Abstract
The China–Pakistan economic corridor (CPEC) is a collection of different ongoing projects including transportation, infrastructure, the Gwadar seaport, oil pipeline, and internet connection zone projects. The Chinese government has adopted a development strategy for infrastructure growth and investment in Pakistani and Asian territories through the CPEC project. Transportation is considered the backbone of the CPEC. In addition to the CPEC project is the linked “belt and road initiative” (BRI) project, which aims to enhance regional connectivity and is a harbinger of the future in Asia, as well as in European countries. However, uncertain situations, such as a lack of proper planning, security, and political stability, hinder the growth and development of infrastructure. Three corridors of the CPEC road transportation network, namely, the eastern, the western, and future central alignment, have been examined through a master supposition group using the Delphi technique, which has never been applied to the road transportation network in the CPEC plan. The review is designed to draw master conclusions and demonstrate an outcome for round one and two in the present work. Round one and two investigate the impact of stakeholder support, politicians’ roles, terrorism, security situations, poverty, and economic crises. Using the Delphi technique within the host country hinders the construction of the road network. The results obtained through the appraisal have justified the present potential endeavor.
1. Introduction
Transportation networks are a pillar of infrastructure growth and the prosperity of a country. The construction of transportation networks has a significant role in regional economic development and upgrading peoples’ living standards. The structure of a transportation network is exposed to project risk, and risk identification is significant for the project schedule plan. Both the situation of the country and the behavior of the host nation towards road networks have played significant roles in the development of the road network plan. Recently, researchers have studied the development of transportation network influence on the construction industry broadly. In the construction industry, there are many factors relating to constructing a project on time, such as enlargement and complexity, rapid changes in the techniques, etc. Construction risks in projects are becoming increasingly diverse and have effects on a project’s life cycle (Beyazit 2015). According to Standish’s statement, a successful construction project depends upon cost, schedule, and quality. An entire project’s expenses should not exceed more than 32% of the integrated project, based on the 2009 report. If the schedule of the project is delayed, then the cost of the project increases by 44%, which results in cancelation reaching up to 24% (Laurenz and Verhoef 2010). Various types of risks are involved in a construction project; however, the project risk in the manufacturing industry is unlikely to enable smooth processes. The risk factors present a problematic forecast for project delays, cost overruns, and subsequent allegations, which can result in the failure of a project. Consequently, investigating and managing various types of risk in the construction industry is very important for project progress. Contrary to this, the relation between the risk factors that are interdependent for the program type has recently increased (Iyer and Sagheer 2010). To construct a transportation network, the host community response is essential for the project life cycle. The success of the project frequently depends on local support from the host community in the construction industry for development processes (Ali et al. 2018).
However, existing literature has examined different project risks and their influence on a project performance plan. Consequently, the China–Pakistan economics corridor (CPEC) project, was marked in April 2015, between the Prime Minister of Pakistan, Nawaz Sharif, and the President of China, Xi Jinping, for regional connectivity, and embraces a brighter future in the Asian market, as well as in the European market. The total investment proportion of the CPEC project is worth around 46 billion USD, which will be covered by a couple of working sectors in Pakistan. The Memorandum of Understanding mentions capital for various projects, such as transportation and infrastructure, the Gwadar seaport, oil pipelines, and internet connection zone projects. According to the CPEC plan, it is anticipated that the mid-term plan will proceed from 2017 until 2025. Additionally, the long-term plan is expected to be completed by 2030 (Zia-ur-Rehman and Tariq Aziz 2017). The foremost notion of the CPEC project is to interconnect various countries by building transitory routes for the rapid delivery of goods. The architect of the CPEC plan is expected to curtail a 12,000 km route into 2700 km. The CPEC will lead an enormous reduction of resources by two-thirds in terms of distance, and will promote in the future bilateral economic trade connectivity (Zia-ur-Rehman and Tariq Aziz 2017). Road transportation networks in the CPEC project start from the Khunjarb pass (border of Pakistan and China) and trace every province of Pakistan. However, the uncertain situation within Pakistan, relating to proper leadership, deprived planning, and the behavior of the host nation, may cause project risk in the construction of the road transportation network. The present work addresses the risks (in terms of roads) in various parts of the CPEC road plan. In general, project risks reflect project cost, quality, and time. However, to identify the project risks in the present work, we use the Delphi technique. The goal of the present work is to create a decision strategy for the future perspective of the road transportation network and to minimize project risks in the construction. Moreover, to the best of our knowledge, in the CPEC project road transportation network, the Delphi technique has never been applied to determine project risk. We only found transportation network influence on the social risk of the host community (Ali et al. 2018). Figure 1 represents the framework of the three corridors. The rest of the paper is organized as follows. Section 2 presents the related work, Section 3 discusses the methodology and techniques used for the current study, Section 4 provides the results and discussion, and Section 5 presents the recommendations and conclusions.
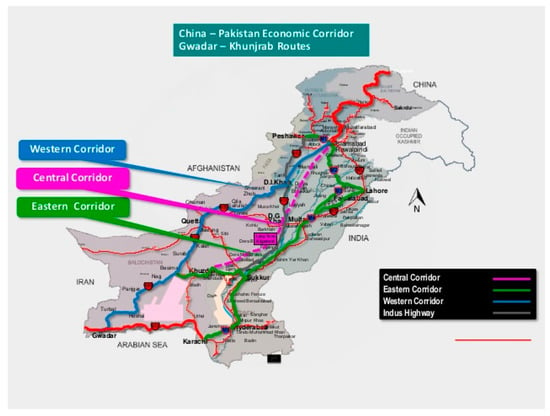
Figure 1.
The framework of the three corridors.
2. Literature Review
After World War II and later in the 1970’s, project risk-based approaches used in the strategy and evaluation of structure were developed for the paramilitary and nuclear industries (e.g., the planning of large-scale mega projects such as the Eurotunnel, Brenner tunnel, and Gottard tunnel since the 1990’s (Neumann and Sistenich 2011)). The literature review for the present work is derived from a past review of project risk in the construction site. According to the Project Management Institute (PMI, USA), any ambiguous occasion that affects project objectives in a positive or negative direction is a project risk (Project Management Institute 2000). Zhang et al. claimed that the risk at the construction site is to distinguish comparatively at each phase of the task activity, and any disregard would cause severe economic mutilation (Zhang and Lin 2012). Park Kyu-young claimed that the risk factors in a building site occur due to a lack of proper planning and management, community suggestions, and involvement in additional objectives (Park 2009). Lee Kang wook et al. claimed that in construction projects, some of the risk factors occur because of erroneous initial planning, which later influences risk factors such as time, cost, and quality, in the running project (Lee et al. 2009). Rodney E. et al. examined the portrayals of the risks identified with ongoing assets that were distinctive, identifying all the factors of the prescribed task (Rodney et al. 2014). Akintola S. et al.claimed that risk in the construction site depends upon three elements: ability, choices, and disclosures of a colleague (Akintoye and MacLeod 1997). Toakely and Uher identified that prior to starting the construction project, the majority of the labor is unfamiliar with the risk course and technique—they are only concerned with the daily phases of working (Uher and Toakely 1999). According to the global Joint construction company, there are mainly three social affairs to recognize the risk factors: outside, inside, and project rectification. Aforementioned investigation of risk legitimizations is used effectively for risk organization (Ling and Hoi 2006). M. Hastak et al. claimed that some authorities had segregated construction risks into two essential classes: market risks and country risks. Country risks are mainly associated with capital, monetary policy, the deterrence of the country’s budget policies, and irregularity. Market risks are related to the particular interests of the firm such as adjacent contenders, availability of the advancement of related resources, and government’s remote help in the construction site (Hastak and Shaked 2000). Li Bing et al. investigated risk factors by interviewing different labor groups and analyzed the fluctuation in the currency rates, cross culture, political changes, and pressure from higher authorities (Li and Tiong 1999). Resource distribution, procuring, and controlling are the risk factors determined, and in terms of minimizing time and budget they have influenced the quality of projects (Mcguire 1999). According to the British Standards Institute, in the mega construction project, stakeholders may create internal and external problems regarding illicit demand from the project, and illicit demand creates risk in the project (British Standards Institute 2010). J. De et al. claimed that, because of poor decision-making using resources possess risk, including frequent maintenance, an effect on the framework, and further challenges to control financial losses (De Brito and Branco 2006). Mulholl B et al. claimed that in the complex project, if the pre-planned methodology was interrupted during the on-going project, it could produce a dynamic environment and time constraints (Mulholland and Christian 1999). In the current study, project risk is the susceptibility in the road network of the CPEC project. The road network project will undergo project risk and further influence cost, time, and quality. The project risk is measured as the integration of the catastrophe for the road network. The vulnerability of the road network-evaluating researchers comes from using a different method. Researchers in (El-Rashidy and Grant-Muller 2014; Ouyang et al. 2014) studied the road network risk through game theory regarding its accessibility. Furthermore, authors also used brainstorming, survey, and, interview techniques (Fiondella et al. 2012; Tang and Huang 2019). However, the current study used the Delphi technique to investigate project risk in the construction industry.
3. The Framework of the Present Study
This section defines the research design and tools for identifying project risk in the construction of the road network. Figure 2 presents the workflow for research methodology.
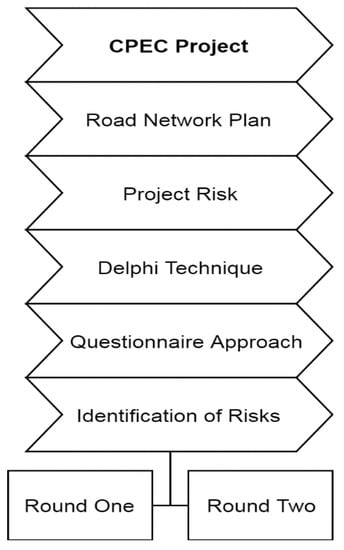
Figure 2.
Framework of the present study.
3.1. Delphi Approach
Regardinghe risk in the construction and estimation of uncertain factors, researchers adopted various tools to find and resolve risk factors. Brainstorming technique, interview, survey, and Ichikawa method are not appropriate for a construction project to access and require their confounding factors (Hallowell and Gambatese 2009). The Delphi technique is an authenticated methodical approach for resolving a complex delinquent through skillful consensus (Judd 1972). Mostly in complex construction projects, researchers use the Delphi technique through an expert panel for resolving project risk in construction and plan in order to avoid risk (Judd 1972). In construction projects, investigators mostly rely on the Delphi technique because Delphi is reliable in the construction industry (Sourani and Sohail 2015). The current work used the Delphi technique to identify the risk factors. Mostly, the Delphi technique is utilized in the report structure and to get an indispensable examination. Likewise, the Delphi technique is employed for instructive determining systems, and customary and anticipating patterns (Hallowell and Gambatese 2009). Figure 3 shows the framework of the Delphi approach used in the presented work. The questionnaire was designed by reviewing prior related problems and collecting the background information of two different locations. Two questionnaires were designed and given to the panel of experts in the related field. After completion of the first round in 10 days, we analyzed the result and reviewed the questionnaire for the second round. Similarly, we distributed the questionnaire again for the second round and analyzed the result, as discussed in Section 4.
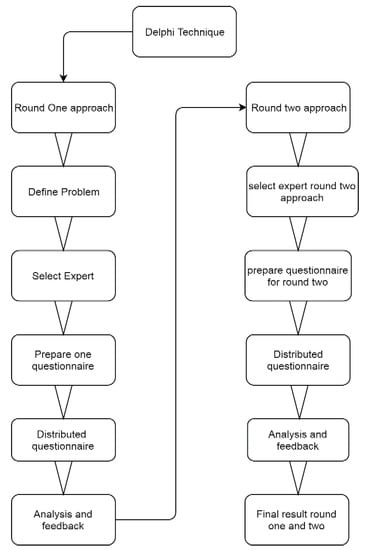
Figure 3.
Framework of the Delphi approach used in the current study.
3.2. Survey Development Strategy
To find an indication of project risk in the construction site, we used the questionnaire developing strategy. For preparing the questionnaire, we studied the literature review and found multiple project risks that occur in the construction industry. Some of the project risks in the construction industry are not favorable for project life scale. The risk influence on the project depends upon the level of its impact factors and probability. Most of the risk arises due to the initial erroneous planning and does not follow risk response techniques. However, we found similarities between the indication of project risk in the road network plan and other research in the construction industry (Hallowell and Gambatese 2009). We gathered background information of three-road alignment, namely, eastern, western, and central alignment, such as security situation, labor, lack of technical knowledge, unavailability of raw materials, etc. A questionnaire was generated with the help of a mentor to address project risk in the current work. The questionnaire was comprised of micro, meso, and macro risk followed by measurement scale. A total of 58 questionnaires distributed in two rounds and a further questionnaire were sub-divided into three investigative impact levels of risk shown in Table 1. The following criteria in Table 1 assess risk factors occurring in the road network CPEC project plan. The response rate from the expert panel is under the range of 1–25, which means risks impact level is favorable and did not influence the project’s cost, quality, and schedule. Medium level of risk had lower impact on the project performance and did not influence the project life cycle. However, compared to medium and lower level risks, unfavorable risk had higher impact on project performance. If the response rate from the expert panel is under the range 51–100, this means that risk level influence on the project cost, quality and time, and the chance of failure increased.

Table 1.
Three impact levels of project risk.
3.3. Study Population
A total of 50 experts were invited to train in two rounds of the Delphi technique from the School of Economics and Management. A panel of 36 experts participated in two round. The aim of the 36 final expert list was to recognize project risk in the construction side of the road network plan. In general, a different number of panels were used in the Delphi studies. According to Weidman, the Delphi study has never specified the number of experts through literature. Nevertheless, seven or eight experts are minimum to the recognized appropriate size in the Delphi technique (Weidman et al. 2011). Mitchell and Mcgoldrick claimed that the Delphi study has widened over time and in terms of monetary consideration, and also requires authorization. However, the number of experts should be at least 8 to 10 members (Mitchell and McGoldrick 1994). Furthermore, Hallowell and Gambatese indicated that in the Delphi study minimum, eight to sixteen expert are needed to specify and determine the study characteristics (Hallowell and Gambatese 2009).
3.4. Data Examination
In the Delphi study, we used statistics for the measurement of “mean, median, and mode (central tendency) and standard deviation (level of dispersion) for presenting information regarding the common findings of respondents (Mulholland and Christian 1999). Harmony on a topic was resolutely grounded on the percentage response, with an agreed range of measurment and stability within a successive iteration. Moreover, the total response rate of higher than 50% epitomizes the fact that project risk does not influence project performance, time, cost, and quality, as per the agreement between expert and self-selection criteria.
4. Result and Discussion
4.1. Delphi Round-One Approach
In this section, we discuss the proposed methodology used in the current study. We have unveiled numerous significant factors regarding the risk in road transportations plan of round one approach. The current methodology applied in the Delphi technique considers the mean, median, and standard deviation while taking into consideration the project risk. Furthermore, we have described the obtained result in the percentage separately. In the first round, we have proposed a meta-classification approach based on the three levels of risk factors, namely, minor, meso, and macro for the construction site of the road network. A total of 31 out of 36 economists responded to either round one (16, 88% response rate) and round two (15, 83%) of the survey. Table 2 represents 86% overall round one and round two response rates of the survey.

Table 2.
The response rate of round 1 and round 2.
4.1.1. First-Round Investigation of Delphi Studies
The data related to the three impact-level risk indicators is presented (the individual indicators are assigned according to certain standards). The actual value is normalized by the percentage system to eliminate the differential limits of the dimension. To construct the total expected value model of project risk, we have used the pairwise comparison method to calculate the standard weights of all the first-level indicators, second-level indicators, and third-level indicators. Moreover, we have calculated the project risk (expected value of the road plan) and analyzed the characteristics of each expected value.
4.1.2. Macro Risk
The CPEC project has enormous importance, not for only Pakistan but also for the entire region. Consequently, there are numerous parties seeking to hinder the road network in the host country and its government to mitigate the different types of risks and their importance for road network life cycle. However, the Pakistani regime has been unstable since independence, and is determined by factors such as the special party politics, family groups, and some complex stakeholder forces in the country. Pakistan is a “strong society and a developing country.” The loyalty of various ethnic groups to the central government is minimal, and generally, there is a lack of recognition of individuality. The instability of the long-term regime may lead to a failure to implement many government decrees in the construction of the CPEC, such as project lags or public protests. Another critical issue from the external side is issues of terrorism and the security situation, which also affect the Pakistani regime, and thereby will affect the implementation efficiency of the construction of the CPEC road plan. The central tendency and level of dispersion score indicated in Table 3 in round one, and each risk factor, are also mentioned. Table 3 represents the Macro level result in the construction of the road transportations plan.

Table 3.
Macro-level risk for round 1.
4.1.3. Meso Risk
The Pakistani regime has issues with maintaining and managing the economy in a steady tactic. The geopolitics and instability of the Pakistani regime leading to the financial crisis over the past few years has been caused by factors such a reduction in gross domestic product (GDP), a reduction in national income (NI), and deficiency of annual budgetary value in the yearly economic report. The yearly downsizing economy is causing an increase in poverty level, unemployment, and export–import differentiation. The poverty level and unemployment in the country hinders the construction of a road network within the country. Contrary to this, geopolitics and the failure of economically dynamic plan in the government sectors influences rural and urban area people within the host country and further increases the failure of the construction of the road network. Aforementioned factors have affected the ability of central government policies to prepare proper plans for controlling the indifferences in the government sectors, which may create risks in the construction road transportations network. Table 4 presents the Meso level of risk factors.

Table 4.
Meso-level risk for round 1.
Geopolitics and instability within ha.
4.1.4. Minor Risk
The reason for the independence of the host country is based on factors such as religion and cultural differences. The population’s inclination towards religion is strong, and they claim that spiritual activities from their ancestors are difficult to ignore without a proper reason. These religious activities and their associated places are veryimportant in urban and rural societies. However, the unique tribe and caste system in rural and urban areas makes for a strong society and is one of the major factors affecting project risk in the construction of the road network in the CPEC project. An expert panel stated that if someone is demolishing religious and historical places or has an influence on cultural activities, then the reaction rate is not favorable for aforesaid activity and inversely influences the project. The recent investigation through the Delphi technique expert panel argues that strong belief in religion and culture affected the construction of road network in the CPEC project. The mean and standard deviation value are demonstrated in Table 5. Table 5 presents the minor level of risk factors.

Table 5.
Minor-level risk for round 1.
4.2. Delphi Round-Two Approach
The second round of data analysis relates to three level indicators as well as value standardized by the percentage system. We have used the pairwise assessment method to analyze the standard weights of the first-level indicator, second-level indicators, and third-level indicator.
4.2.1. Macro Risk
The state has internal and external security issues. The security situation from the external side (Afghanistan war) has many challenges to maintain peaceful stability within the country. The security situation in the country harshly affects the hierarchy system. However, the inner uncertainty within the country hierarchy system is weak. Further, the weak hierarchy system influences government policies. Stakeholders and politicians also receive illicit incentives from government sectors to disrupt government policies and promote internal disputes. Moreover, illegal demand in the government sector leads to failure the construct road transportation network. Table 6 presents the macro level of risk factors for round 2.

Table 6.
Macro-level risk for round 2.
4.2.2. Meso Risk
In meso risk, economic stresses and schedule risk have higher responses in relation to recent investigation in round two. The burden of economic crises on government sectors could influence the lives of common people, which could lead to the failure of a construction road plan. Contrary to this, the time effect has a higher response rate regarding lack of social awareness from the government side, especially in the rural areas, towards road transportation network, which constitutes the primary failure of the road plan. Table 7 presents the Meso level of risk factors for round 2.

Table 7.
Meso-level risk for round 2.
4.2.3. Minor Risk
In minor risk for round two, high religious and strong cultural effects have been investigated on the construction of the road network. Religion and culture embrace faiths that may never change, as they are suppressed by people and are enthusiastically held. The demolishing of religious and historical buildings and constructing the road transportation network may lead to a negative influence on society. Table 8 presents the minor level of risk factors for round 2.

Table 8.
Minor-level risk for round 2.
5. Comparative Analysis Cycle One and Cycle Two
Through the recent investigation of cycle one and cycle two using the Delphi technique, we observed that risk factors in round one and two are analogous. Therefore, stakeholder support, security, terrorism, economic crises, unemployment within the country, and strong religious and cultural beliefs could hinder the contruction of the road network in the CPEC project. Mostly, the aforementioned factors could influence project cost, quality, and time. Whenever cost, quality, and time in any project increase, the risk factor of failure of the project also increases. Recent investigations into the construction industry used the Delphi technique (Jayasudha et al. 2014; Sourani and Sohail 2015).
6. Recommendations
We made a proposal based on the premise of three routes and recent investigation of the road transportation network. Moreover, we provide appropriate direction for the future significance of the road network plan, as follows:
- (1)
- The successful implementation of the road transportation network project and foresightedness concerning security side by adding additional security forces for CPEC project on each route;
- (2)
- Proper planning is needed to assist communication between stakeholders and CPEC officials. The conflict of interest between stakeholders and CPEC officials is a bad sign for road transportation network project.
- (3)
- Provide small contracts/tender to individuals near road network to achieve motivation and prosperity. Consequently, disseminated chances among the concerned area would be reduced.
- (4)
- Prevent the destruction of historical and holy sites. If decimating is necessary, then sacred sites should be shifted to new locations in the nearest neighborhood;
- (5)
- In the commercial hub area, the government should provide the necessary facilities and security for labor and business personnel;
- (6)
- Politician’s illicit demand is unsafe for the CPEC road plan. Therefore, proper decision-making is necessary to prevent illicit demand during construction;
- (7)
- Job opportunities should be given to people in affected areas to add to the stability of the project.
7. Conclusions
The CPEC road transportation network plan should promote bilateral economic trade connectivity in the Asian region in the future. However, it faces significant challenges in the road transportation network, such as stakeholder support, the security and terrorism situation, unemployment, and the economic crisis within the country, which may hinder the construction of the road network in the CPEC project. In the current work, we applied the Delphi technique to evaluate project risk with the aid of an expert panel. We have successfully provided insight regarding project risk through round one and two of the Delphi approach. This was accomplished by investigating related works broadly, and we observed that the Delphi technique successfully corroborated project risk through expert opinion. Furthermore, in the current study, critical recommendations have been reported to avoid project risk in the road network plan.
Author Contributions
S.A. (Sajjad Alam) and N.J. collected the data and prepared the first drift. Z.Y. supervised and mentored the work. A.A., S.A. (Sikander Ali), N.J. and A.N. jointly discussed, analyzed, and looked at the final drift.
Funding
The authors acknowledge the Hebei University of Technology for providing all the necessary materials pertaining to the completion of this paper. Sajjad Alam acknowledges the China Scholarship Council (CSC) for providing a scholarship towards his Master’s study from Hebei University of Technology, Tianjin, China.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Akintoye, Akintola S., and Malcolm J. MacLeod. 1997. Risk analysis and management in construction. International Journal of Project Management 15: 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Liaqat, Jianing Mi, Mussawar Shah, Syed Jamal Shah, Salim Khan, Rizwan Ullah, and Kausar Bibi. 2018. Local residents’ attitude toward road and transport infrastructure (a case of China Pakistan economic corridor). Journal of Chinese Economic and Foreign Trade Studies 11: 104–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyazit, Eda. 2015. Are wider economic impacts of transport infrastructures always beneficial? Impacts of the Istanbul metro on the generation of Spatio-economic inequalities. Journal of Transport Geography 45: 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- British Standards Institute. 2010. Project Management—Part 1: Principles and Guidelines for the Management of Projects. British Standards BS 6079-1. London: British Standards Institute. [Google Scholar]
- De Brito, J., and F. A. Branco. 2006. Bridge Management Policy Using Cost Analysis. Journal of Civil Engineering 244: 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Rashidy, Rawia Ahmed, and Susan M. Grant-Muller. 2014. An assessment method for highway network vulnerability. Journal of Transport Geography 34: 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiondella, Lance, Jun Liu, Sherif Tolba, Sanguthevar Rajasekaran, Reda Ammar, Ashraf-ur Rahman, Nicholas Lownes, and John Ivan. 2012. Game theoretic vulnerability analysis for the optimal defense of high-speed rail. Paper presented at 2012 IEEE Conference on Technologies for Homeland Security (HST), Waltham, MA, USA, November 13–15; pp. 305–11. [Google Scholar]
- Hallowell, Matthew R., and John A. Gambatese. 2009. Qualitative Research: Application of the Delphi Method to CEM Research. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management 136: 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastak, Markarand, and Aury Shaked. 2000. ICRAM-1 Model for international construction risk management. Journal of Management in Engineering 16: 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, K. Chaphalkar, and Mohammed Sagheer. 2010. Hierarchical Structuring of PPP Risks Using Interpretative Structural Modeling. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management 136: 150–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasudha, K., B. Vidivelli, and ER Gokul Surjith. 2014. Risk Assessment and Management in Construction Projects. International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research 5: 387–96. [Google Scholar]
- Judd, Robert C. 1972. Forecasting to consensus gathering: Delphi grows up to college needs. College & University Business 53: 35–38, 43. [Google Scholar]
- Laurenz, J. Laurenz, and Chris Verhoef. 2010. The Rise and Fall of the Chaos Report Figures. IEEE Software 27: 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Kang-Wook, Hwa-Uk Hong, Heedae Park, and Seung-Heon Han. 2009. Developing a Program Performance Management Framework for Mixed-use Development in Urban Regeneration Projects. Korean Journal of Construction Engineering and Management 12: 141–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Bing, and Robert L. K. Tiong. 1999. Risk management model for international construction joint ventures. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management 125: 377–84. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, Florence Yean Ying, and Linda Hoi. 2006. Risks faced by Singapore firms when taking construction projects in India. International Journal of Project Management 24: 261–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcguire, Robin K. 1999. Analyzing of Risk Factors in Construction. Journal of Civil Engineering 116: 76–S5. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, Vincent-Wayne, and Peter J. McGoldrick. 1994. The role of geodemographics in segmenting and targeting consumer markets: A Delphi study. European Journal of Marketing 28: 54–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulholland, B., and J. Christian. 1999. Risk Assessment in Construction Schedules. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management 125: 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, Christof, and Christof Sistenich. 2011. Results of a comparative application of QRA methodology for road tunnels in Germany. Paper presented at the 6th International Conference on Traffic and Safety in Road Tunnels, Hamburg, Germany, May 10–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, Min, Lijing Zhao, Liu Hong, and Zhezhe Pan. 2014. Comparisons of complex network-based models and real train flow model to analyze Chinese railway vulnerability. Reliability Engineering & System Safety 123: 38–46. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Kyu-young. 2009. A Development of Risk Identification Checklist for Stakeholders in the Construction Phase of the Urban Regeneration-Projects. Korean Journal of Construction Engineering and Management 10: 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Project Management Institute. 2000. A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PM Book Guide), 6th ed. Newtown Square: Project Management Institute. ISBN 978-1-62825-184-5. [Google Scholar]
- Rodney, Elodie, Yann Ledoux, Yves Ducq, and Denys Breysse. 2014. Integrating risks in project management. Paper presented at the 16th International Dependency and structure modeling Conference, Paris, France, July 2–4. [Google Scholar]
- Sourani, Amr, and M. Sohail. 2015. The Delphi Method: Review and Use in Construction Management Research. International Journal of Construction Education and Research 11: 54–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Yun, and Shuping Huang. 2019. Assessing the seismic vulnerability of urban road networks by a Bayesian network approach. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uher, E Thomas, and A. Ray Toakely. 1999. Risk management in the conceptual phase of a project. International Journal of Project Management 17: 161–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidman, Justin E., Kevin R. Miller, Jay P. Christofferson, and Jay S. Newitt. 2011. Best practices for dealing with price volatility in commercial construction. International Journal of Construction Education and Research 7: 276–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W. Y., and S. P. Lin. 2012. The Factor Analyses of Risk Decision Traps for Overseas Projects. Journal of Optimization in Infrastructure Management 24: 8–13. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zia-ur-rehman, and Tariq Aziz. 2017. The implications and Geo-Strategic Dimension of China—Pakistan Economic Corridor and its consequences and benefits overall. European Academic Research IV. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).