Detrended Correlation Coefficients Between Exchange Rate (in Dollars) and Stock Markets in the World’s Largest Economies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Methodology and Data
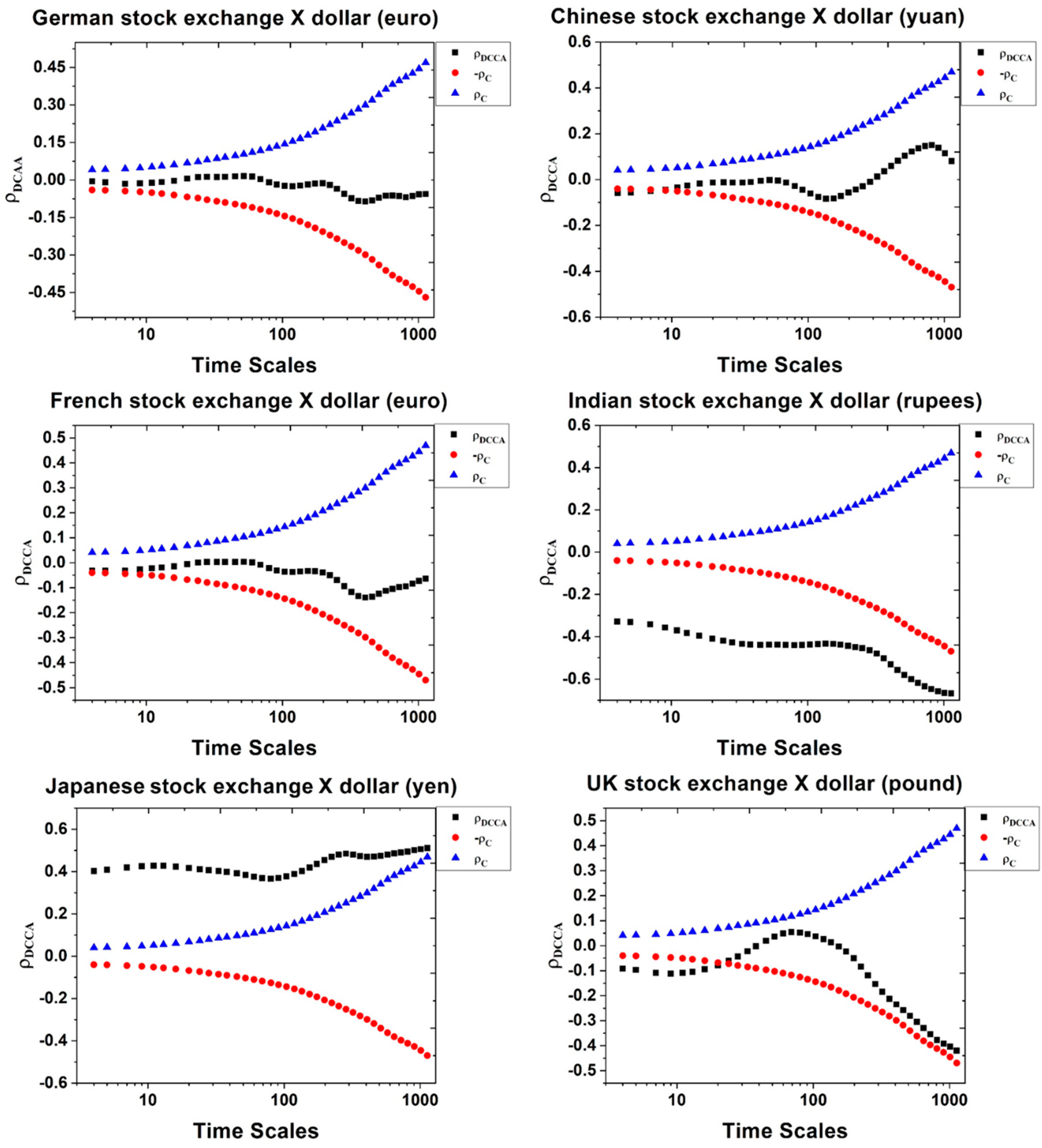
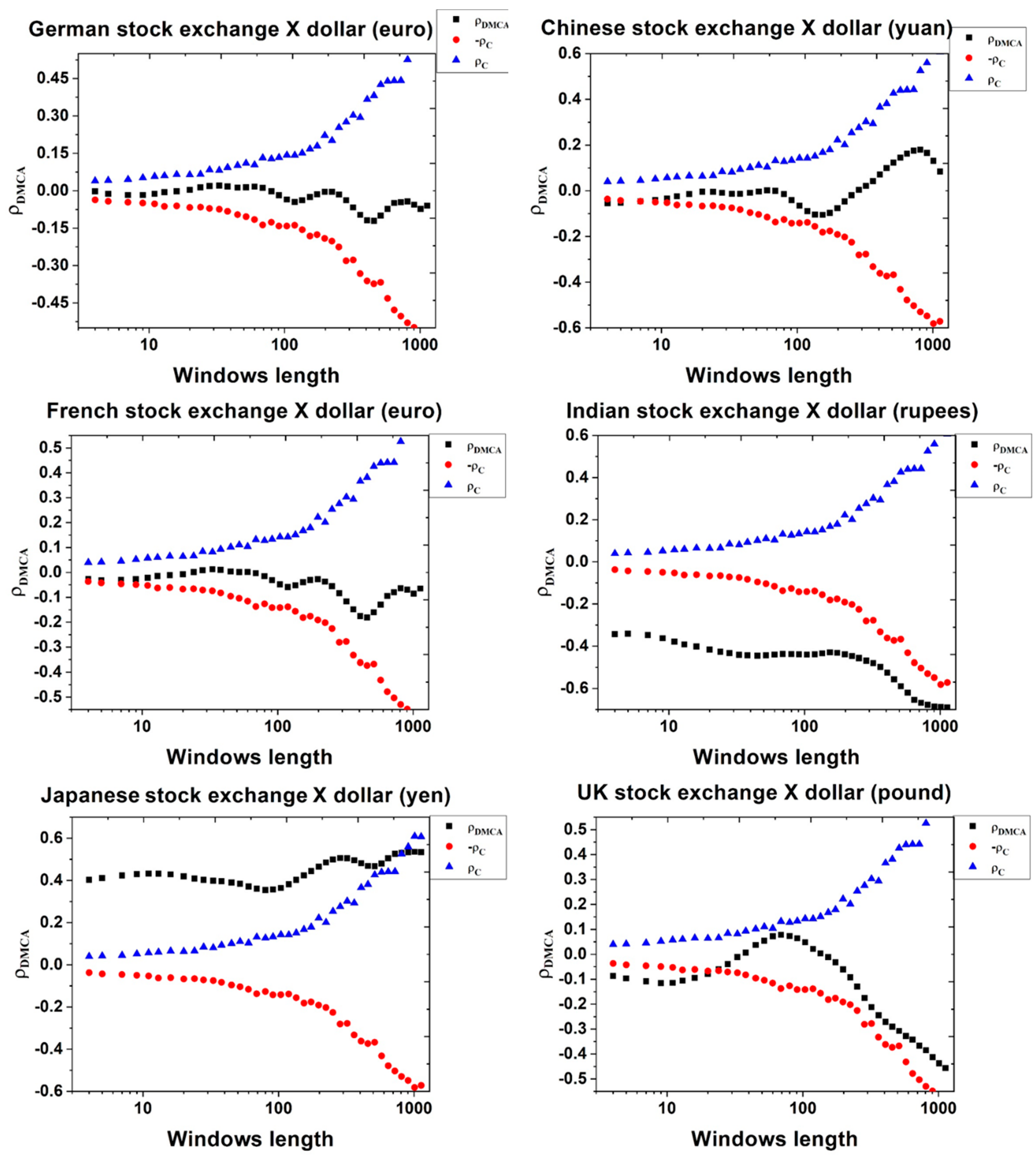
4. Results
5. Concluding Remarks
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdalla, Issam, and Victor Murinde. 1997. Exchange rate and stock price interactions in emerging financial markets: Evidence on India, Korea, Pakistan and the Philippines. Applied Financial Economics 7: 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, Raj. 1981. Exchange Rates and Stock Prices: A Study of the US Capital Markets under Floating Exchange Rates. Akron Business and Economic Review 12: 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ajayi, Richard, and Mbodja Mougoue. 1996. On the Dynamic Relation between Stock Prices and Exchange Rates. Journal of Financial Research 19: 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajayi, Richars, Joseph Friedman, and Seyed Mehdian. 1998. On the relationship between stock returns and exchange rates: Tests of granger causality. Global Finance Journal 9: 241–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, M. Suresh, and K. P. Prabheesh. 2008. Causal relationships between Foreign Institutional Investments and stock returns in India. International Journal of Trade and Global Markets 1: 259–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahmani-Oskooee, Mohsen, and Ahmad Sohrabian. 1992. Stock Prices and the Effective Exchange of the Dollar. Applied Economics 24: 459–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartov, Eli, and Gordon Bodnar. 1994. Firm Valuation, Earnings Expectations, and the Exchange-rate Exposure Effect. Journal of Finance 49: 1755–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barunik, Jozef, and Ladislav Kristoufek. 2010. On Hurst exponent estimation under heavy-tailed distributions. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications 389: 3844–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodnar, Gordon, and William Gentry. 1993. Exchange rate Exposure and Industry Characteristics: Evidence from Canada, Japan, and the USA. Journal of International Money and Finance 12: 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanno, Giovanni, Guido Caldarelli, Fabrizio Lillo, Salvatore Micciche, Nicolas Vandewalle, and Rosario Mantegna. 2004. Networks of Equities in Financial Markets. European Physical Journal B 38: 363–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branson, William. 1983. Macroeconomic Determinants of Real Exchange Rates. In Managing Foreign Exchange Rate Risk. Edited by R. J. Herring. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 33–74. [Google Scholar]
- Caporale, Giuglielmo, John Hunter, and Faek Ali. 2014. On the Linkages Between Stock Prices and Exchange Rates: Evidence from the Banking Crisis of 2007–2010. International Review of Financial Analysis 33: 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cont, Rama. 2001. Empirical properties of asset returns: stylized facts and statistical issues. Quantitative Finance 1: 223–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Matteo, Tiziana, Tomaso Aste, and Michel Dacorogna. 2003. Scaling Behaviors in Differently Developed Markets. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications 324: 183–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Matteo, Tiziana, Tomaso Aste, and Michel Dacorogna. 2005. Long-term memories of developed and emerging markets: Using the scaling analysis to characterize their stage of development. Journal Banking & Finance 29: 827–51. [Google Scholar]
- Doong, Shuh-Chyi, Sheng-Yung Yang, and Alan Wang. 2005. The Dynamic Relationship and Pricing of Stocks and Exchange Rates: Empirical Evidence from Asian Emerging Markets. Journal of American Academy of Business 7: 118–23. [Google Scholar]
- Dornbusch, Rudiger, and Stanley Fischer. 1980. Exchange rates and the current account. The American Economic Review 70: 960–71. [Google Scholar]
- Eom, Cheoljun, Gabjin Oh, Woo-Sung Jung, Hawoong Jeong, and Seunghwan Kim. 2009. Topological properties of stock networks based on minimal spanning tree and random matrix theory in financial time series. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications 388: 900–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, Peter, and Allan Young. 1972. Stock Price reaction of Multinational Firms to Exchange Realignments. Financial Management 1: 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankel, Jeffrey. 1983. Monetary and Portfolio Balance Models of Exchange Rate Determination. In Economic Interdependence and Flexible Exchange Rates. Edited by J. Bhandari and B. Putnam. Cambridge: MIT Press, pp. 84–115. [Google Scholar]
- Giovannini, Alberto, and Philippe Jorion. 1987. Interest Rates and Risk Premia in the Stock Market and in the Foreign Exchange Market. Journal of International Money and Finance 6: 107–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, James, and Poonam Gupta. 2003. Portfolio Flows into India: Do Domestic Fundamentals Matter? Washington, DC: International Monetary Fund. [Google Scholar]
- Griffin, John, René Stulz, and Federico Nardari. 2004. Are Daily Cross-Border Equity Flows Pushed or Pulled? Review of Economics and Statistics 86: 641–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Ling-Yun, and Shu-Peng Chen. 2011. A new approach to quantify power-law cross-correlation and its application to commodity markets. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications 390: 3806–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, Mansor, and Hassanuddeen Aziz. 2003. Macroeconomic Variables and the Malaysian Equity market: A Rolling through Subsamples. Journal of Economic Studies 30: 6–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, Mustafa, Bayram Deviren, and Yusuf Kocakaplan. 2011. Topology of the correlation networks among major currencies using hierarchical structure methods. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications 390: 719–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keynes, John. 1936. The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money. London: Macmillan. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Ki-ho. 2003. Dollar exchange rate and stock price: Evidence from multivariate cointegration and error correction model. Review of Financial Economics 12: 301–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristoufek, Ladislav. 2010a. On Spurious Anti-Persistence in the US Stock Indices. Chaos Solitons Fractals 43: 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristoufek, Ladislav. 2010b. Long-range dependence in returns and volatility of Central European Stock Indices. Bulletin of the Czech Econometric Society 17: 50–67. [Google Scholar]
- Kristoufek, Ladislav. 2014a. Detrending moving-average cross-correlation coefficient: Measuring cross-correlations between non-stationary series. Physica A 406: 169–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristoufek, Ladislav. 2014b. Measuring correlations between non-stationary series with DCCA coefficient. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications 402: 291–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristoufek, Ladislav. 2016. Scaling of Dependence between Foreign Exchange Rates and Stock Markets in Central Europe. Acta Physica Polonica A 129: 908–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurihara, Yutaka, and Eiji Nezu. 2006. Recent stock price relationships between Japanese and US stock markets. Studies in Economics and Finance 23: 211–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, Takayuki, Hideki Takayasu, and Misako Takayasu. 2006. Correlation Networks Among Currencies. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications 364: 336–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley, Bruce, and Eric Pentecost. 2000. Common trends and cycles in G-7 countries exchange rates and stock prices. Applied Economics Letters 7: 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najand, Mohammad, and Bruce Seifert. 1992. Volatility of Exchange Rates, Interest Rates, and Stock Returns. Journal of Multinational Financial Management 2: 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Naylor, Michael, Lawrence Rose, and Brendan Moyle. 2007. Topology of foreign exchange markets using hierarchical structure methods. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications 382: 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieh, Chien-Chung, and Cheng-Few Lee. 2001. Dynamic relationship between stock prices and exchange rates for G-7 countries. The Quarterly Review of Economics and Finance 41: 477–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobi, Ashadun, Seong Maeng, Gyeong Ha, and Jae Lee. 2014. Effects of global financial crisis on network structure in a local stock market. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications 407: 135–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norouzzadeh, Payam, and Bahareh Rahmanic. 2006. A Multifractal Detrended Fluctuation Description of Iranian Rial–US Dollar Exchange Rate. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications 367: 328–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuyan, Hasan, and Erman Erbaykal. 2008. The Relationship Between FDI and Economic Growth in Developing Countries. Economic Approach 19: 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onnela, Jukka-Pekka, Anirban Chakraborti, Kimmo Kaski, Janos Kertesz, and A. Kanto. 2003. Dynamics of market correlations: Taxonomy and portfolio analysis. Physical Review E 68: 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onnela, Jukka-Pekka, Kimmo Kaski, and Janos Kertesz. 2004. Clustering and information in correlation based financial networks. European Physical Journal B 38: 353–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozair, Amber 2006. Causality between Stock prices and Exchange Rates: A Case of The United States. Master of Science Thesis, Florida Atlantic University, Boca Raton, FL, USA.
- Pan, Ming-Shiun, Robert Fok, and Ya-Chiu Liu. 2007. Dynamic Linkages between exchange rates and stock prices: Evidence from East Asian markets. International Review of Economics and Finance 16: 503–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.-K., Sergey Buldyrev, Shlomo Havlin, Michael Simons, Harry Eugene Stanley, and Ary Goldberger. 1994. Mosaic organization of DNA nucleotides. Physical Review E 49: 1685–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phylaktis, Kate, and Fabiola Ravazzolo. 2005. Stock Prices and Exchange rate Dynamics. Journal of International Money and Finance 24: 1031–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podobnik, Boris, and Harry Eugene Stanley. 2008. Detrended Cross-Correlation Analysis: A New Method for Analyzing Two Nonstationary Time Series. Physical Review Letters 100: 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podobnik, Boris, Zhi-Qiang Jiang, Wei-Xing Zhou, and Harry Eugene Stanley. 2011. Statistical tests for power-law cross-correlated processes. Physical Review E 84: 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Yu. 1997. Stock Prices and Exchange Rates: Experience in Leading East Asian Financial Centres: Tokyo, Hong Kong and Singapore. Singapore Economic Review 41: 47–56. [Google Scholar]
- Smyth, Russell, and Mohan Nandha. 2003. Bivariate causality between exchange rates and stock prices in South Asia. Applied Economics Letters 10: 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soenen, Luc, and Elizabeth Hennigar. 1988. An analysis of exchange rates and stock prices—The U.S. experience between 1980 and 1986. Akron Business and Economic Review 19: 7–16. [Google Scholar]
- Tumminello, Michele, Tiziana Di Matteo, Tomaso Aste, and Rosario Mantegna. 2007. Correlation based networks of equity returns sampled at different time horizons. European Physical Journal B 55: 209–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ülkü, Numan, and Ebru Demirci. 2012. Joint Dynamics of Foreign Exchange and Stock Markets in Emerging Europe. Journal of International Financial Markets, Institutions and Money 22: 55–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandewalle, Nicolas, and Marcel Ausloos. 1998. Crossing of two Mobile Averages: A method for Measuring the Roughness Exponent. Physical Review E 58: 6832–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vygodina, Anna. 2006. Effects of size and international exposure of the US firms on the relationship between stock prices and exchange rates. Global Finance Journal 17: 214–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebende, Gilney. 2011. DCCA cross-correlation coefficient: quantifying level of cross-correlation. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications 390: 614–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebende, Gilney, and Aloísio Filho. 2018. Detrended Multiple Cross-Correlation Coefficient. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications 510: 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Mean | Maximum | Minimum | Std. Dev. | Skewness | Kurtosis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | 0.0002 | 0.0940 | −0.0926 | 0.0154 | −0.3090 | 5.3316 |
| Germany | 0.0002 | 0.1080 | −0.0887 | 0.0147 | −0.0507 | 4.5560 |
| France | 0.0001 | 0.1059 | −0.0947 | 0.0147 | −0.0386 | 5.0776 |
| Japan | 0.0001 | 0.1323 | −0.1211 | 0.0146 | −0.3914 | 6.8036 |
| India | 0.0006 | 0.1503 | −0.1288 | 0.0147 | 0.4791 | 7.9063 |
| United Kingdom | 0.0001 | 0.0938 | −0.0927 | 0.0117 | −0.1582 | 6.3288 |
| Mean | Maximum | Minimum | Std. Dev. | Skewness | Kurtosis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese Yuan | −0.0001 | 0.0182 | −0.0203 | 0.0011 | −0.6803 | 54.4709 |
| Euro | 0.0000 | 0.0384 | −0.0462 | 0.0062 | −0.1567 | 2.4937 |
| Japanese Yen | 0.0000 | 0.0384 | −0.0357 | 0.0064 | −0.0943 | 3.0115 |
| Indian Rupee | 0.0000 | 0.0325 | −0.0306 | 0.0037 | 0.2908 | 8.2795 |
| Pound Sterling | 0.0000 | 0.0831 | −0.0447 | 0.0059 | 0.5881 | 11.6940 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferreira, P.; Silva, M.F.d.; Santana, I.S.d. Detrended Correlation Coefficients Between Exchange Rate (in Dollars) and Stock Markets in the World’s Largest Economies. Economies 2019, 7, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/economies7010009
Ferreira P, Silva MFd, Santana ISd. Detrended Correlation Coefficients Between Exchange Rate (in Dollars) and Stock Markets in the World’s Largest Economies. Economies. 2019; 7(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/economies7010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerreira, Paulo, Marcus Fernandes da Silva, and Idaraí Santos de Santana. 2019. "Detrended Correlation Coefficients Between Exchange Rate (in Dollars) and Stock Markets in the World’s Largest Economies" Economies 7, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/economies7010009
APA StyleFerreira, P., Silva, M. F. d., & Santana, I. S. d. (2019). Detrended Correlation Coefficients Between Exchange Rate (in Dollars) and Stock Markets in the World’s Largest Economies. Economies, 7(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/economies7010009






