A Comparison of Developmental Profiles of Preschool Children with Down Syndrome, Global Developmental Delay, and Developmental Language Disorder
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
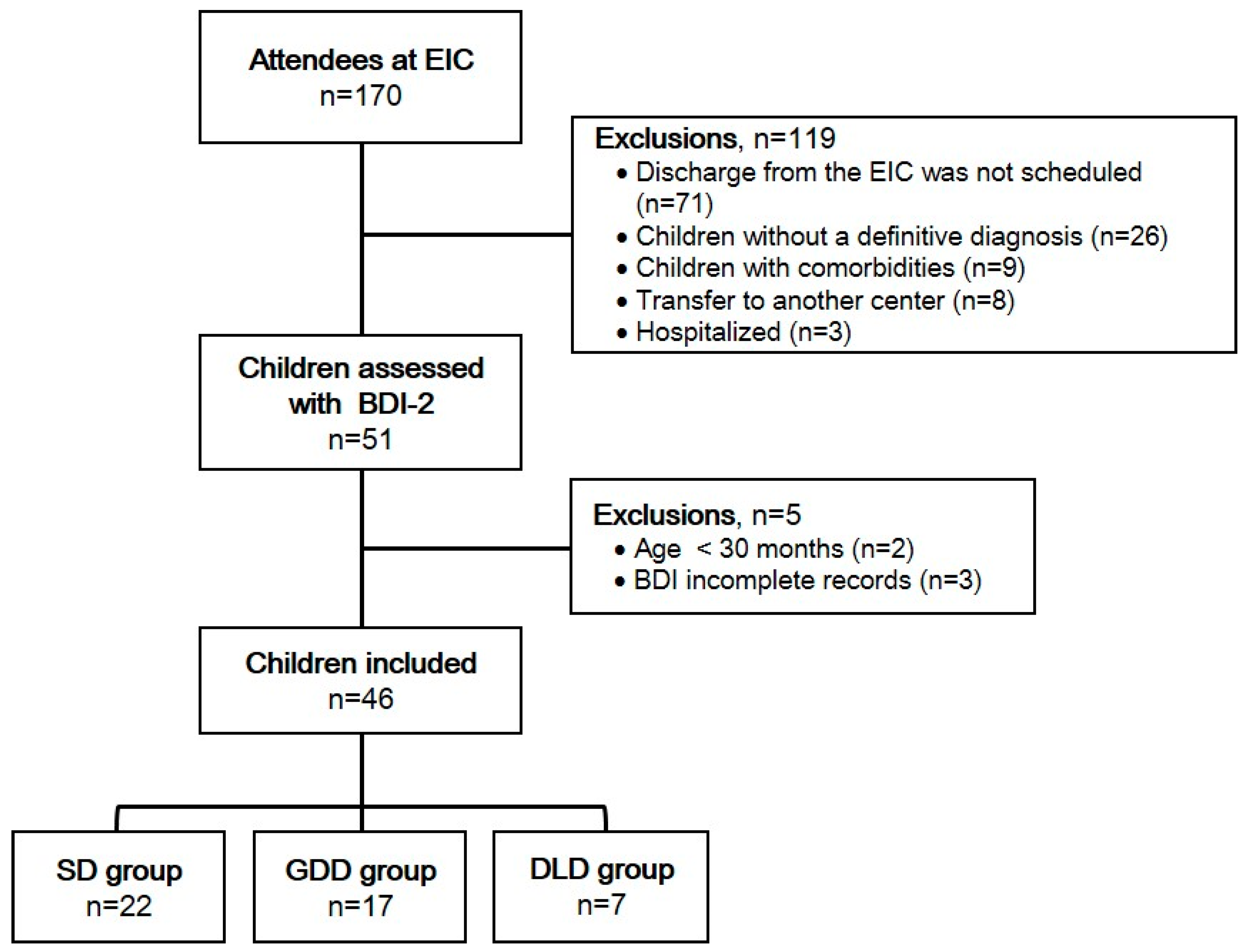
2.1. Design and Participants
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BDI−2 | Battelle® Developmental Inventory, 2nd Edition |
| DQ | Developmental Quotient |
| DS | Down Syndrome |
| EIC | Early Intervention Centre |
| GDD | Global developmental delay |
| DLD | Developmental Language Disorder |
References
- National Research Council (US) and Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Integrating the Science of Early Childhood De-velopment; Shonkoff, J.P.; Phillips, D.A. (Eds.) From Neurons to Neighborhoods: The Science of Early Childhood Development; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2000; p. 9824. ISBN 978-0-309-06988-5. [Google Scholar]
- Choo, Y.Y.; Agarwal, P.; How, C.H.; Yeleswarapu, S.P. Developmental Delay: Identification and Management at Primary Care Level. Singap. Med. J. 2019, 60, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olusanya, B.O.; Kancherla, V.; Shaheen, A.; Ogbo, F.A.; Davis, A.C. Global and Regional Prevalence of Disabilities among Children and Adolescents: Analysis of Findings from Global Health Databases. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 977453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smythe, T.; Zuurmond, M.; Tann, C.J.; Gladstone, M.; Kuper, H. Early Intervention for Children with Developmental Disabilities in Low and Middle-Income Countries—The Case for Action. Int. Health 2021, 13, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Hu, H.; Zhan, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, L. Global, Regional, and National Burden and Trends of Down Syndrome From 1990 to 2019. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 908482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbuzova, S.; Hutchin, T.; Cuckle, H. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Down’s Syndrome. BioEssays 2002, 24, 681–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, K.; Herault, Y.; Lott, I.T.; Antonarakis, S.E.; Reeves, R.H.; Dierssen, M. Down Syndrome: From Understanding the Neurobiology to Therapy. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 14943–14945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dornelas, L.D.F.; Duarte, N.M.D.C.; Magalhães, L.D.C. [Neuropsychomotor developmental delay: Conceptual map, term definitions, uses and limitations]. Rev. Paul. Pediatr. 2015, 33, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevell, M.; Ashwal, S.; Donley, D.; Flint, J.; Gingold, M.; Hirtz, D.; Majnemer, A.; Noetzel, M.; Sheth, R.D.; Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology; et al. Practice Parameter: Evaluation of the Child with Global Developmental Delay: Report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and The Practice Committee of the Child Neurology Society. Neurology 2003, 60, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldosari, A.N.; Aldosari, T.S. Comprehensive Evaluation of the Child with Global Developmental Delays or Intellectual Disability. Clin. Exp. Pediatr. 2024, 67, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.R.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Magar, S.; Kale, A.; Nelanuthala, M.; Singh, S.P. The Etiological Profile of Global Developmental Delay at a Tertiary Care Hospital in India: An Observational Study. Cureus 2023, 15, e41066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, H.S.; Camarata, S. Reconceptualizing Developmental Language Disorder as a Spectrum Disorder: Issues and Evidence. Intl. J. Lang. Comm. Disor. 2019, 54, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, D.V.M.; Snowling, M.J.; Thompson, P.A.; Greenhalgh, T.; The CATALISE-2 Consortium. Phase 2 of CATALISE: A Multinational and Multidisciplinary Delphi Consensus Study of Problems with Language Development: Terminology. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2017, 58, 1068–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Zubair, M.; Gulraiz, A.; Kalla, S.; Khan, S.; Patel, S.; Fleming, M.F.; Oghomitse-Omene, P.T.; Patel, P.; Qavi, M.S.S. An Assessment of Risk Factors of Delayed Speech and Language in Children: A Cross-Sectional Study. Cureus 2022, 14, e29623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, L.B. Specific Language Impairment Across Languages. Child Dev. Perspect. 2014, 8, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, S.D.; Brennan-Jones, C.G.; Robinson, M.; Whitehouse, A.; Hill, E. The Prevalence of and Potential Risk Factors for Developmental Language Disorder at 10 Years in the Raine Study. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2022, 58, 2044–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koul, A.M.; Ahmad, F.; Bhat, A.; Aein, Q.; Ahmad, A.; Reshi, A.A.; Kaul, R.R. Unraveling Down Syndrome: From Genetic Anomaly to Artificial Intelligence-Enhanced Diagnosis. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, P.T.; Guddattu, V.; Solomon, J.M. Response Abilities of Children with Down Syndrome and Other Intellectual Developmental Disorders. Exp. Brain Res. 2017, 235, 1411–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Research on Developmental Disabilities Collaborators Accelerating Progress on Early Childhood Development for Children under 5 Years with Disabilities by 2030. Lancet Glob. Health 2022, 10, e438–e444. [CrossRef]
- Saleem, J.; Zakar, R.; Mushtaq, F.; Bukhari, G.M.J.; Fischer, F. Comparative Analysis of Developmental Profile between Normal and Severe Acute Malnourished Under-Five Children in Pakistan: A Multicentre Cross-Sectional Study. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e048644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehlings, D.; Krishnan, P.; Ragguett, R.M.; Campbell, C.; Gorter, J.W.; Hunt, C.; Kawamura, A.; Kim, M.; McCormick, A.; Mesterman, R.; et al. 95 A Comparison of the Developmental Profiles of Individuals with Hemiplegic Cerebral Palsy Associated with Middle Cerebral Artery and Periventricular Venous Infarctions. Paediatr. Child Health 2019, 24, e36–e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roizen, N.; Friedman, S.; Vanderbilt, D.; Cacia, J.; Fussell, J.; Hansen, R.; Hofer, J.; Sideridis, G.; Stein, R.E.K.; Barbaresi, W. Developmental Profiles of Young Children Referred for Concern for Autism Spectrum Disorder: DBPNet Study. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matson, J.L.; Hess, J.A.; Sipes, M.; Horovitz, M. Developmental Profiles from the Battelle Developmental Inventory: A Comparison of Toddlers Diagnosed with Down Syndrome, Global Developmental Delay and Premature Birth. Dev. Neurorehabil. 2010, 13, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedford, R.; Pickles, A.; Lord, C. Early Gross Motor Skills Predict the Subsequent Development of Language in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Autism Res. 2016, 9, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malak, R.; Kostiukow, A.; Krawczyk-Wasielewska, A.; Mojs, E.; Samborski, W. Delays in Motor Development in Children with Down Syndrome. Med. Sci. Monit. 2015, 21, 1904–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Channell, M.M. Cross-Sectional Trajectories of Mental State Language Development in Children with Down Syndrome. Am. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2020, 29, 760–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Beerse, M.; Ajisafe, T.; Liang, H. Walking Dynamics in Preadolescents with and without Down Syndrome. Phys. Ther. 2015, 95, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.Y.; Min, S.K.; Yoon, T.H.; Jee, Y.S. Gross Motor Function and Health Fitness in Adults with Autistic Spectrum Disorder and Intellectual Disability: Single-Blind Retrospective Trial. J. Exerc. Rehabil. 2020, 16, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olusanya, B.O.; Wright, S.M.; Smythe, T.; Khetani, M.A.; Moreno-Angarita, M.; Gulati, S.; Brinkman, S.A.; Almasri, N.A.; Figueiredo, M.; Giudici, L.B.; et al. Early Childhood Development Strategy for the World’s Children with Disabilities. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1390107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Medical Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenbroucke, J.P.; von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Pocock, S.J.; Poole, C.; Schlesselman, J.J.; Egger, M.; STROBE Initiative. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE): Explanation and Elaboration. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, e297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newborg, J. Battelle Developmental Inventory: Second Edition; Riverside Publishing: Itasca, IL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sipes, M.; Matson, J.L.; Turygin, N. The Use of the Battelle Developmental Inventory-Second Edition (BDI-2) as an Early Screener for Autism Spectrum Disorders. Dev. Neurorehabil. 2011, 14, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderbilt, D.L.; Schrager, S.M.; Llanes, M.A.; Hamilton, A.; Seri, I.; Chmait, R.H. Predictors of Two-Year Cognitive Performance after Laser Surgery for Twin-Twin Transfusion Syndrome. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2014, 211, 388.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraleda-Barreno, E.; Romero-López, M.; Cayetano-Menéndez, M.J. La prueba de cribado del inventario de desarrollo de Battelle para la detección precoz de alteraciones del desarrollo en parálisis cerebral. An. Pediatr. 2011, 75, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfonso, V.C.; Rentz, E.A.; Chung, S. Review of the Battelle Developmental Inventory, Second Edition. J. Early Child Infant. Psychol. 2010, 6, 21–40. [Google Scholar]
- Shevell, M.; Majnemer, A.; Platt, R.W.; Webster, R.; Birnbaum, R. Developmental and Functional Outcomes in Children with Global Developmental Delay or Developmental Language Impairment. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2005, 47, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldin, R.L.; Matson, J.L.; Beighley, J.S.; Jang, J. Autism Spectrum Disorder Severity as a Predictor of Battelle Developmental Inventory—Second Edition (BDI-2) Scores in Toddlers. Dev. Neurorehabil. 2014, 17, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horovitz, M.; Matson, J.L. Developmental Milestones in Toddlers with Atypical Development. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2011, 32, 2278–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattier, M.A.; Matson, J.L.; Sipes, M.; Turygin, N. Communication Deficits in Infants and Toddlers with Developmental Disabilities. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2011, 32, 2108–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.; Feng, J.Y.; Wang, T.T.; Xu, Z.D.; Jia, F.Y. Prevalence and Developmental Profiles of Autism Spectrum Disorders in Children with Global Developmental Delay. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 794238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taddei, M.; Bulgheroni, S.; Toffalini, E.; Pantaleoni, C.; Lanfranchi, S. Developmental Profiles of Young Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder and Global Developmental Delay: A Study with the Griffiths III Scales. Autism Res. 2023, 16, 1344–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.-H.; Chen, C.; Peng, J.; Wu, L.-W.; He, F.; Yang, L.-F.; Zhang, C.-L.; Wang, G.-L.; Peng, P.; Ma, Y.-P.; et al. Diagnosis of Intellectual Disability/Global Developmental Delay via Genetic Analysis in a Central Region of China. Chin. Med. J. 2019, 132, 1533–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masri, A.T.; Oweis, L.; Ali, M.; Hamamy, H. Global Developmental Delay and Intellectual Disability in the Era of Genomics: Diagnosis and Challenges in Resource Limited Areas. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2023, 230, 107799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Li, R. Genetic Analysis of Neurodevelopmental Disorders in Children. Front. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2022, 1, 987339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yue, L.; Jin, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, M.; Chen, G.; Yang, L.; et al. Genetic Testing for Global Developmental Delay in Early Childhood. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2415084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-Vasques, A.T.; Lamônica, D.A.C. Motor, Linguistic, Personal and Social Aspects of Children with Down Syndrome. J. Appl. Oral. Sci. 2015, 23, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Will, E.A.; Roberts, J.E. Motor Influences on Communication: Comparisons between Down Syndrome and Fragile X Syndrome. Am. J. Intellect. Dev. Disabil. 2021, 126, 460–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.D.; Nayak, A.; Karnad, S.D.; Doctor, K.N. Gross Motor Dysfunction and Balance Impairments in Children and Adolescents with Down Syndrome: A Systematic Review. Clin. Exp. Pediatr. 2022, 65, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, M.; Rigoldi, C.; Brunner, R.; Virji-Babul, N.; Giorgio, A. Joint Stiffness and Gait Pattern Evaluation in Children with Down Syndrome. Gait Posture 2008, 28, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padia, N.; Bose, M.; Parab, S. Determinants of Hand Function in Children and Adolescent with Down Syndrome-A Scoping Review. J. Hand Ther. 2023, 36, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, G.; Robinson, C.; Fewell, R.R. The Effects of Early Motor Intervention on Children with Down Syndrome or Cerebral Palsy: A Field-Based Study: J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. 2001, 22, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanò, M.; Mercuri, E.; Randò, T.; Pantò, T.; Gagliano, A.; Henderson, S.; Guzetta, F. Motor and Perceptual–Motor Competence in Children with Down Syndrome: Variation in Performance with Age. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 1999, 3, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, G.E.; Klusek, J.; Estigarribia, B.; Roberts, J.E. Language Characteristics of Individuals with Down Syndrome. Top. Lang. Disord. 2009, 29, 112–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipkin, P.H.; Macias, M.M.; Council on Children with Disabilities, Section on Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics; Norwood, K.W.; Brei, T.J.; Davidson, L.F.; Davis, B.E.; Ellerbeck, K.A.; Houtrow, A.J.; Hyman, S.L.; et al. Promoting Optimal Development: Identifying Infants and Young Children with Developmental Disorders Through Developmental Surveillance and Screening. Pediatrics 2020, 145, e20193449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Hoyo Soriano, L.; Villarreal, J.C.; Sterling, A.; Edgin, J.; Berry-Kravis, E.; Hamilton, D.R.; Thurman, A.J.; Abbeduto, L. The Association between Expressive Language Skills and Adaptive Behavior in Individuals with Down Syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrix, J.A.; Amon, A.; Abbeduto, L.; Agiovlasitis, S.; Alsaied, T.; Anderson, H.A.; Bain, L.J.; Baumer, N.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Bogunovic, D.; et al. Opportunities, Barriers, and Recommendations in down Syndrome Research. Transl. Sci. Rare Dis. 2021, 5, 99–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, R.D.; Vorperian, H.K. Speech Impairment in Down Syndrome: A Review. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2013, 56, 178–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, M.; Igari, K.; Hanawa, S.; Ito, A.; Takahashi, A.; Ishida, N.; Koyama, S.; Ono, T.; Sasaki, K. Tongue Pressure during Swallowing in Adults with down Syndrome and Its Relationship with Palatal Morphology. Dysphagia 2014, 29, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onnivello, S.; Pulina, F.; Locatelli, C.; Marcolin, C.; Ramacieri, G.; Antonaros, F.; Vione, B.; Caracausi, M.; Lanfranchi, S. Cognitive Profiles in Children and Adolescents with Down Syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, R.; Kindelberger, C. Variability of Cognitive Development in Children with Down Syndrome: Relevance of Good Reasons for Using the Cluster Procedure. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2009, 30, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfrey, M.; Lee, N.R. A Comprehensive Examination of the Memory Profile of Youth with Down Syndrome in Comparison to Typically Developing Peers. Child. Neuropsychol. 2020, 26, 721–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tungate, A.S.; Conners, F.A. Executive Function in Down Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2021, 108, 103802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daunhauer, L.A.; Fidler, D.J. The Down Syndrome Behavioral Phenotype: Implications for Practice and Research in Occupational Therapy. Occup. Ther. Health Care 2011, 25, 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, T.; Rapsey, C.M.; Glue, P. Systematic Review of Cognitive Development across Childhood in Down Syndrome: Implications for Treatment Interventions. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2013, 57, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, X.; Li, M. The Effect of Exercise on Improving Cognitive Function in People with Down’s Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2025, 184, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores Camas, R.A.; Leon-Rojas, J.E. Specific Language Impairment and Executive Functions in School-Age Children: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e43163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hick, R.; Botting, N.; Conti-Ramsden, G. Cognitive Abilities in Children with Specific Language Impairment: Consideration of Visuo-spatial Skills. Int. J. Lang. Commun. Disord. 2005, 40, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichenbach, K.; Bastian, L.; Rohrbach, S.; Gross, M.; Sarrar, L. Cognitive Functions in Preschool Children with Specific Language Impairment. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 86, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vugs, B.; Hendriks, M.; Cuperus, J.; Knoors, H.; Verhoeven, L. Developmental Associations Between Working Memory and Language in Children with Specific Language Impairment: A Longitudinal Study. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2017, 60, 3284–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf Estes, K.; Evans, J.L.; Else-Quest, N.M. Differences in the Nonword Repetition Performance of Children with and Without Specific Language Impairment: A Meta-Analysis. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2007, 50, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauls, L.J.; Archibald, L.M.D. Executive Functions in Children with Specific Language Impairment: A Meta-Analysis. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2016, 59, 1074–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, D.V.M. What Causes Specific Language Impairment in Children? Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2006, 15, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomas, E.; Vissers, C. Behind the Scenes of Developmental Language Disorder: Time to Call Neuropsychology Back on Stage. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, M.L. Causal Pathways for Specific Language Impairment: Lessons from Studies of Twins. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2020, 63, 3224–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd-Esenkaya, V.; Russell, A.J.; Clair, M.C.S. What Are the Peer Interaction Strengths and Difficulties in Children with Developmental Language Disorder? A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vissers, C.; Koolen, S. Theory of Mind Deficits and Social Emotional Functioning in Preschoolers with Specific Language Impairment. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivero, M.; Vilaseca, R.; Cantero, M.-J.; Valls-Vidal, C.; Leiva, D. Relations between Positive Parenting Behavior during Play and Child Language Development at Early Ages. Children 2023, 10, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landry, S.H.; Smith, K.E.; Swank, P.R.; Guttentag, C. A Responsive Parenting Intervention: The Optimal Timing across Early Childhood for Impacting Maternal Behaviors and Child Outcomes. Dev. Psychol. 2008, 44, 1335–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Næss, K.-A.B.; Nygaard, E.; Ostad, J.; Dolva, A.-S.; Lyster, S.-A.H. The Profile of Social Functioning in Children with Down Syndrome. Disabil. Rehabil. 2017, 39, 1320–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Will, E.A.; Caravella, K.E.; Hahn, L.J.; Fidler, D.J.; Roberts, J.E. Adaptive Behavior in Infants and Toddlers with Down Syndrome and Fragile X Syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2018, 177, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valera-Pozo, M.; Adrover-Roig, D.; Pérez-Castelló, J.A.; Sanchez-Azanza, V.A.; Aguilar-Mediavilla, E. Behavioral, Emotional and School Adjustment in Adolescents with and without Developmental Language Disorder (DLD) Is Related to Family Involvement. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washington, K.N.; Thomas-Stonell, N.; McLeod, S.; Warr-Leeper, G. Outcomes and Predictors in Preschoolers with Speech-Language and/or Developmental Mobility Impairments. Child Lang. Teach. Ther. 2015, 31, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Pereira, M.; Fernández, M.P.; Gómez-Taibo, M.L.; Martínez-López, Z.; Arce, C. A Follow-Up Study of Cognitive Development in Low Risk Preterm Children. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Research on Developmental Disabilities Collaborators Developmental Disabilities among Children Younger than 5 Years in 195 Countries and Territories, 1990-2016: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Glob. Health 2018, 6, e1100–e1121. [CrossRef]
- Rustom, H.; Hassan Eltorki, Y.; Adil Shah Khoodoruth, M.; Abdallah, O.; Al-Khuzaei, N.; Iqbal, N.; Alabdulla, N. Genetic Etiology of Adult Intellectual Disability (ID) of Unknown Cause in Qatar: A Retrospective Study. Qatar Med. J. 2022, 2022, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zablotsky, B.; Black, L.I.; Maenner, M.J.; Schieve, L.A.; Danielson, M.L.; Bitsko, R.H.; Blumberg, S.J.; Kogan, M.D.; Boyle, C.A. Prevalence and Trends of Developmental Disabilities among Children in the US: 2009–2017. Pediatrics 2019, 144, e20190811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonarakis, S.E.; Skotko, B.G.; Rafii, M.S.; Strydom, A.; Pape, S.E.; Bianchi, D.W.; Sherman, S.L.; Reeves, R.H. Down Syndrome. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, S.; Tomblin, B.; Law, J.; McKean, C.; Mensah, F.K.; Morgan, A.; Goldfeld, S.; Nicholson, J.M.; Wake, M. Specific Language Impairment: A Convenient Label for Whom? Int. J. Lang. Commun. Disord. 2014, 49, 416–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGoey, K.E.; McCobin, A.; Venesky, L.G. Early Childhood Assessment for Diverse Learners. In Psychoeducational Assessment and Intervention for Ethnic Minority Children: Evidence-Based Approaches; Graves, S.L., Blake, J.J., Eds.; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; pp. 115–131. ISBN 978-1-4338-2174-5. [Google Scholar]
- Troxel, M.; Sheldrick, R.C.; Eisenhower, A.; Carter, A.S. Patterns and Correlates of Developmental Profiles Using the Battelle Developmental Inventory Among Children in Early Intervention. J. Early Interv. 2024, 46, 544–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| DS Group N = 22 | GDD Group n = 17 | DLD Group n = 7 | p Value | ES | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (months) | 44.1 ± 5.5 | 40.6 ± 6.7 | 41.4 ± 5.1 | 0.183 | 0.076 |
| Sex: Men Women | 13 (59.1) 9 (40.9) | 12 (70.6) 5 (29.4) | 7 (100) 0 (0) | 0.046 | 0.290 |
| Ethnicity: Caucasian | 22 (100) | 17 (100) | 7 (100) | 1 | - |
| DS Group n = 22 | GDD Group n = 17 | DLD Group n = 7 | Between-Group Differences | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F(2, 43) | p Value | ES | ||||
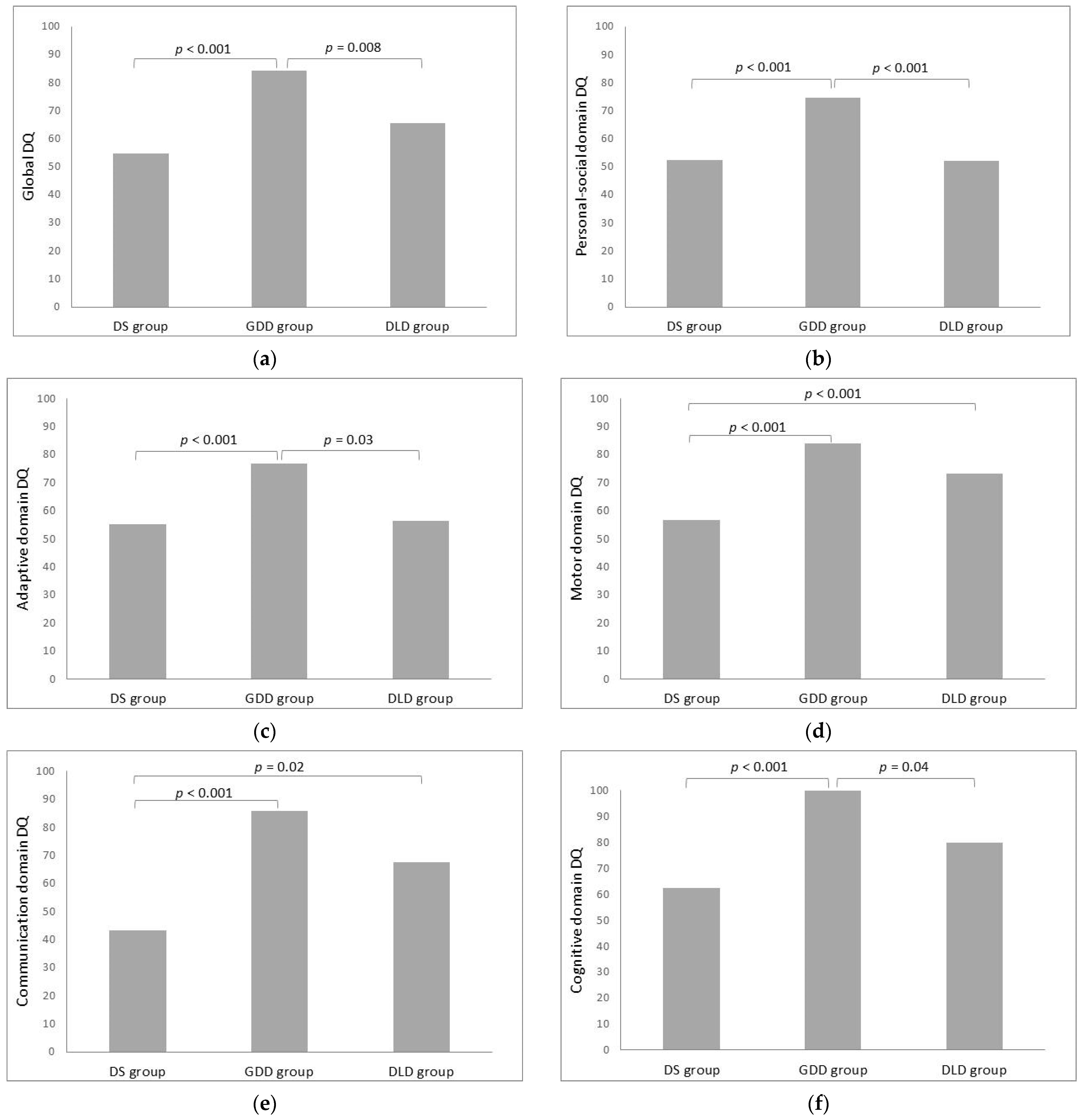
| Global DQ | 54.74 ± 8.65 | 84.25 ± 16.09 | 65.49 ± 16.33 | 24.616 | <0.001 | 0.534 |
| Domain-specific DQs: | ||||||
| Personal-social DQ | 52.32 ± 9.44 | 74.66 ± 15.12 | 52.12 ± 15.69 | 16.472 | <0.001 | 0.434 |
| Adaptive DQ | 55.51 ± 15.37 | 76.92 ± 17.42 | 56.67 ± 19.92 | 8.441 | 0.001 | 0.282 |
| Motor DQ | 56.82 ± 11.17 | 84.10 ± 14.15 | 73.40 ± 11.79 | 23.432 | <0.001 | 0.521 |
| Communication DQ | 43.21 ± 7.22 | 85.87 ± 20.17 | 67.57 ± 17.05 | 40.179 | <0.001 | 0.651 |
| Cognitive DQ | 62.48 ± 13.90 | 100.36 ± 17.52 | 79.98 ± 27.12 | 22.116 | <0.001 | 0.507 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahulló-Fuster, M.-A.; Sánchez-Sánchez, M.L.; Monterrubio-Gordón, A.; Ruescas-Nicolau, M.-A. A Comparison of Developmental Profiles of Preschool Children with Down Syndrome, Global Developmental Delay, and Developmental Language Disorder. Healthcare 2025, 13, 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13141684
Ahulló-Fuster M-A, Sánchez-Sánchez ML, Monterrubio-Gordón A, Ruescas-Nicolau M-A. A Comparison of Developmental Profiles of Preschool Children with Down Syndrome, Global Developmental Delay, and Developmental Language Disorder. Healthcare. 2025; 13(14):1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13141684
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhulló-Fuster, Mónica-Alba, M. Luz Sánchez-Sánchez, Alejandro Monterrubio-Gordón, and Maria-Arantzazu Ruescas-Nicolau. 2025. "A Comparison of Developmental Profiles of Preschool Children with Down Syndrome, Global Developmental Delay, and Developmental Language Disorder" Healthcare 13, no. 14: 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13141684
APA StyleAhulló-Fuster, M.-A., Sánchez-Sánchez, M. L., Monterrubio-Gordón, A., & Ruescas-Nicolau, M.-A. (2025). A Comparison of Developmental Profiles of Preschool Children with Down Syndrome, Global Developmental Delay, and Developmental Language Disorder. Healthcare, 13(14), 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13141684








