Growing Taller without Hormones? Dr. Consult Google—An Evaluation of Online Information Related to Limb Lengthening
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Methods of Assessment
2.2. Statistical Analysis
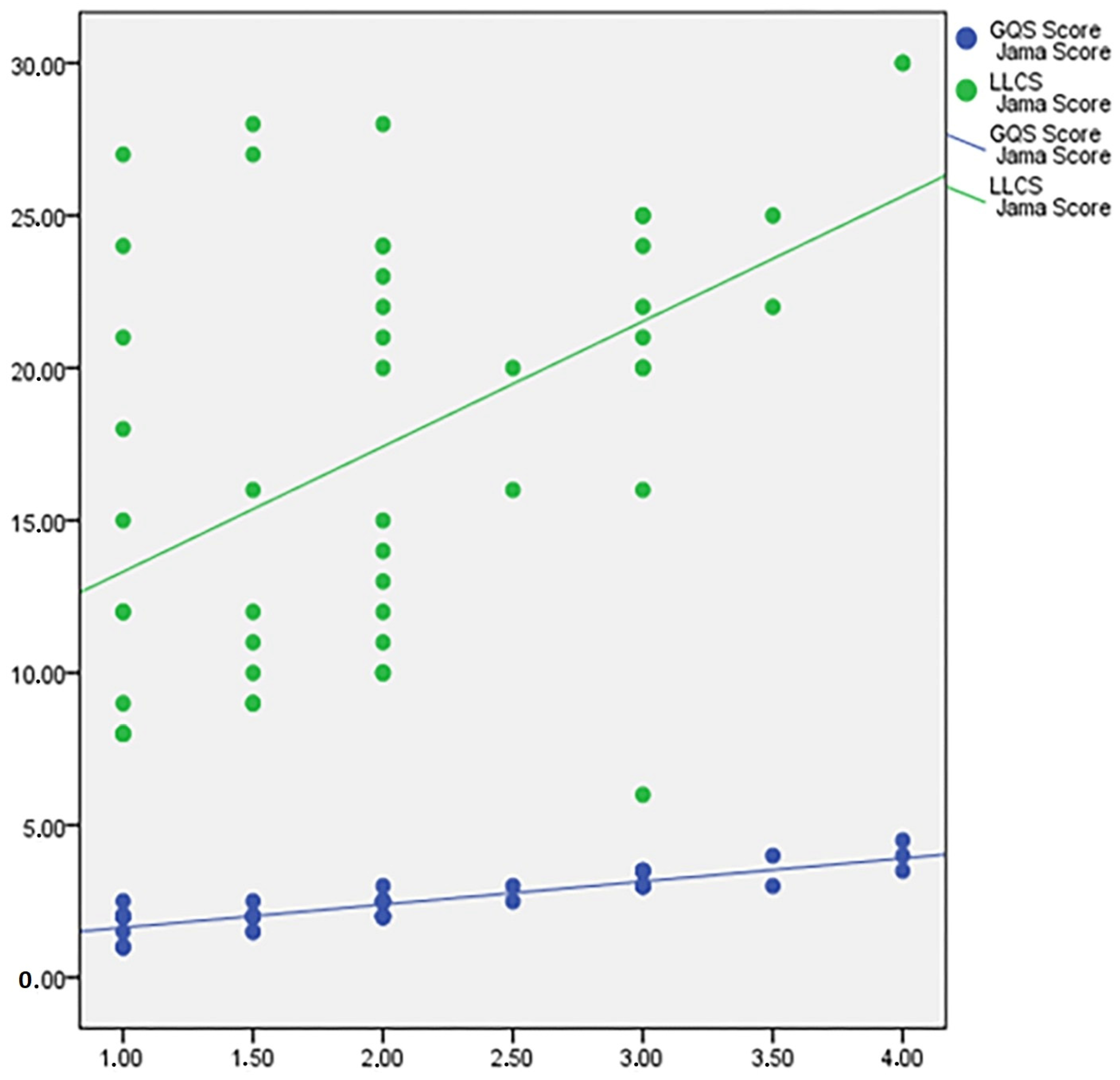
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| American Medical Association | AMA |
| Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor type 3 | FGFR3 |
| Fibroblast-like Growth Factor 23 | FGF23 |
| Flesch Kincaid Grade Level | FKGL |
| Flesch Reading Ease Score | FKRS |
| Flesch-Kincaid Readability Test Tool | FK |
| Global Quality Score | GQS |
| Growth Hormone | GH |
| Health on Net | HON |
| Journal of American Medical Association | JAMA |
| Limb Lengthening Content Score | LLCS |
| National Institutes of Health | NIH |
References
- Gupte, C.M.; Hassan, A.N.A.; McDermott, I.D.; Thomas, R.D. The Internet–Friend or Foe? A Questionnaire Study of Orthopaedic out-Patients. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2002, 84, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hosny, G.A. Limb Lengthening History, Evolution, Complications and Current Concepts. J. Orthop. Traumatol. 2020, 21, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benigeri, M.; Pluye, P. Shortcomings of Health Information on the Internet. Health Promot. Int. 2003, 18, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrrell Burrus, M.; Werner, B.C.; Starman, J.S.; Kurkis, G.M.; Pierre, J.M.; Diduch, D.R.; Hart, J.M. Patient Perceptions and Current Trends in Internet Use by Orthopedic Outpatients. HSS J. 2017, 13, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plusch, K.; Carfagno, J.; Givner, D.; Fletcher, D.; Aita, D.; Gallant, G.G.; Abboudi, J.; Beredjiklian, P. An Evaluation of the Source and Content of Dupuytren’s Disease Information Available on the Internet. Cureus 2021, 13, e19356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mindler, G.T.; Stauffer, A.; Ganger, R. Leg Lengthening and Deformity Correction in Rare Bone Diseases: A Multidisciplinary Approach. Wien. Med. Wochenschr. 2021, 171, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauli, R.M. Achondroplasia: A Comprehensive Clinical Review. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2019, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiang, R.; Thompson, L.M.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Church, D.M.; Fielder, T.J.; Bocian, M.; Winokur, S.T.; Wasmuth, J.J. Mutations in the Transmembrane Domain of FGFR3 Cause the Most Common Genetic Form of Dwarfism, Achondroplasia. Cell 1994, 78, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, D.; Namba, N.; Hanioka, Y.; Ueyama, K.; Sakamoto, N.; Nakano, Y.; Izui, M.; Nagamatsu, Y.; Kashiwagi, H.; Yamamuro, M.; et al. Final Adult Height in Long-Term Growth Hormone-Treated Achondroplasia Patients. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2017, 176, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, V.; McCoy, T.H.; Harbison, M.D.; Fragomen, A.T.; Rozbruch, S.R. Limb Lengthening in Children with Russell–Silver Syndrome: A Comparison to Other Etiologies. J. Child. Orthop. 2013, 7, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supartono, B.; Utami, A.D.; Fuadi, A.R.; Aryandi, B.B. Hormone Therapy as A New Hope for Achondroplasia Patients. J. Ilm. Kedokt. Wijaya Kusuma 2022, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimann, A.; Mindler, G.T.; Kocijan, R.; Bekes, K.; Zwerina, J.; Haeusler, G.; Ganger, R. Multidisciplinary Patient Care in X-linked Hypophosphatemic Rickets: One Challenge, Many Perspectives. Wien. Med. Wochenschr. 2020, 170, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agar, A.; Sahin, A. Kyphosis-Related Information On The Internet Is the Quality, Content and Readability Sufficient for the Patients? Glob. Spine J. 2022, 12, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghodasra, J.H.; Wang, D.; Jayakar, R.G.; Jensen, A.R.; Yamaguchi, K.T.; Hegde, V.V.; Jones, K.J. The Assessment of Quality, Accuracy, and Readability of Online Educational Resources for Platelet-Rich Plasma. Arthroscopy 2018, 34, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Search Engine Market Share Report. Available online: http://www.netmarketshare.com/ (accessed on 13 December 2020).
- Charnock, D.; Shepperd, S.; Needham, G.; Gann, R. DISCERN: An Instrument for Judging the Quality of Written Consumer Health Information on Treatment Choices. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 1999, 53, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xie, B. Quality of Health Information for Consumers on the Web: A Systematic Review of Indicators, Criteria, Tools, and Evaluation Results. J. Assoc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2015, 66, 2071–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenberg, B.T.; Schairer, W.W.; Dekker, T.J.; Lacheta, L.; Millett, P.J. Online Resources for Rotator Cuff Repair: What Are Patients Reading? Arthrosc. Sports Med. Rehabil. 2019, 1, e85–e92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, A.; Langille, M.; Hughes, S.; Rose, C.; Leddin, D.; Veldhuyzen van Zanten, S. A Systematic Review of Patient Inflammatory Bowel Disease Information Resources on the World Wide Web. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 102, 2070–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooley, M.E.; Moriarty, H.; Berger, M.S.; Selm-Orr, D.; Coyle, B.; Short, T. Patient Literacy and the Readability of Written Cancer Educational Materials. Oncol. Nurs. Forum 1995, 22, 1345–1351. [Google Scholar]
- Doak, C.C.; Doak, L.G.; Root, J.H. Teaching Patients with Low Literacy Skills, 2nd ed.; Morton, P.G., Ed.; Lippincott-Raven: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Badarudeen, S.; Sabharwal, S. Readability of Patient Education Materials from the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons and Pediatric Orthopaedic Society of North America Web Sites. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2008, 90, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabharwal, S.; Badarudeen, S.; Unes Kunju, S. Readability of Online Patient Education Materials From the AAOS Web Site. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2008, 466, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vives, M.; Young, L.; Sabharwal, S. Readability of Spine-Related Patient Education Materials from Subspecialty Organization and Spine Practitioner Websites. Spine 2009, 34, 2826–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer, C.; Selby, M.; Scherrer, J.R.; Appel, R.D. The Health On the Net Code of Conduct for Medical and Health Websites. Comput. Biol. Med. 1998, 28, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathur, S.; Shanti, N.; Brkaric, M.; Sood, V.; Kubeck, J.; Paulino, C.; Merola, A.A. Surfing for Scoliosis: The Quality of Information Available on the Internet. Spine 2005, 30, 2695–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, G.H.; Taylor, S.A.; Dy, C.J.; Christ, A.; Patel, R.M.; Dines, J.S. Online Resources for Shoulder Instability: What Are Patients Reading? J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2014, 96, e177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, B.S.; Eiser, A.R. The Patient Physician Relationship in the Internet Age: Future Prospects and the Research Agenda. J. Med. Internet Res. 2001, 3, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morr, S.; Shanti, N.; Carrer, A.; Kubeck, J.; Gerling, M.C. Quality of Information Concerning Cervical Disc Herniation on the Internet. Spine J. 2010, 10, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, L.; Foster, N.E. Back Pain Online: A Cross-Sectional Survey of the Quality of Web-Based Information on Low Back Pain. Spine 2003, 28, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhassan, Y.; Sheridan, G.; Nassiri, M.; Osman, M.; Kiely, P.; Noel, J. Discectomy-Related Information on the Internet: Does the Quality Follow the Surge? Spine 2015, 40, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, B.D. Health Literacy and Patient Safety: Help Patients Understand: Manual for Clinicians, 2nd ed.; American Medical Association: Chicago, IL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, A.D.; Bartel, A.F.P.; Simonson, D.; Roukis, T.S. Is the Internet a Reliable Source of Information for Patients Seeking Total Ankle Replacement? J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2015, 54, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Shin, J.J.; Haro, M.S.; Song, S.H.; Nho, S.J. Evaluating the Quality of Internet Information for Femoroacetabular Impingement. Arthroscopy 2014, 30, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Jayakar, R.G.; Leong, N.L.; Leathers, M.P.; Williams, R.J.; Jones, K.J. Evaluation of the Quality, Accuracy, and Readability of Online Patient Resources for the Management of Articular Cartilage Defects. Cartilage 2017, 8, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Limb lengthening |
| Upper Extremity Limb Lengthening |
| Achondroplasia |
| Deformity |
| Limb-Length Discrepancy |
| Soft Tissue Coverage |
| Angular Deformities |
| Bone Quality |
| Motion |
| Stability |
| Osteotomy |
| Maturity |
| Treatment |
| Complication |
| Pseudoarthrosis |
| X-Ray |
| Decision |
| Computer Analysis |
| Technology |
| Distraction Osteogenesis |
| Weight Bearing |
| Ilizarov |
| External Fixator |
| Intramedullary Nail |
| Bone Healing |
| Special Surgery |
| Indications |
| Reconstructive Surgery |
| Rehabilitation |
| External/Internal Implant |
| Title | Min–Max | Mean ± SD | Median |
|---|---|---|---|
| Discern reviewer 1 | 16–64 | 33.44 ± 12.96 | 30.4 |
| Discern reviewer 2 | 16–67.2 | 34.4 ± 13.92 | 32 |
| Discern score | 16–65.6 | 33.92 ± 13.28 | 32 |
| Jama reviewer 1 | 1–4 | 2.06 ± 0.93 | 2 |
| Jama reviewer 2 | 1–4 | 2.06 ± 0.93 | 2 |
| Jama Score | 1–4 | 2.06 ± 0.89 | 2 |
| GQS reviewer 1 | 1–4 | 2.39 ± 0.7 | 2 |
| GQS reviewer 2 | 1–5 | 2.49 ± 0.95 | 2 |
| GQS Score | 1–4.5 | 2.44 ± 0.77 | 2.5 |
| FKGL | 5–11.9 | 8.43 ± 1.98 | 8.5 |
| FKRS | 21.2–94.9 | 49.85 ± 14.66 | 48.5 |
| LLCS | 6–30 | 17.67 ± 7.14 | 18 |
| Category | Discern Score | JAMA Score | GQS | FKGL | FKRS | LLCS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD (Median) | Mean ± SD (Median) | Mean ± SD (Median) | Mean ± SD (Median) | Mean ± SD (Median) | Mean ± SD (Median) | |
| Academical | 40.64 ± 14.88 (38.4) | 2.61 ± 0.93 (2.8) | 2.86 ± 0.92 (3) | 8.92 ± 1.75 (8.8) | 45.07 ± 12.38 (44.2) | 21.11 ± 7.07 (23) |
| Physician | 33.92 ± 11.36 (30.4) | 1.95 ± 0.91 (2) | 2.45 ± 0.52 (2.5) | 8.16 ± 2.3 (7.9) | 52.74 ± 20.01 (55.3) | 20.09 ± 5.15 (21) |
| Medical | 29.92 ± 10.24 (28.8) | 1.75 ± 0.67 (1.5) | 2.21 ± 0.58 (2) | 8.12 ± 1.98 (8.1) | 52.09 ± 11.17 (50.4) | 13.79 ± 5.79 (12) |
| Commercial | 25.92 ± 11.04 (25.6) | 1.5 ± 0.46 (1.5) | 1.88 ± 0.52 (2) | 8.25 ± 2.17 (8.3) | 52.68 ± 16.41 (49.6) | 13.38 ± 7.21 (10.5) |
| p | 0.021 * | 0.010 * | 0.020 * | 0.599 | 0.290 | 0.006 * |
| Score | HON | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Absent | Present | p | |
| Mean ± SD (Median) | Mean ± SD (Median) | ||
| DISCERN Score | 30.88 ± 11.04 (28.8) | 52.96 ± 10.88 (54.4) | 0.000 * |
| JAMA Score | 1.86 ± 0.76 (2) | 3.29 ± 0.7 (3.5) | 0.000 * |
| GQS Score | 2.3 ± 0.7 (2) | 3.36 ± 0.56 (3.5) | 0.001 * |
| FKGL | 8.4 ± 2.05 (8.5) | 8.61 ± 1.57 (8.4) | 0.913 |
| FKRS | 50.72 ± 15.04 (50) | 44.36 ± 11.4 (41.6) | 0.129 |
| LLCS | 16.73 ± 6.91 (16) | 23.57 ± 5.97 (25) | 0.018 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Key, S.; Yalın, M.; Erten, M. Growing Taller without Hormones? Dr. Consult Google—An Evaluation of Online Information Related to Limb Lengthening. Healthcare 2023, 11, 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11020172
Key S, Yalın M, Erten M. Growing Taller without Hormones? Dr. Consult Google—An Evaluation of Online Information Related to Limb Lengthening. Healthcare. 2023; 11(2):172. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11020172
Chicago/Turabian StyleKey, Sefa, Mustafa Yalın, and Mehmet Erten. 2023. "Growing Taller without Hormones? Dr. Consult Google—An Evaluation of Online Information Related to Limb Lengthening" Healthcare 11, no. 2: 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11020172
APA StyleKey, S., Yalın, M., & Erten, M. (2023). Growing Taller without Hormones? Dr. Consult Google—An Evaluation of Online Information Related to Limb Lengthening. Healthcare, 11(2), 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11020172








