Effect of the Frequency of Rehabilitation Treatments on the Long-Term Mortality of Stroke Survivors with Mild-to-Moderate Disabilities under the Korean National Health Insurance Service System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source and Study Design
2.2. Covariates
2.3. Statistical Analysis
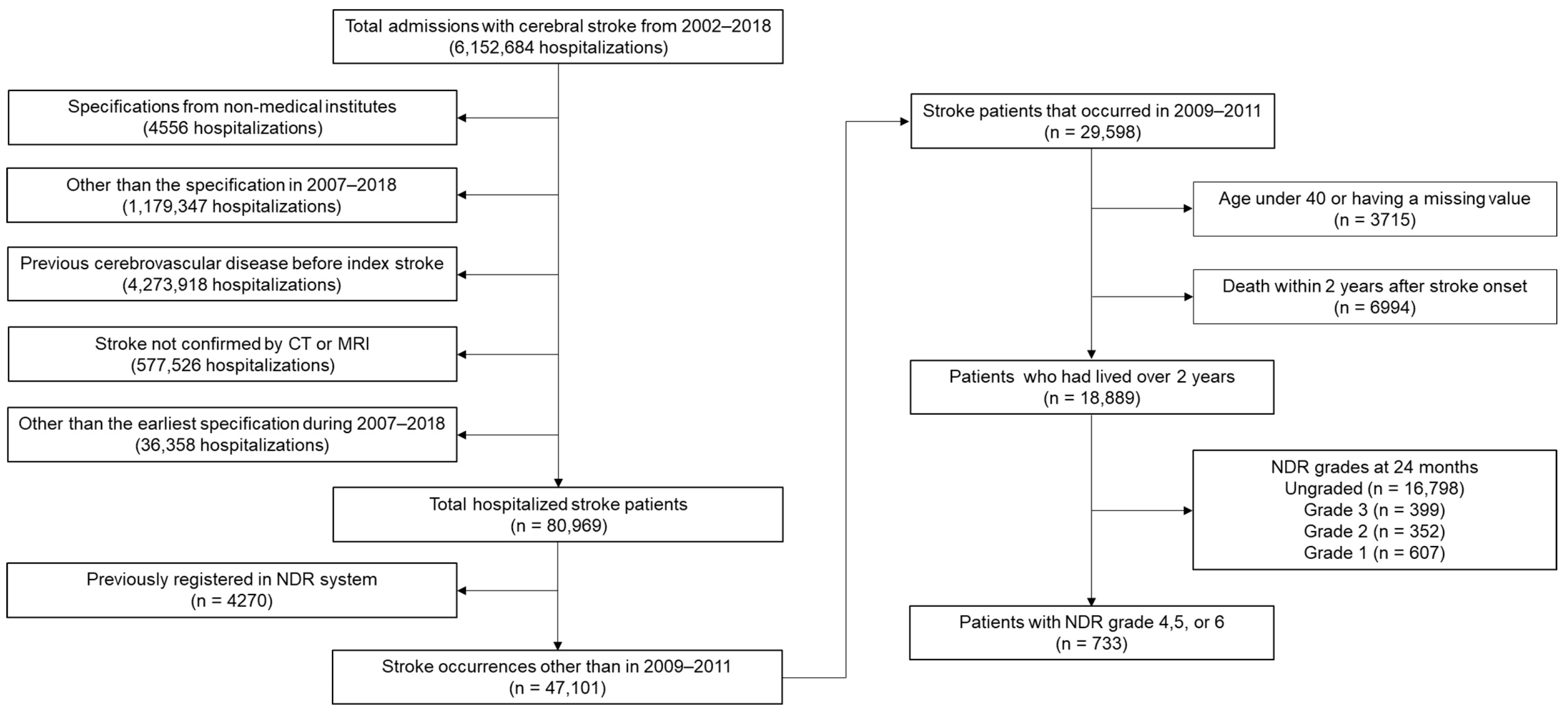
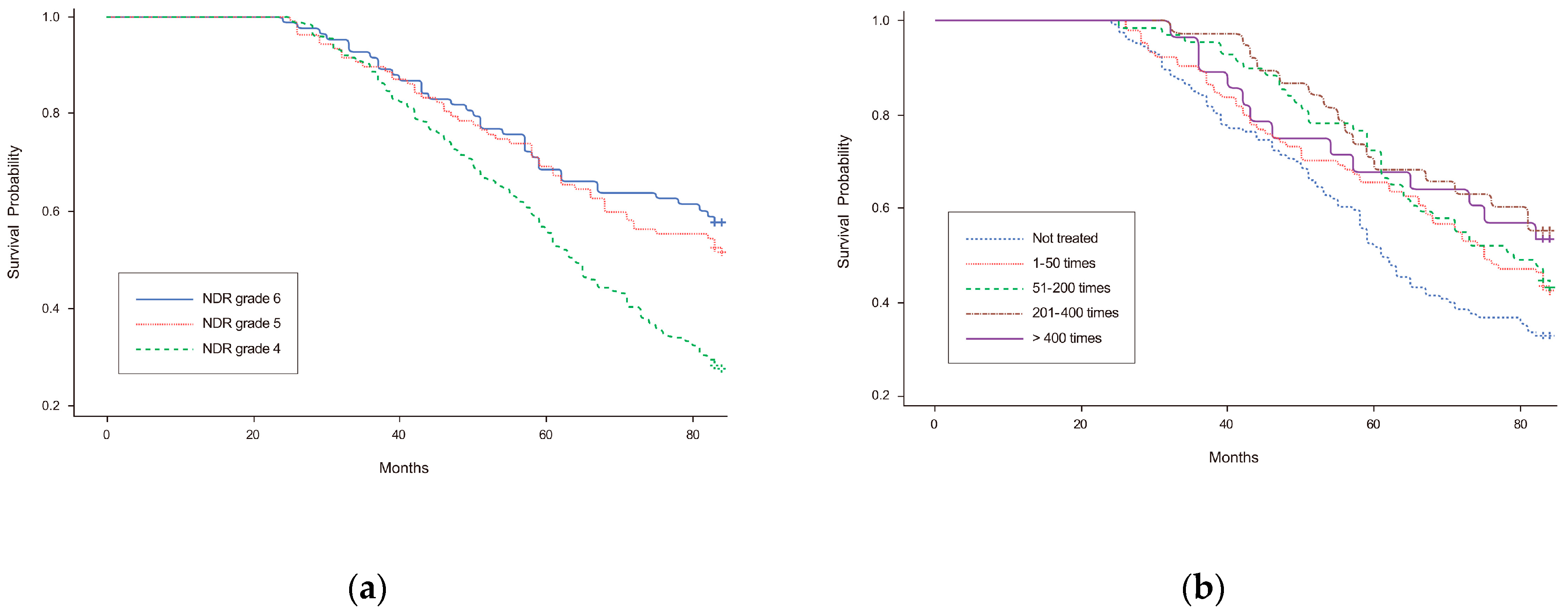
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Features
3.2. Long-Term Mortality and Cox-Proportional Hazards Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Statistic Korea. 2020 Population and Housing Census (Register-Based Census). 2021. Available online: http://kostat.go.kr/ (accessed on 13 December 2021).
- Yousufuddin, M.; Young, N. Aging and ischemic stroke. Aging 2019, 11, 2542–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katan, M.; Luft, A. Global Burden of Stroke. Semin. Neurol. 2018, 38, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Hwang, Y.-H.; Kim, J.-T.; Choi, N.-C.; Kang, S.-Y.; Cha, J.-K.; Ha, Y.S.; Shin, D.-I.; Kim, S.; Lim, B.-H. Establishment of Government-Initiated Comprehensive Stroke Centers for Acute Ischemic Stroke Management in South Korea. Stroke 2014, 45, 2391–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Statistic Korea. Causes of Death Statistics in 2020. 2021. Available online: http://kostat.go.kr/ (accessed on 13 December 2021).
- Sharma, M.; Hart, R.G.; Connolly, S.J.; Bosch, J.; Shestakovska, O.; Ng, K.K.H.; Catanese, L.; Keltai, K.; Aboyans, V.; Alings, M.; et al. Stroke Outcomes in the COMPASS Trial. Circulation 2019, 139, 1134–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.-J.; Chen, S.; Ganesh, A.; Hill, M.D. Long-term neurological, vascular, and mortality outcomes after stroke. Int. J. Stroke 2018, 13, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stinear, C.M.; Lang, C.E.; Zeiler, S.; Byblow, W.D. Advances and challenges in stroke rehabilitation. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuart, M.; Ryser, C.; Levitt, A.; Beer, S.; Kesselring, J.; Chard, S.; Weinrich, M. Stroke Rehabilitation in Switzerland versus the United States: A Preliminary Comparison. Neurorehabil. Neural. Repair. 2016, 19, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, M.; Yasunaga, H.; Matsui, H.; Morita, K.; Fushimi, K.; Fujimoto, M.; Koyama, T.; Fujitani, J. Impact of Rehabilitation on Outcomes in Patients With Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2017, 48, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.-H.; Ni, C.-H.; Li, C.-Y.; Tsai, P.-S.; Lin, L.-F.; Shen, H.-N. Stroke Rehabilitation and Risk of Mortality: A Population-Based Cohort Study Stratified by Age and Gender. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2015, 24, 1414–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-M.; Yang, Y.-H.; Chang, C.-H.; Chen, P.-C. Effects of Transferring to the Rehabilitation Ward on Long-Term Mortality Rate of First-Time Stroke Survivors: A Population-Based Study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2017, 98, 2399–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.-C.; Hung, J.-W.; Lee, H.-C.; Yen, C.-L.; Wu, C.-Y.; Yang, C.-L.; Huang, Y.-C.; Lin, P.-L.; Wang, H.-H. Rehabilitation Reduced Readmission and Mortality Risks in Patients With Stroke or Transient Ischemic Attack. Med. Care 2018, 56, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.Y.; Kim, Y.-H.; Lee, J.; Chang, W.H.; Kim, M.-W.; Pyun, S.-B.; Yoo, W.-K.; Ohn, S.H.; Park, K.D.; Oh, B.-M.; et al. Clinical practice guideline for stroke rehabilitation in Korea 2016. Brain Neurorehabil. 2017, 10, e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.H.; Bae, H.J.; Choi, Y.A.; Lee, S.H.; Shin, H.I. Length of hospital stay after stroke: A Korean nationwide study. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2016, 40, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.K.; Kim, W.S.; Sohn, M.K.; Jee, S.; Shin, Y.I.; Ko, S.H.; Ock, M.; Kim, H.J.; Paik, N.J. Korean model for post-acute comprehensive rehabilitation (KOMPACT): The study protocol for a pragmatic multicenter randomized controlled study on early supported discharge. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 710640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.H.; Sohn, M.K.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.Y.; Lee, S.G.; Shin, Y.I.; Oh, G.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Joo, M.C.; Han, E.Y.; et al. Long-term functional outcomes of patients with very mild stroke: Does a NIHSS score of 0 mean no disability? An interim analysis of the KOSCO study. Disabil. Rehabil. 2017, 39, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teasell, R.; Foley, N.; Salter, K.; Bhogal, S.; Jutai, J.; Speechley, M. Evidence-based review of stroke rehabilitation: Executive summary, 12th edition. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2009, 16, 463–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.; Son, K.J.; Kim, H.S. Chronic phase survival rate in stroke patients with severe functional limitations according to the frequency of rehabilitation treatment. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2023, 104, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boysen, G.; Marott, J.L.; Grønbæk, M.; Hassanpour, H.; Truelsen, T. Long-Term Survival after Stroke: 30 Years of Follow-Up in a Cohort, the Copenhagen City Heart Study. Neuroepidemiology 2009, 33, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, J.S.; Park, S.H.; Shin, S.A.; Kim, K. Cohort Profile: The National Health Insurance Service-National Sample Cohort (NHIS-NSC), South Korea. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hsieh, C.-Y.; Huang, H.-C.; Wu, D.P.; Li, C.-Y.; Chiu, M.-J.; Sung, S.-F. Effect of Rehabilitation Intensity on Mortality Risk After Stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2018, 99, 1042–1048.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.-Y.; Shu, J.-H.; Hsu, H.-C.; Liang, Y.; Chang, S.-T.; Kao, C.-L.; Leu, H.-B. The Impact of Rehabilitation Frequencies in the First Year after Stroke on the Risk of Recurrent Stroke and Mortality. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2017, 26, 2755–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwakkel, G.; Wagenaar, R.C.; Koelman, T.W.; Lankhorst, G.J.; Koetsier, J.C. Effects of Intensity of Rehabilitation After Stroke. Stroke 1997, 28, 1550–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattringer, T.; Posekany, A.; Niederkorn, K.; Knoflach, M.; Poltrum, B.; Mutzenbach, S.; Haring, H.-P.; Ferrari, J.; Lang, W.; Willeit, J.; et al. Predicting Early Mortality of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2019, 50, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wong, K.S. Risk Factors for Early Death in Acute Ischemic Stroke and Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Stroke 1999, 30, 2326–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cumming, T.B.; Marshall, R.S.; Lazar, R.M. Stroke, Cognitive Deficits, and Rehabilitation: Still an Incomplete Picture. Int. J. Stroke 2012, 8, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, S.C.; Wolf, S.L.; Adams, H.P.; Chen, D.; Dromerick, A.W.; Dunning, K.; Ellerbe, C.; Grande, A.; Janis, S.; Lansberg, M.G.; et al. Stroke Recovery and Rehabilitation Research. Stroke 2017, 48, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Martinez-Majander, N.; Ntaios, G.; Liu, Y.Y.; Ylikotila, P.; Joensuu, H.; Saarinen, J.; Perera, K.S.; Marti-Fabregas, J.; Chamorro, A.; Rudilosso, S.; et al. Rivaroxaban versus aspirin for secondary prevention of ischaemic stroke in patients with cancer: A subgroup analysis of the NAVIGATE ESUS randomized trial. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, M.G. Risk Factors for Ischemic Stroke in Younger Adults: A Focused Update. Stroke 2020, 51, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putaala, J. Ischemic stroke in the young: Current perspectives on incidence, risk factors, and cardiovascular prognosis. Eur. Stroke J. 2016, 1, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Langhorne, P.; Bernhardt, J.; Kwakkel, G. Stroke rehabilitation. Lancet 2011, 377, 1693–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhamoon, M.S.; Moon, Y.P.; Paik, M.C.; Boden-Albala, B.; Rundek, T.; Sacco, R.L.; Elkind, M.S. Long-term functional recovery after first ischemic stroke: The Northern Manhattan Study. Stroke 2009, 40, 2805–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kim, W.S.; Bae, H.J.; Lee, H.H.; Shin, H.I. Status of rehabilitation after ischemic stroke: A Korean nationwide study. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 42, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Grade | Degree of Disability |
|---|---|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| Variables | Number of Rehabilitations a | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | 1–50 | 51–200 | 201–400 | >400 | ||
| Total, n | 254 | 209 | 138 | 76 | 56 | |
| Age groups, n (%) | 0.241 | |||||
| 40–49 | 9 (3.54) | 12 (5.74) | 5 (3.62) | 8 (10.53) | 5 (8.93) | |
| 50–59 | 42 (16.54) | 30 (14.35) | 36 (26.09) | 12 (15.79) | 13 (23.21) | |
| 60–69 | 82 (32.28) | 68 (32.54) | 43 (31.16) | 26 (34.21) | 17 (30.36) | |
| 70–79 | 95 (37.40) | 80 (38.28) | 45 (32.61) | 25 (32.89) | 18 (32.14) | |
| ≥80 | 26 (10.24) | 19 (9.09) | 9 (6.52) | 5 (6.58) | 3 (5.36) | |
| Men, n (%) | 146 (57.48) | 122 (58.37) | 85 (61.59) | 45 (59.21) | 28 (50.00) | 0.683 |
| Subtypes, n (%) | 0.021 | |||||
| SAH | 5 (1.97) | 5 (2.39) | 1 (0.72) | 0 (0.00) | 1 (1.79) | |
| ICH | 29 (11.42) | 27 (12.92) | 32 (23.19) | 20 (26.32) | 7 (12.50) | |
| Ischemia | 213 (83.86) | 175 (83.73) | 104 (75.36) | 55 (72.37) | 48 (85.71) | |
| Unspecified | 7 (2.76) | 2 (0.96) | 1 (0.72) | 1 (1.32) | 0 (0.00) | |
| NHIP levels, n (%) | 0.592 | |||||
| Medical aid | 19 (7.48) | 13 (6.22) | 8 (5.80) | 6 (7.89) | 6 (10.71) | |
| First quartile | 48 (18.90) | 38 (18.18) | 17 (12.32) | 9 (11.84) | 11 (19.64) | |
| Second quartile | 44 (17.32) | 32 (15.31) | 16 (11.59) | 11 (14.47) | 8 (14.92) | |
| Third quartile | 60 (23.62) | 51 (24.40) | 41 (29.71) | 15 (19.74) | 14 (25.00) | |
| Fourth quartile | 83 (32.68) | 75 (35.89) | 56 (40.58) | 35 (46.05) | 17 (30.36) | |
| Residential areas, n (%) | 0.037 | |||||
| Capital | 42 (16.54) | 44 (21.05) | 34 (24.64) | 19 (25.00) | 12 (21.43) | |
| Metropolitan | 51 (20.08) | 41 (19.62) | 40 (28.99) | 19 (25.00) | 14 (25.00) | |
| City | 109 (42.91) | 88 (42.11) | 51 (36.96) | 29 (38.16) | 27 (48.21) | |
| County | 52 (20.47) | 36 (17.22) | 13 (9.42) | 9 (11.84) | 3 (5.36) | |
| HTN, n (%) | 216 (85.04) | 169 (80.86) | 116 (84.06) | 59 (77.63) | 43 (76.79) | 0.380 |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 129 (50.79) | 96 (45.93) | 73 (52.90) | 34 (44.74) | 21 (37.50) | 0.261 |
| DL, n (%) | 128 (50.39) | 97 (46.41) | 63 (45.65) | 34 (44.74) | 37 (66.07) | 0.076 |
| IHD, n (%) | 35 (13.78) | 12 (5.74) | 12 (8.70) | 8 (10.53) | 5 (8.83) | 0.069 |
| AF, n (%) | 25 (9.84) | 15 (7.18) | 13 (9.42) | 8 (10.53) | 9 (16.07) | 0.376 |
| CKD, n (%) | 6 (2.36) | 4 (1.91) | 2 (1.45) | 1 (1.32) | 1 (1.79) | 0.965 |
| Disability grades, n (%) | <0.001 | |||||
| Grade 6 | 78 (30.71) | 51 (24.40) | 22 (15.94) | 11 (14.47) | 4 (7.14) | |
| Grade 5 | 67 (26.38) | 72 (34.45) | 42 (30.43) | 17 (22.37) | 17 (30.36) | |
| Grade 4 | 109 (42.91) | 86 (41.15) | 74 (53.62) | 48 (63.16) | 35 (62.50) | |
| Variables | Adjusted HR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disability grades | Grade 6 | 1.00 | ||
| Grade 5 | 1.20 | 0.77–1.86 | 0.420 | |
| Grade 4 | 1.82 | 1.23–2.68 | 0.003 | |
| Number of rehabilitations a | None | 1.00 | ||
| 1–50 | 0.79 | 0.56–1.10 | 0.160 | |
| 51–200 | 0.80 | 0.54–1.19 | 0.277 | |
| 201–400 | 0.67 | 0.39–1.15 | 0.143 | |
| >400 | 0.71 | 0.39–1.31 | 0.279 | |
| Sex | Men | 1.82 | 1.36–2.44 | <0.001 |
| Age groups | 40–49 | 1.00 | ||
| 50–59 | 1.15 | 0.37–3.60 | 0.814 | |
| 60–69 | 3.15 | 1.08–9.17 | 0.036 | |
| 70–79 | 5.80 | 2.01–16.76 | 0.001 | |
| ≥80 | 11.40 | 3.74–34.77 | <0.001 | |
| Subtypes | SAH | 1.00 | ||
| ICH | 0.93 | 0.21–4.09 | 0.925 | |
| Ischemia | 1.03 | 0.26–4.35 | 0.966 | |
| Unspecified | 0.25 | 0.22–2.89 | 0.268 | |
| Co-morbidities | HTN | 0.83 | 0.58–1.19 | 0.300 |
| Diabetes | 1.14 | 0.86–1.51 | 0.374 | |
| DL | 0.96 | 0.72–1.28 | 0.797 | |
| IHD | 0.92 | 0.58–1.45 | 0.712 | |
| AF | 1.23 | 0.79–1.92 | 0.367 | |
| CKD | 2.85 | 1.17–6.96 | 0.021 | |
| NHIP levels | Medical aid | 1.00 | ||
| First quartile | 1.19 | 0.64–2.20 | 0.588 | |
| Second quartile | 1.08 | 0.57–2.07 | 0.814 | |
| Third quartile | 1.20 | 0.67–2.16 | 0.540 | |
| Fourth quartile | 0.69 | 0.39–1.23 | 0.211 | |
| Residential Areas | Capital | 1.00 | ||
| Metropolitan | 1.47 | 0.95–2.29 | 0.084 | |
| City | 1.17 | 0.78–1.74 | 0.456 | |
| County | 1.54 | 0.97–2.44 | 0.066 | |
| Disabilities | Number of Rehabilitations a | Adjusted HR b | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDR grade 4 | None | 1.00 | ||
| 1–50 | 0.64 | 0.40–1.02 | 0.059 | |
| 51–200 | 0.46 | 0.27–0.79 | 0.005 | |
| 201–400 | 0.50 | 0.26–0.97 | 0.040 | |
| >400 | 0.54 | 0.25–1.16 | 0.112 | |
| NDR grade 5 | None | 1.00 | ||
| 1–50 | 0.85 | 0.39–1.84 | 0.677 | |
| 51–200 | 1.80 | 0.83–3.90 | 0.138 | |
| 201–400 | 0.20 | 0.02–1.72 | 0.141 | |
| >400 | 0.58 | 0.13–2.73 | 0.494 | |
| NDR grade 6 | None | 1.00 | ||
| 1–50 | 0.94 | 0.40–2.20 | 0.878 | |
| 51–200 | 0.57 | 0.11–2.86 | 0.494 | |
| 201–400 | 2.15 | 0.62–7.43 | 0.227 | |
| >400 | 15.00 | 2.03–111.10 | 0.008 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, D.; Son, K.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.S. Effect of the Frequency of Rehabilitation Treatments on the Long-Term Mortality of Stroke Survivors with Mild-to-Moderate Disabilities under the Korean National Health Insurance Service System. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11111587
Park D, Son KJ, Kim JH, Kim HS. Effect of the Frequency of Rehabilitation Treatments on the Long-Term Mortality of Stroke Survivors with Mild-to-Moderate Disabilities under the Korean National Health Insurance Service System. Healthcare. 2023; 11(11):1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11111587
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Dougho, Kang Ju Son, Jong Hun Kim, and Hyoung Seop Kim. 2023. "Effect of the Frequency of Rehabilitation Treatments on the Long-Term Mortality of Stroke Survivors with Mild-to-Moderate Disabilities under the Korean National Health Insurance Service System" Healthcare 11, no. 11: 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11111587
APA StylePark, D., Son, K. J., Kim, J. H., & Kim, H. S. (2023). Effect of the Frequency of Rehabilitation Treatments on the Long-Term Mortality of Stroke Survivors with Mild-to-Moderate Disabilities under the Korean National Health Insurance Service System. Healthcare, 11(11), 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11111587





