An Emerging Health Crisis in Turkey and Syria after the Earthquake Disaster on 6 February 2023: Risk Factors, Prevention and Management of Infectious Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
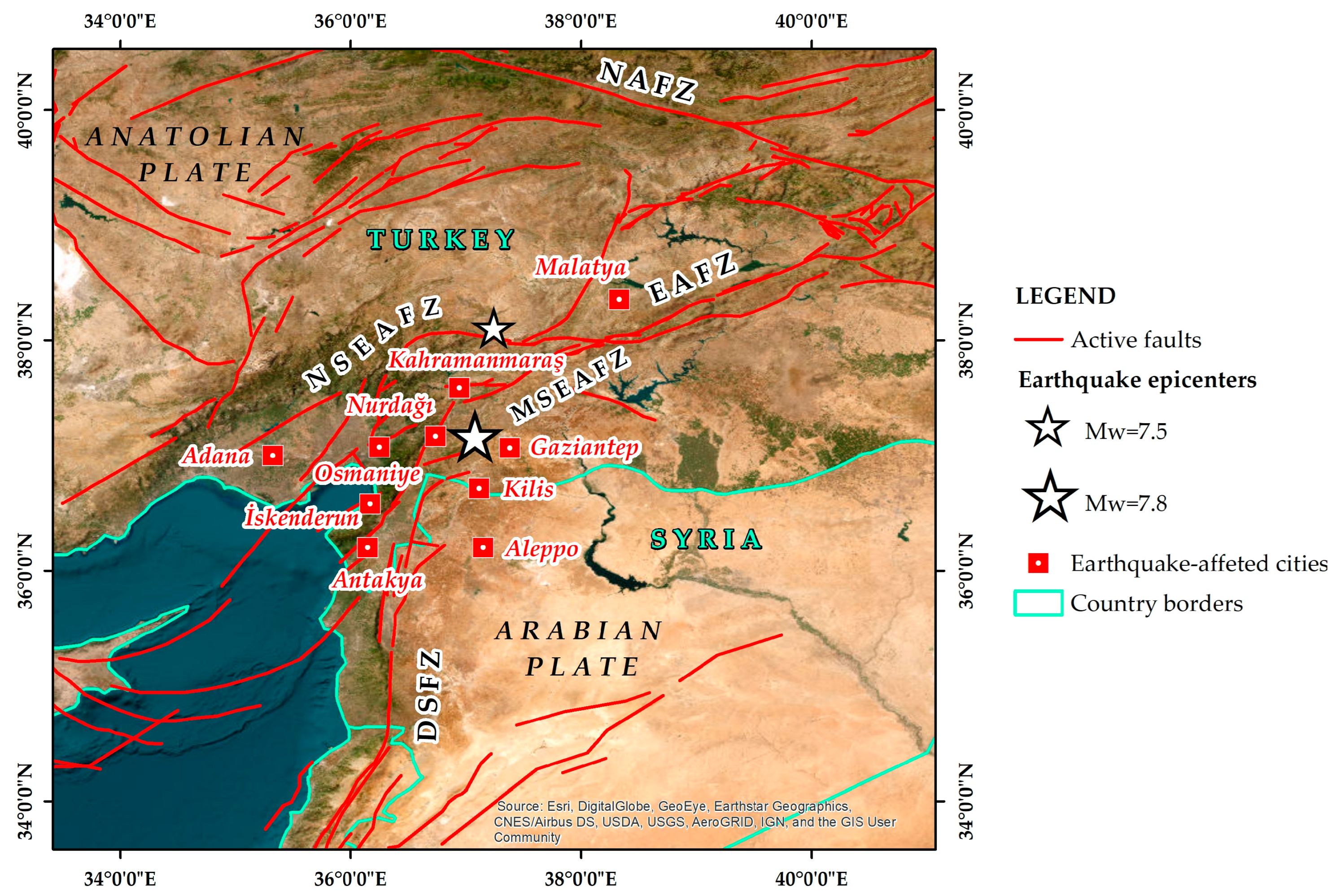
2. Methodology
3. Results
3.1. Infectious Diseases Emerged after Previous Earthquakes in Turkey
3.2. Risk Factors for Emergence of Infectious Diseases in the 2023 Earthquake-Affected Area of East Anatolia
4. Discussion
- The description of the current disease burden and epidemiology, which is critical as it demonstrates and supports the need for public health measures and interventions (e.g., vaccination);
- The monitoring and analysis of disease trends associated not only with numbers of cases but also with causative pathogenic agents;
- The detection of outbreaks and new pathogens.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EMSC. M 7.8—Central Turkey—2023-02-06 01:17:36 UTC. Available online: https://www.emsc-csem.org/Earthquake/earthquake.php?id=1218444 (accessed on 7 February 2023).
- Lekkas, E.; Carydis, P.; Vassilakis, E.; Mavroulis, S.; Argyropoulos, I.; Sarantopoulou, A.; Mavrouli, M.; Konsolaki, A.; Gogou, M.; Katsetsiadou, K.-N.; et al. The 6 February 2023 Turkey-Syria Earthquakes. Newsletter of Environmental, Disaster and Crises Management Strategies, 29. 2023. ISSN 2653-9454. Available online: https://edcm.edu.gr/el/newsletter/newsletter-29-the-6-february-2023-turkey-syria-earthquakes (accessed on 21 February 2023).
- Styron, R.; Pagani, M. The GEM Global Active Faults Database. Earthq. Spectra 2020, 36, 160–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AFAD. Press Bulletin-29 about the Earthquake in Kahramanmaraş. Available online: https://en.afad.gov.tr/press-bulletin-29-about-the-earthquake-in-kahramanmaras, (accessed on 13 February 2023).
- World Health Organization (WHO). Earthquake response in Türkiye and Whole of Syria. Available online: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/documents/emergencies/2023/who_flashappeal_earthquakeresponse_11-feb-2023.pdf?sfvrsn=94d4de2a_1 (accessed on 13 February 2023).
- Ministry of Climate Change and Civil Protection. Press Release on 12 February 2023. Available online: https://civilprotection.gov.gr/deltia-tupou/epestrepse-i-elliniki-apostoli-ereynas-kai-diasosis-apo-tin-toyrkia-ta-meli-tis (accessed on 13 February 2023).
- Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters (CRED). EM-DAT—The International Disaster Database. Available online: https://public.emdat.be/ (accessed on 11 February 2023).
- Mavrouli, M.; Mavroulis, S.; Lekkas, E.; Tsakris, A. The Impact of Earthquakes on Public Health: A Narrative Review of Infectious Diseases in the Post-Disaster Period Aiming to Disaster Risk Reduction. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahaboglu, H.; Gundes, S.; Karadenizli, A.; Mutlu, B.; Cetin, S.; Kolayli, F.; Coskunkan, F.; Dündar, V. Transient increase in diarrheal diseases after the devastating earthquake in Kocaeli, Turkey: Results of an infectious disease surveillance study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 31, 1386–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sencan, I.; Sahin, I.; Kaya, D.; Oksuz, S.; Yildirim, M. Assessment of HAV and HEV seroprevalence in children living in post-earthquake camps from Düzce, Turkey. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2004, 19, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, A.D.; Ozturk, C.E.; Yavuz, T.; Ozaydin, C.; Bahcebasi, T. Changing patterns of hepatitis A and E sero-prevalences in children after the 1999 earthquakes in Duzce, Turkey. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2008, 44, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oztürk, C.E.; Sahin, I.; Yavuz, T.; Oztürk, A.; Akgünoğlu, M.; Kaya, D. Intestinal parasitic infection in children in post-disaster situations years after earthquake. Pediatr. Int. 2004, 46, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayramgürler, D.; Bilen, N.; Namli, S.; Altinaş, L.; Apaydin, R. The effects of 17 August Marmara earthquake on patient admittances to our dermatology department. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2002, 16, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekçibaşı, M.; Hoşoğlu, S.; Deveci, Ö.; Dayan, S. Therapy for wound infections after earthquakes requires inclusion of drugs targeting Gram-negative bacteria. Infect. Dis. 2017, 49, 862–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keven, K.; Ates, K.; Sever, M.S.; Yenicesu, M.; Canbakan, B.; Arinsoy, T.; Ozdemir, N.; Duranay, M.; Altun, B.; Erek, E. Infectious complications after mass disasters: The Marmara earthquake experience. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 35, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oncül, O.; Keskin, O.; Acar, H.V.; Küçükardali, Y.; Evrenkaya, R.; Atasoyu, E.M.; Top, C.; Nalbant, S.; Ozkan, S.; Emekdaş, G.; et al. Hospital-acquired infections following the 1999 Marmara earthquake. J. Hosp. Infect. 2002, 51, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AFAD. Regarding the Evacuation Points of the Disaster Victims—Press Bulletin. Available online: https://reliefweb.int/report/turkiye/afad-press-bulletin-regarding-evacuation-points-disaster-victims-entr (accessed on 13 February 2023).
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Communicable Disease Threats Report. Week 7, 12–18 February 2023. Weekly Bulletin. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/sites/default/files/documents/communicable-disease-threats-report-week-7-2023.pdf (accessed on 19 February 2023).
- Suzuki, M.; Uwano, C.; Ohrui, T.; Ebihara, T.; Yamasaki, M.; Asamura, T.; Tomita, N.; Kosaka, Y.; Furukawa, K.; Arai, H. Shelter-Acquired pneumonia after a catastrophic earthquake in Japan. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2011, 59, 1968–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daito, H.; Suzuki, M.; Shiihara, J.; Kilgore, P.E.; Ohtomo, H.; Morimoto, K.; Ishida, M.; Kamigaki, T.; Oshitani, H.; Hashizume, M.; et al. Impact of the Tohoku earthquake and tsunami on pneumonia hospitalisations and mortality among adults in northern Miyagi, Japan: A multicentre observational study. Thorax 2013, 68, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, H.; Fujimura, S.; Ubukata, S.; Sato, E.; Shoji, M.; Utagawa, M.; Kikuchi, T.; Watanabe, A. Pneumonia after earthquake, Japan, 2011. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1909–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, M.; Peek-Asa, C. Epidemiology of traumatic injuries from earthquakes. Epidemiol. Rev. 2005, 27, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Abdulla, O.; Alaref, M. The forgotten threat of cholera in Syria. J. Water Health. 2022, 20, 1755–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahinoz, T.; Sahinoz, S.; Kaya, N. Trend of measles in Turkey: A retrospective secondary data analysis. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2021, 71, 1527–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozaras, E.; Eronat, A.; Zerdali, E.; Demirel, A.; Sart, G.; Tabak, F.; Ozaras, R. Did Syrian refugees increase the rate of measles in Turkey? Travel. Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 38, 101744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehtar, S.; AlMhawish, N.; Shobak, K.; Reingold, A.; Guha-Sapir, D.; Haar, R.J. Measles in conflict-affected northern Syria: Results from an ongoing outbreak surveillance program. Confl. Health 2021, 15, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’ikanatha, N.M.; Lynfield, R.; Van Beneden, C.A.; de Valk, H. (Eds.) Infectious Disease Surveillance, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; 720p. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, J.; Cohen, A.L. Infectious Disease Surveillance. Int. Encycl. Public Health 2017, 222–229. [Google Scholar]
- Noah, N. Surveillance of Infectious Diseases. Encycl. Virol. 2021, 5, 247–255. [Google Scholar]
- Mavroulis, S.; Mavrouli, M.; Kourou, A.; Thoma, T.; Lekkas, E. Multi-Hazard Emergency Response for Geological Hazards Amid the Evolving COVID-19 Pandemic: Good Practices and Lessons Learned from Earthquake Disaster Management in Greece. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavroulis, S.; Mavrouli, M.; Lekkas, E. Geological and hydrometeorological hazards and related disasters amid COVID-19 pandemic in Greece: Post-disaster trends and factors affecting the COVID-19 evolution in affected areas. Saf. Sci. 2021, 138, 105236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pio, A.; Kirkwood, B.R.; Gove, S. Avoiding hypothermia, an intervention to prevent morbidity and mortality from pneumonia in young children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2010, 29, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Oranization—Regional Office for the Eastern Mediterranean. WHO and UNICEF Launch Cholera Vaccination Campaign in Northwest Syria Amidst Earthquake Response. Available online: https://www.emro.who.int/media/news/who-and-unicef-launch-cholera-vaccination-campaign-in-northwest-syria-amidst-earthquake-response.html (accessed on 9 March 2023).
- Alexander, D. Disease Epidemiology and Earthquake Disaster: The Example of Southern Italy after the 23 November 1980 Earthquake. Soc. Sci. Med. 1982, 16, 1959–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunton, C.; Humphrey, A.; Pink, R. The public health response to microbiological hazards after the Canterbury earthquakes. Pathology 2012, 44, S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrouli, M.; Mavroulis, S.; Lekkas, E.; Tsakris, A. Infectious Diseases Associated with Hydrometeorological Hazards in Europe: Disaster Risk Reduction in the Context of the Climate Crisis and the Ongoing COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socolovschi, C.; Angelakis, E.; Renvoisé, A.; Fournier, P.E.; Marié, J.L.; Davoust, B.; Stein, A.; Raoult, D. Strikes, flooding, rats, and leptospirosis in Marseille, France. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 15, e710–e715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Seventer, J.M.; Hochberg, N.S. Principles of Infectious Diseases: Transmission, Diagnosis, Prevention, and Control. Int. Encycl. Public Health 2017, 22–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouadio, I.K.; Aljunid, S.; Kamigaki, T.; Hammad, K.; Oshitani, H. Infectious diseases following natural disasters: Prevention and control measures. Expert Rev. Anti. Infect. Ther. 2012, 10, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrouli, M.; Mavroulis, S.; Lekkas, E.; Tsakris, A. Respiratory Infections Following Earthquake-Induced Tsunamis: Transmission Risk Factors and Lessons Learned for Disaster Risk Management. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mavrouli, M.; Mavroulis, S.; Lekkas, E.; Tsakris, A. An Emerging Health Crisis in Turkey and Syria after the Earthquake Disaster on 6 February 2023: Risk Factors, Prevention and Management of Infectious Diseases. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11071022
Mavrouli M, Mavroulis S, Lekkas E, Tsakris A. An Emerging Health Crisis in Turkey and Syria after the Earthquake Disaster on 6 February 2023: Risk Factors, Prevention and Management of Infectious Diseases. Healthcare. 2023; 11(7):1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11071022
Chicago/Turabian StyleMavrouli, Maria, Spyridon Mavroulis, Efthymios Lekkas, and Athanassios Tsakris. 2023. "An Emerging Health Crisis in Turkey and Syria after the Earthquake Disaster on 6 February 2023: Risk Factors, Prevention and Management of Infectious Diseases" Healthcare 11, no. 7: 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11071022
APA StyleMavrouli, M., Mavroulis, S., Lekkas, E., & Tsakris, A. (2023). An Emerging Health Crisis in Turkey and Syria after the Earthquake Disaster on 6 February 2023: Risk Factors, Prevention and Management of Infectious Diseases. Healthcare, 11(7), 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11071022





