Abstract
This paper examines the regulation of corporate governance on leverage structure decision-making in Bangladesh from 2003 to 2017. Appropriate panel methods are employed to control the problems of serial correlation, heteroskedasticity, and the cross-sectional nature of manufacturing companies. The study finds that corporate governance attributes such as board size, managerial ownership, and duality are the dominant factors for leverage decision-making. The results also indicate that control variables such as firm size and profitability have an influential role on leverage decision-making in Bangladesh. Our findings substantiate the idea that political and family connections to corporate governance structure greatly influence the leverage decision-making of corporate firms in Bangladesh.
JEL Classification:
C22; C51; L16
1. Introduction
Corporate governance has been an imperative issue in corporate finance and a greatly discussed matter in Bangladesh due to political exploitation. The impact of corporate governance on a firm is enormous. The corporate governance system allocates the proper distribution of corporate responsibilities to principles that regulate the traits of management and decisions in a firm. Therefore, corporate governance variables, such as board size, board composition, managerial ownership, and duality, might have a direct influence on setting the leverage structure in a firm. The separation of ownership and control in a firm may result in managers’ overexerting a lacking workforce, indulging in prerequisites, choosing inputs and outputs that suit their own preferences or otherwise failing to maximize the firm’s value. Fair and free corporate governance practices may have a significant influence on a strategic decision such as external financing or capital structure decision. In the absence of the strong role of corporate governance, agency problems (conflicts of interest within the firm) arise between shareholders and managers. This leads to a weak legal and regulatory system, inconsistent accounting, and auditing standards and poor management practices. Hence, in this situation, corporate governance plays a vital role in the necessary checks and balances between shareholders and management to mitigate agency problems.
A literature review indicated that very few studies have been undertaken on the relationship between corporate governance and leverage structure decision-making in Bangladeshi firms (Haque et al. 2011). The study initially investigated secondary data of corporate variables in Bangladesh, which mostly impede capital structure decision-making. Bangladeshi firms face many problems due to weak corporate governance, such as family issues, institutional issues, political affiliation, corruption, and the lack of a sense of responsibility and accountability. In this circumstance, financial managers cannot freely make optimal financial decisions in terms of firm value and sustainability. Weak financial decision-making incurs a great deal of loss, which threatens sustainability. The previous studies also consider only primary data, and, to the best of our knowledge, they did not consider the main corporate governance attributes of board size, board composition, board independence, managerial ownership, institutional shares, and CEO duality from secondary data. Hence, the relationship between corporate governance and leverage structure decision-making in Bangladesh has not been fully explored. In this respect, in Bangladesh, there is an urgent need to determine whether corporate governance has any impact on leverage structure decision-making or not.
We have investigated the manufacturing sector for several reasons: First, past literature has been primarily dedicated to the analysis of developed countries and there are very few studies focused on developing countries such as Bangladesh. Second, Bangladesh has been experiencing embezzlement in capital markets resulting from political weaponry and government intervention. These consequences radically affect the financial decision-making of manufacturing companies in Bangladesh. Third, the manufacturing sector provides the basic needs of people and fuels economic growth in Bangladesh, and it is highly vulnerable due to a lack of high-quality corporate governance. Poor accounting and auditing standards, bad accountability, low transparency, managerial inefficiency, and political turmoil (Pontines and Siregar 2008) have led to the poor sustainable development of the sector.
The major contributions of the paper are designed to add new insights to the current literature: (i) The previous literature on this subject in Bangladesh is few and partial. To the best of our knowledge, research in this area was initiated by Haque et al. 2011 on the qualitative factors of corporate governance in Bangladesh. The most influential variables for capital structure decision-making, such as board size, board composition, managerial ownership, independence of directors, institutional shares and CEO duality, are not considered in his study. The ownership structure in Bangladesh is formed by families, institutions, and political leaders, whereas dispersed and professional shareholders hold ownership in developed countries. Therefore, this study provides a new approach for corporate governance that will overcome the lack of existing literature concerning Bangladesh. (ii) Important limitations of the existing literature are in terms of either the scope or scale of the analysis. Our study investigated the political and family impact on corporate affairs, which influences leverage decision-making in Bangladeshi firms by using CEO duality and managerial ownership of 63 companies from 2003–2017. In this period, corporate governance has greatly changed because democracy has given way to a dictatorship and all economic power has been seized by activists and leaders of the ruling party. Using political power in connection to government, millions of dollars have been corrupted by a group of people from banks and stock market in Bangladesh. The chairman and CEO have become the same person as a result of family, institution, and political shareholdings, which has resulted in conflict between CEOs and financial managers in terms of leverage decision-making. In this situation, managers are not able to make optimal leverage decision-making, which may lead to the collapse of the manufacturing sector and economic decline. Therefore, this study is an attempt to determine who is responsible for the decline of corporate governance in Bangladesh. (iii) An appropriate panel estimator is used that allows us to control the problems of serial correlation, heteroskedasticity, and cross-sectional nature in the model estimation, making the results more effective and robust. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to consider the variables mentioned earlier for analysis of corporate governance, which is linked to leverage structure decision-making in Bangladesh. Hence, the study aims to examine the impact of leverage structure on firm value in Bangladesh.
The study is organized as follows: Section 2 presents a brief literature review. Section 3 discusses the theoretical concepts and presents our hypotheses. Section 4 presents the data and methodology. Section 5 interprets the empirical results based on theories as well as corporate governance rules and regulations. The final section concludes with policy implications and recommendations for further research.
2. Literature Review
The literature review is carried out to further understanding the relationship between corporate governance and capital structure of listed companies of Dhaka Stock Exchange (DSE) in Bangladesh. Related empirical studies are reviewed to detect the current literature gap and adopted a new methodology has been adopted for the new findings.
Financial literature on board size is studied based on different developed and developing countries. The studies have presented diverse results; for instance, Abor (2007) examined the relationship between corporate governance and capital structure decision of Ghanaian listed firm with the help of multiple regression analysis. The result found that the board size is positively related to capital structure decision because larger board size is inspired to adopt high debt policy. Diversified board size combines the diversity in the knowledge that contributes to the positive role in capital structure decision (Lipton and Lorsch 1992). Therefore, Jaradat (2015) also provided that board size is a positive significant relationship with capital structure decision. Hart (1995) revealed that board size is negatively associated with capital structure decision. The larger board size generates the complexity in decision-making (Abor and Biekpe 2007; Uwugbei 2014; Adegbile 2015). Achchuthan et al. (2013) examine the relationship between board size and leverage structure from the 28 manufacturing companies of the Colombo Stock Exchange. The result revealed that no relationship between board size and a leverage ratio because the authors postulate that if the board size is bigger, they can provide more pressure to the managers to keep the limited leverage and thus this result is also in line with the findings of (Wellalage and Locke 2012).
Board composition is considered to be a significant and positive determinant for capital structure decision (Abor 2007; Somathilake and Udaya Kumara 2015). Adegbile (2015) and Uwugbei (2014) examines the relationship between corporate governance attributes and capital structure decision and derives the inverse connection between board composition and capital structure. Achchuthan et al. (2013) revealed that board composition has no significant impact on capital structure decision.
However, Chen and Chen (2012) argued that managerial ownership makes the force of work and professionalism in management that enhances the shareholders’ interest and reduce the agency problem. Adegbile (2015) investigated the effect of corporate governance on the leverage structure of Nigerian food and beverages industry for the period of 2003–2012. The study revealed that managerial ownership has an inverse relationship with the leverage ratio. Joher et al. (2006) also provided evidence of an inverse association between managerial ownership and leverage structure decision-making with the help of data from 100 Malaysian composite index companies. By employing a two-stage least square method and a data set between 1998 and 2003, Nyonna (2012) estimated the significant but negative correlation between managerial ownership and capital structure. The authors explained that both managerial ownership and capital structure are substituted with each other, and that could reduce the agency cost.
The relationship between institutional ownership and capital structure has been given little attention in previous literature. Crutchley et al. (1999) reported that there is a positive association between institutional investors and capital structure that is statistically significant as well. Lev (1988) argued that institutional investors have the perfect information which aids to make a stronger decision than individual investors. The main fact is that they have easy access to any cell of information.
The relationship between board independence and debt ratio has been accepted in different results from prior research, for example, Bokpin and Arko (2009) used regression analysis towards a panel data set of Ghanaian firms from the period 2002–2007 to find out the relationship between ownership and capital structure. The results established a positive significant correlation between board independence and leverage ratio. The researchers explained that if the board members are independent, they can choose the efficient leverage structure for the company. A positive insignificant relationship between board independence and leverage ratio is indicated by (Kyereboah-Coleman and Biekpe 2006). Meanwhile, Hamid et al. (2011) indicated that there is no relationship between board independence and capital structure. Wen et al. (2002) discovered a negative association between board independence and capital structure decision. Erickson et al. (2005) found that board independence included on board does not have any positive relationship on capital structure decision. They further argued that firms which poorly operate their performance requirements to increase the independent directors in subsequent periods.
There are many kinds of literature are studied on the relationship between CEO duality and capital structure that provided mixed results. Abor (2007) reported the evidence that CEO duality is positively related to capital structure decision. The author mentioned when the CEO is also a member of the board play a vital role to take an efficient decision. At that time, the CEO thinks that he/she is not only an employee of the company but also a partner of it. The level of sincerity would become higher and efficient. Uwugbei (2014) also indicated the positive relationship between CEO duality and leverage ratio. Fosberg (2004) found a significant inverse relationship between CEO duality and the amount of corporate debt. Meanwhile, Jaradat (2015) mentioned that CEO duality has no significant impact on capital structure and the researcher argues that no matter of holding dual position is required for leverage structure decision-making. When any decision needs to make, the CEO must think independently and efficiently without influenced by others.
However, Titman and Wessels (1988) revealed that bankruptcy cost is not generally considered by large-scale firms to choose the leverage ratio. The larger firms tend to use a higher amount of debt in the capital structure. (Friend and Lang 1988; Marsh 1982; Rajan and Zingales 1995) revealed that firm size positively determine the debt level of the firm.
Moreover, the relationship between profitability and leverage has been recognized by several previous literature proved mixed results. Petersen and Rajan (1994) tested the connection between profitability and leverage level and found a significant positive relationship. The authors explained that if the firm is in the profitable condition that could happen for good leverage structure and the theory supports that statement and thus the same results are also related to the findings of (Aharon and Yagil 2019; Titman and Wessels 1988; Rajan and Zingales 1995). Velnampy and Niresh (2012) examined the relationship between profitability and leverage of Sri Lankan Bank over the period of 2002–2009. The results evidence that there is an adverse relationship between profitability and capital structure because most of their assets are covered by the debt, which is 89%.
Concisely, from the above-discussed literature, we found a research gap. Hence, there are still critical issues for the policymakers, practitioners, and academician whether the corporate governance impact on leverage structure. Most of the previous studies are done based on developed and developing countries while very less attention given to Bangladesh, which is an emerging country. Therefore, most of the past studies used just regression analysis, but in contrast, this study applies relatively advanced appropriate statistical tools to generalize the results. Moreover, to fill the bridge gap of previous studies, we used some additional variables that policymakers are always looking for.
3. Variables Definitions and Hypotheses Development
3.1. Variable Definitions and Their Evidence
Leverage structure is defined as total debt or current liabilities plus long-term debt over the total assets (Fathi et al. 2014; Ajanthan 2013; Onaolapo and Kajola 2010; Taani 2013). Total debt is used as leverage structure in the study. Board size consists of several directors on a board in the company. The board should be constituted by at least five members and a maximum of 20 members for diversity in accordance with Bangladesh Security and Exchange Commission. The relationship between the board size and setting the leverage has been well recognized in prior accounting and finance research (Bhagat and Black 2002; Berger et al. 1997; Lipton and Lorsch 1992; Eisenberg et al. 1998; Abor and Biekpe 2007). Board composition represents the ratio of non-functional directors on board. It is calculated through non-functional directors divided by the total number of directors on board. The presence of non-executive directors on board signals the strong monitoring system in the functional management of the company (Dalton et al. 1998; Adegbile 2015). Managerial ownership is the proportionate number of shares held by chief executive, directors, and their family members.
The ownership design is considered an influential element in corporate governance. Managerial ownership is a capable device of corporate governance as it aligns the interests of managers with those of shareholders (Stulz 1988; La Porta et al. 2002; Beck et al. 2004; Gill et al. 2009). Institutional investors have blocked shareholdings held by organizations, including insurance, banks, pension funds. Institutional shareholders place specific seats on the board and the supervisory committee and thus exercise rights to elect and eliminate the management team (Xu and Wang 1999). Independent directors are outside directors who are basically appointed by considering relevant knowledge and experience. They have excellent professionalism to put value in decision and operations in management. They are entirely separated from ownership and control that helps them to raise their voice for free, fair and efficient administration (Erickson et al. 2005; Lefort and Urzúa 2008; Duchin et al. 2010).
CEO duality appears when the CEO assumes the dual responsibilities of managing the firm and deals with the affairs of the board. Duality is a valid measure to help the organization to be faster in decision-making (Jensen 1993; Fosberg 2004; Abor and Biekpe 2007). We include the control variables such as firm size and profitability, resulting in a total of eight variables for measuring the effect of corporate governance on capital structure decision in Bangladeshi firms. Firm size is measured as the natural logarithmic transformation of total assets or sales of a firm (Gurarda et al. 2016). Board size, board composition, and managerial ownership are variant with firm size (Titman and Wessels 1988; Wald 1999; Prasad et al. 2001; Castanias 1983). Return on asset measures the efficiency of total assets employed in the companies. The ratio is estimated by the net income over the total assets (Ajanthan 2013; Ehikioya 2009). According to Hsiao (2003), the panel data approach usages a data set that monitors a specified sample over a period, providing a multiple regression model for each variable in the sample. This approach upsurges the data due to combining the cross-sectional data with time series data.
3.2. Formal Hypotheses Development
Mugenda and Mugenda (2008) provides a structure of relationship between dependent and independent variables in the study. Figure 1 demonstrates the relationship between the dependent and independent variables regarding the connections which exist between corporate governance and leverage structure. The model constructs a co-effect of independent and control variables on leverage structure where independent variables such as board size, board composition, managerial ownership, board independence, institutional ownership, and duality are used as proxies of corporate governance and leverage used as a proxy of capital structure demonstrated below:
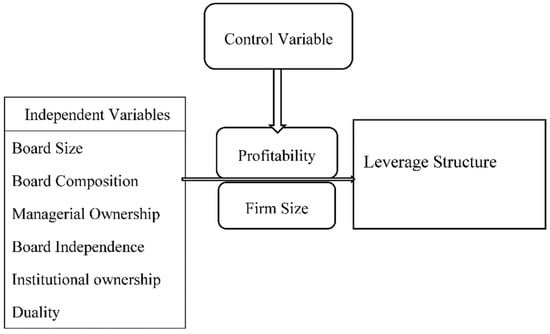
Figure 1.
Relationship between dependent and independent variables. Source: Variables have been compiled by the researchers.
- . There is a positive relationship between board size and leverage structure decision-making.
- . A positive relationship exists between board composition and leverage structure decision-making.
- . Managerial ownership is positively related to leverage structure decision-making.
- . There exists a positive relationship between institutional ownership and leverage structure decision-making.
- . There is an inverse relationship between board independence and leverage structure decision-making.
- . A positive relationship exists between CEO duality and leverage structure decision-making.
3.3. Model Specification and Measurements
The study has adopted an approach to test the relationship between leverage structure decision-making and a set of corporate governance variables (see Table 1) by using a multiple regression model (Chowdhury 2004). The study hypothesizes that the relationship between the outcome variable and predictors to be linear and the residual error term is to be normally distributed. As per the hypothetical relationship, the multiple regression model has been established below:

Table 1.
Name of the variables and their descriptions.
4. Data and Methodology
4.1. Sample Design and Data Collection
The samples have been chosen in terms of data availability and active capital market participation during the studied period. The optimal time scale of 2003–2017 is used based on information available, which is consistent with the financial and non-financial data for the requirements of corporate governance and leverage structure decision-making. The financial sector, including banks, insurance companies, and leasing companies, are totally different in terms of assets, functions, and regulatory requirements of manufacturing sectors, which are excluded (Diamond and Rajan 2000). A fragment of the manufacturing sectors is also diminished from the estimation because there is a shortage of data cell on DSE. The manufacturing companies which did not start their operations before 2003 are also excluded in sample size. The sample includes both financially sound and weak companies but the companies which have found financial anomalies, are removed from sample size in order to avoid survival bias, as the probability of bankruptcy which might have a significant impact on a firm’s financing decisions. During the period of 2003–2017, democracy has been killed, and all sectors of the economy have been seized by the power of the ruling party. The impact of evil politics has changed the corporate governance structure in Bangladesh. Therefore, the aim of the study is urgently required to test the impact of corporate governance on leverage structure in Bangladesh.
The data relevant to variables are collected from the reports of corporate governance, balance sheets, notes of financial statement, management structure, the board of director’s reports, highlights of financial performance from annual reports during 2003 to 2017. This information is publicly accessible on the database of the Dhaka Stock Exchange and website of companies. The data were averaged over the 15 years to smooth the leverage and explanatory variables. For inclusion in a sample of 15 years of data, from 2003–2017 is used, resulting in a panel database of 945 cases for 63 companies. The study has randomly included both companies, which are financially mixed (strong and weak) but those companies have been removed to avoid survival bias, as the probability of bankruptcy which may have a significant impact on a firm’s financing decisions.
4.2. Methodology
We used the panel data estimation for measuring the impact of corporate governance variables on leverage structure in Bangladesh. To test the relationship, panel techniques such as fixed effects and random effects methods have been subsequently tested to analyze the data (Gujarati 2004). Hausman (1978) determined the fixed effects method between two approaches for panel dataset. The study has subsequently tested the problems of endogeneity, unobservable heterogeneity, simultaneity where have been found their significance connections on data set. In this typical panel data, (Arellano and Bover 1995; Blundell and Bond 1998) suggested us to test the panel Generalized Method of Moments (GMM) to make the data efficient for results. The study has also conducted the tests of serial correlation, heteroskedasticity, and cross-section dependency problems and proved their connections. In this typical data, Beck and Katz (1995) suggested that panel corrected standard error (PCSE) needs to be used to find out reliable results. Therefore, the PCSE has been proved a popular empirical testing of panel data (Reed and Ye 2011). The models have produced the differential results due to successive filtering of data for greater acceptability. The two-stage findings have been asserted how actually corporate governance explains the leverage structure decision-making in Bangladesh.
5. Empirical Results and Discussion
This section provides empirical evidence from an analysis of panel data relevant to corporate governance and leverage structure decision-making. The results are interpreted in the light of code and concept of corporate governance in Bangladesh and finance theories. STATA version 13 and E-view 9 version are employed to test the model results. The rationale behind this interpretation is to identify the influential factors of corporate governance to deal with capital structure decision in Bangladesh. The results of the following tests have been presented and interpreted:
5.1. Descriptive Statistics
Table 2 provides descriptive statistics about all variables of corporate control and leverage structure being studied. There are huge divergences between the maximum and minimum value of leverage, board size, board composition, managerial ownership, firm size, and return on asset etc. This affords the understanding of characteristics from discrepancies and heterogeneities of the sample firms. The average leverage size used by Bangladesh firms is 53.7%, which constitutes a more financial risk as of more than 50%. The divergence of leverage between the maximum value and the minimum value is so high, and the median value is 54.9%. The board size of companies is 7.39 which indicate that the maximum companies are constituted with small board size and tend to be less effective in the managerial decision followed by the code of corporate governance in Bangladesh. There are a few companies where boards are constituted by less than five members, but regulation of corporate governance code allows at least five members. The maximum boards limit to 15 members who are allowed by rules of corporate governance of Bangladesh. The maximum board members shall be consisted of 20 members as per the code of corporate governance of Bangladesh.

Table 2.
Descriptive statistics.
The average score of board composition is found less than one that indicates, management of companies are active in operations as of holding least number of non-executive directors on board. The maximum and minimum value of non-functional directors are from 90 to zero percent of total directors indicating that there are a few companies which have 90% non-functional directors and some companies contain zero percent of non-functional directors. These companies are suffering from poor management. There is 24.3% of institutional shareholders of total shareholders, which explains the largest and significant in numbers. Their role and control of the management are indispensable. It is found that 98% shares of some companies are held by institutions which are fully regulated by them as their own way. The standard deviation of institutional ownership is 21.9%. Managerial ownership is explained by 33.1% on Board, which positively encourages the operational activities towards shareholders but may negatively motivate the stakeholders’ compensation if they are irrational in their activities. The maximum and minimum value of managerial ownership is so far distance indicating that there is a high variation of managerial control on board. As per the rule of corporate governance, at least one fifth but not more than two thirds of total directors shall have independent directors. It is indicated that the ratio of independent directors is less than 10%, which is not followed by the code of corporate governance. There are no independent directors in a few companies, but some companies have had 60%, independent directors. Independent directors are professional and plays an active monitoring role in the developing country. The two controlling variables are the firm size and return on asset, and their mean value is the natural logarithm of assets as 20.06, and the average return is 5.18% is not significant. Their maximum, minimum and median value of firm size and profitability are (24.28, 47.9%), (9.63, −0.41) and (20.41, 3.4%) respectively. The profitability of companies is highly volatile and risky. The skewness and kurtosis are required to test the pre-assumptions of multiple regression model whether the data are normally distributed or not. Most of the values for skewness and kurtosis are limited to (±3), which indicate that data in the study are normally distributed (Kallamu 2016).
5.2. Correlation Analysis
Table 3 demonstrates the estimated results obtained from the test of Pearson correlation for a given panel data set. The result displays a significant negative correlation between board size and leverage, board independence and leverage, and positive correlations between managerial ownership and leverage, and between duality and leverage. The co-efficient of significant variables is −0.18**, 0.072**, −0.35** and 0.13** respectively at 1% level of significance. Those explain that the higher board tends to use less leverage. The more managerial shareholdings represent the use of a higher amount of leverage in the capital structure. The firms with greater profitability indicate less debt in the capital structure. The chairman separated from management deals with a larger amount of debt in the capital structure.

Table 3.
Pearson Correlation Matrix of Variables.
The correlation analysis shows the substantial relationship among independent variables, which can cause a problem of multicollinearity. However, the results from VIF calculation indicate that all independent variables have that value, which is less than 2.0, indicating absolute nonexistence of multicollinearity problem among all variables in the model. This value is estimated as where is the co-efficient of determination of regression of independent variables and a VIF of 5 or 10 and above shows a multicollinearity problem (O’Brien 2007). This test was also used by (Huynh and Su 2010; Grill et al. 2010).
5.3. Test of Panel Generalized Method of Moments (GMM)
The GMM is a dynamic panel estimator that controls the heteroskedasticity and good alternative to fixed effects or random effects model. Therefore, to identify the unobservable factors that could affect the residual, we used instrumental variables. The tested results of panel dynamics have been highlighted in the following Table 4.

Table 4.
Panel Generalized Method of Moments.
In the above Table 4 displays the multivariate analysis, the study presents that board size provides a strong and inverse impact on the leverage structure of the firms in Bangladesh. If the members on board are formed with the mix of general, independent, professional, and intuitional shareholders then the board members request to borrow less for befitting the corporation. The board strategy is to follow the pecking order theory when the firms have sufficient internal cash flow to cover the capital deficit. Myers and Majluf (1984) predicted that firms seek the external source of finance at the capital market until no internal cash flow is available. When members on board consist of only family, institutions, and political leaders, they often suggest using more debt for realizing their personal purpose. The finding implies that when board size becomes large by members, then chairman or CEO could not use more debt for their individual purpose and vice-versa. In this situation, the board has preferred the trade-off theory. Trade-off theory assumes that boards require the use of the optimal level of debt when benefits of debt are equal to the marginal cost of debt (the financial distress and agency costs). The member on board increases that put their voices for using the fewer borrowings. Berger et al. (1997) contend that a bigger board enforces the managers to manage the low debt–equity ratio to stimulate the performance of firms. Therefore, the hypothesis on the correlation between board size and leverage structure is accepted.
Concerning the board composition, there is a positive and significant relationship between board composition and leverage ratio. This means that the larger non-executive directors become on board relates to the increase in the debt–equity ratio. Lower non-functional directors make the easier decision regarding debt–equity ratio. The presence of non-executive directors on board seeks the increased amount of debt because it is expected that non-executive directors are appointed by families, governments, and institutions in Bangladesh. The non-executive directors would maximize the profit by using the maximum debt which followed by trade-off theory. The finding is consistent with (Jensen 1986). Berger et al. (1997) also found the identical result that the companies contain larger non-executive directors can raise more leverage. Abor (2007) also provided an indication of the positive relationship between board composition and the setting of leverage structure. The result is contrary to the findings of Wen et al. (2002) and the incidence of outside directors’ guide to taking the low leverage ratio. Hence the hypothesis on the relationship between board composition and leverage structure is accepted.
About the institutional shareholdings, they have a strong influence on the role of setting a leverage ratio at 10% level of significance. The result shows that proportionate of institutional shareholdings upturned on board tends to increase the leverage ratio in the capital structure. Crutchley et al. (1999) indicated that a large trend of institutional shareholdings places the votes for using a higher ratio of debt. The hypothesis on the relationship between institutional shareholdings and leverage structure is accepted.
Regarding the managerial ownership, the percentage of managerial ownership has been playing the positive and active role for using more leverage. The increase of managerial ownership leads to upturn the debt ratio to the fact of maximizing the firm value. Managerial ownership has been entrusted to professionally experienced persons who are responsible for maximizing the firm value. They use more debt to increase the firm value because the cost of debt is the cheapest cost of capital due to the tax shield. The managerial ownership has given preference to use the trade-off theory for setting leverage structure. Gill et al. (2009) find a positive and significant relationship between managerial ownership and leverage structure. Hence the hypothesis on the relationship between managerial ownership and leverage structure is accepted.
The study reveals that there is no basic role of board independence in setting the leverage structure in Bangladeshi firms. Therefore, the hypothesis on the relationship between board independence and leverage structure is rejected.
Regarding the firm size, there is a negative and significant relationship between firm size and leverage structure. Larger firms are more diversified in producing services and making the sources of internal financing available. They prefer internal sources to external borrowing that substantiates the pecking order theory. The hypothesis on the relationship between firm size and leverage structure is accepted.
About the profitability, the study indicates that return on assets is negative and significantly related to leverage structure. The highly profitable firms are intended to borrow less because of using the retained earnings, which is the counter of trade-off theory. Therefore, the hypothesis on the relationship between profitability and leverage structure is accepted.
Regarding the duality, the finding reveals that duality has no significant impact on leverage decision. The findings are supported by (Fosberg 2004; Siromi and Chandrapala 2017). Abor and Biekpe (2007) discover a positive but insignificant association between CEO duality and leverage. Hence the more than five predictors out of eight variables are found significant at 5% or 10%. Since the model is nicely accepted for assessing the impact of corporate governance on leverage structure in Bangladesh.
5.4. Panel Corrected Standard Error (PCSE)
The PCSE estimator has become very popular, as demonstrated by approximately 2000 citations on Web of Science. All of these have opened up numerous choices for pragmatic researchers when they would like to use a panel data estimator. The panel correlated standard error is more appropriate for panel data analysis and estimated results are given below:
The above Table 5 provides efficient results using the PCSE estimator. We observe that there is the same line of direction between board size and leverage ratio, but the relationship is not substantial, signifying a relatively low insistence with capital structure decision which is consistent to Abor (2007). The result is not relevant to the empirical result of Wen et al. (2002). Hence the research hypothesis on the significant relationship between board size and capital structure decision is rejected.

Table 5.
Estimated Results of Panel Corrected Standard Error (PCSE).
Regarding the board composition, the ratio of non-executive directors on total directors revealed a positive and minor relationship with debt–equity ratio alike to board size. This relationship is convergence to the test of Achchuthan et al. (2013) and followed by the opposite direction to the code of corporate governance in Bangladesh. This evidence rejects the existence of developing hypotheses such as the positive substantial association between board composition and leverage structure.
The estimated result confirms that the relationship between institutional shareholdings and debt–equity is statistically insignificant and positive. Therefore, the research hypothesis on a positive significant relationship between institutional shareholdings and capital structure decision is not accepted. The result is consistent with the findings of (Crutchley et al. 1999).
Concerning the managerial ownership, the ratio of shares held by CEOs, directors, and their family members on total shareholdings revealed the statistically substantial and positive correlation with the debt–equity ratio at 10% level of significance. More precisely, the finding reconciles to the family and political intervene in corporate governance in the context of Bangladesh. Consequently, our hypothesis on the inverse relationship between managerial ownership and capital structure is rejected. The result is contrary to the findings of (Nyonna 2012).
The negative and insignificant association between board independence and debt–equity ratio indicates that the presence of independent director on board makes the pressure to the board meeting to use less debt in capital structure and to follow the code of corporate governance in Bangladesh. Therefore, our research hypothesis on a positive relationship between board independence and capital structure decision is rejected (Wen et al. 2002).
Regarding the firm size, there is an inverse and important relationship between firm size and debt–equity ratio. The study revealed that the more diversified firms tend to use less debt–equity ratio because the larger firms prefer to use the internal to external sources as this trend is supported by pecking order theory. Meanwhile, our research hypothesis on the positive relationship between firm size and capital structure decision is rejected.
About the profitability, the result established that there is a negative and significant relationship between profitability and capital structure. This implies that firms with high profitable tend to employ the more retained earnings in the capital structure than external capital of debt, which is in accordance with the pecking order theory. Hence the hypothesis on the positive significant relationship between profitability and leverage structure is rejected (Barton et al. 1989).
Regarding the CEO duality, the finding confirmed that the CEO duality is positively significant related to the debt–equity ratio. This suggests that the CEO holding dual responsibility performs faster than the one separated from the management and to be exact from chairman. When the CEO and chairman become the same person as the firm is led by family or political intervention, the CEO or chairman exerts the pressure to the board to use the higher leverage ratio in the capital structure that violates the code of corporate governance in Bangladesh. In this situation, CEO duality designs the leverage structure based on trade-off theory to maximize the benefits of the tax. The result indicates that ownership of manufacturing companies is held by families and political leaders who control the firms as their own way. When the chairman and CEO are the same person, he/she tends to use boundless debt from banks or issuing debt security, which is beyond the disposition of financial managers. The roles of the board of directors or family members or political leaders intrude the functional approach of organization which creates agency problems. It may be lack of corporate governance. Therefore, the main reason for declining corporate governance is the ownership of firms led by family or political leaders in Bangladesh. Henceforth, our research hypothesis on the positive relationship between CEO duality and capital structure decision is accepted. The finding congregates the result of (Uwugbei 2014).
In the study, it is indicated that 50% of explanatory variables are found significant. Therefore, the model is nicely established. 64.26% of capital structure (debt–equity ratio) has been influenced by the explanatory variables set in the model, and the residual of 35.74% in the capital structure is explained by other factors for which further research may be undertaken. The overall p-value also confirmed the fitness of the model.
6. Conclusions and Policy Implications
The study is intended to evaluate the impact of corporate governance on leverage structure decision-making in Bangladesh. The study reveals that managerial ownership and CEO duality are the main determinants of corporate governance on leverage decision-making in Bangladesh using PCSE, but board size, board composition, institutional shareholdings, managerial ownership, firm size, and profitability are the main influential determinants for leverage decision at 5% or 10% level of significance. Concerning the managerial ownership variable, the finding shows that a greater portion of shares held by CEOs, directors, and their family members with a great portion of shares govern the firm protecting their own interest ignoring the minority interest. Regarding the CEO duality, this is the critical findings from the results which are highly dominating in leverage decision-making in Bangladesh. The family leads most of the firms, and the pressure of managerial shareholdings generally pursues political sustenance in Bangladesh and their ill-motives as well as using the power of CEO duality. The study also finds that contrary to prior research, the main corporate governance variables such as board size, board composition, and institutional owners are found a significant relationship with leverage decision using GMM. The study demonstrates that control variables such as firm size and profitability cause a significant and negative effect on capital structure decision. This finding substantiates the findings of prior research work of (Somathilake and Udaya Kumara 2015). From this result, it can be concluded that the firms that have more assets and generating more profits tend to use less outside borrowing.
Several policy implications result from these conclusions. First, better legislation for improving the internal and external of the corporate governance system need to be developed. The companies in Bangladesh are working with tremendously family and political ownership, which allow the managers to protect their interests only and to seize the minority shareholders. Sophisticated prosecution of law and code of good corporate governance practices might support to improve these problems. Second, additional measures such as an effective audit committee and professional board independence with accountability might help to improve the corporate governance in Bangladesh. Independent directors in Bangladesh are politically appointed, and they normally work for the enforcement of political agenda. Thirdly, the regulatory agencies such as Bangladesh Security and Exchange Commission and Stock Exchanges must enhance the monitoring of the cell for the enforcement of the law as well as the code of corporate governance practice. Removal of these problems are expected to enhance the attributes of corporate governance and positively influence the capital structure decision in Bangladesh. Further research may be investigated using qualitative factors such as ownership and regulatory behavior influences the financing decisions in Bangladesh.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed equally to the entire process of writing this paper.
Funding
The research paper did not receive any kind of funding.
Conflicts of Interest
We declare that the paper is not associated with any kind of conflict of interest.
References
- Abor, Joshua. 2007. Corporate Governance and Financing Decisions of Ghanaian Listed Firms Corporate Governance. The International Journal of Business in Society 7: 83–92. [Google Scholar]
- Abor, Joshua, and Nicholas Biekpe. 2007. Corporate Governance, Ownership Structure and Performance of SMEs in Ghana: Implications for financing opportunities. International Journal of Business in Society 7: 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achchuthan, Sivapalan, Kajananthan Rajendran, and Sivathaasan Nadarajah. 2013. Corporate Governance Practices and Capital Structure: A Case in Sri Lanka. International Journal of Business and Management 21: 114–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegbile, Samuel Abraham. 2015. Corporate Governance Attributes and Capital Structure of Listed Firms in the Nigerian Food and Beverages Industry. International Journal of Public Administration and Management Research 3: 48–56. [Google Scholar]
- Aharon, David Yechiam, and Yossi Yagil. 2019. The Impact of Financial Leverage on the Variance of Stock Returns. International Journal of Financial Studies 7: 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagathurai, Ajanthan. 2013. Impact of Corporate Governance Practices on Firm Capital Structure and Profitability: A Study of selected hotels and restaurant companies in Sri Lanka. Research Journal of Finance and Accounting 10: 115–26. [Google Scholar]
- Arellano, Manuel, and Olympia Bover. 1995. Another look at the instrumental variable estimation of Error-component models. Journal of Econometrics 68: 29–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, Sidney L., Ned C. Hill, and Srinivasan Sundaram. 1989. An Empirical Test of Stakeholder Theory Predictions of Capital. Financial Management Journal 18: 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, Nathaniel, and Jonathan N. Katz. 1995. What to Do (and Not to Do) With Time-Series Cross-Section Data. American Political Science Review 89: 634–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, T., and R. Levine. 2004. Stock markets, banks, and growth: Panel evidence. Journal of Banking and Finance 28: 423–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, Philip G., Eli Ofek, and David L. Yermack. 1997. Managerial Entrenchment and Capital Structure Decisions. Journal of Finance 52: 411–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagat, Sanjai, and Bernard Black. 2002. The Non-Correlation between Board Independence and Long-Term Firm performance. Journal of Corporate Law 27: 231–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blundell, Richard, and Stephen Bond. 1998. Initial conditions and moment restrictions in dynamic panel Data models. Journal of Econometrics 87: 115–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokpin, Godfred A., and Anastacia C. Arko. 2009. Ownership Structure, Corporate Governance and Capital Structure Decisions of Firms: Empirical Evidence from Ghana. Studies in Economics and Finance 26: 246–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanias, Richard. 1983. Bankruptcy risk and optimal capital structure. Journal of Finance 38: 1617–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Sheng-Syan, and I-Ju Chen. 2012. Corporate governance and capital allocations of diversified firms. Journal of Banking & Finance 36: 395–409. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, Mu. 2004. Capital Structure Determinants: Evidence from Japan & Bangladesh. Journal of Business Studies XXV: 23–45. [Google Scholar]
- Crutchley, Claire E., Marlin R. H. Jensen, John S. Jahera, Jr., and Jennie E. Raymond. 1999. Agency problem and the simultaneity of financial decision making: the role of institutional ownership. International Review of Financial Analysis 8: 177–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, Dan R., Catherine M. Daily, Alan E. Ellstrand, and Jonathan L. Johnson. 1998. Meta-Analytic Reviews of Board Composition, Leadership Structure, and Financial Performance. Strategic Management Journal 19: 269–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, Douglas W., and Raghuram G. Rajan. 2000. A theory of bank capital. Journal of Finance 55: 2431–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchin, Ran, John G. Matsusaka, and Oguzhan Ozbas. 2010. When are outside directors effective? Journal of Financial Economics 96: 195–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehikioya, Benjamin I. 2009. Corporate Governance Structure and Firm Performance in Developing Economies: Evidence from Nigeria. Corporate Governance 9: 231–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, Theodore, Stefan Sundgren, and Martin T. Wells. 1998. Larger Board Size and Decreasing Firm Value in Small Firms. Journal of Financial Economics 48: 35–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, Merle, and Shiing-wu Wang. 2005. Earnings Management by Acquiring Firms in Stock for Stock Mergers. Journal of Accounting and Economics 27: 149–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, Saeed, Farzaneh Ghandehari, and Sayyed Ya’ghoub Shirangi. 2014. Comparative Study of Capital Structure Determinants in Selected Stock Exchanges of Developing Countries and Tehran Stock Exchange. International Journal of Academic Research in Accounting, Finance and Management Sciences 4: 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fosberg, Richard H. 2004. Agency Problems and Debt Financing: Leadership Structure Effects, Corporate Governance. International Journal of Business in Society 4: 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Friend, Irwin, and Larry H. P. Lang. 1988. An Empirical Test of the Impact of Managerial Self-interest on Corporate Capital structure. Journal of Finance 43: 271–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanda, Ahmadu U., Aminu S. Mikailu, and Tukur Garba. 2009. Corporate Governance Mechanisms and Firm Performance: A Survey of literature. The University Journal of Corporate Governance 8: 7–21. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, Amarjit, Nahum Biger, and Neil Mathur. 2010. The Relationship between Working capital Management and Profitability: Evidence from The United States. Business and Economic Journal 10: 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Gujarati, Damodar N. 2004. Basic Econometrics, 4th ed. Mcgraw Hill: Boston, p. 650. [Google Scholar]
- Gurarda, Sevin, Emre Ozsoz, and Abidin Ates. 2016. Corporate governance rating and ownership structure in the case of Turkey. International Journal of Financial Studies 4: 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakilifard, Hamid R., Mahdi S. Gerayli, Abolfazl M. Yanesari, and Ali Reza Ma’atoofi. 2011. Effect of Corporate Governance on Capital Structure: Case of the Iranian Listed Firms. European Journal of Economics Finance and Administrative Sciences 35: 1165–72. [Google Scholar]
- Haque, Faizul, Thankom Gopinath Arun, and Colin Kirkpatrick. 2011. Corporate Governance and Capital Structure in Developing Countries: A Case study of Bangladesh. Applied Economics 43: 673–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, Oliver. 1995. Firms, Contracts, and Financial Structure. Oxford: Clarendon Press. [Google Scholar]
- Hausman, Jerry A. 1978. Specification Tests in Econometrics. The Journal of Econometrics 46: 1251–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, Cheng. 2003. Analysis of Panel Data. New York: Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Huynh, Phuong Dong, and Jyh-tay Su. 2010. The Relationship between Working capital Management and Profitability: A Vietnam Case. Internal Research Journal of Finance and Economics 49: 59–67. [Google Scholar]
- Jaradat, Monther S. 2015. Corporate Governance Practices and Capital Structure: A Study with Special Reference to Board Size, Board Gender, Outside Director and CEO Duality. International Journal of Economics, Commerce and Management United Kingdom 3: 264–73. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, Michael C. 1986. Agency Cost of Free Cash Flow. Corporate Finance, and Take-Overs. American Economic Review 72: 323–29. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, Michael C. 1993. The Modern Industrial Revolution, Exit, and the Failure of the Internal Control Systems. Journal of Finance 48: 831–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joher, Huson, Mohd Ali, and M. Nazrul. 2006. The Impact of Ownership Structure on Corporate Debt Policy: Two Stage Least Square Simultaneous Model Approach for Post Crisis Period: Evidence from Kuala Lumpur Stock Exchange. International Business & Economics Research Journal 5: 51–63. [Google Scholar]
- Kallamu, Basiru Salisu. 2016. Impact of the Revised Malaysian Code on Corporate Governance on Audit Committee Attributes and Firm Performance. Global Journal of Management and Business Research: D Accounting and Auditing 16: 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Kyereboah-Coleman, Anthony, and Nicholas Biekpe. 2006. The relationship between board size, board composition, CEO duality and firm performance: Experience from Ghana. Corporate Ownership and Control 4: 114–22. [Google Scholar]
- La Porta, Rafael, Florencio Lopez-de-Silanes, Andrei Shleifer, and Robert Vishny. 2002. Investor Protection and Corporate Valuation. The Journal of Finance 57: 1147–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefort, Fernando, and Francisco Urzúa. 2008. Board independence, firm performance and ownership concentration: Evidence from Chile. Journal of Business Research 61: 615–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lev, Baruch. 1988. Toward a theory of equitable and efficient accounting policy. The Accounting Review 63: 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Lipton, Martin, and Jay W. Lorsch. 1992. A Modest Proposal for Improved Corporate Governance. The Business Lawyer 48: 59–77. [Google Scholar]
- Marsh, Paul. 1982. The choice between equity and debt: An empirical study. The Journal of Finance 37: 121–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugenda, M. O., and A. Mugenda. 2008. Research Methods: Qualitative and Quantitative Approaches. Nairobi: African Centre for Technology Studies. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, Stewart C., and Nicholas S. Majluf. 1984. Corporate financing and investment decisions when firms have information that investors do not have. Journal of Financial Economics 13: 187–221. [Google Scholar]
- Nyonna, Dong Y. 2012. Simultaneous Determination of Insider Ownership and Leverage: The Case of Small Businesses. Economics & Business Journal: Inquiries & Perspectives 4: 9–20. [Google Scholar]
- O’brien, Robert M. 2007. A Caution Regarding Rules of Thumb for Variance Inflation Factors. Quality and Quantity 41: 673–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onaolapo, Adekunle A., and Sunday O. Kajola. 2010. Capital Structure and Firm Performance: Evidence from Nigeria. European Journal of Economics, Finance and Administrative Sciences 25: 70–82. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, Mitchell A., and Raghuram G. Rajan. 1994. The benefits of Firm-creditor Relationships: Evidence from Small Business Research Data. Journal of Finance 49: 3–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontines, Victor, and Reza Siregar. 2008. Fundamental pitfalls of exchange market pressure-based approach to identification of currency crises. International Review of Economics & Finance 17: 345–65. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, Sanjiva, Christopher J. Green, and Victor Murinde. 2001. Company Financing, Capital Structure, and Ownership: A Survey and Implications for Developing Economies. Ph.D. thesis, Cardiff Business School, Cardiff, UK; pp. 1–104. [Google Scholar]
- Rajan, Raghuram G., and Luigi Zingales. 1995. What do we know about Capital structure? Some Evidence from International Data. Journal of Finance 50: 1421–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, W. Robert, and Haichun Ye. 2011. Which panel data estimator should I use? Applied Economics 43: 985–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siromi, Bulathsinhalage, and Pathirawasam Chandrapala. 2017. The Effect of Corporate Governance of Firm’s Capital Structure of Listed Companies in Sri Lanka. Journal of Competitiveness 9: 19–33. [Google Scholar]
- Somathilake, HMDN, and KGA Udaya Kumara. 2015. The Effect of Corporate Governance Attributes on Capital Structure: An Empirical Evidence from Listed Manufacturing Companies in Colombo Stock Exchange. Paper presented at the International Research Symposium, Rajarata University of Sri Lanka, Mihintale, Sri Lanka, January 26; pp. 22–29. [Google Scholar]
- Stulz, René M. 1988. Managerial Control of Voting Rights: Financing Policies and the Market for Corporate Control. Journal of Financial Economics 20: 25–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taani, Khalaf. 2013. The Relationship between Capital Structure and Firm Performance: Evidence from Jordan. Global Advanced Research Journal of Management and Business Studies 2: 542–46. [Google Scholar]
- Titman, Sheridan, and Roberto Wessels. 1988. The determinants of capital structure choice. Journal of Finance 43: 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uwuigbe, Uwalomwa. 2014. Corporate Governance and Capital Structure: Evidence from Listed Firms in Nigeria Stock Exchange. Journal of Accounting and Management 4: 5–14. [Google Scholar]
- Velnampy, T., and Aloy J. Niresh. 2012. The relationship between capital structure and profitability. Global Journal of Management and Business Research 12: 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Wald, John K. 1999. How Firm Characteristics Affect Capital Structure: An International Comparison. Journal of Financial Research 22: 161–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewa Wellalage, Nirosha, and Stuart Locke. 2012. Corporate governance and capital structure decisions of Sri Lankan listed firms. Global review of Business and Economic Research 8: 157–69. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Yu, Kami Rwegasira, and Jan Bilderbeek. 2002. Corporate Governance and Capital Structure Decisions of Chinese Listed Firms. Corporate Governance: An International Review 10: 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Xiaonian, and Yan Wang. 1999. Ownership Structure and Corporate Governance in Chinese Stock Companies. China Economic Review 10: 75–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).