Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for the Treatment of Musculoskeletal Pain: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
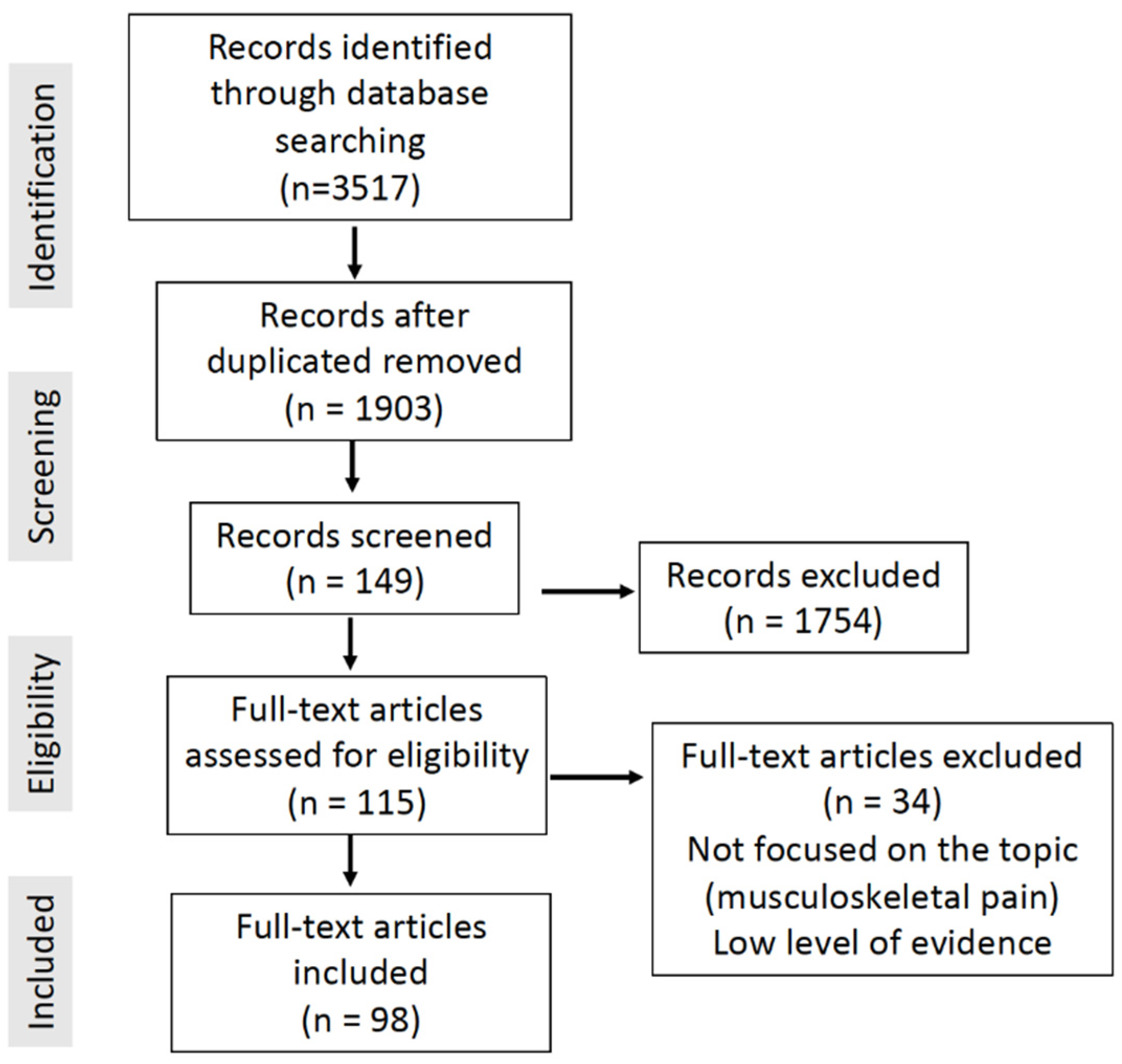
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
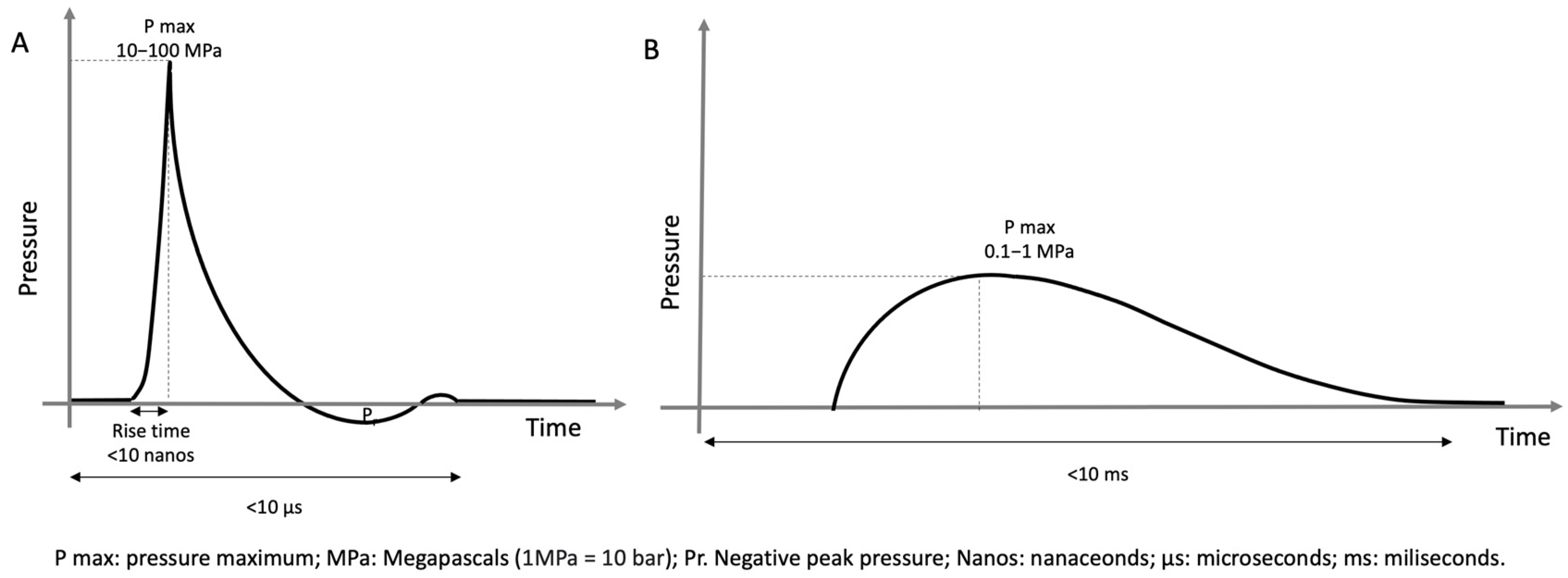
3.1. Mechanism of Action
3.2. Method of Application
3.3. Role of ESWT in Tendinopathies
3.3.1. Calcific Tendinopathy of the Shoulder
3.3.2. Lateral Epicondylitis
3.3.3. Greater Trochanteric Pain Syndrome
3.3.4. Patellar Tendinopathy
3.3.5. Achilles Tendinopathy
3.4. Role of ESWT in Plantar Fasciitis
3.5. Role of ESWT in Axial Pain
3.5.1. Myofascial Pain Syndrome of the Trapezius
3.5.2. Low Back Pain
3.5.3. Coccydynia
3.6. Role of ESWT in Knee Osteoarthritis
3.7. Role of ESWT in Bone Diseases
3.7.1. Fracture Nonunion
3.7.2. Femoral Head Osteonecrosis
3.7.3. Kienbock’s Disease
3.7.4. Pubis Osteitis
3.7.5. Bone Marrow Edema Syndrome of the Hip
3.8. Role of ESWT in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
3.9. Strengths and Weaknesses of the Studies
3.10. Adverse Effects and Contraindications
4. Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wong, C.W.-Y.; Ng, E.Y.-L.; Fung, P.-W.; Mok, K.-M.; Yung, P.S.-H.; Chan, K.-M. Comparison of treatment effects on lateral epicondylitis between acupuncture and extracorporeal shockwave therapy. Asia-Pac. J. Sports Med. Arthrosc. Rehabil. Technol. 2016, 7, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crevenna, R.; Mickel, M.; Keilani, M. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in the supportive care and rehabilitation of cancer patients. Support. Care Cancer 2019, 27, 4039–4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dizon, J.N.C.; Gonzalez-Suarez, C.; Zamora, M.T.G.; Gambito, E.D. Effectiveness of extracorporeal shock wave therapy in chronic plantar fasciitis: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2013, 92, 606–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konjen, N.; Napnark, T.; Janchai, S. A comparison of the effectiveness of radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy and ultrasound therapy in the treatment of chronic plantar fasciitis: A randomized controlled trial. J. Med. Assoc. Thail. 2015, 98 (Suppl. 1), S49–S56. [Google Scholar]
- Simplicio, C.L.; Purita, J.; Murrell, W.; Santos, G.S.; Dos Santos, R.G.; Lana, J.F.S.D. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy mechanisms in musculoskeletal regenerative medicine. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2020, 11 (Suppl. 3), S309–S318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notarnicola, A.; Moretti, B. The biological effects of extracorporeal shock wave therapy (eswt) on tendon tissue. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2012, 2, 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Smallcomb, M.; Khandare, S.M.; Vidt, M.E.; Simon, J.C. Therapeutic Ultrasound and Shockwave Therapy for Tendinopathy: A Narrative Review. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2022, 101, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Wang, P.; He, C. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy as a novel and potential treatment for degenerative cartilage and bone disease: Osteoarthritis. A qualitative analysis of the literature. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2016, 121, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stania, M.; Juras, G.; Chmielewska, D.; Polak, A.; Kucio, C.; Król, P. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for Achilles Tendinopathy. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 3086910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausdorf, J.; Lemmens, M.A.M.; Heck, K.D.W.; Grolms, N.; Korr, H.; Kertschanska, S.; Steinbusch, H.W.M.; Schmitz, C.; Maier, M. Selective loss of unmyelinated nerve fibers after extracorporeal shockwave application to the musculoskeletal system. Neuroscience 2008, 155, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, N.; Wada, Y.; Ohtori, S.; Saisu, T.; Moriya, H. Application of shock waves to rat skin decreases calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactivity in dorsal root ganglion neurons. Auton. Neurosci. 2003, 107, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rompe, J.D.; Hopf, C.; Küllmer, K.; Heine, J.; Bürger, R.; Nafe, B. Low-energy extracorporal shock wave therapy for persistent tennis elbow. Int. Orthop. 1996, 20, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, Y.-H.; Tsuang, Y.-H.; Sun, J.-S.; Chen, L.-T.; Chiang, Y.-F.; Wang, C.-C.; Chen, M.-H. Effects of shock waves on tenocyte proliferation and extracellular matrix metabolism. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2008, 34, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waugh, C.M.; Morrissey, D.; Jones, E.; Riley, G.P.; Langberg, H.; Screen, H.R. In vivo biological response to extracorporeal shockwave therapy in human tendinopathy. Eur. Cells Mater. 2015, 29, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiel, M. Application of shock waves in medicine. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2001, 387, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.J. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy in musculoskeletal disorders. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2012, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.M.; Cook, J.L.; Taunton, J.E.; Bonar, F. Overuse tendinosis, not tendinitis part 1: A new paradigm for a difficult clinical problem. Physician Sportsmed. 2000, 28, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cui, H.S.; Joo, S.Y.; Cho, Y.S.; Park, J.H.; Ro, Y.M.; Kim, J.-B.; Seo, C.H. Effect of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on keratinocytes derived from human hypertrophic scars. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.-S.; Wang, C.-J.; Chen, Y.-J.; Chang, P.-R.; Huang, Y.-T.; Sun, Y.-C.; Huang, H.-C.; Yang, Y.-J.; Yang, K.D. Ras induction of superoxide activates ERK-dependent angiogenic transcription factor HIF-1α and VEGF-A expression in shock wave-stimulated osteoblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 10331–10337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Z.-L.; Yang, F.; Zhang, Q.; Su, X.-Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, N.; Liu, C.-H.; Mao, N.; Zhu, H. Radial shockwave treatment promotes human mesenchymal stem cell self-renewal and enhances cartilage healing. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.-L.; Cheng, J.-H.; Wang, C.-J.; Ko, J.-Y.; Hsu, C.-H. Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy Enhances Expression of Pdia-3 Which Is a Key Factor of the 1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D 3 Rapid Membrane Signaling Pathway in Treatment of Early Osteoarthritis of the Knee. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 14, 1220–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Agostino, M.C.; Craig, K.; Tibalt, E.; Respizzi, S. Shock wave as biological therapeutic tool: From mechanical stimulation to recovery and healing, through mechanotransduction. Int. J. Surg. 2015, 24, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-J.; Yang, K.D.; Ko, J.-Y.; Huang, C.-C.; Huang, H.-Y.; Wang, F.-S. The effects of shockwave on bone healing and systemic concentrations of nitric oxide (NO), TGF-β1, VEGF and BMP-2 in long bone non-unions. Nitric Oxide 2009, 20, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njawaya, M.M.; Moses, B.; Martens, D.; Orchard, J.J.; Driscoll, T.; Negrine, J.; Orchard, J.W. Ultrasound Guidance Does Not Improve the Results of Shock Wave for Plantar Fasciitis or Calcific Achilles Tendinopathy: A Randomized Control Trial. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2018, 28, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surace, S.J.; Deitch, J.; Johnston, R.V.; Buchbinder, R. Shock wave therapy for rotator cuff disease with or without calcification. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 3, CD008962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogden, J.A.; Tóth-Kischkat, A.; Schultheiss, R. Principles of shock wave therapy. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2001, 387, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, C.; Császár, N.B.M.; Milz, S.; Schieker, M.; Maffulli, N.; Rompe, J.-D.; Furia, J.P. Efficacy and safety of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for orthopedic conditions: A systematic review on studies listed in the PEDro database. Br. Med. Bull. 2015, 116, 115–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yan, X.; Wang, C.; Tang, T.; Chai, Y. The dose–effect relationship in extracorporeal shock wave therapy: The optimal parameter for extracorporeal shock wave therapy. J. Surg. Res. 2014, 186, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.-D.; Xie, G.-M.; Tsauo, J.-Y.; Chen, H.-C.; Liou, T.-H. Efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for knee tendinopathies and other soft tissue disorders: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2018, 19, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stania, M.; Król, B.; Franek, A.; Błaszczak, E.; Dolibog, P.; Polak, A.; Dolibog, P.; Durmała, J.; Król, P. A comparative study of the efficacy of radial and focused shock wave therapy for tennis elbow depending on symptom duration. Arch. Med. Sci. 2020, 17, 1686–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizis, P. Analgesic effect of extracorporeal shock wave therapy versus ultrasound therapy in chronic tennis elbow. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2015, 27, 2563–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Haake, M.; König, I.R.; Decker, T.; Riedel, C.; Buch, M.; Müller, H.-H.; Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Clinical Trial Group. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in the treatment of lateral epicondylitis: A randomized multicenter trial. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2002, 84, 1982–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furia, J.P. High-energy extracorporeal shock wave therapy as a treatment for insertional Achilles tendinopathy. Am. J. Sports Med. 2006, 34, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rompe, J.D.; Nafe, B.; Furia, J.P.; Maffulli, N. Eccentric loading, shock-wave treatment, or a wait-and-see policy for tendinopathy of the main body of tendo Achillis: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Sports Med. 2007, 35, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturan, K.E.; Yucel, I.; Cakici, H.; Guven, M.; Sungur, I. Autologous blood and corticosteroid injection and extracoporeal shock wave therapy in the treatment of lateral epicondylitis. Orthopedics 2010, 33, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.; Dunkerley, S.; Silver, D.; Redfern, A.; Talbot, N.; Sharpe, I.; Guyver, P. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) for refractory Achilles tendinopathy: A prospective audit with 2-year follow up. Foot 2016, 26, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Hopewell, S.; Schulz, K.F.; Montori, V.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Devereaux, P.J.; Elbourne, D.; Egger, M.; Altman, D.G.; CONSORT. CONSORT 2010 explanation and elaboration: Updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. Int. J. Surg. 2012, 10, 28–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cai, Y. Utility of Ultrasonography in Assessing the Effectiveness of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy in Insertional Achilles Tendinopathy. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 2580969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Smedt, T.; de Jong, A.; Van Leemput, W.; Lieven, D.; Van Glabbeek, F. Lateral epicondylitis in tennis: Update on aetiology, biomechanics and treatment. Br. J. Sports Med. 2007, 41, 816–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Maffulli, N. Tendon injury and tendinopathy: Healing and repair. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2005, 87, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järvinen, T.A.; Kannus, P.; Maffulli, N.; Khan, K.M. Achilles tendon disorders: Etiology and epidemiology. Foot Ankle Clin. 2005, 10, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.-H.; Huang, Y.-C.; Lau, Y.-C.; Wang, L.-Y. Efficacy of Radial Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy on Lateral Epicondylosis, and Changes in the Common Extensor Tendon Stiffness with Pretherapy and Posttherapy in Real-Time Sonoelastography: A Randomized Controlled Study. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2017, 96, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sansone, V.; Consonni, O.; Maiorano, E.; Meroni, R.; Goddi, A. Calcific tendinopathy of the rotator cuff: The correlation between pain and imaging features in symptomatic and asymptomatic female shoulders. Skelet. Radiol. 2016, 45, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackett, L.; Millar, N.L.; Lam, P.; Murrell, G.A. Are the Symptoms of Calcific Tendinitis Due to Neoinnervation and/or Neovascularization? J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2016, 98, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speed, C. A systematic review of shockwave therapies in soft tissue conditions: Focusing on the evidence. Br. J. Sports Med. 2014, 48, 1538–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louwerens, J.K.; Sierevelt, I.N.; van Noort, A.; van den Bekerom, M.P. Evidence for minimally invasive therapies in the management of chronic calcific tendinopathy of the rotator cuff: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2014, 23, 1240–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabeti-Aschraf, M.; Dorotka, R.; Goll, A.; Trieb, K. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in the treatment of calcific tendinitis of the rotator cuff. Am. J. Sports Med. 2005, 33, 1365–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornese, D.; Mattei, E.; Bandi, M.; Zerbi, A.; Quaglia, A.; Melegati, G. Arm position during extracorporeal shock wave therapy for calcifying tendinitis of the shoulder: A randomized study. Clin. Rehabil. 2011, 25, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, A.; Ahmad, A.; Gilani, S.A.; Darain, H.; Kazmi, S.; Hanif, K. Effects of High-Energy Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy on Pain, Functional Disability, Quality of Life, and Ultrasonographic Changes in Patients with Calcified Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 1230857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydın, A.; Atiç, R. Comparison of extracorporeal shock-wave therapy and wrist-extensor splint application in the treatment of lateral epicondylitis: A prospective randomized controlled study. J. Pain Res. 2018, 11, 1459–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, G.; Chen, J.; Duan, Y.; Chen, X. Efficacy of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for Lateral Epicondylitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 2064781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, D. The management of greater trochanteric pain syndrome: A systematic literature review. J. Orthop. 2016, 13, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazendam, A.; Ekhtiari, S.M.; Axelrod, D.M.; Gouveia, K.B.; Gyemi, L.B.; Ayeni, O.; Bhandari, M. Comparative Efficacy of Nonoperative Treatments for Greater Trochanteric Pain Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2022, 32, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heaver, C.; Pinches, M.; Kuiper, J.H.; Thomas, G.; Lewthwaite, S.; Burston, B.J.; Banerjee, R.D. Greater trochanteric pain syndrome: Focused shockwave therapy versus an ultrasound guided injection: A randomised control trial. Hip Int. 2023, 33, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrokhi, S.; Chen, Y.-F.; Piva, S.R.; Fitzgerald, G.K.; Jeong, J.-H.; Kwoh, C.K. The Influence of Knee Pain Location on Symptoms, Functional Status, and Knee-related Quality of Life in Older Adults With Chronic Knee Pain: Data From the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Clin. J. Pain 2016, 32, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leppänen, M.; Pasanen, K.; Kannus, P.; Vasankari, T.; Kujala, U.M.; Heinonen, A.; Parkkari, J. Epidemiology of Overuse Injuries in Youth Team Sports: A 3-year Prospective Study. Int. J. Sports Med. 2017, 38, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, R.; Fang, L.; Zhu, R.; Wang, J. The effectiveness of shockwave therapy on patellar tendinopathy, Achilles tendinopathy, and plantar fasciitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1193835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taunton, K.M.; Taunton, J.E.; Khan, K.M. Treatment of patellar tendinopathy with extracorporeal shock wave therapy. BC Med. J. 2003, 45, 500–507. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, A.; Ashe, M.C. Common tendinopathies in the upper and lower extremities. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2006, 5, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakked, R.J.; Raikin, S.M. Insertional Tendinopathy of the Achilles: Debridement, Primary Repair, and When to Augment. Foot Ankle Clin. 2017, 22, 761–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rompe, J.D.; Furia, J.; Maffulli, N. Eccentric loading versus eccentric loading plus shock-wave treatment for midportion achilles tendinopathy: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Sports Med. 2009, 37, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notarnicola, A.; Pesce, V.; Vicenti, G.; Tafuri, S.; Forcignanò, M.; Moretti, B. SWAAT study: Extracorporeal shock wave therapy and arginine supplementation and other nutraceuticals for insertional Achilles tendinopathy. Adv. Ther. 2012, 29, 799–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rompe, J.D. Plantar fasciopathy. Sports Med. Arthrosc. Rev. 2009, 17, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rompe, J.D.; Furia, J.; Weil, L.; Maffulli, N. Shock wave therapy for chronic plantar fasciopathy. Br. Med. Bull. 2007, 81–82, 183–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, A.T.; How, C.H.; Tan, B. Management of plantar fasciitis in the outpatient setting. Singap. Med. J. 2016, 57, 168–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, W. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy versus other therapeutic methods for chronic plantar fasciitis. Foot Ankle Surg. 2020, 26, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poveda-Pagán, E.J.; Lozano-Quijada, C.; Segura-Heras, J.V.; Peral-Berna, M.; Lumbreras, B. Referred Pain Patterns of the Infraspinatus Muscle Elicited by Deep Dry Needling and Manual Palpation. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2017, 23, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirri, C.; Fede, C.; Petrelli, L.; De Rose, E.; Biz, C.; Guidolin, D.; De Caro, R.; Stecco, C. Immediate Effects of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy in Fascial Fibroblasts: An In Vitro Study. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Fu, C.; Huang, L.; Xiong, F.; Peng, L.; Liang, Z.; Chen, L.; He, C.; Wei, Q. Efficacy of Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy on Pain and Function in Myofascial Pain Syndrome of the Trapezius: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2020, 101, 1437–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajfur, K.; Rajfur, J.; Matusz, T.; Walewicz, K.; Dymarek, R.; Ptaszkowski, K.; Taradaj, J. Efficacy of Focused Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy in Chronic Low Back Pain: A Prospective Randomized 3-Month Follow-Up Study. Med. Sci. Monit. 2022, 28, e936614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogur, H.U.; Seyfettinoğlu, F.; Tuhanioğlu, Ü.; Cicek, H.; Zohre, S. An evaluation of two different methods of coccygectomy in patients with traumatic coccydynia. J. Pain Res. 2017, 10, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gönen Aydın, C.; Örsçelik, A.; Gök, M.C.; Akman, Y.E. The Efficacy of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for Chronic Coccydynia. Med. Princ. Pract. 2020, 29, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighat, S.; Mashayekhi Asl, M. Effects of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy on Pain in Patients With Chronic Refractory Coccydynia: A Quasi-Experimental Study. Anesth. Pain Med. 2016, 6, e37428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martel-Pelletier, J.; Barr, A.J.; Cicuttini, F.M.; Conaghan, P.G.; Cooper, C.; Goldring, M.B.; Goldring, S.R.; Jones, G.; Teichtahl, A.J.; Pelletier, J.-P. Osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Ye, L.; Liu, H.; Yang, P.; Yang, B. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 1907821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Liu, Y.; Chou, S.W.; Weng, H. Dose-related effects of radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy for knee osteoarthritis: A randomized controlled trial. J. Rehabil. Med. 2021, 53, jrm00144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graff, J.; Pastor, J.; Funke, P.-J.; Mach, P.; Senge, T. Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy for ureteral stones: A retrospective analysis of 417 cases. J. Urol. 1988, 139, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacchio, A.; Giordano, L.; Colafarina, O.; Rompe, J.D.; Tavernese, E.; Ioppolo, F.; Flamini, S.; Spacca, G.; Santilli, V. Extracorporeal shock-wave therapy compared with surgery for hypertrophic long-bone nonunions. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2009, 91, 2589–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, J.A.; Alvarez, R.G.; Levitt, R.; Marlow, M. Shock wave therapy (Orthotripsy) in musculoskeletal disorders. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2001, 387, 22–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-J.; Chen, H.-S.; Chen, C.-E.; Yang, K.D. Treatment of nonunions of long bone fractures with shock waves. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2001, 387, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, C.; Romeo, P.; Lavanga, V.; Pisani, S.; Sansone, V. Effectiveness of extracorporeal shock wave therapy in bone marrow edema syndrome of the hip. Rheumatol. Int. 2014, 34, 1513–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, K.; Mao, Y.; Qu, X.; Dai, K.; Jia, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Yan, M. High-energy extracorporeal shock wave therapy for nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2018, 13, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vulpiani, M.C.; Vetrano, M.; Trischitta, D.; Scarcello, L.; Chizzi, F.; Argento, G.; Saraceni, V.M.; Maffulli, N.; Ferretti, A. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in early osteonecrosis of the femoral head: Prospective clinical study with long-term follow-up. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2012, 132, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Häußer, J.; Wieber, J.; Catalá-Lehnen, P. The use of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for the treatment of bone marrow oedema—A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2021, 16, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sconza, C.; Anzà, M.; Di Matteo, B.; Lipina, M.; Kon, E.; Respizzi, S.; Tibalt, E.; D’Agostino, M.C. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for the treatment of osteonecrosis and bone vascular diseases: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 26, 2949–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, C.; Romeo, P.; Amelio, E.; Sansone, V. Effectiveness of ESWT in the treatment of Kienböck’s disease. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2011, 37, 1452–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöberl, M.; Prantl, L.; Loose, O.; Zellner, J.; Angele, P.; Zeman, F.; Spreitzer, M.; Nerlich, M.; Krutsch, W. Non-surgical treatment of pubic overload and groin pain in amateur football players: A prospective double-blinded randomised controlled study. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2017, 25, 1958–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Sun, W.; Li, Z.; Guo, W.; Kush, N.; Ozaki, K. Intractable bone marrow edema syndrome of the hip. Orthopedics 2015, 38, e263–e270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisstede, B.M.; van den Brink, J.; Randsdorp, M.S.; Geelen, S.J.; Koes, B.W. Effectiveness of Surgical and Postsurgical Interventions for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome-A Systematic Review. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2018, 99, 1660–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liang, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Wan, T.; Xu, F.; Lei, L. Effects of shock wave therapy in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Disabil. Rehabil. 2022, 44, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Dong, C.; Wei, H.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, J.; Tan, M. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy versus local corticosteroid injection for the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome: A meta-analysis. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2020, 15, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.-T.; Chen, Y.-P.; Kuo, Y.-J.; Chiang, M.-H. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Provides Limited Therapeutic Effects on Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicina 2022, 58, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, I.H.Y.; Ieong, E.; Aljalahma, M.A.; Haldar, A.; Welck, M. Extracorporeal shock wave treatment in foot and ankle fracture non-unions—A review. Foot 2022, 51, 101889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haake, M.; Böddeker, I.; Decker, T.; Buch, M.; Vogel, M.; Labek, G.; Maier, M.; Loew, M.; Maier-Boerries, O.; Fischer, J.; et al. Side-effects of extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) in the treatment of tennis elbow. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2002, 122, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notarnicola, A.; Maccagnano, G.; Tafuri, S.; Fiore, A.; Margiotta, C.; Pesce, V.; Moretti, B. Prognostic factors of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for tendinopathies. Musculoskelet. Surg. 2016, 100, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hearnden, A.; Desai, A.; Karmegam, A.; Flannery, M. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in chronic calcific tendonitis of the shoulder--is it effective? Acta Orthop. Belg. 2009, 75, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, W.-Y.; Wang, C.-J.; Wu, K.-T.; Yang, Y.-J.; Cheng, J.-H.; Wang, S.-W. Comparative outcomes of extracorporeal shockwave therapy for shoulder tendinitis or partial tears of the rotator cuff in athletes and non-athletes: Retrospective study. Int. J. Surg. 2018, 51, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.L.; Shepstone, L.; Donell, S.T.; Thomas, T.L. Shock wave therapy for chronic Achilles tendon pain: A randomized placebo-controlled trial. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2005, 440, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Therapeutic Effects | Biological Effects |
|---|---|
| Analgesic effect | Decreased substance P in the area of application [9] |
| Selective loss of unmyelinated nerve fibers [10] | |
| Decreased expression of calcitonin-related peptide in dorsal root ganglia [11] | |
| Activation of the serotonergic system [12] | |
| Tissue repair effect | Proliferation of tenocytes [13] |
| Activation of catabolic processes leading to the elimination of damaged matrix constituents [14] | |
| Microdisruption of avascular or poorly vascularized tissues [15] | |
| Increased tissue neovascularization [16] | |
| Enhanced collagen synthesis, maturation and characteristics [17] | |
| Regulation in proliferation, activation and differentiation of keratinocytes originating from scar tissue (antifibrosis) [18] | |
| Osteogenic effect | Osteoblast growth through osteogenic transcription factors such as vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A) and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α [19] |
| Regulation and stimulation of chondrogenesis and bone regeneration through mesenchymal stem cell metabolism [20] | |
| Enhancement of Pdia-3 expression involved in the 1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D 3 Rapid Membrane Signaling Pathway, related to calcium homeostasis [21] | |
| Stimulation of the periosteum with decreased osteoclast activity [22] | |
| Osteoblast proliferation and differentiation through regulation of nitric oxide (NO), protein kinase B (PKB), bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) and transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1) levels [23] |
| Pathology | Intensity | Sessions | Pulses | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcific tendinopathy of the shoulder | High | 3–4 (every 1–2 weeks) | 1500–2000 | Locate calcification. Patient in supine position with shoulder in extension and internal rotation |
| Lateral epicondylitis | Low | 3 (every 1–2 weeks) | 1500–2000 | Apply to point of maximum pain |
| Greater trochanteric pain syndrome | Low | 3 (every 1–2 weeks) | 2000 | Apply to point of maximum pain |
| Patellar tendinopathy | Low | 3 (every 1–2 weeks) | 1500–2000 | Apply to point of maximum pain |
| Achilles tendinopathy | Low | 4 (every 1–2 weeks) | 2000 | Apply to point of maximum pain |
| Plantar fasciitis | Low | 3 (every 1–2 weeks) | 2000 | Apply to point of maximum pain |
| Trapezius myofascial syndrome | Low | 4–8 (1–2 per week) | 1000 | Apply to point of maximum pain |
| Low back pain | Low | 6–10 (1–2 per week) | 1000 | Apply to point of maximum pain |
| Delayed bone healing | High | 1–4 (every 1–2 weeks) | 2000–4000 | Localize the area using radiology |
| Avascular necrosis of the hip | High | 1–2 (every 1–2 weeks) | 4000–6000 | Locate the area using radiology |
| Osteoarthritis | Low | 4 (every 1–2 weeks) | 2000 | Apply to point of maximum pain |
| Carpal tunnel syndrome | Low | 3 (every 1–2 weeks) | 1000–1500 | Apply to point of maximum pain |
| Pathologies | Level of Evidence |
|---|---|
| Calcific tendinopathy of the shoulder | 1+ |
| Lateral epicondylitis | 1+ |
| Greater trochanteric pain syndrome | 1+ |
| Plantar fasciitis | 1+ |
| Delayed bone healing | 1+ |
| Patellar tendinopathy | 1− |
| Achilles tendinopathy | 1− |
| Trapezius myofascial syndrome | 1− |
| Low back pain | 1− |
| Avascular necrosis of the hip | 1− |
| Osteoarthritis | 1− |
| Femoral head osteonecrosis | 1− |
| Pubis osteitis | 1− |
| Carpal tunnel syndrome | 1− |
| Bone marrow edema syndrome of the hip | 2− |
| Coccigodinia | 3 |
| Kienbock’s disease | 3 |
| Patients with poorly controlled coagulopathies. |
| Acute infection |
| Pregnancy |
| Direct application on growth plate |
| Oncological tissue in the area to be treated |
| Tumor metastases |
| Multiple myeloma |
| Lymphoma |
| Complete tendon rupture |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De la Corte-Rodríguez, H.; Román-Belmonte, J.M.; Rodríguez-Damiani, B.A.; Vázquez-Sasot, A.; Rodríguez-Merchán, E.C. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for the Treatment of Musculoskeletal Pain: A Narrative Review. Healthcare 2023, 11, 2830. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11212830
De la Corte-Rodríguez H, Román-Belmonte JM, Rodríguez-Damiani BA, Vázquez-Sasot A, Rodríguez-Merchán EC. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for the Treatment of Musculoskeletal Pain: A Narrative Review. Healthcare. 2023; 11(21):2830. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11212830
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe la Corte-Rodríguez, Hortensia, Juan M. Román-Belmonte, Beatriz A. Rodríguez-Damiani, Aránzazu Vázquez-Sasot, and Emérito Carlos Rodríguez-Merchán. 2023. "Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for the Treatment of Musculoskeletal Pain: A Narrative Review" Healthcare 11, no. 21: 2830. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11212830
APA StyleDe la Corte-Rodríguez, H., Román-Belmonte, J. M., Rodríguez-Damiani, B. A., Vázquez-Sasot, A., & Rodríguez-Merchán, E. C. (2023). Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for the Treatment of Musculoskeletal Pain: A Narrative Review. Healthcare, 11(21), 2830. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11212830







