Effects of Electrical Stimulation of Acupoints on Xerostomia for Patients Who Undergo Hemodialysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Participants and Setting
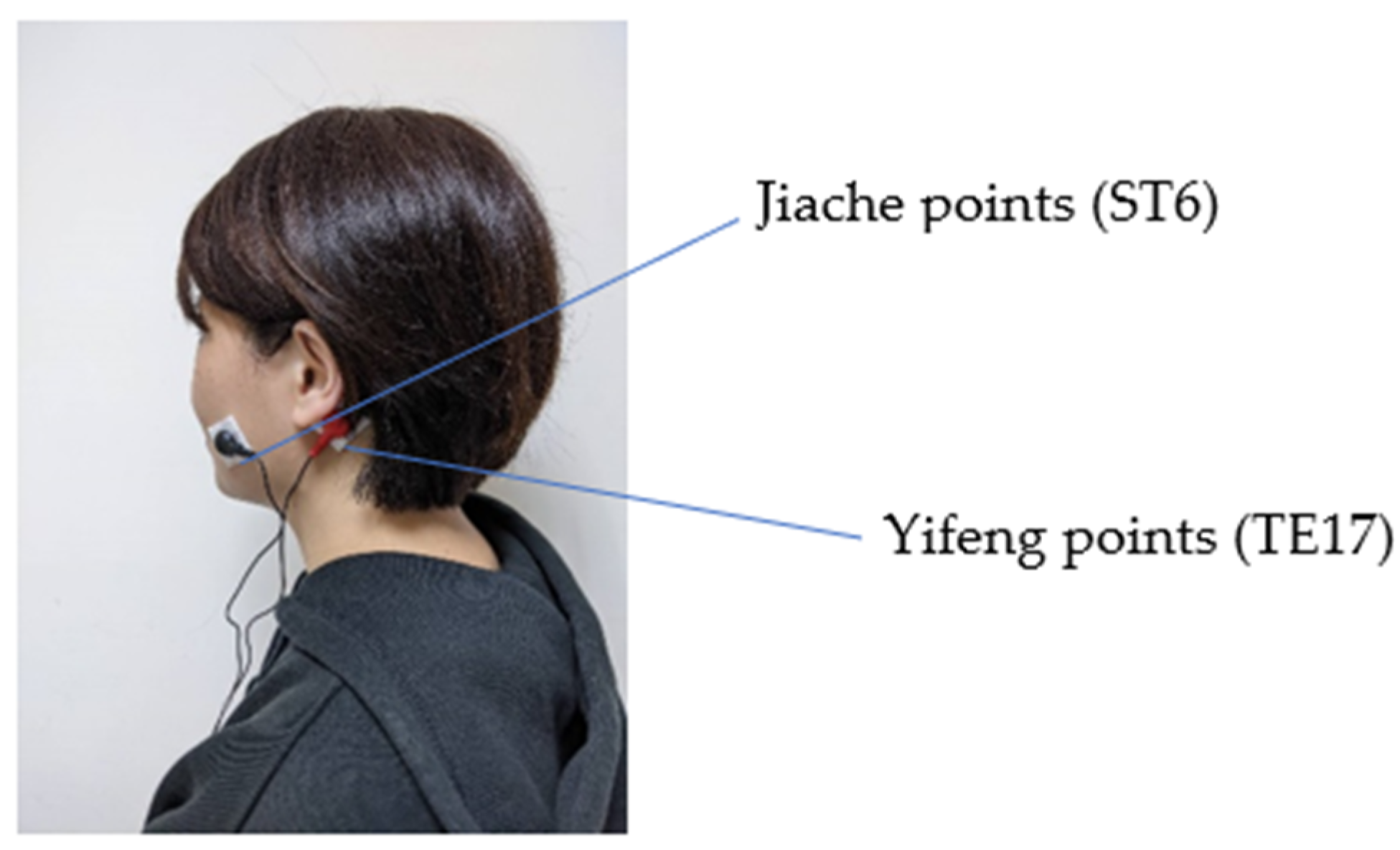
2.3. The Intervention
2.4. Instruments
2.5. Xerostomia Questionnaire (XQ)
2.6. Cotton Rolls and Electronic Balance
2.7. Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulator
2.8. Accuracy in Locating the Stimulation Points
2.9. Data Collection
2.10. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Information
3.2. Effect of Electrical Stimulation of Acupoints
4. Discussion
4.1. Implication
4.2. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saad, T.F.; Hentschel, D.M.; Koplan, B.; Wasse, H.; Asif, A.; Patel, D.V.; Salman, L.; Carrillo, R.; Hoggard, J. Cardiovascular implantable electronic device leads in CKD and ESRD patients: Review and recommendations for practice. Semin. Dial. 2013, 26, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, S.R.; Kotanko, P.; Levin, N.W. Interdialytic weight gain: Implications in hemodialysis patients. Semin. Dial. 2006, 19, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, A.A.; Darawad, M.; Al Gamal, E.; Hamdan-Mansour, A.M.; Abed, M.A. Predictors of dietary and fluid non-adherence in Jordanian patients with end-stage renal disease receiving haemodialysis: A cross-sectional study. J. Clin. Nurs. 2013, 22, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellon, L.; Regan, D.; Curtis, R. Factors influencing adherence among Irish haemodialysis patients. Patient Educ. Couns. 2013, 92, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naalweh, K.S.; Barakat, M.A.; Sweileh, M.W.; Al-Jabi, S.W.; Sweileh, W.M.; Zyoud, S.H. Treatment adherence and perception in patients on maintenance hemodialysis: A cross-sectional study from Palestine. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruzda-Zwiech, A.; Szczepańska, J.; Zwiech, R. Sodium gradient, xerostomia, thirst and inter-dialytic excessive weight gain: A possible relationship with hyposalivation in patients on maintenance hemodialysis. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2014, 46, 1411–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bruzda-Zwiech, A.; Szczepańska, J.; Zwiech, R. Xerostomia, thirst, sodium gradient and inter-dialytic weight gain in hemodialysis diabetic vs. non-diabetic patients. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2018, 23, e406–e412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.-F.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, L.-H.; Niu, J.-Y.; Gu, Y. Study on the clinical significance and related factors of thirst and xerostomia in maintenance hemodialysis patients. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2013, 37, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossola, M.; Tazza, L. Xerostomia in patients on chronic hemodialysis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2012, 8, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Tang, C.; Chen, X.; Zhu, C.; Feng, W.; Li, P.; Lu, C. Poor sleep and reduced quality of life were associated with symptom distress in patients receiving maintenance hemodialysis. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2016, 14, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, P.L.P.; Libório, A.B.; Saintrain, M.V.d.L. Hemodialysis-specific factors associated with salivary flow rates. Artif. Organs 2015, 39, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushik, A.; Reddy, S.S.; Umesh, L.; Devi, B.K.Y.; Santana, N.; Rakesh, N. Oral and salivary changes among renal patients undergoing hemodialysis: A cross-sectional study. Indian J. Nephrol. 2013, 23, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, P.; Hegde, M.N.; Eraly, S.M. Evaluation of salivary parameters and dental status in adult hemodialysis patients in an indian population. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2018, 10, e419–e424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.-Y.; Yates, P.; Chin, C.-C.; Kao, T.-K. Effect of acupressure on thirst in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2010, 33, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bots, C.P.; Brand, H.S.; Veerman, E.C.I.; Korevaar, J.C.; Valentijn-Benz, M.; Bezemer, P.D.; Valentijn, R.M.; Vos, P.F.; Bijlsma, J.A.; ter Wee, P.M.; et al. Chewing gum and a saliva substitute alleviate thirst and xerostomia in patients on haemodialysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2005, 20, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duruk, N.; Eşer, İ. The Null Effect of Chewing Gum During Hemodialysis on Dry Mouth. Clin. Nurse Spec. 2016, 30, E12–E23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T. Acupuncture and somatic nerve stimulation: Mechanism underlying effects on cardiovascular and renal activities. Scand. J. Rehabil. Med. Suppl. 1993, 29, 7–18. [Google Scholar]
- Blom, M.; Dawidson, I.; Fernberg, J.O.; Johnson, G.; Angmar-Månsson, B. Acupuncture treatment of patients with radiation-induced xerostomia. Eur. J. Cancer B Oral. Oncol. 1996, 32B, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blom, M.; Lundeberg, T. Long-term follow-up of patients treated with acupuncture for xerostomia and the influence of additional treatment. Oral Dis. 2000, 6, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Gao, Y.; Qiu, X.; Hong, P.; Zhou, D.; Chen, Q. Acupuncture for the treatment of radiation-induced xerostomia among patients with cancer: A protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2020, 99, e20658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, R.P.; Johnson, M.I. The characteristics of acupuncture-like transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (acupuncture-like TENS): A literature review. Acupunct. Electrother. Res. 2011, 36, 231–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hargitai, I.A.; Sherman, R.G.; Strother, J.M. The effects of electrostimulation on parotid saliva flow: A pilot study. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2005, 99, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshman, A.R.; Babu, G.S.; Rao, S. Evaluation of effect of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation on salivary flow rate in radiation induced xerostomia patients: A pilot study. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2015, 11, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.K.W.; Jones, G.W.; Sagar, S.M.; Babjak, A.-F.; Whelan, T. A Phase I-II study in the use of acupuncture-like transcutaneous nerve stimulation in the treatment of radiation-induced xerostomia in head-and-neck cancer patients treated with radical radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2003, 57, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.Y.; Chen, H.M.; Su, Y.C.; Chin, C.C. The effect of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation on increasing salivary flow rate in hemodialysis patients. Oral Dis. 2019, 25, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krithikadatta, J. Normal distribution. J. Conserv. Dent. 2014, 17, 96–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisbruch, A.; Kim, H.M.; Terrell, J.E.; Marsh, L.H.; Dawson, L.A.; Ship, J.A. Xerostomia and its predictors following parotid-sparing irradiation of head-and-neck cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2001, 50, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawes, C. How much saliva is enough for avoidance of xerostomia? Caries Res. 2004, 38, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postorino, M.; Catalano, C.; Martorano, C.; Cutrupi, S.; Marino, C.; Cozzupoli, P.; Scudo, P.; Zoccali, C. Salivary and lacrimal secretion is reduced in patients with ESRD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2003, 42, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, A.; Connell, C.L.; Abati, S. Diagnosis and management of xerostomia and hyposalivation. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2014, 11, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Affoo, R.H.; Foley, N.; Garrick, R.; Siqueira, W.L.; Martin, R.E. Meta-Analysis of Salivary Flow Rates in Young and Older Adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2015, 63, 2142–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bots, C.P.; Brand, H.S.; Veerman, E.C.I.; Valentijn-Benz, M.; Van Amerongen, B.M.; Valentijn, R.M.; Vos, P.F.; Bijlsma, J.A.; Bezemer, P.D.; Ter Wee, P.M.; et al. Interdialytic weight gain in patients on hemodialysis is associated with dry mouth and thirst. Kidney Int. 2004, 66, 1662–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flanigan, M. Dialysate composition and hemodialysis hypertension. Semin. Dial. 2004, 17, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kugler, C.; Vlaminck, H.; Haverich, A.; Maes, B. Nonadherence with diet and fluid restrictions among adults having hemodialysis. J. Nurs. Scholarsh. 2005, 37, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Vea, A.; García, C.; Gaya, J.; Rivera, F.; Oliver, J.A. Abnormalities of thirst regulation in patients with chronic renal failure on hemodialysis. Am. J. Nephrol. 1992, 12, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenney, W.L.; Chiu, P. Influence of age on thirst and fluid intake. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2001, 33, 1524–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | TEAS (n = 37) n(%)/M (SD) | Contrast (n = 38) n(%)/M(SD) | Total (n = 75) n(%)/M(SD) | χ2/t p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender Female Male | 18 (48.6) 19 (51.4) | 23 (60.5) 15 (39.5) | 41 (54.7) 34 (45.3) | 0.30 b |
| Age (years) | 59.9 (13.0) | 58.8 (11.5) | 59.9 (13) | 0.96 a |
| Education (years) | 6.9 (5.0) | 6.6 (4.7) | 6.8 (4.8) | 0.83 a |
| Duration of HD (months) | 57.7 (54.3) | 102 (62.6) | 80.1 (62.4) | 0.002 a |
| Salivary flow rates (mL/min) | 0.05 (0.03) | 0.05 (0.03) | 0.05(0.03) | 0.69 a |
| Dry mouth (score) | 34.3 (18.9) | 35.4(17.3) | 34.8 (18.0) | 0.80 a |
| %IDWG | 4.3 (1.9) | 4.4 (1.5) | 4.3 (1.7) | 0.82 a |
| Residual urine output 0 mL <100 mL ≧100 mL | 12 (32.4) 17 (46.0) 8 (21.6) | 17 (44.7) 11 (29.0) 10 (26.3) | 29 (38.7) 28 (37.3) 18 (24.0) | 0.31 b |
| Most severe dry mouth no difference the day following HD the days after HD | 24 (64.9) 9 (24.3) 4 (10.8) | 22 (57.9) 13 (34.2) 3 (7.9) | 46 (61.3) 22 (29.3) 7 (9.3) | 0.62 b |
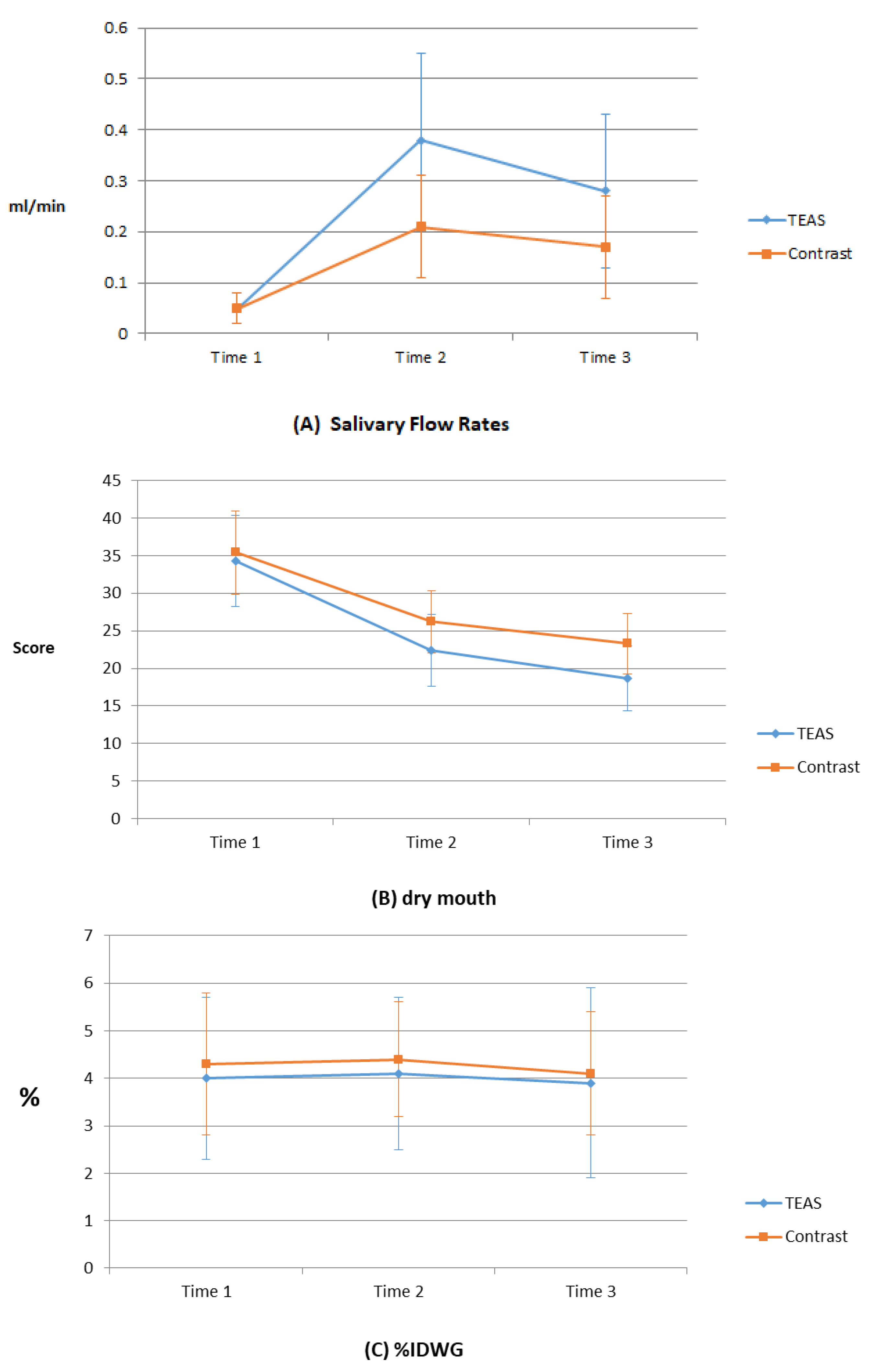
| Variables | Time 1 M(SD) | Time 2 M(SD) | Time 3 M(SD) | F a | Scheffe’ Post Hoc | F b | F c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saliva flow rate (mL/min) | 23.77 *** | 15.28 *** | |||||
| TEAS (n = 37) | 0.05 (0.03) | 0.38 (0.17) | 0.28 (0.15) | 38.39 *** | Time 2 > Time 1 ** Time 3 > Time 1 ** | ||
| Contrast (n = 38) | 0.05 (0.03) | 0.21 (0.10) | 0.17 (0.10) | 18.51 *** | Time 2 > Time 1 ** Time 3 > Time 1 ** | ||
| Dry mouth (score) | 0.95 | 0.94 | |||||
| TEAS (n = 37) | 34.3 (18.9) | 22.4 (15.1) | 18.7 (13.5) | 22.64 *** | |||
| Contrast (n = 38) | 35.4 (17.3) | 26.2 (12.9) | 23.3 (12.4) | 11.54 *** | |||
| %IDWG (%) | 4.0 (1.7) | 4.1 (1.6) | 3.9 (2.0) | 0.07 | 0.94 | 0.44 | |
| TEAS (n = 37) | |||||||
| Contrast (n = 38) | 4.3 (1.5) | 4.4 (1.2) | 4.1 (1.3) | 0.07 |
| Group | Time 1 M(SD) | Time 2 M(SD) | Time 3 M(SD) | Wald χ2 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Groups × Time | 8.31 | 0.016 | |||
| TEAS (n = 6) | 6.6(0.4) | 4.9(0.6) | 5.1(1.2) | 7.57 | 0.006 |
| Contrast (n = 5) | 6.7(0.9) | 6.0(1.6) | 5.9(1.8) | 2.21 | 0.14 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, L.-Y.; Lee, B.-O.; Lee, K.-N.; Chen, C.-A. Effects of Electrical Stimulation of Acupoints on Xerostomia for Patients Who Undergo Hemodialysis. Healthcare 2022, 10, 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10030498
Yang L-Y, Lee B-O, Lee K-N, Chen C-A. Effects of Electrical Stimulation of Acupoints on Xerostomia for Patients Who Undergo Hemodialysis. Healthcare. 2022; 10(3):498. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10030498
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Li-Yu, Bih-O Lee, Kai-Ni Lee, and Chien-An Chen. 2022. "Effects of Electrical Stimulation of Acupoints on Xerostomia for Patients Who Undergo Hemodialysis" Healthcare 10, no. 3: 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10030498
APA StyleYang, L.-Y., Lee, B.-O., Lee, K.-N., & Chen, C.-A. (2022). Effects of Electrical Stimulation of Acupoints on Xerostomia for Patients Who Undergo Hemodialysis. Healthcare, 10(3), 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10030498






