Abstract
With the advancement of modern engineering structures, traditional cement concrete is increasingly unable to meet the mechanical performance requirements under complex conditions. To overcome the performance limitations of materials, modified concrete has become a focal point of research. By incorporating modifying materials such as fibers, polymers, or mineral admixtures, the properties of concrete can be significantly enhanced. Among these, rubberized concrete has attracted considerable attention due to its unique performance advantages. This study conducted fracture tests on rubberized concrete using non-standard concrete three-point bending beam specimens of varying dimensions to evaluate its fracture performance. Employing conventional concrete fracture theoretical models, the fracture toughness parameters of rubberized concrete were calculated, and a comparative analysis was performed regarding the applicability of various theoretical calculation formulas to rubberized concrete. The results indicated that the fracture performance of rubberized concrete varied significantly with changes in specimen size. The initial toughness exhibited a consistent size-dependent variation across different theoretical models. The fracture toughness corresponding to crack height ratios between 0.05 and 0.25 showed contradictory trends; however, for crack height ratios between 0.3 and 0.5, the fracture toughness became consistent. This study integrated boundary effect theory and employed Guinea’s theory to propose an optimization coefficient γ for the double-K fracture toughness formula, yielding favorable optimization results.
1. Introduction
As the most widely used cement-based material, concrete is prone to cracking during both construction and service. Being a quasi-brittle material, concrete exhibits highly complex failure and fracture mechanisms [1]. An in-depth study of the fracture properties and fundamental material parameters of concrete can lead to a better understanding of the morphology and characteristics of fracture damage in concrete structures. Compared to ordinary concrete, rubber concrete forms a structural deformation center that absorbs strain energy, as rubber powder (or granules) fills voids [1,2]. This process thereby restrains the generation and development of microcracks [3], endowing the concrete with excellent shrinkage [4] performance and crack resistance [5,6]. The use of rubber in concrete has been shown to significantly reduce environmental impacts, particularly in waste management and global warming potential [7,8]. From a microscopic perspective, the presence of rubber particles delays and mitigates the propagation of freeze–thaw cracks, leading to the formation of a denser spatial structure in the calcium silicate hydrate (CSH) gel. This enhanced structure improves the frost resistance of the material. Additionally, the Ca/Si ratio within the CSH can vary, influencing its structural and mechanical properties. A lower Ca/Si ratio promotes silicate polymerization, thereby enhancing the mechanical performance of the materials [9,10,11]. In addition, the incorporation of rubber will also have a greater impact on the durability of rubber concrete [12,13]. Thus, rubber concrete has attracted significant attention and holds promise for various engineering applications such as infiltration holes, pavements, and airports [14,15]. However, the fracture mechanism of rubber concrete is affected by factors such as rubber–matrix interface effect and material heterogeneity, and the determination of its fracture parameters faces challenges. In particular, the size effect and theoretical model applicability under non-standard specimens are not yet clear.
At the end of the last century, Xu et al. [16] established the double-K fracture model by taking into account the linear elastic fracture mechanics and the cohesive force in the fracture process zone. On this basis, some scholars have pointed out the importance of the subcritical expansion of concrete cracks before unstable fracture, which is the main reason for the size effect of fracture toughness. Therefore, the double K fracture model can be applied to the fracture performance evaluation of concrete materials [17,18]. At the beginning of the 20th century, Hu believed that the acquisition of fracture parameters was affected by the material-independent size needed to make the initial crack and ligament height of the specimen far away from the boundary, and based on this, the boundary effect theory was established [19]. Based on the basic equations of boundary effect theory, subsequent scholars have developed models and methods to determine the tensile strength and fracture toughness of concrete without size effect [20]. With the development of the size effect model [21] and boundary effect model [22] in recent years, the mechanism and scale law of concrete strength are clearer.
In the fracture process of rubberized concrete, rubber particles can play a role similar to that of elastic fibers to inhibit the expansion of cracks and produce the effect of energy dissipation, which improves the fracture resistance of concrete [23]. Rubber type has a great influence on the performance of concrete. Synthetic rubber, particularly Styrene–Butadiene Rubber (SBR), can significantly enhance the fracture properties of rubber concrete, especially when combined with fibers [24,25]. This enhancement includes improvements in fracture energy, toughness, and interfacial bonding performance. When incorporated at moderate levels, ordinary recycled rubber increases the fracture performance of concrete; however, excessive amounts can lead to a reduction in these properties [26,27]. Han et al. [28] established the fracture energy calculation equation for rubberized concrete with different rubber admixtures by studying the effect of rubber particles on the energy dissipation of concrete. Wang [29] analyzed the fracture mode of rubberized concrete using the digital image correlation (DIC) technique. The large amount of rubber admixture makes the fracture damage mechanism of concrete more complex than that of ordinary concrete. It is important to study the fracture performance of rubberized concrete and reveal the fracture deterioration and failure mechanism of rubberized concrete in order to prolong the service life of concrete structures and promote the application of rubberized concrete in practical engineering.
Due to the large amount of rubber, the fracture mechanism of concrete is more complicated than that of ordinary concrete. Studying the fracture properties of rubber concrete and revealing the fracture degradation and failure mechanism of rubber concrete are of great significance for prolonging the service life of concrete structures and promoting the application of rubber concrete in practical engineering. Liu [30] found that the admixture of rubber prolonged the crack extension process of concrete and improved the deformation capacity of concrete. Existing studies have found that, similar to the fracture process of ordinary concrete, the fracture process of rubber concrete can also be divided into three stages: crack initiation, stable propagation, and unstable propagation. However, the presence of rubber particles introduces new characteristics to rubber concrete. Therefore, whether the fracture theories of ordinary concrete are applicable to rubber concrete still requires further investigation.
The current research is mostly based on standard specimens and classical fracture theory to evaluate the fracture performance of concrete. However, complex-sized components are common in practical engineering, and the introduction of rubber significantly changes the fracture behavior of materials. The applicability of the traditional theoretical model under non-standard specimens is controversial. On the one hand, the influence of geometric parameters such as fracture height ratio and span height ratio on fracture toughness has not been unified. On the other hand, different theories have obvious differences in the ability to characterize rubber viscoelasticity and interface damage, resulting in scattered calculation results. In addition, the existing methods are insufficient for the coupling analysis of multi-size parameters, and it is difficult to accurately guide engineering design and safety assessment.
Previous studies have shown that the fracture process of rubberized concrete, like that of ordinary concrete, can be classified into three distinct stages: crack initiation, stable propagation, and unstable propagation. However, the presence of rubber particles introduces unique characteristics to rubberized concrete, necessitating further investigation into the applicability of conventional concrete fracture theories to this material. To examine the size effect in rubberized concrete and assess the relevance of ordinary concrete fracture theories, this study conducts three-point bending beam tests with small span-to-height ratios. A comparative analysis of fracture parameters derived from various concrete fracture theories is performed, systematically investigating the size effect of fracture parameters in rubberized concrete. Utilizing theoretical frameworks such as boundary effect theory, the double-K model, and the double-G model, the study analyzes the mechanisms by which the height-to-depth ratio and span-to-height ratio influence fracture toughness, thereby elucidating the applicability and limitations of these theoretical models.
2. Comparative Analysis of Existing Fracture Theories
This study provides a brief overview of the process of analyzing the fracture parameters of rubber concrete three-point bending beams based on various theoretical approaches, including the Boundary Effect Model, ASTM standards, methods proposed by Tada et al. and Guinea et al., as well as the double-K and double-G fracture models.
2.1. Boundary Effect Theory
The Boundary Effect Model (BEM) postulates that fracture toughness is an inherent property of the material. The size effect observed in concrete arises from the interaction between the fracture process zone (FPZ) and the specimen boundaries. If the specimen size is sufficiently large, the fracture toughness KIC remains constant and does not increase. Therefore, by applying the Boundary Effect Model, the fracture toughness (KIC) and tensile strength (ft), which are independent of specimen size, can be determined [31].
The improved Boundary Effect Model (BEM) [32,33,34], in conjunction with Equation (1), enables the determination of the fracture toughness () and tensile strength () of rubber concrete using only the peak load ().
Equation (1) can be further transformed into Equation (2):
where represents the characteristic crack length of the material, which is entirely determined by the and , given by ; denotes the equivalent crack length, which is fully dependent on the specimen size, type, and initial crack length a; it can be expressed as , where is the geometric shape parameter of the three-point bending beam specimen [35,36,37,38]. The specific expression is given in Equation (3).
Considering that in laboratory conditions, specimen sizes are relatively small, and the aggregate size cannot be neglected, the maximum aggregate size () is introduced into the analytical formula of the Boundary Effect Model to better reflect the actual fracture mechanism. Additionally, a dispersion coefficient (β) is incorporated to describe the relationship between the virtual crack extension () and the maximum coarse aggregate diameter (). To avoid character conflicts, λ is used in place of the dispersion coefficient β as defined in the literature [38].
The nominal stress expression can be given by Equation (7):
where
2.2. ASTM Standards
In the Standard Test Method for Linear-Elastic Plane-Strain Fracture Toughness of Metallic Materials (ASTM E399) [39], calculation is recommended to be performed using Equations (8) and (9). The applicable specimen size range is , .
2.3. Method of Tada
Tada H et al. [40] provided the relevant formula:
where represents the nominal stress of the three-point bending beam specimen; denotes the crack length; is the shape function for calculating the fracture toughness of a three-point bending beam, which depends on the span-to-height ratio β and a/h.
where CMOD represents the crack mouth opening displacement; E is the calculated elastic modulus of the specimen; is the shape function for calculating a, which depends on the span-to-depth ratio β and the notch-to-depth ratio (α); α represents the notch-to-depth ratio, which satisfies , denotes the knife-edge thickness of the fixed clip gauge.
where represents the initial crack opening compliance measured from the P-CMOD curve of the specimen, .
When the span-to-depth ratio () of the specimen is 4, the shape functions and are given by Equations (14) and (15):
When the span-to-depth ratio () of the specimen is 2.5, the shape functions and are given by Equations (16) and (17):
And for the calculation of fracture toughness of three-point bending beams with non-standard dimensions involved in this paper, referring to the research of Yin et al. [41], the shape functions and of three-point bending beams with β of 4 and 2.5 were linearly interpolated in order to obtain the formulas for the fracture parameters of the three-point bending beams at other spans.
2.4. Method of Guinea
Guinea et al. [42,43,44] derived the formulas for fracture toughness applicable to three-point bending beams with prefabricated cracks (Equations (20)–(23)), with specimen sizes applied to any α, .
By substituting the experimental initiation load , peak load , and their corresponding seam lengths and into Equation (20), the initiation toughness and the destabilization toughness can be obtained, respectively.
When the specimen becomes unstable, the instability toughness of the concrete beam should be calculated based on the effective crack length, considering the subcritical crack growth, which can be calculated by Equation (24).
2.5. Double-K Fracture Model
The Hydraulic Concrete Fracture Testing Code (DL/T5332-2005) [45] provides the fracture toughness calculation Equation (30) under the double-K fracture model, with the specimen size applicable for any α, β = S/h = 4.
By substituting the experimental initiation load , peak load , and their corresponding seam lengths and into Equation (30), the initiation toughness and the destabilization toughness can be obtained, respectively.
2.6. Double-G Fracture Modeling
The double-G fracture model for concrete [44,46] characterizes its properties using the energy release rate as a determining parameter. This model assesses the state of the material based on the relationship between the energy release rate G at the crack tip and two specific parameters. The applicable range for specimen dimensions is arbitrary with respect to α. .
The energy release rate of a three-point bending specimen beam at any instant of time is as follows:
By substituting the experimental initiation load , peak load , and the corresponding seam lengths and into Equation (36), the energy release rate at initiation and the energy release rate at destabilization can be obtained, respectively.
Both the double-K fracture toughness and the double-G fracture toughness have the same validity in determining the steady state of concrete based on modified linear elastic fracture mechanics. In order to see the relationship between the two more objectively and easily, the double G fracture toughness is converted to double K fracture toughness, expressed by Equation (37).
3. Experimental Method
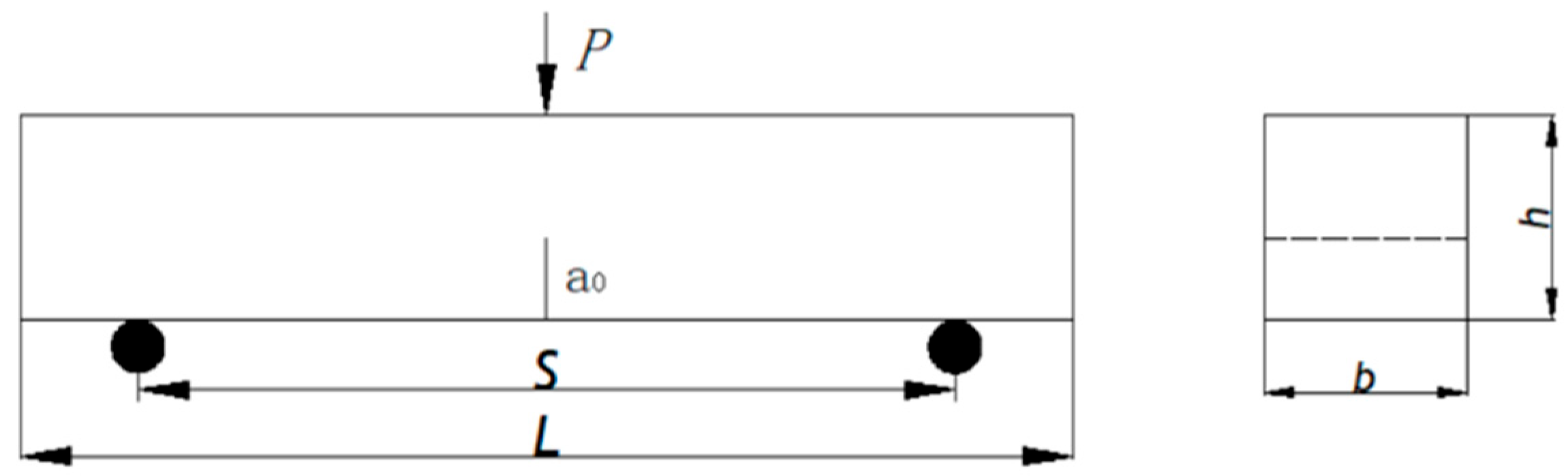
In this experiment, specimens of concrete with varying notch-to-depth ratios and span-to-depth ratios were designed, following the Hydraulic Concrete Fracture Testing Code (DL/T5332-2005) [45]. The experimental variables include the pre-crack height (a0 = 0–50 mm) and span (S = 250–400 mm). The specific dimensions of the specimens are shown in Table 1. The baseline specimen configuration is shown in Figure 1, with a specimen height of h = 100 mm, a section width of b = 100 mm, and a span of 400 mm, with an initial crack length a0 and an initial crack-to-depth ratio a0/h = 0.2.

Table 1.
Design of rubber concrete specimen dimensions.

Figure 1.
Three-point bending beam size diagram.
In this experiment, P.I 42.5 Portland cement was used with a water-to-cement ratio of 0.40. The aggregates consisted of ordinary basalt crushed stone (particle size: 5–20 mm, density: 2760 kg/m3) and natural river sand (maximum particle size: 4.7 mm, well-graded). A PCA-I polycarboxylate high-performance water reducer was used as the admixture. The rubber particles, obtained from crushed waste tires, had a particle size of 3–6 mm and a fineness modulus of 4.99. In this experiment, rubber particles were incorporated by replacing sand on an equal-volume basis, with a replacement rate of 30%. The specimen mix proportions are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Proportions of rubber concrete.
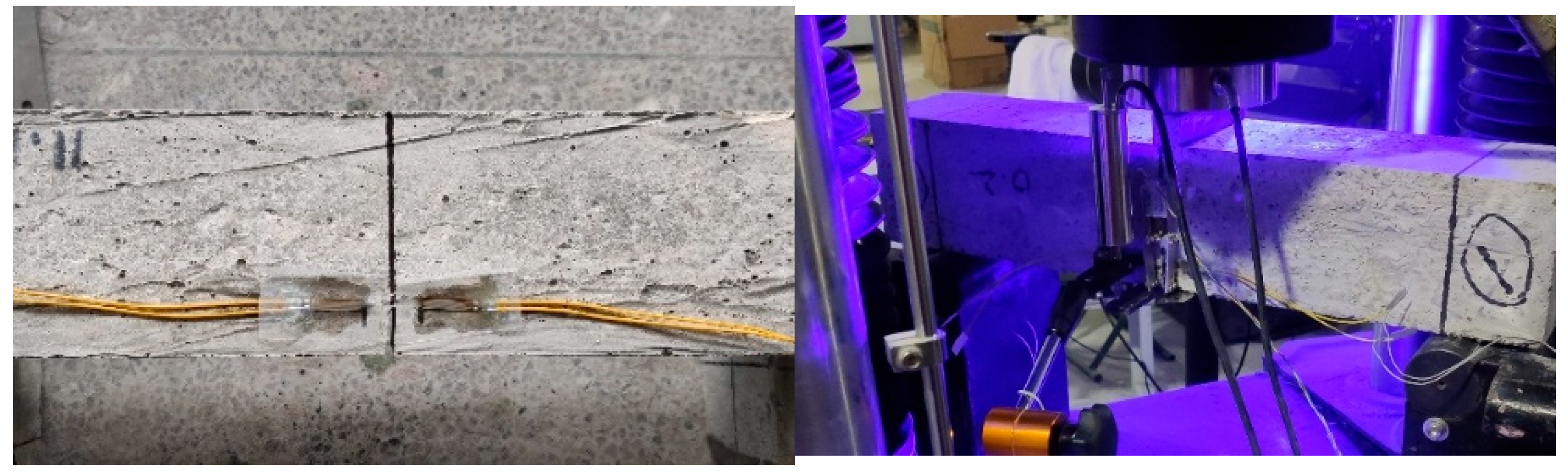
For all fracture tests, a hydraulic servo control testing machine with a range of 500 kN was used, and the loading speed was 0.05 mm/min. The load sensor was used to measure the actual load of the specimen, and the range was 50 kN. The sensor was calibrated on the pressure testing machine. The displacement meter was used to measure the mid-span deflection in the test of the specimen, and the range is 10 mm and the displacement sensor was calibrated by a 100 mm × 100 mm × 100 mm standard test piece. The clamp extensometer was used to measure the opening displacement of the preset crack mouth, and the range was 10 mm. The resistance strain gauge was used to detect the strain change at the crack tip to monitor and measure the crack initiation load, as shown in Figure 2; the DH3816N static strain test system was used to collect and store the actual test data synchronously, and the acquisition frequency was 2 Hz. The DIC method was used to record and observe the surface of the specimen, and the whole field change and failure process during the test were obtained.

Figure 2.
Fracture test process.
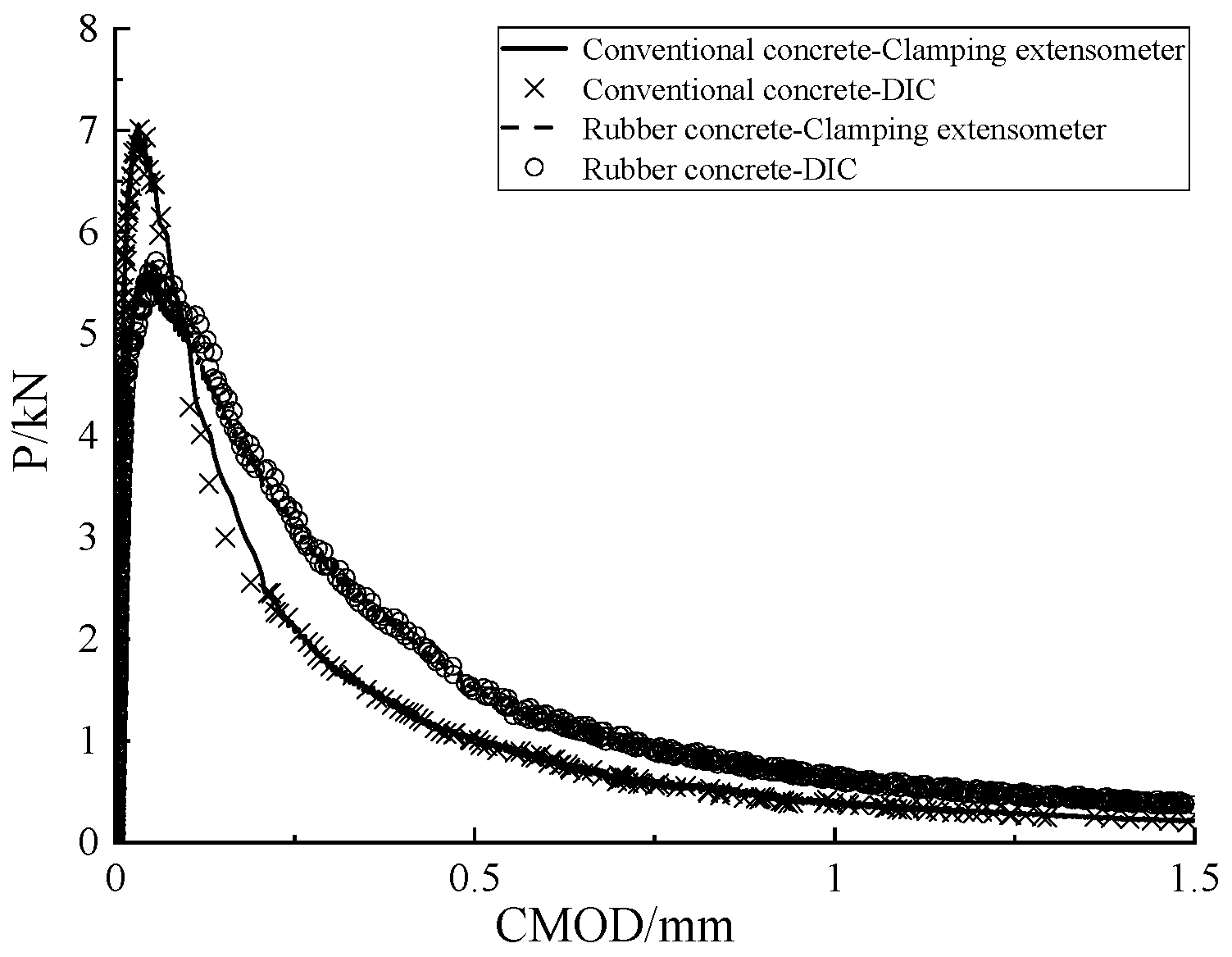
In this experiment, the crack mouth opening displacement (CMOD) of both ordinary concrete and rubberized concrete specimens was measured as the load was applied, using a clip-on extensometer. Additionally, non-contact CMOD values were obtained through the Digital Image Correlation (DIC) method. The resulting load-CMOD (P-CMOD) curves are presented in Figure 3. The P-CMOD curves obtained from both the contact-based clip-on extensometer and the non-contact DIC method exhibited minimal differences, thereby demonstrating the accuracy of the DIC measurements and their feasibility for applications in rubberized concrete fracture testing. Therefore, we conclude that the DIC method can accurately measure crack opening displacement and can be effectively utilized for analyzing displacement field variations and studying the fracture behavior of concrete.
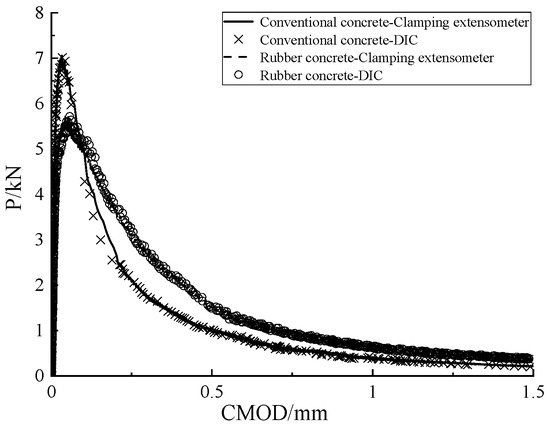
Figure 3.
Test value of P-CMOD curve.
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Determination of Fracture Parameters Based on the Boundary Effect Theory
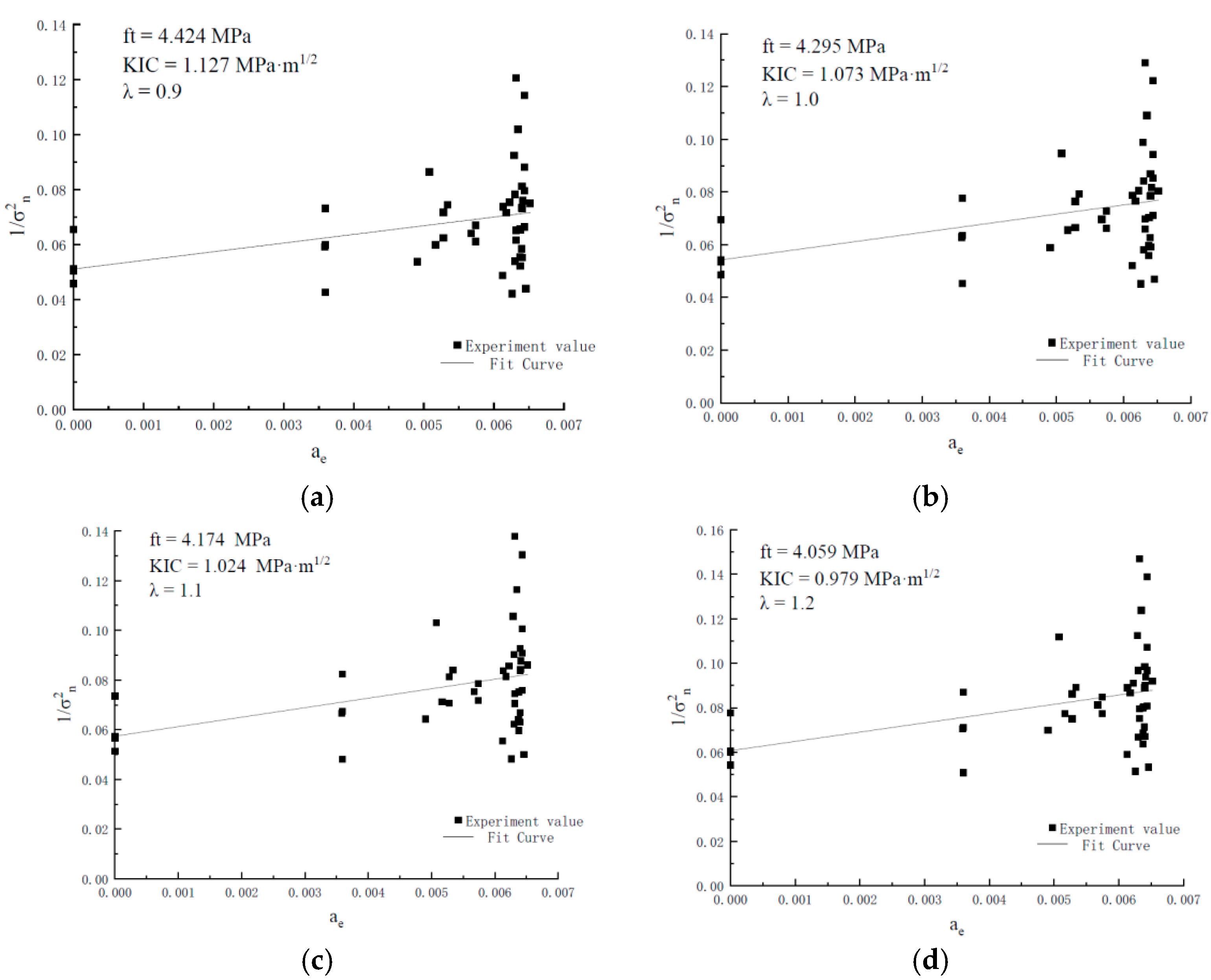
By integrating the peak load of rubber concrete specimens with different sizes obtained from the experiments, the fracture toughness and tensile strength of rubber concrete, independent of specimen size, can be determined based on Equation (2). The fitting results of the fracture toughness and tensile strength values of rubber concrete under different conditions are shown in Figure 4 and Table 3.
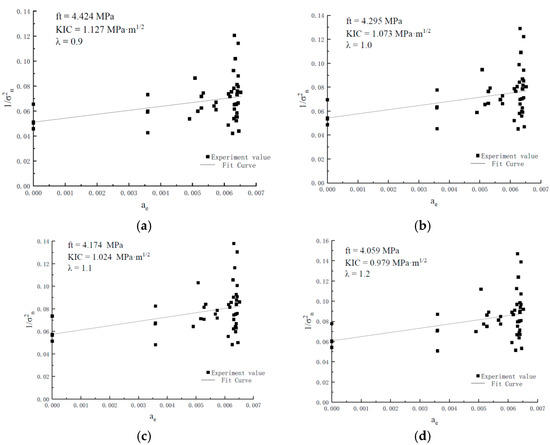
Figure 4.
ft and KIC of rubber concrete specimens at different λ values. (a) ft and KIC of the specimen when λ = 0.9. (b) ft and KIC of the specimen when λ = 1. (c) ft and KIC of the specimen when λ = 1.1. (d) ft and KIC of the specimen when λ = 1.2.

Table 3.
Fitting results of rubber concrete for different ∆a values.
From the above calculation results, it can be observed that when the λ value ranges from 0.9 to 2.4, the tensile strength of rubber concrete ranges from 3.050 MPa to 4.424 MPa, and the fracture toughness ranges from 0.648 MPa·m1/2 to 1.127 MPa·m1/2. The compressive strength of the rubber concrete specimens in this study is 35.98 MPa, while the tensile strength [47] ranges from 2.998 MPa to 4.498 MPa.
Therefore, considering the limitations of various factors, it can be concluded that for small-sized rubber concrete fracture specimens, when the λ value ranges from 0.9 to 1.1, reasonable tensile strength values (4.174 MPa to 4.424 MPa) and fracture toughness values (1.024 MPa·m1/2 to 1.127 MPa·m1/2) can be obtained. According to the definition of ∆a in reference [43], the value refers to the distance from the tip of the pre-existing crack to the point of maximum stress at the moment of peak load. The DIC method allows the acquisition of the stress distribution in the fracture process zone of the specimen at the peak load, thus enabling the measurement of the experimental values of ∆a for specimens of different sizes. The experimental values range from 16.950 mm to 22.139 mm, so the λ value range is from 0.848 to 1.107. Therefore, the selected λ value range is reasonable.
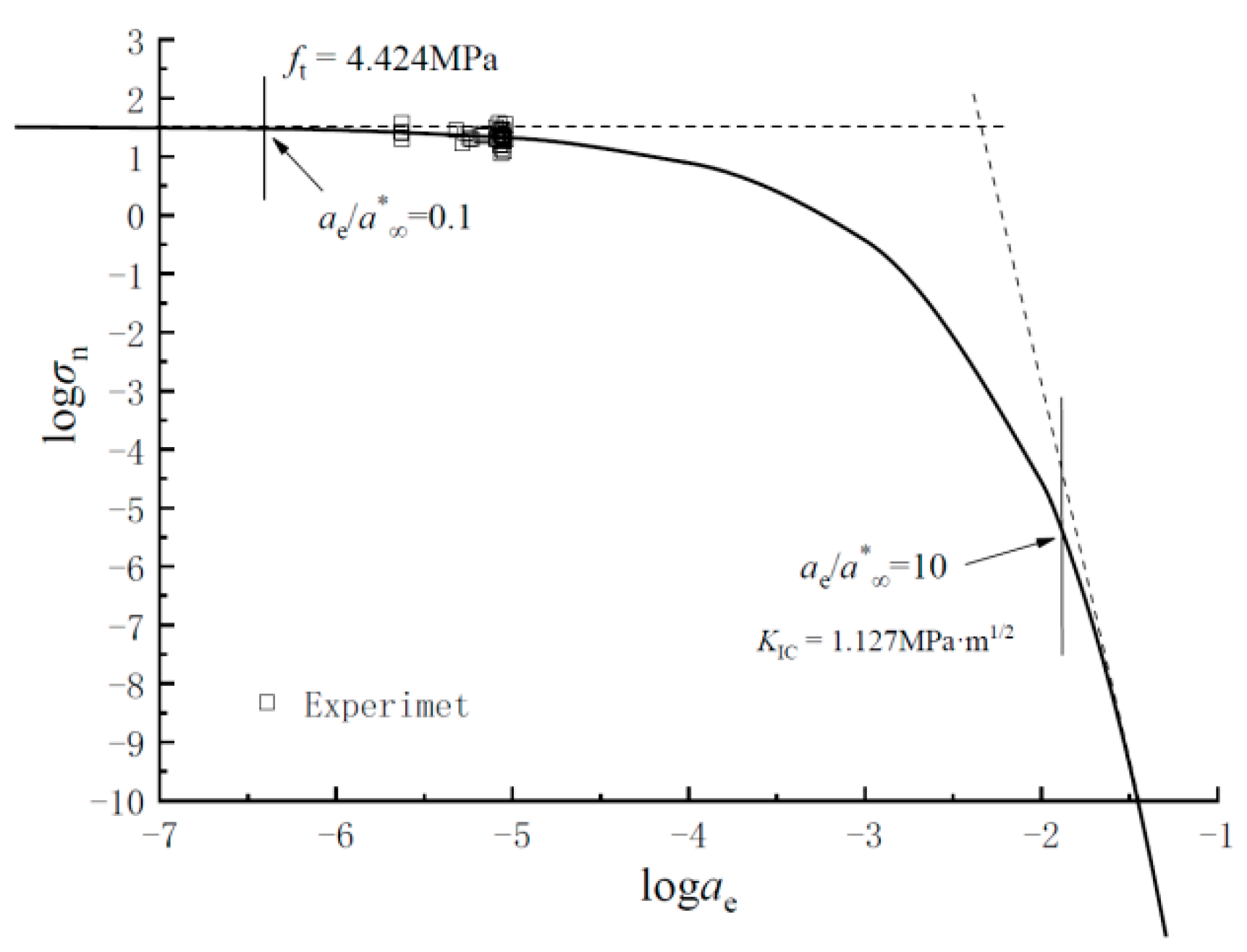
Based on Equation (1), when , it can be simplified to , where the strength criterion dominates. When , the fracture toughness criterion dominates. Therefore, when λ = 0.9, the tensile strength is 4.424 MPa, and the fracture toughness is 1.127 MPa·m1/2. Based on Equation (1), by using as the x-axis and as the y-axis, the structural failure curve of rubber concrete can be established, as shown in Figure 5. From the figure, it can be seen that as the specimen size increases, the rubber concrete specimens generally exhibit quasi-brittle fracture, and the overall failure behavior approaches the strength criterion.
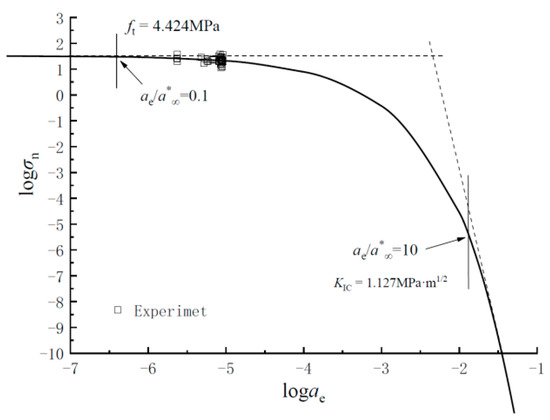
Figure 5.
Structural failure curve for determining the material constants of concrete.
4.2. Fracture Toughness Calculation Based on Different Theories
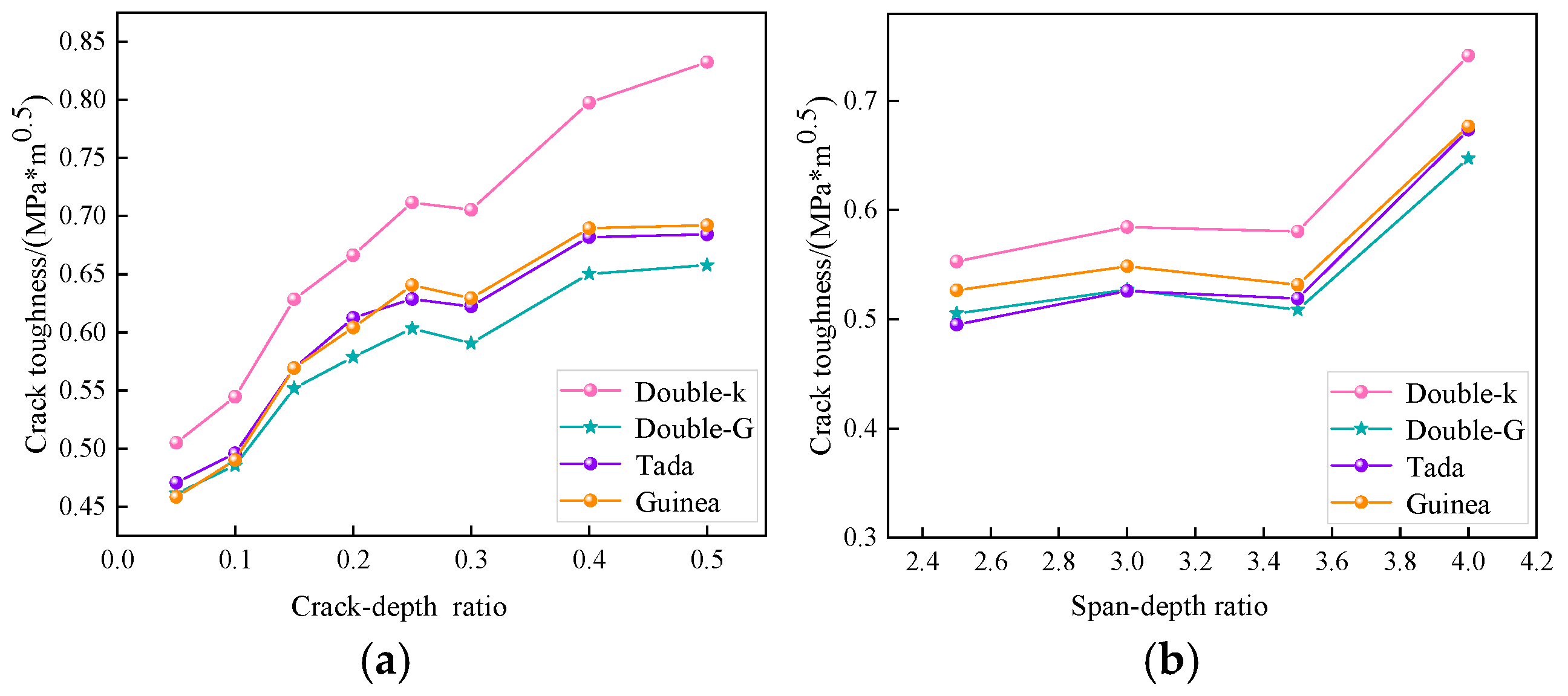
Using the different fracture toughness calculation methods discussed earlier, the experimental data in this chapter were analyzed to determine the crack initiation toughness and instability toughness values of rubber concrete under varying notch-to-depth ratios and span-to-depth ratios. The crack initiation toughness and fracture toughness are not influenced by changes in the initial notch-to-depth ratio. Therefore, the average values from specimens with the same dimensions were taken for comparison, as shown in Figure 6 and Figure 7. Figure 7 shows the variation in crack initiation toughness of rubber concrete with changes in notch-to-depth ratio and span-to-depth ratio under different theoretical analyses. The variation trends are relatively consistent.
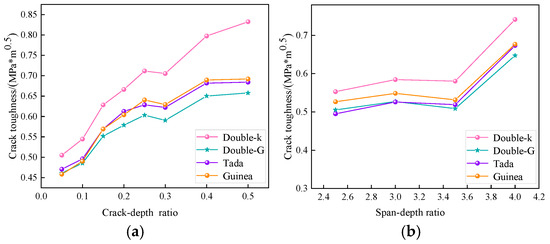
Figure 6.
Crack initiation toughness of rubber concrete. (a) Effect of crack-depth ratio on crack initiation toughness. (b) Effect of span-depth ratio on crack initiation toughness.
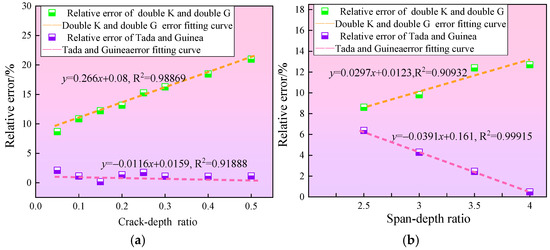
Figure 7.
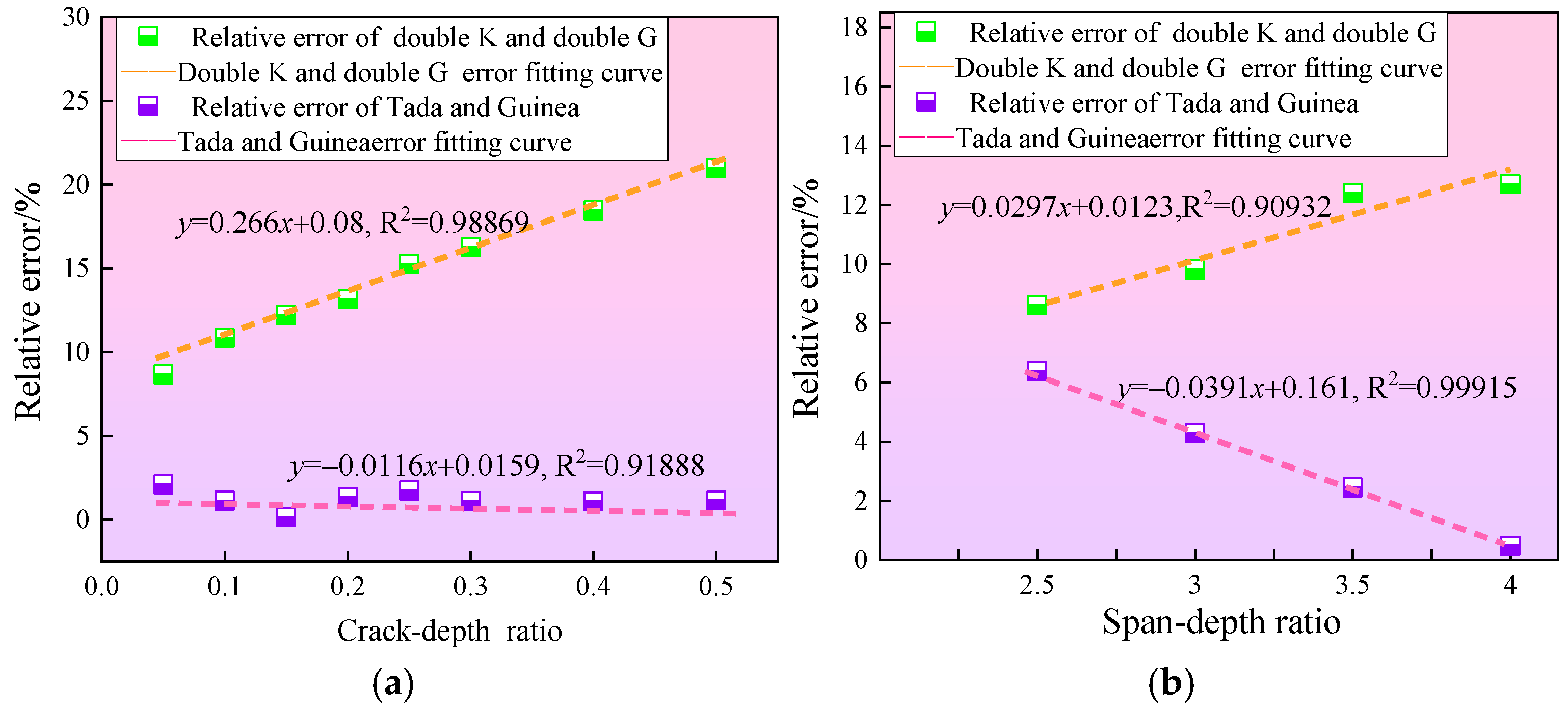
Relative error in crack initiation toughness of rubber concrete under different theories. (a) Effect of crack-depth ratio on relative error. (b) Effect of span-depth ratio on relative error.
From Figure 6a, it can be seen that, under the influence of different notch-to-depth ratios, the crack initiation toughness of rubber concrete gradually increases, reaching the maximum value when the initial notch-to-depth ratio is 0.5. Since the calculation of crack initiation toughness needs to account for the effect of initial crack height, the crack initiation toughness for specimens without pre-existing cracks (α = 0) cannot be calculated.
When the initial notch-to-depth ratio α is less than 0.1, the increase in crack initiation toughness is less than 10%, with a maximum increase of 7.79% under the double-K theory model, which can be considered as stable development. When the initial notch-to-depth ratio increases from 0.1 to 0.2, the increase in crack initiation toughness for all theoretical calculations is greater than 20%. When the initial notch-to-depth ratio α increases from 0.2 to 0.3, the increase in crack initiation toughness becomes smaller, maintaining a stable development trend, with the largest increase of 7.61% under the Tada theory. When the initial notch-to-depth ratio increases from 0.3 to 0.4, the increase in crack initiation toughness for all theoretical calculations is around 10%. When the initial notch-to-depth ratio exceeds 0.4, except for the 4.36% increase under the double-K theory, the other increases are all around 1%. Therefore, the notch-to-depth ratio has a significant impact on the crack initiation toughness of rubber concrete specimens, and the change can be considered to occur in three stages: α < 0.1, 0.2 < α < 0.3, 0.4 < α < 0.5, with a stepwise increase.
Under different theoretical analyses, the crack initiation toughness calculated using the double-K fracture model is generally the largest, while the crack initiation toughness derived from the double-G fracture model is the smallest. Analyzing the errors of the calculations, it is found that the relative error between the two models increases nearly linearly. When the notch-to-depth ratio α is at its smallest value of 0.05, the relative error is the smallest at 8.68%, and when α is at its maximum value of 0.5, the relative error is the largest at 20.99%. Fitting the relative error between the two models results in the curve y = 0.266x + 0.08. Considering the error across all initial notch-to-depth ratios, for rubber concrete specimens with α in the range of 0.05 to 0.5, the crack initiation toughness derived from the double-K fracture model is approximately 15% higher than that from the double-G fracture model. Literature [42] indicates that the crack initiation toughness from the double-K fracture model is about 3% higher than that from the double-G fracture model, indicating that the rubber particles have a significant effect on crack initiation toughness.
The crack initiation toughness calculated using the Tada and Guinea theories is closer to each other across all notch-to-depth ratios. At a notch-to-depth ratio α = 0.05, the maximum relative error is 2.62%. By fitting the relative error to a formula, the resulting curve is y = −0.0116x + 0.0159, with a slope of −0.01163 and an intercept of 0.01588. This indicates that the error is relatively small, and the experimental values from both theories are nearly equal. Upon examining the general derivation steps for the two theories, it was found that when the variable is the notch-to-depth ratio, the key component of the fracture toughness, the shape function kβ(α), is derived from the same shape function used in the Tada theory, which explains why the results are similar.
As shown in Figure 6b, under the influence of different spans, the crack initiation toughness of rubber concrete exhibits a trend of steady increase followed by a gradual rise. The maximum crack initiation toughness is reached when the span-to-depth ratio is 4.
When the span-to-depth ratio β is less than 3.5, the increase in crack initiation toughness at each stage is less than 10%, with the maximum increase of 5.71% observed in the double-K theory model when β changes from 2.5 to 3. This can be considered as a steady development. However, when the span-to-depth ratio β changes from 3.5 to 4, all theoretical values show a significant increase, ranging from 27% to 30%. Therefore, the span-to-depth ratio has a considerable impact on the crack initiation toughness of rubber concrete specimens.
Under different theoretical analyses, the calculated values using the double-K fracture model are generally the largest, while the crack initiation toughness values obtained from the double-G fracture model are the smallest. The error analysis reveals that the relative error between the two increases almost linearly. When the span-to-depth ratio β is at its minimum of 2.5, the relative error is the smallest at 8.61%, and when β is at its maximum of 4, the relative error is the largest at 12.70%. Fitting the relative error between the two models yields the curve y = 0.0297x + 0.0123. Considering the errors across all span-to-depth ratios, for rubber concrete specimens with β ranging from 2.5 to 4, the crack initiation toughness predicted by the double-K fracture model is approximately 10% higher than that predicted by the double-G fracture model. Apart from the influence of rubber particles on the double-G theory, the specimen span also has a significant impact.
The crack initiation toughness values obtained from the Tada and Guinea theories become closer as the span-to-depth ratio increases. The relative error is largest, at 6.38%, when the span-to-depth ratio β is 2.5. Fitting the relative error with a formula results in the curve y = −0.0391x + 0.161, which visually illustrates the trend. Considering the errors across all span-to-depth ratios, for rubber concrete specimens with β ranging from 2.5 to 4, the crack initiation toughness calculated by the double-K fracture model is approximately 3.4% higher than that calculated by the double-G fracture model. In the derivation of the theoretical formulas, the shape function Vβ(α) related to the span is obtained using linear interpolation. Guinea processes the shape functions for β = 4 and β = ∞, while Tada uses shape functions for β = 2.5 and β = 4. This explains the larger error observed for β = 2.5 in the current experiment and the approximation of results at β = 4.
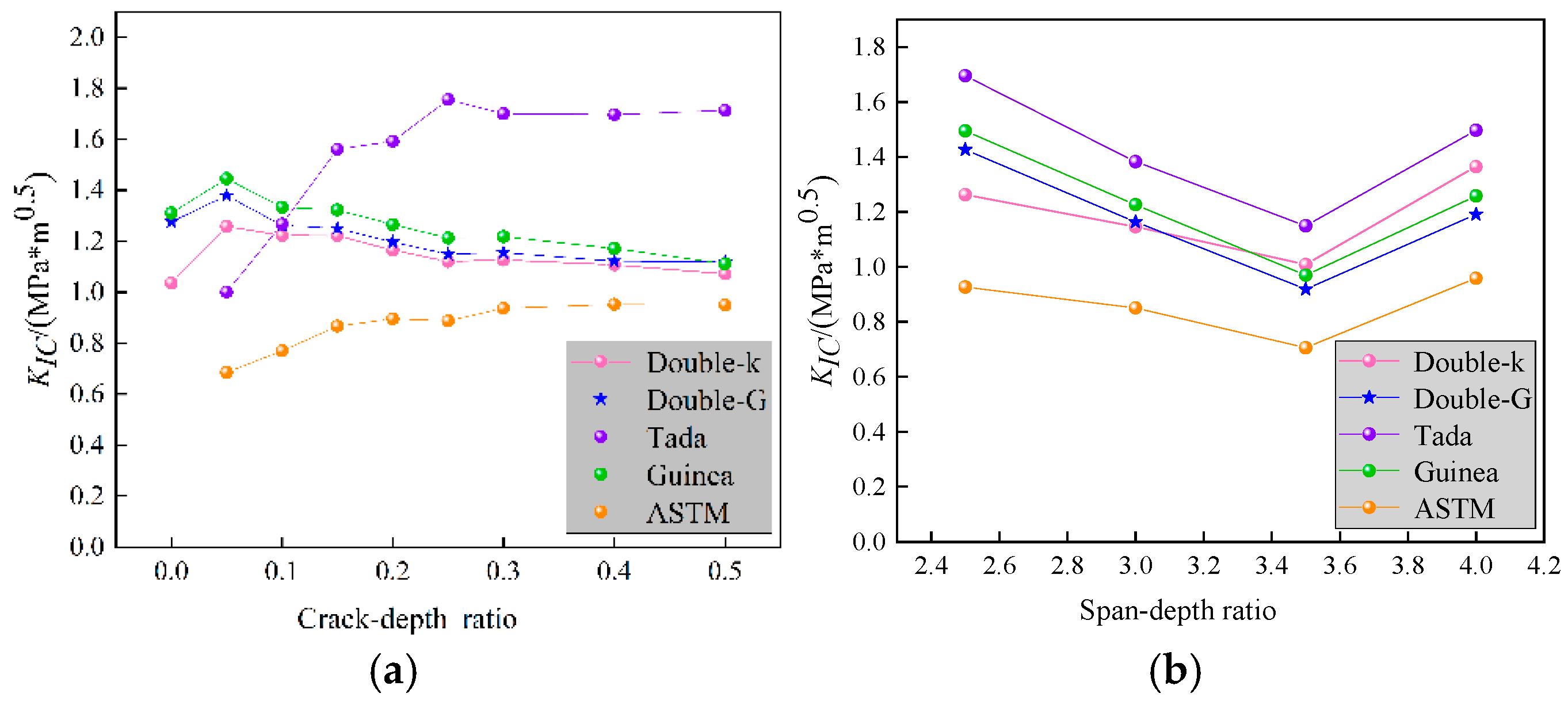
Figure 8 shows the variation in fracture toughness of rubber concrete with notch-to-depth ratio and span-to-depth ratio under different theoretical analyses.
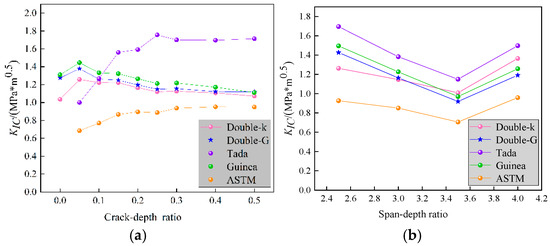
Figure 8.
Fracture toughness of rubber concrete. (a) Influence of crack-depth ratio on fracture toughness. (b) Influence of span-depth ratio on fracture toughness.
As shown in Figure 8a, when considering the effect of the specimen’s notch-to-depth ratio, the fracture toughness trends under the double-K, double-G, and Guinea models are consistent, all increasing as α changes from 0 to 0.05, then gradually decreasing as α exceeds 0.05 and stabilizing after α > 0.25. In contrast, the Tada model and ASTM standards are unable to determine fracture toughness for specimens without pre-existing cracks, but their calculated fracture toughness increases with α and stabilizes after α > 0.3. Therefore, these two scenarios show opposite trends for smaller notch-to-depth ratios (0.05 < α < 0.25), while for larger notch-to-depth ratios (0.3 < α < 0.5), the fracture toughness of rubber concrete stabilizes, suggesting it is not significantly influenced by α. The ASTM standard explicitly states that its formula applies to the range 0.2 < α < 1. Hence, it can be concluded that for small notch-to-depth ratios (0.05 < α < 0.2), the ASTM-recommended formula is not applicable for analyzing the fracture toughness of rubber concrete. Furthermore, the ASTM formula is based on the initial pre-crack height as a variable in fracture toughness calculations, without accounting for the crack propagation behavior in concrete, a quasi-brittle material. This leads to a certain error in the range 0.2 < α < 0.25.
As shown in Figure 8b, when considering the effect of the specimen’s span-to-depth ratio, the fracture toughness trends under all theories are consistent, with a gradual decrease when β < 3.5 and an increase when β > 3.5. Among these, the double-K theory and ASTM standard maintain the same trend but exhibit a noticeable difference from the results of the other theories. The underlying reason is that both theoretical formulas are only applicable to a span-to-depth ratio of β = 4 and do not account for the influence of specimen span, leading to larger relative errors. In contrast, the modified Tada theory and Guinea theory, based on the influence of the notch-to-depth ratio, incorporate the specimen span as a new influencing factor into the theoretical framework through linear interpolation of the shape functions, making them more reasonable. The double-G theory, established from an energy perspective, defines a fracture toughness parameter that relates the initiation and instability criteria by overcoming the localized energy dissipation caused by the cohesive forces at the crack tip [45], thus eliminating the need to consider the span’s influence. Upon analyzing the computed values, the errors in the double-G theory and Guinea theory are relatively small, staying around 5%, while the errors between the Tada theory and double-G theory remain at approximately 18.8% at β = 2.5 and 3, and about 25.4% at β = 3.5 and 4. Thus, it can be concluded that the interpolation of dimensionless shape functions makes it easier to obtain size-independent toughness values.
4.3. Optimization and Fitting of the Fracture Toughness Formula
In the previous comparative analysis of all the theories considered, many experts and scholars have incorporated the crack height ratio of the specimen into the fracture toughness calculation and analysis. They have also thoroughly studied the crack propagation during the fracture process of concrete. However, these studies mainly focus on specimens of a single size, with limited consideration given to situations where crack height remains the same but the span varies. The ASTM standard and dual-K theory have not taken this into account. The improved Tada theory and Guinea theory fit empirical formulas based on experimental results from ordinary concrete with fixed dimensions and obtain shape functions such as and through linear interpolation. In the case of different types of concrete, formulas are applied directly, which introduces certain errors.
Based on the boundary effect theory in Section 4.1, the fracture toughness value independent of material size was obtained as 1.127 MPa·m1/2. According to the various fracture theories described in Section 4.2, the fracture toughness of rubber concrete was obtained. Based on the Guinea theory, the instability fracture toughness varies from 1.111 MPa·m1/2 to 1.445 MPa·m1/2, with an average value of 1.266 MPa·m1/2 and a coefficient of variation of 0.102. Based on the Tada theory, the instability fracture toughness varies from 1.001 MPa·m1/2 to 1.755 MPa·m1/2, with an average value of 1.536 MPa·m1/2 and a coefficient of variation of 0.184. Based on the dual-G fracture theory, the instability fracture toughness varies from 1.118 MPa·m1/2 to 1.379 MPa·m1/2, with an average value of 1.212 MPa·m1/2 and a coefficient of variation of 0.144. Therefore, by comparing the results from different theories, the Guinea theory is found to be more suitable for the calculation and analysis of fracture parameters of rubber concrete influenced by the crack height ratio and span ratio.
To quantitatively validate the applicability of the Guinea theory as a reference model, this study conducted a statistical significance analysis. First, the material size-independent fracture toughness (1.127 MPa·m1/2) obtained from boundary effect theory was used as a baseline value. A paired t-test was employed to compare the significant differences between the theoretical calculations and the baseline value. The results indicate that there is no significant difference between the Guinea theory calculations and the baseline value (t = 0.87, p = 0.412 > 0.05). In contrast, the Tada theory significantly overestimates the fracture toughness (t = 3.42, p = 0.008 < 0.01). Although the results of the double G theory did not show statistical significance (p = 0.062), its coefficient of variation (0.144) was significantly higher than that of the Guinea theory (0.102). In summary, the statistical analysis results, focusing on both central tendency (consistency with the baseline) and dispersion (computational stability), demonstrate that in the fracture analysis of rubber concrete influenced by the combined effects of aspect ratio and span ratio, the Guinea theory not only exhibits the least dispersion (with a 44.6% reduction in variability) but also more accurately approximates the true fracture toughness. The applicability of its empirical formula in rubber concrete is thus supported by statistical significance.
In the study of the fracture properties of concrete, scholars in China generally use the double-K fracture toughness formula provided in the standard “Hydraulic Concrete Fracture Test Code” (DL/T5332-2005) [45]. However, in rubber concrete fracture testing, as analyzed earlier, the double-K fracture formula exhibits some errors under the influence of span. Therefore, it is necessary to optimize the application of the double-K fracture formula for rubber concrete fracture performance. Hence, the Guinea theory is used to optimize the application of the double-K fracture theory for rubber concrete, considering the span effect.
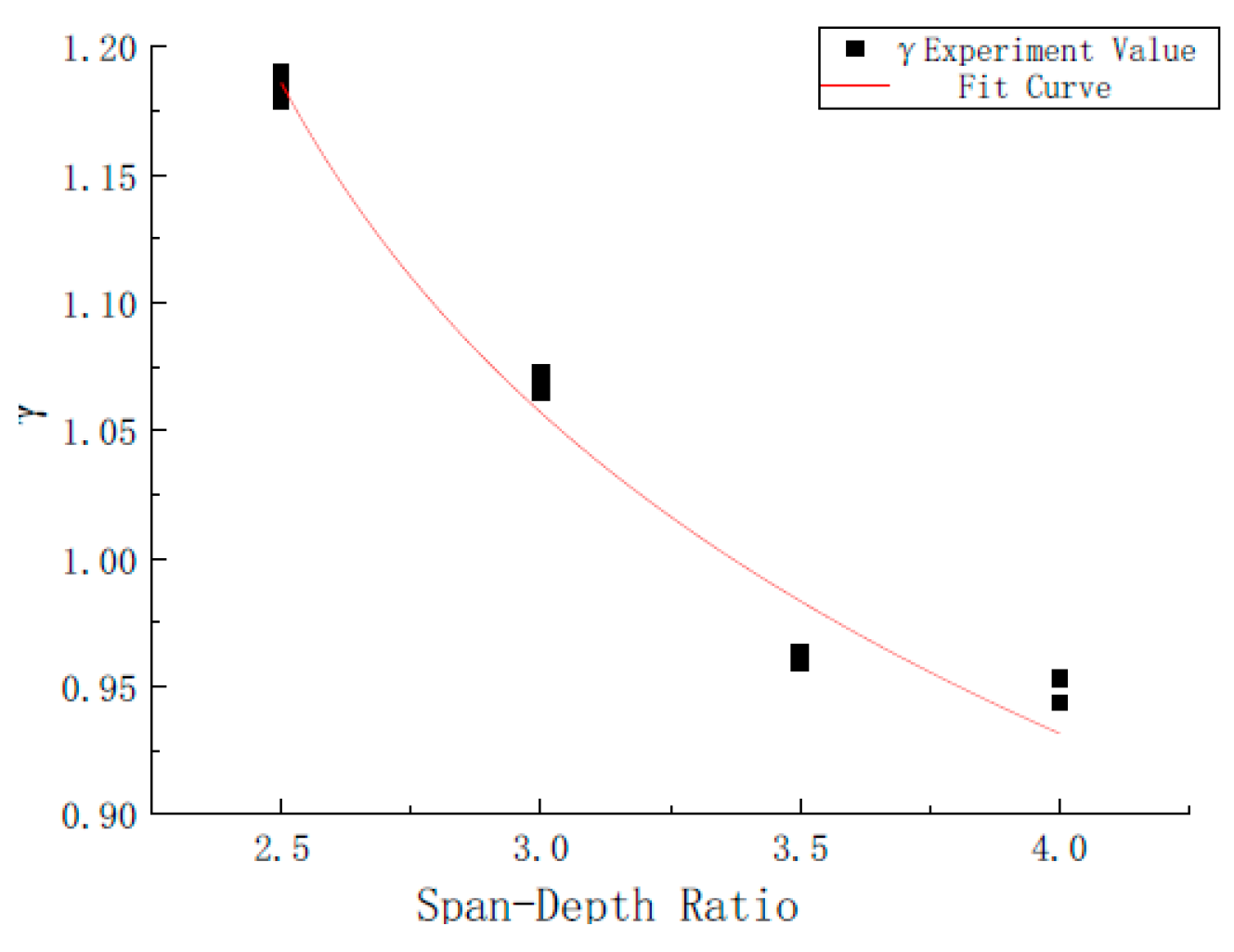
This paper proposes the optimization coefficient γ for the double-K fracture theory based on the Guinea theory, as shown in Equations (38) and (39). The fitting results are shown in Figure 9, with a correlation coefficient of 0.974.
where is the unstable fracture toughness of rubber concrete considering the influence of span-to-height ratio; β is the span of the specimen; is the unstable fracture toughness of rubber concrete calculated based on Guinea’s theory; γ is the optimization coefficient for the dual-K fracture theory; is the unstable fracture toughness of rubber concrete calculated based on the dual-K fracture theory.
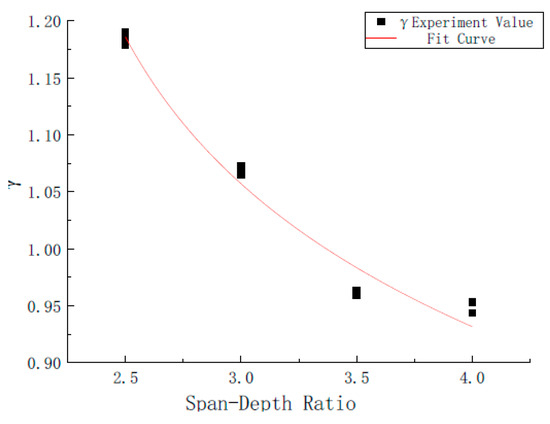
Figure 9.
Fitting results of the Guinea optimization coefficient γ.
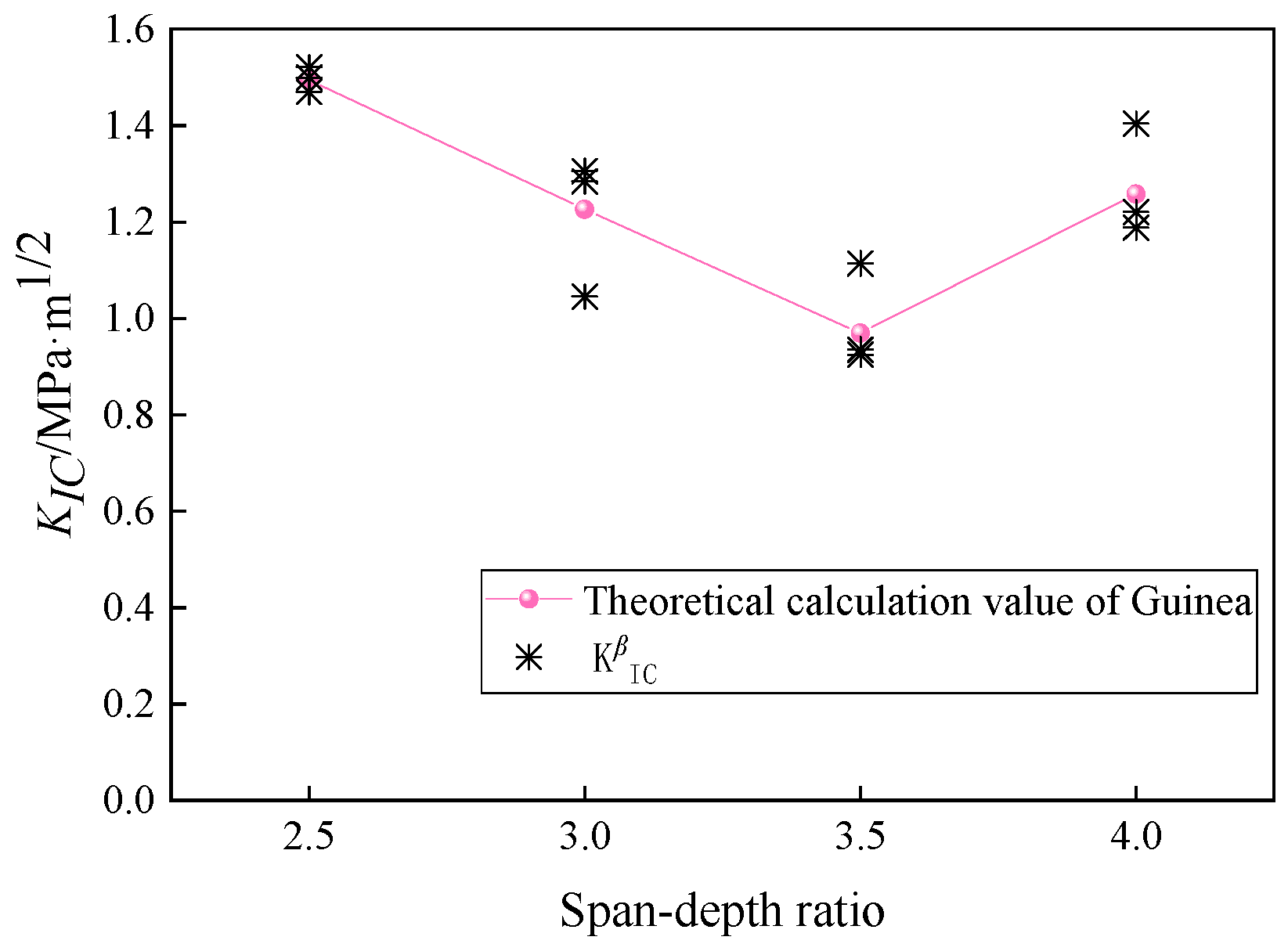
The relative errors between the theoretical values of γ and the fitted values are generally small, usually less than 5%. By substituting Equation (39) into Equation (38), the optimized fracture toughness values for rubber concrete are obtained, as shown in Figure 10 and Table 4. The average values at different spans are 1.4967 MPa·m1/2, 1.2118 MPa·m1/2, 0.9916 MPa·m1/2, 1.2711 MPa·m1/2, and 1.2711 MPa·m1/2, with the corresponding coefficients of variation being 0.017, 0.119, 0.107, and 0.092.
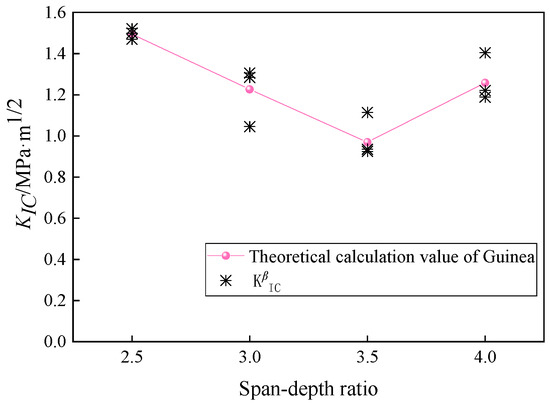
Figure 10.
Fitting results of .

Table 4.
The fitting values of the Guinea optimization coefficient.
5. Conclusions
This study conducted fracture tests on rubber concrete, investigating the effects of different pre-fabricated cracks and spans on the fracture parameters of rubber concrete. The study compared the crack initiation toughness and fracture toughness of rubber concrete under different theoretical models.
- Various concrete fracture theory models, including the dual K, dual G, Tada, Guinea, and boundary effect theories, were applied to calculate parameters such as crack initiation toughness and instability toughness for rubber concrete. A comparative analysis was conducted to evaluate the applicability of each theoretical formula for rubber concrete. The change in crack initiation toughness of rubber concrete under different theories showed consistent trends influenced by size. However, the fracture toughness of rubber concrete was constrained by the applicable range of each theory, leading to contradictory patterns for the crack height ratio between 0.05 and 0.25, while consistent trends were observed when α was between 0.3 and 0.5. Under different theories, the fracture toughness maintained a similar trend with respect to span ratio, although values for span ratios of 2.5 and 3 showed significant discrepancies between the theories.
- Combining boundary effect theory, the study analyzed the variation of tensile strength and fracture toughness with specimen size. Based on the established structural failure curve of rubber concrete varying with specimen size, it was found that rubber concrete exhibits quasi-brittle fracture behavior.
- Fracture tests on rubberized concrete specimens of various sizes were conducted to obtain the peak load of the rubberized concrete samples. For small-sized rubberized concrete fracture specimens, it was found that a λ value between 0.9 and 1.1 yields a relatively reasonable tensile strength value.
- A comprehensive analysis of the fracture toughness values of rubber concrete under various theories shows that Guinea’s theory, which accounts for crack propagation in the instability state and the effect of specimen span, can be effectively applied to the analysis of rubber concrete fracture parameters at different sizes. An optimization coefficient γ for the dual K fracture toughness formula of rubber concrete was proposed based on Guinea’s theory, yielding satisfactory optimization results.
Author Contributions
S.G.: Conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, writing–original draft, and writing—review and editing. Z.W.: Investigation and data curation. J.S.: Methodology conceptualization. J.W.: Validation and supervision. Y.H.: Methodology, investigation, writing—review and editing, and data curation. H.X.: Conceptualization and methodology. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52179145), Open Research Fund Program of State key Laboratory of Hydroscience and Engineering (sklhse-2022-C-01), National Key Scientific Instruments and Equipment Development Project of China (52327812), and Science and Technology Innovative Research Team in Higher Educational Institutions of Henan Province (25IRTSTHN010).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw/processed data required to reproduce these findings cannot be shared at this time, as the data also form part of an ongoing study.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the editor and reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Jiayi Sun was employed by the company Shanghai Water Conservancy Engineering Design and Research Institute Co. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Rong, H.; Dong, W.; Wu, Z.M.; Fan, X.L. Experimental investigation on double-k fracture parameters for large initial crack-depth ratio in concrete. Eng. Mech. 2012, 29, 162–167. [Google Scholar]
- Elbialy, S.; Ibrahim, W.; Mahmoud, S.; Ayash, N.M.; Mamdouh, H. Mechanical characteristics and structural performance of rubberized concrete: Experimental and analytical analysis. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 21, e03727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Chen, W.; Wang, X. Fracture properties of rubberized self-compacting concrete. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2015, 46, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turatsinze, A.; Garros, M. On the modulus of elasticity and strain capacity of Self-Compacting Concrete incorporating rubber aggregates. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2008, 52, 1209–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topcu, I.B.; Avcular, N. Collision behaviors of rubberized concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 1997, 27, 1893–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Ren, H.; Zhang, P. Cracking-resistance and flexural property of rubberized concrete. Acta Mater. Compos. Sin. 2006, 23, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Troncoso, N.; Acosta-Calderon, S.; Flores-Rada, J.; Baykara, H.; Cornejo, M.H.; Riofrio, A.; Vargas-Moreno, K. Effects of Recycled Rubber Particles Incorporated as Partial Sand Replacement on Fresh and Hardened Properties of Cement-Based Concrete: Mechanical, Microstructural and Life Cycle Analyses. Materials 2023, 16, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaleh, M.B.; Asadi, P.; Eftekhar, M.R. Life cycle assessment based method for the environmental and mechanical evaluation of waste tire rubber concretes. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 10687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afifudin, H.; Nadzarah, W.; Hamidah, M.; Hana, H.N. Microbial Participation in the Formation of Calcium Silicate Hydrated (CSH) from Bacillus subtilis. Procedia Eng. 2011, 20, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daghash, S.M.; Servio, P.; Rey, A.D. From Infrared Spectra to Macroscopic Mechanical Properties of sH Gas Hydrates through Atomistic Calculations. Molecules 2020, 25, 5568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Liu, R.; Liu, F.; Wu, M.; Wen, Q. Freeze–thaw resistance mechanisms of rubber-cement soil: Insights from a macro- and micro-level perspective. Environ. Technol. 2025, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albiajawi, M.I.; Alkasawneh, R.W.; Mostafa, S.A.; Johari, I.; Embong, R.; Muthusamy, K. Performance of sustainable concrete containing recycled latex gloves and silicone catheter under elevated temperature. J. King Saud Univ.-Eng. Sci. 2024, 36, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.M.; Elchalakani, M.; Hao, H.; Lai, J.; Ameduri, S.; Tran, T.M. Durability characteristics of lightweight rubberized concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 224, 584–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Liu, F.; Yang, F.; Li, L.; Jing, L. Experimental study on dynamic split tensile properties of rubber concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 165, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Fang, C.; Lu, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, L. Effects of the addition of silica fume and rubber particles on the compressive behaviour of recycled aggregate concrete with steel fibres. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 197, 656–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.L.; Reinhardt, H.W. Determination of double-K criterion for crack propagation in quasi-brittle fracture. Int. J. Fract. 1999, 98, 111–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.M.; Xu, S.L.; Wang, J.L.; Liu, Y. Double-K Fracture Parameter of Concrete and Its Size Effect by Using Three point Bending Beam Method. J. Hydroelectr. Eng. 2000, 71, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Hu, S.; Lu, J. Study on the fracture properties of different type concretes. Concrete 2012, 3, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, K.; Hu, X.; Wittmann, F.H. Scaling of quasi-brittle fracture: Boundary and size effect. Mech. Mater. 2006, 38, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Hu, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Wu, Z. Effect of fracture toughness and tensile strength on fracture based on boundary effect theory. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2016, 47, 1298–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, Q.; Reinhardt, H.-W.; Xu, S. The double-K fracture model: A state-of-the-art review. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2023, 277, 108988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.Z.; Guan, J.F.; Wang, Y.S.; Yang, S. Comparison of boundary and size effect models based on new developments. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2017, 175, 146–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, P. Meso-scale fracture modelling and fracture properties of rubber concrete considering initial defects. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2023, 125, 103834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, L.; Xiong, Z. Investigation on the interfacial behaviour between the rubber-cement matrix of the rubberized concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 1354–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lee, S.; Park, C. Bonding Characteristics of Macro Polypropylene (PP) Fibre in PVA/Macro PP Blended Fibre-Reinforced Styrene Butadiene Latex-Modified Cement-Based Composites. Prog. Rubber Plast. Recycl. Technol. 2014, 30, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaleem, A.; Moawad, M.; Emam, E.H. Long term behavior of rubberized concrete under static and dynamic loads. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e03087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Huang, P.; Zhang, J.; Xie, J.; Guo, Y.; Cen, Y. Experimental study on the fracture behavior of steel fiber and crumb rubber reinforced recycled aggregate concrete. J. Shenzhen Univ. Sci. Eng. 2014, 31, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yu, J.; Hou, D.; Dong, B.; Ma, H. Insights into the interfacial strengthening mechanism of waste rubber/cement paste using polyvinyl alcohol: Experimental and molecular dynamics study. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 114, 103791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, P.; Yuan, Q.; Guan, Q. Fracture properties of rubberized concrete under different temperature and humidity conditions based on digital image correlation technique. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 124106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Lu, J.; Ming, P.; Yin, Y. Study of fracture properties and post-peak softening process of rubber concrete based on acoustic emission. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 313, 125487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Yu, W.; Du, X.; Yang, W. Mesoscopic numerical simulation of dynamic size effect on the splitting-tensile strength of concrete. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2019, 209, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, K.; Hu, X.Z. Scaling of specimen boundary effect on quasi-brittle fracture. In Proceedings of the International Conference, SIF2004, Brisbane, Australia, 26–29 September 2004; pp. 47–68. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, J.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Qing, L.; Song, Z.; Liu, Z. Determination of fracture parameter and prediction of structural fracture using various concrete specimen types. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2019, 100, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Yao, X.; Bai, W.; Chen, J.; Fu, J. Determination of fracture toughness and tensile strength of concrete using small specimens. Eng. Mech. 2019, 36, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Xie, C.; Hu, X.; Bai, W. Determination of fracture toughness and yield strength of hot rolled carbon steel based on boundary effect theory. Eng. Mech. 2019, 36, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Hu, X.; Li, Q. In-depth analysis of notched 3-p-b concrete fracture. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2016, 165, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, X.; Liang, L.; Zhu, W. Determination of tensile strength and fracture toughness of concrete using notched 3-p-b specimens. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2016, 160, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, X. Determination of Tensile Strength and Fracture Toughness of Granite Using Notched Three-Point-Bend Samples. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2017, 50, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E399-24; Standard Test Method for Linear-Elastic Plane-Strain Fracture Toughness of Metallic Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2024.
- Taha, M.M.R.; El-Dieb, A.S.; El-Wahab, M.A.A.; Abdel-Hameed, M.E. Mechanical, Fracture, and Microstructural Investigations of Rubber Concrete. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2008, 20, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Hu, S. Double-k fracture parameters of concrete in threepoint bending beams with small span-depth ratios. Eng. Mech. 2020, 37, 138–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinea, G.V.; Pastor, J.Y.; Planas, J.; Elices, M. Stress Intensity factor, compliance and CMOD for a General Three-Point-Bend Beam. Int. J. Fract. 1998, 89, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Hu, S.; Lu, J. Experimental research on double-K fracture toughness of non-standard three point bending concrete beam. J. Build. Struct. 2012, 33, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yang, L.; Lu, Y. Experimental Study on Fracture Behavior of High-strength Concrete Beams with ModeICracks. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2020, 20, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DL/T 5332-2005; Norm for Fracture Test of Hydraulic Concrete. National Development and Reform Commission, Electric Power Press of China: Beijing, China, 2005.
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, S.; Wu, Z. A Dual-G Criterion for Crack Propahation in Concerte Structures. China Civ. Eng. J. 2004, 37, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Liu, Z.; Yao, X.; Li, L.; He, S.; Zhang, M. Determination of The Cracking Strength, Tensile Strength and Double k Fracture Parameters of Concrete. Eng. Mech. 2020, 37, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).