Impact of Direct-Acting Antivirals on Extrahepatic Manifestations in Chronic Hepatitis C: A Narrative Review with a Hermeneutic Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
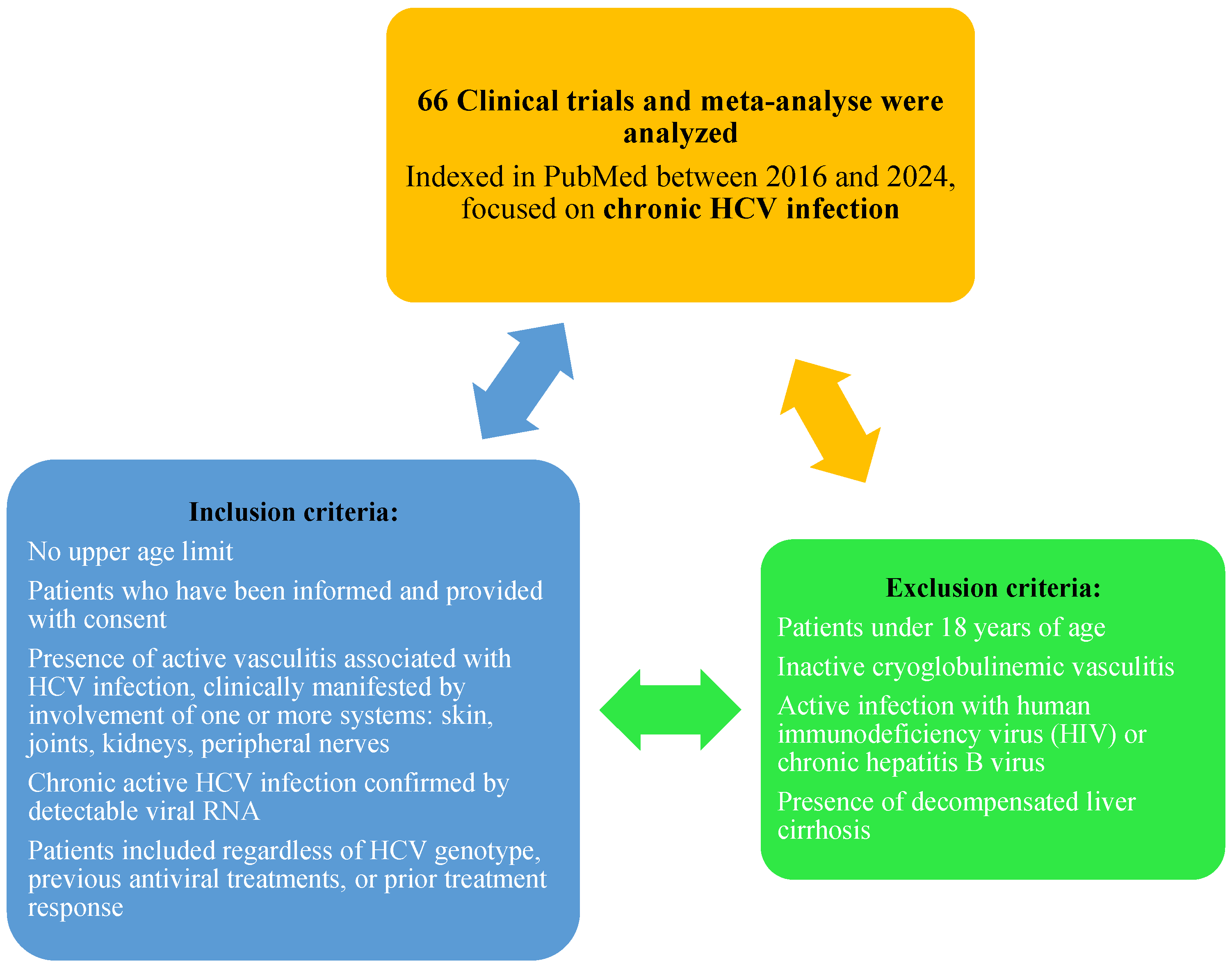
3. Results
3.1. Mixed Cryoglobulinemia (MC)
| Study | Key Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Cacoub et al. | CryoVas remission: 95.2%; severe neuropathy/vasculitis = 3× less likely to achieve full clinical response | [27] |
| DAA era | CryoVas prevalence: 14.3%; better antiviral response when non-antiviral treatment was reduced; the study by Cacoub et al. reported long-term response: 46.9% | [27] |
| French cohort | Use of non-antiviral treatment decreased from 43% (IFN-RBV era) to 4.8% (sofosbuvir + daclatasvir era) | [28,29] |
| Mortality rates | 25% at 5 years; 40% at 10 years in HCV-CryoVas patients | [21,30] |
| DAA-treated patients | 50–61% remained cryoglobulin-positive despite SVR | [31,32] |
| Lauletta et al. | Significant clinical improvement with DAAs; fewer and milder adverse reactions; 27.3% had persistent or worsened symptoms despite SVR12 | [33] |
| Comparison with older therapies | DAAs yielded better outcomes vs. pegylated IFN + RBV and earlier triple therapy with first-generation protease inhibitors | [29,34] |
| Small pilot studies (IFN + RBV) | IFN + RBV improved outcomes in chronic HCV + mixed cryoglobulinemia | [34,35] |
| DAA in IFN non-responders | Among IFN-α monotherapy non-responders, 19–54% achieved SVR and mixed cryoglobulinemia remission with DAAs | [36] |
3.2. Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma (NHL) and B-Cell Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma (B-NHL)
3.3. Arthralgia, Myalgia, and Sicca Syndrome
3.4. Autoantibody Production
3.5. Type 2 Diabetes with Insulin Resistance (IR)
3.6. Cardiovascular Disorders (Carotid Atherosclerosis, Coronary Artery Disease, and Ischemic Heart Disease with Coronary Vasculitis)
3.7. Renal Insufficiency and Glomerulonephritis
3.8. Porphyria Cutanea Tarda
3.9. Lichen Planus
3.10. Thyroid Disorders
3.11. Neuropsychiatric Disorders
3.12. Study Limitations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Guidelines on HIV, Viral Hepatitis and Sexually Transmitted Infections. Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/global-hiv-hepatitis-and-stis-programmes/guidelines (accessed on 11 May 2025).
- Cacoub, P.; Comarmond, C. New insights into HCV-related rheumatologic disorders: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2017, 8, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzaro, C.; Quartuccio, L.; Adinolfi, L.E.; Roccatello, D.; Pozzato, G.; Nevola, R.; Tonizzo, M.; Gitto, S.; Andreone, P.; Gattei, V. A Review on Extrahepatic Manifestations of Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection and the Impact of Direct-Acting Antiviral Therapy. Viruses 2021, 13, 2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacoub, P.; Gragnani, L.; Comarmond, C.; Zignego, A.L. Extrahepatic manifestations of chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Dig. Liver Dis. 2014, 46 (Suppl. S5), S165–S173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zignego, A.L.; Bréchot, C. Extrahepatic manifestations of HCV infection: Facts and controversies. J. Hepatol. 1999, 31, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrier, B.; Cacoub, P. Renal involvement in HCV-related vasculitis. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2013, 37, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.H.; Yang, H.I.; Lu, S.N.; Jen, C.L.; You, S.L.; Wang, L.Y.; Wang, C.H.; Chen, W.J.; Chen, C.J.; Reveal-HCV Study Group. Chronic hepatitis C virus infection increases mortality from hepatic and extrahepatic diseases: A community-based long-term prospective study. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 206, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omland, L.H.; Jepsen, P.; Krarup, H.; Schønning, K.; Lind, B.; Kromann-Andersen, H.; Homburg, K.M.; Christensen, P.B.; Sørensen, H.T.; Obel, N.; et al. Increased mortality among persons infected with hepatitis C virus. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 9, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uto, H.; Stuver, S.O.; Hayashi, K.; Kumagai, K.; Sasaki, F.; Kanmura, S.; Numata, M.; Moriuchi, A.; Hasegawa, S.; Oketani, M.; et al. Increased rate of death related to presence of viremia among hepatitis C virus antibody-positive subjects in a community-based cohort study. Hepatology 2009, 50, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kamary, S.S.; Jhaveri, R.; Shardell, M.D. All-cause, liver-related, and non-liver-related mortality among HCV-infected individuals in the general US population. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 53, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://quizlet.com/370092963/body-internal-organs-flash-cards/ (accessed on 16 July 2025).
- Jeong, D.; Wong, S.; Karim, M.E.; Manges, A.R.; Makuza, J.D.; Velásquez García, H.A.; Adu, P.A.; Binka, M.; Yu, A.; Bartlett, S.R.; et al. Direct-Acting Antivirals and Risk of Hepatitis C Extrahepatic Manifestations. JAMA Netw. Open 2025, 8, e2514631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tani, J.; Masaki, T.; Oura, K.; Tadokoro, T.; Morishita, A.; Kobara, H. Extrahepatic Cancer Risk in Patients with Hepatitis C Virus Infection Treated with Direct-Acting Antivirals. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://amstar.ca/Amstar_Checklist.php (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- Greenhalgh, T.; Thorne, S.; Malterud, K. Time to challenge the spurious hierarchy of systematic over narrative reviews? Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 48, e12931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, C.M.; Seeff, L.B.; Stehman-Breen, C.O.; Hoofnagle, J.H. Hepatitis C and renal disease: An update. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2003, 42, 631–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sise, M.E.; Bloom, A.K.; Wisocky, J.; Lin, M.V.; Gustafson, J.L.; Lundquist, A.L.; Steele, D.; Thiim, M.; Williams, W.W.; Hashemi, N.; et al. Treatment of hepatitis C virus-associated mixed cryoglobulinemia with direct-acting antiviral agents. Hepatology 2016, 63, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadoun, D.; Pol, S.; Ferfar, Y.; Alric, L.; Hezode, C.; Si Ahmed, S.N.; de Saint Martin, L.; Comarmond, C.; Bouyer, A.S.; Musset, L.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Sofosbuvir Plus Daclatasvir for Treatment of HCV-Associated Cryoglobulinemia Vasculitis. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 49–52.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Casals, M.; Stone, J.H.; Cid, M.C.; Bosch, X. The cryoglobulinaemias. Lancet 2012, 379, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacoub, P.; Comarmond, C.; Domont, F.; Savey, L.; Saadoun, D. Cryoglobulinemia Vasculitis. Am. J. Med. 2015, 128, 950–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balta, A.A.S.; Ignat, M.D.; Barbu, R.E.; Baroiu, L.; Moroianu, L.A.; Lutenco, V.; Bulza, V.; Patriciu, M.; Dumitru, C.; Debita, M. HBV, HCV, and HDV Triple-Infection—A Therapeutic Challenge. Diseases 2025, 13, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastyr, E.J., III; Price, K.L.; Bril, V.; MBBQ Study Group. Development and validity testing of the neuropathy total symptom score-6: Questionnaire for the study of sensory symptoms of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Clin. Ther. 2005, 27, 1278–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luqmani, R.A.; Bacon, P.A.; Moots, R.J.; Janssen, B.A.; Pall, A.; Emery, P.; Savage, C.; Adu, D. Birmingham Vasculitis Activity Score (BVAS) in systemic necrotizing vasculitis. QJM 1994, 87, 671–678. [Google Scholar]
- Gragnani, L.; Visentini, M.; Fognani, E.; Urraro, T.; De Santis, A.; Petraccia, L.; Perez, M.; Ceccotti, G.; Colantuono, S.; Mitrevski, M.; et al. Prospective study of guideline-tailored therapy with direct-acting antivirals for hepatitis C virus-associated mixed cryoglobulinemia. Hepatology 2016, 64, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinloch, A.; Lundberg, K.; Wait, R.; Wegner, N.; Lim, N.H.; Zendman, A.J.W.; Saxne, T.; Malmström, V.; Venables, P.J. Synovial fluid is a site of citrullination of autoantigens in inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 2287–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacoub, P.; Si, N.S.A.; Ferfar, Y.; Pol, S.; Thabut, D.; Hézode, C.; Alric, L.; Comarmond, C.; Ragab, G.; Quartuccio, L.; et al. Long-Term Efficacy of Interferon-Free Antiviral Treatment Regimens in Patients with Hepatitis C Virus-Associated Cryoglobulinemia Vasculitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadoun, D.; Resche-Rigon, M.; Thibault, V.; Piette, J.C.; Cacoub, P. Antiviral therapy for hepatitis C virus-associated mixed cryoglobulinemia vasculitis: A long-term follow-up study. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 3696–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadoun, D.; Resche-Rigon, M.; Pol, S.; Thibault, V.; Blanc, F.; Pialoux, G.; Karras, A.; Bazin-Kara, D.; Cazorla, C.; Vittecoq, D.; et al. PegIFNα/ribavirin/protease inhibitor combination in severe hepatitis C virus-associated mixed cryoglobulinemia vasculitis. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrier, B.; Cacoub, P. Cryoglobulinemia vasculitis: An update. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2013, 25, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadoun, D.; Thibault, V.; Ahmed, S.N.S.; Alric, L.; Mallet, M.; Guillaud, C.; Cacoub, P. Sofosbuvir plus ribavirin for hepatitis C virus-associated cryoglobulinaemia vasculitis: VASCUVALDIC study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 1777–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonacci, M.; Lens, S.; Londoño, M.C.; Mariño, Z.; Cid, M.C.; Ramos-Casals, M.; Sánchez-Tapias, J.M.; Forns, X.; Hernández-Rodríguez, J. Virologic, clinical, and immune response outcomes of patients with hepatitis C virus–associated cryoglobulinemia treated with direct-acting antivirals. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauletta, G.; Russi, S.; Pavone, F.; Vacca, A.; Dammacco, F. Direct-acting antiviral agents in the therapy of hepatitis C virus-related mixed cryoglobulinaemia: A single-centre experience. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dammacco, F.; Tucci, F.A.; Lauletta, G.; Gatti, P.; De Re, V.; Conteduca, V.; Sansonno, S.; Russi, S.; Mariggiò, M.A.; Chironna, M.; et al. Pegylated interferon-α, ribavirin, and rituximab combined therapy of hepatitis C virus–related mixed cryoglobulinemia: A long-term study. Blood 2010, 116, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHutchison, J.G.; Gordon, S.C.; Schiff, E.R.; Shiffman, M.L.; Lee, W.M.; Rustgi, V.K.; Goodman, Z.D.; Ling, M.H.; Cort, S.; Albrecht, J.K. Interferon alfa-2b alone or in combination with ribavirin as initial treatment for chronic hepatitis C. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 1485–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calleja, J.L.; Albillos, A.; Rossi, P.; Cacho, G.; Domper, J.; Yebra, M.; Escartín, P. Sustained response to interferon-α or to interferon-α plus ribavirin in hepatitis C virus-associated symptomatic mixed cryoglobulinaemia. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1999, 13, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrier, B.; Semoun, O.; Saadoun, D.; Sène, D.; Resche-Rigon, M.; Cacoub, P. Prognostic factors in patients with hepatitis C virus infection and systemic vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 1748–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Retamozo, S.; Díaz-Lagares, C.; Bosch, X.; Bové, A.; Brito-Zerón, P.; Gómez, M.E. Life-threatening cryoglobulinemic patients with hepatitis C: Clinical description and outcome of 279 patients. Medicine 2013, 92, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrier, B.; Karras, A.; Cluzel, P.; Collet, J.P.; Sène, D.; Saadoun, D. Presentation and prognosis of cardiac involvement in hepatitis C virus-related vasculitis. Am. J. Cardiol. 2013, 111, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzaro, C.; Di Maso, L.; Quartuccio, L.; Ghersetti, M.; Lenzi, M.; Mauro, E.; Bond, M.; Casarin, P.; Gattei, V.; Crosato, I.M.; et al. Long-term effects of the new direct antiviral agents (DAAs) therapy for HCV-related mixed cryoglobulinaemia without renal involvement: A multicentre open-label study. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2018, 36, 107–114. [Google Scholar]
- Passerini, M.; Schiavini, M.; Magni, C.F.; Landonio, S.; Niero, F.; Passerini, S.; Croci, A.L.; Bolis, M.; Scalzi, V.; Gubertini, G.; et al. Are direct-acting antivirals safe and effective in hepatitis C virus-cryoglobulinemia? virological, immunological, and clinical data from a real-life experience. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 30, 1208–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, J.S.; Kuczynski, M.; La, D.; Al Marzooqi, S.; Kowgier, M.; Shah, H.; Wong, D.; Janssen, H.L.; Feld, J.J. Efficacy and Safety of Direct Acting Antivirals for the Treatment of Mixed Cryoglobulinemia. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 112, 1298–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozzato, G.; Mazzaro, C.; Artemova, M.; Abdurakhmanov, D.; Grassi, G.; Crosato, I.; Mauro, E.; Ghersetti, M.; Zorat, F.; Bomben, R.; et al. Direct-acting antiviral agents for hepatitis C virus-mixed cryoglobulinaemia: Dissociated virological and haematological responses. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 191, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naudin, S.; Biessy, C.; McKenzie, F.; Duell, E.J.; Ferrari, P.; Brennan, P. Risk of pancreatic cancer and non-Hodgkin lymphoma associated with healthy lifestyle behaviors in the EPIC study. Rev. Epidemiol. Sante Publique 2018, 66, S305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taborelli, M.; Montella, M.; Libra, M.; Tedeschi, R.; Crispo, A.; Grimaldi, M.; Dal Maso, L.; Serraino, D.; Polesel, J. The dose-response relationship between tobacco smoking and the risk of lymphomas: A case-control study. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melenotte, C.; Mezouar, S.; Mège, J.L.; Gorvel, J.P.; Kroemer, G.; Raoult, D. Bacterial infection and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 46, 270–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, H.C.; Banerjee, S.; Robertson, E.S. The role of gammaherpesviruses in cancer pathogenesis. Pathogens 2016, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peveling-Oberhag, J.; Arcaini, L.; Bankov, K.; Zeuzem, S.; Herrmann, E. The anti-lymphoma activity of antiviral therapy in HCV-associated B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas: A meta-analysis. J. Viral Hepat. 2016, 23, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisbert, J.P.; García-Buey, L.; Pajares, J.M.; Moreno-Otero, R. Prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 1723–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzato, G.; Mazzaro, C.; Dal Maso, L.; Mauro, E.; Zorat, F.; Moratelli, G.; Bu-lian, P.; Serraino, D.; Gattei, V. Hepatitis C virus and non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas: Meta-analysis of epidemiology data and therapy options. World J. Hepatol. 2016, 8, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Songtanin, B.; Nugent, K. Burden, Outcome, and Comorbidities of Extrahe-patic Manifestations in Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Biology 2023, 12, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo, K.; Kusano, A.; Sugumar, A.; Nakamura, S.; Tajima, K.; Mueller, N.E. Effect of hepatitis C virus infection on the risk of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: A meta-analysis of epidemiological studies. Cancer Sci. 2004, 95, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dammacco, F.; Sansonno, D.; Piccoli, C.; Recorelli, V.; D’Amore, F.P.; Lauletta, G. The lymphoid system in hepatitis C virus infection: Autoimmunity, mixed cryoglobulinemia, and overt B-cell malignancy. Semin. Liver Dis. 2000, 20, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ascoli, V.; Lo Coco, F.; Artini, M.; Levrero, M.; Martelli, M.; Negro, F. Extranodal lymphomas associated with hepatitis C virus infection. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1998, 109, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumi, T.; Sasaki, R.; Tsunoda, S.; Akutsu, M.; Okamoto, H.; Miura, Y. B cell malignancy and hepatitis C virus infection. Leukemia 1997, 11 (Suppl. S3), 516–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokni, M.; Rybojad, M.; Puppin, D.; Catala, S.; Venezia, F.; Djian, R.; Morel, P. Lichen planus and hepatitis C virus. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1991, 24, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Pola, M.; Rodríguez-Fonseca, L.; Suárez-Fernández, C.; Sanjuán-Pardavila, R.; Seoane-Romero, J.; Rodríguez-López, S. Bidirectional Association between Lichen Planus and Hepatitis C-An Update Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarisco, R.; Bellis, L.; Puoti, C. Extrahepatic manifestations of chronic HCV infection. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2007, 16, 65–73. [Google Scholar]
- De Vita, S.; Sacco, C.; Sansonno, D.; Gloghini, A.; Dammacco, F.; Crovatto, M.; Santini, G.; Dolcetti, R.; Boiocchi, M.; Carbone, A.; et al. Characterization of overt B-cell lymphomas in patients with hepatitis C virus infection. Blood 1997, 90, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariette, X. Hepatitis C virus, arthritides, and arthromyalgia. Jt. Bone Spine 2003, 70, 246–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansonno, D.; Cornacchiulo, V.; Iacobelli, A.R.; Di Stefano, R.; Lospalluti, M.; Dammacco, F. Localization of hepatitis C virus antigens in liver and skin tissues of chronic hepatitis C virus-infected patients with mixed cryoglobulinemia. Hepatology 1995, 21, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lormeau, C.; Falgarone, G.; Roulot, D.; Boissier, M.C. Rheumatologic manifestations of chronic hepatitis C infection. Jt. Bone Spine 2006, 73, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, B.; Arbabi, A.; Kirkland, P.A. Extrahepatic manifestations of chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. Cureus 2024, 16, e57343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacoub, P.; Renou, C.; Rosenthal, E.; Cohen, P.; Loury, I.; Loustaud-Ratti, V.; Yamamoto, A.M.; Camproux, A.C.; Hausfater, P.; Musset, L.; et al. Extrahepatic manifestations associated with hepatitis C virus infection: A prospective multicenter study of 321 patients. Medicine 2000, 79, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degenhardt, L.; Charlson, F.; Stanaway, J.; Larney, S.; Alexander, L.T.; Hickman, M.; Cowie, B.; Hall, W.D.; Strang, J.; Whiteford, H.; et al. Estimating the burden of disease attributable to injecting drug use as a risk factor for HIV, hepatitis C, and hepatitis B: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 1385–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Ji, J.; Yeon, J.; Byun, K.; Lee, C.; Song, G. Cryoglobulinaemia and rheumatic manifestations in patients with hepatitis C virus infection. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1998, 57, 728–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Casals, M.; García-Carrasco, M.; Cervera, R.; Rosas, J.; Trejo, O.; de la Red, G.; Sánchez-Tapias, J.M.; Font, J.; Ingelmo, M. Hepatitis C virus infection mimicking primary Sjögren syndrome. A clinical and immunologic description of 35 cases. Medicine 2001, 80, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacoub, P.; Comarmond, C.; Domont, F.; Savey, L.; Desbois, A.C.; Saadoun, D. Extrahepatic manifestations of chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Ther. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2016, 3, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnello, V. Mixed Cryoglobulinemia and Other Extrahepatic Manifestations of HCV Infection. In Hepatitis C; Liang, T.J., Hoofnagle, J.H., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 295–315. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera, J.; de Diego, A.; Trinchet, M.; Garcia Monforte, A. Fibromyalgia-associated hepatitis C virus infection. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1997, 36, 981–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnello, V.; De Rosa, F.G. Extrahepatic disease manifestations of HCV infection: Some current issues. J. Hepatol. 2004, 40, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, S.H.; Brancati, F.L.; Strathdee, S.A.; Pankow, J.S.; Netski, D.; Coresh, J.; Szklo, M.; Thomas, D.L. Hepatitis C virus infection and incident type 2 diabetes. Hepatology 2003, 38, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, D.L.; Ratziu, V.; El-Serag, H.B. Hepatitis C infection and risk of diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2008, 49, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desbois, A.C.; Cacoub, P. Diabetes mellitus, insulin resistance and hepatitis C virus infection: A contemporary review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adinolfi, L.E.; Rinaldi, L.; Guerrera, B.; Restivo, L.; Marrone, A.; Giordano, M.; Zampino, R. NAFLD and NASH in HCV infection: Prevalence and significance in hepatic and extrahepatic manifestations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.P.M.; de Jesus, R.P.; Boulhosa, R.S.S.B.; Onofre, T.; Mendes, C.M.C.; Vinhas, L.; Waitzberg, D.L.; Lemaire, D.C.; Cavalcante, L.N.; Lyra, A.C.; et al. Factors associated with insulin resistance in patients with chronic HCV genotype 1 infection without obesity or type 2 diabetes. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2016, 35, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veldt, B.J.; Poterucha, J.J.; Watt, K.D.S.; Wiesner, R.H.; Hay, J.E.; Rosen, C.B.; Heimbach, J.K.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Charlton, M.R. Insulin resistance, serum adipokines and risk of fibrosis progression in patients transplanted for hepatitis C. Am. J. Transplant. 2009, 9, 1406–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petta, S.; Camma, C.; Di Marco, V.; Calvaruso, V.; Enea, M.; Bronte, F.; Butera, G.; Cabibi, D.; Craxì, A. Insulin resistance is a major determinant of liver stiffness in nondiabetic patients with HCV genotype 1 chronic hepatitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 30, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negro, F.; Alaei, M. Hepatitis C virus and type 2 diabetes. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, M.E.; Wreghitt, T.; Palmer, C.R.; Alexander, G.J. Evidence for a link between hepatitis C virus infection and diabetes mellitus in a cirrhotic population. J. Hepatol. 1994, 21, 1135–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caronia, S.; Taylor, K.; Pagliaro, L.; Carr, C.; Palazzo, U.; Petrik, J.; O’Rahilly, S.; Shore, S.; Tom, B.D.; Alexander, G.J. Further evidence for an association between non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology 1999, 30, 1059–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, A.L.; Lau, J.Y.; Hoang, N.; Qian, K.; Alexander, G.J.; Xu, L.; Guo, L.; Jacob, S.; Regenstein, F.G.; Zimmerman, R.; et al. Association of diabetes mellitus and chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology 1999, 29, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serfaty, L.; Capeau, J. Hepatitis C, insulin resistance and diabetes: Clinical and pathogenic data. Liver Int. 2009, 29 (Suppl. S2), 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gordon, S.C.; Rupp, L.B.; Zhang, T.; Trudeau, S.; Holmberg, S.D.; Moorman, A.C.; Spradling, P.R.; Teshale, E.H.; Boscarino, J.A.; et al. Sustained virological response to hepatitis C treatment decreases the incidence of complications associated with type 2 diabetes. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 49, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, N. Hepatitis C virus, insulin resistance, and diabetes: A review. Microbiol. Immunol. 2022, 66, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, A.A.; Xiaoqiang, W.; Budoff, M.; Leaf, D.; Kuller, L.H.; Justice, A.C. Hepatitis C virus infection and the risk of coronary disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forde, K.A.; Haynes, K.; Troxel, A.B.; Trooskin, S.; Osterman, M.T.; Kimmel, S.E. Risk of myocardial infarction associated with chronic hepatitis C virus infection: A population-based cohort study. J. Viral Hepat. 2012, 19, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momiyama, Y.; Ohmori, R.; Kato, R.; Taniguchi, H.; Nakamura, H.; Ohsuzu, F. Lack of any association between persistent hepatitis B or C virus infection and coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis 2005, 181, 211–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcari, C.M.; Nelson, K.E.; Netski, D.M.; Nieto, F.J.; Gaydos, C.A. No association between hepatitis C virus seropositivity and acute myocardial infarction. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 43, e53–e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.C.; Su, T.C.; Sung, F.C.; Chou, W.H.; Chen, T.L. Does hepatitis C virus infection increase risk for stroke? A population-based cohort study. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.S.; Kao, J.H.; Chao, Y.C.; Lin, H.H.; Fan, Y.C.; Huang, C.J. Interferon-based therapy reduces risk of stroke in chronic hepatitis C patients: A population-based cohort study in Taiwan. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 38, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adinolfi, L.E.; Restivo, L.; Guerrera, B.; Sellitto, A.; Ciervo, A.; Iuliano, N. Chronic HCV infection is a risk factor of ischemic stroke. Atherosclerosis 2013, 231, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enger, C.; Forssen, U.M.; Bennett, D.; Theodore, D.; Shantakumar, S.; McAfee, A. Thromboembolic events among patients with hepatitis C virus infection and cirrhosis: A matched-cohort study. Adv. Ther. 2014, 31, 891–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, Y.; Lin, J.; Ho, H.; Kao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Hsiao, N. Antiviral treatment for hepatitis C virus infection is associated with improved renal and cardiovascular outcomes in diabetic patients. Hepatology 2014, 59, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pothineni, N.V.; Delongchamp, R.; Vallurupalli, S.; Ding, Z.; Dai, Y.; Hagedorn, C.H. Impact of hepatitis C seropositivity on the risk of coronary heart disease events. Am. J. Cardiol. 2014, 114, 1841–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, A.A.; Khan, U.A.; McGinnis, K.A.; Skanderson, M.; Kwoh, C.K. Co-morbid medical and psychiatric illness and substance abuse in HCV-infected and uninfected veterans. J. Viral Hepat. 2007, 14, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petta, S. Hepatitis C virus and cardiovascular: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2017, 8, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampino, R.; Marrone, A.; Restivo, L.; Guerrera, B.; Sellitto, A.; Rinaldi, L.; Romano, C.; Adinolfi, L.E. Chronic HCV infection and inflammation: Clinical impact on hepatic and extra-hepatic manifestations. World J. Hepatol. 2013, 5, 528–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petta, S.; Torres, D.; Fazio, G.; Camma, C.; Cabibi, D.; Di Marco, V.; Licata, A.; Marchesini, G.; Mazzola, A.; Parrinello, G.; et al. Carotid atherosclerosis and chronic hepatitis C: A prospective study of risk associations. Hepatology 2012, 55, 1317–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drazilova, S.; Gazda, J.; Janicko, M.; Jarcuska, P. Chronic hepatitis C association with diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular risk in the era of DAA therapy. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 2018, 6150861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.W.; Yang, S.S.; Fu, S.C.; Wang, T.C.; Hsu, C.K.; Chen, D.S.; Hu, J.T.; Kao, J.H. Increased risk of cirrhosis and its decompensation in chronic hepatitis C patients with new-onset diabetes: A nationwide cohort study. Hepatology 2014, 60, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizaka, Y.; Ishizaka, N.; Takahashi, E.; Unuma, T.; Tooda, E.I.; Hashimoto, H.; Nagai, R.; Yamakado, M. Association between hepatitis C virus core protein and carotid atherosclerosis. Circ. J. 2003, 67, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama, S.; Koda, M.; Oyake, N.; Sato, H.; Fujii, Y.; Horie, Y.; Murawaki, Y. Myocardial injury in patients with chronic hepatitis C infection. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.; Wong, S.; Karim, M.E.; Manges, A.R.; Makuza, J.D.; Bartlett, S.R.; Velásquez García, H.A.; Luster, D.; Adu, P.A.; Binka, M.; et al. Treatment of HCV with direct-acting antivirals on reducing mortality related to extrahepatic manifestations: A large population-based study in British Columbia, Canada. Lancet Reg. Health Am. 2023, 29, 100658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsoum, R.S. Hepatitis C virus: From entry to renal injury—Facts and potentials. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2007, 22, 1840–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Iñigo, E.; Casqueiro, M.; Bartolomé, J.; Barat, A.; Caramelo, C.; Ortiz, A.; Albalate, M.; Oliva, H.; Manzano, M.L.; Carreño, V. Hepatitis C virus RNA in kidney biopsies from infected patients with renal diseases. J. Viral Hepat. 2000, 7, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansonno, D.; Gesualdo, L.; Manno, C.; Schena, F.P.; Dammacco, F. Hepatitis C virus-related proteins in kidney tissue from hepatitis C virus-infected patients with cryoglobulinemic membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis. Hepatology 1997, 25, 1237–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkok, A.; Yildiz, A. Hepatitis C virus associated glomerulopathies. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 7544–7554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.F.; Chuang, W.L.; Dai, C.Y.; Ho, C.K.; Hwang, S.J.; Chen, S.C.; Lin, Z.Y.; Wang, L.Y.; Chang, W.Y.; Yu, M.L. Viral hepatitis and proteinuria in an area endemic for hepatitis B and C infections: Another chain of link? J. Intern. Med. 2006, 260, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, J.M.; Campistol, J.M. Transplantation in the patient with hepatitis C. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2000, 11, 1343–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalrymple, L.S.; Koepsell, T.; Sampson, J.; Louie, T.; Dominitz, J.A.; Young, B.; Kestenbaum, B. Hepatitis C virus infection and the prevalence of renal insufficiency. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 2, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fargion, S.; Piperno, A.; Cappellini, M.D.; Sampietro, M.; Fracanzani, A.L.; Romano, R.; Caldarelli, R.; Marcelli, R.; Vecchi, L.; Fiorelli, G. Hepatitis C virus and porphyria cutanea tarda: Evidence of a strong association. Hepatology 1992, 16, 1322–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgescu, S.R.; Tampa, M.; Mitran, M.I.; Mitran, C.I.; Sarbu, M.I.; Nicolae, I.; Matei, C.; Caruntu, C.; Neagu, M.; Popa, M.I. Potential pathogenic mechanisms involved in the association between lichen planus and hepatitis C virus infection. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 17, 1045–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallahi, P.; Ferrari, S.M.; Politti, U.; Giuggioli, D.; Ferri, C.; Antonelli, A. Autoimmune and neoplastic thyroid diseases associated with hepatitis C chronic infection. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 2014, 935131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccatello, D.; Sciascia, S.; Baldovino, S.; Rossi, D.; Alpa, M.; Naretto, C.; Di Simone, D.; Menegatti, E. Improved (4 Plus 2) rituximab protocol for severe cases of mixed cryoglobulinemia: A 6-year observational study. Am. J. Nephrol. 2016, 43, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, X.-L.; Xie, J.-P.; Shao, J.-G.; Lu, Y.-H.; Zhang, S.; Qin, G. Thyroid disturbance in patients with chronic hepatitis C infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2016, 25, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Wang, C.; Sumpter, R., Jr.; Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L.; Gale, M., Jr. Disruption of hepatitis C virus RNA replication through inhibition of host protein geranylgeranylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15865–15870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafi, M.; Modabbernia, A.; Dalir, M.; Taslimi, S.; Karami, M.; Ostovaneh, M.R.; Malekzadeh, R.; Poustchi, H. Predictors of mental and physical health in non-cirrhotic patients with viral hepatitis: A case control study. J. Psychosom. Res. 2012, 73, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sockalingam, S.; Abbey, S.E.; Alosaimi, F.; Novak, M. A review of sleep disturbance in hepatitis C. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2010, 44, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poynard, T.; Cacoub, P.; Ratziu, V.; Myers, R.P.; Dezailles, M.H.; Mercadier, A.; Ghillani, P.; Charlotte, F.; Piette, J.C.; Moussalli, J.; et al. Fatigue in patients with chronic hepatitis C. J. Viral Hepat. 2002, 9, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, S.; Mariotto, S.; Ferrari, S.; Calabrese, M.; Zanusso, G.; Gajofatto, A.; Sansonno, D.; Dammacco, F. Hepatitis C virus-associated neurocognitive and neuropsychiatric disorders: Advances in 2015. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 11974–11983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallman, J.; O’Neil, M.M.; Larive, B.; Boparai, N.; Calabrese, L.; Younossi, Z.M. Fatigue and health-related quality of life (HRQL) in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2007, 52, 2531–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solinas, A.; Piras, M.R.; Deplano, A. Cognitive dysfunction and hepatitis C virus infection. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 922–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, D.; Coughlan, B.; McCarthy, O.; Crowe, J. Investigating health-related quality of life, mood and neuropsychological test performance in a homogeneous cohort of Irish female hepatitis C patients. J. Viral. Hepat. 2010, 17, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, J.; Radkowski, M.; Laskus, T. Hepatitis C virus neuroinvasion: Identification of infected cells. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 1312–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, M.; Capuron, L.; Friebe, A.; Diez-Quevedo, C.; Robaeys, G.; Neri, S.; Foster, G.R.; Kautz, A.; Forton, D.; Pariante, C.M. Hepatitis C infection, antiviral treatment and mental health: A European expert consensus statement. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 1379–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskus, T.; Radkowski, M.; Adair, D.M.; Wilkinson, J.; Scheck, A.C.; Rakela, J. Emerging evidence of hepatitis C virus neuroinvasion. AIDS 2005, 19, S140–S144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzi, A.; Zignego, A.L.; Carpendo, R.; Biagiotti, T.; Aldinucci, A.; Monti, M.; Giannini, C.; Rosselli, M.; Laffi, G.; Moroni, F. Low serum tryptophan levels, reduced macrophage IDO activity and high frequency of psychopathology in HCV patients. J. Viral Hepat. 2006, 13, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, C.; Zignego, A.L.; Pileri, S.A. Cryoglobulins. J. Clin. Pathol. 2002, 55, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanni, E.; Bugianesi, E.; Kotronen, A.; De Minicis, S.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; Svegliati-Baroni, G. From the metabolic syndrome to NAFLD or vice versa? Dig. Liver Dis. 2010, 42, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petit, J.M.; Bour, J.B.; Galland-Jos, C.; Minello, A.; Verges, B.; Guiguet, M.; Brun, J.M.; Hillon, P.; Zarski, J.P. Risk factors for diabetes mellitus and early insulin resistance in chronic hepatitis C. J. Hepatol. 2001, 35, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
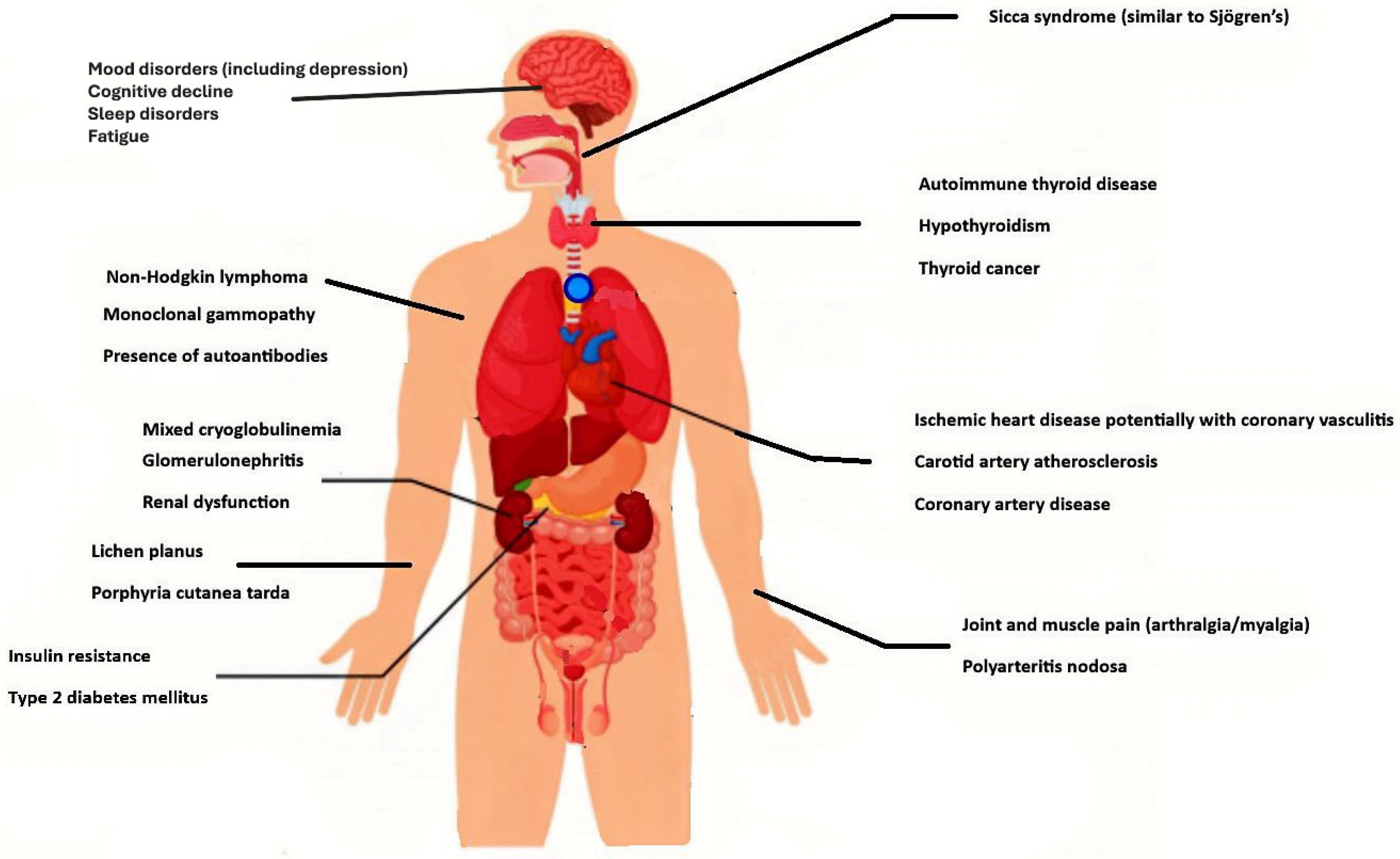
| Category | Associated Conditions |
|---|---|
| Immune | Mixed cryoglobulinemia |
| Non-Hodgkin lymphoma | |
| Joint and muscle pain (arthralgia/myalgia) | |
| Sicca syndrome (similar to Sjögren’s) | |
| Polyarteritis nodosa | |
| Monoclonal gammopathy | |
| Presence of autoantibodies | |
| Inflammatory/Metabolic/Vascular | Glomerulonephritis |
| Renal dysfunction | |
| Insulin resistance | |
| Type 2 diabetes mellitus | |
| Ischemic heart disease, potentially with coronary vasculitis | |
| Carotid artery atherosclerosis | |
| Coronary artery disease | |
| Dermatological | Lichen planus Porphyria cutanea tarda |
| Thyroid | Autoimmune thyroid disease |
| Hypothyroidism | |
| Thyroid cancer | |
| Neuropsychiatric | Mood disorders (including depression) |
| Cognitive decline | |
| Sleep disorders | |
| Fatigue |
| Author | Type of Study | No. of Patients | Age (Mean, Range) | Baseline HCV-RNA (log10 IU/mL) | ALT (IU/L) | Purpura n (%) | Arthralgia n (%) | Polyneuropathy n (%) | Skin Ulcer n (%) | Renal Involvement n (%) | DAA Regimen | Duration (Weeks) | Virological Response (SVR) | Clinical Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gragnani et al., 2016 [25] | Prospective | 44 | 65.3 ± 10.1 | 2.9 ± 3.6 | 77.7 ± 77.2 | 32 (73) | 26 (59) | 28 (63) | 6 (14) | 4 (9) | SOF + RBV 24: 18 (41%) SOF + SIM (+RBV): 12 (27%) SOF + DAC (+RBV): 4 (32%) SOF + LED (+RBV): 10 (23%) | 12 or 24 | 100% | CR: 66% PR: 42% NR: 7% |
| Saadoun et al., 2017 [19] | Prospective | 41 | 56 (50–62) | 5.9 ± 0.2 | 55.3 ± 6.4 | 31 (75.6) | 26 (63.4) | 21 (51.2) | 7 (17.1) | 5 (12.2) | SOF + DAC: 32 (78%) SOF + DAC: 9 (22%) | 12 or 24 | 100% | CR: 90% PR: 4% NR: 0 |
| Lauletta et al., 2017 [33] | Prospective | 22 | 66.9 ± 11.2 (46–84) | 6.02 ± 1.2 | 104.8 ± 144.7 | 12 (55) | 12 (55) | 10 (45) | NA | NA | 3D: 3 (14%) SOF + RBV: 10 (45%) SOF + SIM ± RBV: 4 (18%) SOF + LED ± RBV: 5 (23%) | 12 or 24 | 100% | CR: 64% PR: 23% NR: 14% |
| Emery et al., 2017 [42] | Retrospective | 18 symptomatic 65 asymptomatic 10 severe | 58 | NA | NA | 15 (83.3) | NA | 6 (33) | NA | 10 (55) | IFN/RBV/DAA: 7 (39%) IFN-free: 11 (61%) SOF + RBV: 5 (28%) SOF + SIM: 3 (28%) SOF + LED ± RBV: 3 (16%) 3D + RBV: 2 (11%) | 12 or 24 | 88.9% (symptomatic), 90.8% (asymptomatic) | CR: 39% PR: 22% NR: 39% |
| Passerini et al., 2018 [41] | Prospective | 35 | 67 (12.7) | 4.72–5.85 | 46 (27–84) | 24 (69) | 6 (17) | 11 (31) | NA | 2 (6) | SOF-based regimen: 31 (88%) 2D regimen: 1 (9%) 3D regimen: 3 (8%) | 12 or 24 | 100% | CR: 43% PR: 37% NR: 20% |
| Bonacci et al., 2018 [32] | Retrospective | 46 | 61 (53–01) | 5.9 (5.4–6.2) | 65 (34–119) | 29 (63) | 16 (35) | 19 (41) | NA | 9 (20) | SOF-based regimen: 21 (46%) 3D regimen: 13 (28%) SIM + DAC: 4 (9%) GZB + EBR: 3 (6%) PegIFN + DAAs: 4 (9%) FDV + LDR: 1 (2%) | 12 or 24 | 100% | CR: 80% PR: 11% NR: 9% |
| Mazzaro et al., 2018 [40] | Retrospective | 22 | 69 (39–74) | 5.80 (4.31–7.00) | 72 (12–173) | 12 (55) | 12 (55) | 10 (45) | NA | NA | 3D: 3 (14%) SOF + RBV: 10 (45%) SOF + SIM ± RBV: 4 (18%) SOF + LED ± RBV: 5 (23%) | 12 or 24 | 95% | CR: 64% PR: 14% NR: 23% |
| Cacoub et al., 2019 [27] | Prospective | 148 | 57 (51–67) | 5.3 ± 6.5 | 24 ± 77 | 85 (57.4) | 94 (64.4) | 86 (58.1) | 15 (10.1) | 25 (16.9) | SOF + RBV: 51 (34%) SOF + DAC: 53 (36%) SOF + LED: 23 (16%) SOF + SIM: 18 (12%) | 12 or 24 | 95.2% | CR: 72% PR: 22% NR: 5% |
| Pozzato et al., 2020 [43] | Retrospective | 67 | NA | NA | NA | 33 (49) | 36 (54) | 28 (42) | NA | NA | SOF-based: 52 (78%) 3D regimen: 12 (18%), Asunaprevir/DAC: 4 (6%) | 12 | 95% | CR: 60% NR: 40% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balta, A.A.S.; Ignat, M.D.; Barbu, R.E.; Dumitru, C.; Radaschin, D.S.; Bulza, V.; Mateescu Costin, S.A.; Pleșea-Condratovici, C.; Baroiu, L. Impact of Direct-Acting Antivirals on Extrahepatic Manifestations in Chronic Hepatitis C: A Narrative Review with a Hermeneutic Approach. Healthcare 2025, 13, 1953. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13161953
Balta AAS, Ignat MD, Barbu RE, Dumitru C, Radaschin DS, Bulza V, Mateescu Costin SA, Pleșea-Condratovici C, Baroiu L. Impact of Direct-Acting Antivirals on Extrahepatic Manifestations in Chronic Hepatitis C: A Narrative Review with a Hermeneutic Approach. Healthcare. 2025; 13(16):1953. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13161953
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalta, Alexia Anastasia Stefania, Mariana Daniela Ignat, Raisa Eloise Barbu, Caterina Dumitru, Diana Sabina Radaschin, Valentin Bulza, Silvia Aura Mateescu Costin, Catalin Pleșea-Condratovici, and Liliana Baroiu. 2025. "Impact of Direct-Acting Antivirals on Extrahepatic Manifestations in Chronic Hepatitis C: A Narrative Review with a Hermeneutic Approach" Healthcare 13, no. 16: 1953. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13161953
APA StyleBalta, A. A. S., Ignat, M. D., Barbu, R. E., Dumitru, C., Radaschin, D. S., Bulza, V., Mateescu Costin, S. A., Pleșea-Condratovici, C., & Baroiu, L. (2025). Impact of Direct-Acting Antivirals on Extrahepatic Manifestations in Chronic Hepatitis C: A Narrative Review with a Hermeneutic Approach. Healthcare, 13(16), 1953. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13161953






