Assessing the Alignment Between the Humpty Dumpty Fall Scale and Fall Risk Nursing Diagnosis in Pediatric Patients: A Retrospective ROC Curve Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. Participants
2.3. Variables and Data Collection
- Demographic and clinical variables.
- Nursing-related variables.
- Structured fall risk assessment.
2.4. Ethical Considerations
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics According to the Presence of a Fall Risk ND
3.2. Patient Characteristics According to HDFS Items, Stratified by the Presence of a Fall Risk ND
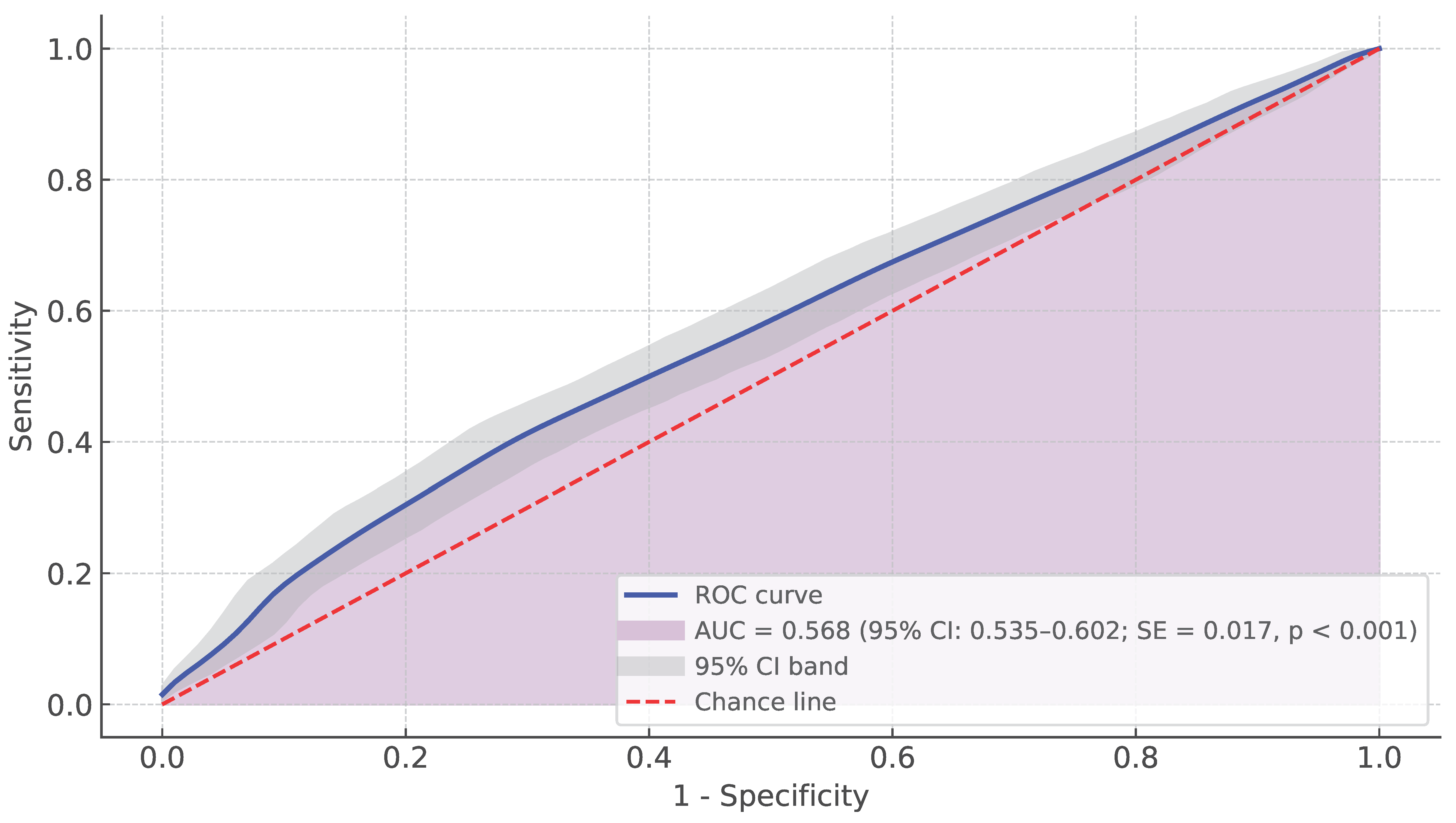
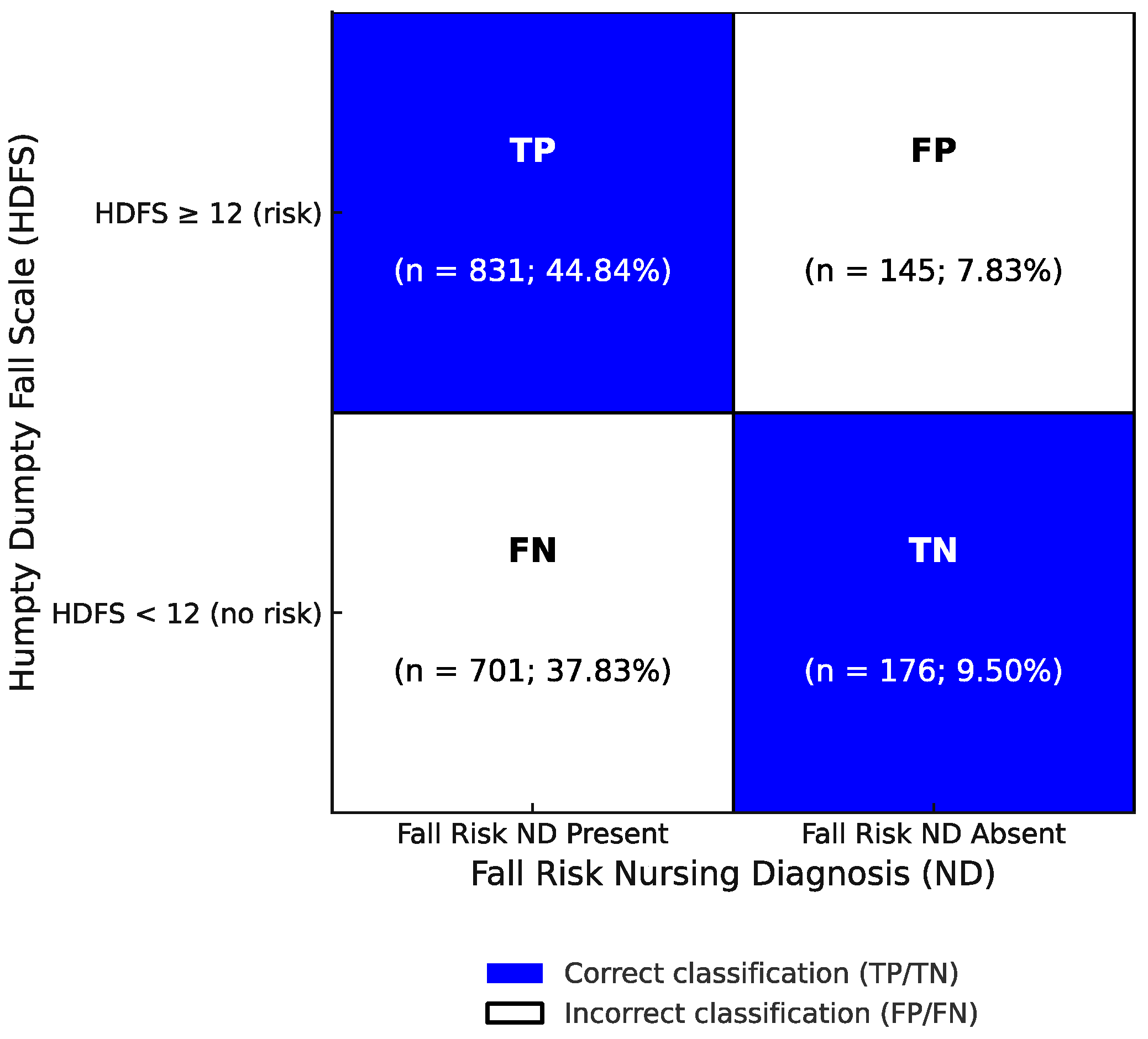
3.3. Diagnostic Accuracy of the HDFS in Detecting Fall Risk ND
3.4. Predictive Validity of the HDFS in Identifying a Fall Risk ND
4. Discussion
Implications for Nursing Practice, Research, Education, and Policy
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| CCC | Clinical Care Classification |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| DRG | Diagnosis-Related Group |
| FN | False Negative |
| FP | False Positive |
| HDFS | Humpty Dumpty Fall Scale |
| HDR | Hospital Discharge Register |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| LOS | Length of Stay |
| ND | Nursing Diagnosis |
| NI | Nursing Intervention |
| NPV | Negative Predictive Value |
| PAIped | Neonatal and Pediatric Professional Assessment Instrument |
| PPV | Positive Predictive Value |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| STARD | Standards for Reporting Diagnostic Accuracy Studies |
| TN | True Negative |
| TP | True Positive |
References
- Omaki, E.; Shields, W.; Rouhizadeh, M.; Delgado-Barroso, P.; Stefanos, R.; Gielen, A. Understanding the circumstances of paediatric fall injuries: A machine learning analysis of NEISS narratives. Inj. Prev. 2023, 29, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Qian, M.-L.; Shan, X.; Liu, X.-Q. Risk factors for falls among children aged 0–18 years: A systematic review. World J. Pediatr. 2022, 18, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.-J.; Kim, G.-M.; Lim, J.-Y. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Fall Prevention Programs for Pediatric Inpatients. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, C.; Kellaway, J.; Stockton, K. Analysis of Falls within Paediatric Hospital and Community Healthcare Settings. J. Pediatr. Nurs. 2020, 50, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strini, V.; Schiavolin, R.; Prendin, A. Fall Risk Assessment Scales: A Systematic Literature Review. Nurs. Rep. 2021, 11, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brás, A.M.R.; Quitério, M.M.d.S.L.; Nunes, E.M.G.T. Nurse’s interventions in preventing falls in hospitalized children: Scoping review. Rev. Bras. De Enferm. 2020, 73, e20190409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiGerolamo, K.; Davis, K.F. An Integrative Review of Pediatric Fall Risk Assessment Tools. J. Pediatr. Nurs. 2017, 34, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez-Fernández, S.; Ajejas-Bazán, M.J.; Pérez-Rivas, F.J. Evaluation of the use of a nursing diagnosis Risk for Falls in the Community of Madrid (Spain) Primary Care System. Int. J. Nurs. Knowl. 2023, 35, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill-Rodriguez, D.; Messmer, P.R.; Williams, P.D.; Zeller, R.A.; Williams, A.R.; Wood, M.; Henry, M. The Humpty Dumpty Falls Scale: A Case–Control Study. J. Spéc. Pediatr. Nurs. 2009, 14, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herdman, T.H.; Kamitsuru, S.; Takao Lopes, C. NANDA International Nursing Diagnoses: Definitions and Classification, 2024–2026, 13th ed.; Thieme Medical Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Saba, V. Clinical Care Classification (CCC) System Version 2.5: User’s Guide, 2nd ed.; Springer Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cesare, M.; Cocchieri, A. Can an increase in nursing care complexity raise the risk of intra-hospital and intensive care unit transfers in children? A retrospective observational study. J. Pediatr. Nurs. 2024, 80, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.J.; Lim, J.Y.; Kim, G.M.; Min, J. An electronic medical record-based fall risk assessment tool for pediatric inpatients in South Korea: Improved sensitivity and specificity. Child Health Nurs. Res. 2021, 27, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossuyt, P.M.; Reitsma, J.B.; Bruns, D.E.; Gatsonis, C.A.; Glasziou, P.P.; Irwig, L.; Lijmer, J.G.; Moher, D.; Rennie, D.; de Vet, H.C.; et al. STARD 2015: An Updated List of Essential Items for Reporting Diagnostic Accuracy Studies. Radiology 2015, 277, 826–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Agostino, F.; Sanson, G.; Cocchieri, A.; Vellone, E.; Welton, J.; Maurici, M.; Alvaro, R.; Zega, M. Prevalence of nursing diagnoses as a measure of nursing complexity in a hospital setting. J. Adv. Nurs. 2017, 73, 2129–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolaus, S.; Crelier, B.; Donzé, J.D.; E Aubert, C. Definition of patient complexity in adults: A narrative review. J. Multimorb. Comorbidity 2022, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierannunzio, D.; Maraschini, A.; Lopez, T.; Donati, S.; Amodio, R.; Bianconi, F.; Bruni, R.; Castaing, M.; Cirilli, C.; Fantaci, G.; et al. Cancer and Pregnancy: Estimates in Italy from Record-Linkage Procedures between Cancer Registries and the Hospital Discharge Database. Cancers 2023, 15, 4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeffiro, V.; Sanson, G.; Vanalli, M.; Cocchieri, A.; Ausili, D.; Alvaro, R.; D’AGostino, F. Translation and cross-cultural adaptation of the Clinical Care Classification system. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2021, 153, 104534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanalli, M.; Cesare, M.; Cocchieri, A.; D’Agostino, F. Natural language processing and String Metric-assisted Assessment of Semantic Heterogeneity method for capturing and standardizing unstructured nursing activities in a hospital setting: A retrospective study. Ann. Ig. 2023, 35, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocchieri, A.; Di Sarra, L.; D’Agostino, F.; Bravetti, C.; Pignocco, M.; Vellone, E.; Alvaro, R.; Zega, M. Development and implementation of pediatric and neonatal nursing information system in an hospital setting: The pediatric PAI. Ig. E Sanità Pubblica 2019, 74, 315–328. [Google Scholar]
- Zega, M.; D’AGostino, F.; Bowles, K.H.; De Marinis, M.G.; Rocco, G.; Vellone, E.; Alvaro, R. Development and Validation of a Computerized Assessment Form to Support Nursing Diagnosis. Int. J. Nurs. Knowl. 2013, 25, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesare, M.; D’agostino, F.; Cocchieri, A. Exploring the Association between Complexity of Care, Medical Complexity, and Length of Stay in the Paediatric Setting Using a Nursing Minimum Data Set: A Study Protocol. Nurs. Rep. 2024, 14, 2923–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-Y. Statistical notes for clinical researchers: Assessing normal distribution (2) using skewness and kurtosis. Restor. Dent. Endod. 2013, 38, 52–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahm, F.S. Receiver operating characteristic curve: Overview and practical use for clinicians. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2022, 75, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çorbacıoğlu Ş, K.; Aksel, G. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis in diagnostic accuracy studies: A guide to interpreting the area under the curve value. Turk. J. Emerg. Med. 2023, 23, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monaghan, T.F.; Rahman, S.N.; Agudelo, C.W.; Wein, A.J.; Lazar, J.M.; Everaert, K.; Dmochowski, R.R. Foundational Statistical Principles in Medical Research: Sensitivity, Specificity, Positive Predictive Value, and Negative Predictive Value. Medicina 2021, 57, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, C.; Sahagún, B.E.; Su, M.K. Biostatistics and Epidemiology Principles for the Toxicologist: The “Testy” Test Characteristics Part II: Positive Predictive Value and Negative Predictive Value. J. Med. Toxicol. 2023, 19, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocchieri, A.; Pezzullo, A.M.; Cesare, M.; De Rinaldis, M.; Cristofori, E.; D’AGostino, F. Association between health literacy and nursing care in hospital: A retrospective study. J. Clin. Nurs. 2023, 33, 642–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alemdaroğlu, E.; Özbudak, S.D.; Mandiroğlu, S.; Biçer, S.A.; Özgirgin, N.; Uçan, H. Predictive Factors for Inpatient Falls among Children with Cerebral Palsy. J. Pediatr. Nurs. 2016, 32, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reader, B.; Javens, T.B.; Albert, J.; Nelson, A.; Wessells, D.P. Falls among Pediatric Patients Receiving Home Care. Home Healthc. Now 2024, 42, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, K.; Kramlich, D.; Chapman, J.; Parker, J.; Blades, E. Exploring and evaluating five paediatric falls assessment instruments and injury risk indicators: An ambispective study in a tertiary care setting. J. Nurs. Manag. 2010, 18, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarik, D.A.; Hill-Rodriguez, D.; Gattamorta, K.A.; Gonzalez, J.L.; Esteves, J.; Zamora, K.; Cordo, J. The revised Humpty Dumpty Fall Scale: An update to improve tool performance and predictive validity. J. Pediatr. Nurs. 2022, 67, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fhon, J.R.S.; Diogo, R.; Dos Santos Neto, A.P.; Djinan, A.; Lima, E.F.C.; Rodrigues, R.A.P. Clinical validation of the nursing diagnosis "Fall risk in adults (00303)" in elderly people in the community-dwelling. Int. J. Nurs. Knowl. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassallo, M.; Poynter, L.; Sharma, J.C.; Kwan, J.; Allen, S.C. Fall risk-assessment tools compared with clinical judgment: An evaluation in a rehabilitation ward. Age Ageing 2008, 37, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Huesmann, L.; Sudacka, M.; Durning, S.J.; Georg, C.; Huwendiek, S.; Kononowicz, A.A.; Schlegel, C.; Hege, I. Clinical reasoning: What do nurses, physicians, and students reason about. J. Interprof. Care 2023, 37, 990–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joplin-Gonzales, P.; Rounds, L. The Essential Elements of the Clinical Reasoning Process. Nurse Educ. 2022, 47, E145–E149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arıca, E.Ö.; Koç, Z. Investigating nurses’ attitudes towards the prevention of falls: A mixed-method study. Geriatr. Nurs. 2025, 62, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Sánchez, J.M.; Sánchez-Almagro, C.P.; White-Ríos, M.; Paloma-Castro, O. Prevalence and clustering of NANDA-I nursing diagnoses in the pre-hospital emergency care setting: A retrospective records review study. J. Clin. Nurs. 2024, 33, 3128–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesare, M.; D’Agostino, F.; Maurici, M.; Zega, M.; Zeffiro, V.; Cocchieri, A. Standardized Nursing Diagnoses in a Surgical Hospital Setting: A Retrospective Study Based on Electronic Health Data. SAGE Open Nurs. 2023, 9, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Agostino, F.; Tuinman, A.; Lopes, C.T.; Leoni-Scheiber, C.; Widmann, M.; Barrientos-Trigo, S.; Batista-Santos, V.; Zeffiro, V. A review of nursing diagnoses prevalence in different populations and healthcare settings. Acta Paul. De Enferm. 2024, 37, eAPE01173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.J.; Lim, J.Y.; Kim, G.M.; Lee, M.K. Meta-analysis of the Diagnostic Test Accuracy of Pediatric Inpatient Fall Risk Assessment Scales. Child Health Nurs. Res. 2019, 25, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffith, P.B.; Mariani, B.; Kelly, M.M. Diagnostic Reasoning Outcomes in Nurse Practitioner Education: A Scoping Review. J. Nurs. Educ. 2022, 61, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, P.; Poeira, A.; Mendes, D.A.; Batalha, N.; Franco, H.; Nunes, L.; Marques, F.; Pađen, L.; Stefaniak, M.; Pérez-Perdomo, A.; et al. Teaching and Learning Clinical Reasoning in Nursing Education: A Student Training Course. Healthcare 2024, 12, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chimonas, S.C.; Diaz-MacInnis, K.L.; Lipitz-Snyderman, A.N.; Barrow, B.E.; Korenstein, D.R. Why Not? Persuading Clinicians to Reduce Overuse. Mayo Clin. Proceedings: Innov. Qual. Outcomes 2020, 4, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubbeling, D. Overtreatment: Is a solution possible? J. Evaluation Clin. Pr. 2021, 28, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohlmannstetter, M. Overtreatment in nursing-does it exist? Med. Klin. Intensivmed. Notfmed. 2019, 114, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seçer, S.; Karaca, A. Evaluation of Nurses’ Perceptions of Nursing Diagnoses and Their Opinions Regarding the Application of Nursing Process. Florence Nightingale J. Nurs. 2021, 29, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, N.; Christian, R.; Palokas, M.; Upchurch, L. Fall prevention in a pediatric unit: A best practice implementation project. JBI Evid. Implement. 2024, 22, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciofi, D.; Albolino, S.; Dagliana, G.; Biermann, K.; Savelli, A.; Frangioni, G.; Fantoni, M.; Gheri, C.; Neri, S.; Festini, F.; et al. Prevalence and multicenter observational study on falls of hospitalized children and Italian, linguistic-cultural validation of the Humpty Dumpty Fall Scale. Prof. Inferm. 2020, 73, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variable | Descriptive Statistics | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients Without Fall Risk ND (N = 397) | Patients with Fall Risk ND (N = 1689) | p-Value a | Patients Not at Risk for Falls (HDFS < 12) (N = 877) | Patients with Fall Risk (HDFS ≥ 12) (N = 976) | p-Value a | |||||
| Age (years) (mean; SD) | 9.25 | 5.91 | 7.80 | 5.85 | <0.001 | 10.81 | 5.02 | 5.01 | 4.81 | <0.001 |
| Gender (N; %) | 0.641 | <0.001 | ||||||||
| Male | 221 | 55.7 | 962 | 57.0 | 393 | 44.8 | 658 | 67.4 | ||
| Female | 176 | 44.3 | 727 | 43.0 | 484 | 55.2 | 318 | 32.6 | ||
| Comorbidities (mean; SD) | 1.64 | 0.94 | 1.89 | 1.21 | <0.001 | 1.85 | 1.22 | 1.90 | 1.13 | 0.394 |
| Chronic conditions (mean; SD) | 0.75 | 0.92 | 1.02 | 1.05 | <0.001 | 0.85 | 1.02 | 1.17 | 1.05 | <0.001 |
| DRG weight (median, IQR) | 0.7350 | 0.54 | 0.7933 | 0.74 | <0.001 | 0.8102 | 0.69 | 0.6807 | 0.54 | <0.001 |
| LOS (days) (median, IQR) | 4.00 | 4 | 4.00 | 4 | <0.001 | 4.00 | 5 | 5.00 | 4 | 0.670 |
| NDs (N = 8504) (mean; SD) | 2.40 | 1.92 | 4.47 | 2.72 | <0.001 | 4.41 | 2.53 | 3.86 | 2.87 | <0.001 |
| NIs (N = 23720) (mean; SD) | 10.63 | 2.56 | 11.54 | 2.86 | <0.001 | 11.44 | 2.77 | 11.60 | 2.64 | 0.209 |
| (N = 321) | (N = 1532) | |||||||||
| HDFS score (N = 1853) (mean; SD) | 11.37 | 2.32 | 12.02 | 2.61 | <0.001 | 9.69 | 1.10 | 13.90 | 1.76 | <0.001 |
| HDFS Item | Descriptive Statistics | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients Without Fall Risk ND (N = 321) | Patients with Fall Risk ND (N = 1532) | p-Value a | |||
| N | % | N | % | ||
| Age | 0.098 | ||||
| Less than 3 years old | 77 | 19.4 | 424 | 27.7 | |
| 3 to less than 7 years old | 67 | 20.9 | 339 | 22.1 | |
| 7 to less than 13 years old | 75 | 23.4 | 384 | 25.1 | |
| 13 years and above | 102 | 31.8 | 385 | 25.1 | |
| Gender | 0.660 | ||||
| Male | 178 | 55.5 | 870 | 56.8 | |
| Female | 143 | 44.5 | 662 | 43.2 | |
| Diagnosis | <0.001 | ||||
| Neurological diagnosis | 61 | 19.0 | 422 | 27.5 | |
| Alterations in oxygenation (respiratory diagnosis, dehydration, anemia, anorexia, syncope/dizziness, etc.) | 15 | 4.7 | 53 | 3.5 | |
| Psych/behavioral disorders | 42 | 13.1 | 102 | 6.7 | |
| Other diagnosis | 203 | 63.2 | 955 | 62.3 | |
| Cognitive Impairments | 0.003 | ||||
| Not Aware of Limitations | 50 | 15.6 | 366 | 23.9 | |
| Forgets Limitations | 32 | 10.0 | 161 | 10.5 | |
| Oriented to Own Ability | 239 | 74.5 | 1005 | 65.6 | |
| Environmental Factors | 0.001 | ||||
| History of falls or infant–toddler placed in bed | 5 | 1.6 | 30 | 2.0 | |
| Patient uses assistive devices or infant–toddler in crib or furniture/lighting (tripled room) | 2 | 0.6 | 41 | 2.7 | |
| Patient placed in bed | 288 | 89.7 | 1402 | 91.5 | |
| Outpatient area | 26 | 8.1 | 59 | 3.9 | |
| Response to Surgery/Sedation/Anesthesia | 0.516 | ||||
| Within 24 h | 36 | 11.2 | 154 | 10.1 | |
| Within 48 h | 4 | 1.2 | 32 | 2.1 | |
| More than 48 h/none | 281 | 87.5 | 1346 | 87.9 | |
| Medication Usage | 0.002 | ||||
| Multiple usage of sedatives (excluding ICU patients sedated and paralyzed), hypnotics, barbiturates, phenothiazines, antidepressants, laxatives/diuretics, narcotics | 1 | 0.3 | 43 | 2.8 | |
| One of the meds listed above | 13 | 4.0 | 115 | 7.5 | |
| Other medications/none | 307 | 95.6 | 1374 | 89.7 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cesare, M.; D’Agostino, F.; Hill-Rodriguez, D.; Sarik, D.A.; Cocchieri, A. Assessing the Alignment Between the Humpty Dumpty Fall Scale and Fall Risk Nursing Diagnosis in Pediatric Patients: A Retrospective ROC Curve Analysis. Healthcare 2025, 13, 1748. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13141748
Cesare M, D’Agostino F, Hill-Rodriguez D, Sarik DA, Cocchieri A. Assessing the Alignment Between the Humpty Dumpty Fall Scale and Fall Risk Nursing Diagnosis in Pediatric Patients: A Retrospective ROC Curve Analysis. Healthcare. 2025; 13(14):1748. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13141748
Chicago/Turabian StyleCesare, Manuele, Fabio D’Agostino, Deborah Hill-Rodriguez, Danielle Altares Sarik, and Antonello Cocchieri. 2025. "Assessing the Alignment Between the Humpty Dumpty Fall Scale and Fall Risk Nursing Diagnosis in Pediatric Patients: A Retrospective ROC Curve Analysis" Healthcare 13, no. 14: 1748. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13141748
APA StyleCesare, M., D’Agostino, F., Hill-Rodriguez, D., Sarik, D. A., & Cocchieri, A. (2025). Assessing the Alignment Between the Humpty Dumpty Fall Scale and Fall Risk Nursing Diagnosis in Pediatric Patients: A Retrospective ROC Curve Analysis. Healthcare, 13(14), 1748. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13141748







