Systemic Inflammation Response Index (SIRI) and Monocyte-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (MLR) Are Predictors of Good Outcomes in Surgical Treatment of Periprosthetic Joint Infections of Lower Limbs: A Single-Center Retrospective Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
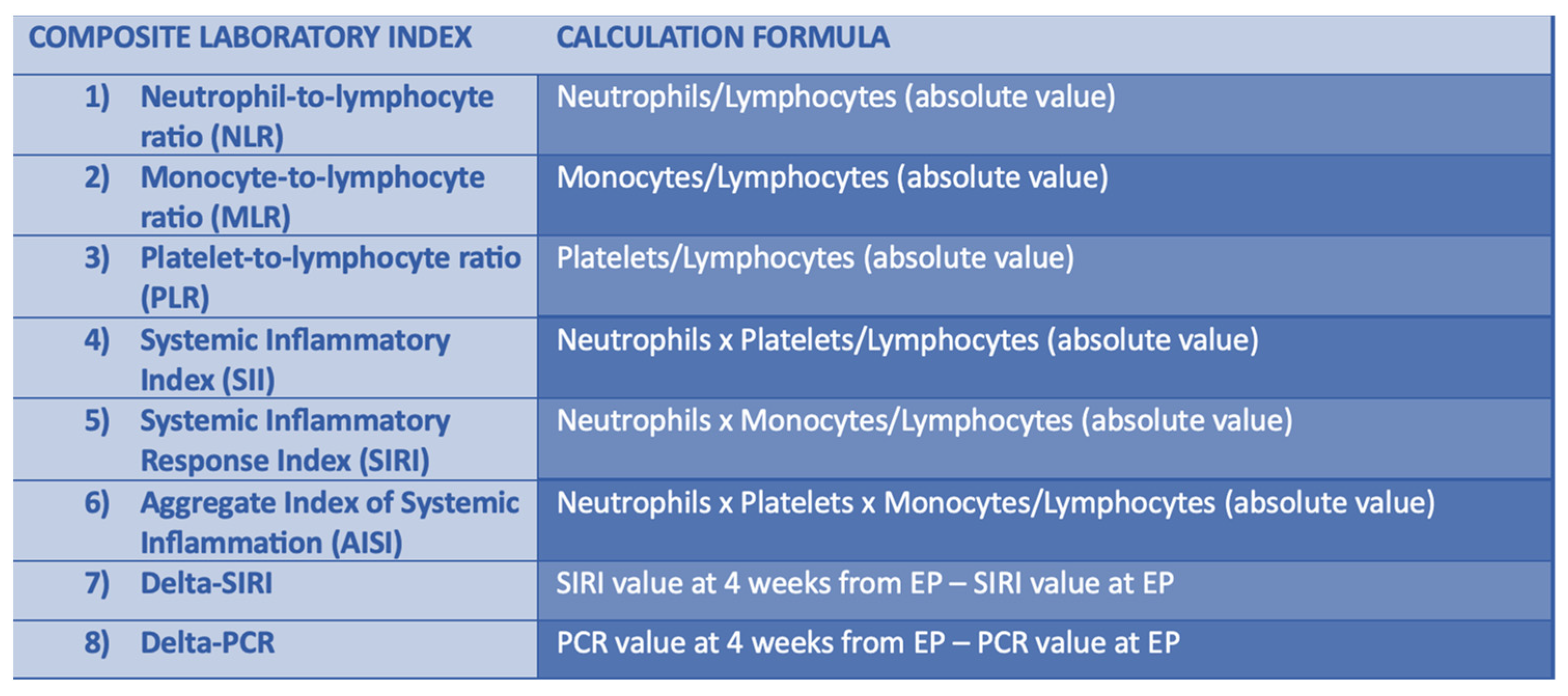
2. Materials and Methods
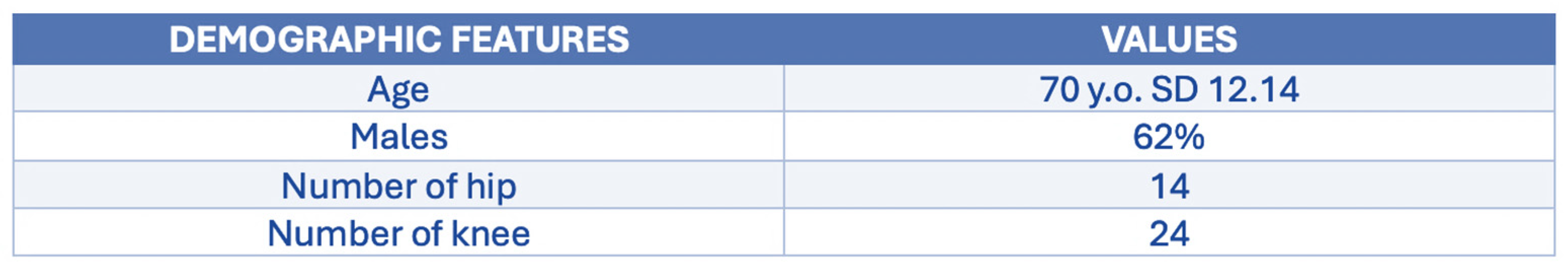
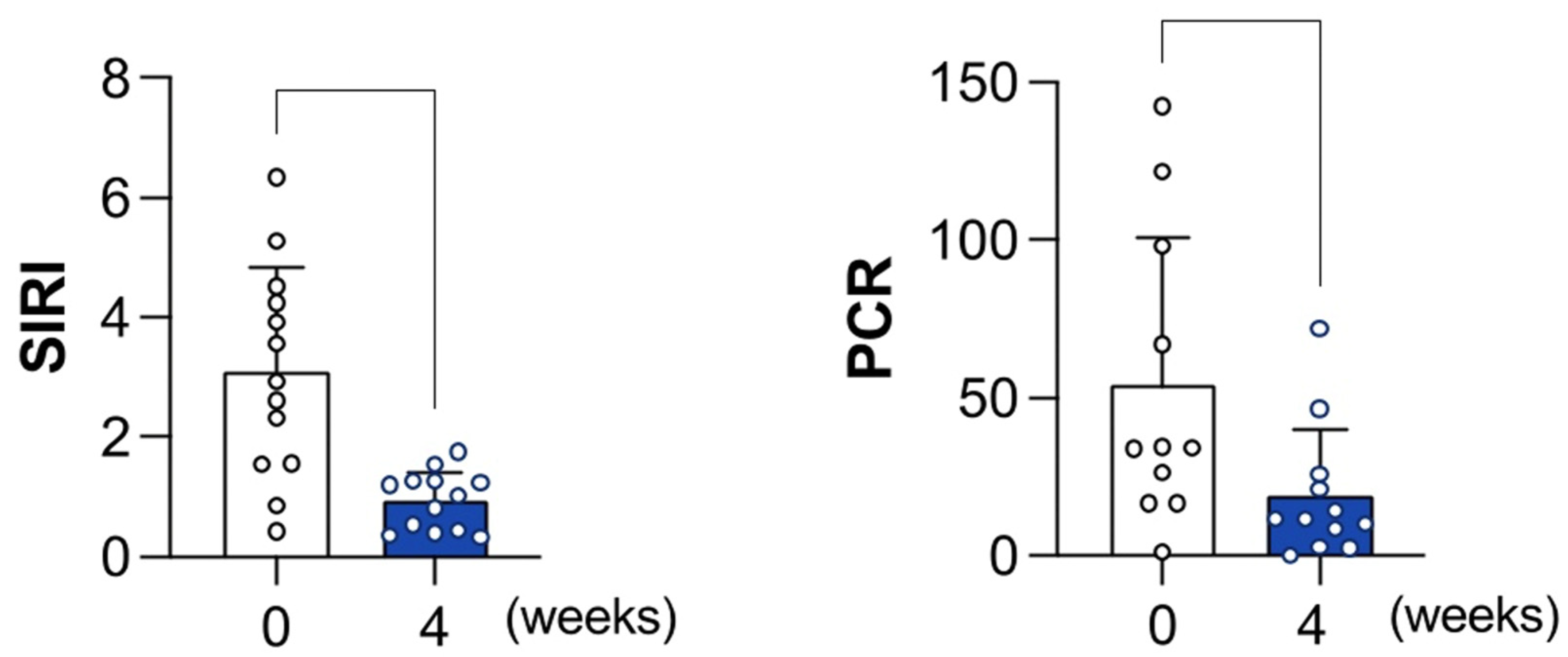
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fiore, M.; Rondinella, C.; Paolucci, A.; Morante, L.; De Paolis, M.; Sambri, A. Functional Outcome after Reimplantation in Patients Treated with and without an Antibiotic-Loaded Cement Spacers for Hip Prosthetic Joint Infections. Hip Pelvis 2023, 35, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lee, Q.J.; Mak, W.P.; Wong, Y.C. Risk factors for periprosthetic joint infection in total knee arthroplasty. J. Orthop. Surg. 2015, 23, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jämsen, E.; Varonen, M.; Huhtala, H.; Lehto, M.U.; Lumio, J.; Konttinen, Y.T.; Moilanen, T. Incidence of prosthetic joint infections after primary knee Arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2010, 25, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huotari, K.; Peltola, M.; Jämsen, E. The incidence of late prosthetic joint infections: A registry-based study of 112,708 primary hip and knee replacements. Acta Orthop. 2015, 86, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, J.E.; Crane, T.P.; Noy, M.; Elliott, T.S.J.; Grimer, R.J. The incidence of deep prosthetic infections in a specialist orthopedic hospital: A 15-YEAR PROSPECTIVE SURVEY. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. Vol. 2006, 88, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtz, S.M.; Lau, E.; Watson, H.; Schmier, J.K.; Parvizi, J. Economic Burden of Periprosthetic Joint Infection in the United States. J. Arthroplast. 2012, 27, 61–65.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtz, S.M.; Lau, E.; Schmier, J.; Ong, K.L.; Zhao, K.; Parvizi, J. Infection burden for hip and knee Arthroplasty in the United States. J. Arthroplast. 2008, 23, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamath, A.F.; Ong, K.L.; Lau, E.; Chan, V.; Vail, T.P.; Rubash, H.E.; Berry, D.J.; Bozic, K.J. Quantifying the Burden of Revision Total Joint Arthroplasty for Periprosthetic Infection. J. Arthroplast. 2015, 30, 1492–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tande, A.J.; Gomez-Urena, E.O.; Berbari, E.F.; Osmon, D.R. Management of Prosthetic Joint Infection. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 31, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.-H.; Lee, S.-H.; Lin, Y.-C.; Wang, Y.-C.; Chang, C.-J.; Hsieh, P.-H. Increased periprosthetic hip and knee infection projected from 2014 to 2035 in Taiwan. J. Infect. Public Health 2020, 13, 1768–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carender, C.N.; Glass, N.A.; DeMik, D.E.; Elkins, J.M.; Brown, T.S.; Bedard, N.A. Projected prevalence of obesity in primary total hip arthroplasty: How big will the problem get? J. Arthroplast. 2022, 37, 874–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicenti, G.; Bizzoca, D.; Nappi, V.; Pesce, V.; Solarino, G.; Carrozzo, M.; Moretti, F.; Dicuonzo, F.; Moretti, B. Serum biomarkers in the diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection: Consolidated evidence and recent developments. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23 (Suppl. S2), 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izakovicova, P.; Borens, O.; Trampuz, A. Periprosthetic joint infection: Current concepts and outlook. EFORT Open Rev. 2019, 4, 482–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerli, W.; Trampuz, A.; Ochsner, P.E. Prosthetic-joint infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1645–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, K.; Bozic, K.J.; Silverton, C.; Nelson, A.J.; Makhni, E.C.; Davis, J.J. Reconsidering strategies for managing chronic periprosthetic joint infection in total knee arthroplasty: Using decision analytics to find the optimal strategy between one-stage and two-stage total knee revision. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2019, 101, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, N.M.; Buchanan, M.W.; Seyler, T.M.; Wellman, S.S.; Seidelman, J.; Jiranek, W.A. 1.5-Stage exchange arthroplasty for total knee arthroplasty periprosthetic joint infections. J. Arthroplast. 2021, 36, 1114–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, T.L.; Kheir, M.M.; Rondon, A.J.; Parvizi, J.; George, J.; Higuera, C.A.; Shohat, N.; Chen, A.F. Determining the role and duration of the “antibiotic holiday” period in Periprosthetic joint infection. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 2976–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Tan, T.L.; Chen, J.-Y. Positive culture during reimplantation increases the risk of reinfection in two-stage exchange arthroplasty despite administrating prolonged antibiotics: A retrospective cohort study and meta-analysis. J. Arthroplast. 2019, 34, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapadia, B.H.; Berg, R.A.; Daley, J.A.; Fritz, J.; Bhave, A.; Mont, M.A. Periprosthetic joint infection. Lancet 2016, 387, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNally, M.; Sousa, R.; Wouthuyzen-Bakker, M.; Chen, A.F.; Soriano, A.; Vogely, H.C.; Clauss, M.; Higuera, C.A.; Trebše, R. The EBJIS definition of periprosthetic joint infection: A practical guide for clinicians. Bone Jt. Lett. J. 2021, 103, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigmund, I.K.; Luger, M.; Windhager, R.; McNally, M.A. Diagnosing periprosthetic joint infections: A comparison of infection definitions: EBJIS 2021, ICM 2018, and IDSA 2013. Bone Jt. Res. 2022, 11, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Margaryan, D.; Ojeda-Thies, C.; Perka, C.; Trampuz, A. Meta-analysis of serum and/or plasma D-dimer in the diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2020, 15, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Papalini, C.; Pucci, G.; Cenci, G.; Mencacci, A.; Francisci, D.; Caraffa, A.; Antinolfi, P.; Pasticci, M.B. Prosthetic joint infection diagnosis applying the three-level European Bone and Joint Infection Society (EBJIS) approach. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2022, 41, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maimaiti, Z.; Xu, C.; Fu, J.; Chai, W.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J. The Potential Value of Monocyte to Lymphocyte Ratio, Platelet to Mean Platelet Volume Ratio in the Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infections. Orthop. Surg. 2022, 14, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Stojkovic Lalosevic, M.; Pavlovic Markovic, A.; Stankovic, S.; Stojkovic, M.; Dimitrijevic, I.; Radoman Vujacic, I.; Lalic, D.; Milovanovic, T.; Dumic, I.; Krivokapic, Z. Combined Diagnostic Efficacy of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR), Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (PLR), and Mean Platelet Volume (MPV) as Biomarkers of Systemic Inflammation in the Diagnosis of Colorectal Cancer. Dis. Markers 2019, 2019, 6036979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, B.; Ma, N.; Tang, Q.; Wei, T.; Yang, M.; Fu, H.; Hu, Z.; Liang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhong, R. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet to lymphocyte ratio (PLR) were useful markers in assessment of inflammatory response and disease activity in SLE patients. Mod. Rheumatol. 2016, 26, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, C.D.; Parajuli, A.; Gale, H.J.; Bulteel, N.S.; Schuetz, P.; de Jager, C.P.; Loonen, A.J.; Merekoulias, G.I.; Baillie, J.K. The utility of peripheral blood leucocyte ratios as biomarkers in infectious diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Infect. 2019, 78, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agha, R.A.; Sohrabi, C.; Mathew, G.; Franchi, T.; Ker-wan, A.; O’Neill, N.; PROCESS Group. The PROCESS 2020 Guideline: Updating Consensus Pre-ferred Reporting of CasESeries in Surgery (PRO-CESS) Guidelines. Int. J. Surg. 2020, 84, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, R.; Ribau, A.; Alfaro, P.; Burch, M.A.; Ploegmakers, J.; McNally, M.; Clauss, M.; Wouthuyzen-Bakker, M.; Soriano, A. The European Bone and Joint Infection Society definition of periprosthetic joint infection is meaningful in clinical practice: A multicentric validation study with comparison with previous definitions. Acta Orthop. 2023, 94, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- George, J.; Kwiecien, G.; Klika, A.K.; Ramanathan, D.; Bauer, T.W.; Barsoum, W.K.; Higuera, C.A. Are Frozen Sections and MSIS Criteria Reliable at the Time of Reimplantation of Two-stage Revision Arthroplasty? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2016, 474, 1619–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, K.; Dai, K.; Qu, X.; Yan, M. Serum and synovial fluid Interleukin-6 for the diagnosis of Periprosthetic joint infection. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, J.M.; George, J.; Klika, A.K.; Hatem, S.F.; Barsoum, W.K.; North, T.W.; Higuera, C.A. What is the diagnostic accuracy of aspirations performed on hips with antibiotic cement spacers? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2017, 475, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Fu, J.; Chai, W.; Hao, L.B.; Zhou, Y.G.; Xu, C.; Chen, J.Y. Two-stage exchange arthroplasty is a viable treatment for Periprosthetic joint infection in inflammatory diseases. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2020, 21, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xu, H.; Xie, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, D.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, Z. Potential Blood Biomarkers for Diagnosing Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Single-Center, Retrospective Study. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Parvizi, J.; Ghanem, E.; Menashe, S.; Barrack, R.L.; Bauer, T.W. Periprosthetic infection: What are the diagnostic challenges? J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2006, 20, 6212–6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.Y.; Chun, D.-H.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, N.K.; Baik, S.H.; Hong, J.H.; Kim, K.S.; Shin, C.-S. Prognostic Value of Systemic Inflammatory Indices, NLR, PLR, and MPV, for Predicting 1-Year Survival of Patients Undergoing Cytoreductive Surgery with HIPEC. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebuzzi, S.E.; Signori, A.; Banna, G.L.; Maruzzo, M.; De Giorgi, U.; Pedrazzoli, P.; Sbrana, A.; Zucali, P.A.; Masini, C.; Naglieri, E.; et al. Inflammatory indices and clinical factors in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients treated with nivolumab: The development of a novel prognostic score (Meet-URO 15 study). Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2021, 13, 17588359211019642, Erratum in Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2021, 13, 17588359211036552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gazendam, A.; Wood, T.J.; Tushinski, D.; Bali, K. Diagnosing periprosthetic joint infection: A scoping review. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2022, 15, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ecki, M.; Poilvache, H.; Randy Buzisa, M.; VANCauter, M.; Rodriguez-Villalobos, H.; Yombi, J.C.; Cornu, O. Are C-reactive protein (CRP) and neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) predictive markers of successful two-stage prosthetic joint infection management? Acta Orthop. Belg. 2023, 89, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, R.; Serrano, P.; Gomes Dias, J.; Oliveira, J.C.; Oliveira, A. Improving the accuracy of synovial fluid analysis in the diagnosis of prosthetic joint infection with simple and inexpensive biomarkers: C-reactive protein and adenosine deaminase. Bone Jt. J. 2017, 15, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pannu, T.S.; Villa, J.M.; Higuera, C.A. Diagnosis and management of infected arthroplasty. SICOT J. 2021, 7, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tirumala, V.; Klemt, C.; Xiong, L.; Chen, W.; van den Kieboom, J.; Kwon, Y.M. Diagnostic Utility of Platelet Count/Lymphocyte Count Ratio and Platelet Count/Mean Platelet Volume Ratio in Periprosthetic Joint Infection Following Total Knee Arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2021, 36, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klemt, C.; Tirumala, V.; Smith, E.J.; Xiong, L.; Kwon, Y.M. Complete blood platelet and lymphocyte ratios increase diagnostic accuracy of periprosthetic joint infection following total hip arthroplasty. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2023, 143, 1441–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Xia, C.; Wu, L.; Li, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, J. Systemic Immune Inflammation Index (SII), System Inflammation Response Index (SIRI) and Risk of All-Cause Mortality and Cardiovascular Mortality: A 20-Year Follow-Up Cohort Study of 42,875 US Adults. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Djordjevic, D.; Rondovic, G.; Surbatovic, M.; Stanojevic, I.; Udovicic, I.; Andjelic, T.; Zeba, S.; Milosavljevic, S.; Stankovic, N.; Abazovic, D.; et al. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, Monocyte-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, and Mean Platelet Volume-to-Platelet Count Ratio as Biomarkers in Critically Ill and Injured Patients: Which Ratio to Choose to Predict Outcome and Nature of Bacteremia? Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 3758068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hu, B.; Yang, X.R.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Y.F.; Sun, C.; Guo, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.M.; Qiu, S.J.; Zhou, J.; et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts prognosis of patients after curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 6212–6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.T.; Wang, T.C.; Zhang, W. Preoperative Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index is a Potential Biomarker in Adult Patients with High-Grade Gliomas Undergoing Radical Resection. J. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 12, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vitiello, R.; Smimmo, A.; Matteini, E.; Micheli, G.; Fantoni, M.; Ziranu, A.; Maccauro, G.; Taccari, F. Systemic Inflammation Response Index (SIRI) and Monocyte-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (MLR) Are Predictors of Good Outcomes in Surgical Treatment of Periprosthetic Joint Infections of Lower Limbs: A Single-Center Retrospective Analysis. Healthcare 2024, 12, 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12090867
Vitiello R, Smimmo A, Matteini E, Micheli G, Fantoni M, Ziranu A, Maccauro G, Taccari F. Systemic Inflammation Response Index (SIRI) and Monocyte-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (MLR) Are Predictors of Good Outcomes in Surgical Treatment of Periprosthetic Joint Infections of Lower Limbs: A Single-Center Retrospective Analysis. Healthcare. 2024; 12(9):867. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12090867
Chicago/Turabian StyleVitiello, Raffaele, Alessandro Smimmo, Elena Matteini, Giulia Micheli, Massimo Fantoni, Antonio Ziranu, Giulio Maccauro, and Francesco Taccari. 2024. "Systemic Inflammation Response Index (SIRI) and Monocyte-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (MLR) Are Predictors of Good Outcomes in Surgical Treatment of Periprosthetic Joint Infections of Lower Limbs: A Single-Center Retrospective Analysis" Healthcare 12, no. 9: 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12090867
APA StyleVitiello, R., Smimmo, A., Matteini, E., Micheli, G., Fantoni, M., Ziranu, A., Maccauro, G., & Taccari, F. (2024). Systemic Inflammation Response Index (SIRI) and Monocyte-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (MLR) Are Predictors of Good Outcomes in Surgical Treatment of Periprosthetic Joint Infections of Lower Limbs: A Single-Center Retrospective Analysis. Healthcare, 12(9), 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12090867






