Feasibility and Preliminary Efficacy of a Telerehabilitation Intervention for Diastasis Recti Abdominis—A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
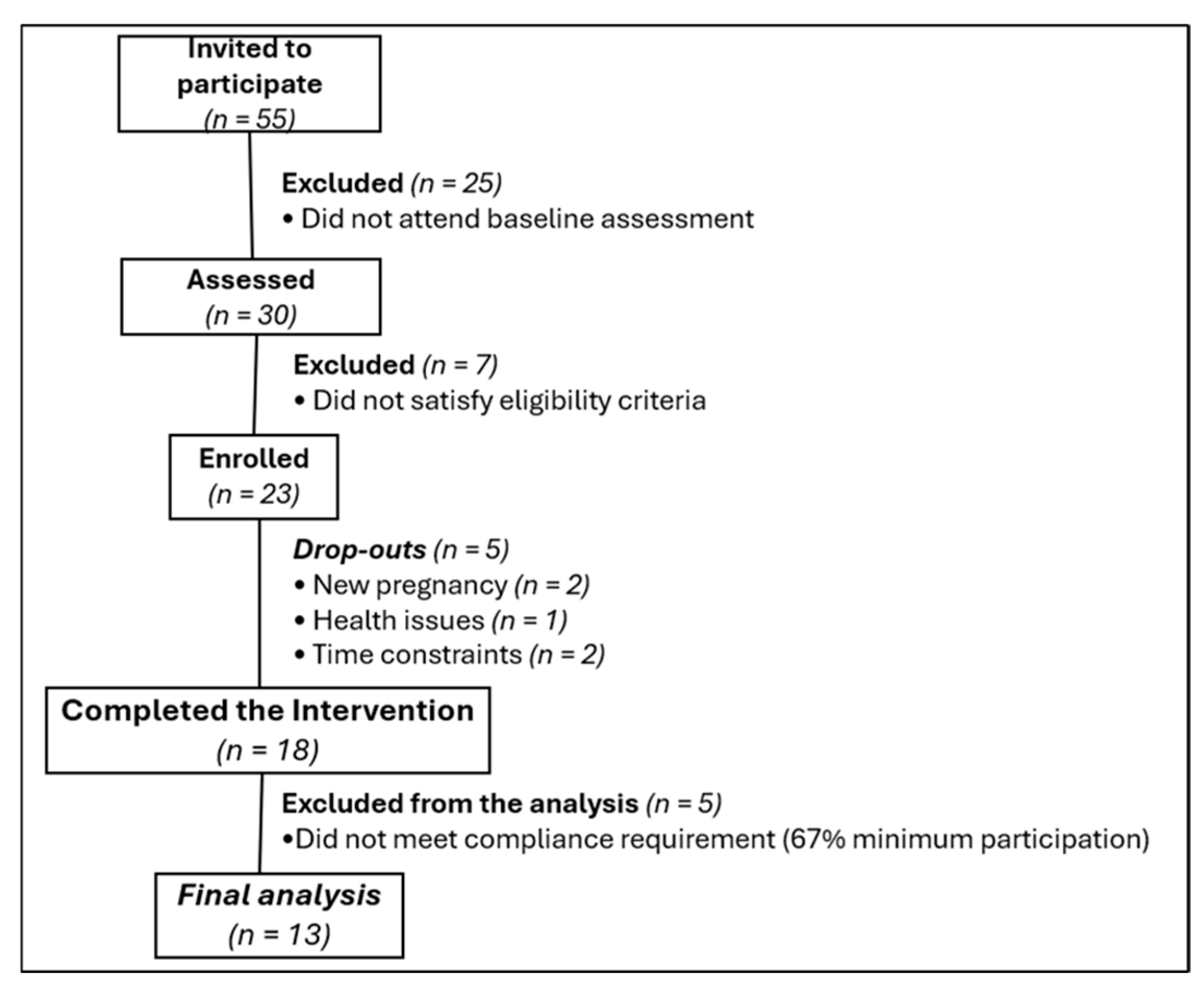
2.2. Participants
2.3. Procedures
2.4. Intervention
2.5. Primary Outcome
2.6. Secondary Outcomes
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
3.2. Primary Outcome—Usability and Participant Satisfaction
3.3. Secondary Outcomes
3.3.1. Inter-Recti Distance (IRD) and Body Image
3.3.2. Trunk Muscle Endurance
3.3.3. Exercise Adherence
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DRA | Diastasis recti abdominis |
| TUQ | Telehealth Usability Questionnaire |
| IRD | Inter-recti distance |
| BISS | Body Image States Scale |
References
- da Mota, P.G.F.; Pascoal, A.G.B.A.; Carita, A.I.A.D.; Bø, K. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Diastasis Recti Abdominis from Late Pregnancy to 6 Months Postpartum, and Relationship with Lumbo-Pelvic Pain. Man. Ther. 2015, 20, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperstad, J.B.; Tennfjord, M.K.; Hilde, G.; Ellström-Engh, M.; Bø, K. Diastasis Recti Abdominis during Pregnancy and 12 Months after Childbirth: Prevalence, Risk Factors and Report of Lumbopelvic Pain. Br. J. Sports Med. 2016, 50, 1092–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boissonnault, J.S.; Blaschak, M.J. Incidence of Diastasis Recti Abdominis during the Childbearing Year. Phys. Ther. 1988, 68, 1082–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rath, A.M.; Attali, P.; Dumas, J.L.; Goldlust, D.; Zhang, J.; Chevrel, J.P. The Abdominal Linea Alba: An Anatomo-Radiologic and Biomechanical Study. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 1996, 18, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, D.R.; Frawley, H.C.; Shields, N.; van de Water, A.T.M.; Taylor, N.F. Relationship between Diastasis of the Rectus Abdominis Muscle (DRAM) and Musculoskeletal Dysfunctions, Pain and Quality of Life: A Systematic Review. Physiotherapy 2019, 105, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnarsson, U.; Stark, B.; Dahlstrand, U.; Strigård, K. Correlation between Abdominal Rectus Diastasis Width and Abdominal Muscle Strength. Dig. Surg. 2015, 32, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, M.A.; Millar, A.L.; Dugan, S.A. Diastasis Rectus Abdominis and Lumbo-Pelvic Pain and Dysfunction-Are They Related? J. Women’s Health Phys. Ther. 2009, 33, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlstedt, A.; Bringman, S.; Egberth, M.; Emanuelsson, P.; Olsson, A.; Petersson, U.; Pålstedt, J.; Sandblom, G.; Sjödahl, R.; Stark, B.; et al. Management of Diastasis of the Rectus Abdominis Muscles: Recommendations for Swedish National Guidelines. Scand. J. Surg. 2021, 110, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoura, A.; Billis, E.; Papanikolaou, D.T.; Xergia, S.; Tsarbou, C.; Tsekoura, M.; Kortianou, E.; Maroulis, I. Diastasis Recti Abdominis Rehabilitation in the Postpartum Period: A Scoping Review of Current Clinical Practice. Int. Urogynecology J. 2024, 35, 491–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruett, M.D.; Caputo, J.L. Exercise Guidelines for Pregnant and Postpartum Women. Strength Cond. J. 2011, 33, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laframboise, F.C.; Schlaff, R.A.; Baruth, M. Postpartum Exercise Intervention Targeting Diastasis Recti Abdominis. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2021, 14, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopold, M.; Santiago, K.; Cheng, J.; Keller, L.; Abutalib, Z.; Bonder, J.; Sharma, G.; Tenforde, A.; Casey, E. Efficacy of a Core Strengthening Program for Diastasis Rectus Abdominis in Postpartum Women: A Prospective Observational Study. J. Womens Health Phys. Ther. 2021, 45, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Yi, D.; Yim, J. The Effect of Core Exercise Using Online Videoconferencing Platform and Offline-Based Intervention in Postpartum Woman with Diastasis Recti Abdominis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, P.; Pascoal, A.G.; Carita, A.I.; Bø, K. Normal Width of the Inter-Recti Distance in Pregnant and Postpartum Primiparous Women. Musculoskelet. Sci. Pract. 2018, 35, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherburn, M.; Murphy, C.A.; Carroll, S.; Allen, T.J.; Galea, M.P. Investigation of Transabdominal Real-Time Ultrasound to Visualise the Muscles of the Pelvic Floor. Aust. J. Physiother. 2005, 51, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentín-Mazarracin, I.; Nogaledo-Martín, M.; López-De-Uralde-Villanueva, I.; Fernández-De-las-Peñas, C.; Stokes, M.; Arias-Buría, J.L.; Díaz-Arribas, M.J.; Plaza-Manzano, G. Article Reproducibility and Concurrent Validity of Manual Palpation with Rehabilitative Ultrasound Imaging for Assessing Deep Abdominal Muscle Activity: Analysis with Preferential Ratios. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshwani, N.; McLean, L. Ultrasound Imaging in Postpartum Women with Diastasis Recti: Intrarater between-Session Reliability. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2015, 45, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billis, E.; Skoura, A.; Papakonstantinou, T.-E.; Papanikolaou, D.T.; Tsekoura, M.; Andriopoulou, M.; Matzaroglou, C.; Lampropoulou, S.; Koumoundourou, D.; Trachani, E.; et al. Physiotherapists’ Reliability of Inter-Recti Distance Measurement with Real-Time Ultrasound across a Mixed Women Population Sample. Womens Health 2025, 21, 17455057251361999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, S.; Bernard, S.; Murray-Davis, B.; Graham, N. Establishing Expert-Based Recommendations for the Conservative Management of Pregnancy-Related Diastasis Rectus Abdominis: A Delphi Consensus Study. J. Womens Health Phys. Ther. 2019, 43, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmanto, B.; Lewis, A.N., Jr.; Graham, K.M.; Bertolet, M.H. Development of the Telehealth Usability Questionnaire (TUQ). Int. J. Telerehabilitation 2016, 8, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoniou, M. Telerehabilitation in Women with Diastasis Recti Abdominis: Effectiveness and Patient Satisfaction. Master’s Thesis, University of Patras, Patras, Greece, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, A.; Kale, S.; Chandel, S.; Pal, D.K. Likert Scale: Explored and Explained. Curr. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2015, 7, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tore, N.G.; Oskay, D.; Haznedaroglu, S. The Quality of Physiotherapy and Rehabilitation Program and the Effect of Telerehabilitation on Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2023, 42, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billis, E.; Kafetzi, V.; Xergia, S.A.; Tsarbou, C.; Sideris, V.; Skoura, A.; Gkogkas, A.; Gliatis, A. Investigation of Rectus Abdominis Electromyographic Activity in Women with and without Rectus Abdominis Diastasis: Pilot Study. In Proceedings of the IFOMPT 2024 Conference, Basel, Switzerland, 4–6 July 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Keshwani, N.; Mathur, S.; McLean, L. The Impact of Exercise Therapy and Abdominal Binding in the Management of Diastasis Recti Abdominis in the Early Post-Partum Period: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Physiother. Theory Pract. 2021, 37, 1018–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, S.M.; Childs, A.; Liebenson, C. Endurance Times for Low Back Stabilization Exercises: Clinical Targets for Testing and Training from a Normal Database. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1999, 80, 941–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cash, T.F.; Fleming, E.C.; Alindogan, J.; Steadman, L.; Whitehead, A. Beyond Body Image as a Trait: The Development and Validation of the Body Image States Scale. Eat. Disord. 2002, 10, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latanioti, E. Cross-Cultural Adaptation of Body Image States Scale (BISS) in Greek Population. Master’s Thesis, University of Patras, Patras, Greece, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ceprnja, D.; Clark, T.; Young, J.; Lee, R.; Flynn, K.; Maka, K. Evaluating Experiences, Usability and Patient Satisfaction with Telehealth for Tertiary Outpatient Physiotherapy Services during COVID-19: A Mixed-Methods Study. Physiother. Theory Pract. 2023, 39, 1929–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okusa, S.; Saegusa, H.; Miyakawa, K.; Tsutsumi, Y.; Ishida, S.; Nishikata, K.; Nukariya, T.; Tezuka, T.; Nihei, Y.; Kitagawa, Y.; et al. Satisfaction, Effectiveness, and Usability of Telerehabilitation for Parkinson’s Disease Patients. J. Rehabil. Med. 2025, 57, jrm39819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, D.; Rathod, V.; Phadnis, A.; Bansal, S.S. Telehealth for Consultation and Shoulder Rehabilitation: A Preliminary Study on the Perspectives of 30 Patients during the COVID-19 Lockdown. Clin. Shoulder Elb. 2021, 24, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalfani, A.; Bigdeli, N.; Gandomi, F. Comparing the Effects of Suspension and Isometric-Isotonic Training on Postural Stability, Lumbopelvic Control, and Proprioception in Women with Diastasis Recti Abdominis: A Randomized, Single-Blinded, Controlled Trial. Physiother. Theory Pract. 2023, 39, 2596–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gluppe, S.B.; Ellström Engh, M.; Bø, K. Curl-Up Exercises Improve Abdominal Muscle Strength without Worsening Inter-Recti Distance in Women with Diastasis Recti Abdominis Postpartum: A Randomised Controlled Trial. J. Physiother. 2023, 69, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walton, L.M.; Costa, A.; LaVanture, D.; McIlrath, S.; Stebbins, B. The Effects of a 6 Week Dynamic Core Stability Plank Exercise Program Compared to a Traditional Supine Core Stability Strengthening Program on Diastasis Recti Abdominis Closure, Pain, Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) and Pelvic Floor Disability Index Scores (PFDI). Phys. Ther. Rehabil. 2016, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coldron, Y.; Stokes, M.J.; Newham, D.J.; Cook, K. Postpartum Characteristics of Rectus Abdominis on Ultrasound Imaging. Man. Ther. 2008, 13, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsia, M.; Jones, S. Natural Resolution of Rectus Abdominis Diastasis. Two Single Case Studies. Aust. J. Physiother. 2000, 46, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, G.M.; Schuster, A.; Seifert, B.; Manestar, M.; Mihic-Probst, D.; Weber, S.A. The Normal Width of the Linea Alba in Nulliparous Women. Clin. Anat. 2009, 22, 706–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veríssimo, P.; Nahas, F.X.; Barbosa, M.V.J.; de Carvalho Gomes, H.F.; Ferreira, L.M. Is It Possible to Repair Diastasis Recti and Shorten the Aponeurosis at the Same Time? Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2014, 38, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsson, R.J.; Oikarinen, A.; Krogell, J.; Kankkunen, P. Group-Based Cardiac Telerehabilitation Interventions and Health Outcomes in Coronary Patients: A Scoping Review. Clin. Rehabil. 2024, 38, 184–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bø, K. Physiotherapy Management of Urinary Incontinence in Females. J. Physiother. 2020, 66, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Sánchez, E.; Ávila-Gandía, V.; López-Román, J.; Martínez-Rodríguez, A.; Rubio-Arias, J. What Pelvic Floor Muscle Training Load Is Optimal in Minimizing Urine Loss in Women with Stress Urinary Incontinence? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay-Smith, E.J.C.; Herderschee, R.; Dumoulin, C.; Herbison, G.P. Comparisons of Approaches to Pelvic Floor Muscle Training for Urinary Incontinence in Women. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beamish, N.; Green, N.; Nieuwold, E.; McLean, L. Differences in linea alba stiffness and linea alba distortion between women with and without diastasis recti abdominis: The impact of measurement site and task. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2019, 49, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, D.d.A.; Nahas, F.X.; Veiga, D.F.; Mendes, F.V.; Figueiras, R.G.; Gomes, H.C.; Ely, P.B.; Novo, N.F.; Ferreira, L.M. Ultrasonography for measuring rectus abdominis muscles diastasis. Acta Cir. Bras. 2007, 22, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, E.; Wu, J.; Zhang, M.; Wu, L.; Zhang, T.; Xu, J.; Zhang, X. The ultrasound diagnostic criteria for diastasis recti and its correlation with pelvic floor dysfunction in early postpartum women. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2021, 11, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Category | Mean (SD) |
| Age (years) | 37.54 (5.5) |
| Height (cm) | 165.31 (4.6) |
| Weight (kg) | 63.54 (9.5) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.25 (3.4) |
| Time postpartum (months) | 26.69 (21.1) |
| Types and number of births | Percentage (Frequency) |
| Primiparous (n = 5) | 38.46% |
| -vaginal birth (n = 2) | 40% |
| -cesarean (n = 3) | 60% |
| Multiparous (n = 8) | 61.54% |
| -vaginal birth (n = 5) | 62.5% |
| -cesarean (n = 3) | 37.5% |
| TUQ_Greek Factors | Mean (SD) | Median | Min–Max | IQR * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Usefulness (Items 1–3) | 6.10 (0.98) | 6.33 | 12–21 | 1.83 |
| Ease of Use and Learnability (Items 4–6) | 6.77 (0.44) | 7.00 | 17–21 | 0.33 |
| Interface Quality (Items 7–10) | 6.63 (0.57) | 6.75 | 20–28 | 0.50 |
| Interaction Quality (Items 11–14) | 6.54 (0.59) | 6.75 | 21–28 | 0.75 |
| Reliability (Items 15–17) | 5.00 (1.56) | 5.33 | 5–21 | 2.34 |
| Satisfaction and Future Use (Items 18–21) | 6.65 (0.54) | 7.00 | 21–28 | 0.62 |
| Overall TUQ_Greek (total score) | 6.28 (0.60) | 6.26 | 104–147 | 0.87 |
| Outcome | Pre-Intervention | Post-Intervention | Mean Difference (95% CI) | p-Value | Effect Sizes (Cohen’s d) | 95% CI (Lower–Upper) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | ||||||
| IRD—2 cm below umbilicus | 2.60 (0.93) | 2.39 (0.74) | 0.21 (−0.24 to 0.66) | 0.321 | 0.30 | −0.29 to 0.87 |
| IRD—2 cm above umbilicus | 3.70 (0.76) | 3.40 (0.81) | 0.29 (0.12 to 0.47) | * 0.004 | 1.00 | 0.31 to 1.66 |
| IRD—5 cm above umbilicus | 3.31 (0.98) | 2.97 (0.88) | 0.33 (0.08 to 0.58) | * 0.013 | 0.81 | 0.16 to 1.42 |
| BISS_Greek | 5.69 (1.84) | 6.64 (1.15) | −0.95 (−1.75 to −0.16) | * 0.023 | −0.73 | −1.33 to −0.10 |
| Test | Baseline | Week 4 | Week 8 | Week 12 | Significant Pairwise Comparisons (Bonferroni-Adjusted)/p-Value (Repeated Measures ANOVA) | Partial η2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) in sec | ||||||
| Curl-up | 119.06 (84.5) | 99.10 (57.4) | 168.68 (97.5) | 203.97 (114.4) | p = 0.134 (No significant pairwise comparisons) | 0.488 |
| Front Plank | 46.57 (29.4) | 60.99 (27.6) | 72.60 (28.7) | 80.41 (28.6) | p = 0.113 (No significant pairwise comparisons) | 0.441 |
| Right Side Plank | 31.73 (17.3) | 37.66 (12.5) | 41.32 (8.3) | 51.21 (17.4) | Baseline< Week 12 (p = 0.029 *) | 0.483 |
| Left Side Plank | 28.26 (18.2) | 35.36 (15.3) | 42.16 (13.0) | 49.45 (15.1) | Baseline < Week 12 (p = 0.028 *) Week 4 < Week 12 (p = 0.010 *) Week 8 < Week 12 (p = 0.028 *) | 0.562 |
| McGill’s Trunk Flexor Endurance | 62.00 (28.0) | 92.01 (28.8) | 117.45 (60.9) | 128.93 (61.2) | Baseline < Week 4 (p = 0.036 *) Baseline < Week 12 (p = 0.023 *) | 0.477 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skoura, A.; Antoniou, M.; Thanatsis, N.; Papanikolaou, D.T.; Tsirogiannis, G.; Drakonaki, E.; Billis, E. Feasibility and Preliminary Efficacy of a Telerehabilitation Intervention for Diastasis Recti Abdominis—A Pilot Study. Healthcare 2025, 13, 2224. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13172224
Skoura A, Antoniou M, Thanatsis N, Papanikolaou DT, Tsirogiannis G, Drakonaki E, Billis E. Feasibility and Preliminary Efficacy of a Telerehabilitation Intervention for Diastasis Recti Abdominis—A Pilot Study. Healthcare. 2025; 13(17):2224. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13172224
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkoura, Anastasia, Maria Antoniou, Nikolaos Thanatsis, Dimitra Tania Papanikolaou, George Tsirogiannis, Elena Drakonaki, and Evdokia Billis. 2025. "Feasibility and Preliminary Efficacy of a Telerehabilitation Intervention for Diastasis Recti Abdominis—A Pilot Study" Healthcare 13, no. 17: 2224. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13172224
APA StyleSkoura, A., Antoniou, M., Thanatsis, N., Papanikolaou, D. T., Tsirogiannis, G., Drakonaki, E., & Billis, E. (2025). Feasibility and Preliminary Efficacy of a Telerehabilitation Intervention for Diastasis Recti Abdominis—A Pilot Study. Healthcare, 13(17), 2224. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13172224







