Effect of Family and Personal Medical History on Treatment Outcomes of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKIs) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Definition of FPMH
2.3. Patient Population
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
3.2. Tumor Characteristics, Staging, and Genetic Markers
3.3. Treatment Characteristics and Toxicity
3.4. Laboratory Findings and Medication Use
Correlation and Regression Analyses
3.5. Survival Analysis
3.6. Cox Regression Analysis
3.7. Predictors of FPMH (Logistic Regression)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
5.1. Summary
5.2. Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts & Figures 2023. 2023. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/research/cancer-facts-and-statistics/annual-cancer-facts-and-figures/2023/2023-cancer-facts-and-figures.pdf (accessed on 25 June 2025).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Smoking and Cancer. 2022. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/campaign/tips/diseases/cancer.html (accessed on 25 June 2025).
- Chen, Y.T. EGFR mutations in non-small cell lung cancer: A focus on demographic disparities. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12 (Suppl. S1), S45–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainor, J.F.; Shaw, A.T. Emerging paradigms in the development of resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3987–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstraw, P.; Chansky, K.; Crowley, J.; Rami-Porta, R.; Asamura, H.; Eberhardt, W.E.; Nicholson, A.G.; Groome, P.; Mitchell, A.; Bolejack, V.; et al. The IASLC lung cancer staging project: Proposals for revision of the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (eighth) edition of the TNM classification for lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigolon, R.B.; Lasio, L. Precision medicine in NSCLC: Challenges and opportunities. In Lung Cancer International; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2023; p. 123456. [Google Scholar]
- Hecht, S.S. Tobacco carcinogens, their biomarkers and tobacco-induced cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellmann, M.D.; Paz-Ares, L.; Bernabe Caro, R.; Zurawski, B.; Kim, S.-W.; Carcereny Costa, E.; Park, K.; Alexandru, A.; Lupinacci, L.; de la Mora Jimenez, E.; et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in advanced non–small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2020–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, F.R.; Scagliotti, G.V.; Mulshine, J.L.; Kwon, R.; Curran, W.J.; Wu, Y.-L.; Paz-Ares, L. Lung cancer: Current therapies and new targeted treatments. Lancet 2017, 389, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans: Volume 100D—Radiation. 2009. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/iarc-monographs-on-the-evaluation-of-carcinogenic-risks-to-humans-volume-100d (accessed on 25 June 2025).
- Li, Y.; Xiao, X.; Han, Y.; Zhang, L. Family history of lung cancer and its association with actionable mutations in NSCLC. Thorac. Cancer 2021, 12, 789–796. [Google Scholar]
- Midha, A.; Dearden, S.; McCormack, R. EGFR mutation incidence in non-small-cell lung cancer of adenocarcinoma histology: A systematic review and global perspective. J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 7, 1508–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cancer Institute. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment (PDQ®)–Health Professional Version. 2022. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/types/lung/hp/non-small-cell-lung-treatment-pdq (accessed on 25 June 2025).
- Obiols, C.; Call, S.; Rami-Porta, R. Tyrosine kinase inhibitor outcomes in NSCLC patients with a family history of cancer: A retrospective analysis. Clin. Lung Cancer 2022, 23, e245–e251. [Google Scholar]
- Pao, W.; Girard, N. New driver mutations in non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, S.; Camidge, D.R.; Shaw, A.T.; Gadgeel, S.; Ahn, J.S.; Kim, D.-W.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Pérol, M.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Rosell, R.; et al. Alectinib versus crizotinib in untreated ALK-positive non–small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reck, M.; Rabe, K.F. Precision diagnosis and treatment for advanced non–small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 849–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reck, M.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Robinson, A.G.; Hui, R.; Csőszi, T.; Fülöp, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peled, N.; Tafreshi, A.; Cuffe, S.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for PD-L1–positive non–small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soria, J.-C.; Ohe, Y.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Lee, K.H.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Kurata, T.; et al. Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non–small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travis, W.D. Pathology of lung cancer. Clin. Chest Med. 2014, 35, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, N.; Domchek, S.M.; Stadler, Z. Counselling framework for moderate-penetrance cancer-susceptibility mutations. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 13, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, J.C.M.; Massie, C.; Garcia-Corbacho, J.; Mouliere, F.; Brenton, J.D.; Caldas, C.; Pacey, S.; Baird, R.; Rosenfeld, N. Liquid biopsies come of age: Towards implementation of circulating tumour DNA. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Cancer Fact Sheet. 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer (accessed on 25 June 2025).


| Characteristic | Without FPMH (n = 102) | With FPMH (n = 34) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (Female, %) | 54.9 (56/102) | 47.1 (16/34) | 0.552 |
| Smoking Status (Never, %) | 62.7 (64/102) | 55.9 (19/34) | 0.612 |
| Chronic Disease (Yes, %) | 15.7 (16/102) | 58.8 (20/34) | <0.001 |
| ECOG ≥ 3 (Yes, %) | 1.0 (1/102) | 8.8 (3/34) | 0.048 |
| Recurrence Post-Treatment (%) | 20.6 (21/102) | 41.2 (14/34) | 0.031 |
| Age (Mean ± SD, years) | 62.73 ± 12.62 | 63.21 ± 12.01 | 0.846 |
| Smoking Pack-Years (Mean ± SD) | 33.03 ± 21.11 | 39.06 ± 22.6 | 0.352 |
| Overall Survival (Mean ± SD, months) | 29.05 ± 24.03 | 30.03 ± 29.39 | 0.846 |
| Recurrence Duration (Mean ± SD, months) | 44.79 ± 36.85 | 51.94 ± 43.49 | 0.363 |
| Characteristic | Without FPMH (n = 102) | With FPMH (n = 34) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| TNM Stage 1–2 (%) | 17.6 (18/102) | 23.5 (8/34) | 0.720 |
| EGFR Mutation (Yes, %) | 83.3 (85/102) | 91.2 (31/34) | 0.402 |
| ALK Mutation (Yes, %) | 12.7 (13/102) | 2.9 (1/34) | 0.192 |
| ROS1 Mutation (Yes, %) | 2.9 (3/102) | 5.9 (2/34) | 0.792 |
| Surgical Intervention (Yes, %) | 16.7 (17/102) | 29.4 (10/34) | 0.172 |
| Non-Squamous Histology (%) | 97.1 (99/102) | 94.1 (32/34) | 0.792 |
| PD-L1 Expression (Mean ± SD, %) | 2.35 ± 11.07 | 0.76 ± 4.29 | 0.562 |
| Characteristic | Without FPMH (n = 102) | With FPMH (n = 34) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
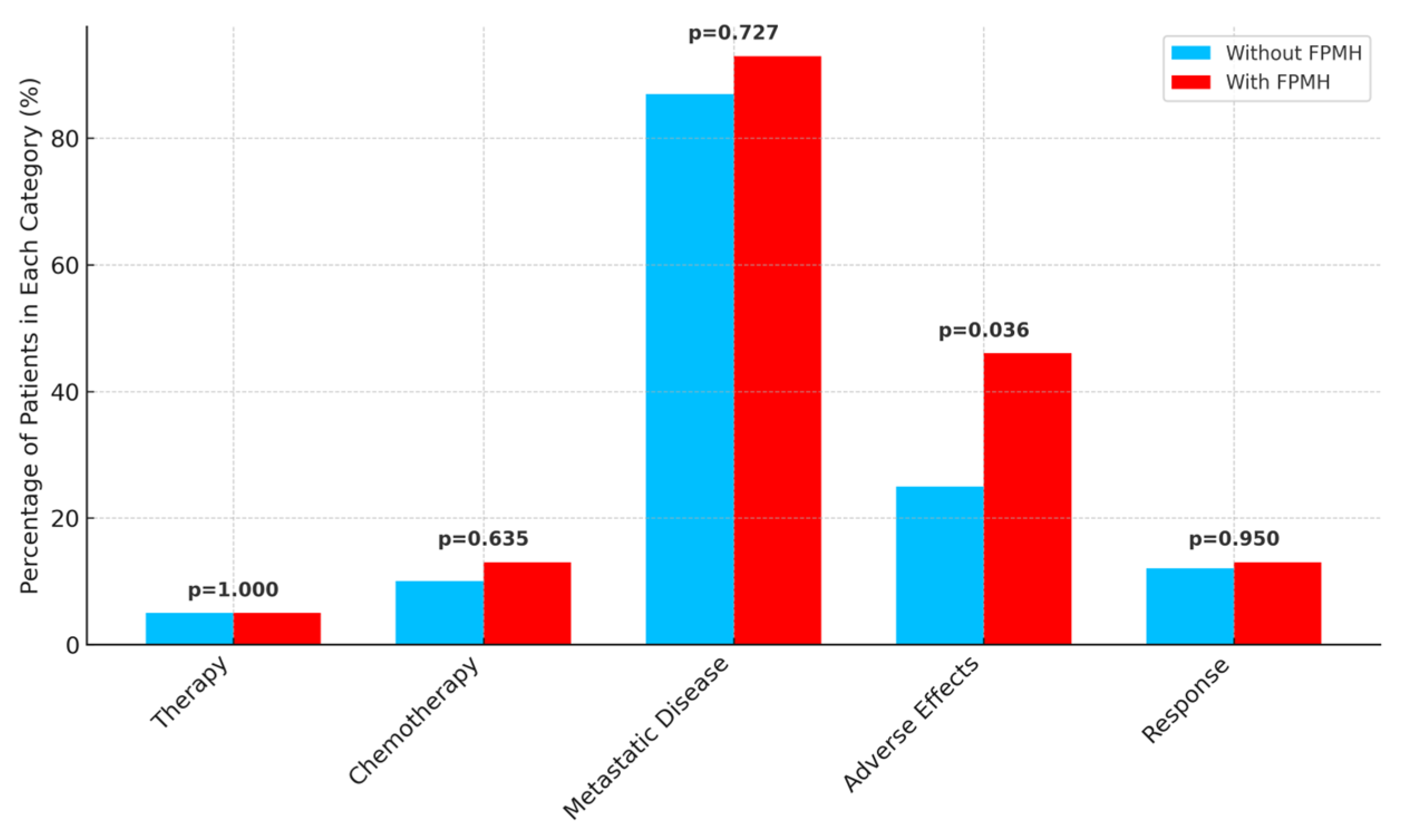
| Neoadjuvant Therapy (Yes, %) | 4.9 (5/102) | 5.9 (2/34) | 1.000 |
| Adjuvant Chemotherapy (Yes, %) | 9.8 (10/102) | 14.7 (5/34) | 0.635 |
| Metastatic Disease (Yes, %) | 90.2 (92/102) | 94.1 (32/34) | 0.727 |
| Chemotherapy Adverse Effects (%) | 28.4 (29/102) | 50.0 (17/34) | 0.036 |
| First-Line Response (CR, %) | 12.7 (13/102) | 14.7 (5/34) | 0.950 |
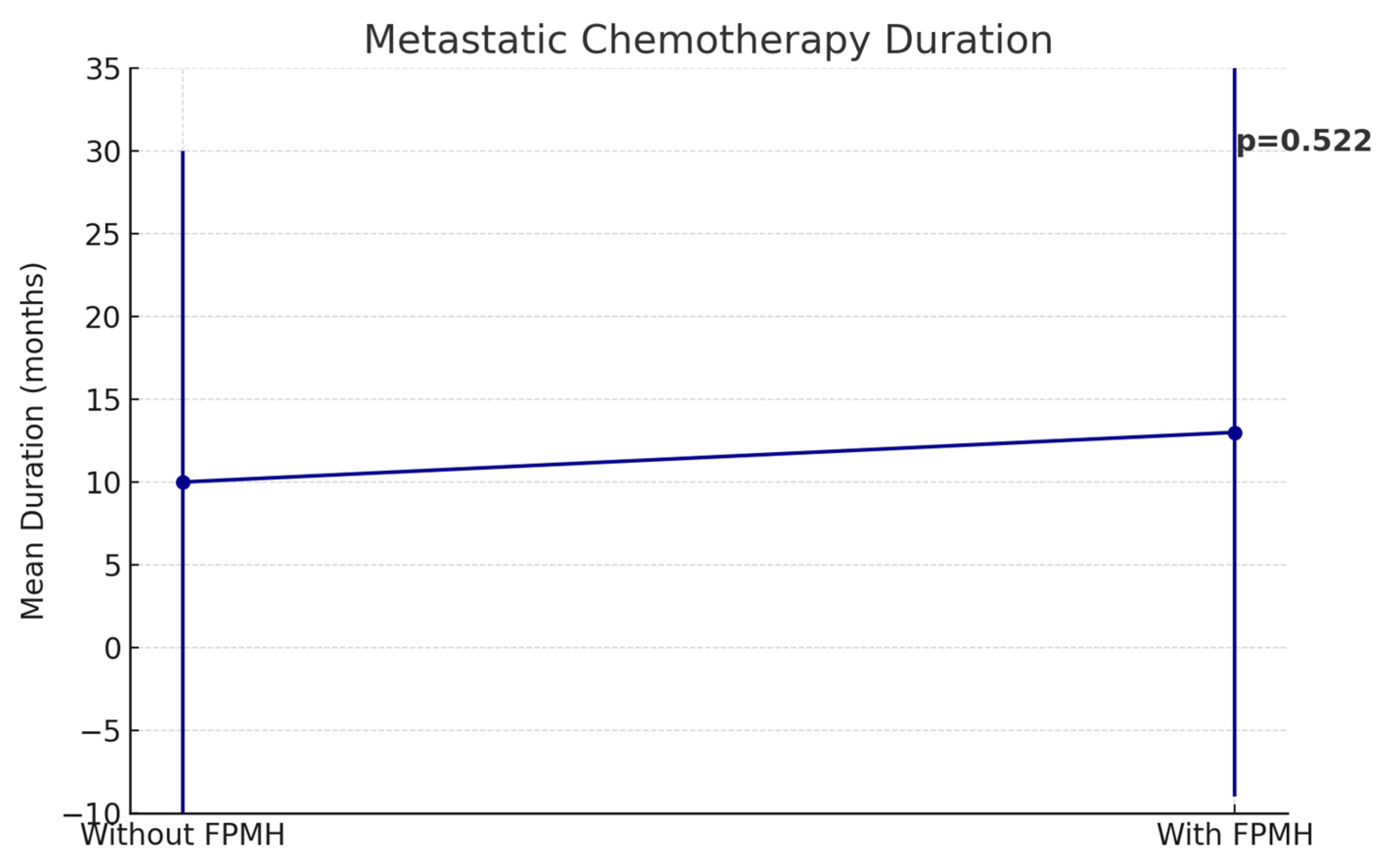
| Metastatic Chemo Duration (Mean ± SD, months) | 9.82 ± 18.25 | 13.06 ± 17.65 | 0.522 |
| Characteristic | Without FPMH (n = 102) | With FPMH (n = 34) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| CEA (Mean ± SD, ng/mL) | 80.36 ± 182.7 | 88.91 ± 238.74 | 0.782 |
| AST (Mean ± SD, U/L) | 23.53 ± 20.79 | 22.53 ± 12.67 | 0.909 |
| WBC (Mean ± SD, per μL) | 8327.42 ± 3707.12 | 8365.67 ± 3175.8 | 0.959 |
| Hemoglobin (Mean ± SD, g/dL) | 12.21 ± 1.8 | 12.46 ± 1.88 | 0.517 |
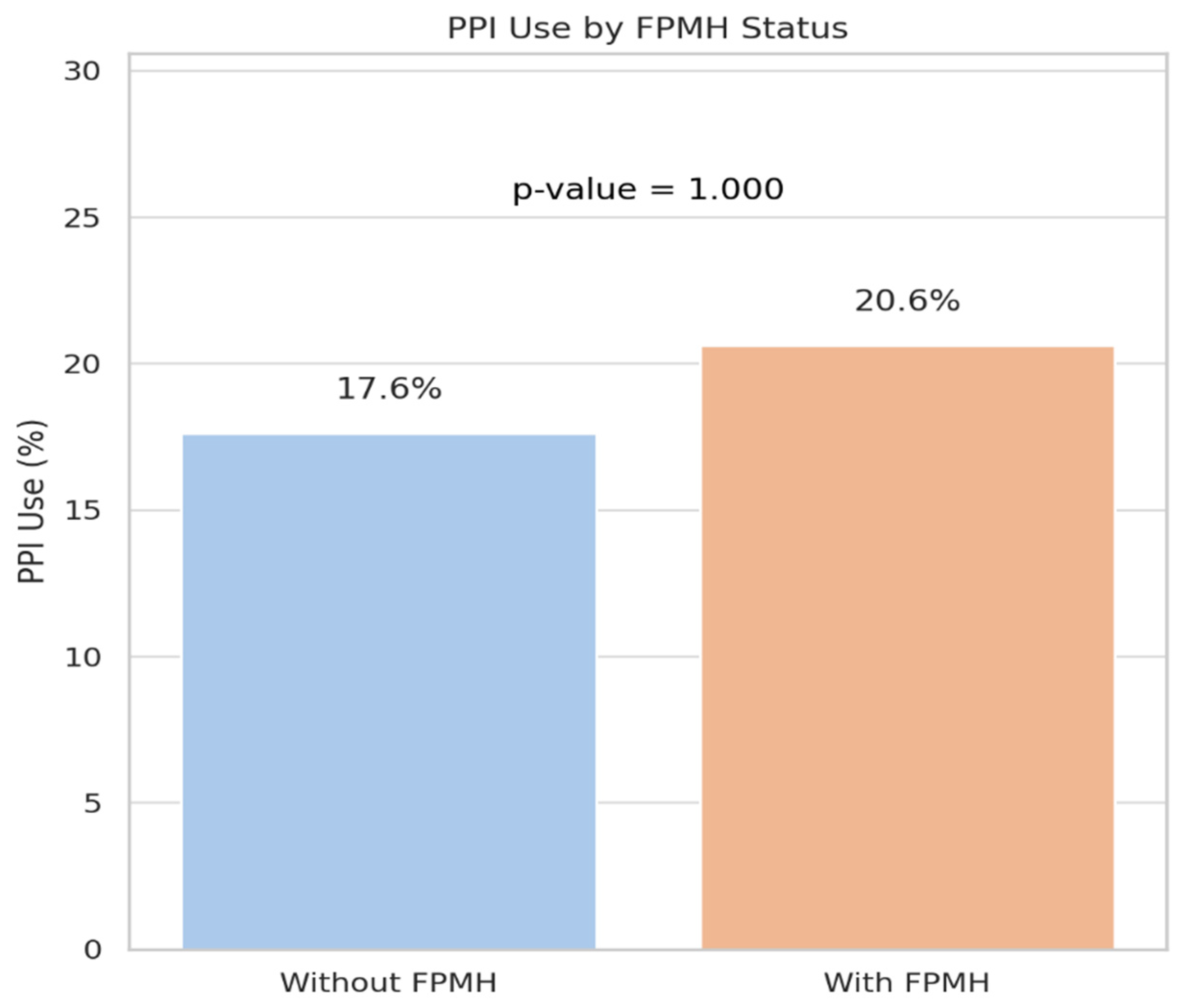
| PPI Use (Yes, %) | 17.6 (18/102) | 20.6 (7/34) | 1.000 |
| Variable | Correlation Coefficient (r) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
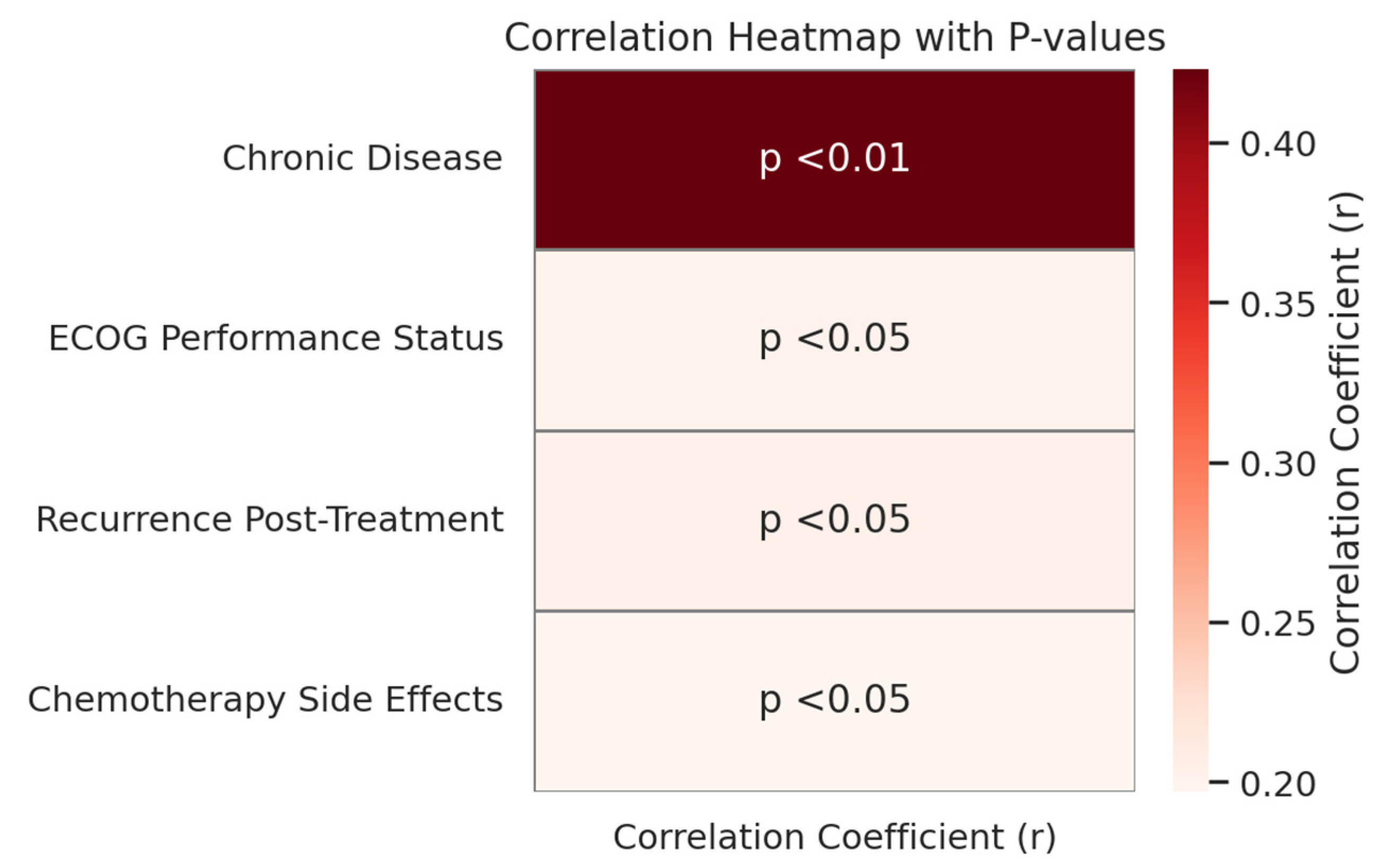
| Chronic Disease | 0.423 | <0.01 |
| ECOG Performance Status | 0.201 | <0.05 |
| Recurrence Post-Treatment | 0.204 | <0.05 |
| Chemotherapy Side Effects | 0.197 | <0.05 |
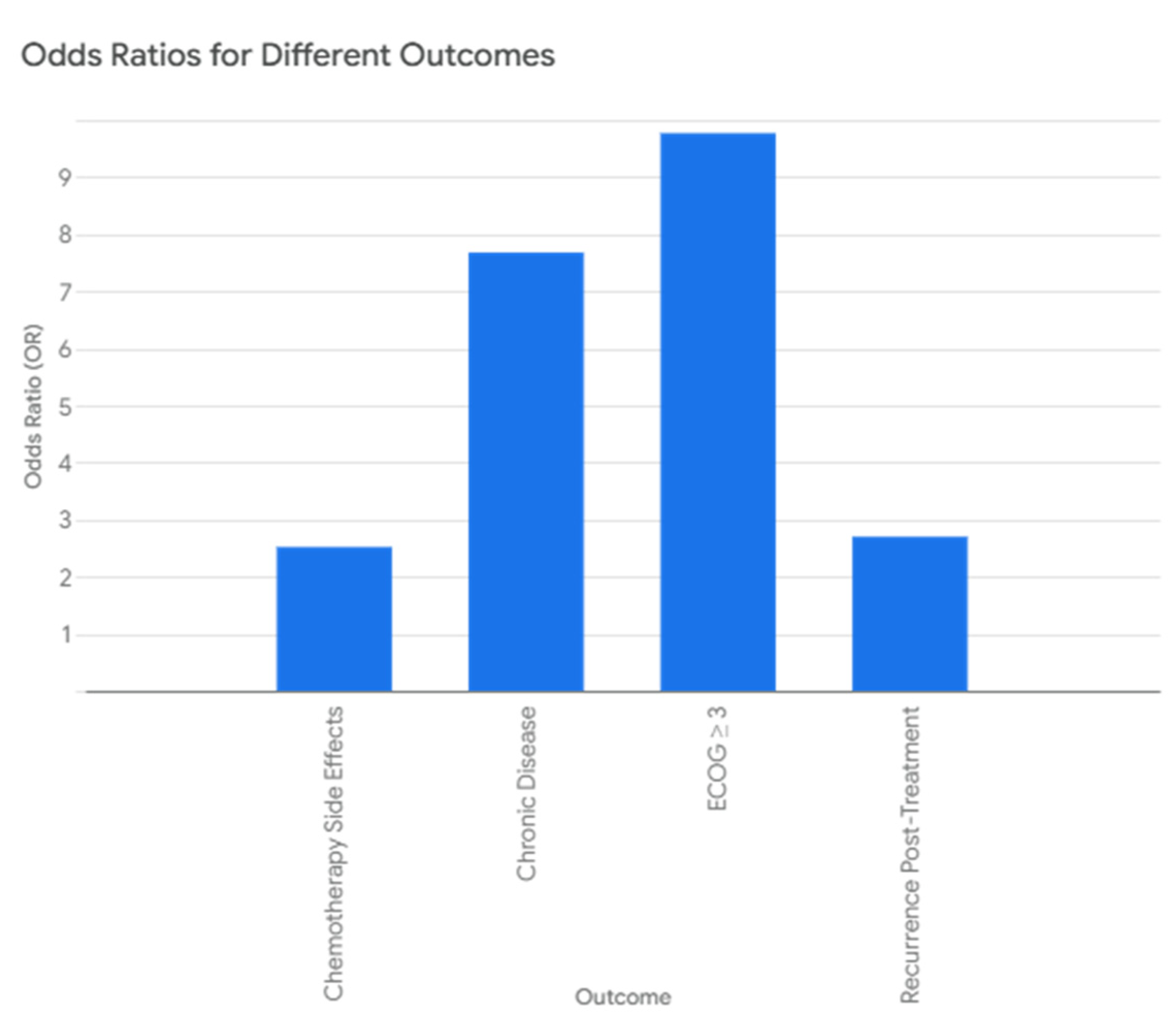
| Outcome | Odds Ratio (OR) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Chronic Disease | 7.68 | <0.001 |
| ECOG ≥ 3 | 9.77 | 0.052 |
| Recurrence Post-Treatment | 2.70 | 0.020 |
| Chemotherapy Side Effects | 2.52 | 0.023 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Surmeli, H.; Turkoglu, E.; Isik, D.; Kinikoglu, O.; Altintas, Y.E.; Ozkerim, U.; Oksuz, S.; Basoglu, T.; Odabas, H.; Turan, N. Effect of Family and Personal Medical History on Treatment Outcomes of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKIs) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). Healthcare 2025, 13, 1810. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13151810
Surmeli H, Turkoglu E, Isik D, Kinikoglu O, Altintas YE, Ozkerim U, Oksuz S, Basoglu T, Odabas H, Turan N. Effect of Family and Personal Medical History on Treatment Outcomes of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKIs) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). Healthcare. 2025; 13(15):1810. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13151810
Chicago/Turabian StyleSurmeli, Heves, Ezgi Turkoglu, Deniz Isik, Oguzcan Kinikoglu, Yunus Emre Altintas, Ugur Ozkerim, Sila Oksuz, Tugba Basoglu, Hatice Odabas, and Nedim Turan. 2025. "Effect of Family and Personal Medical History on Treatment Outcomes of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKIs) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)" Healthcare 13, no. 15: 1810. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13151810
APA StyleSurmeli, H., Turkoglu, E., Isik, D., Kinikoglu, O., Altintas, Y. E., Ozkerim, U., Oksuz, S., Basoglu, T., Odabas, H., & Turan, N. (2025). Effect of Family and Personal Medical History on Treatment Outcomes of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKIs) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). Healthcare, 13(15), 1810. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13151810






