Brain Tumors in Saudi Arabia: An Observational and Descriptive Epidemiological Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
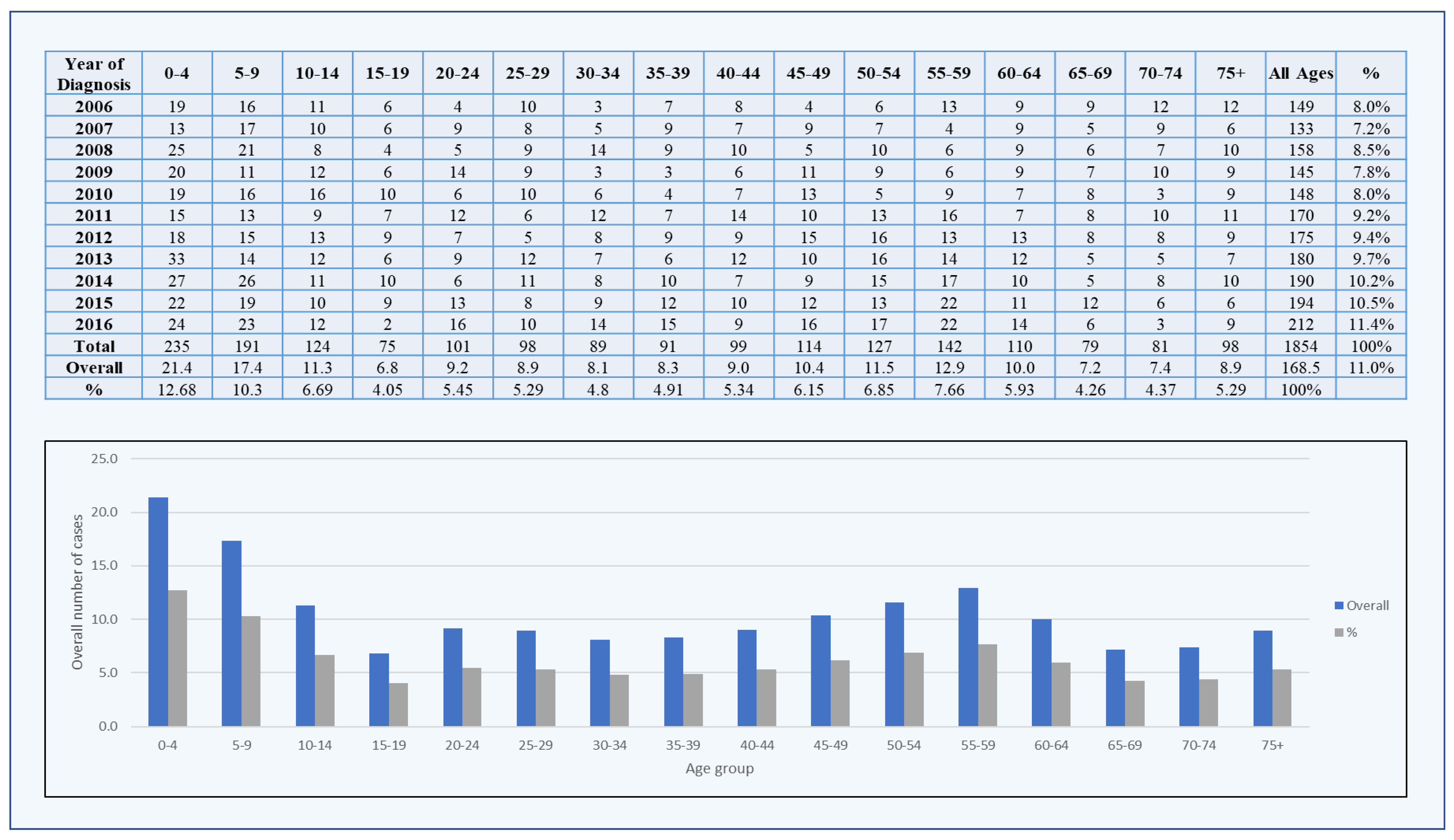
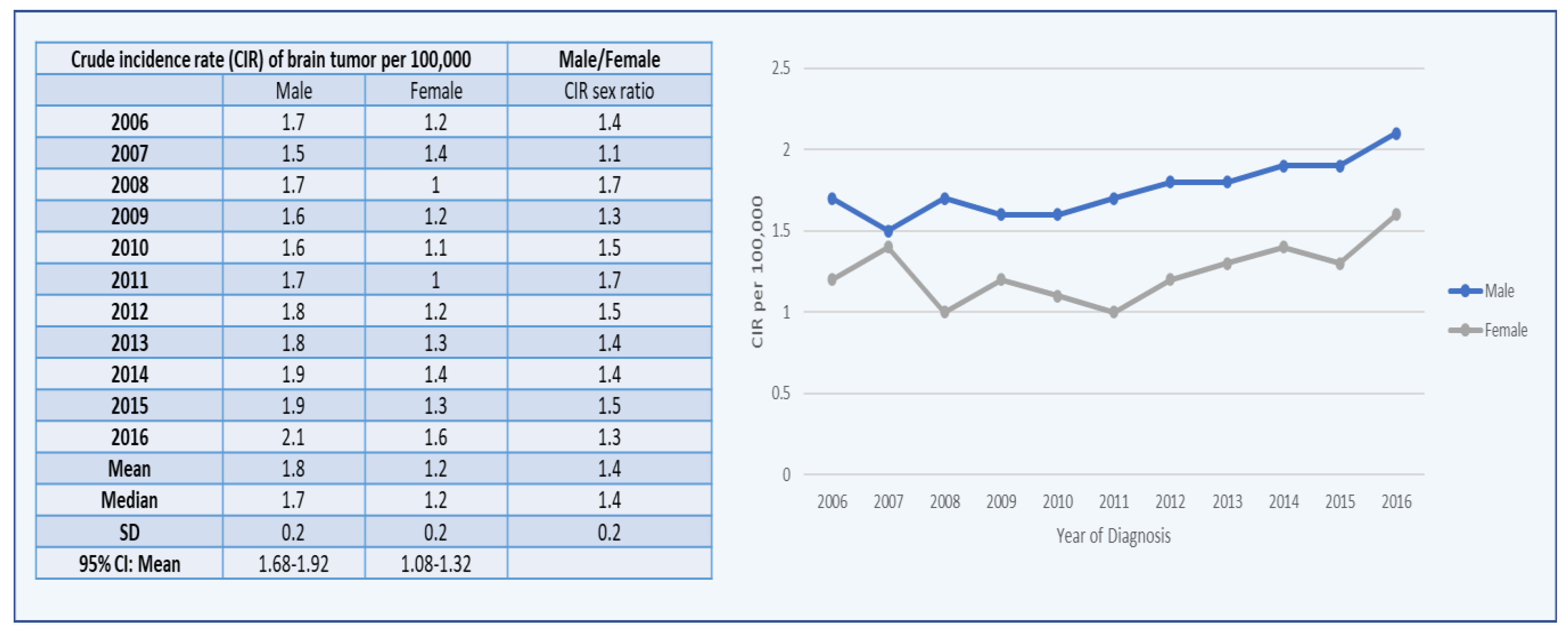
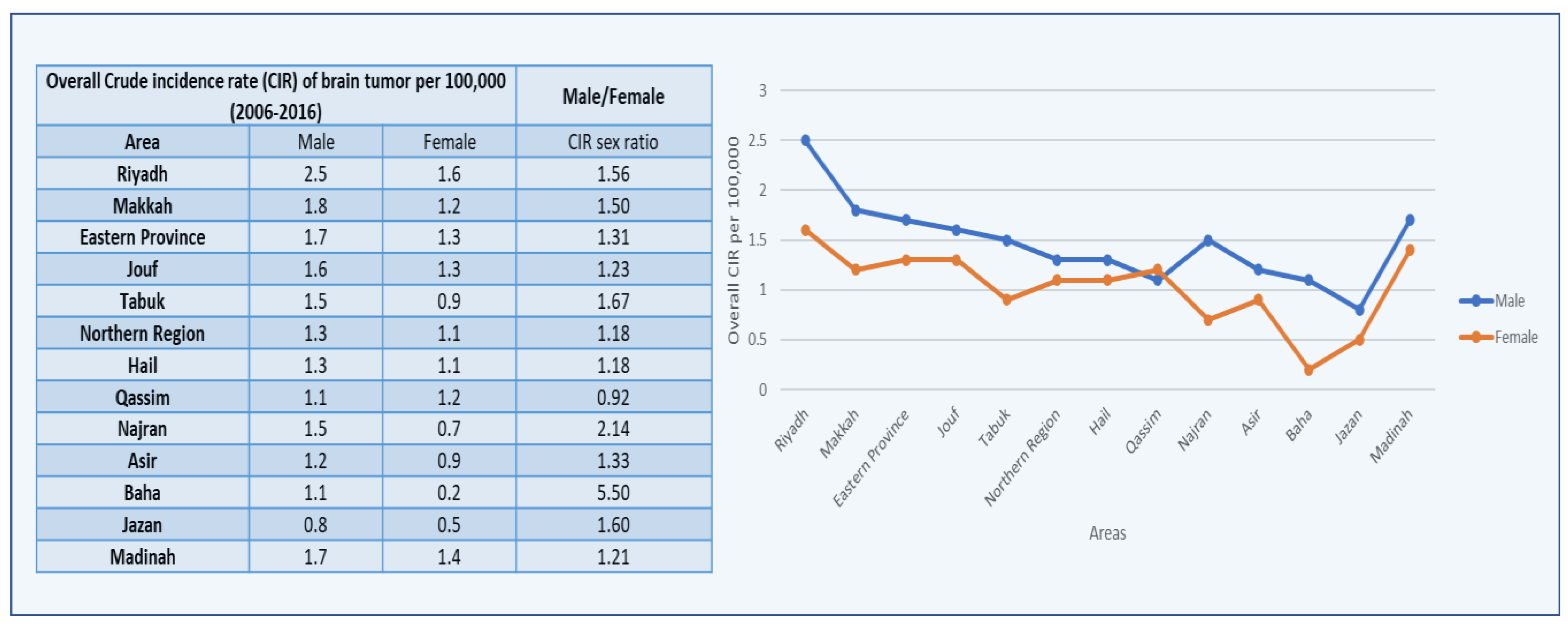
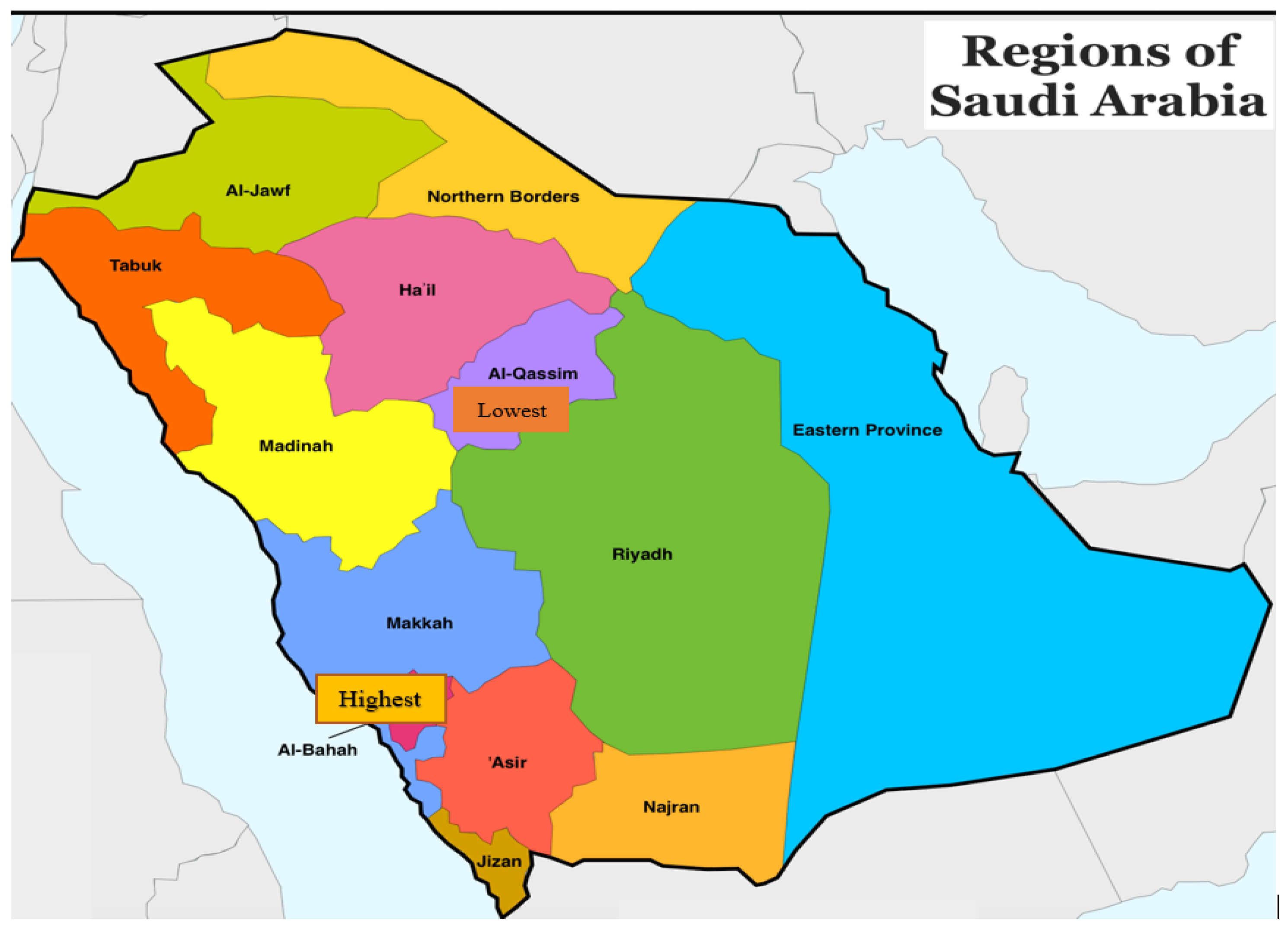
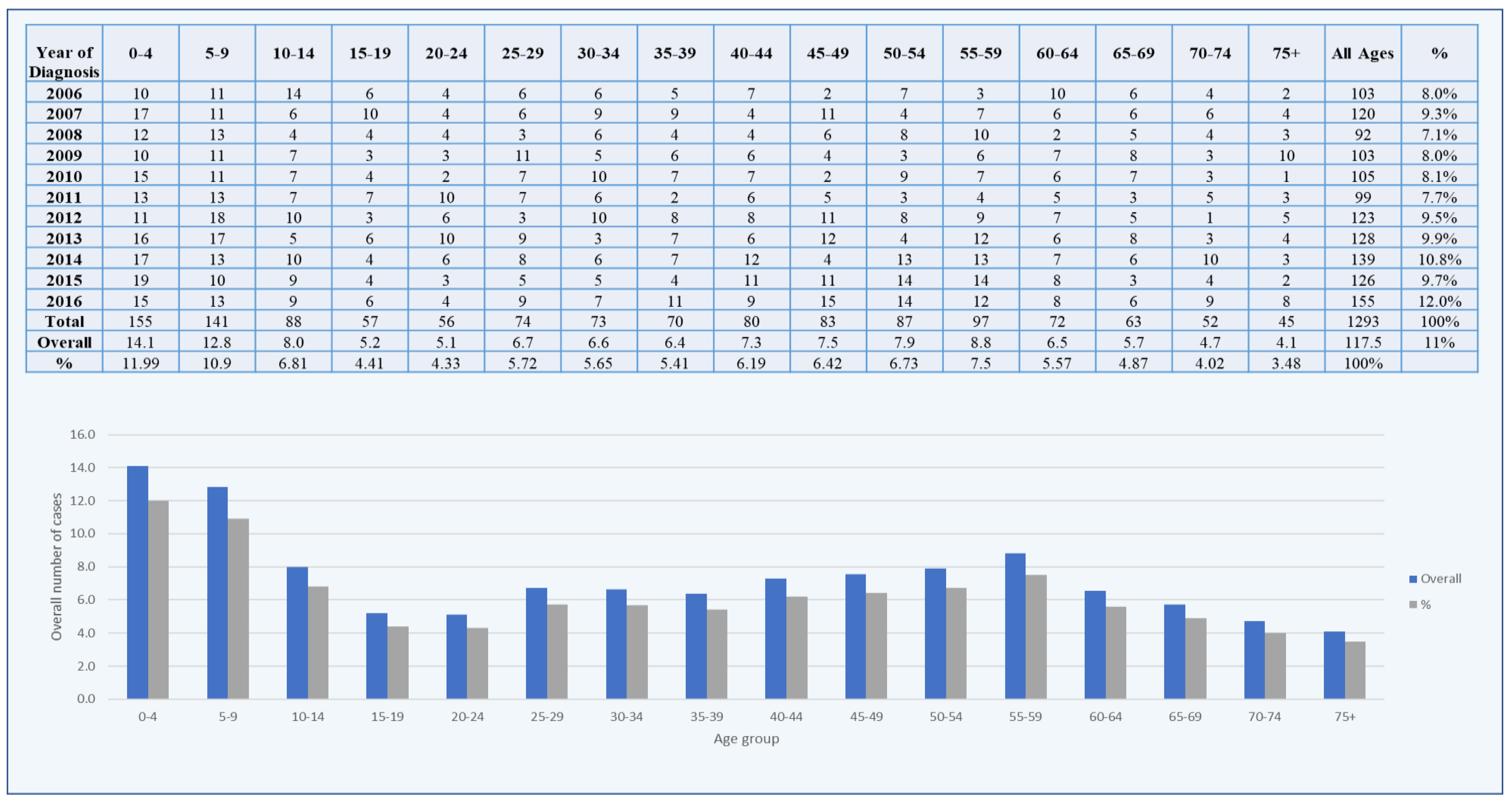
3. Results
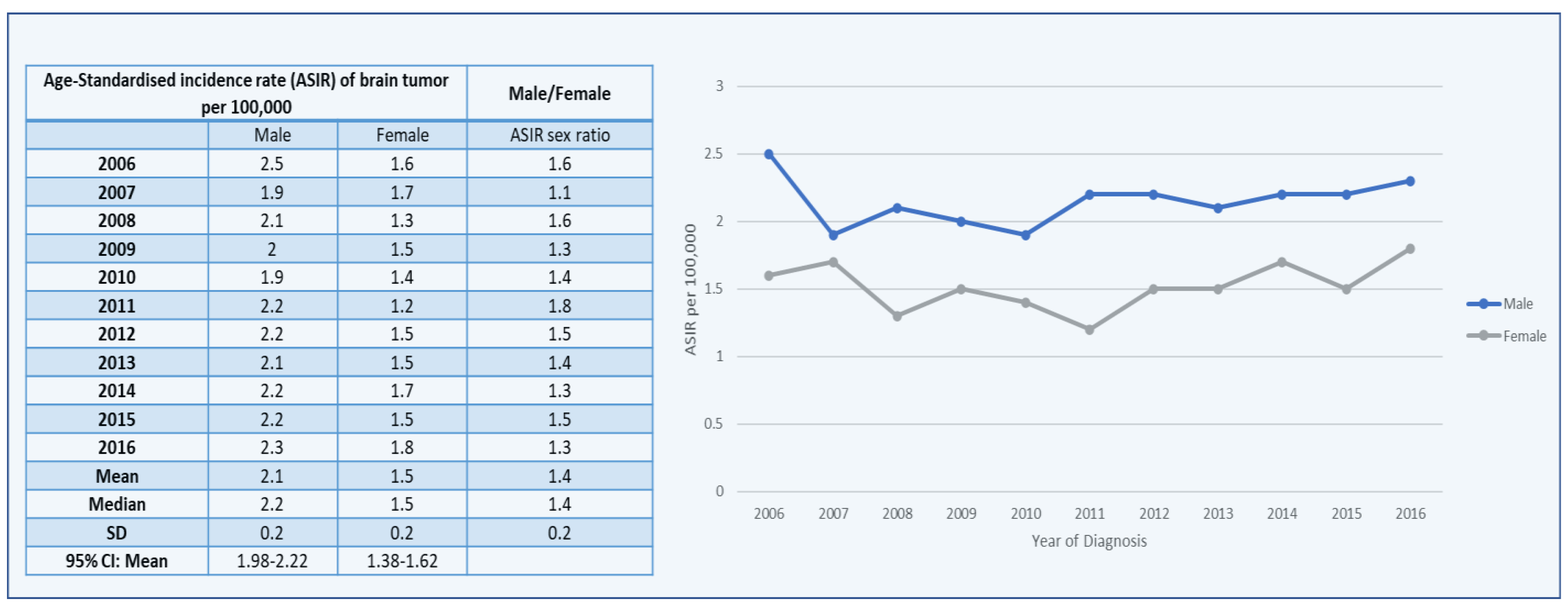
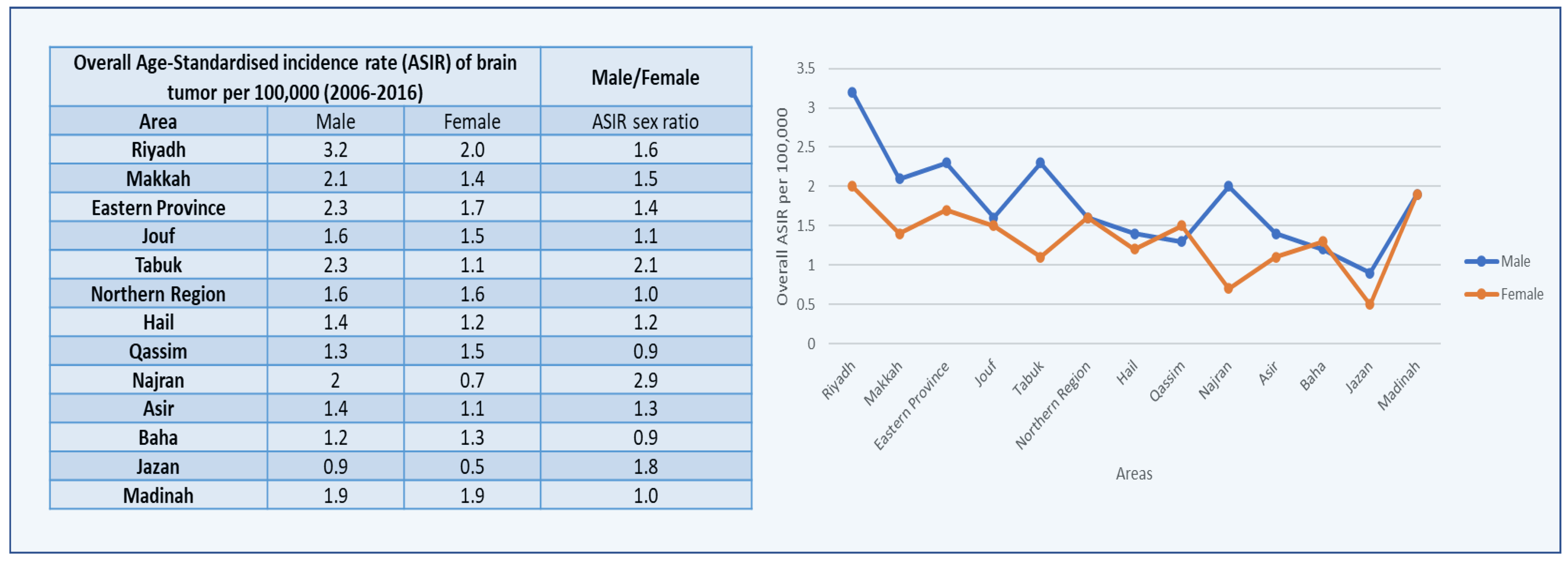
3.1. Brain Tumors among Males
3.2. Brain Tumors among Females
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda-Filho, A.; Piñeros, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Deltour, I.; Bray, F. Cancers of the brain and CNS: Global patterns and trends in incidence. Neuro-Oncology 2017, 19, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeill, K.A. Epidemiology of Brain Tumors. Neurol. Clin. 2016, 34, 981–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; Liao, P.; Rouse, C.; Chen, Y.; Dowling, J.; Wolinsky, Y.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2007–2011. Neuro-Oncology 2014, 16, iv1–iv63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellur, S.N.; Chandra, V. Meningioma Size: Its Relationship to Other Diseases. Arch. Neurol. 1981, 38, 458–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakasu, S.; Hirano, A.; Shimura, T.; Llena, J.F. Incidental meningiomas in autopsy study. Surg. Neurol. 1987, 27, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausing, A.; Ybo, W.; Stenflo, J. Intracranial Meningioma—A Population Study of Ten Years. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1970, 46, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, Z.; Whiteley, W.N.; Longstreth, W.T.; Weber, F.; Lee, Y.-C.; Tsushima, Y.; Alphs, H.; Ladd, S.C.; Warlow, C.; Wardlaw, J.M.; et al. Incidental findings on brain magnetic resonance imaging: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2009, 339, b3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernooij, M.W.; Ikram, M.A.; Tanghe, H.L.; Vincent, A.J.P.E.; Hofman, A.; Krestin, G.P.; Niessen, W.J.; Breteler, M.M.B.; van der Lugt, A. Incidental Findings on Brain MRI in the General Population. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 1821–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, R.J.; Muzi, M.; Peck, M.; Krohn, K.A. Continuing education: Multi-modality brain tumor imaging–MRI, PET, and PET/MRI. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2015, 56, 1554–1561. [Google Scholar]
- Dolecek, T.A.; Dressler, E.V.M.; Thakkar, J.P.; Liu, M.; Al-Qaisi, A.; Villano, J.L. Epidemiology of meningiomas post-Public Law 107-206: The Benign Brain Tumor Cancer Registries Amendment Act. Cancer 2015, 121, 2400–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Cavenee, W.K. WHO Classification of Tumours of the Central Nervous System. Available online: https://publications.iarc.fr/Book-And-Report-Series/Who-Classification-Of-Tumours/WHO-Classification-Of-Tumours-Of-The-Central-Nervous-System-2007 (accessed on 19 August 2021).
- Rivkin, M.; Kanoff, R.B. Metastatic brain tumors: Current therapeutic options and historical perspective. J. Am. Osteopath. Assoc. 2013, 113, 418–423. [Google Scholar]
- Fokas, E.; Steinbach, J.P.; Rödel, C. Biology of brain metastases and novel targeted therapies: Time to translate the research. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1835, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisusi, F.A.; Schätzlein, A.G.; Uchegbu, I.F. Nanomedicines in the treatment of brain tumors. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, M.; Cloughesy, T.; Perry, J.R.; Wick, W. Standards of care for treatment of recurrent glioblastoma—Are we there yet? Neuro-Oncology 2013, 15, 4–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.D.; Jaeckle, K.; Ballman, K.V.; Farace, E.; Cerhan, J.H.; Anderson, S.K.; Carrero, X.W.; Barker, F.G., II; Deming, R.; Burri, S.H.; et al. Effect of radiosurgery alone vs. radiosurgery with whole brain radiation therapy on cognitive function in patients with 1 to 3 brain metastases: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2016, 316, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, S.B.; Gettinger, S.N.; Mahajan, A.; Chiang, A.C.; Herbst, R.S.; Sznol, M.; Tsiouris, A.J.; Cohen, J.; Vortmeyer, A.; Jilaveanu, L.; et al. Pembrolizumab for patients with melanoma or non-small-cell lung cancer and untreated brain metastases: Early analysis of a non-randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 976–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, H.; Sharma, A.K.; Mahant, S.; Kapoor, D.N. Recent advancements in brain tumor targeting using magnetic nanoparticles. Ther. Deliv. 2020, 11, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almatroudi, A. The Incidence Rate of Colorectal Cancer in Saudi Arabia: An Observational Descriptive Epidemiological Analysis. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2020, 13, 977–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today. WHO, Globocan. Available online: http://gco.iarc.fr/today/home (accessed on 30 May 2021).
- Moin, A.; Rizvi, S.M.D.; Hussain, T.; Gowda, D.V.; Subaiea, G.M.; Elsayed, M.M.A.; Ansari, M.; Alanazi, A.S.; Yadav, H. Current Status of Brain Tumor in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia and Application of Nanobiotechnology for Its Treatment: A Comprehensive Review. Life 2021, 11, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taha, M.S.; Almsned, F.M.; Hassen, M.A.; Atean, I.M.; Alwbari, A.M.; Alharbi, Q.K.; Abdulkader, M.M.; Almuhaish, H.S. Demographic and histopathological patterns of neuro-epithelial brain tumors in Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia. Neurosci. J. 2018, 23, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saudi Cancer Registry: Annual Reports. 2020. Available online: https://nhic.gov.sa/en/eServices/Pages/TumorRegistration.aspx (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Alqahtani, W.S.; Almufareh, N.A.; Domiaty, D.M.; Albasher, G.; Alduwish, M.A.; Alkhalaf, H.; Almuzzaini, B.; Al-Marshidy, S.S.; Alfraihi, R.; Elasbali, A.M.; et al. Epidemiology of cancer in Saudi Arabia thru 2010-2019: A systematic review with constrained meta-analysis. AIMS Public Health 2020, 7, 679–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forouzanfar, M.H.; Alexander, L.; Anderson, H.R.; Bachman, V.F.; Biryukov, S.; Brauer, M.; Burnett, R.; Casey, D.; Coates, M.M.; Cohen, A.; et al. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks in 188 countries, 1990–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2015, 386, 2287–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.P.; Fisher, J.L.; Nichols, E.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdela, J.; Abdelalim, A.; Abraha, H.N.; Agius, D.; Alahdab, F.; Alam, T.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of brain and other CNS cancer, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 376–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ahmadi, K.; Al-Zahrani, A. NO(2) and cancer incidence in Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 5844–5862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, D.; Krishnan, A.V.; Swami, S.; Giovannucci, E.; Feldman, B.J. The role of vitamin D in reducing cancer risk and progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 342–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.N.; Alkhenizan, A.H.; El Shaker, M.; Raef, H.; Gabr, A. Increasing trends and significance of hypovitaminosis D: A population-based study in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Arch. Osteoporos. 2014, 9, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Elq, A.H. The status of Vitamin D in medical students in the preclerkship years of a Saudi medical school. J. Fam. Community Med. 2012, 19, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqarni, S.S.M. A Review of Prevalence of Obesity in Saudi Arabia. J. Obes. Eat. Disord. 2016, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, J.B.; Reed, C.E. Epidemiology of esophageal cancer. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 92, 1077–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braveman, P.; Gottlieb, L. The Social Determinants of Health: It’s Time to Consider the Causes of the Causes. Public Health Rep. 2014, 129, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, D.; Hamilton, W.; Walter, F.M.; Watts, C. Strategies to accelerate diagnosis of primary brain tumors at the primary–secondary care interface in children and adults. CNS Oncol. 2013, 2, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Country | Both Sexes | Males | Females | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| New Cases | Deaths | New Cases | Deaths | New Cases | Deaths | |
| Iraq | 1600 | 1366 | 851 | 734 | 749 | 632 |
| Saudi Arabia | 598 | 486 | 425 | 347 | 173 | 139 |
| UAE | 119 | 98 | 73 | 62 | 46 | 36 |
| Oman | 113 | 93 | 87 | 70 | 26 | 23 |
| Kuwait | 68 | 57 | 51 | 45 | 17 | 12 |
| Bahrain | 40 | 32 | 24 | 18 | 16 | 14 |
| Qatar | 39 | 31 | 30 | 23 | 9 | 8 |
| Area | Sex | ASIR/CIR | 2016 | 2006 | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Riyadh | Male | ASIR | 3.4 | 2.8 | 0.6 |
| CIR | 3 | 2 | 1 | ||
| Female | ASIR | 2.9 | 1.8 | 1.1 | |
| CIR | 2.4 | 1.3 | 1.1 | ||
| Makkah | Male | ASIR | 2.3 | 2.1 | 0.2 |
| CIR | 2 | 1.6 | 0.4 | ||
| Female | ASIR | 1.6 | 1.3 | 0.3 | |
| CIR | 1.5 | 1.1 | 0.4 | ||
| Eastern Province | Male | ASIR | 2.9 | 2.9 | 0 |
| CIR | 2.4 | 1.8 | 0.6 | ||
| Female | ASIR | 1.6 | 1.3 | 0.3 | |
| CIR | 1.3 | 1.1 | 0.2 | ||
| Jouf | Male | ASIR | 2.3 | 2.3 | 0 |
| CIR | 2.1 | 1.8 | 0.3 | ||
| Female | ASIR | 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.4 | |
| CIR | 0.5 | 0.6 | −0.1 | ||
| Tabuk | Male | ASIR | 1.9 | 7.7 | −5.8 |
| CIR | 1.6 | 3.4 | −1.8 | ||
| Female | ASIR | 1.7 | 1.6 | 0.1 | |
| CIR | 1.4 | 1 | 0.4 | ||
| Northern Region | Male | ASIR | 1.1 | 2.7 | −1.6 |
| CIR | 1.4 | 2.4 | −1 | ||
| Female | ASIR | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0 | |
| CIR | 0.7 | 0.8 | −0.1 | ||
| Hail | Male | ASIR | 0.8 | 1.1 | −0.3 |
| CIR | 0.8 | 1.3 | −0.5 | ||
| Female | ASIR | 1.2 | 2.8 | −1.6 | |
| CIR | 1.1 | 2.5 | −1.4 | ||
| Qassim | Male | ASIR | 1.5 | 2.3 | −0.8 |
| CIR | 1.4 | 1.6 | −0.2 | ||
| Female | ASIR | 1.1 | 0.6 | 0.5 | |
| CIR | 1 | 0.7 | 0.3 | ||
| Najran | Male | ASIR | 4 | 1.1 | 2.9 |
| CIR | 3.7 | 0.5 | 3.2 | ||
| Female | ASIR | 0.4 | 1.6 | −1.2 | |
| CIR | 0.5 | 1.6 | −1.1 | ||
| Asir | Male | ASIR | 1.2 | 1.7 | −0.5 |
| CIR | 1.2 | 1.2 | 0 | ||
| Female | ASIR | 1.5 | 0.4 | 1.1 | |
| CIR | 1.4 | 0.5 | 0.9 | ||
| Baha | Male | ASIR | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| CIR | 1.1 | 0 | 1.1 | ||
| Female | ASIR | 1.1 | 1 | 0.1 | |
| CIR | 1.1 | 0.6 | 0.5 | ||
| Jazan | Male | ASIR | 0.3 | 1.3 | −1 |
| CIR | 0.3 | 1.2 | −0.9 | ||
| Female | ASIR | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0 | |
| CIR | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.1 | ||
| Madinah | Male | ASIR | 1.7 | 1.9 | −0.2 |
| CIR | 1.6 | 1.9 | −0.3 | ||
| Female | ASIR | 2.5 | 4.9 | −2.4 | |
| CIR | 2.2 | 2.8 | −0.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almatroudi, A. Brain Tumors in Saudi Arabia: An Observational and Descriptive Epidemiological Analysis. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1796. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10091796
Almatroudi A. Brain Tumors in Saudi Arabia: An Observational and Descriptive Epidemiological Analysis. Healthcare. 2022; 10(9):1796. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10091796
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmatroudi, Ahmad. 2022. "Brain Tumors in Saudi Arabia: An Observational and Descriptive Epidemiological Analysis" Healthcare 10, no. 9: 1796. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10091796
APA StyleAlmatroudi, A. (2022). Brain Tumors in Saudi Arabia: An Observational and Descriptive Epidemiological Analysis. Healthcare, 10(9), 1796. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10091796








