Primary Headache Is Related to Reduced Health-Related Quality of Life in Children with Epilepsy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Headache Questionnaire
2.2. Epilepsy-Related and Sociological Data
2.3. Quality of Life Questionnaire
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
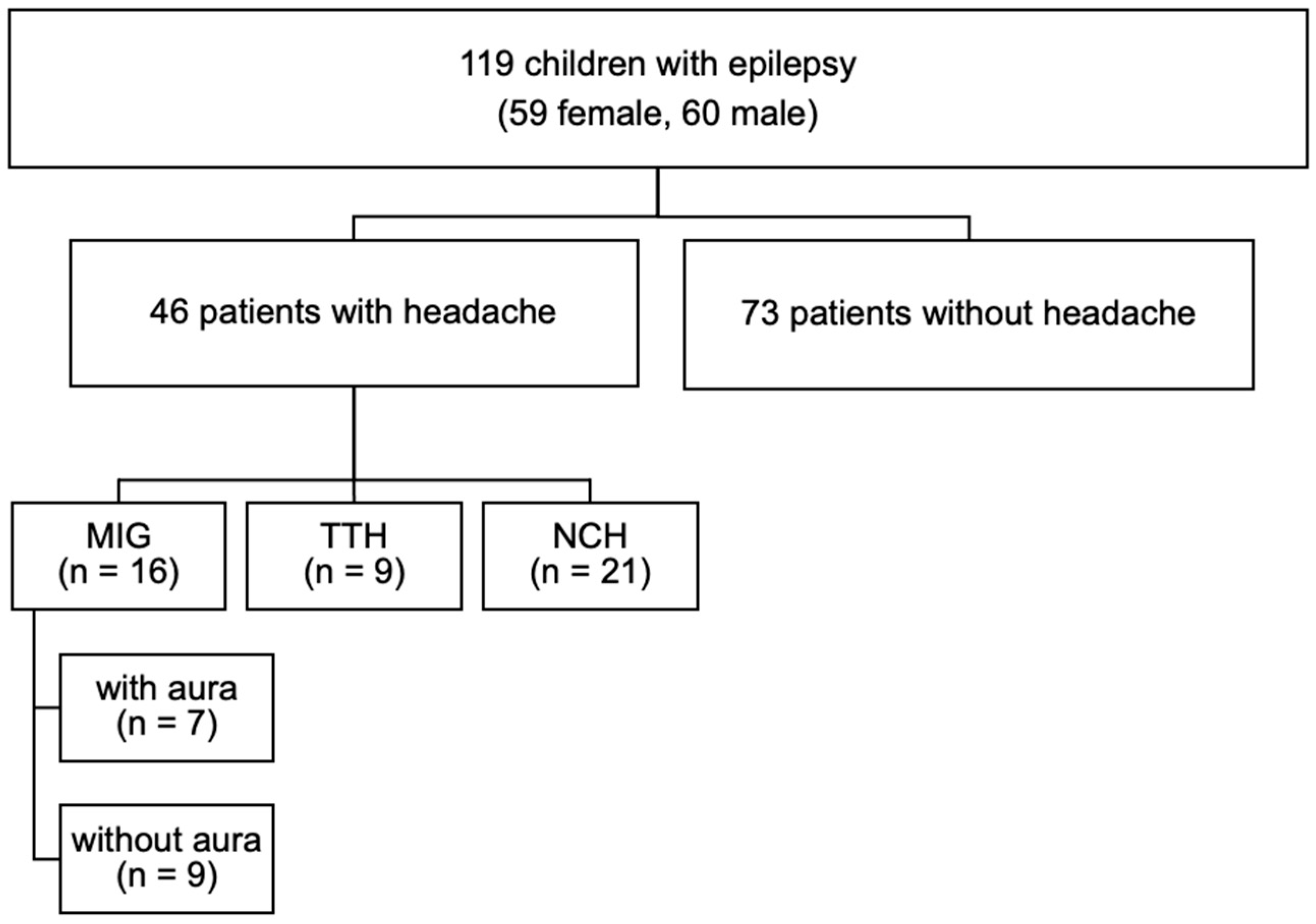
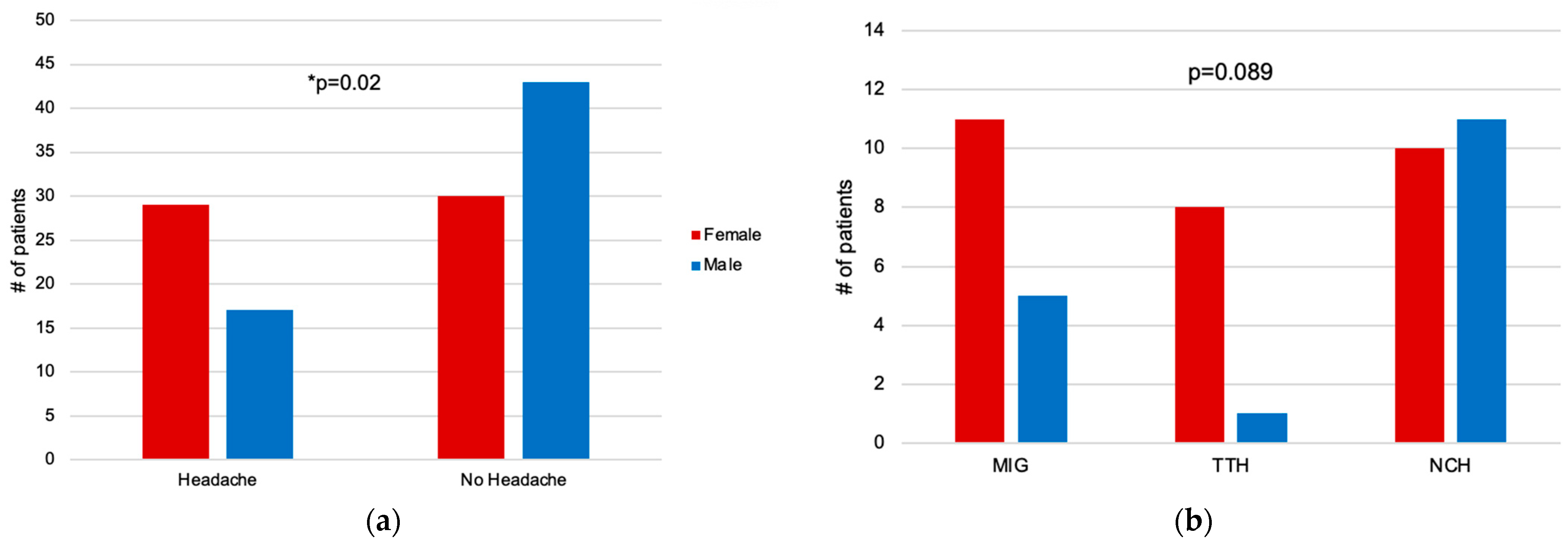
3.1. Distribution of Headache
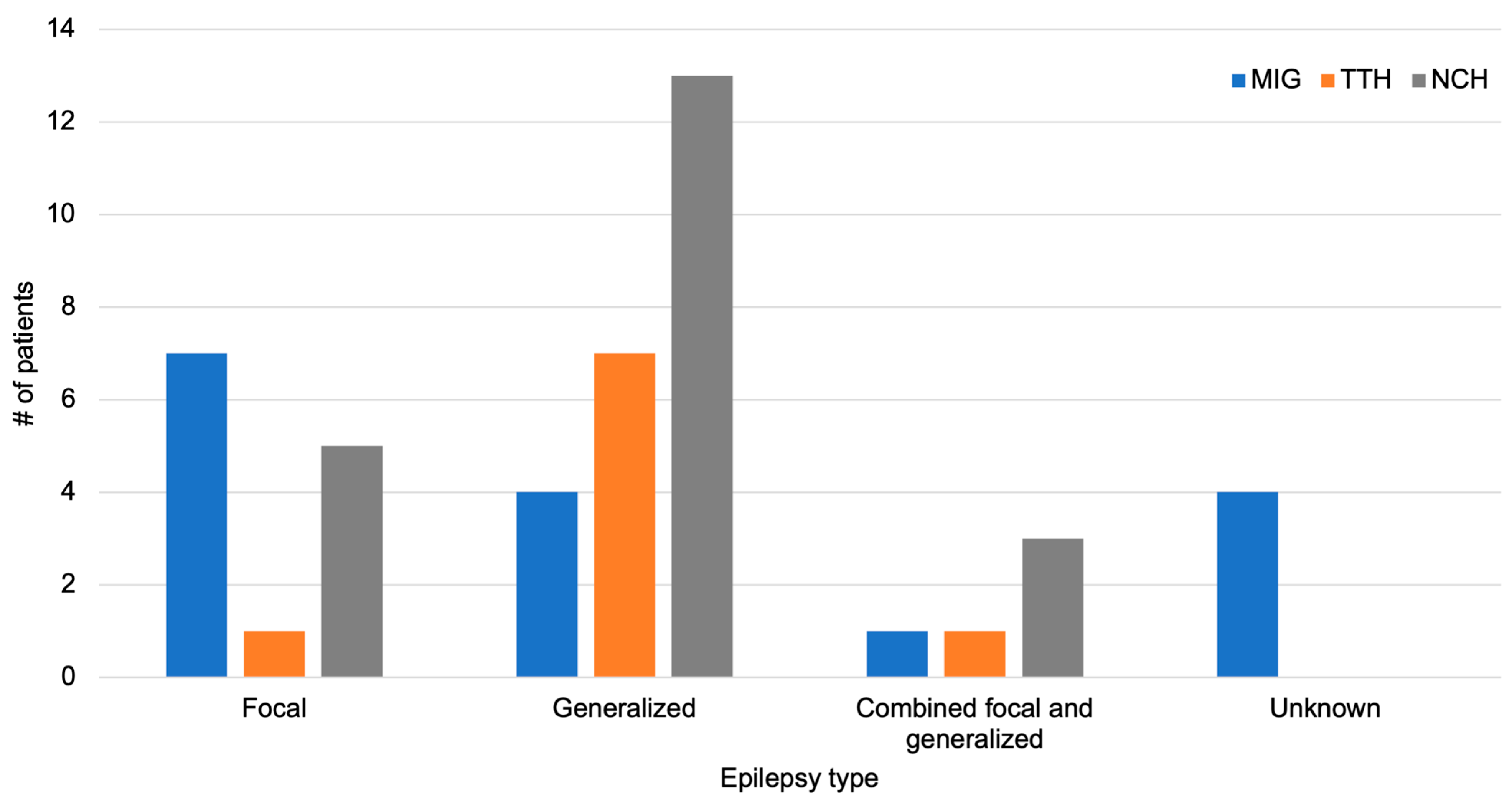
3.2. Headache in Relation to Epilepsy Type
3.3. Headache within Female and Male Patients
3.4. Seizure-Associated Headache
3.5. Headache and Seizure Freedom
3.6. Headache and Sociological Variables
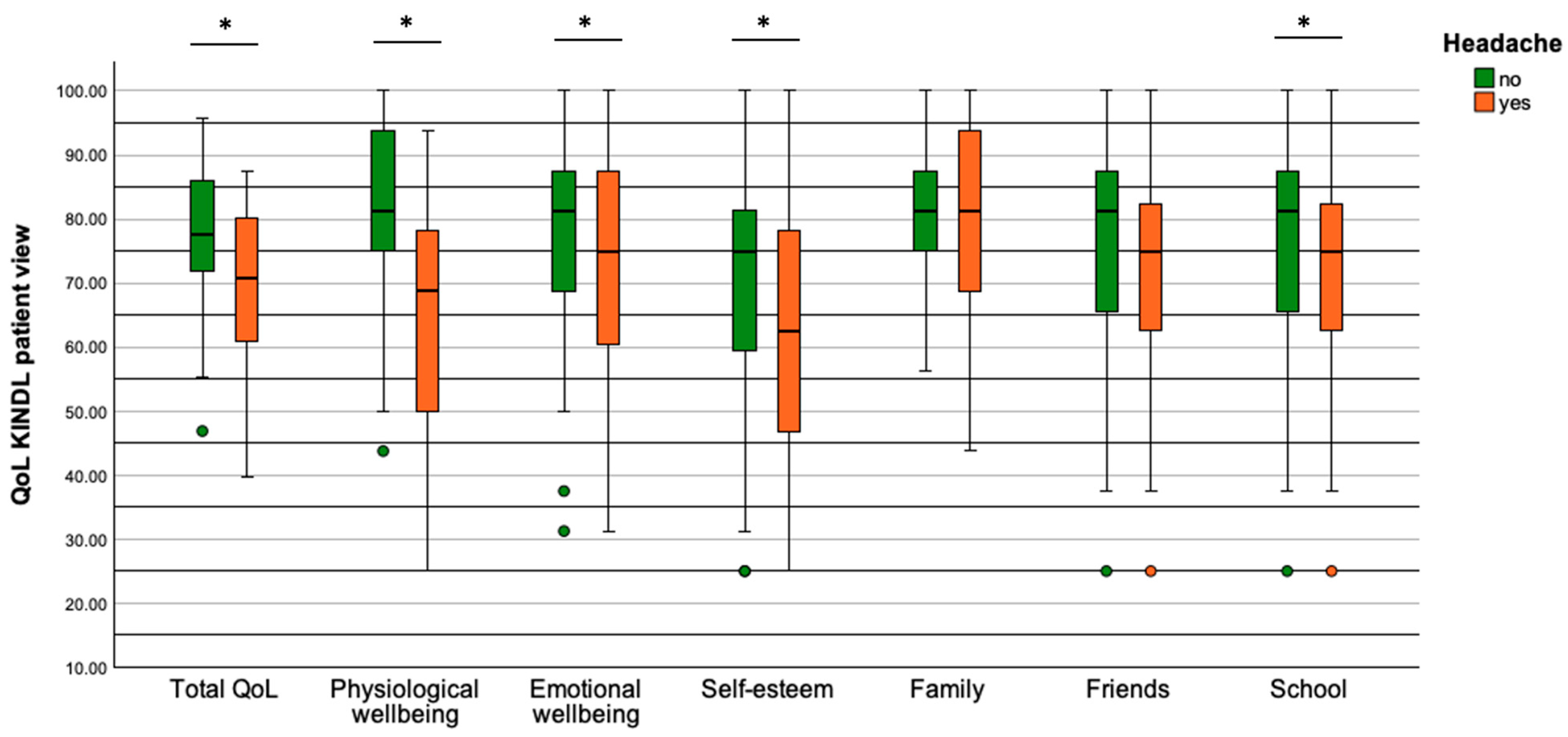
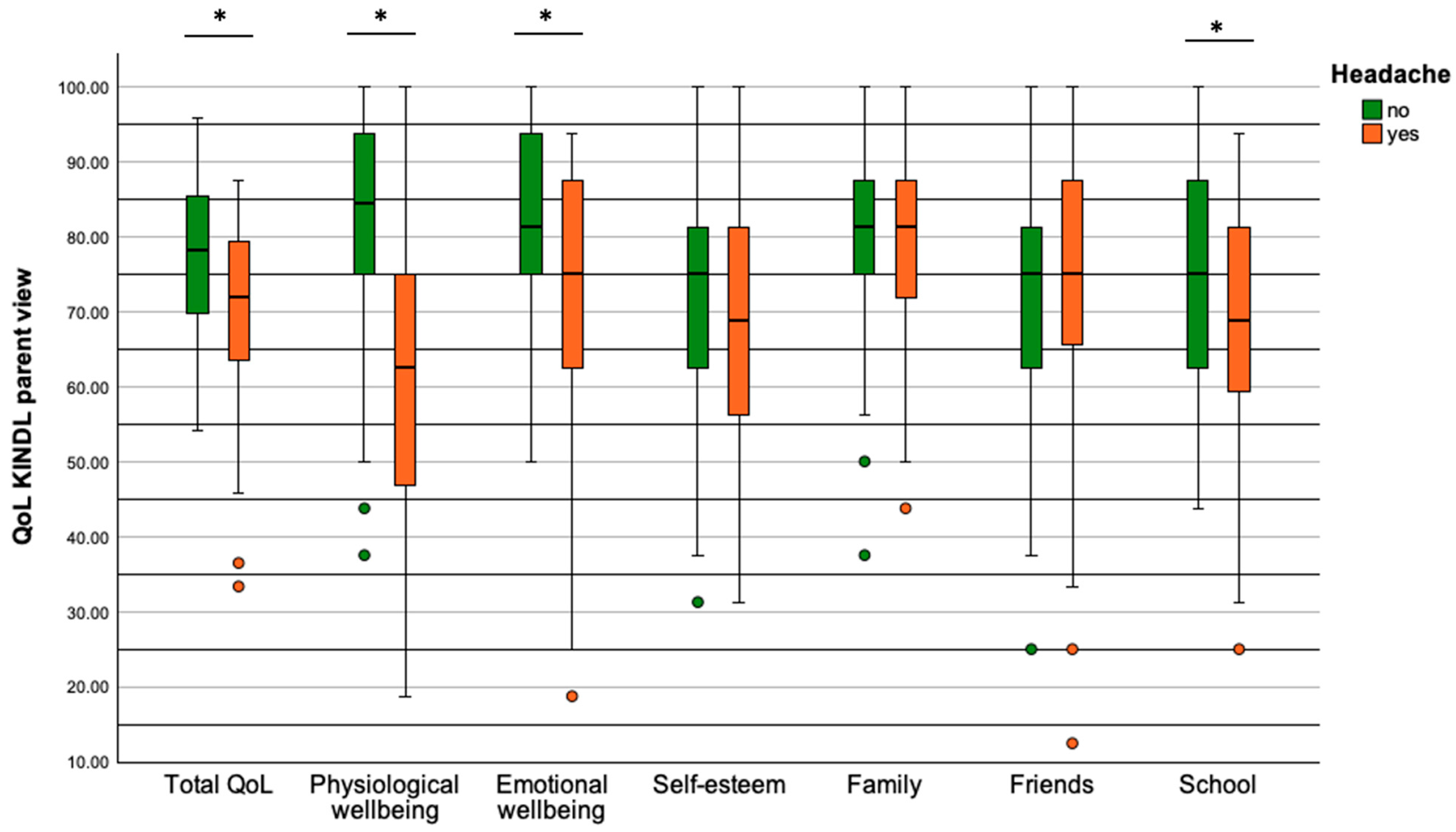
3.7. Quality of Life
3.8. Quality of Life and Sociological Variables
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Keezer, M.R.; Sisodiya, S.M.; Sander, J.W. Comorbidities of epilepsy: Current concepts and future perspectives. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Lee, S.K. Headache and Epilepsy. J. Epilepsy Res. 2017, 7, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Papetti, L.; Nicita, F.; Parisi, P.; Spalice, A.; Villa, M.P.; Kasteleijn-Nolst Trenite, D.G. “Headache and epilepsy”—How are they connected? Epilepsy Behav. 2013, 26, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society. The International Classification of Headache Disorders: 2nd edition. Cephalalgia 2004, 24, 9–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society. The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition (beta version). Cephalalgia 2013, 33, 629–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hershey, A.D.; Winner, P.; Kabbouche, M.A.; Gladstein, J.; Yonker, M.; Lewis, D.; Pearlman, E.; Linder, S.L.; Rothner, A.D.; Powers, S.W. Use of the ICHD-II criteria in the diagnosis of pediatric migraine. Headache 2005, 45, 1288–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, P.E.; Mack, K.J. Episodic and chronic migraine in children. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2020, 62, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Arefeh, I.; Russell, G. Prevalence of headache and migraine in schoolchildren. Bmj 1994, 309, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aromaa, M.; Sillanpää, M.L.; Rautava, P.; Helenius, H. Childhood headache at school entry: A controlled clinical study. Neurology 1998, 50, 1729–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onofri, A.; Pensato, U.; Rosignoli, C.; Wells-Gatnik, W.; Stanyer, E.; Ornello, R.; Chen, H.Z.; De Santis, F.; Torrente, A.; Mikulenka, P.; et al. Primary headache epidemiology in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Headache Pain. 2023, 24, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowell, M.K.; Youssef, P.E. The Comorbidity of Migraine and Epilepsy in Children and Adolescents. Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. 2016, 23, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toldo, I.; Perissinotto, E.; Menegazzo, F.; Boniver, C.; Sartori, S.; Salviati, L.; Clementi, M.; Montagna, P.; Battistella, P.A. Comorbidity between headache and epilepsy in a pediatric headache center. J. Headache Pain. 2010, 11, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Storey, J.R.; Calder, C.S.; Hart, D.E.; Potter, D.L. Topiramate in migraine prevention: A double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Headache 2001, 41, 968–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, J.L.; Saper, J.R.; Diamond, M.; Couch, J.R.; Lewis, D.W.; Schmitt, J.; Neto, W.; Schwabe, S.; Jacobs, D.; Group, M.-S. Topiramate for migraine prevention: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2004, 291, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hering, R.; Kuritzky, A. Sodium valproate in the prophylactic treatment of migraine: A double-blind study versus placebo. Cephalalgia 1992, 12, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, S.W.; Coffey, C.S.; Chamberlin, L.A.; Ecklund, D.J.; Klingner, E.A.; Yankey, J.W.; Korbee, L.L.; Porter, L.L.; Hershey, A.D. Trial of Amitriptyline, Topiramate, and Placebo for Pediatric Migraine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, D.Y.; Yuan Ong, J.J.; Goadsby, P.J. Cluster Headache: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, and Diagnosis. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2018, 21, S3–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozensztrauch, A.; Kołtuniuk, A. The Quality of Life of Children with Epilepsy and the Impact of the Disease on the Family Functioning. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fayed, N.; Davis, A.M.; Streiner, D.L.; Rosenbaum, P.L.; Cunningham, C.E.; Lach, L.M.; Boyle, M.H.; Ronen, G.M. Children’s perspective of quality of life in epilepsy. Neurology 2015, 84, 1830–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aaberg, K.M.; Bakken, I.J.; Lossius, M.I.; Lund Søraas, C.; Håberg, S.E.; Stoltenberg, C.; Surén, P.; Chin, R. Comorbidity and Childhood Epilepsy: A Nationwide Registry Study. Pediatrics 2016, 138, e20160921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camfield, C.S.; Camfield, P.R. Long-term social outcomes for children with epilepsy. Epilepsia 2007, 48, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genizi, J.; Halevy, A.; Schertz, M.; Osman, K.; Assaf, N.; Segal, I.; Srugo, I.; Kessel, A.; Engel-Yeger, B. Sensory Processing Difficulties Correlate with Disease Severity and Quality of Life among Children with Migraine. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Ghadeer, H.A.; AlSalman, S.A.; Albaqshi, F.M.; Alsuliman, S.R.; Alsowailem, F.A.; Albusror, H.A.; AlAbdi, Z.I.; Alwabari, E.M.; Alturaifi, Z.A.; AlHajji, A.M. Quality of Life and Disability among Migraine Patients: A Single-Center Study in AlAhsa, Saudi Arabia. Cureus 2021, 13, e19210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuberi, S.M.; Wirrell, E.; Yozawitz, E.; Wilmshurst, J.M.; Specchio, N.; Riney, K.; Pressler, R.; Auvin, S.; Samia, P.; Hirsch, E.; et al. ILAE classification and definition of epilepsy syndromes with onset in neonates and infants: Position statement by the ILAE Task Force on Nosology and Definitions. Epilepsia 2022, 63, 1349–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsche, G.; Hueppe, M.; Kukava, M.; Dzagnidze, A.; Schuerks, M.; Yoon, M.S.; Diener, H.C.; Katsarava, Z. Validation of a german language questionnaire for screening for migraine, tension-type headache, and trigeminal autonomic cephalgias. Headache 2007, 47, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 1–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravens-Sieberer, U.; Bullinger, M. Assessing health-related quality of life in chronically ill children with the German KINDL: First psychometric and content analytical results. Qual. Life Res. 1998, 7, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullinger, M.; Brutt, A.L.; Erhart, M.; Ravens-Sieberer, U.; Group, B.S. Psychometric properties of the KINDL-R questionnaire: Results of the BELLA study. Eur. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2008, 17, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duko, B.; Ayalew, M.; Toma, A. The epidemiology of headaches among patients with epilepsy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Headache Pain 2020, 21, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, S.A.; Hartman, A.L.; Kossoff, E.H. Comorbidity of migraine in children presenting with epilepsy to a tertiary care center. Neurology 2012, 79, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamane, L.E.; Montenegro, M.A.; Guerreiro, M.M. Comorbidity headache and epilepsy in childhood. Neuropediatrics 2004, 35, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchin, M.M.; Londero, R.G.; Lima, J.E.; Bigal, M.E. Migraine and epilepsy: A focus on overlapping clinical, pathophysiological, molecular, and therapeutic aspects. Curr. Pain. Headache Rep. 2010, 14, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haan, J.; van den Maagdenberg, A.M.; Brouwer, O.F.; Ferrari, M.D. Migraine and epilepsy: Genetically linked? Expert Rev. Neurother. 2008, 8, 1307–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheffer, I.E.; Berkovic, S.; Capovilla, G.; Connolly, M.B.; French, J.; Guilhoto, L.; Hirsch, E.; Jain, S.; Mathern, G.W.; Moshé, S.L.; et al. ILAE classification of the epilepsies: Position paper of the ILAE Commission for Classification and Terminology. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuki, M.; Matsumori, Y.; Kawahara, J.; Yamagishi, C.; Koh, A.; Kawamura, S.; Kashiwagi, K.; Kito, T.; Oguri, M.; Mizuno, S.; et al. School-based online survey on chronic headache, migraine, and medication-overuse headache prevalence among children and adolescents in Japanese one city—Itoigawa Benizuwaigani study. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2023, 226, 107610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiller, K.; Rauchenzauner, M.; Avidgor, T.; Hannan, S.; Lorenzen, C.; Kaml, M.; Walser, G.; Unterberger, I.; Filippi, V.; Broessner, G.; et al. Primary headache types in adult epilepsy patients. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verrotti, A.; Coppola, G.; Spalice, A.; Di Fonzo, A.; Bruschi, R.; Tozzi, E.; Iannetti, P.; Villa, M.P.; Parisi, P. Peri-ictal and inter-ictal headache in children and adolescents with idiopathic epilepsy: A multicenter cross-sectional study. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2011, 27, 1419–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leniger, T.; Isbruch, K.; von den Driesch, S.; Diener, H.C.; Hufnagel, A. Seizure-associated headache in epilepsy. Epilepsia 2001, 42, 1176–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yankovsky, A.E.; Andermann, F.; Bernasconi, A. Characteristics of headache associated with intractable partial epilepsy. Epilepsia 2005, 46, 1241–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprara, F.; Letícia, A.; Rissardo, J.P.; Leite, M.T.B.; Silveira, J.O.F.; Jauris, P.G.M.; Arend, J.; Kegler, A.; Royes, F.; Fernando, L.; et al. Characteristics of Post-Ictal Headaches in Patients with Epilepsy: A Longitudinal Study. Seizure 2020, 81, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodore, W.H.; Spencer, S.S.; Wiebe, S.; Langfitt, J.T.; Ali, A.; Shafer, P.O.; Berg, A.T.; Vickrey, B.G. Epilepsy in North America: A report prepared under the auspices of the global campaign against epilepsy, the International Bureau for Epilepsy, the International League Against Epilepsy, and the World Health Organization. Epilepsia 2006, 47, 1700–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanstraten, A.F.; Ng, Y.T. What is the worst part about having epilepsy? A children’s and parents’ perspective. Pediatr. Neurol. 2012, 47, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moeijes, J.; van Busschbach, J.T.; Bosscher, R.J.; Twisk, J.W.R. Sports participation and health-related quality of life: A longitudinal observational study in children. Qual. Life Res. 2019, 28, 2453–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkson, J. Limitations of the application of fourfold table analysis to hospital data. Biometrics 1946, 2, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cianchetti, C.; Bianchi, E.; Guerrini, R.; Baglietto, M.G.; Briguglio, M.; Cappelletti, S.; Casellato, S.; Crichiutti, G.; Lualdi, R.; Margari, L.; et al. Symptoms of anxiety and depression and family’s quality of life in children and adolescents with epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2018, 79, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| All Patients with Epilepsy | Patients with Epilepsy and Primary Headache | |
|---|---|---|
| N= | 119 | 46 |
| Age, y (mean ± SD) | 11.5 ± 3.1 | 11.3 ± 3.2 |
| Sex (female/male) | 59/60 | 29/17 |
| Epilepsy duration, y (mean ± SD) | 3.9 ± 3.5 | 4.6 ± 4.3 |
| Types of epilepsy, n (%) | ||
| Focal | 39 (32.8%) | 13 (28.3%) |
| Generalized | 56 (47.0%) | 24 (52.1%) |
| Combined focal and generalized | 11 (9.3%) | 5 (10.9%) |
| Unknown | 13 (10.9%) | 4 (8.7%) |
| Etiology | ||
| Genetic | 95 (79.8%) | 35 (76.1%) |
| Structural | 12 (10.1%) | 6 (13.0%) |
| Unknown | 12 (10.1%) | 5 (10.9%) |
| Antiseizure medication, n (%) | ||
| Monotherapy | 63 (52.9%) | 24 (52.2%) |
| Polytherapy | 29 (24.4%) | 14 (30.4%) |
| No medication | 27 (22.7%) | 8 (17.4%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schiller, K.; Schiller, V.; Kortas, A.; Unterholzner, G.; Raffler, S.; Schimmel, M.; Rauchenzauner, M. Primary Headache Is Related to Reduced Health-Related Quality of Life in Children with Epilepsy. Healthcare 2024, 12, 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12040426
Schiller K, Schiller V, Kortas A, Unterholzner G, Raffler S, Schimmel M, Rauchenzauner M. Primary Headache Is Related to Reduced Health-Related Quality of Life in Children with Epilepsy. Healthcare. 2024; 12(4):426. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12040426
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchiller, Katharina, Veronika Schiller, Aline Kortas, Gabriele Unterholzner, Sabine Raffler, Mareike Schimmel, and Markus Rauchenzauner. 2024. "Primary Headache Is Related to Reduced Health-Related Quality of Life in Children with Epilepsy" Healthcare 12, no. 4: 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12040426
APA StyleSchiller, K., Schiller, V., Kortas, A., Unterholzner, G., Raffler, S., Schimmel, M., & Rauchenzauner, M. (2024). Primary Headache Is Related to Reduced Health-Related Quality of Life in Children with Epilepsy. Healthcare, 12(4), 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12040426


_MD__MPH_PhD.png)



