Association of Basic Psychological Need Fulfillment and School Happiness with Obesity Levels and Intensity of Physical Activity during Physical Education Classes in South Korean Adolescents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants and Sampling
2.2. Validity and Reliability of Measurement Tools
2.3. Data Processing Method
3. Results
3.1. Cluster Analysis
3.2. Fulfillment of Basic Psychological Needs According to Physical Activity Intensity and Obesity
3.3. School Happiness According to Physical Activity Intensity and Obesity
3.4. Basic Psychological Needs According to the Interaction between Physical Activity Intensity and Obesity
3.5. School Happiness According to the Interaction between Physical Activity Intensity and Obesity
4. Discussion
4.1. Interpretation of Findings
4.2. Practical Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, G.A.; Champagne, C.M. Obesity: A disease of overnutrition. In Nutritional Health Strategies for Disease Prevention, 4th ed.; Temple, N.J., Wilson, T., Jacobs, D.R., Jr., Bray, G.A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.H.; Lee, W.Y.; Kim, S.S.; Kang, J.H.; Kang, J.H.; Kim, K.K.; Kim, B.Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, W.J.; Kim, E.M.; et al. Korean society for the study of obesity guidelines for the management of obesity in Korea. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2020, 30, 81–92. [Google Scholar]
- Janssen, I.; LeBlanc, A.G. Systematic review of the health benefits of physical activity and fitness in school-aged children and youth. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2010, 7, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marker, A.M.; Steele, R.G.; Noser, A.E. Physical activity and health-related quality of life in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Health Psychol. 2018, 37, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telama, R.; Yang, X.; Viikari, J.; Välimäki, I.; Wanne, O.; Raitakari, O. Physical activity from childhood to adulthood: A 21-year tracking study. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2005, 28, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Bueno, C.; Pesce, C.; Cavero-Redondo, I.; Sánchez-López, M.; Garrido-Miguel, M.; Martínez-Vizcaíno, V. Academic achievement and physical activity: A meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2017, 140, e20171498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.; Fedewa, A.L. A meta-analysis of the relationship between children’s physical activity and mental health. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2011, 36, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Must, A.; Strauss, R.S. Risks and consequences of childhood and adolescent obesity. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 1999, 23 (Suppl. 2), S2–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldhaber-Fiebert, J.D.; Rubinfeld, R.E.; Bhattacharya, J.; Robinson, T.N.; Wise, P.H. The utility of childhood and adolescent obesity assessment in relation to adult health. Med. Decis. Mak. 2013, 33, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inge, T.H.; King, W.C.; Jenkins, T.M.; Courcoulas, A.P.; Mitsnefes, M.; Flum, D.R.; Wolfe, B.M.; Pomp, A.; Dakin, G.F.; Khandelwal, S.; et al. The effect of obesity in adolescence on adult health status. Pediatrics 2013, 132, 1098–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumith, S.C.; Ramires, V.V.; Souza, M.A.; Moraes, D.S.; Petry, F.G.; Oliveira, E.S.; Ramires, S.V.; Hallal, P.C. Overweight/obesity and physical fitness among children and adolescents. J. Phys. Act. Health 2010, 7, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okely, A.D.; Booth, M.L.; Chey, T. Relationships between body composition and fundamental movement skills among children and adolescents. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2004, 75, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamtsios, S.; Digelidis, N. Physical activity levels, exercise attitudes, self-perceptions, and BMI type of 11 to 12-year-old children. J. Child Health Care 2008, 12, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjöberg, R.L.; Nilsson, K.W.; Leppert, J. Obesity, shame, and depression in school-aged children: A population-based study. Pediatrics 2005, 116, e389–e392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Li, W.; Zhao, Q.; Li, M. Including overweight and obese students in physical education: An urgent need and effective teaching strategies. J. Phys. Educ. Recreat. Danc. 2017, 88, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Pérez, E.M.; Núñez Enríquez, O.; Gastélum-Cuadras, G.; Horta-Gim, M.A.; González-Bernal, J.J.; de Paz, J.A. Assessment of Attitudes Toward Physical Education by the Implementation of an Extracurricular Program for Obese Children. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanelli, E.; Abate, D.F.; Pappaccogli, M.; Eula, E.; Astarita, A.; Mingrone, G.; Schiavone, D.; Rabbone, L.; Gollin, M.; Rabbia, F.; et al. A structured physical activity program in an adolescent population with overweight or obesity: A prospective interventional study. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2022, 47, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trost, S.G.; Loprinzi, P.D. Exercise-promoting healthy lifestyles in children and adolescents. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2008, 2, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines on Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- NASPE (National Association for Sport and Physical Education). Understanding the defference: Is it physical education or physical activity? NASPE position statement. Strategies 2005, 19, 33–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guthold, R.; Stevens, G.A.; Riley, L.M.; Bull, F.C. Global trends in insufficient physical activity among adolescents: A pooled analysis of 298 population-based surveys with 1.6 million participants. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2020, 4, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youm, Y.S. Korean Children and Youth Well-Being Index Survey, 2021: Middle School and High School Students. Korean J. Soc. Dev. Stud. 2021, 65–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Lee, H.J. Determinants of subjective well-being among Korean adolescents. Korean J. Stress Res. 2013, 21, 73–84. [Google Scholar]
- Uusitalo-Malmivaara, L. Global and school-related happiness in Finnish children. J. Happiness Stud. 2012, 13, 601–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.Y. Cause-of-death statistics in 2018 in the Republic of Korea. J. Korean Med. Assoc. 2018, 63, 286–297. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.B.; Kim, T.E. The development and validation of Korean school happiness scale. Korean J. Educ. Psychol. 2008, 22, 259–279. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.B.; Kim, N.H. Effects of teacher perceived student-teacher relationship and changes in student perceived student-teacher relationships on academic achievement mediated by school happiness and classroom engagement. Korean J. Youth Stud. 2014, 21, 285–315. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, R.M.; Deci, E.L. Self-determination theory and the facilitation of intrinsic motivation, social development, and well-being. Am. Psychol. 2000, 55, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koucheki, A.M.; Shariatnia, K.; Asadi, A.; Mirani, A. The mediating role of psychological basic needs in the relationship between personality traits and students’ happiness. J. Psychol. 2022, 21, 2091–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeve, J. Understanding Motivation and Emotion, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Vansteenkiste, M.; Ryan, R.; Soenens, B. Basic psychological need theory: Advancements, critical themes, and future directions. Motiv. Emot. 2020, 44, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, C.W.; Yang, H.F.; Huang, W.T.; Fan, S.Y. The relationships between physical activity and life satisfaction and happiness among young, middle-aged, and older adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, W.; Lee, B.; Joung, K. A Study on the Relationships between Playfulness, Physical Selfefficacy and School Happiness among Middle School Students participating in “0th-Period Physical Education Class” in South Korea. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1232508. [Google Scholar]
- Knaus, M.C.; Lechner, M.; Reimers, A.K. For better or worse?–The effects of physical education on child development. Lab. Econ. 2020, 67, 101904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, R.W.; McWilliams, M.E.; Schwartz, J.T.; Cavera, R.S. The role of exercise in reducing childhood and adolescent PTSD, anxiety, and depression. J. Appl. Sch. Psychol. 2012, 28, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, W. A systematic review of the relationship between physical activity and happiness. J. Happiness Stud. 2019, 20, 1305–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Hermoso, A.; Alonso-Martínez, A.M.; Ramírez-Vélez, R.; Pérez-Sousa, M.Á.; Ramírez-Campillo, R.; Izquierdo, M. Association of physical education with improvement of health-related physical fitness outcomes and fundamental motor skills among youths: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 2020, 174, e200223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strong, W.B.; Malina, R.M.; Blimkie, C.J.; Daniels, S.R.; Dishman, R.K.; Gutin, B.; Hergenroeder, A.C.; Must, A.; Nixon, P.A.; Pivarnik, J.M.; et al. Evidence based physical activity for school-age youth. J. Pediatr. 2005, 146, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, O.; Jung, W.H.; Kwon, H.J.; Woo, S.S.; Song, B.K.; Cho, K.O.; Kim, Y.S. Association between physical education class and subjective well-being in Korean adolescents: The 8th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey, 2012. Korean J. Phys. Educ. 2015, 54, 219–230. [Google Scholar]
- Nagata, J.M.; Cortez, C.A.; Dooley, E.E.; Iyer, P.; Ganson, K.T.; Pettee Gabriel, K. Moderate-to-vigorous intensity physical activity among adolescents in the USA during the COVID-19 pandemic. Prev. Med. Rep. 2022, 25, 101685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Jo, S.J. Comparison of physical activity according to the presence middle school physical education. J. Inst. Sch. Health Amp Phys. Educ. 2013, 20, 172–179. [Google Scholar]
- Prince, S.A.; Adamo, K.B.; Hamel, M.E.; Hardt, J.; Gorber, S.C.; Tremblay, M. A comparison of direct versus self-report measures for assessing physical activity in adults: A systematic review. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2008, 5, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troiano, R.P.; Berrigan, D.; Dodd, K.W.; Mâsse, L.C.; Tilert, T.; McDowell, M. Physical activity in the United States measured by accelerometer. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2008, 40, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänggi, J.M.; Phillips, L.R.S.; Rowlands, A.V. Validation of the GT3X ActiGraph in children and comparison with the GT1M ActiGraph. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2013, 16, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudor-Locke, C.; Tudor-Locke, C.; Craig, C.L.; Aoyagi, Y.; Bell, R.C.; Croteau, K.A.; De Bourdeaudhuij, I.; Ewald, B.; Gardner, A.W.; Hatano, Y.; et al. How many steps/day are enough? For older adults and special populations. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2011, 8, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrow, J.S.; Webster, J. Quetelet’s index (W/H2) as a measure of fatness. Int. J. Obes. 1985, 9, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nuttall, F.Q. Body mass index: Obesity, BMI, and health: A critical review. Nutr. Today 2015, 50, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.H. The development and verification of the measurement of children’s basic psychological needs on the primary school. Korean J. Sport Psychol. 2009, 20, 87–100. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, H.K.; Cho, J.H. The impacts of basic psychological needs satisfaction in physical education class on positive leisure lifestyle: A case of female high school students. Korean 2018, 42, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.H. Exploring the constructs of happiness of elementary students. Korean J. Elem. Educ. 2008, 21, 159–177. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, H.K.; Cho, J.H. Influences of Elementary Schoolers’ Physical Education Class Attitudes and Playfulness on School Happiness. J. Korea Contents Assoc. 2018, 18, 579–591. [Google Scholar]
- Kline, R.B. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling, 3rd ed.; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Eum, H.J.; Ko, M.S. The relationships among persived psychological needs, sports character and Sportpersonship by elementary school students. Korean J. Elem. Phys. Educ. 2014, 20, 65–76. [Google Scholar]
- Mayorga-Vega, D.; Martínez-Baena, A.; Viciana, J. Does school physical education really contribute to accelerometer-measured daily physical activity and non sedentary behaviour in high school students? J. Sports Sci. 2018, 36, 1913–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.I.; Yang, T.Y. Analysis of physical activity level and traits of male and female middle school students in daily life according to time (school days with PE class, school days without PE class, weekends) and sex. Korean J. Sport Pedagog. 2021, 28, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, C.M. Effect of sport club league participation on basic psychological needs and exercise persistence, school life satisfaction of elementary school students. Korean J. Elem. Phys. Educ. 2018, 24, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemiec, C.P.; Ryan, R.M. Autonomy, competence, and relatedness in the classroom: Applying self-determination theory to educational practice. Theory Res. Educ. 2009, 7, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.M.; Deci, E.L. Overview of self-determination theory: An organismic dialectical perspective. In Handbook of Self-Determination Research; Deci, E.L., Ryan, R.M., Eds.; The University of Rochester Press: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 3–33. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.M.; Park, S.R. Latent profile analysis of loneliness, basic psychological need satisfaction, and behavioral regulation and their impacts on sedentary behavior, moderate-to-vigorous physical activity, and body mass index. J. Korean Soc. Wellness 2018, 13, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.B.; Kim, B.J. Obesity and fitness and their relationships with physical self-concept, intrinsic motivation and stress in physical education. Korean J. Phys. Educ. 2014, 53, 131–142. [Google Scholar]
- Pengpid, S.; Peltzer, K. Sedentary behaviour, physical activity and life satisfaction, happiness and perceived health status in university students from 24 countries. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.Y.; Kim, K.M. The effect of physical activities on the mental health in Korean middle school adolescents: Based on the web-based survey on adolescents health behavior from 2013. J. Digit. Converg. 2014, 12, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.H. The effect of body mass index (BMI) on body image, stress, happiness of normal-weight female adolescents–Focus on double-mediator effect of body image and stress. Reg. Policy Rev. 2017, 28, 127–151. [Google Scholar]
- Cornelisse-Vermaat, J.R.; Antonides, G.; Van Ophem, J.A.C.; Van Den Brink, H.M. Body mass index, perceived health, and happiness: Their determinants and structural relationships. Soc. Indic. Res. 2006, 79, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stunkard, A.J.; Faith, M.S.; Allison, K.C. Depression and obesity. Biol. Psychiatry 2003, 54, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, R.; Gupta, T. Psychological aspects of obesity in children and adolescents. Indian J. Pediatr. 2018, 85, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atlantis, E.; Baker, M. Obesity effects on depression: Systematic review of epidemiological studies. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.R.; Kim, J.H. The effect of obesity on the adolescent development in Korea. Korean J. Youth Welf. 2011, 13, 91–117. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, G.S.; Qi, Y.Q. The socioeconomic determinants of obesity in China: Gender and urban-rural divergences. Sociol. Rev. China 2017, 5, 79–96. [Google Scholar]
- Swallen, K.C.; Reither, E.N.; Haas, S.A.; Meier, A.M. Overweight, obesity, and health-related quality of life among adolescents: The National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent Health. Pediatrics 2005, 115, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, L.; Hagedorn, A. How is obesity associated with happiness? Evidence from China. J. Health Psychol. 2022, 27, 568–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Jung, C.W. Relation between mental health and academic achievement of Korean teenagers in accordance with physical education and physical activity. Korean J. Sports Sci. 2012, 21, 553–570. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.I.; Kwon, S.Y.; Jung, C.H. The relationship among body weight, self-esteem, depression and anxiety in community adolescents. J. Korean Soc. Biol. Ther. Psychiatry 2010, 16, 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, B.J.; Kang, S.G. The effect on physiological and psychological variable after exercise participation of obese adolescents. Korean J. Phys. Educ. 2001, 40, 429–439. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Rukavina, P. The nature, occurring contexts, and psychological implications of weight-related teasing in urban physical education programs. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2012, 83, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trout, J.; Graber, K.C. Perceptions of overweight students concerning their experiences in physical education. J. Teach. Phys. Educ. 2009, 28, 272–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukavina, P.B.; Li, W. School physical activity interventions: Do not forget about obesity bias. Obes. Rev. 2008, 9, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.I. Assessment of levels of moderate-to-vigorous physical activity in physical education classes using 3-dimensional accelerometer: Competition domain. Korean J. Sports Sci. 2019, 30, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavarry, O.; Bernard, T.; Giacomoni, M.; Seymat, M.; Euzet, J.P.; Falgairette, G. Continuous heart rate monitoring over 1 week in teenagers aged 11–16 years. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1998, 77, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dale, D.; Corbin, C.B.; Dale, K.S. Restricting opportunities to be active during school time: Do children compensate by increasing physical activity levels after school? Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2000, 71, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.I.; Hong, D.K. Navigating the role of Health Promotion in K-12 physical education: Implication of school-wide moderate to vigorous physical activity programs. Korean J. Sport Pedagog. 2017, 24, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairclough, S.; Stratton, G. Physical education makes you fit and healthy. Physical education’s contribution to young people’s physical activity levels. Health Educ. Res. 2005, 20, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairclough, S.J.; Stratton, G. A review of physical activity levels during elementary school physical education. J. Teach. Phys. Educ. 2006, 25, 240–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puhl, R.M.; Latner, J.D. Stigma, obesity, and the health of the nation’s children. Psychol. Bull. 2007, 133, 557–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenleaf, C.; Weiller, K. Perceptions of youth obesity among physical educators. Soc. Psychol. Educ. 2005, 8, 407–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Category | n | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 270 | 50.8 |
| Female | 262 | 49.2 | |
| Physical activity intensity | High intensity | 204 | 38.3 |
| Low intensity | 328 | 61.7 | |
| Obesity level (BMI kg/m2) | Underweight < 20.0 | 193 | 36.3 |
| Normal 20.0–24.9 | 228 | 42.9 | |
| Obesity ≥ 25.0 | 111 | 20.9 | |
| Variable | Mean ± SD | n | % |
| Age (year) | 13.57 ± 0.68 | 532 | 100.0 |
| Height (cm) | 162.05 ± 7.17 | 532 | 100.0 |
| Weight (kg) | 58.54 ± 20.84 | 532 | 100.0 |
| Category (Number of Questions) | Example of Questions | |
|---|---|---|
| Demographic characteristics | Gender, Age, Height, and Weight | |
| Basic psychological needs (13) | Autonomy (4) |
|
| Competence (4) |
| |
| Relationship (5) (relatedness) |
| |
| School happiness (17) | Self-esteem (6) |
|
| Optimism (5) |
| |
| Relationships with friends (3) |
| |
| Relationship with teacher (3) |
| |
| Variables | χ2/df | RMSEA | SRMR | GFI | CFI | NFI | TLI | Cronbach’s α |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard | ≤3.0 | ≤0.08 | ≤0.08 | ≥0.90 | ≥0.90 | ≥0.90 | ≥0.90 | >0.70 |
| Basic psychological needs | 107.062/37 (2.89) | 0.059 | 0.029 | 0.971 | 0.989 | 0.983 | 0.976 | 0.945 |
| School happiness | 254.201/85 (2.99) | 0.060 | 0.036 | 0.950 | 0.964 | 0.947 | 0.942 | 0.921 |
| Variables | Intensity Level | F | |
|---|---|---|---|
| High | Low | ||
| MVPA | 15.29 | 6.20 | 1172.322 *** |
| n | 204 | 328 | |
| Variable | n | M | SD | t | ES | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical activity intensity | High | 204 | 3.70 | 0.77 | 5.284 *** | 0.474 |
| Low | 328 | 3.34 | 0.75 | |||
| Variable | n | M | SD | F | η2 | Post Hoc | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obesity level | Underweight | 193 | 3.48 | 0.86 | 1.593 | 0.006 | NS |
| Normal | 228 | 3.53 | 0.74 | ||||
| Obesity | 111 | 3.37 | 0.69 | ||||
| Variable | n | M | SD | t | ES | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical activity intensity | High | 204 | 3.51 | 0.66 | 3.870 *** | 0.356 |
| Low | 328 | 3.28 | 0.63 | |||
| Variable | n | M | SD | F | η2 | Post Hoc | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obesity level | Underweight | 193 | 3.40 | 0.61 | 1.272 | 0.005 | 0.005 |
| Normal | 228 | 3.40 | 0.67 | ||||
| Obese | 111 | 3.28 | 0.69 | ||||
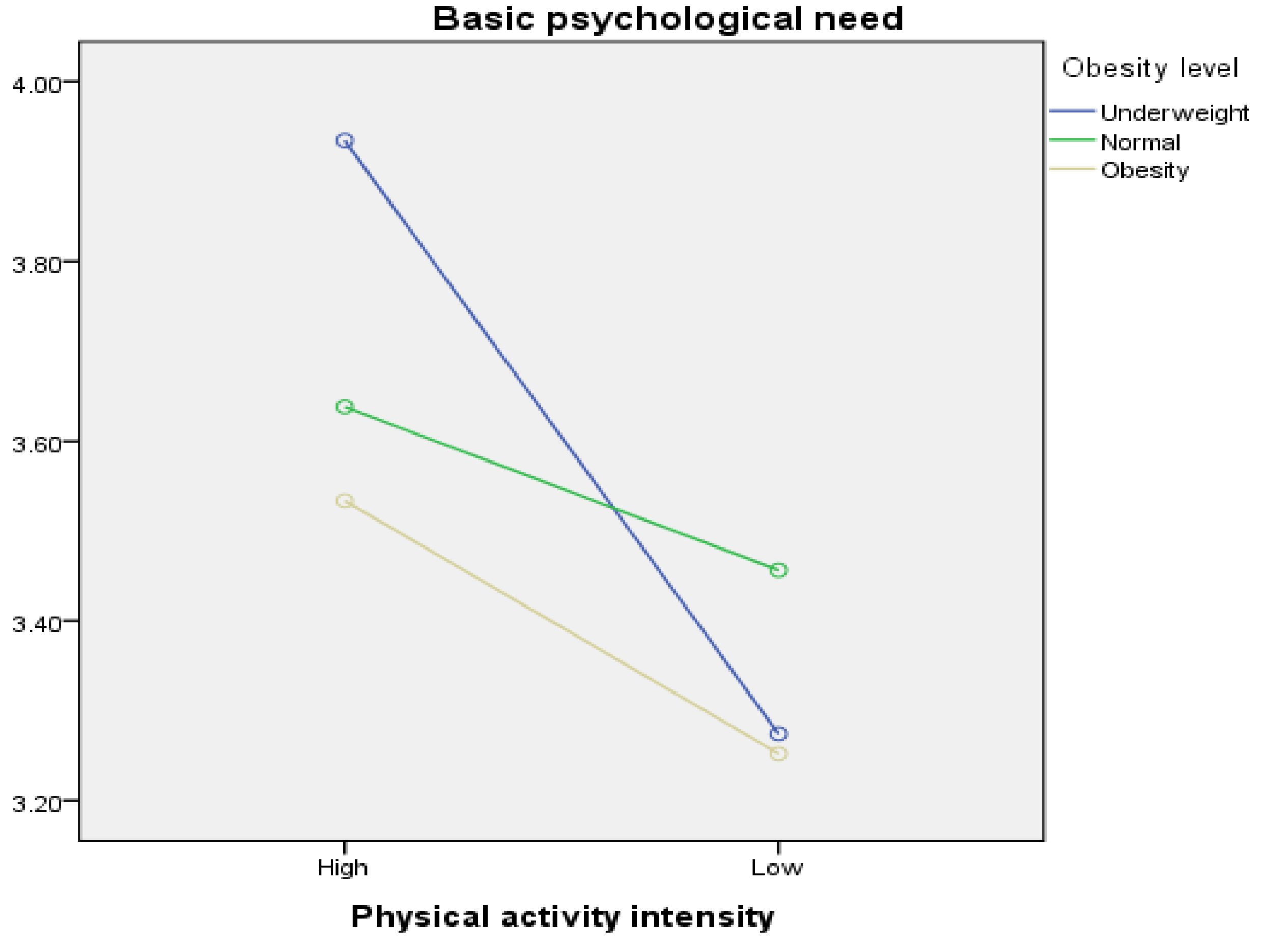
| Physical Activity Intensity | Obesity Level | n | M | SD | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High | Underweight (①) | 62 | 3.93 | 0.81 | ||
| Normal (②) | 95 | 3.64 | 0.74 | |||
| Obese (③) | 47 | 3.53 | 0.70 | |||
| Total | 204 | 3.70 | 0.77 | |||
| Low | Underweight (④) | 131 | 3.27 | 0.80 | ||
| Normal (⑤) | 133 | 3.45 | 0.73 | |||
| Obese (⑥) | 64 | 3.25 | 0.66 | |||
| Total | 328 | 3.34 | 0.75 | |||
| Variable | SS | df | MS | F | η2 | Post hoc |
| Physical activity intensity | 16.020 | 1 | 16.020 | 28.252 *** | 0.051 | ① > ④, ⑤, ⑥ ② > ④, ⑥ |
| Obesity level | 3.024 | 2 | 1.512 | 2.667 | 0.010 | |
| Physical activity intensity × obesity level | 5.715 | 2 | 2.857 | 5.039 ** | 0.019 | |
| Error | 298.259 | 526 | 0.567 | |||
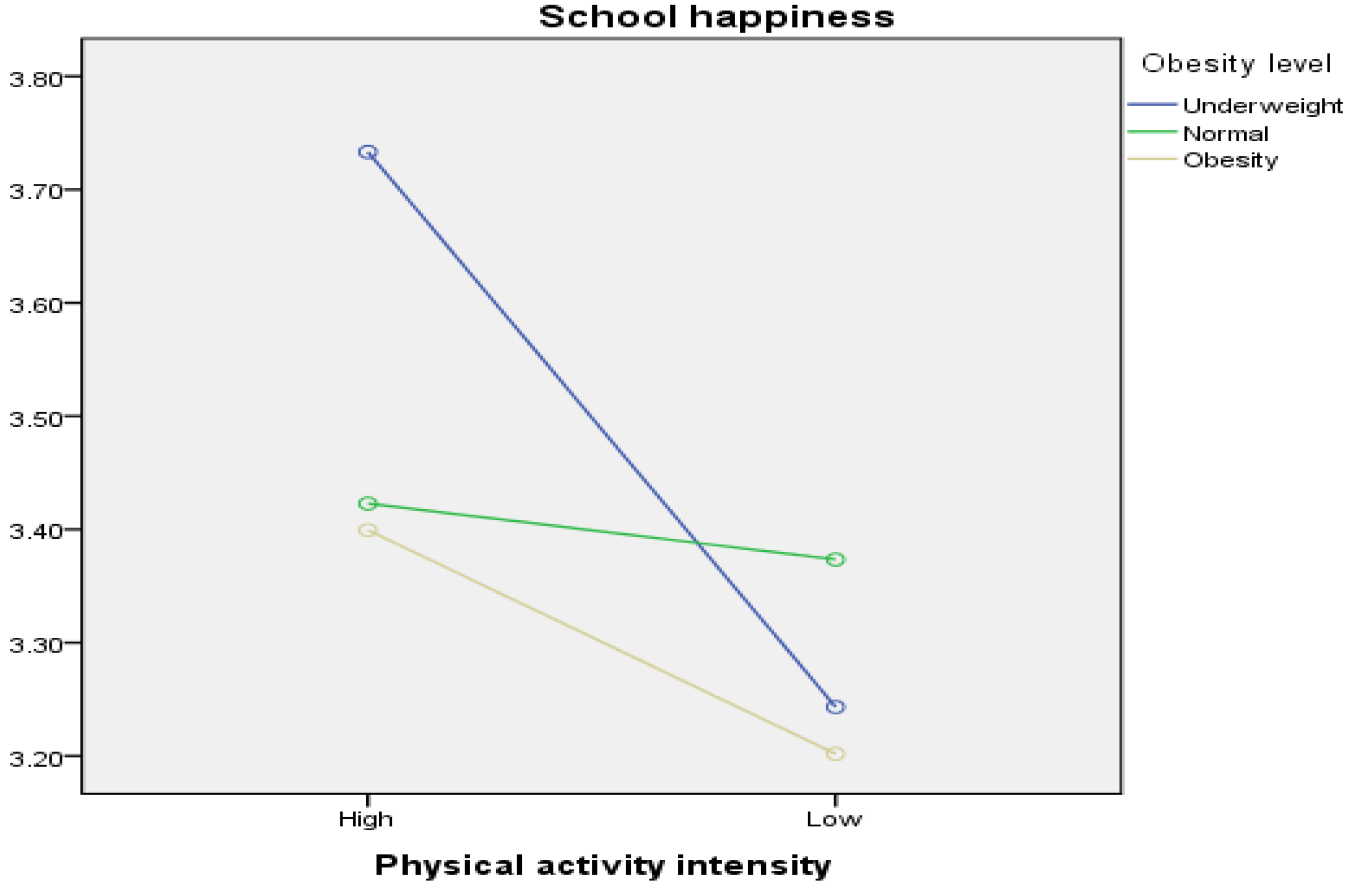
| Physical Activity Intensity | Obesity Level | n | M | SD | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High | Underweight (①) | 62 | 3.73 | 0.62 | ||
| Normal (②) | 95 | 3.42 | 0.69 | |||
| Obese (③) | 47 | 3.39 | 0.58 | |||
| Total | 204 | 3.51 | 0.66 | |||
| Low | Underweight (④) | 131 | 3.24 | 0.54 | ||
| Normal (⑤) | 133 | 3.37 | 0.65 | |||
| Obese (⑥) | 64 | 3.20 | 0.75 | |||
| Total | 328 | 3.28 | 0.63 | |||
| Variable | SS | df | MS | F | η2 | Post Hoc |
| Physical activity intensity | 6.900 | 1 | 6.900 | 16.737 *** | 0.031 | ① > ②, ④, ⑤, ⑥ |
| Obesity level | 2.354 | 2 | 1.177 | 2.855 | 0.011 | |
| Physical activity intensity × Obesity level | 4.682 | 2 | 2.341 | 5.678 ** | 0.021 | |
| Error | 216.857 | 526 | 0.412 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yun, J.-S.; Lee, G.-I.; Kim, B.-R. Association of Basic Psychological Need Fulfillment and School Happiness with Obesity Levels and Intensity of Physical Activity during Physical Education Classes in South Korean Adolescents. Healthcare 2024, 12, 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12010040
Yun J-S, Lee G-I, Kim B-R. Association of Basic Psychological Need Fulfillment and School Happiness with Obesity Levels and Intensity of Physical Activity during Physical Education Classes in South Korean Adolescents. Healthcare. 2024; 12(1):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12010040
Chicago/Turabian StyleYun, Ju-Seok, Gyu-Il Lee, and Bo-Ram Kim. 2024. "Association of Basic Psychological Need Fulfillment and School Happiness with Obesity Levels and Intensity of Physical Activity during Physical Education Classes in South Korean Adolescents" Healthcare 12, no. 1: 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12010040
APA StyleYun, J.-S., Lee, G.-I., & Kim, B.-R. (2024). Association of Basic Psychological Need Fulfillment and School Happiness with Obesity Levels and Intensity of Physical Activity during Physical Education Classes in South Korean Adolescents. Healthcare, 12(1), 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12010040







