A Study on the Effectiveness of VR Rehabilitation Training Content for Older Individuals with Total Knee Replacement: Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
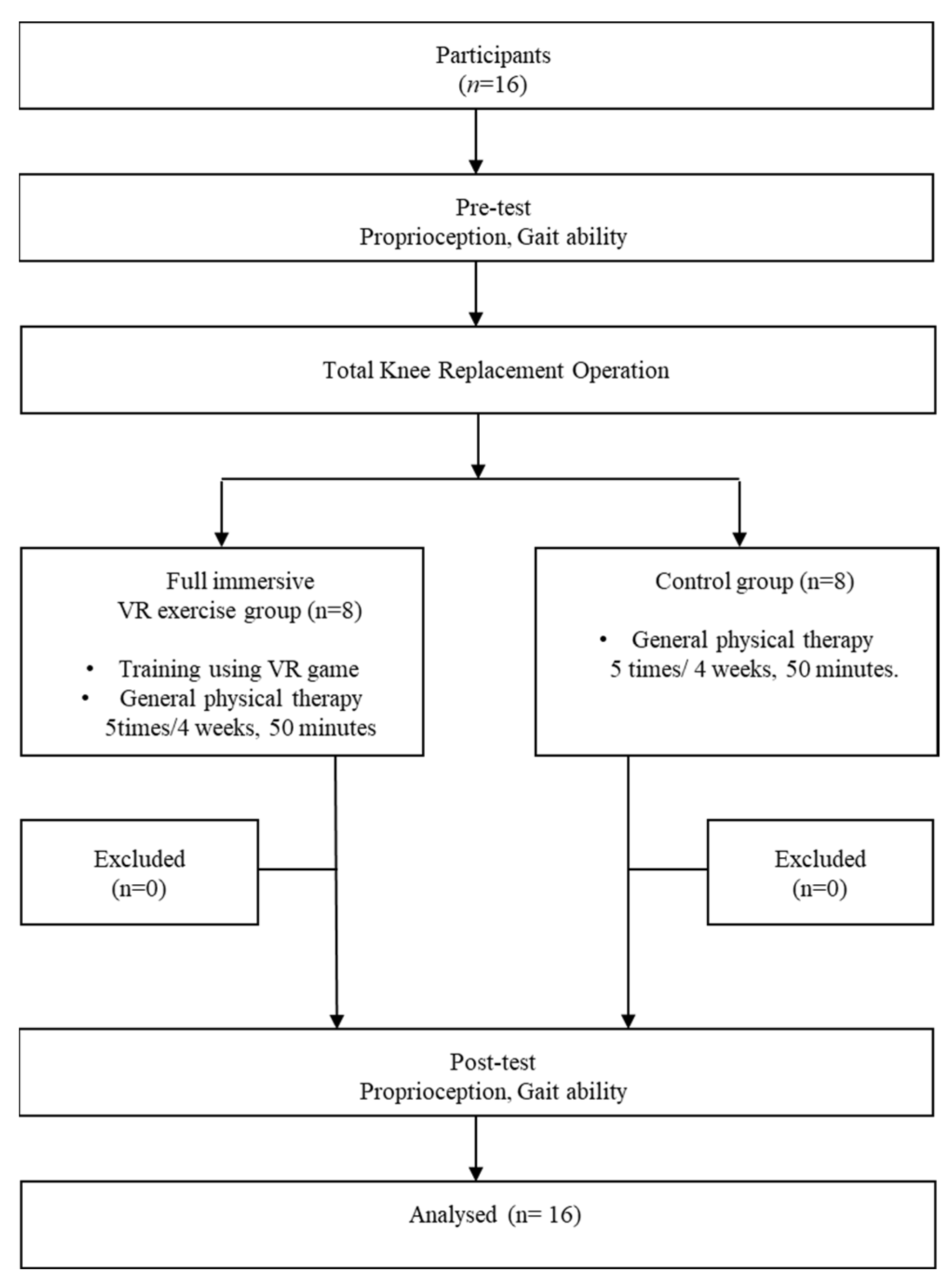
2.1. Participants
2.2. Research Procedures
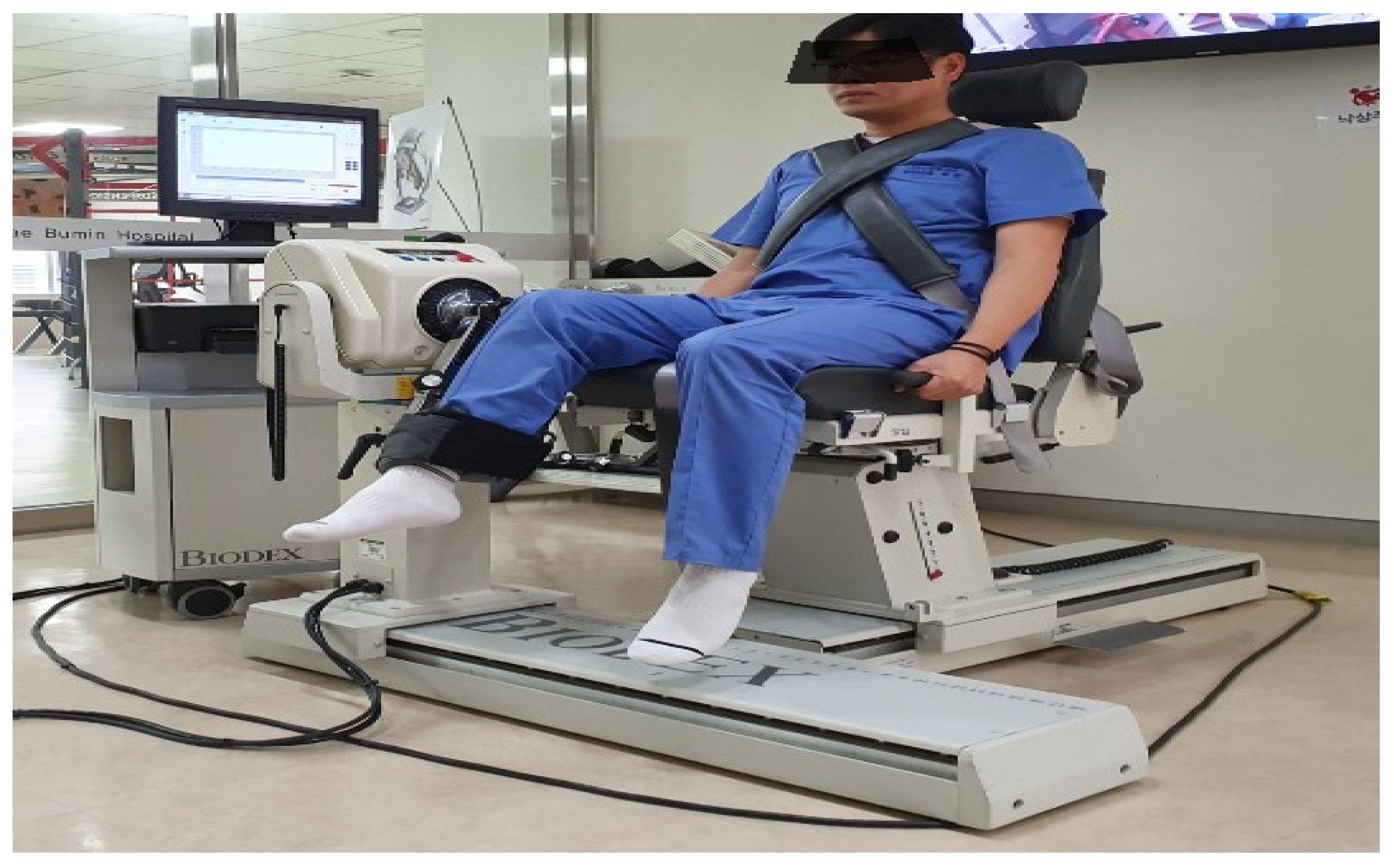
2.3. Proprioception
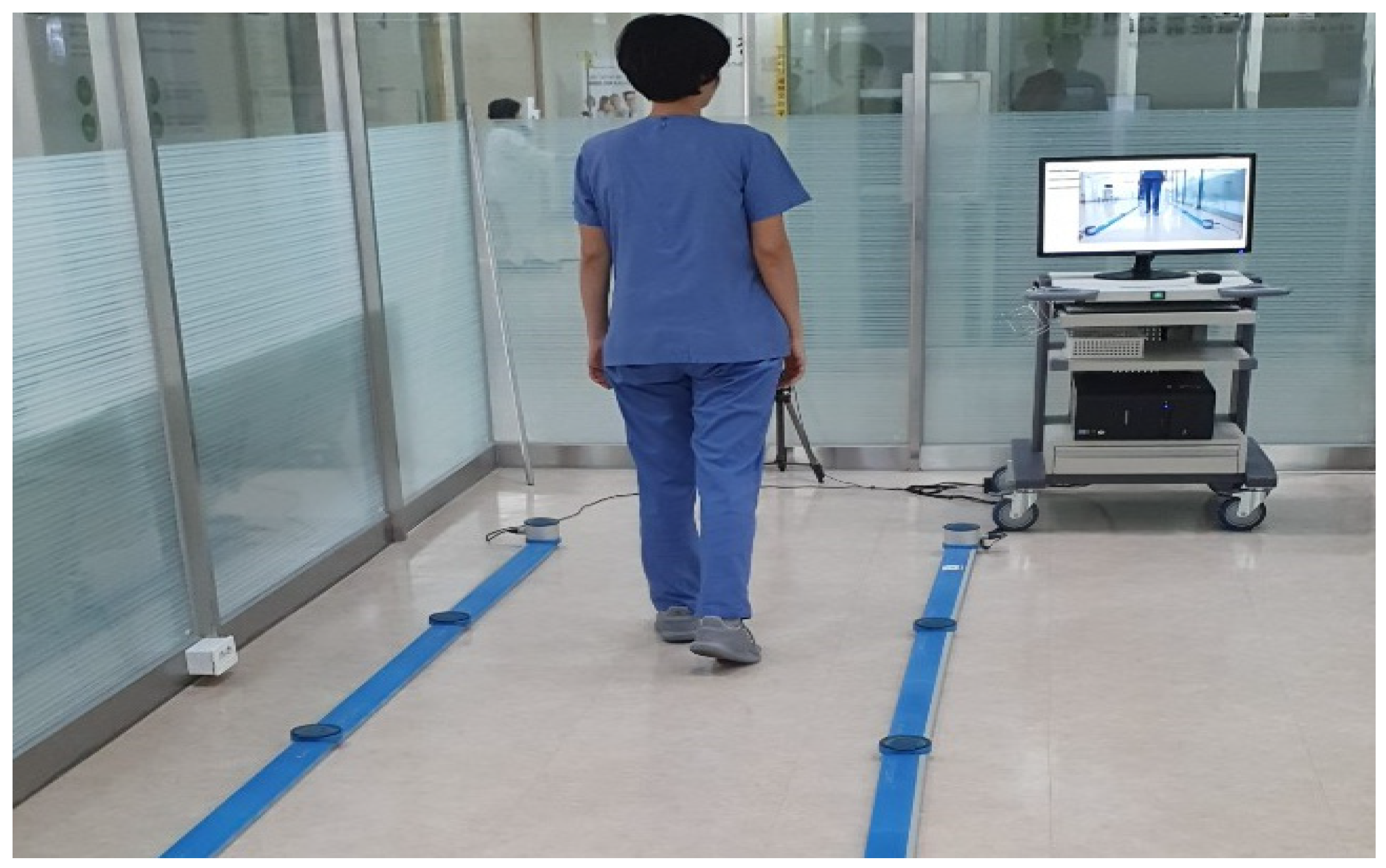
2.4. Gait Ability
2.5. Training Using a Fully Immersive VR Game
2.6. Conventional Physical Therapy
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yoon, J.D.; Lee, J.N. The effects of ankle mobilization with movements on the ankle range of motion, balance, and gait of patients after total knee arthroplasty. J. Korean Acad. Orthop. Man. Ther. 2021, 27, 51–62. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Xue, Z.; Sun, J.; Jia, Z.; Fu, F.; Zhao, Y.; Song, M.; Ye, H.; Wang, C. Traditional Chinese Patent medicine for knee osteoarthritis pain: Systematic review. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2020, 28, S150–S151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baliunas, A.J.; Hurwitz, D.E.; Ryals, A.B.; Karrar, A.; Case, J.P.; Block, J.A.; Andriacchi, T.P. Increased knee joint loads during walking are present in subjects with knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2002, 10, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manetta, J.; Franx, L.H.; Moon, C. Comparison of hip and knee muscle moments in subjects with and without knee pain. Gait Posture 2002, 16, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, G.H.; Kim, T.W.; Song, H.B. Effect of knee stabilization exercise on balance and walking ability in patients with total knee replacement. J. Korean Acad. Orthop. Man. Ther. 2021, 27, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Min, D.; Lee, S. The effect of an exercise program with patella mobilization on range of motion, muscle strength and gait in patients with total knee arthroplasty. J. Korean Soc. Integr. Med. 2020, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.H.; Kang, T.W.; Kim, B.R. The effect of proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation exercise on the range of motion, pain, and functional activity of total knee arthroplasty patients. PNF Mov. 2018, 16, 75–83. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, J.; Jung, B.C.; Yu, K.T. The effects of active exercise program using sling on the pain and balance following total knee replacement. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Technol. 2022, 12, 174–183. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.J. The Effects of Exercise Program on Pain and Balance ability in Patients with total knee replacement: Meta-analysis. Korean J. Comp. Inf. 2021, 26, 119–126. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.O.; Lee, J.S. Utilization exercise rehabilitation using metaverse (VR·AR·MR·XR). Korean J. Sport Biomech. 2021, 31, 249–258. [Google Scholar]
- Ceradini, M.; Losanno, E.; Micera, S.; Bandini, A.; Orlandi, S. Immersive VR for upper-extremity rehabilitation in patients with neurological disorders: A scoping review. J. NeuroEngineering Rehabil. 2024, 21, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.G.; Kim, E.K.; Kim, Y.N.; Kim, Y.S.; Hwang, T.Y. Effects of a VR training program on balance and lower muscular strength of Parkinson’s disease patients. J. Korean Phys. Ther. 2013, 25, 96–102. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, W.S.; Lee, S.M. Effects of rehabilitation exercise using VR on functional recovery in the persons with stroke. J. Spec. Educ. Rehabil. 2009, 48, 49–64. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.K.; Lee, G. Effects of an immersive VR environment on muscle strength, proprioception, balance, and gait of a middle-aged woman who had total knee replacement: A case report. Am. J. Case Rep. 2019, 20, 1636–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nooranida, A.; Noor, A.; Wan, A. Intrarater test-retest reliability of static and dynamic stability indexes measurement using the biodex stability system during unilateral stance. J. Appl. Biomech. 2013, 30, 300–304. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.M.; Song, C.H.; Lee, K.J.; Jung, S.W.; Shin, D.C.; Shin, S.H. Concurrent validity and test-retest reliability of the OPTOGait photoelectric cell system for the assessment of spatio-temporal parameters of the gait of young adults. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2014, 26, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, R.; Duarte, J.A.; Cabri, J.M. An acute bout of quadriceps muscle stretching has no influence on knee joint proprioception. J. Hum. Kinet. 2012, 34, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinner, H.B.; Barrack, R.L.; Cook, S.D. Age-related decline in proprioception. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1984, 184, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizner, R.L.; Snyder-Mackler, L. Altered loading during walking and sit-to-stand is affected by quadriceps weakness after total knee arthroplasty. J. Orthop. Res. 2005, 23, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deblock-Bellamy, A.; Batcho, C.S.; Mercier, C.; Blanchette, A.K. Quantification of upper limb position sense using an exoskeleton and a VR display. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2018, 15, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewal, G.S.; Sayeed, R.; Schwenk, M.; Bharara, M.; Menzies, R.; Talal, T.K.; Armstrong, D.G.; Najafi, B. Balance rehabilitation: Promoting the role of VR in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 2013, 103, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramers-de Quervain, I.A.; Stüssi, E.; Müller, R.; Drobny, T.; Munzinger, U.; Gschwend, N. Quantitative gait analysis after bilateral total knee arthroplasty with two different systems within each subject. J. Arthroplast. 1997, 12, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedetti, M.G.; Catani, F.; Bilotta, T.W.; Marcacci, M.; Mariani, E.; Giannini, S. Muscle activation pattern and gait biomechanics after total knee replacement. Clin. Biomech. 2003, 18, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holden, J.P.; Chou, G.; Stanhope, S.J. Changes in knee joint function over a wide range of walking speeds. Clin. Biomech. 1997, 12, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamoth, C.J.; van Deudekom, F.J.; van Campen, J.P.; Appels, B.A.; de Vries, O.J.; Pijnappels, M. Gait stability and variability measures show effects of impaired cognition and dual tasking in frail people. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2011, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baram, Y.; Miller, A. VR cues for improvement of gait in patients with multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2006, 66, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamontagne, A.; Fung, J.; McFadyen, B.J.; Faubert, J. Modulation of walking speed by changing optic flow in persons with stroke. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2007, 4, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.R.; Tsai, M.P.; Chuang, T.Y.; Sung, W.H.; Wang, R.Y. VR-based training improves community ambulation in individuals with stroke: A randomized controlled trial. Gait Posture 2008, 28, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judge, J.O.; Schechtman, K.; Cress, E. The relationship between physical performance measures and independence in instrumental activities of daily living. The FICSIT Group. Frailty and injury: Cooperative studies of Intervention Trials. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1996, 44, 1332–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | Study Group (n = 8) | Control Group (n = 8) |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 66.00 ± 2.35 | 67.20 ± 2.39 |
| Height (cm) | 156.60 ± 8.02 | 152.80 ± 2.95 |
| Weight (kg) | 56.80 ± 5.54 | 65.80 ± 6.72 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.12 ± 0.75 | 28.29 ± 2.76 |
| Variables | Experimental Group (n = 8) | Control Group (n = 8) | t | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proprioception (°) | Pre | 4.58 ± 2.75 | 6.73 ± 2.86 | −1.530 |
| Post | 2.91 ± 1.51 | 4.83 ± 3.44 | ||
| Change | 1.66 ± 1.84 | 1.90 ± 2.95 | −1.930 | |
| t | 2.555 * | 1.819 |
| Variables | Experimental Group (n = 8) | Control Group (n = 8) | t | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gait velocity (m/s) | Pre | 0.87 ± 0.13 | 0.96 ± 0.15 | −1.351 |
| Post | 0.92 ± 0.13 | 0.89 ± 0.17 | ||
| Change | −0.05 ± 0.05 | 0.08 ± 0.04 | −5.305 ** | |
| t | −2.754 * | 5.123 ** | ||
| Cadence (step/min) | Pre | 98.27 ± 11.03 | 102.45 ± 16.67 | −0.591 |
| Post | 103.39 ± 8.38 | 99.00 ± 18.27 | ||
| Change | −5.11 ± 3.54 | 3.45 ± 4.67 | −4.134 ** | |
| t | −4.087 ** | 2.090 | ||
| Step length (cm) | Pre | 47.44 ± 5.65 | 50.30 ± 3.39 | −1.229 |
| Post | 50.19 ± 3.63 | 48.55 ± 3.20 | ||
| Change | −2.75 ± 2.75 | 1.75 ± 1.50 | −4.067 ** | |
| t | −2.829 ** | 3.309 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, D.; Hong, S. A Study on the Effectiveness of VR Rehabilitation Training Content for Older Individuals with Total Knee Replacement: Pilot Study. Healthcare 2024, 12, 1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12151500
Shin D, Hong S. A Study on the Effectiveness of VR Rehabilitation Training Content for Older Individuals with Total Knee Replacement: Pilot Study. Healthcare. 2024; 12(15):1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12151500
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, DooChul, and SoungKyun Hong. 2024. "A Study on the Effectiveness of VR Rehabilitation Training Content for Older Individuals with Total Knee Replacement: Pilot Study" Healthcare 12, no. 15: 1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12151500
APA StyleShin, D., & Hong, S. (2024). A Study on the Effectiveness of VR Rehabilitation Training Content for Older Individuals with Total Knee Replacement: Pilot Study. Healthcare, 12(15), 1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12151500





