Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Unhealthy Lifestyle in Adolescence: Unforeseen Role of Allostatic Overload and Psychological Well-Being
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
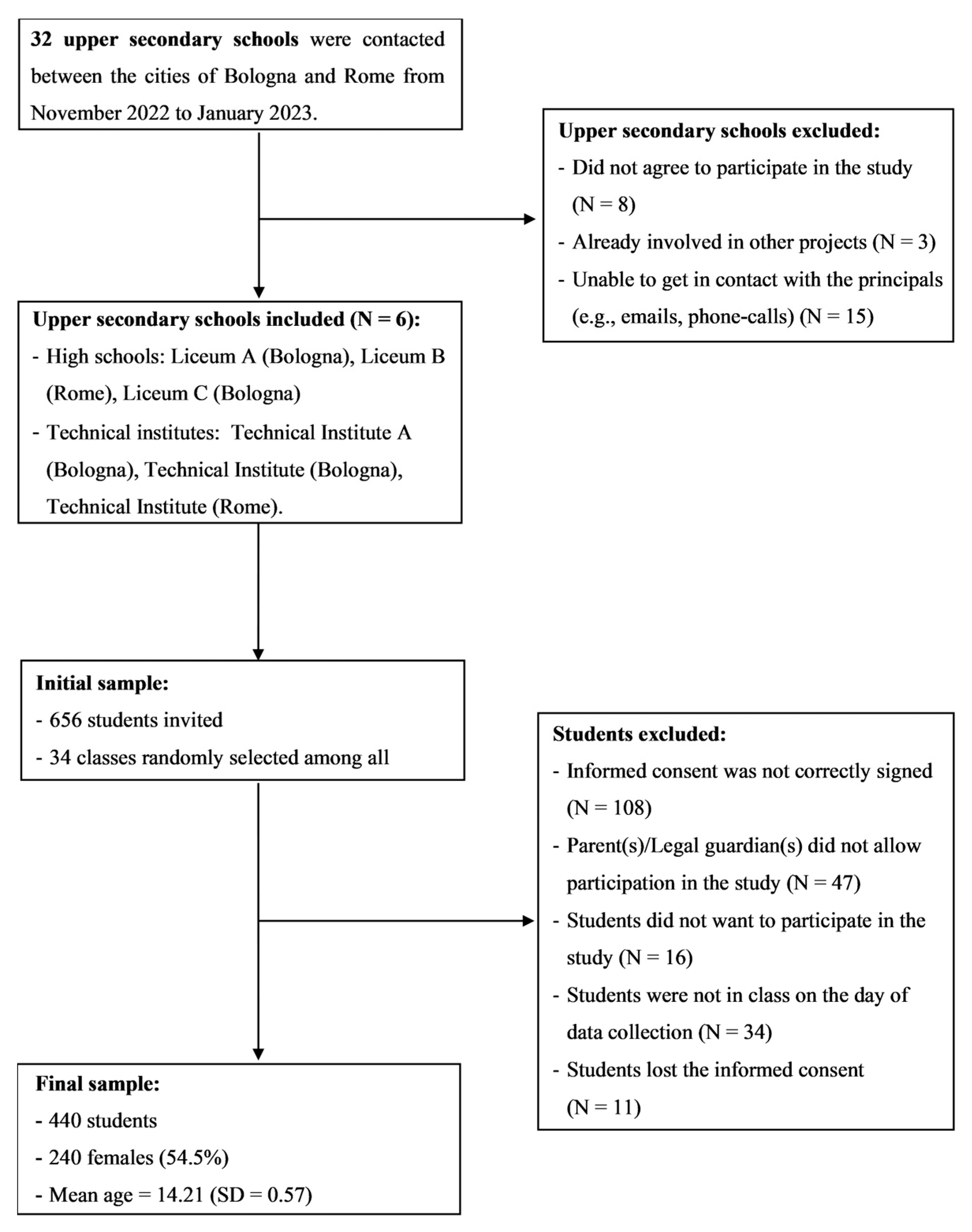
2.1. Design and Procedures
2.2. Sample
2.3. Assessment Instruments
2.3.1. ULBs
2.3.2. ADHD
2.3.3. Psychosocial Factors
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Substances Use
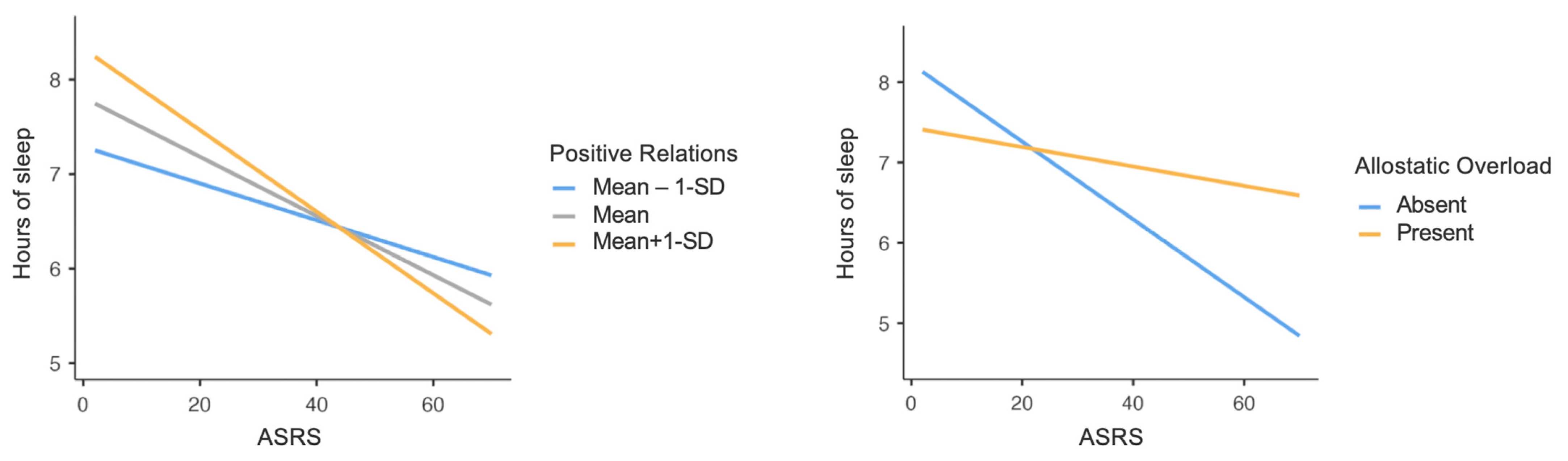
3.2. Sleep
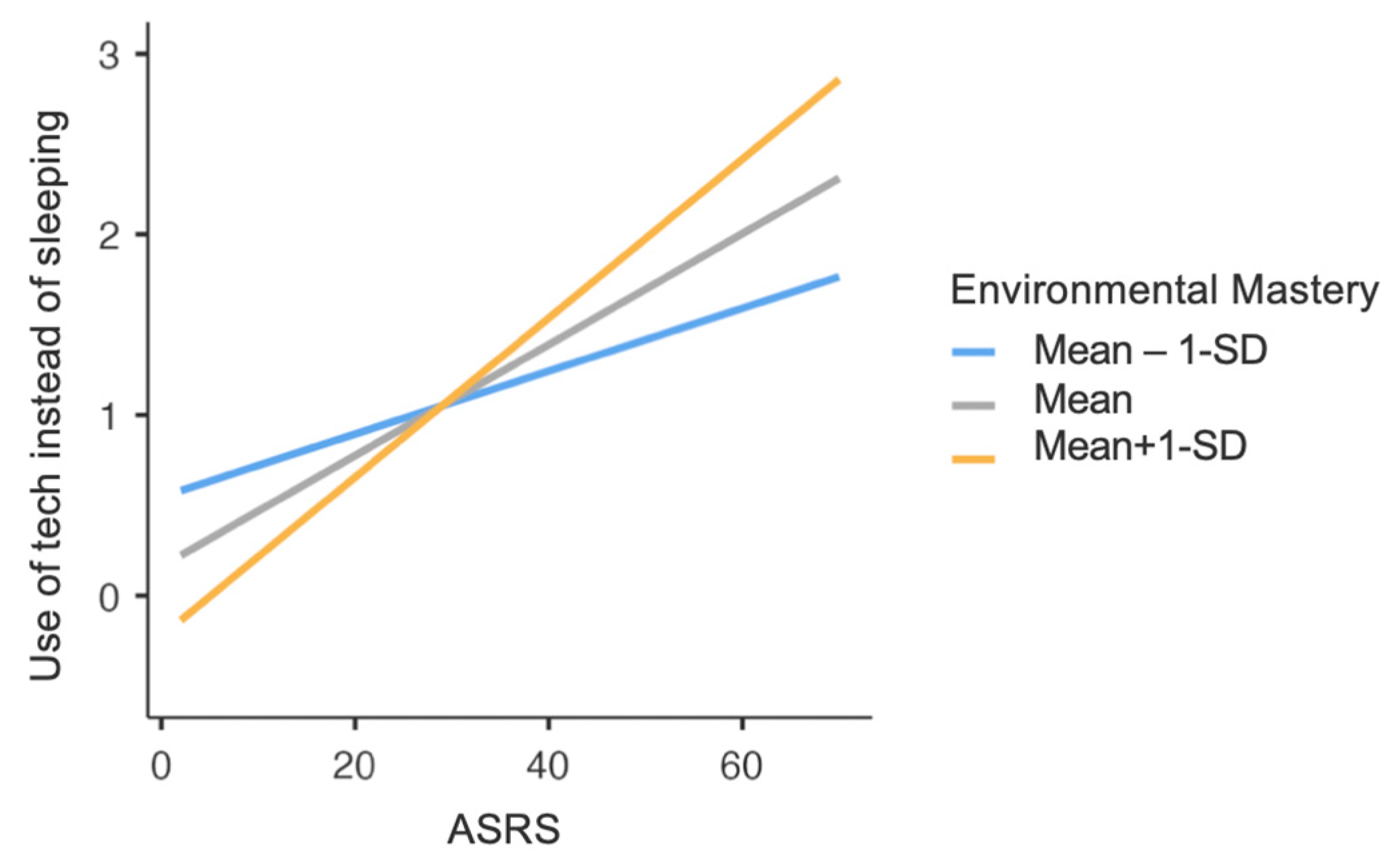
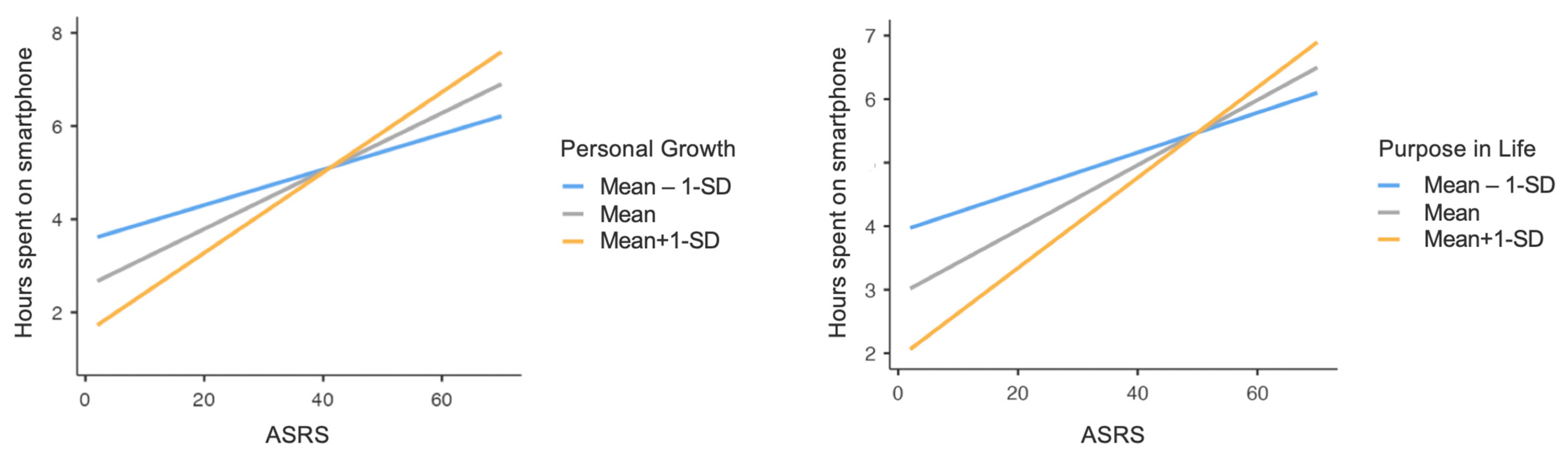
3.3. Technological Devices Use
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| ASRS Total Score | IAT Compromised Time Control | PWBs Self-Acceptance | PWBs Environmental Mastery | PWBs Personal Growth | PWBs Positive Relations | PWBs Purpose in Life | Daily Hours Spent on Smartphone | Daily Hours Spent on PC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASRS total score | - | ||||||||
| IAT Compromised Time Control | 0.382 ** | - | |||||||
| PWBs Self-Acceptance | −0.306 ** | −0.174 ** | - | ||||||
| PWBs Environmental mastery | −0.442 ** | −0.367 ** | 0.443 ** | - | |||||
| PWBs Personal growth | −0.102 * | −0.002 | 0.371 ** | 0.077 | - | ||||
| PWBs Positive relations | −0.239 ** | −0.124 ** | 0.506 ** | 0.341 ** | 0.254 ** | - | |||
| PWBs Purpose in life | −0.315 ** | −0.207 ** | 0.411 ** | 0.466 ** | 0.371 ** | 0.291 ** | - | ||
| Daily hours spent on smartphone | 0.263 ** | 0.228 ** | −0.190 ** | −0.241 ** | −0.126 ** | −0.103 * | −0.235 ** | - | |
| Daily hours spent on PC | 0.075 | −0.007 | 0.005 | −0.002 | −0.042 | 0.016 | −0.007 | 0.134 ** | - |
| Daily hours spent using technological devices instead of sleeping | 0.237 ** | 0.177 ** | −0.147 ** | −0.100 * | −0.189 ** | −0.063 | −0.251 ** | 0.340 ** | 0.147 ** |
References
- Marttila-Tornio, K.; Ruotsalainen, H.; Miettunen, J.; Männikkö, N.; Kääriäinen, M. Association between psychosocial problems and unhealthy health behavior patterns among Finnish adolescents. Child. Psychiatry Hum. Dev. 2020, 51, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, M.B.; Walker, M.W.; Alexander, T.N.; Jordan, J.W.; Wagner, D.E. Why peer crowds matter: Incorporating youth subcultures and values in health education campaigns. Am. J. Public Health 2017, 107, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bener, A.; Yildirim, E.; Torun, P.; Çatan, F.; Bolat, E.; Alıç, S.; Akyel, S.; Griffiths, M.D. Internet addiction, fatigue, and sleep problems among adolescent students: A large-scale study. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2019, 17, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firth, J.; Solmi, M.; Wootton, R.E.; Vancampfort, D.; Schuch, F.B.; Hoare, E.; Gilbody, S.; Torous, J.; Teasdale, S.B.; Jackson, S.E.; et al. A meta-review of “lifestyle psychiatry”: The role of exercise, smoking, diet and sleep in the prevention and treatment of mental disorders. World Psychiatry 2020, 19, 360–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayne, S.L.; Virudachalam, S.; Fiks, A.G. Clustering of unhealthy behaviors in a nationally representative sample of US children and adolescents. Prev. Med. 2020, 130, 105892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kappes, C.; Stein, R.; Körner, A.; Merkenschlager, A.; Kiess, W. Stress, stress reduction and obesity in childhood and adolescence. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2023, 96, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holliday, E.; Gould, T.J. Nicotine, adolescence, and stress: A review of how stress can modulate the negative consequences of adolescent nicotine abuse. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 65, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.L.; Jordan, H.R.; Madson, M.B. The moderating effects of college stress on the relationship between protective behavioral strategies and alcohol outcomes. Subst. Use Misuse 2019, 54, 1845–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, J.G.; Allen, S.; Perlis, M.; Grandner, M.; Gardani, M.; Espie, C. Sleep reactivity and psychological health in normal sleepers: The moderating role of stress. PsyArXiv 2018, PPR334301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Jiang, S.; Chen, J. Academic expectation stress and online gaming disorder among Chinese adolescents: The mediating role of psychological distress and the moderating role of stress mindset. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 2024, 158, 107492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwen, B.S.; Stellar, E. Stress and the individual. Mechanisms leading to disease. Arch. Intern. Med. 1993, 153, 2093–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fava, G.A.; McEwen, B.S.; Guidi, J.; Gostoli, S.; Offidani, E.; Sonino, N. Clinical characterization of allostatic overload. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2019, 108, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryff, C.D. Happiness is everything, or is it? Explorations on the meaning of psychological well-being. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1989, 57, 1069–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gostoli, S.; Fantini, L.; Casadei, S.; De Angelis, V.A.; Rafanelli, C. Binge drinking in 14-year-old Italian students is correlated with low or high psychological well-being: A cross-sectional study. Drugs Educ. Prev. Policy 2021, 28, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Gostoli, S.; Benasi, G.; Patierno, C.; Petroni, M.L.; Nuccitelli, C.; Marchesini, G.; Fava, G.A.; Rafanelli, R. The role of psychological well-being in weight loss: New insights from a comprehensive lifestyle intervention. Int. J. Clin. Health Psychol. 2022, 22, 100279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šporčić, B.; Glavak-Tkalić, R. The moderating role of well-being in the relationship between gaming motivation and problematic gaming. Int. J. Gaming Comput.-Mediat. Simul. 2023, 15, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; Text Revision; American Psychiatric Association Publishing: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Stanton, K.; Watson, D. Adult ADHD: Associations with personality and other psychopathology. J. Psychopathol. Behav. Assess. 2016, 38, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antolini, G.; Colizzi, M. Where do neurodevelopmental disorders go? Casting the eye away from childhood towards adulthood. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reale, L.; Bonati, M. ADHD prevalence estimates in Italian children and adolescents: A methodological issue. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2018, 44, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollak, Y.; Dekkers, T.J.; Shoham, R.; Huizenga, H.M. Risk-taking behavior in attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): A review of potential underlying mechanisms and of interventions. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2019, 21, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marten, F.; Keuppens, L.; Baeyens, D.; Boyer, B.E.; Danckaerts, M.; Cortese, S.; Van der Oord, S. Sleep parameters and problems in adolescents with and without ADHD: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JCPP Adv. 2023, 3, e12151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocyigit, S.; Guzel, H.S.; Acikel, B.; Cetinkaya, M. Comparison of smartphone addiction level, temperament and character and parental attitudes of adolescents with and without attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2021, 19, 1372–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istituto Superiore di Sanità. A.U.D.I.T.-C Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (Italian Version). Available online: https://www.epicentro.iss.it/alcol/apd2014/scheda%20test%20audit%20c.pdf (accessed on 14 December 2022).
- Bush, K.; Kivlahan, D.R.; McDonell, M.B.; Fihn, S.D.; Bradley, K.A.; Ambulatory Care Quality Improvement Project (ACQUIP). The AUDIT alcohol consumption questions (AUDIT-C): An effective brief screening test for problem drinking. Arch. Intern. Med. 1998, 158, 1789–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronbach, L.J. Coefficient alpha and the internal structure of tests. Psychometrika 1951, 16, 297–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etter, J.F.; Duc, T.V.; Perneger, T.V. Validity of the Fagerstrom test for nicotine dependence and of the Heaviness of Smoking Index among relatively light smokers. Addiction 1999, 94, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiani, L.; Siciliano, V.; Curzio, O.; Luppi, C.; Gori, M.; Grassi, M.; Molinaro, S. Optimal scaling of the CAST and of SDS Scale in a national sample of adolescents. Addict. Behav. 2013, 38, 2060–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legleye, S.; Karila, L.; Beck, F.; Reynaud, M. Validation of the CAST, a general population Cannabis Abuse Screening Test. J. Subst. Use 2007, 12, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buysse, D.J.; Reynolds III, C.F.; Monk, T.H.; Berman, S.R.; Kupfer, D.J. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: A new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Res. 1989, 28, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraro, G.; Di Blasi, M.; D’Amico, A.; Caci, B. Internet Addiction Disorder: Un contributo di ricerca. Internet Addict. Disord. 2007, 2006/1, 7–25. [Google Scholar]
- Young, K.S. Internet addiction: The emergence of a new clinical disorder. CyberPsychology Behav. 1998, 3, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fioravanti, G.; Casale, S. Evaluation of the psychometric properties of the Italian Internet Addiction Test. Cyberpsychol Behav. Soc. Netw. 2015, 18, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somma, A.; Borroni, S.; Fossati, A. Construct validity and diagnostic accuracy of the Italian translation of the 18-Item World Health Organization Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale (ASRS-18) Italian translation in a sample of community-dwelling adolescents. Psychiatry Res. 2019, 273, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, R.C.; Adler, L.; Ames, M.; Demler, O.; Faraone, S.; Hiripi, E.; Howes, M.J.; Jin, R.; Secnik, K.; Spencer, T.; et al. The World Health Organization Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale (ASRS): A short screening scale for use in the general population. Psychol. Med. 2005, 35, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnby, K.; Skordas, K.; Olofsdotter, S.; Vadlin, S.; Nilsson, K.W.; Ramklint, M. Validation of the World Health Organization adult ADHD self-report scale for adolescents. Nord. J. Psychiat 2015, 69, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piolanti, A.; Offidani, E.; Guidi, J.; Gostoli, S.; Fava, G.A.; Sonino, N. Use of the psychosocial index: A sensitive tool in research and practice. Psychother. Psychosom. 2016, 85, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonino, N.; Fava, G.A. A simple instrument for assessing stress in clinical practice. Postgrad. Med. J. 1998, 74, 408–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirigatti, S.; Stefanile, C.; Giannetti, E.; Iani, L.; Penzo, I.; Mazzeschi, A. Assessment of factor structure of Ryff’s Psychological Well-Being Scales in Italian adolescents. Boll. Psicol. Appl. 2009, 56, 30–50. [Google Scholar]
- Casale, S.; Lecchi, S.; Fioravanti, G. The association between psychological well-being and problematic use of internet communicative services among young people. J. Psychol. 2015, 149, 480–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liga, F.; Lo Coco, A.; Musso, P.; Inguglia, C.; Costa, S.; Lo Cricchio, M.G.; Ingoglia, S. Parental psychological control, autonomy support and Italian emerging adult’s psychosocial wellbeing: A cluster analytic approach. Eur. J. Dev. Psychol. 2020, 17, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallucci, M. GAMLj: General Analyses for Linear Models. [Jamovi Module] (Version 2.6.6). 2019. Available online: https://gamlj.github.io/ (accessed on 2 May 2023).
- Jamovi Project. Jamovi (Version 2.3); 2022. Available online: https://www.jamovi.org./ (accessed on 2 May 2023).
- Lee, C.T.; McClernon, F.J.; Kollins, S.H.; Fuemmeler, B.F. Childhood ADHD symptoms and future illicit drug use: The role of adolescent cigarette use. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2018, 43, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, J.D.; Pelham, W.E.; Gnagy, E.M.; Shiffman, S.; Derefinko, K.J.; Molina, B.S.G. Cigarette smoking and ADHD: An examination of prognostically relevant smoking behaviors among adolescents and young adults. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2016, 30, 588–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, K.; Manza, P.; Tejeda, H.A.; Courville, A.B.; Volkow, N.D.; Joseph, P.V. Risk assessment of maladaptive behaviors in adolescents: Nutrition, screen time, prenatal exposure, childhood adversities-adolescent brain cognitive development study. J. Adolesc. Health 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urry, H.L.; Nitschke, J.B.; Dolski, I.; Jackson, D.C.; Dalton, K.M.; Mueller, C.J.; Rosenkranz, M.A.; Ryff, C.D.; Singer, B.H.; Davidson, R.J. Making a life worth living: Neural correlates of well-being. Psychol. Sci. 2004, 15, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaksson, J.; Nilsson, K.W.; Lindblad, F. The Pressure–Activation–Stress scale in relation to ADHD and cortisol. Eur. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2015, 24, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öster, C.; Ramklint, M.; Meyer, J.; Isaksson, J. How do adolescents with ADHD perceive and experience stress? An interview study. Nord. J. Psychiatry 2020, 74, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokeach, A.; Wiener, J. Friendship quality in adolescents with ADHD. J. Atten. Disord. 2020, 24, 1156–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heiman, T. An examination of peer relationships of children with and without attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Sch. Psychol. Int. 2005, 26, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smahel, D.; Brown, B.B.; Blinka, L. Associations between online friendship and Internet addiction among adolescents and emerging adults. Dev. Psychol. 2012, 48, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alimoradi, Z.; Lin, C.Y.; Broström, A.; Bülow, P.H.; Bajalan, Z.; Griffiths, M.D.; Ohayon, M.M.; Pakpour, A.H. Internet addiction and sleep problems: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep. Med. Rev. 2019, 47, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.G.; Park, J.; Kim, H.T.; Pan, Z.; Lee, Y.; McIntyre, R.S. The relationship between smartphone addiction and symptoms of depression, anxiety, and attention-deficit/hyperactivity in South Korean adolescents. Ann. Gen. Psychiatry 2019, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pironti, V.A.; Lai, M.C.; Müller, U.; Bullmore, E.T.; Sahakian, B.J. Personality traits in adults with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and their unaffected first-degree relatives. BJPsych Open 2016, 2, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fava, G.A. Well-Being Therapy: Treatment Manual and Clinical Applications; Karger Publishers: Basel, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Magen, H. The relations between executive functions, media multitasking and polychronicity. Comput. Human. Behav. 2017, 67, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fava, G.A.; Bech, P. The concept of euthymia. Psychother. Psychosom. 2016, 85, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
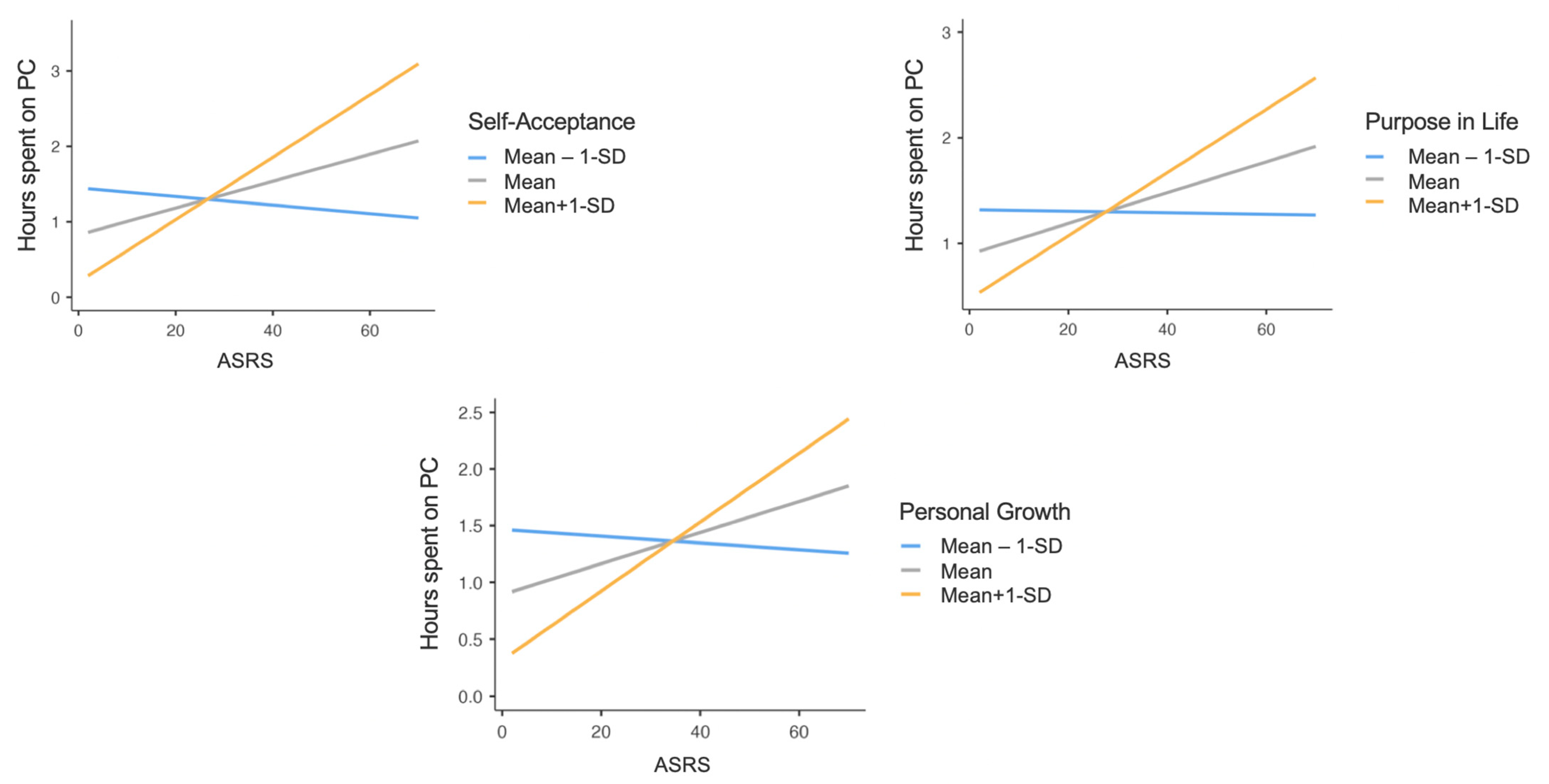
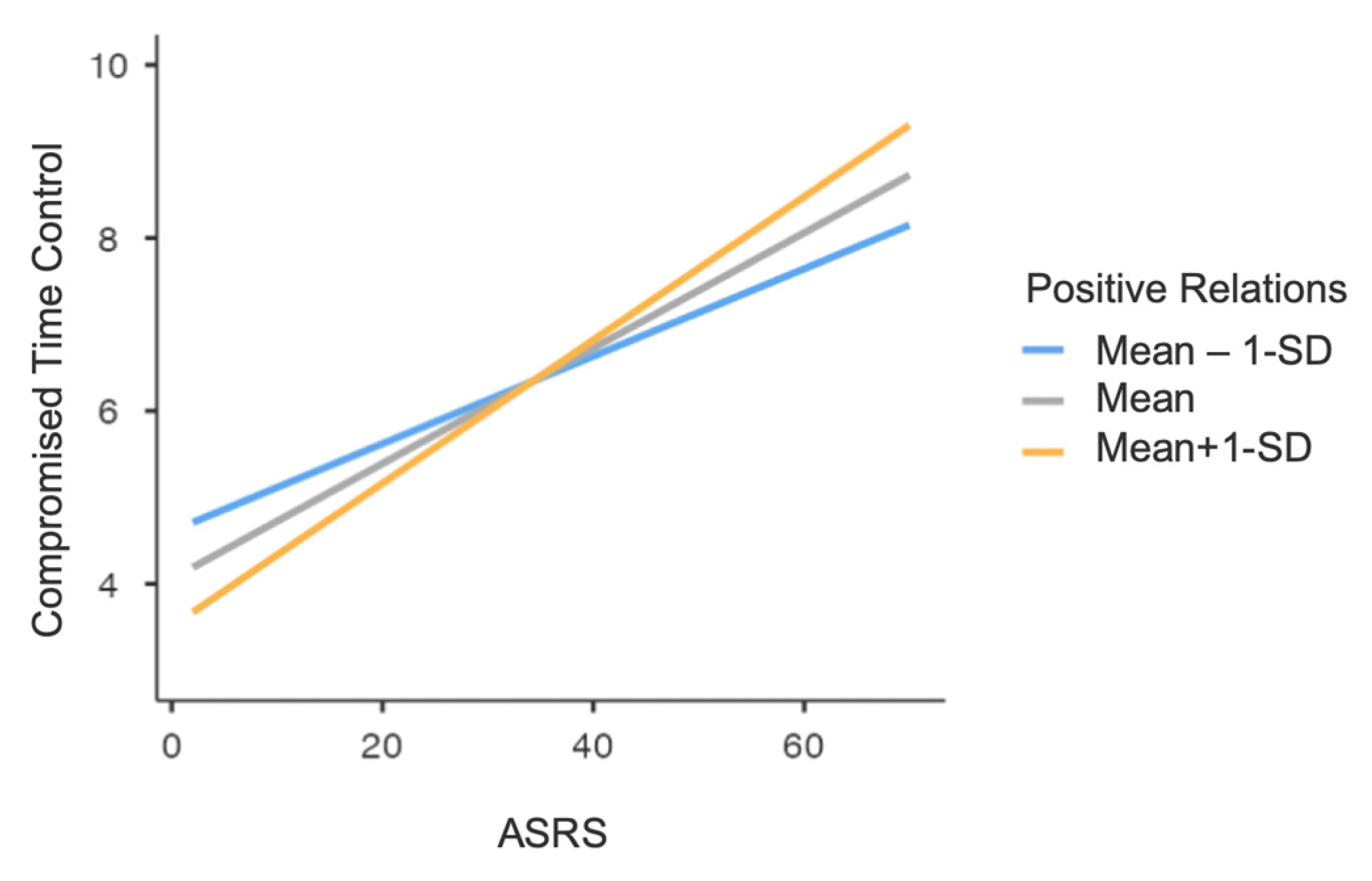
| Variables | N/Mean | %/(SD) |
|---|---|---|
| Biological sex (female) | 240 | 54.5% |
| Age | 14.21 | (0.57) |
| Nationality (Italian vs. other) | 399 | 90.7% |
| Mother’s level of education | ||
| Elementary/Middle school | 34 | 7.7% |
| High school | 173 | 39.3% |
| Bachelor degree or higher | 232 | 52.7% |
| Father’s level of education | ||
| Elementary/Middle school | 66 | 15% |
| High school | 193 | 43.9% |
| Bachelor degree or higher | 176 | 40% |
| Mother’s job status | ||
| Retired | 0 | 0% |
| Unemployed | 8 | 1.8% |
| Employed | 374 | 85% |
| Father’s job status | ||
| Retired | 6 | 1.4% |
| Unemployed | 8 | 1.8% |
| Employed | 408 | 92.7% |
| Family socio-economic status | ||
| Poor | 30 | 6.8% |
| Middle | 332 | 75.5% |
| Rich | 78 | 17.7% |
| High school attended | ||
| Liceum A | 110 | 25% |
| Liceum B | 86 | 19.5% |
| Liceum C | 76 | 17.3% |
| Technical institute A | 56 | 12.7% |
| Liceum D | 41 | 9.3% |
| Technical institute B | 37 | 8.4% |
| Technical institute C | 34 | 7.7% |
| Living with family members (vs. other) | 363 | 82.4% |
| AUDIT-C—Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test (Consumption) | 1.50 | (1.60) |
| HSI—Heaviness of Smoking Index | 0.75 | (1.35) |
| CAST—Cannabis Abuse Screening Test | 5.37 | (4.98) |
| Daily hours of sleep | 6.90 | (1.21) |
| Quality of sleep | 2.72 | (0.77) |
| Daily hours spent: | ||
| Watching TV | 7.67 | (82.23) |
| Listening to the Radio | 5.00 | (67.33) |
| Using Smartphone | 15.67 | (105.57) |
| Using Tablet | 7.45 | (82.26) |
| Using PC | 8.08 | (82.21) |
| Playing Videogames | 7.65 | (82.24) |
| Daily hours spent using technological devices instead of sleeping | 1.01 | (1.32) |
| IAT—Internet Addiction Test (total score) | 14.02 | (3.94) |
| CSQL—Compromised Social Quality of Life | 14.99 | (4.67) |
| CIQL—Compromised Individual Quality of Life | 10.27 | (4.05) |
| CUI—Compensatory Usage of the Internet | 5.96 | (2.21) |
| CAWC—Compromised Academic/Working Careers | 4.87 | (2.15) |
| CTC—Compromised Time Control | 6.01 | (1.82) |
| EUI—Excitatory Usage of the Internet | 4.10 | (1.78) |
| ASRS—Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale (total score) | 29.82 | (10.46) |
| ASRS—Inattention | 16.03 | (6.18) |
| ASRS—Hyperactivity/Impulsivity | 13.78 | (5.54) |
| PSI-Y—PsychoSocial Index-Young | ||
| Allostatic Overload (yes) | 229 | 52% |
| PWB—Psychological Well-Being scales | ||
| Self-Acceptance | 7.93 | (2.35) |
| Autonomy | 8.42 | (2.13) |
| Environmental Mastery | 7.92 | (2.19) |
| Personal Growth | 8.93 | (2.12) |
| Positive Relationship | 8.74 | (2.31) |
| Purpose in Life | 7.99 | (2.21) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gostoli, S.; Raimondi, G.; Rafanelli, C.; Gremigni, P. Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Unhealthy Lifestyle in Adolescence: Unforeseen Role of Allostatic Overload and Psychological Well-Being. Healthcare 2024, 12, 956. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12100956
Gostoli S, Raimondi G, Rafanelli C, Gremigni P. Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Unhealthy Lifestyle in Adolescence: Unforeseen Role of Allostatic Overload and Psychological Well-Being. Healthcare. 2024; 12(10):956. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12100956
Chicago/Turabian StyleGostoli, Sara, Giulia Raimondi, Chiara Rafanelli, and Paola Gremigni. 2024. "Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Unhealthy Lifestyle in Adolescence: Unforeseen Role of Allostatic Overload and Psychological Well-Being" Healthcare 12, no. 10: 956. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12100956
APA StyleGostoli, S., Raimondi, G., Rafanelli, C., & Gremigni, P. (2024). Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Unhealthy Lifestyle in Adolescence: Unforeseen Role of Allostatic Overload and Psychological Well-Being. Healthcare, 12(10), 956. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12100956







