Management, and Incidence of Neonatal Jaundice in Healthy Neonates Cared for in Primary Care: A Prospective Cohort Study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giouleka, S.; Gkiouleka, M.; Tsakiridis, I.; Daniilidou, A.; Mamopoulos, A.; Athanasiadis, A.; Dagklis, T. Diagnosis and Management of Neonatal Hypoglycemia: A Comprehensive Review of Guidelines. Children 2023, 10, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, Y.; Arai, J.; Cho, K.; Yukitake, Y.; Kajikawa, D.; Hinata, A.; Miura, R. Diagnosis and Management of Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Japan: A National Survey. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2023, 64, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhassen, Z.; Vali, P.; Guglani, L.; Lakshminrusimha, S.; Ryan, R.M. Recent Advances in Pathophysiology and Management of Transient Tachypnea of Newborn. J. Perinatol. 2021, 41, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilfillan, M.; Bhandari, A.; Bhandari, V. Diagnosis and Management of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. BMJ 2021, 375, n1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Zhu, H.; Lance Gould, K.; Lai, D. Comparing Heart PET Scans: An Adjustment of Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test under Spatial Autocorrelation. J. Appl. Stat. 2025, 52, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogale, A.; Borko, U.D.; Abreha, S.; Balta, B. Determinants of Mortality among Preterm Neonates Admitted at Wolaita Sodo University Comprehensive Specialized Hospital, Southern Ethiopia: An Unmatched Case-Control Study. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0314632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekasha, A.; Tazu, Z.; Muhe, L.; Abayneh, M.; Gebreyesus, G.; Girma, A.; Berhane, M.; McClure, E.M.; Goldenberg, R.L.; Nigussie, A.K. Factors Associated with the Death of Preterm Babies Admitted to Neonatal Intensive Care Units in Ethiopia: A Prospective, Cross-Sectional, and Observational Study. Glob. Pediatr. Health 2020, 7, 2333794X20970005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tembo, D.; Abobo, F.D.N.; Kaonga, P.; Jacobs, C.; Bessing, B. Risk Factors Associated with Neonatal Mortality among Neonates Admitted to Neonatal Intensive Care Unit of the University Teaching Hospital in Lusaka. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguma, N.; Ekak, S.; Emetu, L.; Ojok, S.; Akera, P. Prevalence and Factors Associated with Neonatal Mortality at the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit at St. Mary’s Hospital Lacor, Northern Uganda. BMC Pediatr. 2025, 25, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, M.; Nilsson, D.; Trygg, J.; Håkansson, S. Perinatal Risk Factors for Mortality in Very Preterm Infants—A Nationwide, Population-based Discriminant Analysis. Acta Paediatr. 2022, 111, 1526–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirore, L.L.; Erkalo, D.; Abose, S.; Melaku, L.M.; Mulugeta, E.; Shiferaw, A.; Habte, A.; Gebremeskel, M.G. Incidence of Mortality and Its Predictors among Preterm Neonates in Nigist Eleni Mohammed Memmorial Comprehensive Specialized Hospital, Hossana, Ethiopia: A Prospective Follow-up Study. BMC Pediatr. 2024, 24, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebaw, E.; Reta, A.; Kibret, G.D.; Wagnew, F. Incidence and Predictors of Mortality among Preterm Neonates Admitted to the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit at Debre Markos Referral Hospital, Northwest Ethiopia. Ethiop. J. Health Sci. 2021, 31, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, H.A.; Shiferaw, Z.; Roble, A.K.; Kure, M.A. Neonatal Mortality and Associated Factors among Neonates Admitted to Neonatal Intensive Care Unit at Public Hospitals of Somali Regional State, Eastern Ethiopia: A Multicenter Retrospective Analysis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0268648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toma, T.M.; Merga, H.; Dube, L. Incidence and Predictors of Mortality Among Preterm Neonates Admitted to Jimma University Medical Center, Southwest Ethiopia: A Retrospective Follow-Up Study. Int. J. Public Health 2024, 69, 1606897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
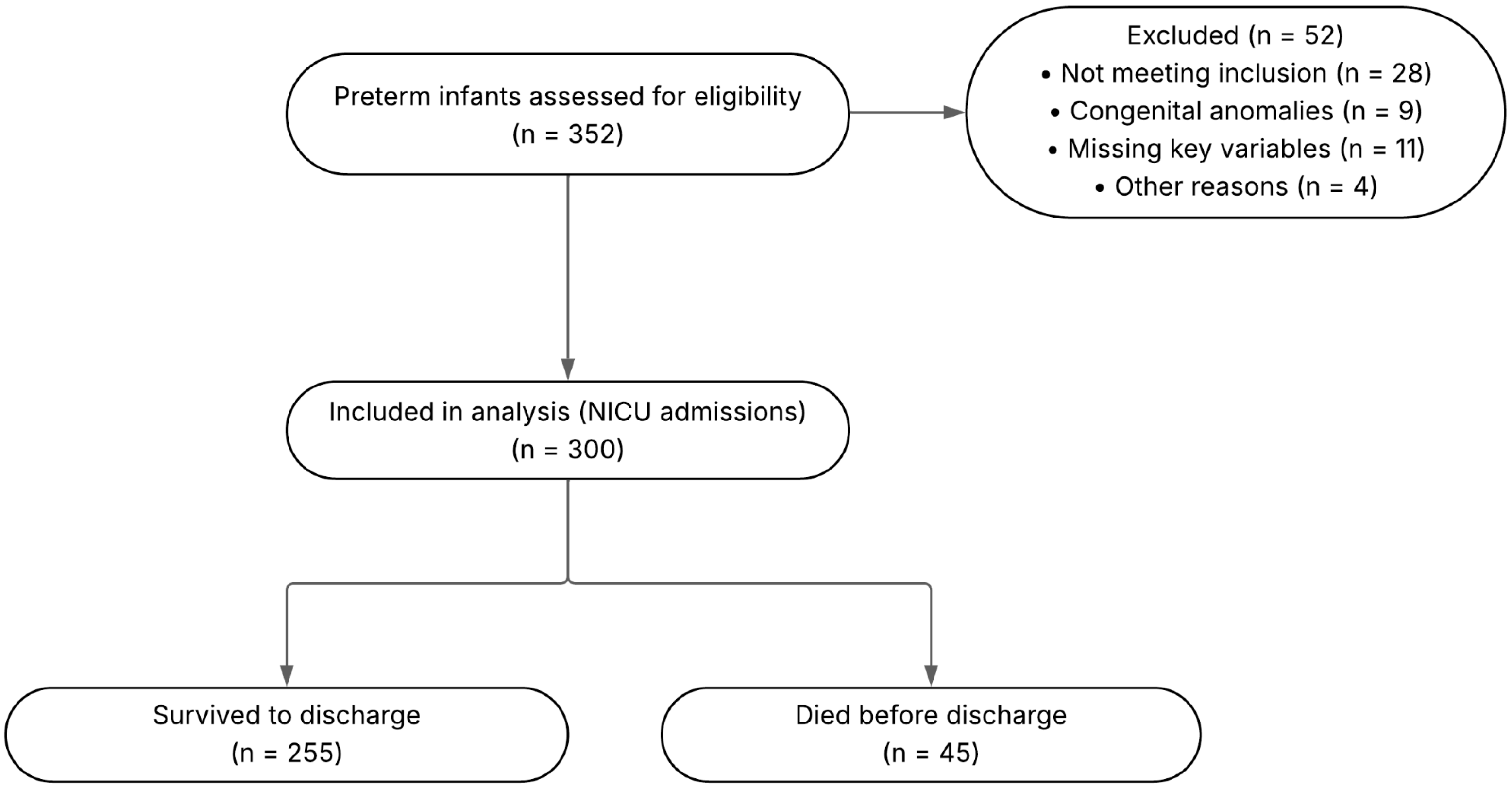
| Characteristic | N (%) |
|---|---|
| Sex | |
| Female | 147 (49.0) |
| Male | 153 (51.0) |
| Mode of delivery | |
| Vaginal | 42 (14.0) |
| Cesarean section | 258 (86.0) |
| Birth weight (categorical) | |
| Extremely low birth weight (<1000 g) | 54 (18.0) |
| Very low birth weight (1000–1499 g) | 78 (26.0) |
| Low birth weight (1500–2499 g) | 167 (55.67) |
| Adequate birth weight for gestational age | 1 (0.33) |
| Birth weight (numeric) 1 | 1620.5 (IQR 1246–1923) |
| Apgar score at 1 min | |
| 7–10 (reassuring/normal) | 245 (81.7) |
| 4–6 (moderately abnormal) | 20 (6.6) |
| 0–3 (low/severe) | 35 (11.7) |
| Neonatal infection | |
| No | 47 (15.7) |
| Yes | 253 (84.3) |
| Perinatal asphyxia | |
| No | 55 (18.3) |
| Yes | 245 (81.7) |
| Hypothermia | |
| No | 47 (15.7) |
| Yes | 253 (84.3) |
| Intraventricular hemorrhage | |
| No | 97 (32.3) |
| Yes | 203 (67.7) |
| Neonatal jaundice | |
| No | 218 (72.7) |
| Yes | 82 (27.3) |
| Hypoglycemia | |
| No | 245 (81.7) |
| Yes | 55 (18.3) |
| Hyaline membrane disease | |
| No | 79 (26.3) |
| Yes | 221 (73.7) |
| Transient tachypnea of the newborn | |
| No | 221 (73.7) |
| Yes | 79 (26.3) |
| Bronchopulmonary dysplasia | |
| No | 79 (26.3) |
| Yes | 221 (73.7) |
| Mortality | |
| No | 255 (85.0) |
| Yes | 45 (15.0) |
| Characteristic | Mortality | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | ||
| (n = 255) | (n = 45) | ||
| Sex | 0.201 | ||
| Female | 121 (47.45) | 26 (57.78) | |
| Male | 134 (52.55) | 19 (42.22) | |
| Mode of delivery | 0.744 | ||
| Vaginal | 35 (13.73) | 7 (15.56) | |
| Cesarean section | 220 (86.27) | 38 (84.44) | |
| Birth weight (categorical) | <0.001 * | ||
| Extremely low birth weight (<1000 g) | 33 (12.94) | 21 (46.67) | |
| Very low birth weight (1000–1499 g) | 71 (27.84) | 7 (15.56) | |
| Low birth weight (1500–2499 g) | 150 (58.82) | 17 (37.78) | |
| Adequate birth weight for gestational age | 1 (0.39) | 0 (00) | |
| Birth weight (numeric) 1 | 1622 (IQR 1204–1920) | 1590 (IQR 1344–1928) | 0.843 |
| Apgar score at 1 min | <0.001 * | ||
| Normal | 222 (87.06) | 23 (51.11) | |
| Mild depression | 10 (3.92) | 10 (22.22) | |
| Severe depression | 23 (9.02) | 12 (26.67) | |
| Neonatal infection | 0.002 | ||
| No | 47 (18.43) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Yes | 208 (81.57) | 45 (100.0) | |
| Perinatal asphyxia | <0.001 | ||
| No | 33 (12.94) | 22 (48.89) | |
| Yes | 222 (87.06) | 23 (51.11) | |
| Hypothermia | 0.002 | ||
| No | 47 (18.43) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Yes | 208 (81.57) | 45 (100.0) | |
| Intraventricular hemorrhage | 0.220 | ||
| No | 86 (33.73) | 11 (24.44) | |
| Yes | 169 (66.27) | 34 (75.56) | |
| Neonatal jaundice | 0.637 | ||
| No | 184 (72.16) | 34 (75.56) | |
| Yes | 71 (27.84) | 11 (24.44) | |
| Hypoglycemia | <0.001 | ||
| No | 222 (87.06) | 23 (51.11) | |
| Yes | 33 (12.94) | 22 (48.89) | |
| Hyaline membrane disease | 0.497 | ||
| No | 69 (27.06) | 10 (22.22) | |
| Yes | 186 (72.94) | 35 (77.78) | |
| Transient tachypnea of the newborn | 0.497 | ||
| No | 186 (72.94) | 35 (77.78) | |
| Yes | 69 (27.06) | 10 (22.22) | |
| Bronchopulmonary dysplasia | 0.497 | ||
| No | 69 (27.06) | 10 (22.22) | |
| Yes | 186 (72.94) | 35 (77.78) | |
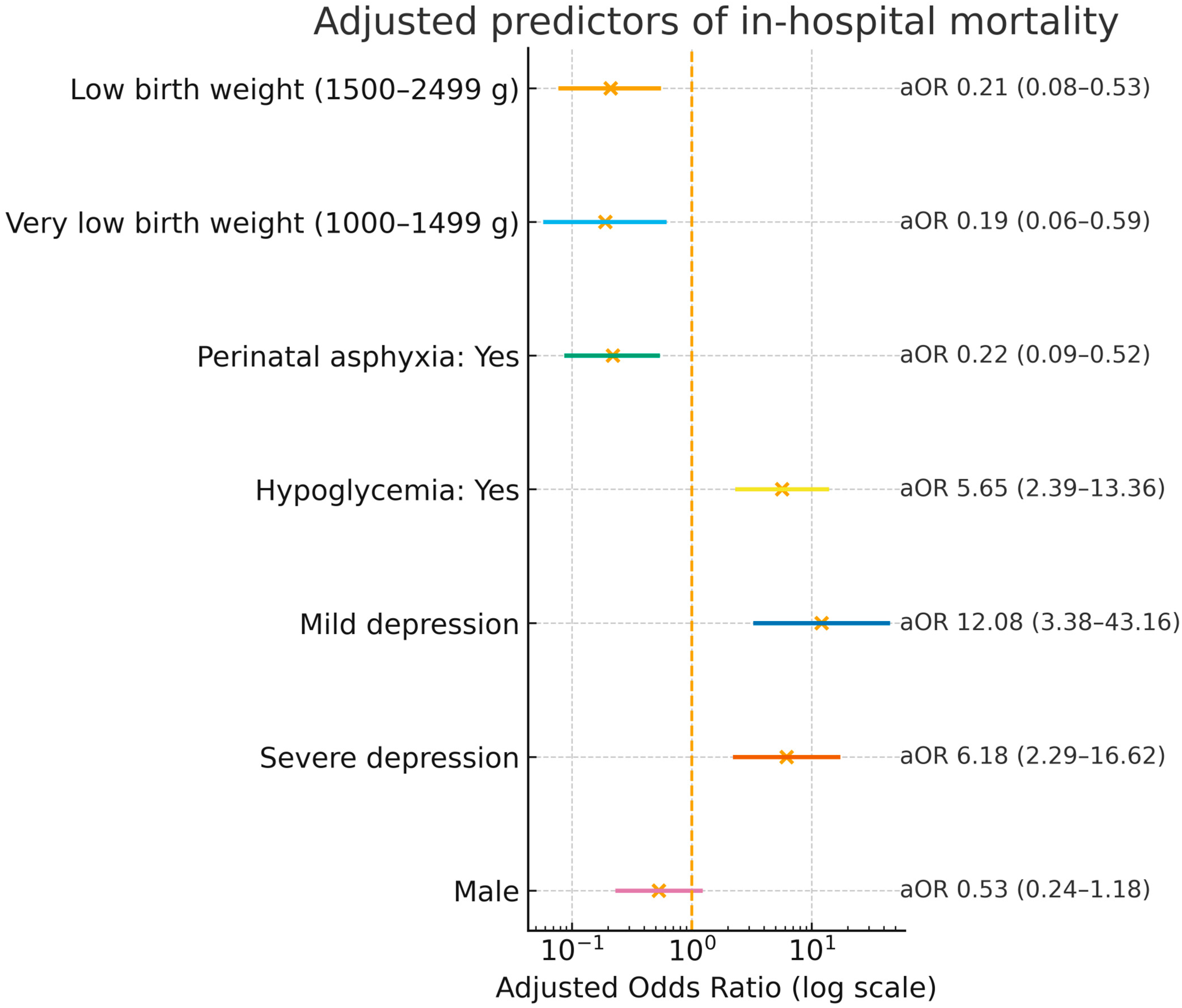
| Variable | Crude OR (95% CI) | p-Value | Adjusted OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||||
| Female | Reference | Reference | ||
| Male | 0.66 (0.35–1.26) | 0.212 | 0.53 (0.24–1.18) | 0.118 |
| Birth weight (categorical) | ||||
| Extremely low birth weight (<1000 g) | Reference | Reference | ||
| Very low birth weight (1000–1499 g) | 0.15 (0.06–0.40) | <0.001 | 0.19 (0.06–0.59) | 0.004 |
| Low birth weight (1500–2499 g) | 0.17 (0.08–0.37) | <0.001 | 0.21 (0.08–0.53) | 0.001 |
| Apgar score at 1 min | ||||
| Normal | Reference | Reference | ||
| Mild depression | 9.60 (3.62–25.50) | <0.001 | 12.08 (3.38–43.16) | <0.001 |
| Severe depression | 5.01 (2.21–11.38) | <0.001 | 6.18 (2.29–16.62) | <0.001 |
| Perinatal asphyxia | ||||
| No | Reference | Reference | ||
| Yes | 0.16 (0.08–0.31) | <0.001 | 0.22 (0.09–0.52) | 0.001 |
| Hypoglycemia | ||||
| No | Reference | Reference | ||
| Yes | 6.41 (3.21–12.77) | <0.001 | 5.65 (2.39–13.36) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haro-Norabuena, R.S.; Gonzales-Carrillo, J.J.; Arce-Huamani, M.A. Neonatal Factors Associated with Mortality Among Preterm Infants Admitted to Neonatal Intensive Care in a Peruvian National Hospital. Healthcare 2025, 13, 2420. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13192420
Haro-Norabuena RS, Gonzales-Carrillo JJ, Arce-Huamani MA. Neonatal Factors Associated with Mortality Among Preterm Infants Admitted to Neonatal Intensive Care in a Peruvian National Hospital. Healthcare. 2025; 13(19):2420. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13192420
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaro-Norabuena, Rosana S., Javier J. Gonzales-Carrillo, and Miguel A. Arce-Huamani. 2025. "Neonatal Factors Associated with Mortality Among Preterm Infants Admitted to Neonatal Intensive Care in a Peruvian National Hospital" Healthcare 13, no. 19: 2420. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13192420
APA StyleHaro-Norabuena, R. S., Gonzales-Carrillo, J. J., & Arce-Huamani, M. A. (2025). Neonatal Factors Associated with Mortality Among Preterm Infants Admitted to Neonatal Intensive Care in a Peruvian National Hospital. Healthcare, 13(19), 2420. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13192420


_MD__MPH_PhD.png)



