Assessing Occupational Work-Related Stress and Anxiety of Healthcare Staff During COVID-19 Using Fuzzy Natural Language-Based Association Rule Mining
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Material and Methods
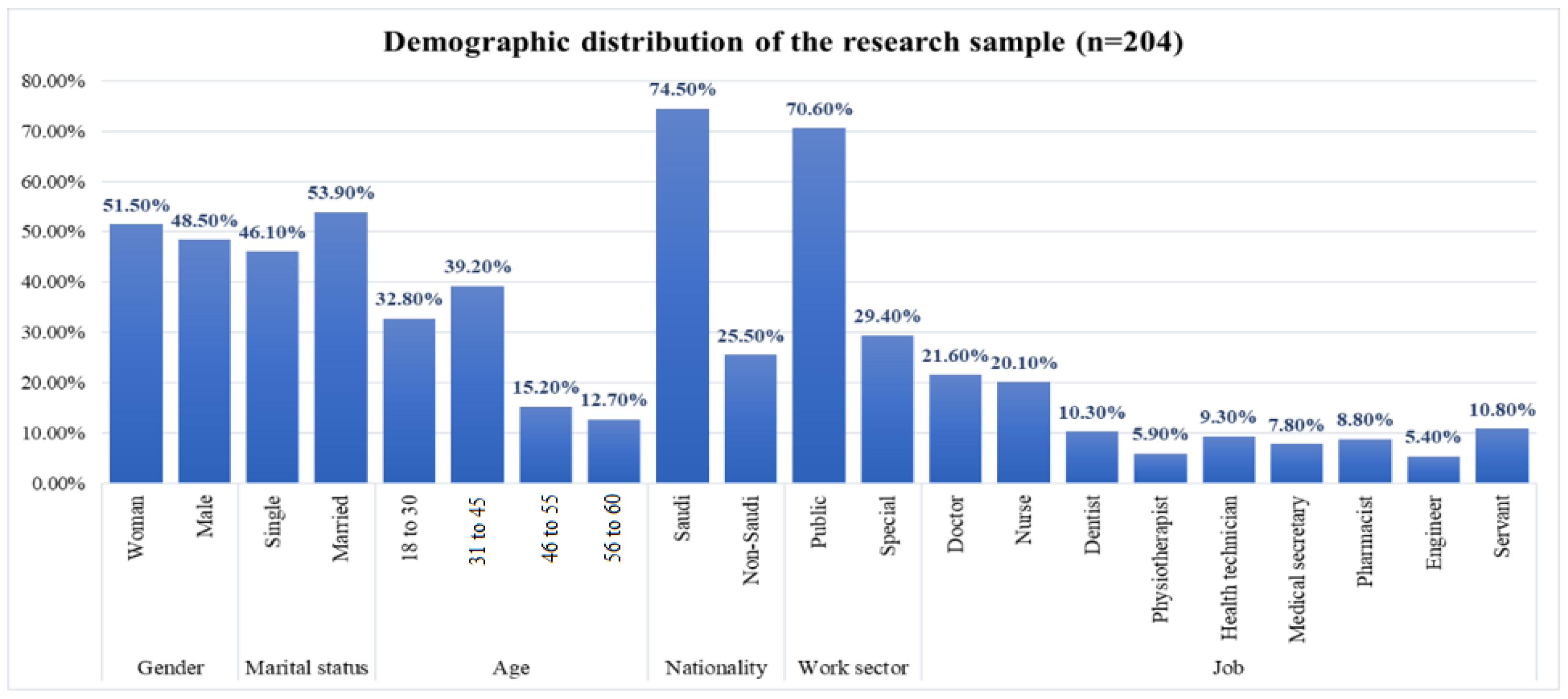
3.1. Data Collection Method
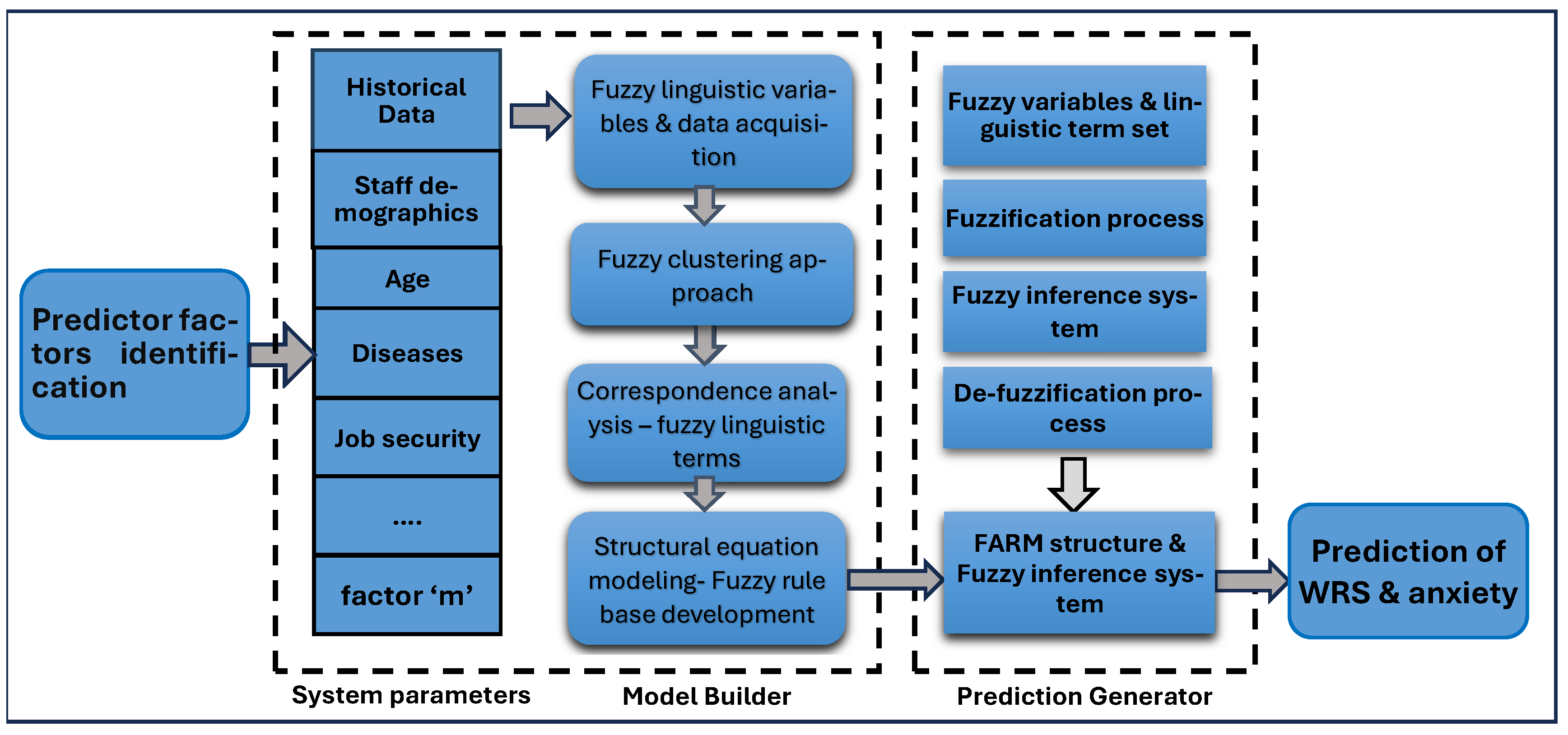
3.2. Fuzzy Association Rules Mining (FARM) and Fuzzy Transactions
4. Results and Findings
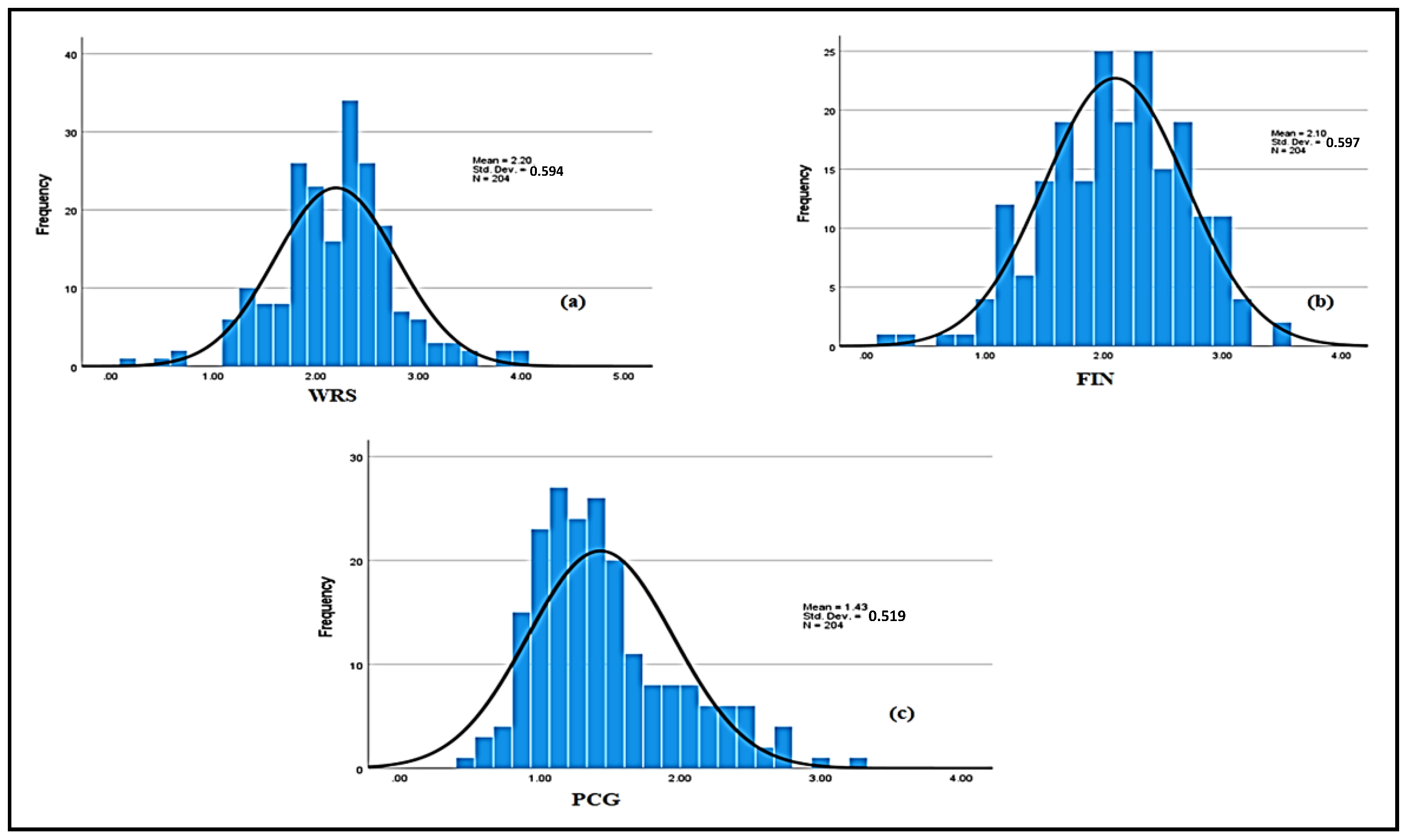
4.1. Statistical Analysis and Consequences of COVID-19 Pandemic
4.1.1. Psychological Consequences
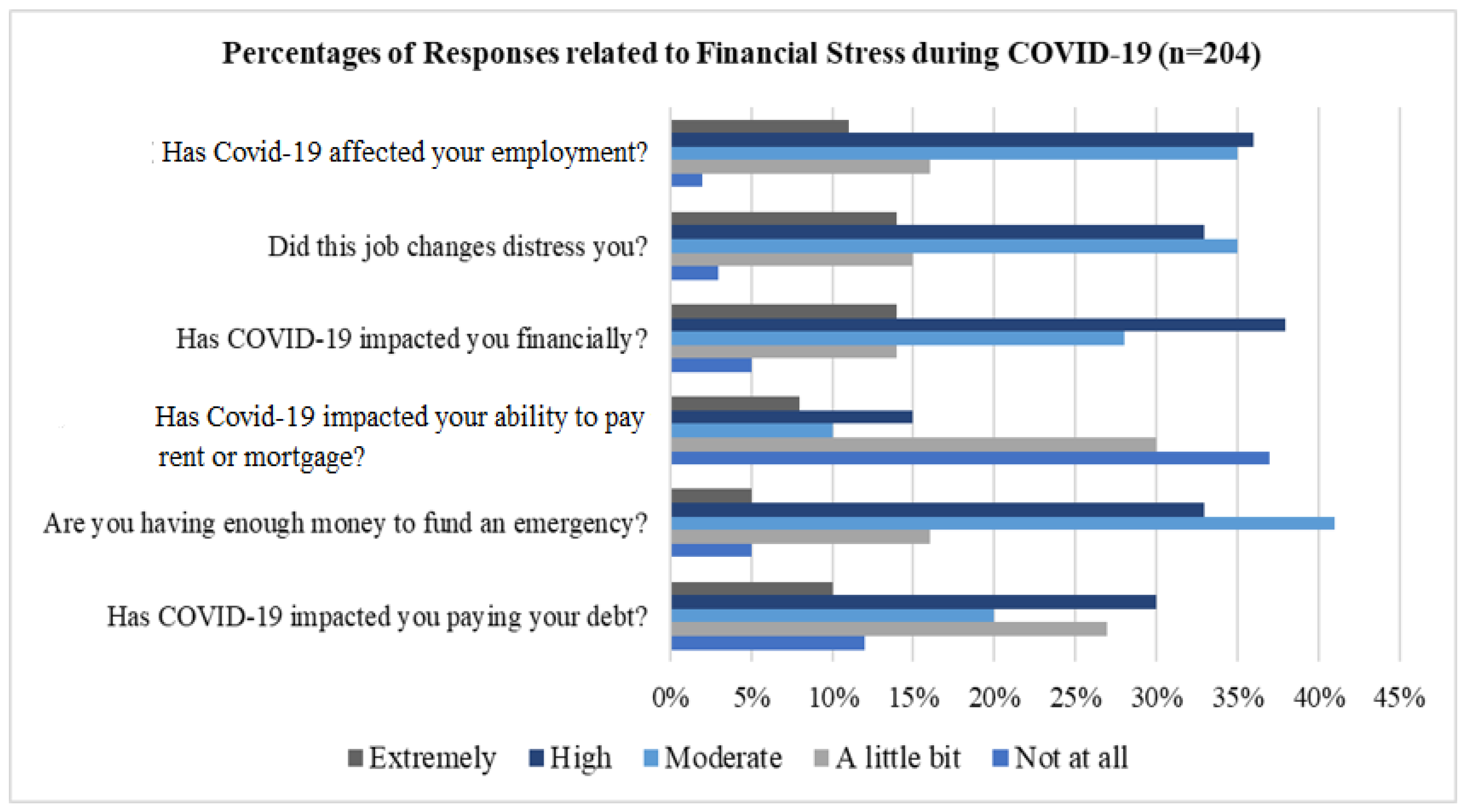
4.1.2. Financial Consequences
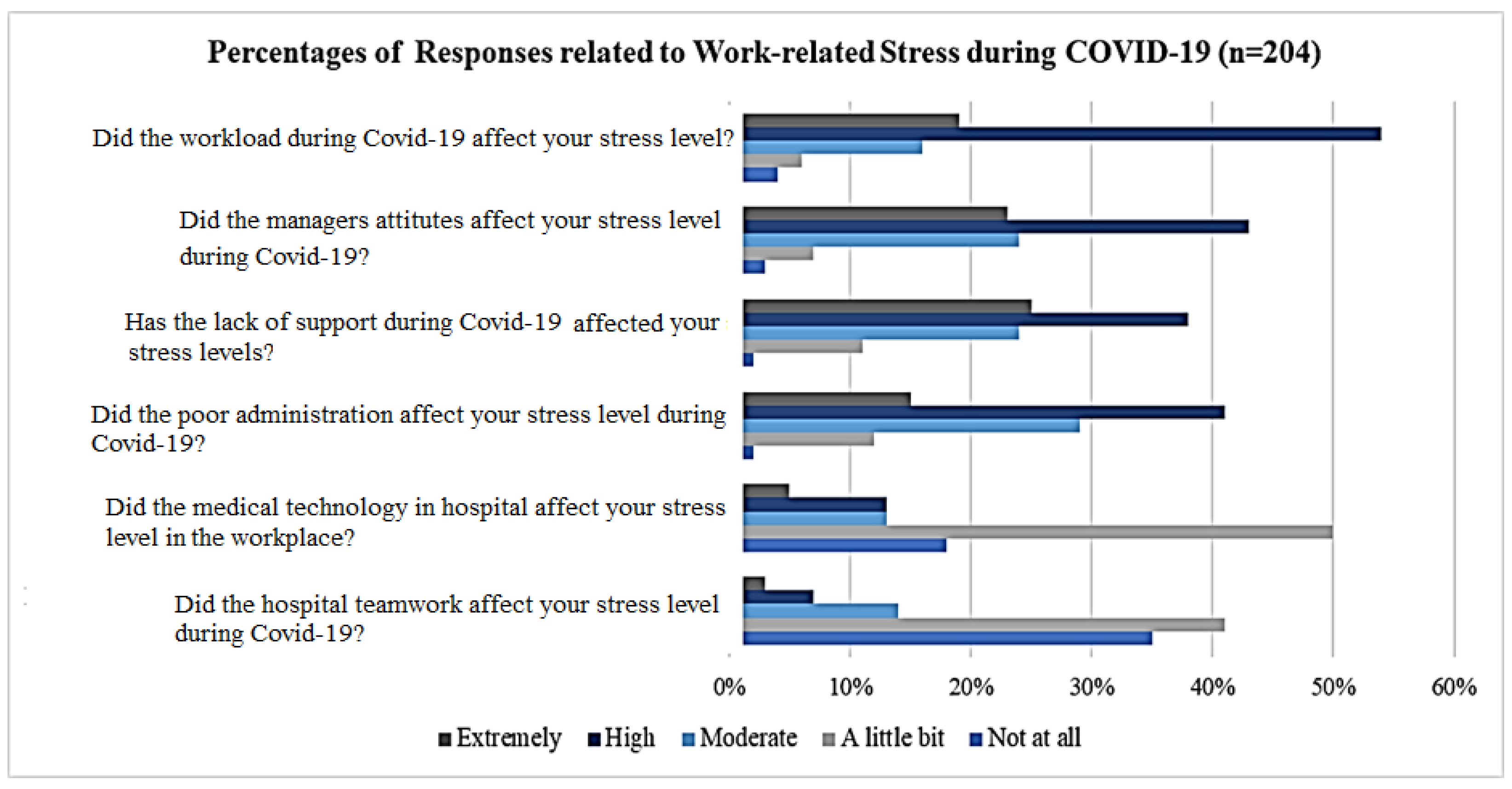
4.1.3. Work-Related Stress and Anxiety Consequences
4.1.4. Socio-Demographic Factors (SCFs) vs. WRS and Anxiety
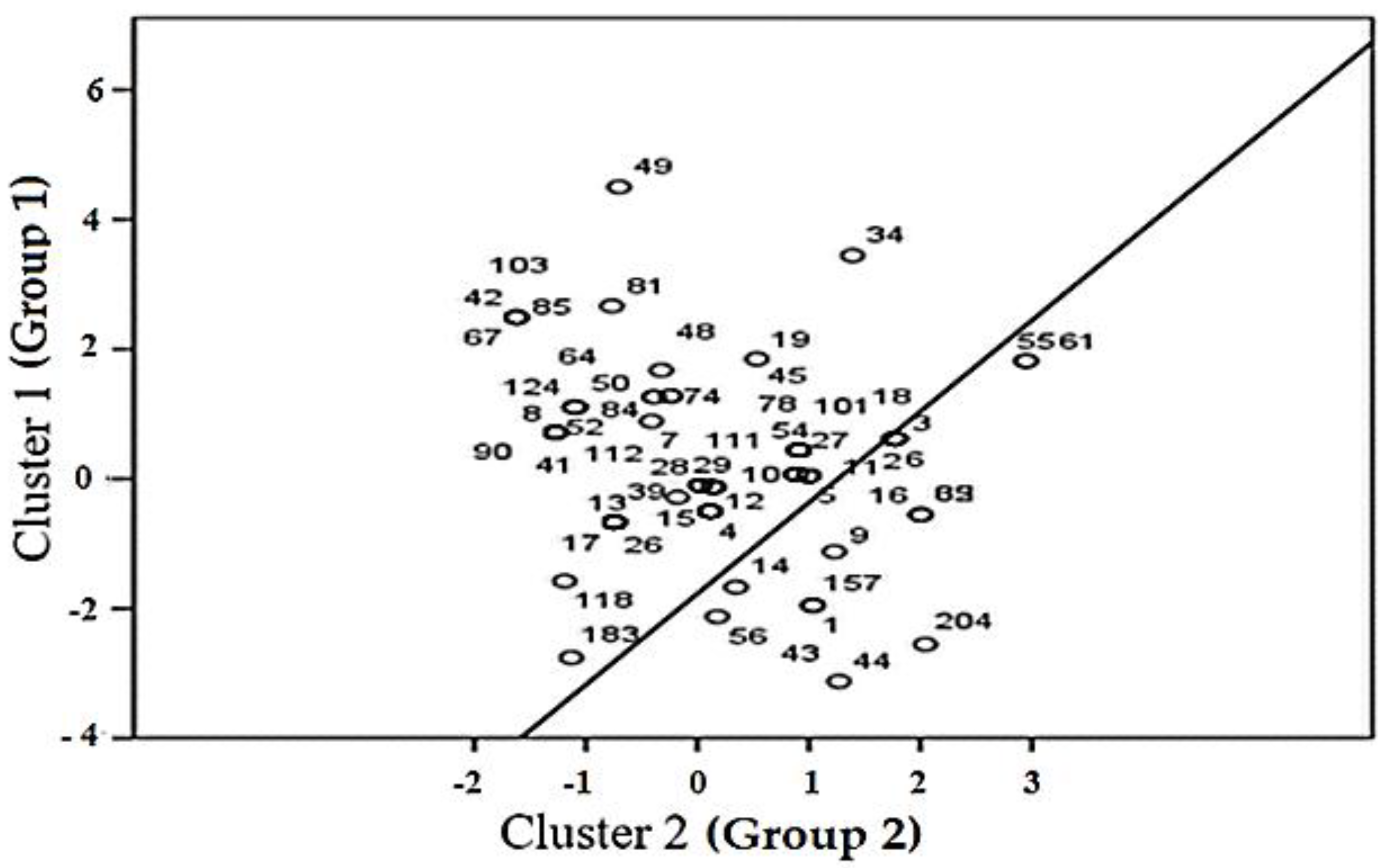
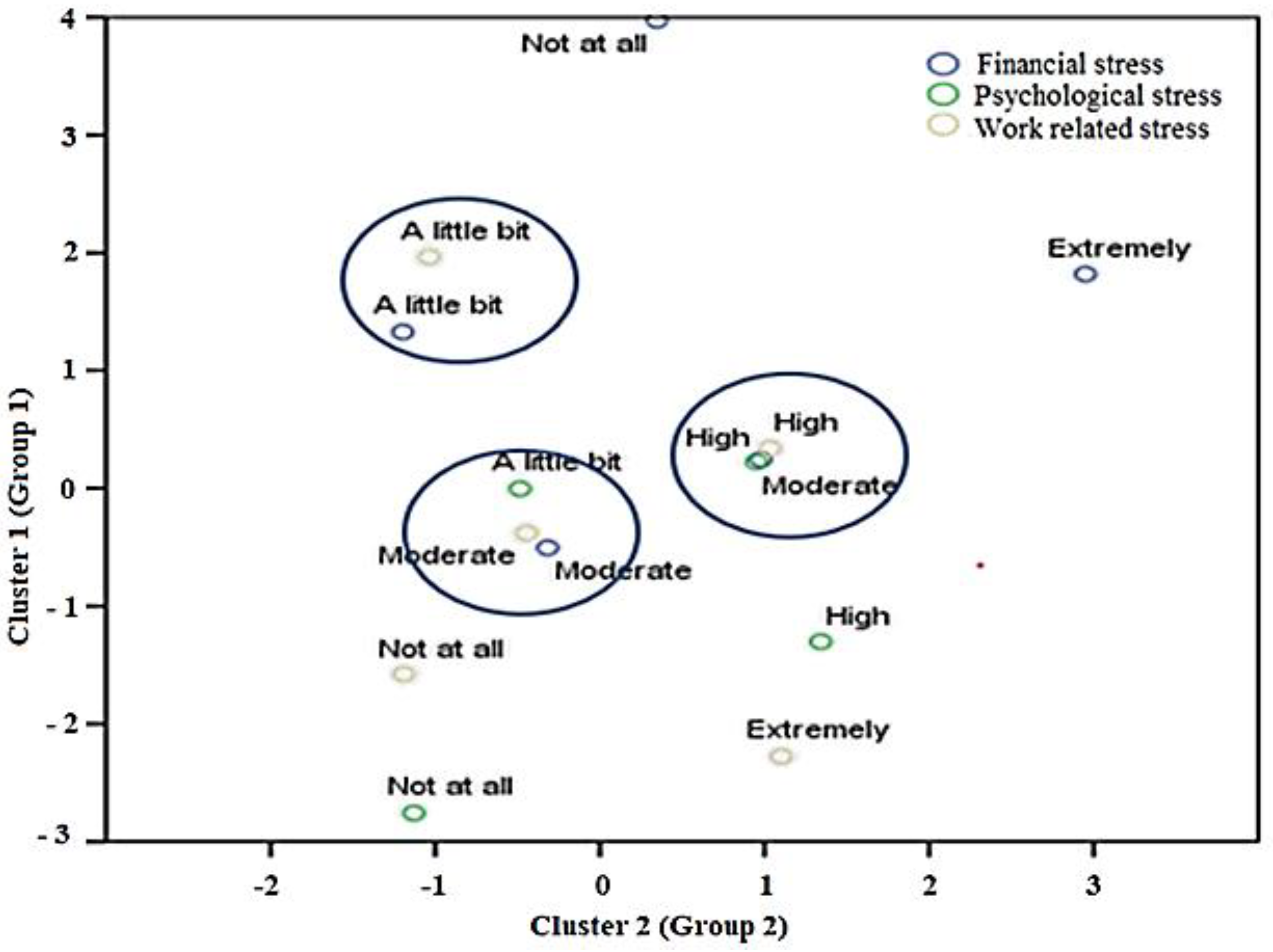
4.2. Fuzzy Clustering Analysis of WRS & Anxiety
4.3. Correspondance Analysis
4.4. Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) Approach
4.5. Application of FARM and Fuzzy Transactions to WRS and Anxiety
5. Conclusions and Discussions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chung, H.J.; Kim, M.H.; Ahn, S.; Yeo, J.; Lee, K.; Kim, S.; Kang, S.; Suh, W. Development of the Stress and Anxiety to Viral Epidemics-9 (SAVE-9) Scale for Assessing Work-related Stress and Anxiety in Healthcare Personnel in Response to Viral Epidemics. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2021, 36, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. 2023. Available online: https://covid19.who.int (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Adiguzel, O. The Effect of Work-Related Stress, Role Conflict and Role Ambiguity on Expected Turnover. Appl. Nurses 2012, 8, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.; Hu, X.; Zheng, B.; Li, L. Mental Health Outcomes Among Civil. Servants Aiding in Coronavirus Disease 2019 Control. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 60179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, M. Job stress and job performance controversy: An empirical assessment. Organ. Behav. Hum. Perform. 1984, 33, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Cooper, C.L.; Kao, S.; Zhou, Y. Work stress, cultural control beliefs and well-being in Greater China: An exploration of sub-differences between the PRC and Taiwan. J. Manager. Psychol. 2003, 18, 479–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyahya, S.; Abo Gazalah, F. Work-Related Stressors among the Healthcare Professionals in the Fever Clinic Centers for Individuals with Symptoms of COVID-19. Healthcare 2021, 9, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, K.; Cho, I.K.; Ahn, M.H.; Shin, Y.W.; Park, J.; Chung, S. Resilience and Work-Related Stress May Affect Depressive Symptoms in Nursing Professionals during the COVID-19 Pandemic Era. Psychiatry Investig. 2021, 18, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katragadda, S.; Gottumukkala, R.; Bhupatiraju, R.T.; Kamal, A.M.; Raghavan, V.; Chu, H.; Kolluru, R.; Ashkar, Z. Association mining based approach to analyze COVID 19 response and case growth in the United States. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandan, M.; Acharya, Y.; Pokharel, S.; Timilsina, M. Discovering symptom patterns of COVID-19 patients using association rule mining. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 131, 104249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyupoglu, S.Z.; Jabbarova, K.; Saner, T. Job satisfaction: An evaluation using a fuzzy approach. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 120, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, T.J. Fuzzy Logic with Engineering Applications; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Taylan, O. Neural and Fuzzy Model Performance Evaluation of a Dynamic Production System. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2009, 44, 1093–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer-Baese, A.; Schmid, V. Pattern Recognition and Signal Analysis in Medical Imaging, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 291–323. [Google Scholar]
- Mangalampalli, A.; Pudi, V. Fuzzy Association Rule Mining Algorithm for Fast and Efficient Performance on Very Large Datasets. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems, Jeju, Republic of Korea, 20–24 August 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, B.W.; Valdes, A.R.; Memari, A. Customer Segmentation Based on Compensatory Fuzzy Logic within a Sustainability CRM for Intermodal Mobility. In Soft Computing for Business Intelligence; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 537, ISBN 978-3-642-53736-3. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrer-Estevez, M.; Chalmeta, R. Sustainable customer relationship management, Mark. Intell. Plan. 2023, 41, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, D.; Vila, M.; Cerda, L.; Serrano, J. Association rules applied to credit card fraud detection. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 3630–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari, S.; Hussain, A. E-Transactional Fraud Detection Using Fuzzy Association Rule Mining. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Information Systems & Management Science (ISMS), Agartala, India, 1 January 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hajek, P. Interpretable Fuzzy Rule-Based Systems for Detecting Financial Statement Fraud. In Artificial Intelligence Applications and Innovations. AIAI 2019. IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, O.; Kem, F.C.; Oztaysi, B. Fuzzy association rule mining approach to identify e-commerce product association considering sales amount. Complex Intell. Syst. 2022, 8, 1551–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Cho, J.; Pedrycz, W.; Fujita, H.; Herawan, T. Soft set-based association rule mining. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2016, 111, 268–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, J.; Sesma-Sara, M.; Bustince, H. A fuzzy association rule-based classifier for imbalanced classification problems. Inf. Sci. 2021, 577, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, J.; Bustince, H. A wrapper methodology to learn interval-valued fuzzy rule-based classification systems. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 104, 107249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocco, A. A Biologically Plausible Action Selection System for Cognitive Architectures: Implications of Basal Ganglia Anatomy for Learning and Decision-Making Models. Cogn. Sci. 2017, 42, 457–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottl, V.; Krasotkina, O.; Seredin, O.; Muchnik, I. Principles of Multi-kernel Data Mining. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Machine Learning and Data Mining in Pattern Recognition, New York, NY, USA, 9–15 July 2015; pp. 52–61. [Google Scholar]
- Alan, M.A. Association Rules Mining on Medical Data. CU Iktis. Ve Idari Bilim. Dergisi. 2019, 20, 410–441. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, B.R.; Kumar, Y.V.; Prabhakar, M. Clustering large amounts of healthcare datasets using fuzzy c-means algorithm. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2019 5th International Conference on Advanced Computing & Communication Systems (ICACCS), Coimbatore, India, 15–16 March 2019; pp. 93–97. [Google Scholar]
- Setiawan, K.E.; Kurniawan, A.; Chowanda, A.; Suhartono, D. Clustering models for hospitals in Jakarta using fuzzy c-means and k-means. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2023, 216, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdusalomov, A.B.; Mukhiddinov, M.; Whangbo, T.K. Brain Tumor Detection Based on Deep Learning Approaches and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Cancers 2023, 15, 4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, P.; Kumar, R.; Jain, A.; Singh, A.; Sharma, S.; Gupta, M.; Verma, S.; Malik, P.; Bansal, D.; Thakur, N. An Extensive Review of Machine Learning and Deep Learning Techniques on Heart Disease Classification and Prediction. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2024, 31, 3331–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khushal, R.; Fatima, U. Fuzzy Logic and Machine Learning for Diabetes Risk Prediction Using Modifiable Factors. Int. J. Adv. Appl. Sci. 2024, 11, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, H.; Ebadzadeh, M.M. MFRFNN: Multi-Functional Recurrent Fuzzy Neural Network for Chaotic Time Series Prediction. Neurocomputing 2022, 507, 292–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tính, N.V.; Điều, N.C. A New Hybrid Fuzzy Time Series Forecasting Model Based on Combining Fuzzy C-Means Clustering and Particle Swarm Optimization. J. Comput. Sci. Cybern. 2019, 35, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, P.M.; Nematizadeh, M.; Saghazade, M.; Saghazadeh, A.; Rezaei, N. Computed tomography scan in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pol. J. Radiol. 2022, 87, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egrioglu, E.; Aladag, C.H.; Yolcu, U. Fuzzy Time Series Forecasting with a Novel Hybrid Approach Combining Fuzzy C-Means and Neural Networks. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 854–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, H.R.; Alnoamani, H.H.; Jalil, A.A. Improved Fuzzy C-Mean Algorithm for Image Segmentation. Int. J. Adv. Res. Artif. Intell. 2016, 5, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fatima, M.; Pasha, M. Survey of Machine Learning Algorithms for Disease Diagnostic. J. Intell. Learn. Syst. Appl. 2017, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampavathi, A.; Saradhi, T.V. Multi-Disease-Prediction Framework Using Hybrid Deep Learning: An Optimal Prediction Model. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 24, 1146–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’emeh, W.M.; Yacoub, M.I.; Sama’an Shahwan, B. Work-Related Stress and Anxiety Among Frontline Nurses During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Psychosoc. Nurs. Ment. Health Serv. 2021, 59, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widhiastuti, H.; Yuliasih, G.; Kurniawan, Y. The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Work Stress of Employees. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Banking, Accounting, Management and Economics (ICOBAME 2020); Atlantis Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zareei, M.; Tabanejad, Z.; Oskouie, F.; Ebadi, A.; Mesri, M. Job Burnout among Nurses during COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review. J. Educ. Health Promot. 2022, 11, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Ryu, W. The Role of Interdisciplinary Convergence for Mental Health Among Korean Military Servicemen: Focusing on Depression and Salivary Dehydroepiandrosterone-Sulfate. Healthcare 2025, 13, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroes, S.; McKim, H.; Petrakis, M. Workforce Perspectives of Sustaining the Utilisation of a Harm Reduction Instrument in a Mental Health Residential Setting. Healthcare 2024, 12, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, X.T.T.; Dang, A.K.; Toweh, J.; Nguyen, Q.N.; Le, H.T.; Do, T.T.T.; Phan, H.B.T.; Nguyen, T.T.; Pham, Q.T.; Ta, N.K.T.; et al. Evaluating the Psychological Impacts Related to COVID-19 of Vietnamese People Under the First Nationwide Partial Lockdown in Vietnam. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Master, A.N.; Su, X.; Zhang, S.; Guan, W.; Li, J. Psychological impact of COVID-19 outbreak on frontline nurses: A cross-sectional survey study. J. Clin. Nurs. 2020, 29, 4217–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morán, R.C.D.; Soto, J.M.S.; Gómez, H.E.l.; Camus, F.C.E.; Quispe, J.F.P.; Llaja, L.C.; Tavera, Z.R.D.; Wong, F.M.R. Work Stress as a Consequence of the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrashed, F.A.; Ahmad, T.; Sattar, K.; Aldaihan, M.M.; Almurdi, M.M.; Alrashed, L.K.; Shaheen, A.A.M.; Alsubiheen, A.M. Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Stress and Coping Strategies among Medical Students: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Adv. Appl. Sci. 2023, 10, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, N.; He, C.; Rahman, N.; Faherty, C.; Chan, C.; DePierro, J.M.; Clark, U.; Peccoralo, L.A.; Ripp, J.H. Coping Mechanisms and Their Associations with Depression and Anxiety Among Healthcare Workers in the Aftermath of COVID-19 Pandemic. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2024, 66, 857–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Snyder, V.N.S.; Villatoro, A.P.; McDaniel, M.D.; Ocegueda, A.S.; Garcia, D.; Parra-Medina, D. Occupational Stress and Mental Health Among Healthcare Workers Serving Socially Vulnerable Populations During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 782846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.; Kim, H.R. Factors Associated with Job Stress and Their Effects on Mental Health among Nurses in COVID-19 Wards in Four Hospitals in Korea. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anger, W.K.; Dimoff, J.K.; Alley, L. Addressing Health Care Workers’ Mental Health: A Systematic Review of Evidence-Based Interventions and Current Resources. Am. J. Public Health 2024, 114, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.H.; Becene, I.A.; Nguyen, K.T.N.H.; Stuart, J.J.; West, M.G.; Berrill, J.E.S.; Hankins, J.; Borba, C.P.C.; Rich-Edwards, J.W. A qualitative analysis of psychosocial stressors and health impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on frontline healthcare personnel in the United States. SSM—Qual. Res. Health 2022, 2, 100130. [Google Scholar]
- Sahebi, A.; Nejati-Zarnaqi, B.; Moayedi, S.; Yousefi, K.; Torres, M.; Golitaleb, M. The prevalence of anxiety and depression among healthcare workers during the COVID-19 pandemic: An umbrella review of meta-analyses. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 10, 110247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norhayati, M.N.; Che Yusof, R.; Azman, M.Y. Prevalence of Psychological Impacts on Healthcare Providers during COVID-19 Pandemic in Asia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschalia, Y.P.M.; Doondori, A.K.K.; Avila, T.; Seto Se, B.R. The relationship between work stress and quality life among Indonesian health workers during the COVID-19 pandemic. Public Health Indones. 2022, 8, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puia, A.; Pop, S.R.; Manzat, B.O.C.; Pintea, S.; Puia, I.C.; Fadgyas-Stanculete, M. Coping Strategies Among Healthcare Workers During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Emotional Responses, Challenges, and Adaptive Practices. Medicina 2025, 61, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, L.; Khaira, F. The role of social support in pandemic-related stress among university students. Int. J. Res. Couns. Educ. 2021, 5, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylan, O.; Karagozoglu, B. An Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Model for Prediction of Student’s Academic Performance. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2009, 57, 732–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, R.; Ahmed, T.; Sarwar Uddin, M.d.Y. Structural modeling of COVID-19 spread in relation to human mobility. Transp. Res. Interdiscip. Perspect. 2021, 13, 100528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgelt, C.; Kruse, R. Induction of Association Rules: Apriori Implementation. In Compstat; Härdle, W., Rönz, B., Eds.; Physica-Verlag HD: Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bora, D.J.; Gupta, D.A.K. A Comparative Study Between Fuzzy Clustering Algorithm and Hard Clustering Algorithm. Int. J. Comput. Trends Technol. 2014, 10, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Alharbi, R.; Taylan, O. Job Stress Assessment and Analyzing the Factors Influencing Health Care Workers during COVID-19 Pandemic in Saudi Arabia. J. Sci. Technol. Eng. Res. 2021, 2, 12–34. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo, O.; Melin, F. Forecasting of COVID-19 Time Series for Countries in the World Based on a Hybrid Approach Combining the Fractal Dimension and Fuzzy Logic. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 140, 110242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punniyamoorthy, M.; Mathiyalagan, P.; Parthiban, P. A strategic model using structural equation modeling and fuzzy logic in supplier selection. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 38, 458–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafish, M.A.; Masudin, I.; Zulfikarijah, F.; Nasyiah, T.; Restuputri, D.P. An integrated structural equation modeling and fuzzy qualitative comparative analysis model for examining green procurement adoption drivers. Decis. Anal. J. 2024, 11, 100469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flesia, L.; Monaro, M.; Mazza, C.; Fietta, V.; Colicino, E.; Segatto, B.; Roma, P. Predicting Perceived Stress Related to the COVID-19 Outbreak through Stable Psychological Traits and Machine Learning Models. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcoulides, K.M.; Yuan, K.-H. New ways to evaluate goodness of fit: A note on using equivalence testing to assess structural equation models. Struct. Equ. Model. 2017, 24, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, S.; Dameneh, M.M.; Esmaeili, R.; Kazemi, R.; Naseri, S.; Panahi, D. Occupational stress assessment of health care workers (HCWs) facing COVID-19 patients in Kerman province hospitals in Iran. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancet, T. COVID-19: Protecting health-care workers. Lancet 2020, 395, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Correlation | Psychological Factor (PCGs) | Financial Factors (FINs) | WRS and Anxiety | People Living Together | Time Spent Outdoors Before Lockdown |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Psychological factors (PCGs) | 1 | ||||
| Financial factors (FINs) | 0.344 | 1 | |||
| WRS and anxiety | 0.376 | 0.401 | 1 | ||
| People living together | −0.210 | 0.337 | −0.269 | 1 | |
| Times spent outdoors before lockdown | 0.255 | 0.270 | 0.425 | −0.172 | 1 |
| Model Fitness Index | GFI | CFI | RMSE | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model value | 2.78 | 0.82 | 0.75 | 0.09 | 0.00 |
| Recommended value | <5 | >0.9 | >0.9 | <0.09 | <0.05 |
| Sources of Occupational Stress | Financial Stress | Psychological Stress | Total WRS and Anxiety |
|---|---|---|---|
| WRS-5 | 0.142 | 0.463 | 0.697 |
| WRS-6 | 0.152 | 0.495 | 0.745 |
| FIN-6 | 0.630 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| FIN-4 | 0.412 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| FIN-3 | 0.850 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| FIN-2 | 0.466 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| FIN-1 | 0.173 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| PCG-1 | 0.000 | 0.590 | 0.000 |
| PCG-3 | 0.000 | 0.632 | 0.000 |
| PCG-4 | 0.000 | 0.393 | 0.000 |
| PCG-5 | 0.000 | 0.628 | 0.000 |
| PCG-6 | 0.000 | 0.482 | 0.000 |
| PCG-7 | 0.000 | 0.350 | 0.000 |
| PCG-8 | 0.000 | 0.606 | 0.000 |
| PCG-9 | 0.000 | 0.464 | 0.000 |
| PCG-10 | 0.000 | 0.848 | 0.000 |
| PCG-11 | 0.000 | 0.810 | 0.000 |
| PCG-12 | 0.000 | 0.390 | 0.000 |
| PCG-14 | 0.000 | 0.238 | 0.000 |
| PCG-15 | 0.000 | 0.346 | 0.000 |
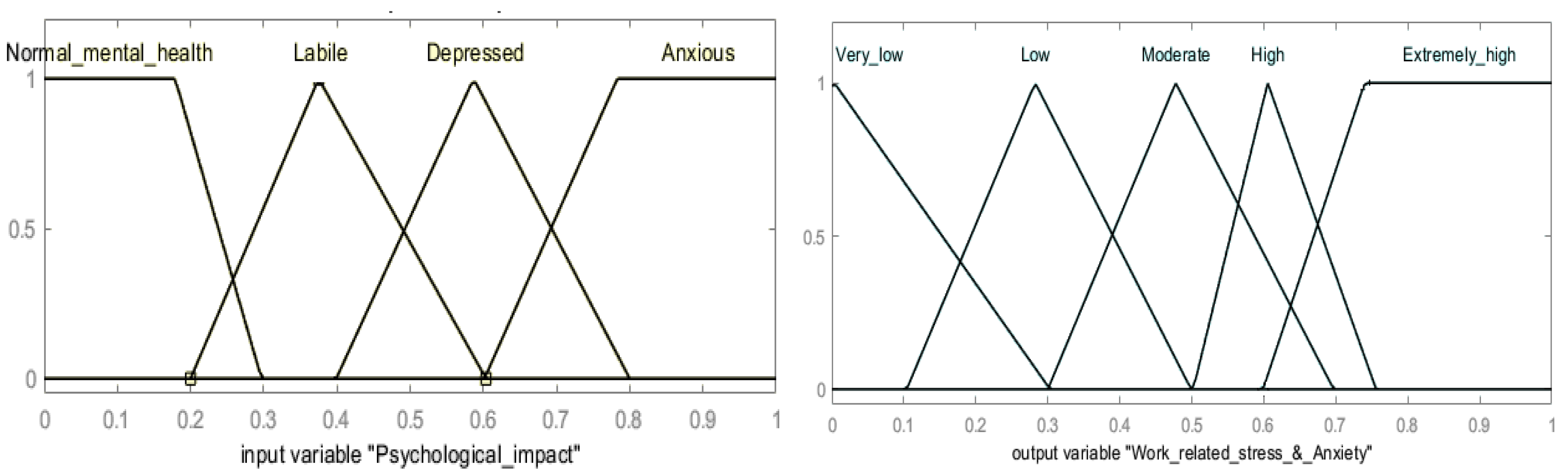
| Fuzzy Variables | Fuzzy Term Sets |
|---|---|
| Psychological (PCG) impact | normal mental health, labile (mood swing), depressed, anxious |
| Financial (FIN) impact | deteriorating, not changed, improved |
| Socio-demographic (SCF) impact | not associated, mild association, moderate association, strong association, |
| Technological (TECH) impact | negative impact, no impact, positive impact improve stress in workplace |
| Work-related stress and anxiety | very low, low, moderate, high, extremely high, |
| Fuzzy Rules | Fuzzy Confidence | |
|---|---|---|
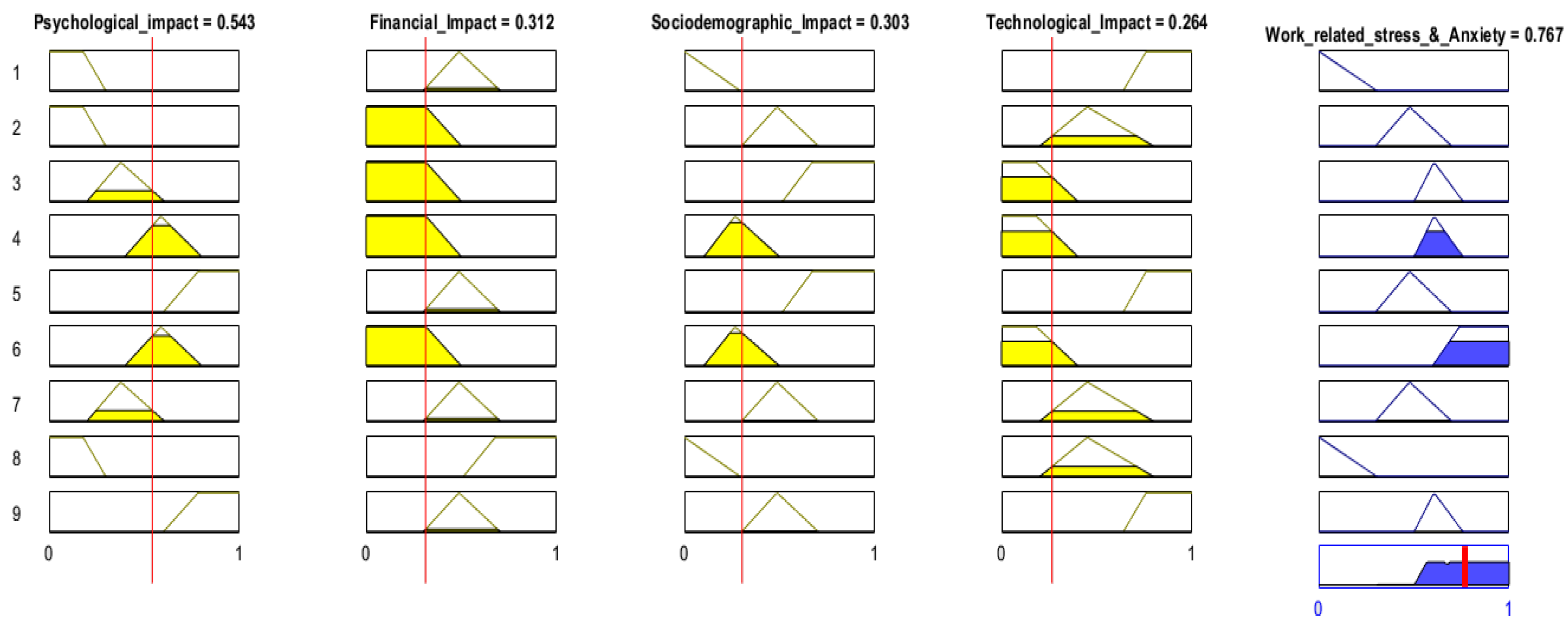
| Rule 1 | If (Psychological_impact is depressed) and (Financial_impact is deteriorating) and (Sociodemographic_impact is mild_associated) and (Technological _impact is negative) then (WRS and Anxiety is moderate high (0.767). | 0.76 |
| Rule 2 | If (Psychological_impact is labile) and (Financial_impact is not_changing) and (Sociodemographic_impact is moderately_associated) and (Technological_impact is positive) then (WRS and Anxiety is moderate (0.496). | 0.92 |
| Rule 3 | If (Psychological_impact is in normal mental_health) and (Financial_impact is not changing) and (Sociodemographic_impact is not_associated) and (Technological _impact is High) then (WRS and Anxiety is very_low) (0.13). | 0.71 |
| Rule 4 | If (Psychological_impact is depressed) and (Financial_impact is deteriorating) and (Sociodemographic_impact is Strong_association) and (Technological _impact is Negative_impact) then (WRS_and_Anxiety is extremely_high) (1). | 0.57 |
| Fuzzy Rules | Fuzzy Support | Fuzzy Confidence |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.36 | 0.76 |
| 2 | 0.39 | 0.92 |
| 3 | 0.45 | 0.71 |
| 4 | 0.56 | 0.57 |
| 5 | 0.62 | 0.35 |
| 6 | 0.72 | 0.63 |
| 7 | 0.41 | 0.53 |
| 8 | 0.52 | 0.56 |
| 9 | 0.51 | 0.67 |
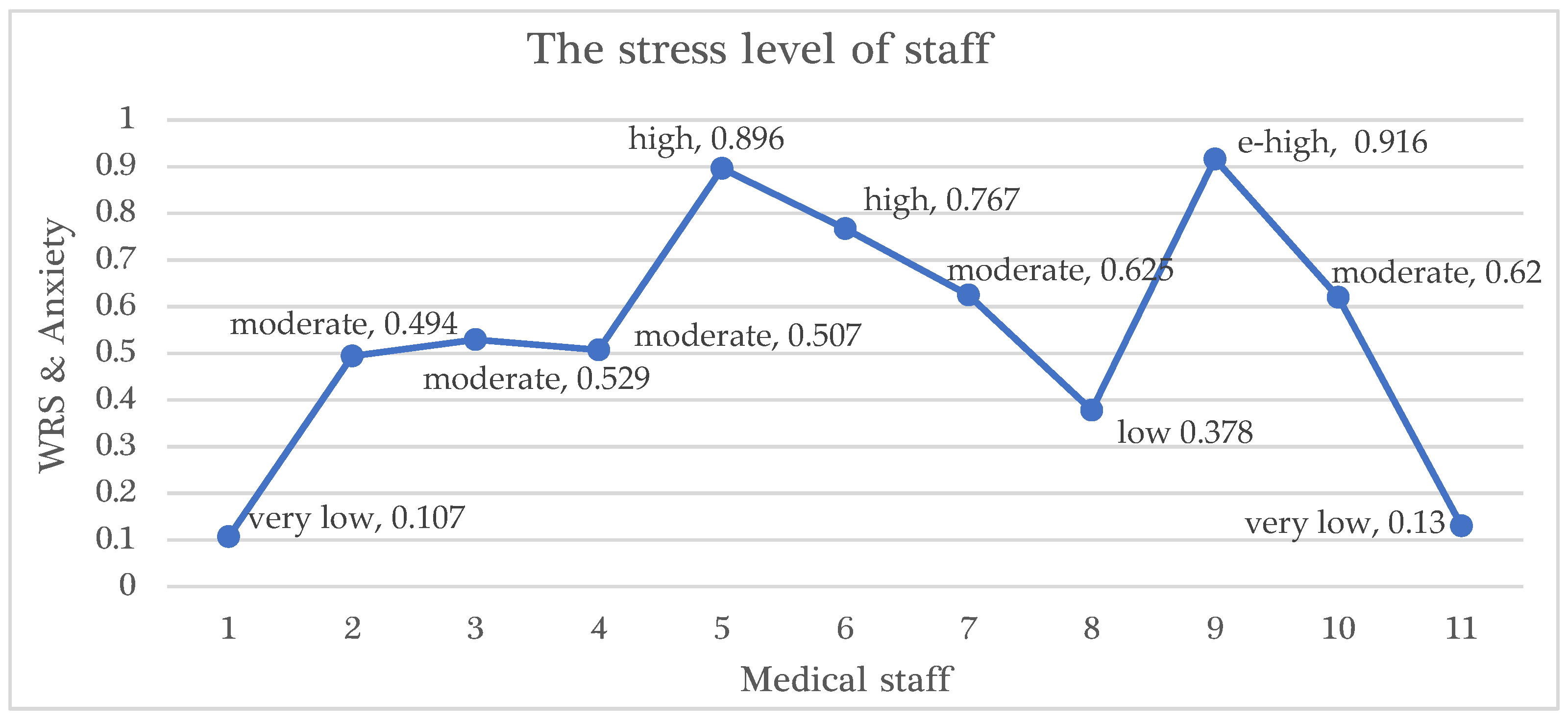
| Medical Staff | Fuzzy Input Parameters | The Stress Level of Staff | Stress Level in Terms | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCG Impact | FIN Impact | SCF Impact | TECH Impact | WRS and Anxiety | WRS and Anxiety | |
| 1 | 0.184 | 0.5 | 0.0947 | 0.731 | 0.107 | very low |
| 2 | 0.244 | 0.387 | 0.428 | 0.633 | 0.494 | moderate |
| 3 | 0.628 | 0.402 | 0.564 | 0.716 | 0.529 | moderate |
| 4 | 0.718 | 0.538 | 0.663 | 0.716 | 0.507 | moderate |
| 5 | 0.898 | 0.643 | 0.761 | 0.867 | 0.896 | high |
| 6 | 0.534 | 0.312 | 0.303 | 0.264 | 0.767 | high |
| 7 | 0.695 | 0.620 | 0.375 | 0.913 | 0.625 | moderate |
| 8 | 0.237 | 0.199 | 0.337 | 0.223 | 0.378 | low |
| 9 | 0.959 | 0.635 | 0.936 | 0.875 | 0.916 | e-high |
| 10 | 0.750 | 0.519 | 0.511 | 0.772 | 0.620 | moderate |
| 11 | 0.146 | 0.332 | 0.153 | 0.690 | 0.130 | very low |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alkabaa, A.S.; Taylan, O.; Alqabbaa, H.S.; Guloglu, B. Assessing Occupational Work-Related Stress and Anxiety of Healthcare Staff During COVID-19 Using Fuzzy Natural Language-Based Association Rule Mining. Healthcare 2025, 13, 1745. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13141745
Alkabaa AS, Taylan O, Alqabbaa HS, Guloglu B. Assessing Occupational Work-Related Stress and Anxiety of Healthcare Staff During COVID-19 Using Fuzzy Natural Language-Based Association Rule Mining. Healthcare. 2025; 13(14):1745. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13141745
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlkabaa, Abdulaziz S., Osman Taylan, Hanan S. Alqabbaa, and Bulent Guloglu. 2025. "Assessing Occupational Work-Related Stress and Anxiety of Healthcare Staff During COVID-19 Using Fuzzy Natural Language-Based Association Rule Mining" Healthcare 13, no. 14: 1745. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13141745
APA StyleAlkabaa, A. S., Taylan, O., Alqabbaa, H. S., & Guloglu, B. (2025). Assessing Occupational Work-Related Stress and Anxiety of Healthcare Staff During COVID-19 Using Fuzzy Natural Language-Based Association Rule Mining. Healthcare, 13(14), 1745. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13141745






