Effect of the Frequency of Rehabilitation Treatments on the Long-Term Mortality of Stroke Survivors with Mild-to-Moderate Disabilities under the Korean National Health Insurance Service System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
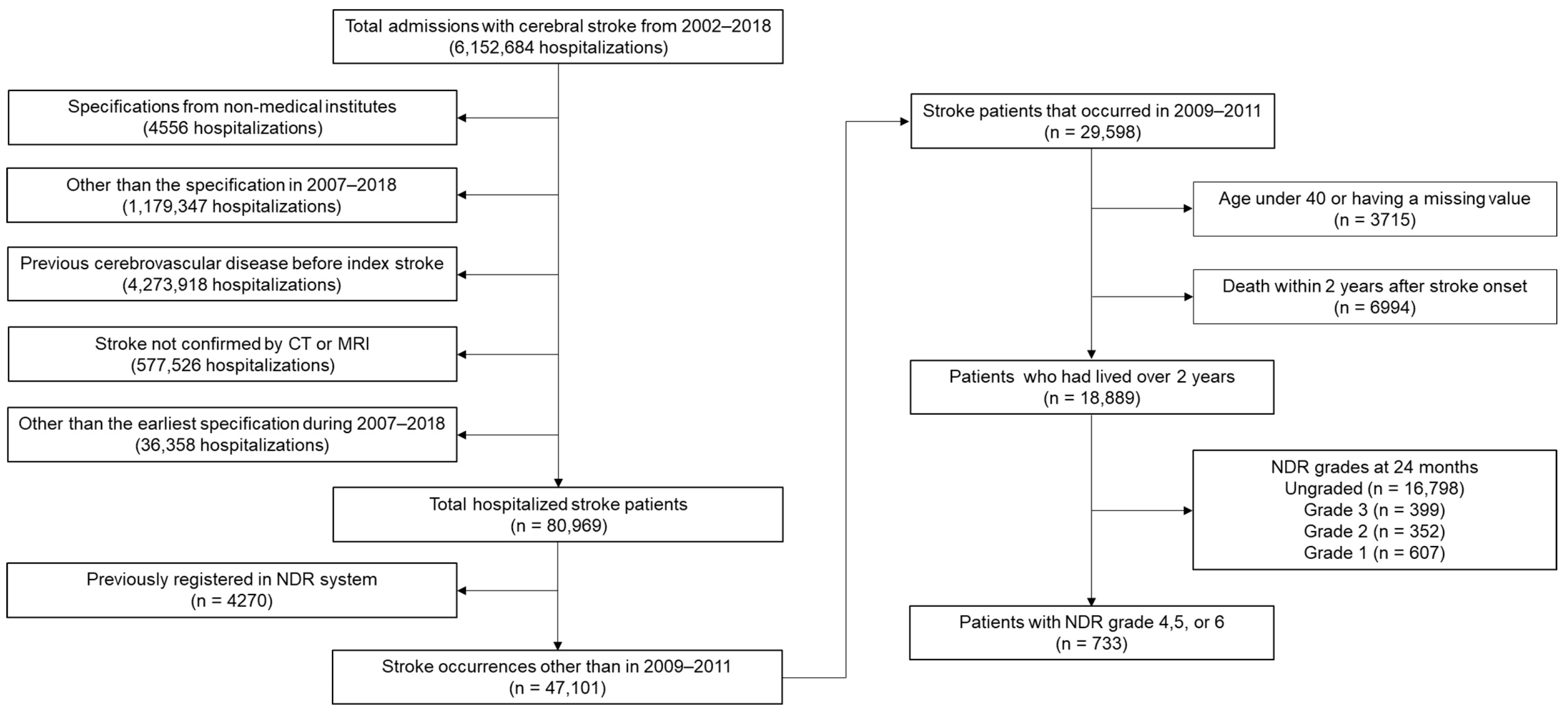
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source and Study Design
2.2. Covariates
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Features
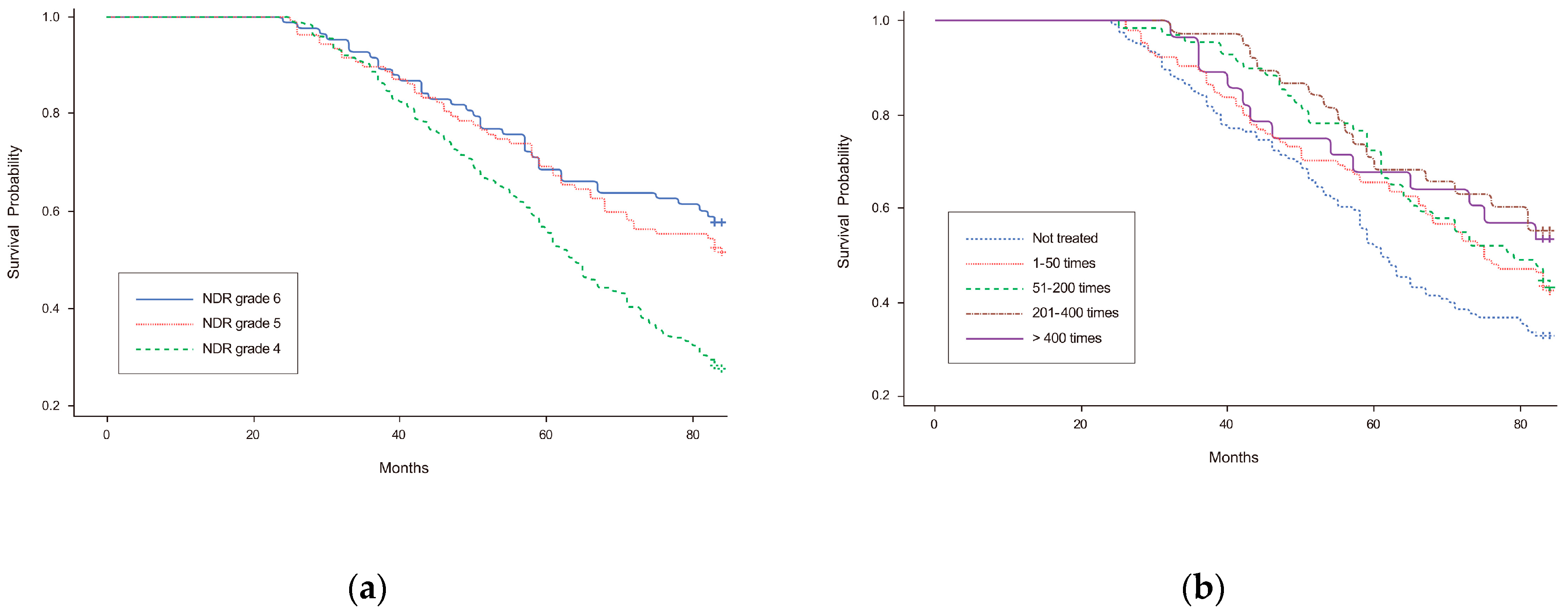
3.2. Long-Term Mortality and Cox-Proportional Hazards Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Statistic Korea. 2020 Population and Housing Census (Register-Based Census). 2021. Available online: http://kostat.go.kr/ (accessed on 13 December 2021).
- Yousufuddin, M.; Young, N. Aging and ischemic stroke. Aging 2019, 11, 2542–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katan, M.; Luft, A. Global Burden of Stroke. Semin. Neurol. 2018, 38, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Hwang, Y.-H.; Kim, J.-T.; Choi, N.-C.; Kang, S.-Y.; Cha, J.-K.; Ha, Y.S.; Shin, D.-I.; Kim, S.; Lim, B.-H. Establishment of Government-Initiated Comprehensive Stroke Centers for Acute Ischemic Stroke Management in South Korea. Stroke 2014, 45, 2391–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistic Korea. Causes of Death Statistics in 2020. 2021. Available online: http://kostat.go.kr/ (accessed on 13 December 2021).
- Sharma, M.; Hart, R.G.; Connolly, S.J.; Bosch, J.; Shestakovska, O.; Ng, K.K.H.; Catanese, L.; Keltai, K.; Aboyans, V.; Alings, M.; et al. Stroke Outcomes in the COMPASS Trial. Circulation 2019, 139, 1134–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.-J.; Chen, S.; Ganesh, A.; Hill, M.D. Long-term neurological, vascular, and mortality outcomes after stroke. Int. J. Stroke 2018, 13, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stinear, C.M.; Lang, C.E.; Zeiler, S.; Byblow, W.D. Advances and challenges in stroke rehabilitation. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuart, M.; Ryser, C.; Levitt, A.; Beer, S.; Kesselring, J.; Chard, S.; Weinrich, M. Stroke Rehabilitation in Switzerland versus the United States: A Preliminary Comparison. Neurorehabil. Neural. Repair. 2016, 19, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, M.; Yasunaga, H.; Matsui, H.; Morita, K.; Fushimi, K.; Fujimoto, M.; Koyama, T.; Fujitani, J. Impact of Rehabilitation on Outcomes in Patients With Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2017, 48, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.-H.; Ni, C.-H.; Li, C.-Y.; Tsai, P.-S.; Lin, L.-F.; Shen, H.-N. Stroke Rehabilitation and Risk of Mortality: A Population-Based Cohort Study Stratified by Age and Gender. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2015, 24, 1414–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-M.; Yang, Y.-H.; Chang, C.-H.; Chen, P.-C. Effects of Transferring to the Rehabilitation Ward on Long-Term Mortality Rate of First-Time Stroke Survivors: A Population-Based Study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2017, 98, 2399–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.-C.; Hung, J.-W.; Lee, H.-C.; Yen, C.-L.; Wu, C.-Y.; Yang, C.-L.; Huang, Y.-C.; Lin, P.-L.; Wang, H.-H. Rehabilitation Reduced Readmission and Mortality Risks in Patients With Stroke or Transient Ischemic Attack. Med. Care 2018, 56, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.Y.; Kim, Y.-H.; Lee, J.; Chang, W.H.; Kim, M.-W.; Pyun, S.-B.; Yoo, W.-K.; Ohn, S.H.; Park, K.D.; Oh, B.-M.; et al. Clinical practice guideline for stroke rehabilitation in Korea 2016. Brain Neurorehabil. 2017, 10, e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.H.; Bae, H.J.; Choi, Y.A.; Lee, S.H.; Shin, H.I. Length of hospital stay after stroke: A Korean nationwide study. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2016, 40, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.K.; Kim, W.S.; Sohn, M.K.; Jee, S.; Shin, Y.I.; Ko, S.H.; Ock, M.; Kim, H.J.; Paik, N.J. Korean model for post-acute comprehensive rehabilitation (KOMPACT): The study protocol for a pragmatic multicenter randomized controlled study on early supported discharge. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 710640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.H.; Sohn, M.K.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.Y.; Lee, S.G.; Shin, Y.I.; Oh, G.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Joo, M.C.; Han, E.Y.; et al. Long-term functional outcomes of patients with very mild stroke: Does a NIHSS score of 0 mean no disability? An interim analysis of the KOSCO study. Disabil. Rehabil. 2017, 39, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teasell, R.; Foley, N.; Salter, K.; Bhogal, S.; Jutai, J.; Speechley, M. Evidence-based review of stroke rehabilitation: Executive summary, 12th edition. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2009, 16, 463–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.; Son, K.J.; Kim, H.S. Chronic phase survival rate in stroke patients with severe functional limitations according to the frequency of rehabilitation treatment. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2023, 104, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boysen, G.; Marott, J.L.; Grønbæk, M.; Hassanpour, H.; Truelsen, T. Long-Term Survival after Stroke: 30 Years of Follow-Up in a Cohort, the Copenhagen City Heart Study. Neuroepidemiology 2009, 33, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, J.S.; Park, S.H.; Shin, S.A.; Kim, K. Cohort Profile: The National Health Insurance Service-National Sample Cohort (NHIS-NSC), South Korea. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.-Y.; Huang, H.-C.; Wu, D.P.; Li, C.-Y.; Chiu, M.-J.; Sung, S.-F. Effect of Rehabilitation Intensity on Mortality Risk After Stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2018, 99, 1042–1048.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.-Y.; Shu, J.-H.; Hsu, H.-C.; Liang, Y.; Chang, S.-T.; Kao, C.-L.; Leu, H.-B. The Impact of Rehabilitation Frequencies in the First Year after Stroke on the Risk of Recurrent Stroke and Mortality. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2017, 26, 2755–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwakkel, G.; Wagenaar, R.C.; Koelman, T.W.; Lankhorst, G.J.; Koetsier, J.C. Effects of Intensity of Rehabilitation After Stroke. Stroke 1997, 28, 1550–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattringer, T.; Posekany, A.; Niederkorn, K.; Knoflach, M.; Poltrum, B.; Mutzenbach, S.; Haring, H.-P.; Ferrari, J.; Lang, W.; Willeit, J.; et al. Predicting Early Mortality of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2019, 50, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, K.S. Risk Factors for Early Death in Acute Ischemic Stroke and Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Stroke 1999, 30, 2326–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumming, T.B.; Marshall, R.S.; Lazar, R.M. Stroke, Cognitive Deficits, and Rehabilitation: Still an Incomplete Picture. Int. J. Stroke 2012, 8, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, S.C.; Wolf, S.L.; Adams, H.P.; Chen, D.; Dromerick, A.W.; Dunning, K.; Ellerbe, C.; Grande, A.; Janis, S.; Lansberg, M.G.; et al. Stroke Recovery and Rehabilitation Research. Stroke 2017, 48, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Majander, N.; Ntaios, G.; Liu, Y.Y.; Ylikotila, P.; Joensuu, H.; Saarinen, J.; Perera, K.S.; Marti-Fabregas, J.; Chamorro, A.; Rudilosso, S.; et al. Rivaroxaban versus aspirin for secondary prevention of ischaemic stroke in patients with cancer: A subgroup analysis of the NAVIGATE ESUS randomized trial. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, M.G. Risk Factors for Ischemic Stroke in Younger Adults: A Focused Update. Stroke 2020, 51, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putaala, J. Ischemic stroke in the young: Current perspectives on incidence, risk factors, and cardiovascular prognosis. Eur. Stroke J. 2016, 1, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhorne, P.; Bernhardt, J.; Kwakkel, G. Stroke rehabilitation. Lancet 2011, 377, 1693–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhamoon, M.S.; Moon, Y.P.; Paik, M.C.; Boden-Albala, B.; Rundek, T.; Sacco, R.L.; Elkind, M.S. Long-term functional recovery after first ischemic stroke: The Northern Manhattan Study. Stroke 2009, 40, 2805–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.S.; Bae, H.J.; Lee, H.H.; Shin, H.I. Status of rehabilitation after ischemic stroke: A Korean nationwide study. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 42, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Grade | Degree of Disability |
|---|---|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| Variables | Number of Rehabilitations a | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | 1–50 | 51–200 | 201–400 | >400 | ||
| Total, n | 254 | 209 | 138 | 76 | 56 | |
| Age groups, n (%) | 0.241 | |||||
| 40–49 | 9 (3.54) | 12 (5.74) | 5 (3.62) | 8 (10.53) | 5 (8.93) | |
| 50–59 | 42 (16.54) | 30 (14.35) | 36 (26.09) | 12 (15.79) | 13 (23.21) | |
| 60–69 | 82 (32.28) | 68 (32.54) | 43 (31.16) | 26 (34.21) | 17 (30.36) | |
| 70–79 | 95 (37.40) | 80 (38.28) | 45 (32.61) | 25 (32.89) | 18 (32.14) | |
| ≥80 | 26 (10.24) | 19 (9.09) | 9 (6.52) | 5 (6.58) | 3 (5.36) | |
| Men, n (%) | 146 (57.48) | 122 (58.37) | 85 (61.59) | 45 (59.21) | 28 (50.00) | 0.683 |
| Subtypes, n (%) | 0.021 | |||||
| SAH | 5 (1.97) | 5 (2.39) | 1 (0.72) | 0 (0.00) | 1 (1.79) | |
| ICH | 29 (11.42) | 27 (12.92) | 32 (23.19) | 20 (26.32) | 7 (12.50) | |
| Ischemia | 213 (83.86) | 175 (83.73) | 104 (75.36) | 55 (72.37) | 48 (85.71) | |
| Unspecified | 7 (2.76) | 2 (0.96) | 1 (0.72) | 1 (1.32) | 0 (0.00) | |
| NHIP levels, n (%) | 0.592 | |||||
| Medical aid | 19 (7.48) | 13 (6.22) | 8 (5.80) | 6 (7.89) | 6 (10.71) | |
| First quartile | 48 (18.90) | 38 (18.18) | 17 (12.32) | 9 (11.84) | 11 (19.64) | |
| Second quartile | 44 (17.32) | 32 (15.31) | 16 (11.59) | 11 (14.47) | 8 (14.92) | |
| Third quartile | 60 (23.62) | 51 (24.40) | 41 (29.71) | 15 (19.74) | 14 (25.00) | |
| Fourth quartile | 83 (32.68) | 75 (35.89) | 56 (40.58) | 35 (46.05) | 17 (30.36) | |
| Residential areas, n (%) | 0.037 | |||||
| Capital | 42 (16.54) | 44 (21.05) | 34 (24.64) | 19 (25.00) | 12 (21.43) | |
| Metropolitan | 51 (20.08) | 41 (19.62) | 40 (28.99) | 19 (25.00) | 14 (25.00) | |
| City | 109 (42.91) | 88 (42.11) | 51 (36.96) | 29 (38.16) | 27 (48.21) | |
| County | 52 (20.47) | 36 (17.22) | 13 (9.42) | 9 (11.84) | 3 (5.36) | |
| HTN, n (%) | 216 (85.04) | 169 (80.86) | 116 (84.06) | 59 (77.63) | 43 (76.79) | 0.380 |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 129 (50.79) | 96 (45.93) | 73 (52.90) | 34 (44.74) | 21 (37.50) | 0.261 |
| DL, n (%) | 128 (50.39) | 97 (46.41) | 63 (45.65) | 34 (44.74) | 37 (66.07) | 0.076 |
| IHD, n (%) | 35 (13.78) | 12 (5.74) | 12 (8.70) | 8 (10.53) | 5 (8.83) | 0.069 |
| AF, n (%) | 25 (9.84) | 15 (7.18) | 13 (9.42) | 8 (10.53) | 9 (16.07) | 0.376 |
| CKD, n (%) | 6 (2.36) | 4 (1.91) | 2 (1.45) | 1 (1.32) | 1 (1.79) | 0.965 |
| Disability grades, n (%) | <0.001 | |||||
| Grade 6 | 78 (30.71) | 51 (24.40) | 22 (15.94) | 11 (14.47) | 4 (7.14) | |
| Grade 5 | 67 (26.38) | 72 (34.45) | 42 (30.43) | 17 (22.37) | 17 (30.36) | |
| Grade 4 | 109 (42.91) | 86 (41.15) | 74 (53.62) | 48 (63.16) | 35 (62.50) | |
| Variables | Adjusted HR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disability grades | Grade 6 | 1.00 | ||
| Grade 5 | 1.20 | 0.77–1.86 | 0.420 | |
| Grade 4 | 1.82 | 1.23–2.68 | 0.003 | |
| Number of rehabilitations a | None | 1.00 | ||
| 1–50 | 0.79 | 0.56–1.10 | 0.160 | |
| 51–200 | 0.80 | 0.54–1.19 | 0.277 | |
| 201–400 | 0.67 | 0.39–1.15 | 0.143 | |
| >400 | 0.71 | 0.39–1.31 | 0.279 | |
| Sex | Men | 1.82 | 1.36–2.44 | <0.001 |
| Age groups | 40–49 | 1.00 | ||
| 50–59 | 1.15 | 0.37–3.60 | 0.814 | |
| 60–69 | 3.15 | 1.08–9.17 | 0.036 | |
| 70–79 | 5.80 | 2.01–16.76 | 0.001 | |
| ≥80 | 11.40 | 3.74–34.77 | <0.001 | |
| Subtypes | SAH | 1.00 | ||
| ICH | 0.93 | 0.21–4.09 | 0.925 | |
| Ischemia | 1.03 | 0.26–4.35 | 0.966 | |
| Unspecified | 0.25 | 0.22–2.89 | 0.268 | |
| Co-morbidities | HTN | 0.83 | 0.58–1.19 | 0.300 |
| Diabetes | 1.14 | 0.86–1.51 | 0.374 | |
| DL | 0.96 | 0.72–1.28 | 0.797 | |
| IHD | 0.92 | 0.58–1.45 | 0.712 | |
| AF | 1.23 | 0.79–1.92 | 0.367 | |
| CKD | 2.85 | 1.17–6.96 | 0.021 | |
| NHIP levels | Medical aid | 1.00 | ||
| First quartile | 1.19 | 0.64–2.20 | 0.588 | |
| Second quartile | 1.08 | 0.57–2.07 | 0.814 | |
| Third quartile | 1.20 | 0.67–2.16 | 0.540 | |
| Fourth quartile | 0.69 | 0.39–1.23 | 0.211 | |
| Residential Areas | Capital | 1.00 | ||
| Metropolitan | 1.47 | 0.95–2.29 | 0.084 | |
| City | 1.17 | 0.78–1.74 | 0.456 | |
| County | 1.54 | 0.97–2.44 | 0.066 | |
| Disabilities | Number of Rehabilitations a | Adjusted HR b | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDR grade 4 | None | 1.00 | ||
| 1–50 | 0.64 | 0.40–1.02 | 0.059 | |
| 51–200 | 0.46 | 0.27–0.79 | 0.005 | |
| 201–400 | 0.50 | 0.26–0.97 | 0.040 | |
| >400 | 0.54 | 0.25–1.16 | 0.112 | |
| NDR grade 5 | None | 1.00 | ||
| 1–50 | 0.85 | 0.39–1.84 | 0.677 | |
| 51–200 | 1.80 | 0.83–3.90 | 0.138 | |
| 201–400 | 0.20 | 0.02–1.72 | 0.141 | |
| >400 | 0.58 | 0.13–2.73 | 0.494 | |
| NDR grade 6 | None | 1.00 | ||
| 1–50 | 0.94 | 0.40–2.20 | 0.878 | |
| 51–200 | 0.57 | 0.11–2.86 | 0.494 | |
| 201–400 | 2.15 | 0.62–7.43 | 0.227 | |
| >400 | 15.00 | 2.03–111.10 | 0.008 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, D.; Son, K.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.S. Effect of the Frequency of Rehabilitation Treatments on the Long-Term Mortality of Stroke Survivors with Mild-to-Moderate Disabilities under the Korean National Health Insurance Service System. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11111587
Park D, Son KJ, Kim JH, Kim HS. Effect of the Frequency of Rehabilitation Treatments on the Long-Term Mortality of Stroke Survivors with Mild-to-Moderate Disabilities under the Korean National Health Insurance Service System. Healthcare. 2023; 11(11):1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11111587
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Dougho, Kang Ju Son, Jong Hun Kim, and Hyoung Seop Kim. 2023. "Effect of the Frequency of Rehabilitation Treatments on the Long-Term Mortality of Stroke Survivors with Mild-to-Moderate Disabilities under the Korean National Health Insurance Service System" Healthcare 11, no. 11: 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11111587
APA StylePark, D., Son, K. J., Kim, J. H., & Kim, H. S. (2023). Effect of the Frequency of Rehabilitation Treatments on the Long-Term Mortality of Stroke Survivors with Mild-to-Moderate Disabilities under the Korean National Health Insurance Service System. Healthcare, 11(11), 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11111587





