Association between Elevated De Ritis Ratio and Mortality Outcome in Adult Patients with Thoracoabdominal Trauma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
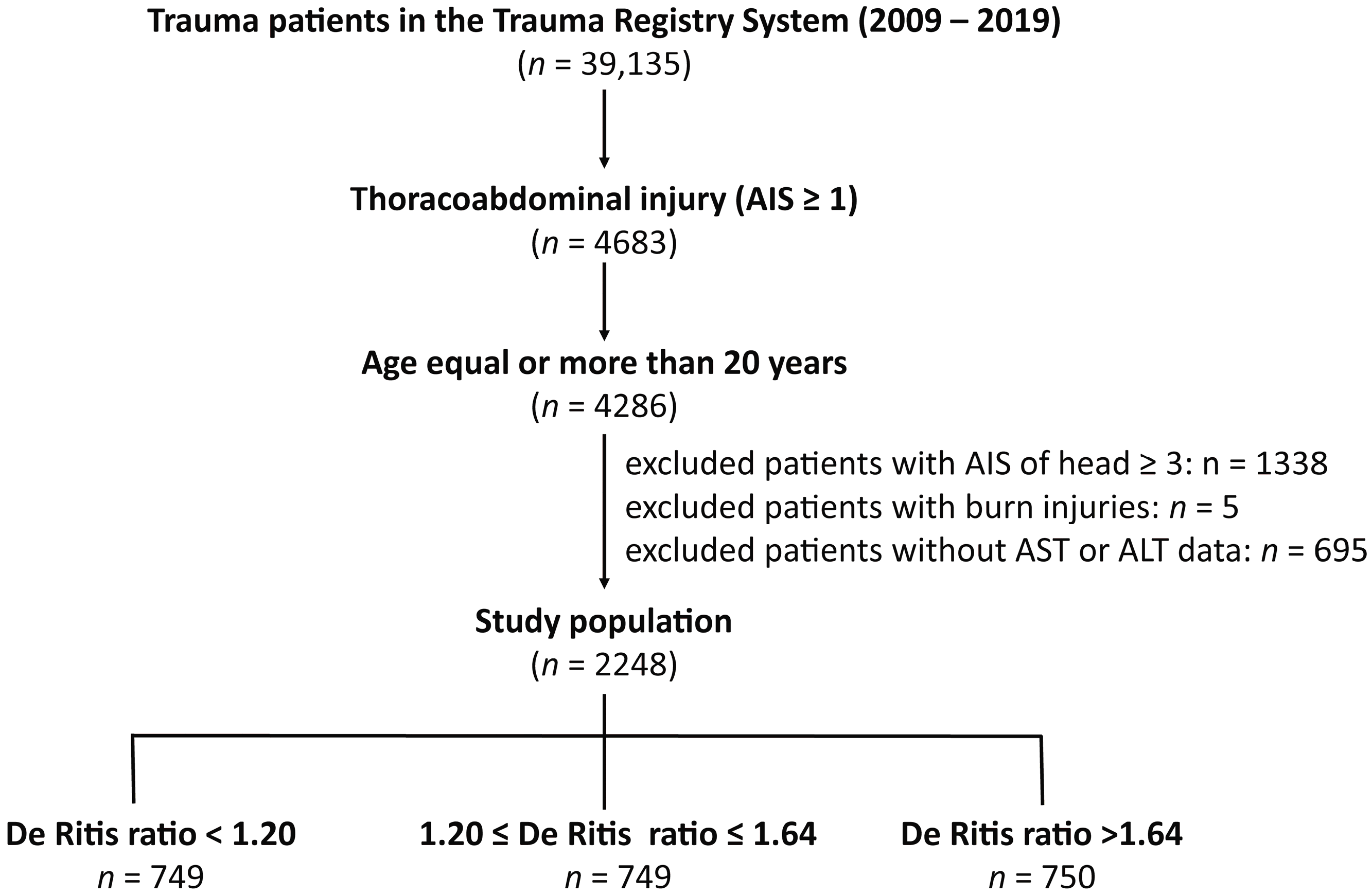
2.1. Study Population and Data Collection
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient and Injury Characteristics
3.2. Adjusted Outcomes of the Propensity Score-Matched Patients
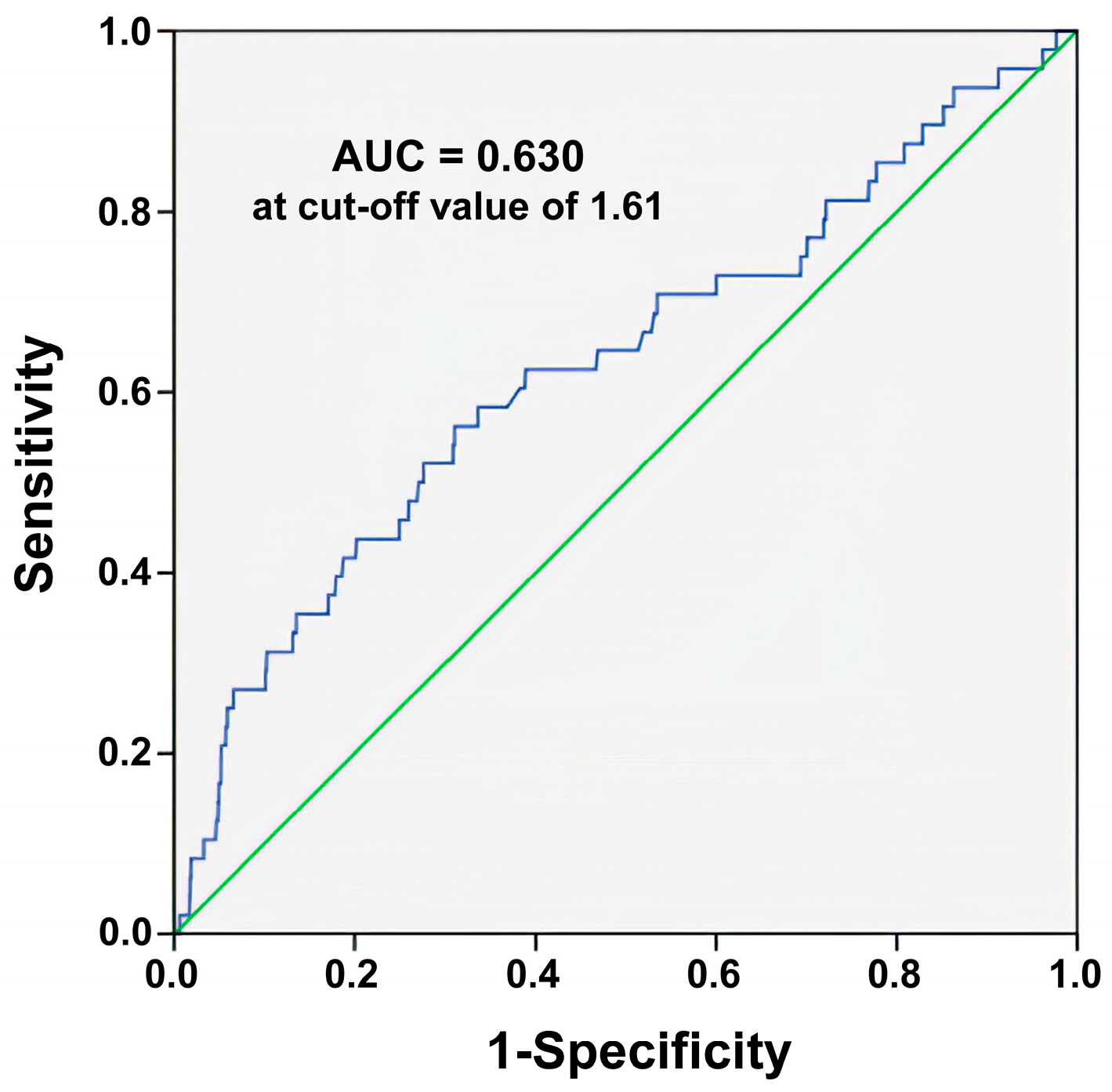
3.3. ROC Curve Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lecky, B.O.; Alexandrescu, R.; O’Brien, S.J. Changing Epidemiology of Polytrauma; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 3, pp. 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, R.J.; Okoye, O.; Teixeira, P.G.; Inaba, K.; Demetriades, D. The double jeopardy of blunt thoracoabdominal trauma. Arch. Surg. 2012, 147, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Demir, B.; Şaşmaz, M.; Saglam Gurmen, E.; Bilge, A. Prognostic value of lactate to hematocrit ratio score in patients with severe thoracoabdominal trauma. Ulus. Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2022, 28, 927–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriles, K.E.; Azer, S.A. Alanine Amino Transferase. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing, StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Otto-Ślusarczyk, D.; Graboń, W.; Mielczarek-Puta, M. Aspartate aminotransferase--key enzyme in the human systemic metabolism. Postepy Hig. Med. Dosw. 2016, 70, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suciu, A.; Abenavoli, L.; Pellicano, R.; Luzza, F.; Dumitrascu, D.L. Transaminases: Oldies but goldies. A narrative review. Minerva Gastroenterol. Dietol. 2020, 66, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, P.C. Biochemical detection and monitoring of alcohol abuse and abstinence. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2001, 38, 652–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Botros, M.; Sikaris, K.A. The de ritis ratio: The test of time. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2013, 34, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Ritis, F.; Coltorti, M.; Giusti, G. An enzymic test for the diagnosis of viral hepatitis: The transaminase serum activities. 1957. Clin. Chim. Acta 2006, 369, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Li, R.; Gong, W.; Xiang, B.; Tang, W.; Yu, H. Prognostic Value of Aspartate Transaminase/Alanine Transaminase Ratio in Patients With Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma Undergoing Hepatectomy. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 876900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darstein, F.; Häuser, F.; Straub, B.K.; Wenzel, J.J.; Conradi, R.; Mittler, J.; Lang, H.; Galle, P.R.; Zimmermann, T. Hepatitis E virus genotype 3 is a common finding in liver-transplanted patients undergoing liver biopsy for elevated liver enzymes with a low De Ritis ratio and suspected acute rejection: A real-world cohort. Clin. Transpl. 2018, 32, e13411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghahari, M.; Salari, A.; Ghafoori Yazdi, M.; Nowroozi, A.; Fotovat, A.; Momeni, S.A.; Nowroozi, M.R.; Amini, E. Association Between Preoperative De Ritis (AST/ALT) Ratio and Oncological Outcomes Following Radical Cystectomy in Patients With Urothelial Bladder Cancer. Clin. Genitourin Cancer 2022, 20, e89–e93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukui-Kawaura, S.; Kawahara, T.; Araki, Y.; Nishimura, R.; Uemura, K.; Namura, K.; Mizuno, N.; Yao, M.; Uemura, H.; Ikeda, I. A higher De Ritis ratio (AST/ALT) is a risk factor for progression in high-risk non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Oncotarget 2021, 12, 917–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janisch, F.; Klotzbücher, T.; Marks, P.; Kienapfel, C.; Meyer, C.P.; Yu, H.; Fühner, C.; Hillemacher, T.; Mori, K.; Mostafei, H.; et al. Predictive value of De Ritis ratio in metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with tyrosine-kinase inhibitors. World J. Urol. 2021, 39, 2977–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olcucu, M.T.; Karamik, K.; Yilmaz, K.; Okuducu, Y.; Cakir, S.; Ates, M. Preoperative Inflammation Markers and De Ritis Ratio in Predicting Clinical Presentation and Prognosis of Patients with Testicular Germ Cell Tumors. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2020, 30, 1041–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazo, M.; Clark, J.M. The epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A global perspective. Semin. Liver Dis. 2008, 28, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Ma, G.; Chen, L. De-Ritis Ratio Is Associated with Mortality after Cardiac Arrest. Dis. Markers 2020, 2020, 8826318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucukseymen, S.; Cekin, A.H.; Bayar, N.; Arslan, S.; Uygur Kucukseymen, E.; Mercan, T.; Ozdemir, S. A novel biomarker for prediction of atrial fibrillation susceptibility in patients with celiac disease. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, H.M.; He, C.; Zhang, S.C.; You, Z.B.; Lin, X.Q.; Luo, M.Q.; Lin, M.Q.; Guo, Y.S.; Zheng, W.P.; Lin, K.Y. Predictive value of aspartate aminotransferase-to-alanine aminotransferase ratio for contrast-associated acute kidney injury in patients undergoing elective percutaneous coronary intervention. J. Cardiol. 2022, 79, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilarczyk, K.; Carstens, H.; Heckmann, J.; Canbay, A.; Koch, A.; Pizanis, N.; Jakob, H.; Kamler, M. The aspartate transaminase/alanine transaminase (DeRitis) ratio predicts mid-term mortality and renal and respiratory dysfunction after left ventricular assist device implantation. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2017, 52, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.Y.; Yu, J.; Hong, J.H.; Lim, B.; Kim, Y.; Hwang, J.H.; Kim, Y.K. Elevated De Ritis Ratio as a Predictor for Acute Kidney Injury after Radical Retropubic Prostatectomy. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.Y.; Yao, R.Q.; Ren, C.; Li, S.Y.; Li, Y.X.; Zhu, S.Y.; Yao, Y.M.; Du, X.H. De Ritis Ratio as a Significant Prognostic Factor in Patients with Sepsis: A Retrospective Analysis. J. Surg. Res. 2021, 264, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinellu, A.; Arru, F.; De Vito, A.; Sassu, A.; Valdes, G.; Scano, V.; Zinellu, E.; Perra, R.; Madeddu, G.; Carru, C.; et al. The De Ritis ratio as prognostic biomarker of in-hospital mortality in COVID-19 patients. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 51, e13427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pranata, R.; Huang, I.; Lim, M.A.; Yonas, E.; Vania, R.; Lukito, A.A.; Nasution, S.A.; Siswanto, B.B.; Kuswardhani, R.A.T. Elevated De Ritis Ratio Is Associated With Poor Prognosis in COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 676581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzey-Aras, Y.; Yazar, H.; Acar, T.; Kayacan, Y.; Acar, B.A.; Boncuk, S.; Eryilmaz, H.A. The Role of De Ritis Ratio as a Clinical Prognostic Parameter in COVID 19 Patients. Clin. Lab. 2021, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yashashwini, A.; Vedavathi, R. The Study of De Ritis (Ast/Alt) Ratio in Comparision with Other Parameters for Predicting Poor Prognosis in Covid 19 Patients. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2022, 70, 11–12. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Hu, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, B.; Kong, W.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, K.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Wu, G.; et al. Aspartate transaminase/alanine transaminase (De Ritis ratio) predicts survival in major burn patients. Burns 2022, 48, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Kim, H.Y.; Kong, Y.G.; Park, J.H.; Seo, Y.J.; Kim, Y.K. De Ritis ratio as a predictor of 1-year mortality after burn surgery. Burns 2021, 47, 1865–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Man, C.; Liao, S.; Qiu, H. The Prognosis Role of AST/ALT (De Ritis) Ratio in Patients with Adult Secondary Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 5719751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steininger, M.; Winter, M.P.; Reiberger, T.; Koller, L.; El-Hamid, F.; Forster, S.; Schnaubelt, S.; Hengstenberg, C.; Distelmaier, K.; Goliasch, G.; et al. De-Ritis Ratio Improves Long-Term Risk Prediction after Acute Myocardial Infarction. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rief, P.; Pichler, M.; Raggam, R.; Hafner, F.; Gerger, A.; Eller, P.; Brodmann, M.; Gary, T. The AST/ALT (De-Ritis) ratio: A novel marker for critical limb ischemia in peripheral arterial occlusive disease patients. Medicine 2016, 95, e3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.H.; Hsu, S.Y.; Hsieh, H.Y.; Chen, Y.C. Differences between the sexes in motorcycle-related injuries and fatalities at a Taiwanese level I trauma center. Biomed. J. 2017, 40, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.H.; Liu, H.T.; Hsu, S.Y.; Hsieh, H.Y.; Chen, Y.C. Motorcycle-related hospitalizations of the elderly. Biomed. J. 2017, 40, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Hsu, S.Y.; Hsieh, H.Y.; Chien, P.C. Defining polytrauma by abbreviated injury scale >/= 3 for a least two body regions is insufficient in terms of short-term outcome: A cross-sectional study at a level I trauma center. Biomed. J. 2018, 41, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opio, C.K.; Seremba, E.; Ocama, P.; Lalitha, R.; Kagimu, M.; Lee, W.M. Diagnosis of alcohol misuse and alcoholic liver disease among patients in the medical emergency admission service of a large urban hospital in Sub-Saharan Africa; a cross sectional study. Pan. Afr. Med. J. 2013, 15, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torkadi, P.P.; Apte, I.C.; Bhute, A.K. Biochemical Evaluation of Patients of Alcoholic Liver Disease and Non-alcoholic Liver Disease. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2014, 29, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feldstein, A.E.; Canbay, A.; Angulo, P.; Taniai, M.; Burgart, L.J.; Lindor, K.D.; Gores, G.J. Hepatocyte apoptosis and fas expression are prominent features of human nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| De Ritis Ratio | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | <1.20 (Tertile 1) n = 749 | 1.20–1.64 (Tertile 2) n = 749 | >1.64 (Tertile 3) n = 750 | p |
| Gender | 0.001 | |||
| Male, n (%) | 558 (69.8) * | 474 (61.2) | 456 (67.7) * | |
| Female, n (%) | 242 (30.2) * | 300 (38.8) | 218 (32.3) * | |
| Age (years) | 47.0 ± 16.4 * | 50.4 ± 17.6 | 49.9 ± 18.1 | <0.001 |
| AST (U/L) | 115.8 ± 174.9 | 115.7 ± 262.0 | 140.5 ± 209.7 | 0.049 |
| ALT (U/L) | 115.9 ± 158.1 * | 74.5 ± 107.0 | 61.9 ± 86.0 | <0.001 |
| Comorbidities | ||||
| DM, n (%) | 104 (13.0) | 88 (11.4) | 79 (11.7) | 0.580 |
| HTN, n (%) | 181 (22.6) | 160 (20.7) | 160 (23.7) | 0.361 |
| CAD, n (%) | 16 (2.0) | 20 (2.6) | 13 (1.9) | 0.633 |
| CVA, n (%) | 7 (0.9) | 12 (1.6) | 16 (2.4) | 0.068 |
| CHF, n (%) | 2 (0.2) | 4 (0.5) | 5 (0.7) | 0.399 |
| ESRD, n (%) | 10 (1.2) | 4 (0.5) | 6 (0.9) | 0.301 |
| ISS, median (IQR) | 10 (8–16) * | 13 (8–18) | 13 (9–18) * | <0.001 |
| 1–15, n (%) | 581 (72.6) * | 508 (65.6) | 413 (61.3) | <0.001 |
| 16–24, n (%) | 161 (20.1) * | 196 (25.3) | 189 (28.0) | 0.001 |
| ≥25, n (%) | 58 (7.2) | 70 (9.0) | 72 (10.7) | 0.069 |
| Mortality, n (%) | 13 (1.6) | 10 (1.3) | 25 (3.7) * | 0.003 |
| Propensity Score Matched-Cohort | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| De Ritis Ratio | OR (95% CI) | p | Standardized Difference | |||||
| >1.64 (Tertile 3) n = 604 | 1.20–1.64 (Tertile 2) n = 604 | |||||||
| Male, n (%) | 403 | (66.7) | 403 | (66.7) | 1.00 | (0.79–1.27) | 1.000 | 0.00% |
| Age (years) | 48.9 | ±17.9 | 48.7 | ±18.0 | - | 0.839 | 1.17% | |
| DM, n (%) | 59 | (9.8) | 59 | (9.8) | 1.00 | (0.68–1.46) | 1.000 | 0.00% |
| HTN, n (%) | 126 | (20.9) | 126 | (20.9) | 1.00 | (0.76–1.32) | 1.000 | 0.00% |
| CAD, n (%) | 8 | (1.3) | 8 | (1.3) | 1.00 | (0.37–2.68) | 1.000 | 0.00% |
| CVA, n (%) | 6 | (1.0) | 6 | (1.0) | 1.00 | (0.32–3.12) | 1.000 | 0.00% |
| CHF, n (%) | 1 | (0.2) | 1 | (0.2) | 1.00 | (0.06–16.02) | 1.000 | 0.00% |
| ESRD, n (%) | 0 | (0.0) | 0 | (0.0) | - | - | - | |
| GCS | 15 | (15–15) | 15 | (15–15) | - | 0.479 | −4.07% | |
| ISS | 13 | (9–18) | 13 | (9–18) | - | 0.966 | −0.24% | |
| Mortality | 19 | (3.1) | 5 | (0.8) | 3.89 | (1.44–10.50) | 0.004 | - |
| Propensity Score Matched-Cohort | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| De Ritis Ratio | OR (95% CI) | p | Standardized Difference | |||||
| <1.20 (Tertile 1) n = 647 | 1.20–1.64 (Tertile 2) n = 647 | |||||||
| Male, n (%) | 426 | (65.8) | 426 | (65.8) | 1.00 | (0.80–1.26) | 1.000 | 0.00% |
| Age (years) | 48.0 | ±16.2 | 48.6 | ±16.7 | - | 0.539 | −3.42% | |
| DM, n (%) | 71 | (11.0) | 71 | (11.0) | 1.00 | (0.71–1.42) | 1.000 | 0.00% |
| HTN, n (%) | 136 | (21.0) | 136 | (21.0) | 1.00 | (0.77–1.31) | 1.000 | 0.00% |
| CAD, n (%) | 9 | (1.4) | 9 | (1.4) | 1.00 | (0.39–2.54) | 1.000 | 0.00% |
| CVA, n (%) | 4 | (0.6) | 4 | (0.6) | 1.00 | (0.25–4.02) | 1.000 | 0.00% |
| CHF, n (%) | 0 | (0.0) | 0 | (0.0) | - | - | - | |
| ESRD, n (%) | 2 | (0.3) | 2 | (0.3) | 1.00 | (0.14–7.12) | 1.000 | 0.00% |
| GCS | 15 | (15–15) | 15 | (15–15) | - | 0.655 | −2.48% | |
| ISS | 11 | (8–17) | 12 | (8–17) | - | 0.703 | −2.12% | |
| Mortality | 11 | (1.7) | 6 | (0.9) | 1.85 | (0.68–5.03) | 0.222 | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, W.-T.; Rau, C.-S.; Chou, S.-E.; Tsai, C.-H.; Liu, H.-T.; Hsu, S.-Y.; Hsieh, C.-H. Association between Elevated De Ritis Ratio and Mortality Outcome in Adult Patients with Thoracoabdominal Trauma. Healthcare 2022, 10, 2082. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10102082
Su W-T, Rau C-S, Chou S-E, Tsai C-H, Liu H-T, Hsu S-Y, Hsieh C-H. Association between Elevated De Ritis Ratio and Mortality Outcome in Adult Patients with Thoracoabdominal Trauma. Healthcare. 2022; 10(10):2082. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10102082
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Wei-Ti, Cheng-Shyuan Rau, Sheng-En Chou, Ching-Hua Tsai, Hang-Tsung Liu, Shiun-Yuan Hsu, and Ching-Hua Hsieh. 2022. "Association between Elevated De Ritis Ratio and Mortality Outcome in Adult Patients with Thoracoabdominal Trauma" Healthcare 10, no. 10: 2082. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10102082
APA StyleSu, W.-T., Rau, C.-S., Chou, S.-E., Tsai, C.-H., Liu, H.-T., Hsu, S.-Y., & Hsieh, C.-H. (2022). Association between Elevated De Ritis Ratio and Mortality Outcome in Adult Patients with Thoracoabdominal Trauma. Healthcare, 10(10), 2082. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10102082







