Cross-Cultural Adaptation and Psychometric Properties of the Chinese Version of the Knee Osteoarthritis Fears and Beliefs Questionnaire
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Sample Size Estimation
2.3. Development of Chinese KOFBeQ
2.4. Test Procedure
2.5. Data Analysis
2.5.1. Factor Analysis
2.5.2. Internal Consistency
2.5.3. Convergent Validity
2.5.4. Test–Retest Reliability
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
3.2. Validity of Chinese KOFBeQ
3.2.1. Data Completeness
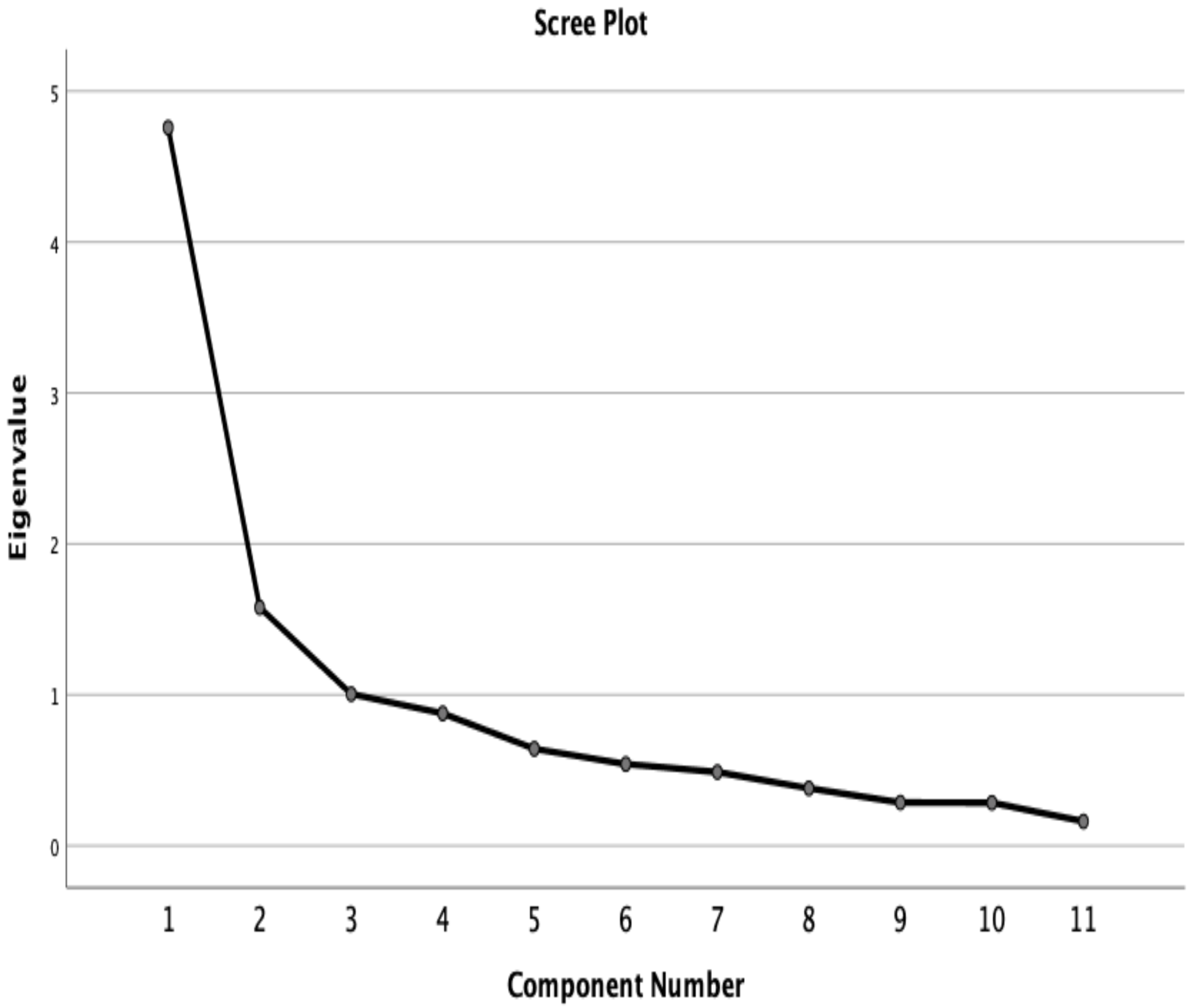
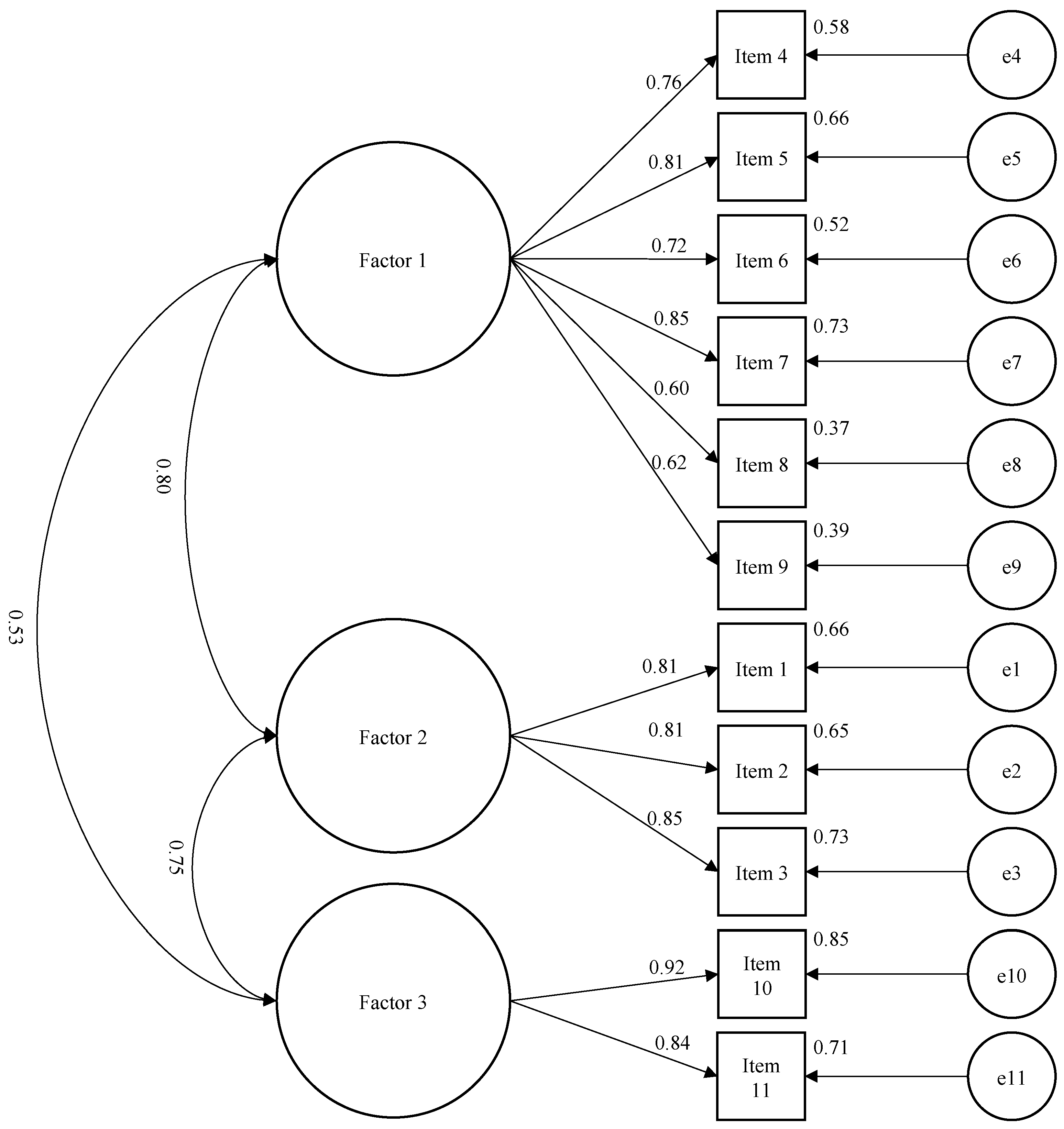
3.2.2. Factor Analysis
3.2.3. Internal Consistency
3.2.4. Convergent Validity
3.2.5. Test–Retest Reliability
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OA | Osteoarthritis |
| KOFBeQ | The Knee Osteoarthritis Fears and Beliefs Questionnaire |
| ADLs | Daily Living Activities |
| EFA | Exploratory Factor Analysis |
| CFA | Confirmatory Factor Analysis |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| WOMAC | the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities OA index |
| KOOS | the Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score |
| IPAQ | the International Physical Activity Questionnaire short form |
| METs | multiples of the resting metabolic rate |
| PCA | principal component analysis |
| GFI | Goodness of Fit Index |
| IFI | Incremental Fit Index |
| CFI | the Comparative Fit Index |
| RMSEA | Root Mean Square Error of Approximation |
| Chi-square | |
| df | degree of freedom |
| ICC | The Intraclass Correlation Coefficient |
| LoA | The limits of agreement |
| MD | The Mean of Difference |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| SE | Standard Error |
| SEM | Standard Error of Measurement |
| SDC90 | The Smallest Detectable Change at 90% confidence interval |
| IQR | interquartile range |
References
- McAlindon, T.; Cooper, C.; Kirwan, J.; Dieppe, P. Knee pain and disability in the community. Rheumatology 1992, 31, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, A.; Li, H.; Wang, D.; Zhong, J.; Chen, Y.; Lu, H. Global, regional prevalence, incidence and risk factors of knee osteoarthritis in population-based studies. EClinicalMedicine 2020, 29, 100587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World-Health-Organization. MS Windows NT China Country Assessment Report on Ageing and Health. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241509312 (accessed on 16 February 2015).
- Mora, J.C.; Przkora, R.; Cruz-Almeida, Y. Knee osteoarthritis: Pathophysiology and current treatment modalities. J. Pain Res. 2018, 2018, 2189–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benhamou, M.; Baron, G.; Dalichampt, M.; Boutron, I.; Alami, S.; Rannou, F.; Ravaud, P.; Poiraudeau, S. Development and validation of a questionnaire assessing fears and beliefs of patients with knee osteoarthritis: The Knee Osteoarthritis Fears and Beliefs Questionnaire (KOFBeQ). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boersma, K.; Linton, S.J. Psychological processes underlying the development of a chronic pain problem: A prospective study of the relationship between profiles of psychological variables in the fear-avoidance model and disability. Clin. J. Pain 2006, 22, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rainville, J.; Smeets, R.J.; Bendix, T.; Tveito, T.H.; Poiraudeau, S.; Indahl, A.J. Fear-avoidance beliefs and pain avoidance in low back pain—translating research into clinical practice. Spine J. 2011, 11, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, L.; Xia, J.; Yan, J. Cross-cultural adaptation, reliability and validity of the Chinese version of the Fear Avoidance Beliefs Questionnaire. J. Int. Med Res. 2010, 38, 1985–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, C.; Guiguet-Auclair, C.; Mourgues, C.; Gerbaud, L.; Coudeyre, E. Physical activity level and association with behavioral factors in knee osteoarthritis. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2019, 62, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raud, B.; Gay, C.; Guiguet-Auclair, C.; Bonnin, A.; Gerbaud, L.; Pereira, B.; Duclos, M.; Boirie, Y.; Coudeyre, E. Level of obesity is directly associated with the clinical and functional consequences of knee osteoarthritis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S. Exploratory factor analysis with small sample sizes: A comparison of three approaches. Behav. Process. 2013, 97, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoukri, M.M.; Asyali, M.; Donner, A. Sample size requirements for the design of reliability study: Review and new results. Stat. Methods Med Res. 2004, 13, 251–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaton, D.E.; Bombardier, C.; Guillemin, F.; Ferraz, M.B. Guidelines for the process of cross-cultural adaptation of self-report measures. Spine 2000, 25, 3186–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symonds, T.; Hughes, B.; Liao, S.; Ang, Q.; Bellamy, N. Validation of the Chinese Western Ontario and McMaster universities osteoarthritis index in patients from mainland China with osteoarthritis of the knee. Arthritis Care Res. 2015, 67, 1553–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, R.T.; Ngai, S.P.; Ho, K.K. Chinese adaptation and validation of the Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (KOOS) in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Rheumatol. Int. 2016, 36, 1449–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macfarlane, D.J.; Lee, C.C.; Ho, E.Y.; Chan, K.L.; Chan, D.T. Reliability and validity of the Chinese version of IPAQ (short, last 7 days). J. Sci. Med. Sport 2007, 10, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinno, A. Exploring the sensitivity of Horn’s parallel analysis to the distributional form of random data. Multivar. Behav. Res. 2009, 44, 362–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Statistics notes: Cronbach’s alpha. BMJ 1997, 314, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, I. Sample size determination in test-retest and Cronbach alpha reliability estimates. Br. J. Contemp. Educ. 2022, 2, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware Jr, J.E.; Gandek, B. Methods for testing data quality, scaling assumptions, and reliability: The IQOLA Project approach. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1998, 51, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Measuring agreement in method comparison studies. Stat. Methods Med Res. 1999, 8, 135–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenaszchuk, C.; MacMillan, K.; van Soeren, M.; Reeves, S. Interprofessional simulated learning: Short-term associations between simulation and interprofessional collaboration. BMC Med. 2011, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjersing, L.; Caplehorn, J.R.; Clausen, T. Cross-cultural adaptation of research instruments: Language, setting, time and statistical considerations. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2010, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghebreyesus, T.A.; Fore, H.; Birtanov, Y.; Jakab, Z. Primary health care for the 21st century, universal health coverage, and the Sustainable Development Goals. Lancet 2018, 392, 1371–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, M.K. Strengthening primary care in Hong Kong: Fostering continuity of care from a health system perspective. Hong Kong Med. J. 2020, 26, 543–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayers, P.M.; Machin, D. Quality of Life: The Assessment, Analysis and Reporting of Patient-Reported Outcomes; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, I. Western ontario and mcMaster universities osteoarthritis index (WOMAC). Aust. J. Physiother. 2009, 55, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, E.M.; Lohmander, L.S. The Knee injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (KOOS): From joint injury to osteoarthritis. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2003, 1, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.H.; Macfarlane, D.J.; Lam, T.H.; Stewart, S.M. Validity of the international physical activity questionnaire short form (IPAQ-SF): A systematic review. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2011, 8, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| N | Mean (SD) or Median (IQR) or n (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Sociodemographic characteristics | ||
| Age (years) | 241 | 68.0 (7.8) |
| Female, n (%) | 241 | 190 (78.8) |
| Height (cm) | 241 | 156.8 (7.9) |
| Weight (kg) | 240 | 63.3 (12.2) |
| BMI (kg/cm2) | 240 | 25.8 (5.0) |
| IPAQ, median (IQR) | ||
| Total MET-min/week | 238 | 2056.5 (1053.0–4678.5) |
| Walking MET-min/week | 238 | 1368.0 (693–2772) |
| Moderate MET-min/week | 238 | 240.0 (0–740) |
| Vigorous MET-min/week | 238 | 0 (0–0) |
| Sitting hours/day | 238 | 4 (2–5) |
| Levels of physical activity, n (%) | ||
| Low | 28 (11.8) | |
| Moderate | 238 | 120 (50.4) |
| High | 90 (37.8) | |
| Medical status | ||
| Duration of knee OA (years) | 240 | 6.9 (5.4) |
| Side of knee OA, n (%) | ||
| Left | 43 (17.8) | |
| Right | 240 | 34 (14.1) |
| Both | 162 (67.2) | |
| Functional status | ||
| WOMAC pain | 240 | 8.0 (4.1) |
| WOMAC stiffness | 240 | 3.1 (1.7) |
| WOMAC function | 240 | 23.8 (13.3) |
| WOMAC global score | 240 | 34.9 (17.9) |
| KOOS symptom | 240 | 57.3 (20.2) |
| KOOS pain | 240 | 61.8 (19.8) |
| KOOS ADLs | 240 | 67.3 (20.4) |
| KOOS Sports&Recreation | 240 | 35.5 (27.7) |
| KOOS QoL | 240 | 44.4 (23.9) |
| Missing Values (%) | Mean (SD) | Median | Range | Floor Effect (%) | Ceiling Effect (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Items | ||||||
| Item 1 | 0 | - | 4 | 0–9 | 13.3 | 19.5 |
| Item 2 | 0 | - | 3 | 0–9 | 22.8 | 9.5 |
| Item 3 | 0 | - | 5 | 0–9 | 7.9 | 22.8 |
| Item 4 | 0 | - | 4 | 0–9 | 13.3 | 15.8 |
| Item 5 | 0 | - | 5 | 0–9 | 7.5 | 17.4 |
| Item 6 | 0 | - | 5 | 0–9 | 15.8 | 23.2 |
| Item 7 | 0 | - | 4 | 0–9 | 17.0 | 13.3 |
| Item 8 | 0 | - | 4 | 0–9 | 22.0 | 12.0 |
| Item 9 | 0 | - | 4 | 0–9 | 15.8 | 12.0 |
| Item 10 | 0 | - | 4 | 0–9 | 22.4 | 25.3 |
| Item 11 | 0 | - | 3 | 0–9 | 27.0 | 12.4 |
| Subscales | ||||||
| Physicians & Disease | 0 | 13.1 (7.8) | 13 | 0–54 | 2.1 | 1.7 |
| ADLs | 0 | 26.9 (12.6) | 26 | 0–27 | 6.2 | 6.6 |
| Sports | 0 | 8.1 (6.2) | 8 | 0–18 | 19.1 | 10.8 |
| Global score | 0 | 48.1 (21.7) | 46 | 0–99 | 0.4 | 1.2 |
| Variable | Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Factor 1 (Physicians and Disease) | |||
| Item 7 | 0.744 | ||
| Item 5 | 0.733 | ||
| Item 4 | 0.703 | ||
| Item 6 | 0.636 | ||
| Item 8 | 0.606 | ||
| Item 9 | 0.579 | ||
| Factor 2 (ADLs) | |||
| Item 1 | 0.899 | ||
| Item 3 | 0.810 | ||
| Item 2 | 0.682 | 0.446 | |
| Factor 3 (Sports) | |||
| Item 10 | 0.869 | ||
| Item 11 | 0.856 | ||
| Scale Mean If Item Deleted | Scale Variance If Item Deleted | Corrected Item-Total Correlation | Squared Multiple Correlation | Cronbach’s If Item Deleted | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item 1 | 46.4398 | 398.281 | 0.529 | 0.556 | 0.847 |
| Item 2 | 45.2697 | 392.373 | 0.604 | 0.487 | 0.841 |
| Item 3 | 47.0041 | 388.212 | 0.634 | 0.594 | 0.839 |
| Item 4 | 46.4315 | 402.396 | 0.517 | 0.418 | 0.848 |
| Item 5 | 47.0249 | 406.308 | 0.521 | 0.453 | 0.847 |
| Item 6 | 46.8423 | 396.392 | 0.503 | 0.367 | 0.849 |
| Item 7 | 46.0041 | 407.654 | 0.460 | 0.353 | 0.852 |
| Item 8 | 45.7095 | 400.340 | 0.508 | 0.477 | 0.848 |
| Item 9 | 46.0000 | 390.558 | 0.611 | 0.552 | 0.841 |
| Item 10 | 46.3776 | 379.369 | 0.601 | 0.634 | 0.841 |
| Item 11 | 45.4440 | 393.673 | 0.537 | 0.592 | 0.846 |
| KOFBeQ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physicians and Disease | ADLs | Sports | Global Score | |
| Correlation of the subscales and global scores of the KOFBeQ with the other knee-related scores | ||||
| WOMAC pain | 0.223 † | 0.465 † | 0.353 † | 0.408 † |
| WOMAC stiffness | 0.188 † | 0.385 † | 0.328 † | 0.342 † |
| WOMAC physical function | 0.223 † | 0.439 † | 0.325 † | 0.394 † |
| WOMAC total score | 0.230 † | 0.465 † | 0.343 † | 0.412 † |
| KOOS symptom | −0.183 † | −0.383 † | −0.317 † | −0.336 † |
| KOOS pain | −0.186 † | −0.496 † | −0.339 † | −0.394 † |
| KOOS ADLs | −0.219 † | −0.482 † | −0.350 † | −0.416 † |
| KOOS Sports & Recreation | −0.179 † | −0.449 † | −0.327 † | −0.367 † |
| KOOS QoL | −0.147 * | −0.419 † | −0.309 † | −0.336 † |
| Comparing the scores of KOFBeQ across levels of physical activity | ||||
| Low | 27.46 (12.34) | 15.86 (7.99) | 9.96 (6.77) | 53.29 (21.51) |
| Moderate | 27.69 (12.53) | 13.20 (7.39) | 8.44 (6.30) | 49.33 (21.65) |
| High | 26.40 (12.37) | 12.46 (8.21) | 7.27 (5.81) | 46.12 (21.24) |
| p-value | 0.696 | 0.127 | 0.122 | 0.246 |
| N | Mean at Baseline (SD) | Mean at 2nd Time (SD) | Mean Difference (SD) | ICC2,1 (95%CI) | SEM | SDC90 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global score | 59 | 51.5 (24.8) | 50.0 (21.4) | −1.4 (12.2) | 0.93 (0.88, 0.96) | 3.2 | 7.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, S.; Yu, C.C.-W.; Cheing, G.L.-Y.; Chung, R.C.-K.; Tsang, S.M.-H.; Chan, L.-L.; Tang, T.W.-S.; Cheung, W.; Lee, Q.J.; Kwong, P.W.-H. Cross-Cultural Adaptation and Psychometric Properties of the Chinese Version of the Knee Osteoarthritis Fears and Beliefs Questionnaire. Healthcare 2024, 12, 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12030310
Su S, Yu CC-W, Cheing GL-Y, Chung RC-K, Tsang SM-H, Chan L-L, Tang TW-S, Cheung W, Lee QJ, Kwong PW-H. Cross-Cultural Adaptation and Psychometric Properties of the Chinese Version of the Knee Osteoarthritis Fears and Beliefs Questionnaire. Healthcare. 2024; 12(3):310. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12030310
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Shan, Clare Chung-Wah Yu, Gladys Lai-Ying Cheing, Raymond Chi-Keung Chung, Sharon Man-Ha Tsang, Lok-Lok Chan, Tracy Wing-Shan Tang, Winky Cheung, Qunn Jid Lee, and Patrick Wai-Hang Kwong. 2024. "Cross-Cultural Adaptation and Psychometric Properties of the Chinese Version of the Knee Osteoarthritis Fears and Beliefs Questionnaire" Healthcare 12, no. 3: 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12030310
APA StyleSu, S., Yu, C. C.-W., Cheing, G. L.-Y., Chung, R. C.-K., Tsang, S. M.-H., Chan, L.-L., Tang, T. W.-S., Cheung, W., Lee, Q. J., & Kwong, P. W.-H. (2024). Cross-Cultural Adaptation and Psychometric Properties of the Chinese Version of the Knee Osteoarthritis Fears and Beliefs Questionnaire. Healthcare, 12(3), 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12030310







