Exercise Interventions for Metabolic Diseases: An Analysis of the Evolution of Aerobic Exercise Bibliometrics in the Field of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
1. Introduction
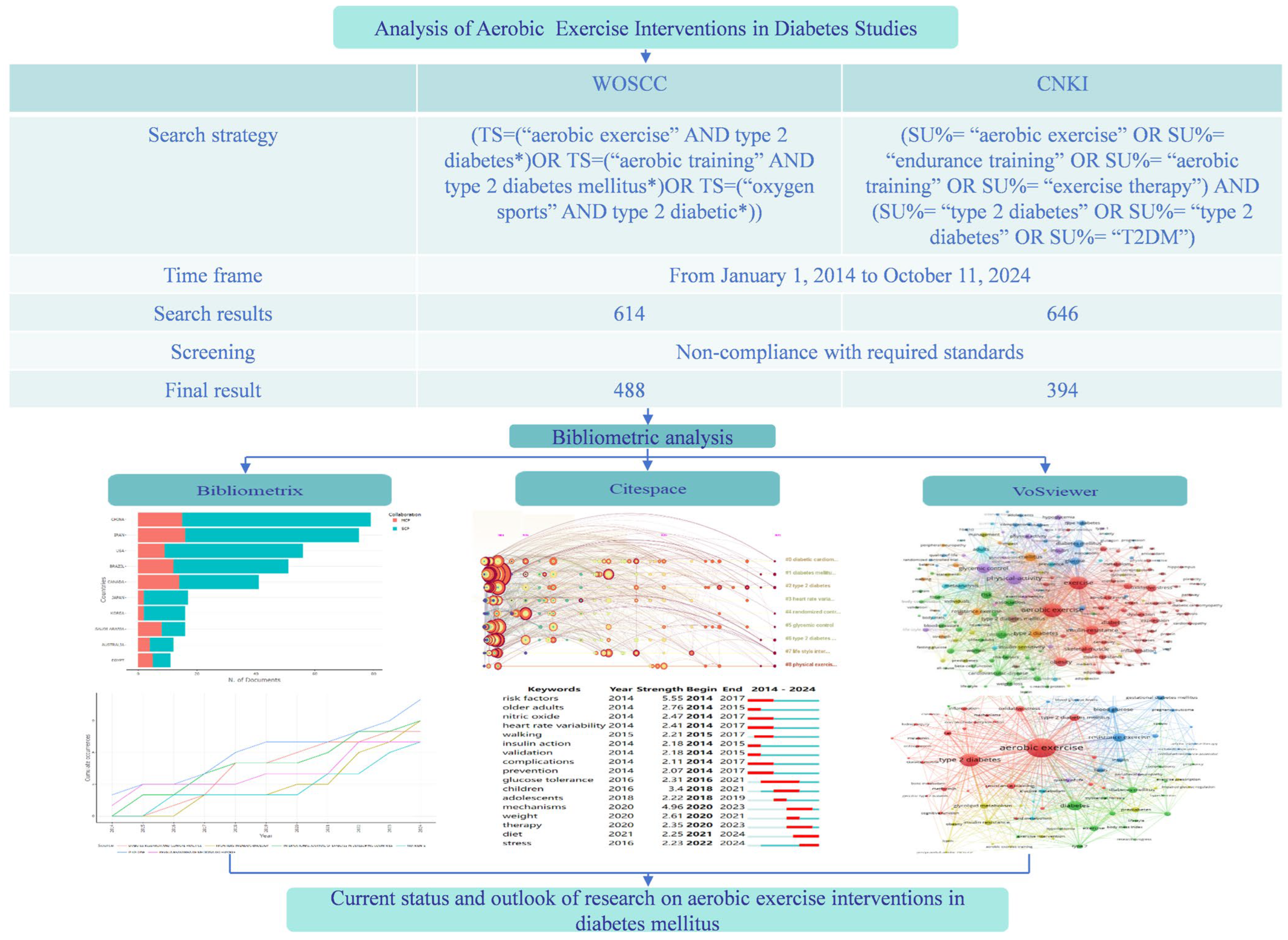
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Screening Process
2.4. Data Analysis and Visualization
3. Results
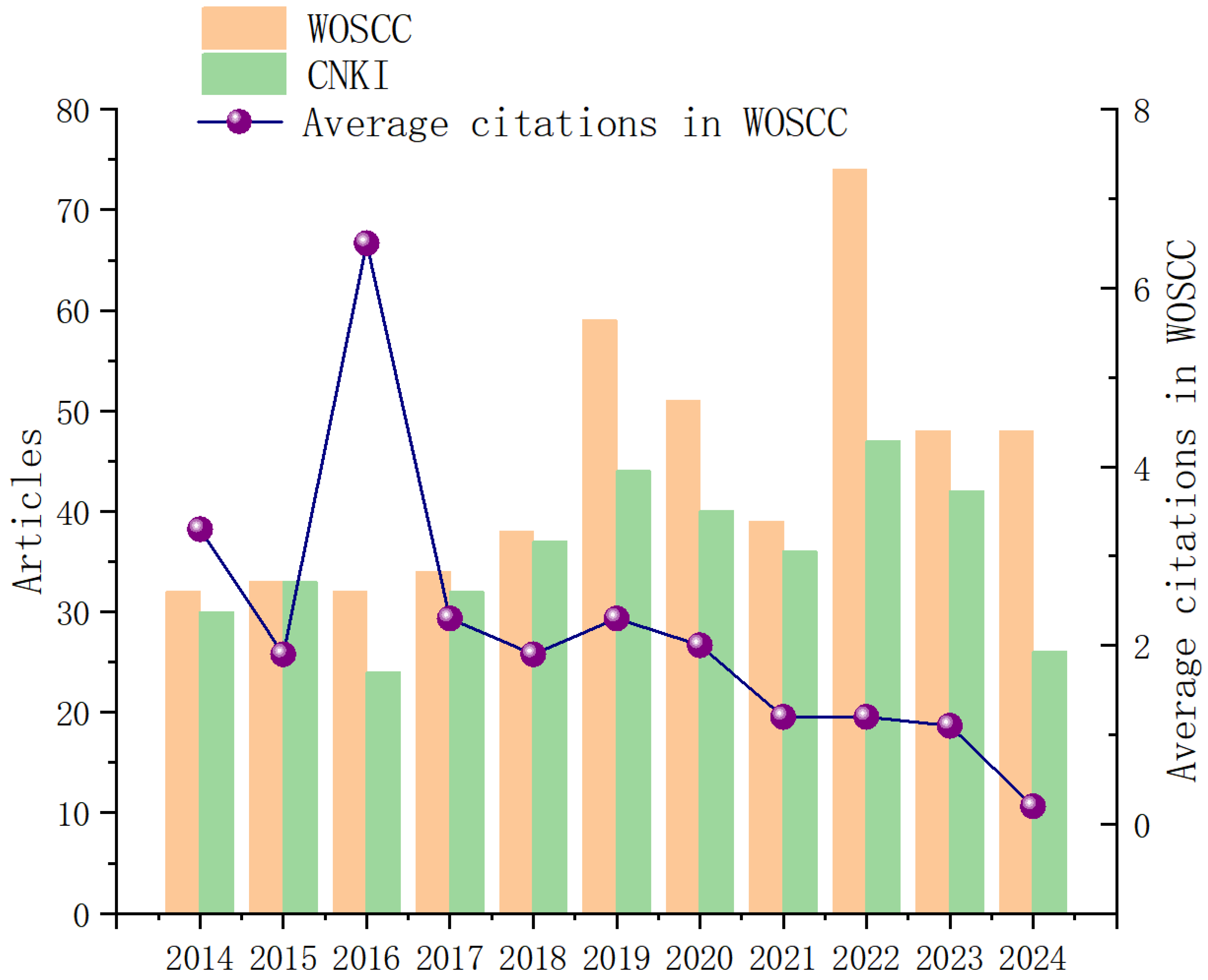
3.1. Trends in Publications and Core Journals
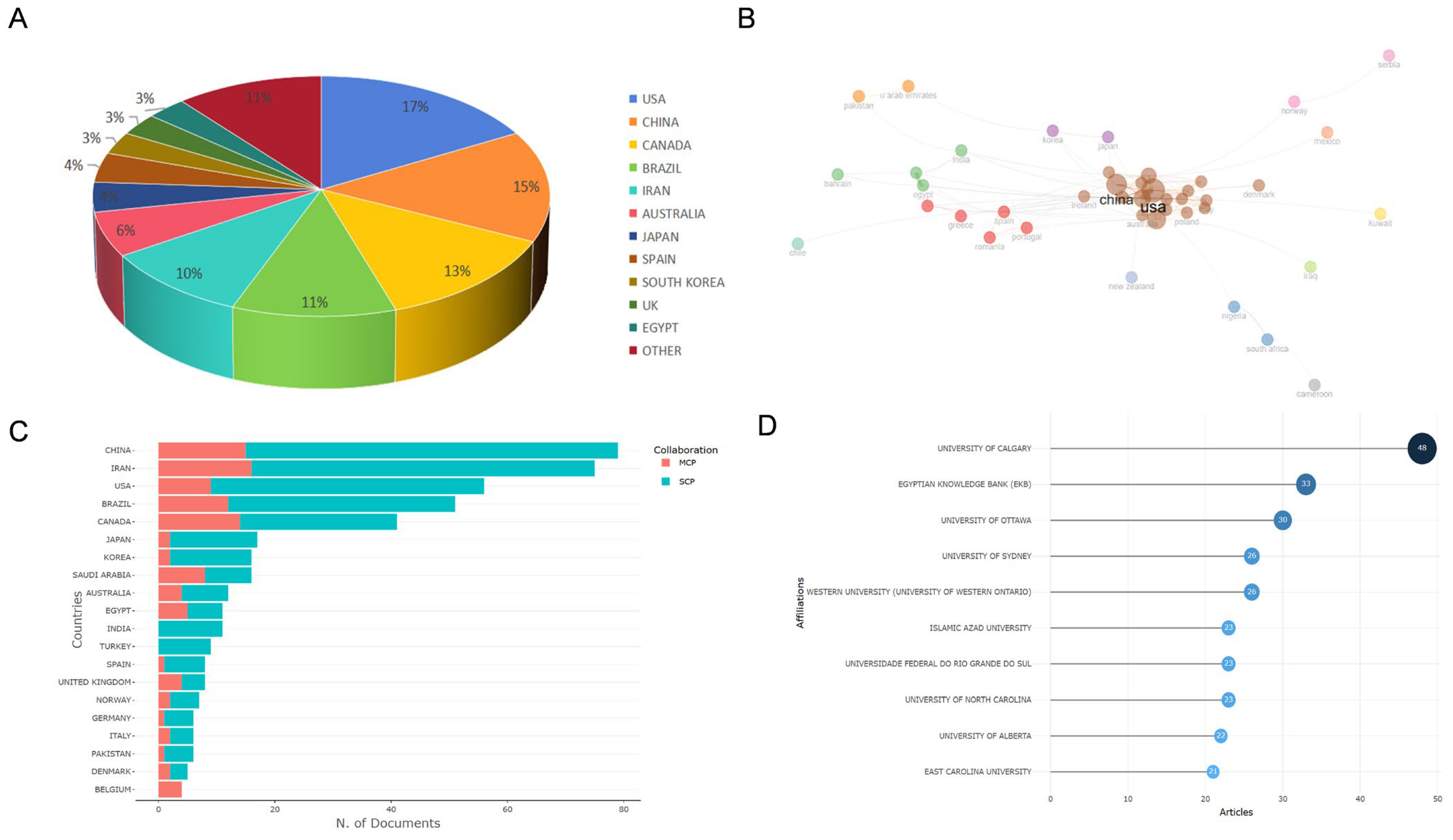
3.2. Overview of Countries/Areas, Institutions, and Active Authors
3.3. Co-Citation Analysis of Highly Influential Literature and Research Hotspot Evolution
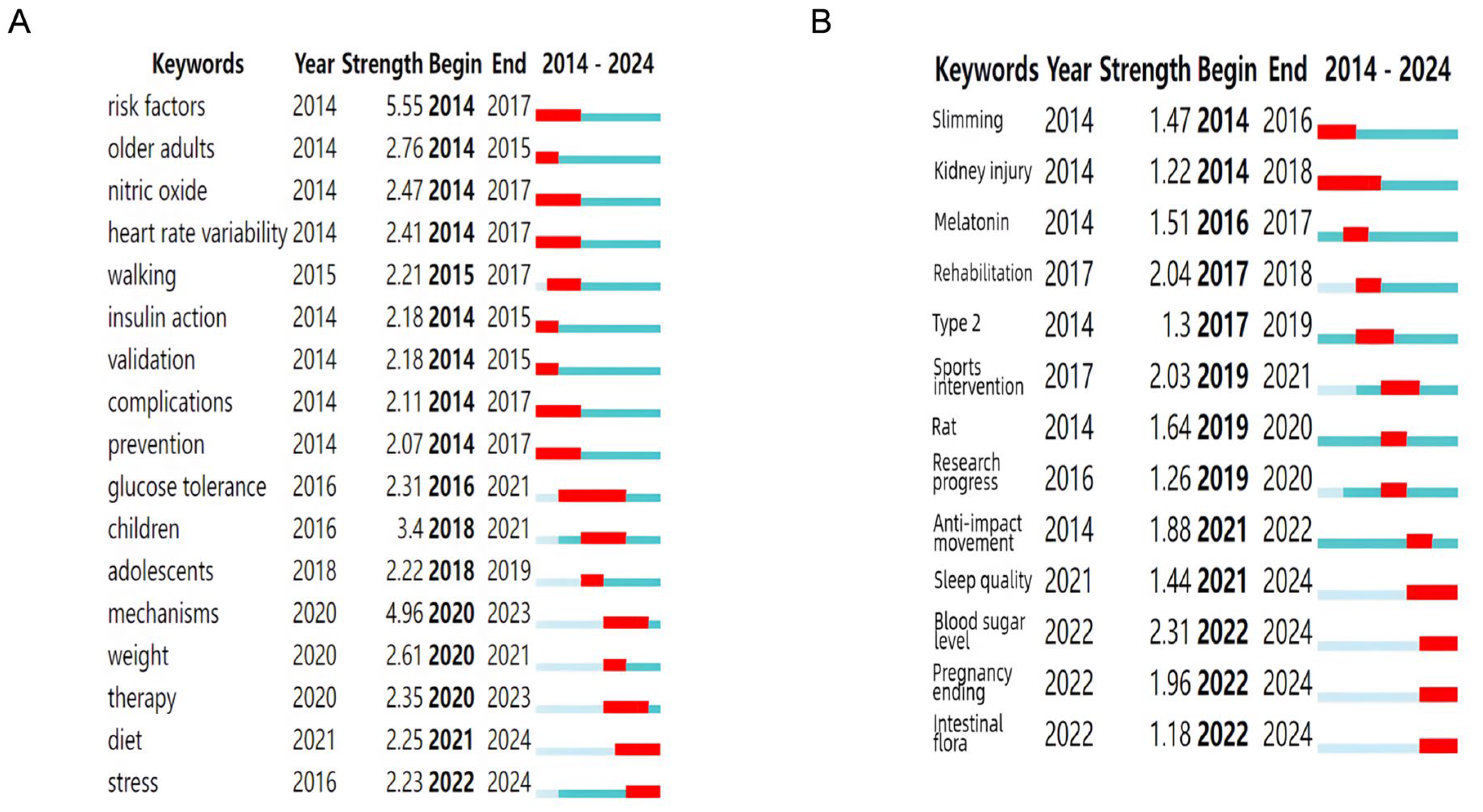
3.4. Keyword Co-Occurrence Network and Clustering Evolution Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Limitations of the Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| T2DM | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus |
| AE | Aerobic Exercise |
| WOSCC | Web of Science Core Collection |
| CNKI | China National Knowledge Infrastructure |
| GLUT4 | Glucose Transporter 4 |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-α |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| RT | Resistance Training |
| HIIT | High-intensity Interval Training |
| HbA1c | Glycated Hemoglobin |
| NO | Nitric Oxide |
| ADA | American Diabetes Association |
| IDF | International Diabetes Federation |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| MCP | Multi-Country Collaboration Papers |
| SCP | Single-Country Collaboration Papers |
| EKB | Egyptian Knowledge Bank |
| IF | Impact Factor |
References
- Dharmalingam, M.; Marcus, S.R. Pathogenetic Mechanism of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and its Clinical Implications. Ann. Natl. Acad. Med. Sci. 2019, 55, 132–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowan, C.P.; Riddell, M.C.; Gledhill, N.; Jamnik, V.K. Aerobic Exercise Training Modalities and Prediabetes Risk Reduction. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2017, 49, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.N.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleicher, E.; Gerdes, C.; Petersmann, A.; MüllerWieland, D.; Müller, U.A.; Freckmann, G.; Heinemann, L.; Nauck, M.; Landgraf, R. Definition, Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2022, 130, S1–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harreiter, J.; Roden, M. Diabetes mellitus—Definition, classification, diagnosis, screening and prevention (Update 2019). Wien Klin. Wochenschr. 2019, 131, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draznin, B.; Aroda, V.R.; Bakris, G.; Benson, G.; Brown, F.M.; Freeman, R.S.; Green, J.; Huang, E.; Isaacs, D.; Kahan, S.; et al. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care 2022, 45 (Suppl. 1), S17–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabapathy, I.; Periyasamy, V.; Jayaraman, S.; Manikkam, R. Novel Triterpenoids from Cassia fistula Stem Bark Depreciates STZ-Induced Detrimental Changes in IRS-1/Akt-Mediated Insulin Signaling Mechanisms in Type-1 Diabetic Rats. Molecules 2021, 26, 6812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Fujita, N.; Tsuruo, T. Involvement of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 in the MEK/MAPK signal transduction pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 33759–33767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bati, K.; Baeti, P.B.; Gaobotse, G.; Kwape, T.E. Leaf extracts of Euclea natalensis A.D.C ameliorate biochemical abnormalities in high-fat-low streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats through modulation of the AMPK-GLUT4 pathway. Egypt. J. Basic. Appl. Sci. 2024, 11, 232–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Wefers, J.; Meier, J.J. Treatment of type 2 diabetes: Challenges, hopes, and anticipated successes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 525–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, G.; Riddell, M.C.; Adegoke, O.A.J. Effects of Acute Muscle Contraction on the Key Molecules in Insulin and Akt Signaling in Skeletal Muscle in Health and in Insulin Resistant States. Diabetology 2022, 3, 423–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzaffar, M.M.; Rashid, M.; Alghamdi, M.A.A.; Wani, J.I.; Zia Ul, S.; Jeelani, M.; Vijaya, M.; Shahzada Khalid, S.; O’haj, M.; Alharthi, M.H.; et al. Differential Association of Selected Adipocytokines, Adiponectin, Leptin, Resistin, Visfatin and Chemerin, with the Pathogenesis and Progression of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) in the Asir Region of Saudi Arabia: A Case Control Study. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, R.; Mokhtari, Y.; Yousefi, A.M.; Bashash, D. The PI3K/Akt signaling axis and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM): From mechanistic insights into possible therapeutic targets. Cell Biol. Int. 2024, 48, 1049–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Liu, S.F. Research Progress on Inflammation, Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes, and Genome-Wide Association Studies. J. Shandong Med. Coll. 2015, 37, 239–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, I.; Koo, D.J.; Lee, W.Y. Insulin Resistance, Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Clinical and Experimental Perspective. Diabetes Metab. J. 2024, 48, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Palyha, O.; Mu, J. Restoration of insulin receptor improves diabetic phenotype in T2DM mice. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e124945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tryggestad, J.B.; Willi, S.M. Complications and comorbidities of T2DM in adolescents: Findings from the TODAY clinical trial. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2015, 29, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łukasiewicz, A.; Cichoń, E.; Kostecka, B.; Kiejna, A.; JodkoModlińska, A.; Obrębski, M.; Kokoszka, A. Association of Higher Rates of Type 2 Diabetes (T2DM) Complications with Psychological and Demographic Variables: Results of a Cross-Sectional Study. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2022, 15, 3303–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, X.P.; Cao, Y.X.; Li, S.C.; Sun, J.Z.; Ding, H.L.; Shang, H.Y.; Su, Q.S. Effects and Mechanisms of Different Exercises on the Structure and Function of Peripheral Nerves in Diabetic Rats. Chin. J. Sports Med. 2018, 37, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, D.; Berg, A. Physical exercise as treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Internist 2012, 53, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Chen, W.; Zhang, M.; Gao, M. Effects of Aerobic Combined with Resistance Exercise on Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Chin. J. Rehabil. Theory Pract. 2018, 24, 1465–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, A.H.; Almutairi, N.S.; Mousa, N.; Elsayed, A.; El Sehrawy, A.; Elmetwalli, A. Aerobic exercise as a non-pharmacological intervention for improving metabolic and hemodynamic profiles in type 2 diabetes. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2024, 193, 2781–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezema, C.I.; Okwuchukwu, C.K.; Amarachukwu, C.N.; Nweke, M.C.; Obiekwe, C.; Okafor, C.I.; Okoye, G.C. Effect of a Single Bout Interval Aerobic Exercise on Blood Glucose Level in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients. Indian J. Physiother. Occup. Ther. 2019, 13, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos Pinto, P.; Del Bianco, V.; Garcia Bochi, A.P.; Silva Ferreira, G.; da Silva Trevisani, M.; Gomes Rodrigues, L.; Nakandakare, E.R.; Okamoto, M.; Fabres Machado, U.; Catanozi, S.; et al. Aerobic Exercise Training Counteracts Insulin Resistance Induced By Low Sodium Diet by Increasing Insulin Signaling in Muscle. Atherosclerosis 2019, 287, e94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, W.; Huang, C.; Hu, J.; Chen, X.; Lv, X.; Qin, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, H. Aerobic Exercise Improves Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus-Related Cognitive Impairment by Inhibiting JAK2/STAT3 and Enhancing AMPK/SIRT1 Pathways in Mice. Dis. Markers 2022, 2022, 6010504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizi, M.; Tadibi, V.; Behpour, N. The effect of aerobic exercise training on β-cell function and circulating levels of adipsin in community of obese women with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Diabetes Dev. Ctries. 2017, 37, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Butler, A.E.; Sahebkar, A. Aerobic exercise can modulate the underlying mechanisms involved in the development of diabetic complications. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 12508–12515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nataraj, M.; Maiya, A.G.; Nagaraju, S.P.; Shastry, B.A.; Shivashankara, K.N. Effect of exercise on renal function in diabetic nephropathy-a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Taibah Univ. Med. Sci. 2023, 18, 526–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shui, X.P.; Li, C.Y.; Li, S.C.; Sun, J.Z.; Su, Q.S. Expression of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor, Nuclear Factor-κB and Inflammatory Indexes in Skeletal Muscle of Type 2 Diabetic Rats after Aerobic and Resistance Exercise Interventions. Chin. J. Tissue Eng. Res. 2022, 26, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donthu, N.; Kumar, S.; Mukherjee, D.; Pandey, N.; Lim, W.M. How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 133, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.-S. Classic Articles on Social Work Field in Social Science Citation Index: A Bibliometric Analysis. Scientometrics 2014, 98, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandasari, D.; Tjahjana, D.; Dwidienawati, D.; Sugiarto, M. Bibliometric and visualized analysis of social network analysis research on Scopus databases and VOSviewer. Cogent Bus. Manag. 2024, 11, 2376899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Miao, F.R.; Fan, Y.S. A bibliometric analysis of diabetic gastroparesis from 1979 to 2024. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1445276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.-L.; Li, X.-X.; Li, M.-X.; He, Y.-Y.; Sun, M.-Y.; Deng, Q.-Y.; Liu, W.; Song, R.-L.; Ma, J.-M.; Zheng, Y.; et al. A bibliometric analysis of lipid peroxidation in alcoholic liver disease from 2001 to 2024. Food Med. Homol. 2024, 1, 9420009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.P. Research trends and areas of focus on the Chinese Loess Plateau: A bibliometric analysis during 1991–2018. Catena 2020, 194, 104798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Železnik, U.; Kokol, P.; Starc, J.; Železnik, D.; Završnik, J.; Blažun Vošner, H. Research Trends in Motivation and Weight Loss: A Bibliometric-Based Review. Healthcare 2023, 11, 3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.M.; Guo, Q.; Yang, W.G.; Wang, Y.L.; Sun, Z.J.; Wu, H.Y. Mapping Knowledge Landscapes and Emerging Trends of the Links Between Bone Metabolism and Diabetes Mellitus: A Bibliometric Analysis From 2000 to 2021. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 918483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, L.K.; Tam, H.L.; Mao, A.M. A Bibliometric Review of Person-Centered Care Research 2010–2024. Healthcare 2025, 13, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Chae, Y.B.; Park, H.J.; Lee, I.S. A Bibliometric Analysis of Atopic Dermatitis Research over the Past Three Decades and Future Perspectives. Healthcare 2021, 9, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, S.; Lynch, J.; D’Alton, P.; Carr, A. Psycho-Oncology: A Bibliometric Review of the 100 Most-Cited Articles. Healthcare 2021, 9, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colberg, S.R.; Sigal, R.J.; Yardley, J.E.; Riddell, M.C.; Dunstan, D.W.; Dempsey, P.C.; Horton, E.S.; Castorino, K.; Tate, D.F. Physical Activity/Exercise and Diabetes: A Position Statement of the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 2065–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashino, Y.; Jackson, J.L.; Hirata, T.; Fukumori, N.; Nakamura, F.; Fukuhara, S.; Tsuji, S.; Ishii, H. Effects of exercise on C-reactive protein, inflammatory cytokine and adipokine in patients with type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Metabolism 2014, 63, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitranun, W.; Deerochanawong, C.; Tanaka, H.; Suksom, D. Continuous vs. interval training on glycemic control and macro and microvascular reactivity in type 2 diabetic patients. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2014, 24, e69–e76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Cai, X.; Yin, H.; Sun, Z.; Zügel, M.; Steinacker, J.M.; Schumann, U. Exercise Training and Endothelial Function in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, E.; Durrer, C.; Simtchouk, S.; Jung, M.E.; Bourne, J.E.; Voth, E.; Little, J.P. Short-term High-intensity Interval and Moderate-intensity Continuous Training Reduce Leukocyte TLR4 in Inactive Adults at Elevated Risk of Type 2 Diabetes. J. Appl. Physiol. 2015, 119, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liubaerjijin, Y.; Terada, T.; Fletcher, K.; Boulé, N.G. Effect of Aerobic Exercise Intensity on Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta - analysis of Head - to - Head Randomized Trials. Acta Diabetol. 2016, 53, 769–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, S.; Maiya, A.G.; Shastry, B.A. Effect of Aerobic Exercise on Peripheral Nerve Functions of Population with Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetes: A Single Blind, Parallel Group Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2014, 28, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donley, D.A.; Fournier, S.B.; Reger, B.L.; DeVallance, E.; Bonner, D.E.; Olfert, I.M.; Frisbee, J.C.; Chanter, P.D. Aerobic Exercise Training Reduces Arterial Stiffness in Metabolic Syndrome. J. Appl. Physiol. 2014, 116, 1345–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharieva, D.P.; Turksoy, K.; McGaugh, S.M.; Pooni, R.; Vienneau, T.; Ly, T.; Riddell, M.C. Lag Time Remains with Newer Real—Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring Technology During Aerobic Exercise in Adults Living with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2019, 21, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, S.; Colberg, S.R.; Parson, H.K.; Vinik, A.I. Exercise Improves Gait, Reaction Time and Postural Stability in Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes and Neuropathy. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2014, 28, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Ge, J.; Zhao, C.; Le, S.L.; Yang, Y.F.; Ke, D.D.; Wu, N.; Tan, X.; Zhang, X.B.; Du, X.M.; et al. Effect of Aerobic Exercise and Diet on Liver Fat in Pre - Diabetic Patients with Non–Alcoholic–Fatty–Liver–Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelbasset, W.K.; Tantawy, S.A.; Kamel, D.M.; Alqahtani, B.A.; Elnegamy, T.E.; Soliman, G.S.; Ibrahim, A. Effects of High-Intensity Interval and Moderate-Intensity Continuous Aerobic Exercise on Diabetic Obese Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Comparative Randomized Controlled Trial. Medicine 2020, 99, e19471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, M.; Rodrigues-Krause, J.; O’Hagan, C.; Medlow, P.; Davison, G.; Susta, D.; Boreham, C.; Newsholme, P.; O’Donnell, M.; Murphy, C.; et al. The Effects of Aerobic Exercise Training at Two Different Intensities in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes: Implications for Oxidative Stress, Low - Grade Inflammation and Nitric Oxide Production. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2014, 114, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, K.; Riddell, M.C.; Guinhouya, B.C.; Adolfsson, P.; Hanas, R. Exercise in Children and Adolescents with Diabetes (ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2014 Compendium). Pediatr. Diabetes 2014, 15 (Suppl. 20), 203–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelbasset, W.K.; Tantawy, S.A.; Kamel, D.M.; Alqahtani, B.A.; Soliman, G.S. A Randomized Controlled Trial on the Effectiveness of 8—Week High—Intensity Interval Exercise on Intrahepatic Triglycerides, Visceral Lipids, and Health—Related Quality of Life in Diabetic Obese Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Medicine 2019, 98, e14918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.M.; Zhou, K.H.; Chen, Y.; Ling, Y.C.; Qin, Q.Q.; Lu, J.Y. Global Trends in Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Support for Circulatory Failure: A Bibliometric Analysis. Healthcare 2025, 13, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunaseelan, V.; Selvarajan, S.; Kamalanathan, S.; Kadhiravan, T.; Venkatraman, S. Effect of metformin on exercise capacity in treatment naïve type 2 diabetes patients. Drug Metab. Pers. Ther. 2024, 40, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Liu, J.J.; Zhang, L.M.; Wang, X.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Q. Morphological and functional characterization of diabetic cardiomyopathy in db/db mice following exercise, metformin alone, or combination treatments. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 584, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgio, O.; Pugh, J.; Faulkner, S.; Balducci, S.; Sacchetti, M.; Pugliese, G.; Bazzucchi, I.; Haxhi, J.; MartinezValdes, E.; Falla, D.; et al. Muscular Adaptations to Concurrent Resistance Training and High-Intensity Interval Training in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 6746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, J.P.; Santos, D.A.; Correia, I.R.; Hetherington-Rauth, M.; Ribeiro, R.; Raposo, J.F.; Matos, A.; Bicho, M.D.; Sardinha, L.B. Impact of combined training with different exercise intensities on inflammatory and lipid markers in type 2 diabetes: A secondary analysis from a 1-year randomized controlled trial. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2020, 19, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, R.A.L. Brief report of the effects of the aerobic, resistance, and high-intensity interval training in type 2 diabetes mellitus individuals. Int. J. Diabetes Dev. Ctries. 2018, 38, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wu, L.D.; Zhang, J.X. Research Progress on the Mechanism of Resveratrol in Preventing and Treating Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Adv. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2024, 45, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.J.; Wu, A.N.; Hou, N.; Li, N. Effects of Aerobic Exercise and Resveratrol on Inflammation and Apoptosis in Renal Tissue of Rats with Diabetic Nephropathy. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2024, 36, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q. Effect of Aerobic Exercise Combined with Different Resistance Training on Blood Glucose and Blood Lipid Metabolism in Elderly Patients with T2DM. J. Xi’an Phys. Educ. Inst. 2021, 38, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Li, N.C.; Xiao, L.; Tao, R.; Zhang, Z.K. Research on Treatment Effect of Different Aerobics on Type II Diabetes for the Elderly of Orchid Community. Sports Technol. Lit. Bull. 2015, 23, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Yao, J.M.; Zhou, G.J.; Li, M.Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, M. Effect of High-Intensity Interval Training on Exercise Intervention in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Based on “WHO Guidelines on Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior” and WHO-FICs. Chin. J. Rehabil. Theory Pract. 2022, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.Q.; Lu, J.Y.; Li, R. Effect of Exercise Nursing Intervention Based on FATmax Theory on Community Elderly Patients with T2DM. J. Qilu Nurs. 2021, 27, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.N.; Weng, Y.J.; Zhang, W.W.; Dong, D.; Shi, J.J.; Cheng, H.L. Efficacy Observation of High-Intensity Interval Aerobic Training and Continuous Moderate-Intensity Aerobic Training in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Chin. J. Rehabil. 2021, 36, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.C.; Li, W.G.; Yu, M.M. Optimization of Research Paradigm of Chinese Journal Knowledge Graph. Chin. Distance Educ. 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templer, S.; Abdo, S.; Wong, T. Preventing diabetes complications. Intern. Med. J. 2024, 54, 1264–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memelink, R.G.; Hijlkema, A.; Valentin, B.; Streppel, M.T.; Pasman, W.J.; Wopereis, S.; de Vogel-van den Bosch, J.; Tieland, M.; Schoufour, J.D.; Bautmans, I.; et al. Long-term preservation of lean mass and sustained loss of fat mass after completion of an intensive lifestyle intervention in older adults with obesity and type 2 diabetes. Lifestyle Med. 2024, 5, e2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.X.; Wang, C.F.; Xin, J. Short-Chain Fatty Acids Inhibit Apoptosis of Mouse Pancreatic β-Cells by Activating GPR43 to Up-Regulate the AMPK Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Lab. Med. 2023, 44, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Li, X.Q.; Tu, N.; Xu, X.; Yang, L.P. Application of Continuous Glucose Monitoring System in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Chin. J. Prev. Contr. Chron. Dis. 2021, 29, 700–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.L.; Li, L.; Wang, N.; Maimaiti, M.; Zhao, F.G. Effects of Gut Microbiota Transplantation and Probiotic Supplements on Anti-Inflammation, Antioxidation, and Pregnancy Outcomes in Rats with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Chin. J. Microbiol. 2024, 36, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.Y.; Zhu, Y.P.; Nie, L.; Luo, Y.S.; Qiu, S.Y.; Ren, T.Y. Exploring the Mechanism of Action of Rosa roxburghii Tratt Quercetin in Ameliorating Type 2 Diabetes in Mice Based on the Intestinal Microbiome and Metabolomics. J. Funct. Foods 2025, 124, 106640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.X.; Li, Z. Research Progress of Gut Microbiota as a Target for Treating Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Youjiang Med. Univ. Natl. 2024, 46, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nian, L.; Xia, Y.H.; He, Q.; Xing, X.H. Analysis of Research Hotspots in Diabetes Management in China. Prev. Med. 2020, 32, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, N.; Jia, L.Y.; Cheng, A.; Ren, H.H.; Fu, Y.; Ding, X.H.; Haq, I.U.; Liu, E.Q. Global research trends on gut microbiota and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis: Insights from bibliometric and scientometric analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1390483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassir, D.S.; Adhikari, P.; Rao, N.L. IDF23-0359 Role of 25(OH)vitamin D with CAD Risk Factors, Glycation Biomarkers, Insulin Resistance and Syntax Score in T2DM with CAD. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2024, 209, 111229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnuaimi, S.; Reljic, T.; Abdulla, F.; Memon, H.; Al Ali, S.; Smith, T.; Serdarevic, F.; Asimi, Z.V.; Kumar, A.; Semiz, S. IDF23-0213 Effects of adding thiazolidinediones to metformin in Type 2 diabetes management: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2024, 209, 111214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.H.; Qi, Y.G. Research on Aerobic Exercise Intervention for Type II Diabetes Patients. Contemp. Sports Technol. 2012, 2, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, Y.Q.; Yang, Y.J. Analysis on serum leptin and adiponectin levels in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Jilin Med. Coll. 2015, 36, 334–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.X.; Jing, Q.P.; Zhao, C.H. Effects of Combined Aerobic and Resistance Exercise on Oxidative Stress and Glucose-Lipid Metabolism in Elderly Type 2 Diabetes Patients. Chin. J. Gerontol. 2019, 39, 591–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, B.K.; Li, S.C.; Gao, D.R.; Ke, Z.F.; Wang, R.Y.; Su, Q.S. Role of Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway in Aerobic Exercise-Induced Intervention on Skeletal Muscle Oxidative Stress in Type 2 Diabetic Rats. Chin. J. Pain. Med. 2022, 37, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.H.; Lin, X. Advances in the Relationship between Dietary Fiber, Gut Microbiota and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Chin. J. Microcirc. 2024, 34, 82–85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagasabai, T.; Riddell, M.C.; Ardern, C.I. Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Antioxidant Micronutrients as Mediators of the Relationship Between Sleep, Insulin Sensitivity, and Glycosylated Hemoglobin. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 888331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Y.F.; Zhai, L.; Liu, Y.H.; Ma, C.; Huang, S.; Zhong, X.; Dai, X. Effects of Different Exercise Modes on Intestinal Flora and Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. J. Guangxi Med. Univ. 2022, 39, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, P.K.; Sales, M.M.; de Almeida, J.A.; Motta-Santos, D.; de Sousa, C.V.; Simões, H.G. Effects of aerobic exercise intensity on 24-h ambulatory blood pressure in individuals with type 2 diabetes and prehypertension. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2015, 27, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyeguli, M.; Mugerili, M.; Li, X.M.; Senaewa, A.; Yemusier, H. Characteristics of Gut Microbiota Structure and Serum Metabolites in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Based on Gut Microbiology and Metabolomics. Guangdong Med. J. 2024, 45, 139–146. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.13820/j.cnki.gdyx.20233391 (accessed on 30 July 2025).
- Li, C.W.; Li, D.Y.; Liu, H.J.; Zhang, N.; Dang, L.Y.; Wang, M.S.; Tian, H.T.; Jha, R.; Li, C. Synbiotic supplementation with xylooligosaccharide derived probiotic Lactobacillus gasseri and prebiotic mixture exerts antidiabetic effects via collaborative action. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydemir, D.; Salman, N.; Kerimzade, U.; Anapali Aykac, M.; Ulutin, T.; Komurcu Bayrak, E.; Kaya Dagistanli, F.; Erdem Alaca, B.; Nuray Ulusu, N. The impact of the vitamin D and resveratrol administration on the stiffness and elasticity of T2DM rat aorta associated with the trace element and mineral levels. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2024, 86, 127497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Rank | Source | Local Citations | Articles | H-Index | Impact Factor (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DIABETES CARE | 1388 | 5 | 5 | 14.8 |
| 2 | MED SCI SPORT EXER | 540 | 4 | 4 | 4.1 |
| 3 | DIABETES | 495 | 2 | 5 | 6.2 |
| 4 | DIABETOLOGIA | 456 | 3 | 2 | 8.4 |
| 5 | J APPL PHYSIOL | 384 | 4 | 3 | 3.3 |
| 6 | PLOS ONE | 318 | 11 | 6 | 2.9 |
| 7 | CIRCULATION | 278 | 3 | 3 | 35.6 |
| 8 | JAMA-J AM MED ASSOC | 276 | 1 | 5 | 63.5 |
| 9 | DIABETES RES CLIN PR | 251 | 8 | 5 | 6.1 |
| 10 | J CLIN ENDOCR METAB | 239 | 4 | 2 | 5.0 |
| Rank | Periodicals | Volume of Publications |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tissue Engineering Research in China | 13 |
| 2 | The New World of Diabetes | 11 |
| 3 | Chinese Journal of Sports Medicine | 11 |
| 4 | Chinese Journal of Gerontology | 10 |
| 5 | Chinese Journal of Applied Physiology | 10 |
| 6 | Chinese Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine | 9 |
| 7 | Bulletin of Scientific and Technical Literature on Sports | 8 |
| 8 | Contemporary Sports Technology | 7 |
| 9 | Sichuan Sports Science | 6 |
| 10 | Chinese and foreign medical research | 5 |
| Rank | Countries | Articles | Total Citations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | USA | 269 | 2571 |
| 2 | CHINA | 258 | 817 |
| 3 | CANADA | 226 | 649 |
| 4 | BRAZIL | 202 | 608 |
| 5 | IRAN | 192 | 546 |
| 6 | AUSTRALIA | 84 | 141 |
| 7 | JAPAN | 65 | 313 |
| 8 | SPAIN | 58 | 47 |
| 9 | SOUTH KOREA | 47 | 206 |
| 10 | UK | 44 | 167 |
| Rank | Author | Country | Articles | Total Citations | H-Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | RIDDELL MC | CANADA | 12 | 85 | 9 |
| 2 | MELLING CWJ | CANADA | 8 | 14 | 6 |
| 3 | NOBLE EG | CANADA | 8 | 14 | 6 |
| 4 | SIGAL RJ | CANADA | 8 | 71 | 6 |
| 5 | KENNY GP | CANADA | 7 | 7 | 5 |
| 6 | MCDONALD MW | USA | 7 | 14 | 6 |
| 7 | YARDLEY JE | CANADA | 7 | 73 | 4 |
| 8 | KARIMI H | USA | 6 | 5 | 5 |
| 9 | DELEVATTI RS | BRAZIL | 5 | 8 | 4 |
| 10 | DIXIT S | INDIA | 5 | 14 | 5 |
| No. | Title | DOI | Year | LCS | GCS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Physical activity/exercise and diabetes: a position statement of the American Diabetes Association [41] | https://doi.org/10.2337/dc16-1728 | 2016 | 64 | 1509 |
| 2 | Effects of exercise on C-reactive protein, inflammatory cytokine and adipokine in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials controlled trials [42] | https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2013.08.018 | 2014 | 5 | 167 |
| 3 | Continuous vs. interval training on glycemic control and macro- and microvascular reactivity in type 2 diabetic patients [43] | https://doi.org/10.1111/sms.12112 | 2014 | 19 | 23 |
| 4 | Exercise training and endothelial function in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis [44] | https://doi.org/10.1186/s12933-018-0711-2 | 2018 | 1 | 98 |
| 5 | Short-term high-intensity interval and moderate-intensity continuous training reduce leukocyte TLR4 in inactive adults at elevated risk of type 2 diabetes [45] | https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00334.2015 | 2015 | 0 | 90 |
| 6 | Effect of aerobic exercise intensity on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of head-to-head randomized trials [46] | https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-016-0870-0 | 2016 | 0 | 85 |
| 7 | Effect of aerobic exercise on peripheral nerve functions of population with diabetic peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes: a single blind, parallel group randomized controlled trial [47] | https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2013.12.006 | 2013 | 9 | 84 |
| 8 | Aerobic exercise training reduces arterial stiffness in metabolic syndrome [48] | https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00151.2014 | 2014 | 1 | 83 |
| 9 | Lag time remains with newer real-time continuous glucose monitoring technology during aerobic exercise in adults living with type 1 diabetes [49] | https://doi.org/10.1089/dia.2018.0364 | 2018 | 2 | 76 |
| 10 | Exercise improves gait, reaction time and postural stability in older adults with type 2 diabetes and neuropathy [50] | https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2014.04.007 | 2014 | 1 | 71 |
| 11 | Effect of aerobic exercise and diet on liver fat in pre-diabetic patients with non-alcoholic-fatty-liver-disease: a randomized controlled trial [51] | https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-16159-x | 2017 | 1 | 69 |
| 12 | Effects of high-intensity interval and moderate-intensity continuous aerobic exercise on diabetic obese patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a comparative randomized controlled trial [52] | https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000019471 | 2020 | 2 | 67 |
| 13 | The effects of aerobic exercise training at two different intensities in obesity and type 2 diabetes: implications for oxidative stress, low-grade inflammation and nitric oxide production [53] | https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-013-2769-6 | 2014 | 6 | 67 |
| 14 | Exercise in children and adolescents with diabetes [54] | https://doi.org/10.1111/pedi.12176 | 2014 | 2 | 66 |
| 15 | A randomized controlled trial on the effectiveness of 8-week high-intensity interval exercise on intrahepatic triglycerides, visceral lipids, and health-related quality of life in diabetic obese patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [55] | https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000014918 | 2019 | 0 | 65 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Ullah, A.; Fang, S.; Liu, D.; Cui, Z.; Kou, G. Exercise Interventions for Metabolic Diseases: An Analysis of the Evolution of Aerobic Exercise Bibliometrics in the Field of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Healthcare 2025, 13, 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13172087
Li Y, Ullah A, Fang S, Liu D, Cui Z, Kou G. Exercise Interventions for Metabolic Diseases: An Analysis of the Evolution of Aerobic Exercise Bibliometrics in the Field of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Healthcare. 2025; 13(17):2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13172087
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yang, Amin Ullah, Shuhao Fang, Donglin Liu, Zhenwei Cui, and Guangning Kou. 2025. "Exercise Interventions for Metabolic Diseases: An Analysis of the Evolution of Aerobic Exercise Bibliometrics in the Field of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus" Healthcare 13, no. 17: 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13172087
APA StyleLi, Y., Ullah, A., Fang, S., Liu, D., Cui, Z., & Kou, G. (2025). Exercise Interventions for Metabolic Diseases: An Analysis of the Evolution of Aerobic Exercise Bibliometrics in the Field of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Healthcare, 13(17), 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13172087







