Effects of Cost Factors on National Manufacturing Based on Global Perspectives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
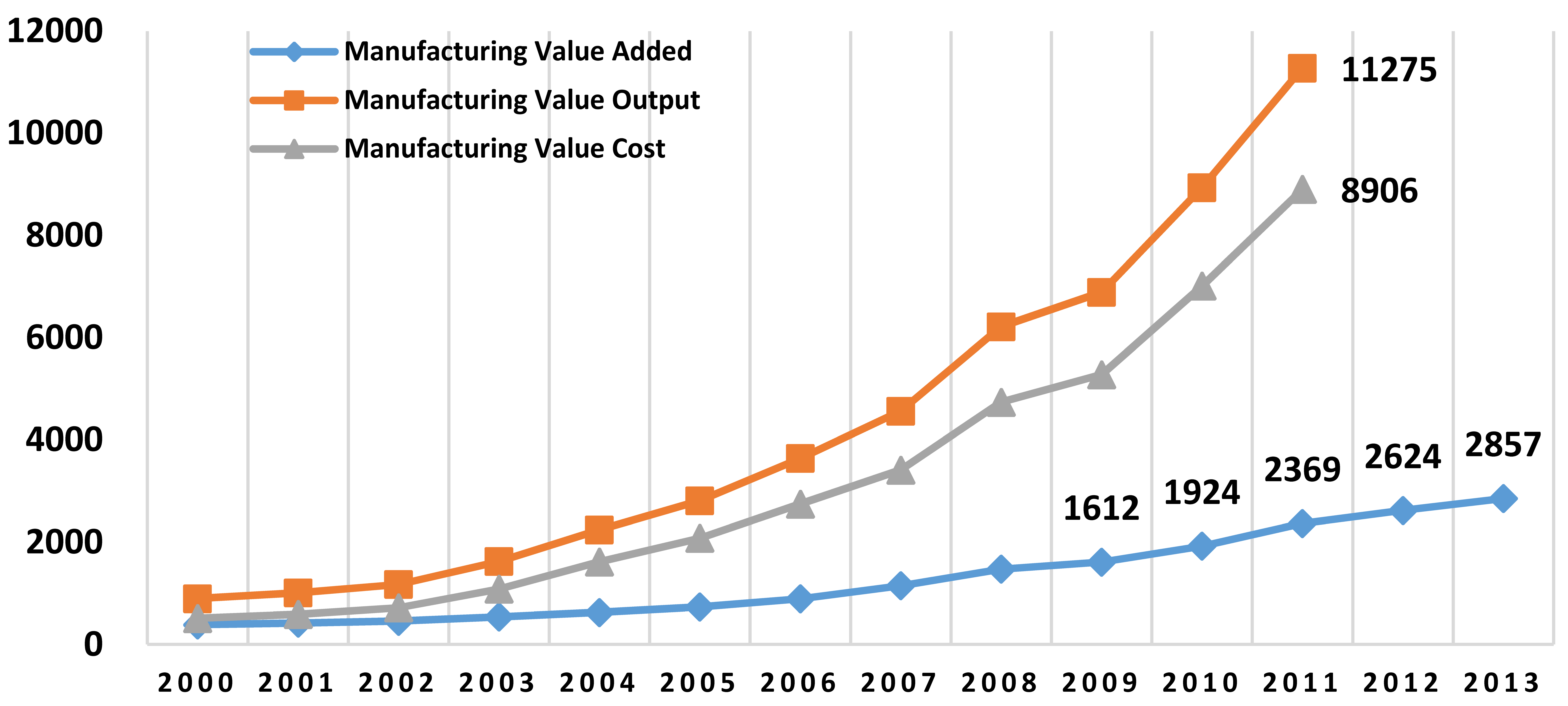
1.1. Global Manufacturing Development
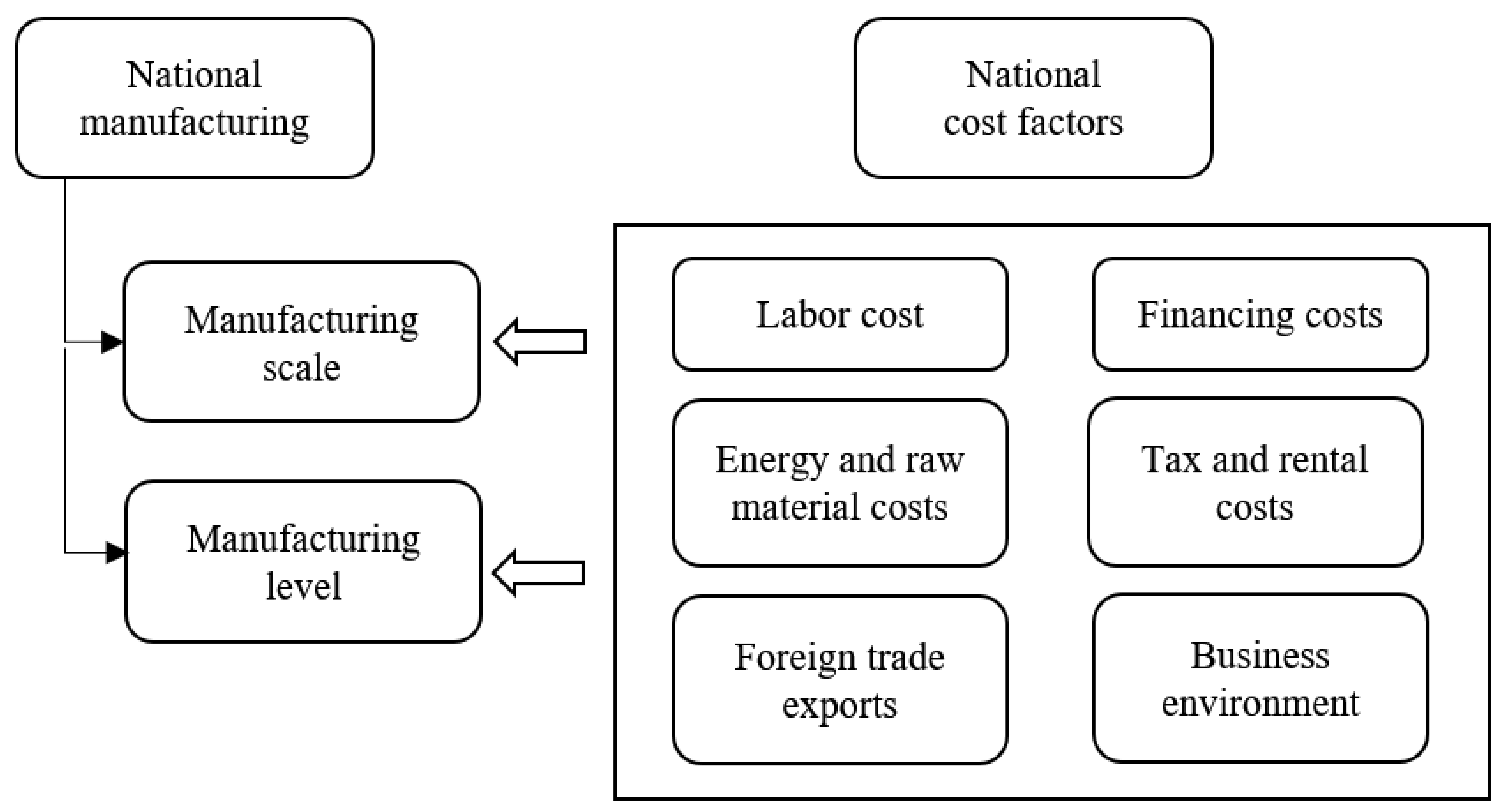
1.2. National Cost Factors
2. Literature Review
2.1. Manufacturing Development
2.2. National Cost Factors
2.3. China’s Manufacturing and Cost
3. Research Design
Data and Methods
4. Results
4.1. Factors of National Manufacturing Development
4.2. Effects of Cost Factors on National Manufacturing
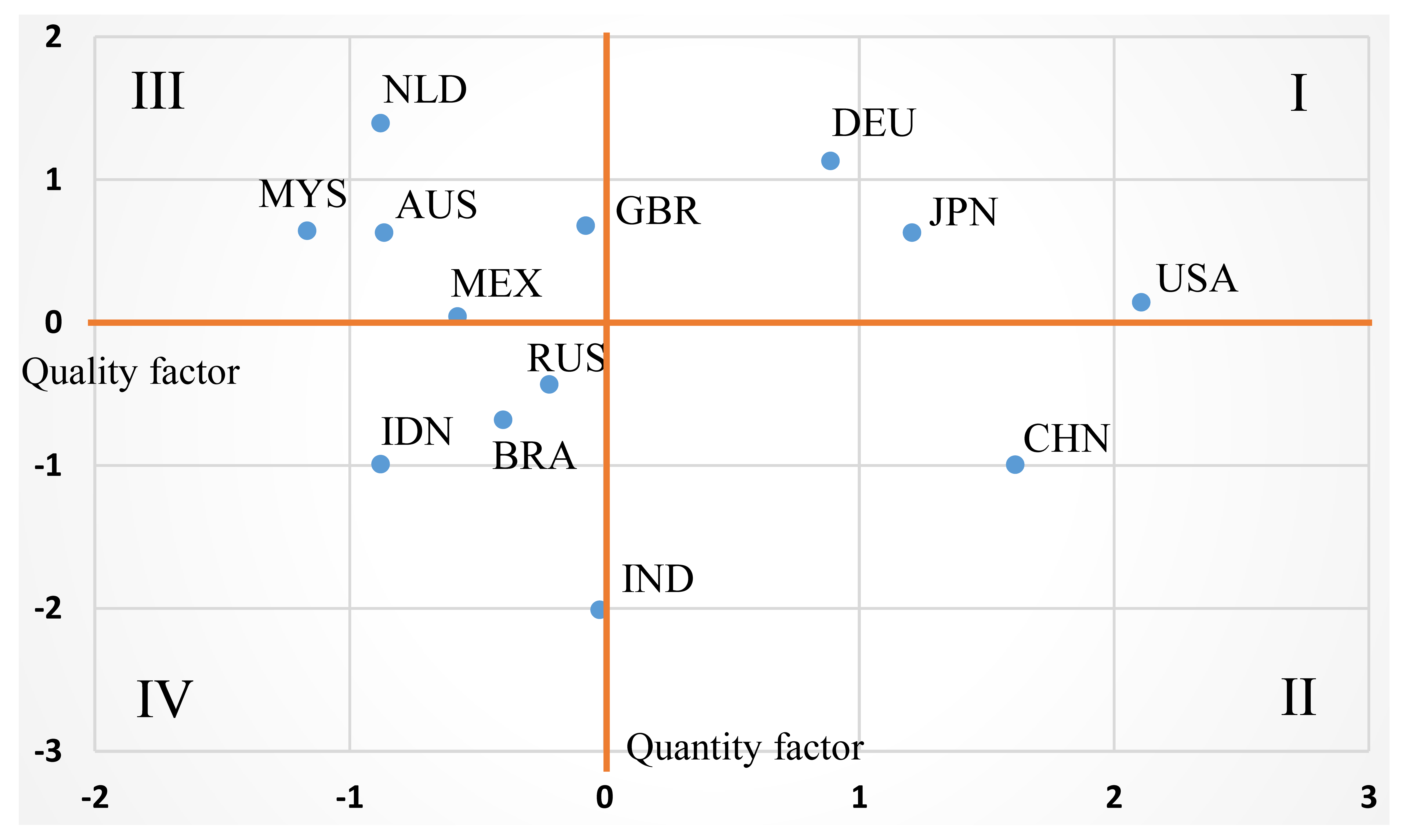
4.3. Key Cost Factor Analysis
5. Discussion and Conclusions
5.1. Manufacturing Development Trends
5.2. Policy Suggestion to Improve China’s Manufacturing Competitiveness
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Battisti, Giuliana, and Paul Stoneman. 2007. The prices of material and intermediate inputs in UK manufacturing: Identifying the contributions of world prices and domestic factor costs. Applied Economics 39: 859–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhanawat, Shurveer S. 2010. An analysis of raw material cost in Indian manufacturing industry. Journal of Accounting Research & Audit Practices 9: 65. [Google Scholar]
- Bureau of Labor Statistics. 2017. U.S. “Multifactor Productivity—Overview”; Washington: Department of Labor. Available online: https://www.bls.gov/mfp/ (accessed on 11 March 2017).
- Ceglowski, Janet, and Stephen Golub. 2007. Just how low are China’s labor costs? World Economy 30: 597–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceglowski, Janet, and Stephen S. Golub. 2011. Does China Still Have a Labor Cost Advantage? Rochester: Social Science Electronic Publishing, vol. 12, pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Chisik, Richard, Bill Battaile, and Harun Onder. 2014. The Distribution of Natural Resource Rents and the Dutch Disease. Working papers. Toronto: Department of Economics, Ryerson University. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, Adrian. 2010. The impact of interest rates and the housing market on the UK economy. Economic Outlook 28: 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Economic and Social Affairs Statistics Division. 2008. International Standard Industrial Classification of All Economic Activities Revision. New York: United Nation, p. 85. [Google Scholar]
- Duve, Munyaradz. 2012. Effect of Tax Incentives on Growth in the Manufacturing Sector. Saarbrücken: LAP LAMBERT Academic Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- Executive Office of the President of the United States. 2009. A Framework for Revitalizing American Manufacturing. Washington: Executive Office of the President of the United States. [Google Scholar]
- Gopinath, Munisamy, and Mukti P. Upadhyay. 2002. Human capital, technology and specialization: A comparison of developed and developing countries. Journal of Economics 75: 161–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Government Office for Science and Department for Business, Innovation & Skills. 2013. The Future of Manufacturing: A New Era of Opportunity and Challenge for the UK; London: The Government Office for Science.
- Guisan, Maria-Carmen. 2008. Manufacturing and economic development: Inter-sectoral relationships in Europe, America, Africa and Asia-Pacific, 1999–2006. Regional & Sectoral Economic Studies 8: 73–88. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, Joseph F., Rolph E. Anderson, Ronald L. Tatham, and William C. Black. 1998. Multivariate Data Analysis. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall. [Google Scholar]
- James, William E., and Oleksandr Movshuk. 2004. Shifting international competitiveness: An analysis of market share in manufacturing industries in Japan, Korea, Taiwan and the USA. Asian Economic Journal 18: 121–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanawaty, George, ed. 1992. UNESCO-UNEVOC Online Library. Geneva: International Labour Organization. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, Atsushi, and Takahiro Sato. 2014. The effect of corruption on the manufacturing sector in India. Economics of Governance 15: 155–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kepplinger, D., M. Templ, and S. Upadhyaya. 2013. Analysis of energy intensity in manufacturing industry using mixed-effects models. Energy 59: 754–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lall, Somik V., and Taye Mengistae. 2005. The Impact of Business Environment and Economic Geography on Plant-Level Productivity: An Analysis of Indian Industry. Policy Research Working paper 3664. Washington, DC, USA: World Bank. [Google Scholar]
- Lasi, Heiner, Peter Fettke, Thomas Feld, and Michael Hoffmann. 2014. Industry 4.0. Business & Information Systems Engineering 6: 239–42. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Ai-Dong, Wen-Jing Liu, Hui-Xiang Zeng, and School of Business, Central South University. 2014. Carbon emissions measure and influencing factors involved in the anti-dumping industry from ten countries. Economic Geography 34: 127–35. [Google Scholar]
- Menzler-Hokkanen, Ingeborg. 1989. Can international competitiveness be measured by the relative unit labor cost approach? A comment on professor Artto. Management International Review 29: 72–77. [Google Scholar]
- Miketa, Asami. 2001. Analysis of energy intensity developments in manufacturing sectors in industrialized and developing countries. Energy Policy 29: 769–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, Steven I. 1982. Quality and quantity: Another view of analytic induction as a research technique. Quality & Quantity 16: 281–95. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry of Japan. 2015. Summary of the White Paper on Manufacturing Industries (Monodzukuri) 2015; Tokyo: Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry of Japan.
- Ostwald, Phillip F., and Timothy S. McLaren. 2003. Cost analysis and estimating for engineering and management. American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology 211: 15–17. [Google Scholar]
- Ragacs, Christian, and Klaus Vondra. 2009. Austria’s exports to Eastern Europe: Facts and forecasts likely impact of slowing exports on growth in Austria. Monetary Policy & the Economy Q 1: 29–43. [Google Scholar]
- Roudaut, Nolwenn. 2006. Influences of the business environment on manufacturing firms’ technical efficiencies: The Côte d’lvoire case. Journal of Productivity Analysis 25: 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seshaiah, S. Venkata, and I. R. S. Sarma. 2007. Cost structure of Indian manufacturing sector, 1971–2003. Regional & Sectoral Economic Studies 7: 19–32. [Google Scholar]
- Shahidul, M. I., and S. T. Syed Shazali. 2011. Dynamics of manufacturing productivity: Lesson learnt from labor intensive industries. Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management 22: 664–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirkin, Harold, Michael Zinser, and Justin Rose. 2014. The Shifting Economics of Global Manufacturing: How Cost Competitiveness Is Changing Worldwide. Boston: The Boston Consulting Group. [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian, Annapoornima M., and Pek-Hooi Soh. 2010. An empirical examination of the science-technology relationship in the biotechnology industry. Journal of Engineering & Technology Management 27: 160–71. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, Aixiang. 2011. Research on relationship between energy consumption quality and education, science and technology based on grey relation theory. Energy Procedia 5: 1718–21. [Google Scholar]
- Transparency International. 2011. Global Corruption Report: Climate Change. Berlin: Transparency International. [Google Scholar]
- UNIOD (The United Nations Industrial Development Organization). 2017. Available online: http://www.unido.org/resources/statistics/statistical-databases.html (accessed on 10 September 2017).
- Van Ark, Bart, Abdul Azeez Erumban, Vivian Chen, and Utsav Kumar. 2010. The Cost Competitiveness of Manufacturing in China and India. Working Paper 228. New Delhi: Indian Council for Research on International Economic Relations. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank. 2011. The Changing Wealth of Nations: Measuring Sustainable Development in the New Millennium. In Environment and Development. Washington: World Bank. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Nuo, and Xiao Jie Zhang. 2014. Model analysis of the impact of logistics factors on economy. Applied Mechanics & Materials 687–691: 5057–60. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Zhen, Jianbai Huang, and Feitao Jiang. 2017. Subsidy competition, industrial land price distortions and overinvestment: Empirical evidence from China’s manufacturing enterprises. Applied Economics 49: 4851–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, Benjamin, and Delvin Grant. 2017. Exploring the factors affecting global manufacturing performance. Information Technology for Development, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Abraham, and George Q. Huang. 2012. Impacts of business environment changes on global manufacturing outsourcing in China. Supply Chain Management 17: 138–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1 | Labor cost in per unit = Compensation levels/Labor productivity. |
| Factor | Indicator | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Labor costs | Labor cost in per unit Employer’s social security contribution rate | Menzler-Hokkanen 1989 Kanawaty 1992 Ostwald and McLaren 2003 Ceglowski and Golub 2007 Van Ark et al., 2010 |
| Financing costs | Interest rate spread | Yeo and Grant 2017 |
| Tax and rental costs | Corporate tax rate on profit Office rent | Duve 2012 |
| Energy and raw material costs | Energy intensity Total natural resource rent (% of GDP) Inventory change (current dollar) | Miketa 2001 Battisti and Stoneman 2007 Zhang and Huang 2012 Kepplinger et al., 2013 Chisik et al., 2014 Liu et al., 2014 |
| Foreign trade exports | Merchandise trade (% of GDP) Manufacture exports (% of merchandise exports) Manufacture imports (% of merchandise imports) | Ragacs and Vondra 2009 |
| Business environments | Corruption Perceptions Index | Transparency International 2011 World Bank 2011 Roudaut 2006 Kato and Sato 2014 |
| Cost Factors | National Manufacturing Scale | National Manufacturing Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | |
| Labor cost per unit | 0.9630 *** (0.1410) | 1.2510 *** (0.0945) | ||
| Employer’s social security contribution rate | 0.0071 ** (0.0017) | 0.0158 *** (0.0022) | ||
| Interest rate spread | −0.0239 *** (0.0029) | −0.0172 *** (0.0016) | ||
| Corporate tax rate on profit | 0.0094 * (0.0040) | 0.0065 (0.0040) | ||
| Office rent | −0.2550 *** (0.0255) | −0.2240 *** (0.0246) | ||
| Energy intensity | 0.2150 ** (0.0641) | −0.2140 ** (0.0540) | ||
| Total natural resource rent (% of GDP) | −0.0119 ** (0.0039) | −0.0045 (0.0033) | ||
| Inventory change (current dollar) | 0.0043 *** (0.0006) | 0.0015 * (0.0005) | ||
| Merchandise trade (% of GDP) | −0.3890 *** (0.0253) | −0.0599 (0.0314) | ||
| Manufacture exports (% of merchandise exports) | 0.2270 *** (0.0521) | 0.4990 *** (0.0349) | ||
| Manufacture imports (% of merchandise imports) | 1.2430 *** (0.2200) | 0.4620 * (0.1650) | ||
| Corruption Perceptions Index | −0.0097 *** (0.0014) | −0.0085 *** (0.0013) | ||
| Total population | 0.9600 *** (0.0365) | 0.7830 *** (0.0289) | −0.2550 *** (0.0360) | −0.4070 *** (0.0245) |
| GDP per capita | 1.1560*** (0.0373) | 0.9890 *** (0.0300) | 0.7750 *** (0.0441) | 0.4520 *** (0.0307) |
| 2000 year–2015 year | / | / | / | / |
| Constant | −28.84 *** (0.953) | −28.48 *** (1.334) | −2.766 * (0.984) | 1.421 (0.866) |
| R-squared | 0.887 | 0.982 | 0.883 | 0.983 |
| Country = 13 and observation = 208. *** p value < 0.01; ** p value < 0.05; * p value < 0.1. | ||||
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, F.; Ding, Y.; Gao, J.; Gong, P. Effects of Cost Factors on National Manufacturing Based on Global Perspectives. Economies 2017, 5, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/economies5040045
Liu F, Ding Y, Gao J, Gong P. Effects of Cost Factors on National Manufacturing Based on Global Perspectives. Economies. 2017; 5(4):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/economies5040045
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Fangtao, Yong Ding, Jia Gao, and Pu Gong. 2017. "Effects of Cost Factors on National Manufacturing Based on Global Perspectives" Economies 5, no. 4: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/economies5040045
APA StyleLiu, F., Ding, Y., Gao, J., & Gong, P. (2017). Effects of Cost Factors on National Manufacturing Based on Global Perspectives. Economies, 5(4), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/economies5040045