Abstract
The objective of this paper is to analyze the relationship between the social and environmental practices of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR), and the economic–financial, social, and environmental performance in Mozambican companies, from the managers’ perspectives. The data were collected from a sample of 227 companies through a survey questionnaire. We used structural equation modelling to analyze how the managers correlate the different social and environmental practices with performance at the financial, social, and environmental levels. The results showed that the relationship between all major components of the social and environmental practices, and the economic–financial, social, and environmental performance is positive but insignificant with the exception of the social practices of community support, which has a weak relationship with the economic–financial performance, environmental performance, and social performance, as well as the environmental practices. The data indicate that there is a need for strengthening the appropriate economic–financial incentive policies and strategies for the agents who promote good CSR practices in the country, in order to obtain satisfactory, measurable, and comparable economic–financial, social, and environmental performance.
1. Introduction
Climate change has become a topic of regular attention for societies in recent years and has been brought into the debate as an ‘inconvenient truth’ that requires a concerted policy approach (Kolk and Pinkse 2008). Business, by its very nature, has a significant impact on the environment and lifestyles of society. The business sector has the power to influence both present and future policy settings. The more that companies adhere to the philosophy and practices of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR), the more opportunity one has to prevent disasters and promote sustainable development (Barbieri and Cajazeira 2012).
With the development of the stakeholder theory, the philosophy and concept of CSR has been integrated into the systemic vision according to the ways companies relate dynamically with their stakeholders, whose actions affect the environment, and, from which, they also suffer the consequences. From this perspective, companies should be concerned not only with the interests of shareholders and investors, but also with socially responsible production methods. Given this reality, companies have started to integrate policies and strategies that promote social and environmental practices into their business plans (Carneiro and Rodrigues 2014). From this new approach to business management, a change has occurred in the business sector with the migration from philanthropy to CSR, which is founded on the voluntary relationship between social and environmental concerns from companies through their actions and interactions with employees, the community, suppliers and customers, shareholders and investors, public bodies, and nongovernmental organizations, among other stakeholders. Therefore, CSR is a new business management model that is based on sustainable ethics and preserving the interests of all parties that, directly or indirectly, are related to the company, as well as the interests of the whole society (Mello and Mello 2018). In this vision of business ethics, companies not only adhere to CSR to increase their economic and financial performance, but also their contribution to the well-being of their stakeholders and the community in which they are located, for the sake of sustainable development.
Today, the importance of CSR is undeniable, so much so that there is a worldwide movement around the topic. Proof of this are the numerous academic researches and initiatives promoted by business entities, NGOs, and bodies linked to the UN (Barbieri and Cajazeira 2012). However, scientific studies regarding the benefits of CSR and their impact on the performance of the company have contradictory results (Elliott et al. 2014; Gonçalves et al. 2021a; Hahn and Kühnen 2013; Hong et al. 2012; Huang and Watson 2015). Karabolad (2008) states that since its origin, the socio-environmental movement is not configured as an integrated and homogeneous movement. On the contrary, it presents a multifaceted character, due to the plurality of visions, values, and objectives in which the formation of a global movement incurs. While some company sectors see CSR as a financial waste, others see it as a strategy to increase their economic–financial, social, and environmental performance.
Given the above, the main objective of the present study is to identify the relationships between social and environmental CSR practices and the economic–financial, social, and environmental performance in Mozambican companies from the perspectives of their managers.
We use a survey questionnaire, which was adapted from the literature, to understand how managers perceive the main social and environmental practices in their business on a 5-point Likert scale, as well as their impact on the economic–financial, social, and environmental performance. We surveyed 227 firms under a stratified sampling. Using structural equation modelling, we analyzed how the respondents, which are top management or sustainability managers, perceive this relationship.
We contributed to the literature in several ways. Firstly, we analyzed the nexus between CSR practices and performance in a geography that is significantly understudied, Mozambique, which faces greater challenges in implementing a stakeholder view of business under the context of an underdeveloped economy. A large stream of literature on sustainability has called attention to the need for analysis of African countries (as well as other underdeveloped countries) from the firm level perspective, which is abundantly applicable to developed or developing economies, but is difficult to generalize for the former countries (Pinto et al. 2019).
Secondly, we address these matters from the point of view of the managers’ perspectives, which has a significant impact on business decisions. Previous research has focused on CSR impact on capital markets, stock, or financial performance (Boubaker et al. 2017, 2020; Benkraiem et al. 2021; Hunjra et al. 2021; Liu et al. 2021; Lu and Abeysekera 2021), and mostly using the public disclosure of the firms’ CSR (Pizzi et al. 2021). We analyze Mozambique, which has weak institutional settings and underdeveloped capital markets, requiring a different point of view in terms of research strategies. As such, we focus on the managers’ perspectives, which provides a proxy both for the firms’ actions and the perceived institutional pressures.
Finally, we perform our analysis under a structural equation modelling, which presents advantages when compared to the regression analysis that is overwhelmingly used in the previous literature. In fact, we are able to understand, with less restrictive assumptions, how the multiple interactions and perceptions of CSR practices impact the several layers of performance from the point of view of the managers.
Our results significantly point to a low consistency in the managers’ perceptions of the full extent of the consequences of the social and environmental practices on the several aspects of performance previously mentioned—i.e., economical–financial, social, and environmental. Although the association between those practices and their consequences on the several aspects of performance are correctly and consistently perceived by Mozambican managers, the correlation structure implied in their answers is worryingly low, pointing to challenges in the correct framing of the incentives for managers to incorporate CSR into their business model in order to reap the benefits of these consequences through performance. We find that managers only correlate, weakly, the implementation of social practices with achieving superior economic–financial and environmental performance and identify, weakly as well, the introduction of social practices with improvements in environmental performance. The remaining tested perceptions of the implications of the different CSR practices show an insignificant perceived impact on the different levels of performance.
The paper is structured as follows, the theoretical framework is presented in Section 2 and a literature review to enable the elaboration of the hypotheses is presented in Section 3. Section 4 presents the methodology. Section 5 presents the analysis of the results of the descriptive and factorial analysis, as well as the structural equation model. Finally, Section 6 presents the conclusions.
2. Theoretical Framework
The search for the social contributions of companies began to be a relevant topic in social debates during the neoliberalist period after World War II when the world was faced with a widespread social crisis, which was characterized by unemployment, irrational use of natural resources and subsequent scarcity, social exclusion, air and water pollution, social inequalities, and slave and child labor, among other social difficulties in the face of the ineffectiveness of governments to resolve them (Carneiro and Rodrigues 2014; Tenório 2006).
For Carroll (2008), it is useless to try to describe CSR practices before the 1950s. Business orientation prior to this decade focused on serving only the interests of the shareholders, which became insufficient with the need to incorporate political objectives and social and environmental actions into strategic business plans as a means of creating links between companies and society (Tenório 2006). From this period, some companies implemented certain practices to improve the well-being and performance of workers, as well as mitigate their problems, through the creation of facilities such as hospital clinics, social centers, and other incentives, among which was participation in company profits (Wren 2005). Until then, CSR practices were regarded as philanthropic (Ramesh 2010).
CSR has been framed under two theories: that of the Shareholder and that of the Interested Parties (Stakeholders). The former dates back to the 18th century and has undergone several developments. For the purposes of this study, Friedman (1962), a Nobel prize winner in economics, argued that the company has only one objective: economic performance. The second theory is based on the work of Freeman (1984). The two theories have different origins and are studied in different management fields. The shareholder theory is addressed in the area of finance, whose tradition is to employ quantitative methods in empirical studies. The stakeholder theory, on the other hand, has its origins in sociology, organizational behavior, and conflict management, where qualitative methods predominate in empirical studies. These differences in the conceptual origin and methodological approaches between the two theories are sufficient to explain the complexity surrounding the discussion of this theme.
According to Carroll (2008), it was as from a text by Friedman (1962) that the debate on CSR actually gained greater interest when accusing the doctrine of social responsibility of being subversive. Friedman’s (1962) ideas on this theme gained greater notoriety in the business world with a short article in the New York Times, in which the author categorically states that corporate responsibility is to generate profits within the scope of the law.
According to Friedman (1970), shareholders and managers who want to contribute to solving social problems should use their own resources and not those of the company. One of the purposes of this approach is to minimize the conflicts between owners and managers regarding the allocation of the company’s resources, bearing in mind the idea that the latter are agents of the owners and should therefore apply the company’s resources with a view to maximizing the return on invested capital. This approach led later to the Agency Theory, which we will not develop in this study.
Arrow (1997), also a winner of the Nobel prize in economics, shows situations where the profit maximizing rule is socially inefficient, for example, when there are unpaid costs—as in the case of pollution—or when the seller has considerably more information about his product than the buyer, particularly regarding safety. For reasons such as these, it is clearly desirable, according to the author, that there should be some idea about CSR that expresses ethical and legal obligations. As the author does not expect such responsibilities to be created spontaneously by the companies themselves, he recommends that they be institutionalized through regulations, codes of ethics, and taxes. These understandings expand the concept of corporate responsibility beyond the issues related to the shareholder–manager and recognize other stakeholders in its actions (Barbieri and Cajazeira 2012).
The stakeholder theory defines that the purpose of a business is to create as much value as possible for the stakeholders in order to be successful and sustainable over time. In business, managers must keep the interest of the employees and that of the stakeholders aligned and in the same direction.
Stakeholder theory has emerged as the dominant paradigm in CSR discussions. According to stakeholder theory, Freeman (1984) states that companies have relationships with many constituent groups that always have an interest in their activities and outcomes. These groups, among others, include employees, customers, suppliers, environmentalists, and the community as a whole (Donaldson and Preston 1995; Margolis and Walsh 2001).
The stakeholder theory is the basis of CSR (Donaldson and Preston 1995; Tench et al. 2007). Moreover, CSR has been presented as a tool to treat the stakeholders in a reasonable and responsible manner. In line with this line of argument, Khoury et al. (1999) and Velinov and Cincalova (2021) stated that CSR is the overall relationship between the organization and its internal and external stakeholders, including the customers, employees, communities, government, suppliers, business owners or investors, and competitors.
The stakeholder theory suggests that the social and environmental practices of companies are positively related to their economic–financial performance, since the improvement of the former increases the satisfaction of the stakeholders and, consequently, the external reputation of the company—reflecting on the whole as economic–financial progress (Allouche and Laroche 2005). In the view of these authors, CSR practices should not be seen as expenditures but rather as investments, since they have a positive influence on company performance.
3. Literature Review and Hypothesis Development
For decades, the literature has sought to find a relationship between social responsibility and corporate performance through a variety of methodologies, which on the whole have different meanings, from positive and negative to neutral relationships. Moskowitz (1972) was the first to find a positive relationship between the social performance and financial performance in listed companies. Parket and Eilbirt (1975) also found positive signs of this relationship. Later, the authors Pava and Krausz (1996), after a long literature review in the period from 1972 to 1992, also found a positive relationship in 12 out of 21 studies, and one with a negative relationship while the rest showed neutral relationships. Similarly, the authors Van Beurden and Gössling (2008) concluded that there was a positive relationship in 68% of the articles, while 6% showed a negative relationship and 26% had a neutral situation (da Silva Faria 2015).
According to Allouche and Laroche (2005) and Preston and O’Bannon (1997), the relationship between CSR and corporate economic performance is negative, which can be explained by two hypotheses. Firstly, the hypothesis emphasizes that the practice of social responsibility results in an increase in costs, which leads to the loss of competitive advantage in relation to less socially responsible companies. Thus, socially responsible companies will tend to achieve lower economic and financial performance. Secondly, the managerial opportunism trade-off hypothesis which states that when a firm’s accounting result is favorable, managers seek to increase their earnings by reducing social costs. Conversely, when the company’s economic–financial performance is poor, managers seek to improve social performance by incurring costs with socially responsible actions and attribute the poor results to the investments made in these actions.
Contrary to the previous idea that the whole process of CSR only entails expenses and costs for companies, and is only applied in accordance with legal requirements, the European Union argues that CSR can generate good results, advantages, profits, and growth for the companies themselves and for the economy in general. Thus, the authors Fernandes (2010) and Tsoutsoura (2004) present some advantages in adopting a CSR strategy, such as anticipating the problems and risks that may arise from their activities, and which cause deep scars on their image and survival; the reduction of costs arising from the activity, such as the reduction of consumption of natural resources and the management of waste produced; and enable a higher rate of innovation by taking advantage of opportunities and stimulating creativity. Innovation brings added value and higher perceived quality, making customers loyal.
In the same vein, Porter and Kramer (2006) also consider that instead of companies viewing CSR practices as detrimental, and therefore disconnected from business and strategy to the point of overshadowing many opportunities for them to benefit society, if they were to analyze their perspectives on social responsibility using the same frameworks that guide their core business choices, they would discover that CSR can be much more than a cost, constraint, or charitable action, but rather that it can be a source of opportunity, innovation, and competitive advantage.
In short, the effect of CSR practices is not uniform because not all of the stakeholders of companies consider the sustainability criterion in their decisions, which, therefore, Huang and Watson (2015) contradicts this trend of thinking that the relationship between social and environmental practices and company performance is always positive because, for them, although there is considerable evidence on the relationship between CSR and financial performance, the results are mixed—making it difficult to draw a definitive conclusion. In the same approach, Gonçalves et al. (2021a) and Margolis et al. (2009) argue that the relationship of CSR practices varies over time, suffering the effect of the innovation of technologies. Servaes and Tamayo (2013) reinforce this approach by proclaiming that the impacts of CSR on company performances depend on the level of customer or stakeholder awareness regarding CSR. Hahn and Kühnen (2013) also show divergent results on the relationship between CSR practices and firm performances in several studies analyzed by them.
A socially responsible company is not restricted to strict compliance with worker’s laws, it moves in the direction of constituting a community, refuses child labor, offers employees decent working conditions, and supports their families and the community in general (Tenório 2006).
The exercise of CSR social practices represents a method for the growth of companies, because they all essentially depend on support for the greater engagement of their employees. CSR social practices are beneficial to managers and employees because they give meaning and coherence to work activities. Employees feel good because they act according to their principles and values, thereby increasing their self-esteem. They feel happy and gratified, and their work and their lives gain new meaning because they are recognized and appreciated (Barbieri and Cajazeira 2012).
Several studies have shown a positive relationship between CSR practices and stakeholder satisfaction. Delautre and Abriata (2018) detected the positive relationship between the social dimension of CSR and economic performance. Albasu and Nyameh (2017) found that social practices can contribute in improving employee performance. For Lucato et al. (2018), social practices have positive impacts on consumer satisfaction and loyalty. Good social practices strongly influence financial performance and company reputation (Stanaland et al. 2011).
The approach of the relationship found between CSR social practices and business performances leads us to formulate the following hypotheses:
Hypothesis 1a (H1a).
Managers of Mozambican companies consider that social practices are positively related to economic–financial performance.
Hypothesis 1b (H1b).
Managers of Mozambican companies consider that social practices are positively related to social performance.
Hypothesis 1c (H1c).
Managers of Mozambican companies consider that social practices are positively related to environmental performance.
Many studies, such as those by Pondeville et al. (2013), have proven the positive relationship between environmental practices and company performances. They found that companies that are more proactive in environmental strategies are more likely to develop environmental practices.
Russo and Fouts (1997), based on a correlation analysis research, tested hypotheses of the relationship between environmental practices and a firm’s economic performance in 243 firms for two years and the results showed a positive relationship between environmental practices and the firms’ economic performances.
The studies conducted by Bagur-Femenias et al. (2013) and Baldarelli et al. (2017) explain how environmental practices positively affect the economic–financial, social, and environmental performances of the company. Environmental practices improve the efficiency of the company and its financial performance because they generate the same result using fewer economic resources. These environmental practices also improve the ability of companies to be viable in times of crisis. A reduction in fixed costs makes the cost structure more flexible and less volatile, as companies have a low break-even point, which results in improved competitiveness. Additionally, increased environmental awareness enables companies to determine whether their stakeholders’ expectations have been met before they become dissatisfied and sever their relationship with the company. When a company is a leader in applying environmental CSR practices, it enhances its reputation and also increases its level of sales and market share. Finally, environmental practices enable the development and establishment for the functioning of a comprehensive environmental management system that leads to significant benefits for human health.
Based on the survey done on the relationship between environmental CSR practices and company performances, it was possible to formulate the following hypotheses:
Hypothesis 2a (H2a).
Managers of Mozambican companies perceive a positive relationship between environmental practices and economic–financial performance.
Hypothesis 2b (H2b).
Managers of Mozambican companies perceive a positive relationship between environmental practices and social performance.
Hypothesis 2c (H2c).
Managers of Mozambican companies perceive a positive relationship between environmental practices and environmental performance.
Figure 1 shows the system of hypotheses (conceptual model) for the present study:
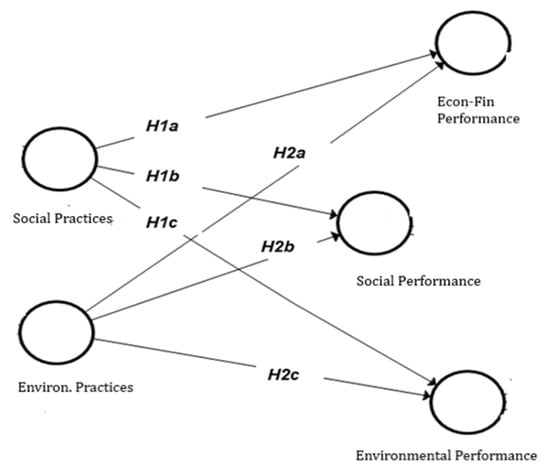
Figure 1.
Conceptual model.
4. Methodological Framework
The methodology of the study is exploratory, and is based on a factorial analysis and correlation of variables, as these explain the phenomena studied for the verification of the hypotheses. It is also characterized by an empirical and analytical study, under a structural equation model, using sample data for the achievement of the proposed objectives. Research of this nature assumes that the measures used are both accurate and reliable, and built from models that allow for description and show causal relationships (Ramírez 2010).
The sample was drawn from a 2017 database file of the National Institute of Statistics (INE), which had 99,158 legal entities (companies, non-profit institutions (NPIs), and public administration institutions), of which 74,525 are companies. The enterprises were classified according to the turnover (VN) and the number of staff in service (NPS), and using the scale from the Institute for the Promotion of Small and Medium Enterprises (IPEME)1, which is as follows: micro, small, medium, and large enterprises. From the universe of 74,525 units, due to the nature of the work, micro enterprises, small sole-proprietorship enterprises, and the activities of sections with very little environmental impact were excluded, thus constituting the sample base of 15,688.
To ensure representativeness, the sample size was distributed by branches of activities. For the present study, the sections of the Economic Activities Classification (CAE) were considered, according to the representativeness. The weight of each section was obtained by the ratio between the number of firms in each section and the total number of firms of the same size, which resulted in 227 firms. We developed a sample size, according to the different firms’ sizes, to meet a maximum sampling error of 10%.
The selection of the companies to be surveyed for each stratum was made by the systematic random selection method.
The sample covered firms from different parts of the country. Most of the companies are from Maputo city and Maputo province—with percentages of 48 and 17, respectively—given that these geographical places have more investments and a higher concentration of companies.
Data were collected by applying a questionnaire survey to the sample selected through stratified sampling according to the size and nature of the activities.
To find out the managers’ perceptions of CSR practices, the following question was asked:
- What do you think the company should gather as an indicator for compliance with CSR?
Different items identified and adapted from previous literature are offered as answers to the aforementioned question. Items include Social Responsibility Practices variables and Environmental Responsibility Practices variables.
To find out the perception of the respondents regarding the consequences of social and environmental CSR practices on the economic–financial, social, and environmental performance, the following question was asked:
- 2.
- In your opinion, what benefit can a company derive from practicing social and environmental responsibility actions?
Similarly, different items identified and adapted from previous literature are offered as answers to this survey question as well. Items include Economic–financial Performance variables, Social Performance variables, and Environmental Performance variables.
The items (statements to obtain the observed variables) of the questionnaire were on a Likert scale from 1 to 5 (1—Strongly Disagree to 5—Strongly Agree). Table 1 shows the operational variables (items):

Table 1.
Research Variables (Constructs) and Indicators (Survey questioned items).
We obtained a response rate of 100% from the sample defined to represent the Mozambican companies following the criteria previously mentioned. Taking into account the content and subject matter of the questions posed in the questionnaire, and in comparison with studies carried out in this area within the functions related to sustainability, the questionnaires were addressed to the heads of the sustainability departments—where these existed. In the absence of the departments in question, other managers were made responsible for completing the questionnaire. In order to assess the competence of the respondents, they were asked to indicate the number of years they had been with the company working in their respective function and their academic degree.
The respondents who are managers of sustainability departments were only 8 out of 227, which corresponds to 3.5%. Therefore, we worked with people who hold important management positions in companies, as they are people responsible for the company’s economic, social, and environmental issues.
About the seniority of the respondents in the company, it was found that most respondents had about 6 to 10 years in the company with an absolute frequency of 119, which corresponds to 52.4%. The other variable considered for the respondent was the knowledge they have acquired in other companies they have passed through. For this case, most of the respondents (45.4%) had between 6 to 10 years of professional experience, followed by employees with more than 15 years of professional experience with 20.7%.
Considering that the themes of corporate responsibility and sustainability have received much attention in research and part of training programs, due to their importance in the construction of a society and in a context where everyone is called upon to make their contribution to the sustainable development of companies and society, it was assumed that the higher the level of education, the greater the engagement would be as messenger of this new social and environmental paradigm. Thus, the academic degree of the respondents was also taken into consideration, with the master’s degree and the graduate degree occupying the majority of the sample (62.5%), which was a fact judged to be a requirement for having general knowledge of the relevance of the themes of corporate, social, and environmental responsibility (CSR).
5. Results
5.1. Descriptive Analysis and Internal Consistency
Social practices, as shown in Table 2, have a high internal consistency (Cronbach’s alpha α = 0.735). The main social practices perceived by managers of Mozambican companies that, according to the data, have higher averages and lower standard deviation, are:

Table 2.
Descriptive Statistics of “Social Responsibility Practices” survey indicators.
- The company must develop employee skills;
- The company must recruit employees with different socio-demographic characteristics (i.e., gender, age, race, disabled);
- The company must ensure the employees’ quality of life item;
- The company should promote actions to ensure employee satisfaction at work.
The practices with the lowest averages were:
- The company should spend time and money on community projects and charities;
- The company should have family support policies.
Although they have lower averages, these variables are important for the model as they also have a framework in the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) (UNDP 2015). In Mozambique, there are no specific regulations for social issues. The support for these practices is found in the various ratified international and regional conventions, and in various national legislation, namely the Constitution of the Republic that establishes the principle of universality and equality—of gender equality and of people with disabilities (Articles 35, 36 and 37, respectively)—Labor Law no.23/2007 of 1 August, which establishes the obligation of the employer to promote the adoption of adequate measures so that a worker with a disability or chronic disease enjoys the same rights and obeys the same duties as the other workers regarding access to employment, training, and professional promotion, as well as reduced working conditions (article 28); and Law no. 4/2007 of 7 February that establishes the legal framework on social security, among other norms that have a framework in the functions exercised by the Ministry of Gender, Children, and Social Action, as a competent organization, as indicated by the Government to direct and coordinate the execution of gender, children, and social action policies of the country in coordination with the Ministries of Labor, Social Security, State Administration, and Public Function.
According to Table 3, the data of the construct “Environmental Practices” has high internal consistency (Cronbach’s Alpha = 0.818). The main indicators of the environmental practices pointed out by respondents are: energy and water saving processes, reduction of products that harm the environment, environmental awareness, solid waste selection, and possession of an environmental management system. The variable with the highest discrepancy of values is “The company should include in its budget planning the purchase of environmentally responsible goods and services (ecological products)”.

Table 3.
Descriptive Statistics of “Environmental Responsibility Practices” survey indicators.
Most of these variables, in addition to being framed in the sustainable development goals (SDG) (UNDP 2015), have a large, specific national regulatory support, and international and regional conventions ratified by Mozambique. For this construct, there is a ministry that coordinates all activities on the environment and an agency that supervises the implementation of the activities of companies, which is subject to an environmental audit.
In Table 4, we observe that the descriptive statistics of the construct “Economic–Financial Performance”, which shows a high internal consistency between the data (Cronbach’s alpha 0.832).

Table 4.
Descriptive Statistics of “Economic and Financial Performance” survey indicators.
The variable that had the greatest discrepancy of values is the variable “low production costs”, which indicates little agreement from the respondents. According to them, the main advantage of social and environmental practices is “Saving energy and water” with the highest average of 4.06. The analysis indicates that more importance was given to natural resources issues, which shows some awareness of the scarcity of these.
According to the data in Table 5, the main social performance of social and environmental practices in companies is “Improves safety and health of workers in the workplace” with the highest average of 4.32 and the variable observed with the least agreement is “Improves the welfare of the company’s stakeholders”.

Table 5.
Descriptive Statistics of the variable “Social Performance” survey indicators.
It is notable that all variables deserved attention from the respondents as the averages are approximate, which shows that the managers recognize that environmental practices imply sustainable production methods, such as opting for greener and environmentally-friendly products that enable the company to reduce production costs and, consequently, raise environmental performance.
Table 6 presents the statistics of the construct “environmental performance” of the social and environmental CSR practices, where a high internal consistency of 0.776 is also observed. The main performance is “Improves environmental awareness” with an average of 4.25. The variable with less agreement from respondents is “Reduces energy and water consumption”, however, compared to other constructs, this was the construct that showed better averages in almost all variables, which shows that all the constructs have almost the same importance in the perspective of the respondents.

Table 6.
Descriptive statistics of the variable “Environmental Performance” survey indicators.
5.2. Factor Analysis: Principal Components
Factor analysis is carried out to understand the interdependencies (correlations) that exist between the variables. In this process, some information is lost, but a smaller number of variables are reached that are easier to work with. According to Hair et al. (2009), the purpose of the principal components analysis is to reach a simple structure that is easy to explain. The correlation between a variable and a factor is called factorial load. A principal components analysis (PCA) is one of the extraction methods of an exploratory factor analysis (FA), since the algorithm is the same. The two tools differ in terms of the intended objective, but they can present similar solutions depending on the data structure. In most cases, both PCA and FA reach the same results if the number of variables exceeds 30 or if communalities exceed 0.60 for most variables. For Tabachnick and Fidell (2007), in an empirical summary of the data set, the principal component analysis is a better choice.
Table 7 shows the main results of the principal component analysis performed. All constructs showed conditions for analysis since the determinant of the matrices is positive. Additionally, all constructs have sample adequacy conditions (KMO tests greater than 0.5).

Table 7.
Factor analysis and principal components extracted.
The constructs Social Practices and Environmental Performance showed sums for the percentages of the total variance explained (VTE) as less than 60%, so the variables with lower eigenvalues (communalities) were eliminated until reaching a VTE equal to or greater than 60%.
Through principal component analysis, new subconstructs were obtained, which grouped variables with similar characteristics.
5.3. Structural Equation Modelling
We performed structural equation modelling to test our conceptual model, as defined in the methodology section. Our analysis firstly addresses the measurement model to warrant model convergence in order to proceed with the results and implications of our structural model. Following previous literature, we defined and tested a formative measurement model since our constructs are formed out of the different items, from which we extracted the factors under the principal component analysis.
5.3.1. Validity of Model Convergence
The first aspect to be observed in the measurement models are the convergent validities, which were obtained from the average variance extracted (AVE) using Fornell and Larcker (1981), who establish that for the AVEs to be valid, they must be greater than 0.5 (AVE ˃ 0.5). The AVE is how much, on average, the observed variables (VO) positively correlate with their respective constructs or latent variables (VL). Therefore, when AVEs are greater than 0.5, it is accepted that the model converges to a satisfactory result (Sarstedt et al. 2011).
Table 8 shows the values of the internal consistency (Cronbach’s alpha—AC) and composite reliability (CC) of each latent variable, which both serve as indicators to measure whether the answers are reliable. AC or CC are satisfactory when they are greater than 0.6 and 0.7, respectively, for exploratory research (Hair et al. 2014). The values presented show satisfactory AVEs, Cronbach’s alphas, and composite reliability, which proves the convergence of the constructs in the model.

Table 8.
Convergent Validity.
5.3.2. Discriminant Validity
The discriminant validity (DV) of a model is defined as an indicator that assesses whether constructs or latent variables are independent of each other (Hair et al. 2014). Discriminant validity indicates whether or not the measurement variable of a given latent variable is correlated with the measurement variables of other constructs. According to the Fornell and Larcker (1981) criterion, the square roots of the AVEs of each construct are compared with the (Pearson) correlations between the constructs. Given this, the square roots of the AVEs should be greater than the correlations between the constructs (Ringle et al. 2014). For this study, as can be seen in Table 9, the discriminant validity is satisfactory because for all the components, the AVE is greater than their correlation with other constructs.

Table 9.
Discriminant Validity (Fornell and Larcker Criterion).
With the assurance of the Discriminant Validity, the measurement model adjustments were completed and then the structural model analysis was performed.
5.3.3. Discriminant Validity
The first analysis at this point is the evaluation of the Pearson’s coefficients of determination (R2). The R2 evaluates the portion of the variance of the endogenous variables that is explained by the structural model. It indicates the quality of the adjusted model. For the social and behavioral sciences area, R2 = 2% is classified as small effect, R2 = 13% as medium effect, and R2 = 26% as large effect. Table 10 shows that all constructs have large effects.

Table 10.
Pearson’s coefficients of determination (R2).
The Student’s t-test, whose purpose is to measure the significance of the correlations and regressions, was then evaluated. According to the criteria of Hair et al. (2014), we define the t ≥ 1.96 and the p-value ≤ 0.05. In Table 11, all the relationships between the components have acceptable significance except the relationships between Social Practices of Human Resource Development with Economic–Financial Performance and Social Performance, as they have p-values greater than 0.05 and t-values less than 1.96. Regarding the correlations between the variables observed with the constructs presented in Appendix A, it appears that all meet the conditions with the exception of variable DA5, “Increases the use of renewable resources”, given that t = 1.886.

Table 11.
Relationship between variables (Student’s t-test).
Subsequently, the values of the other model adjustment quality indicators were evaluated. These values are expressed as the Relevance or Predictive Validity (Q2), or the Stone–Geisser indicator and Effect Size (f2) or Cohen’s Indicator. Predictive validity (Q2) assesses how close the model is to what was expected of it (predictive quality or accuracy of the adjusted model). As an evaluation criterion, values greater than zero should be obtained (Hair et al. 2014). On the other hand, the Effect Size (f2) is obtained by including and excluding constructs from the model (one by one). It evaluates how much each construct is “useful” for the model fit. Values of 0.02, 0.15, and 0.35 are considered small, medium, and large, respectively (Hair et al. 2014).
For this study, as can be seen in Table 12, all dependent construct values are greater than zero, which proves good predictive quality and effect sizes that range from medium (Human Resource Development Social Practices; Community Support Social Practices; Social Performance and Environmental Performance) to large (Environmental Practices and Economic–Financial Performance).

Table 12.
Relevance or Predictive Validity (Q2) and Effect Size (f2).
Once the evaluation of the quality of fit of the model was concluded, we analyzed the path coefficients, or the correlations, between the constructs. The correlation coefficient between constructs can have a range of values from −1 to +1. Thus, a value of zero indicates no association between the two variables; a value greater than zero indicates a positive association, that is, as the value of one variable increases, so does the value of the other variable; and a value that is less than zero indicates a negative association, that is, as the value of one variable increases, the value of the other variable decreases (O’Brien 1979; Wong 2013). Additionally, following the previous literature; 0.9, positive or negative, indicates a very strong correlation; 0.7 to 0.9, positive or negative, indicates a strong correlation; values 0.5 to 0.7, positive or negative, indicates a moderate correlation; values between 0.3 to 0.5, positive or negative, indicate a weak correlation; and, finally, 0 to 0.3, positive or negative, indicates an insignificant correlation.
In Table 13 and Figure 2, it is observed that all constructs have insignificant relationships except for the relationships between Community Supportive Social Practices → Economic–Financial Performance; Community Supportive Social Practices → Environmental Performance and Environmental Practices → Social Performance, which recorded weak relationships.

Table 13.
Path Coefficients (correlations) between constructs.
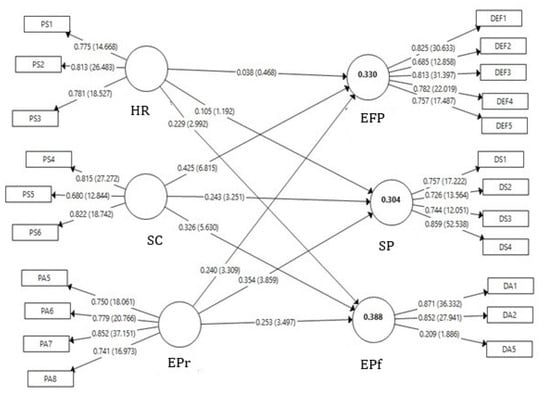
Figure 2.
Structural coefficients and t-values between constructs (between parentheses).
These results, although low—and similar to Gonçalves et al. (2020)—show agreement with the study of Delautre and Abriata (2018), who recorded a positive relationship between the social dimension of CSR and economic performance, and Lucato et al. (2018), who showed through a survey that social practices have positive impacts on consumer satisfaction and loyalty. Stanaland et al. (2011) also concluded that good social practices influence financial performance and company reputation. Several other studies, including Pondeville et al. (2013), Bagur-Femenias et al. (2013), and Baldarelli et al. (2017) concur with these findings by suggesting the positive relationship between these constructs. The studies, as in Gonçalves et al. (2021b), show that sustainable philosophy, principles, and techniques tend to contribute to the saving of resources invested in production. The results are also explained by the stakeholder theory, which suggests that social and environmental actions taken by a company increase its reputation or prestige in society.
Thus, the results prove the hypothesis that the social and environmental practices in Mozambique have a positive relationship with the economic–financial, social, and environmental performances of a company.
Based on this data, it was possible to verify that, in relation to the hypotheses presented above, the study had the following results:
Regarding H1a. (Managers of Mozambican companies consider that social practices are positively related with economic–financial performance); H1b. (Managers of Mozambican companies consider that social practices are positively related with social performance); and H1c. (Managers of Mozambican companies consider that social practices are positively related to environmental performance), are confirmed with an insignificant value in all main components of the social practices of human resources development with a relationship of 0.04, 0.1, and 0.2 for economic–financial, social, and environmental performance, respectively, and, for the social practices of community support with social performance, a relationship of 0.2. Note that for the first two correlations, there was also a t-value below the desirable 1.96 with a significance above 0.05.
For hypotheses H2a. (Managers of Mozambican companies perceive a positive relationship between environmental practices and economic–financial performance); H2b. (Managers of Mozambican companies perceive a positive relationship between environmental practices and social performance); and H2c. (Managers of Mozambican companies perceive a positive relationship between environmental practices and environmental performance) the correlation was insignificant for both the economic–financial performance and environmental performance with a 0.2 and a weak relationship for social performance.
The factorial loadings of each variable in relation to the principal component and latent variable, as well as the t-value of each observed variable presented in Figure 2, are also found in Appendix A. As can be observed of the variables that were considered for the model, all loadings are positive, and the t-values are greater than 1.96. The variables that were removed from the model were: PA1—The company must have clear and concrete policies; PA2—The company must include in budget planning the purchase of environmentally responsible goods and services (environmentally friendly products); PA3—The company must integrate in marketing and culture programs, environmental management plans, the environmental vision, and mission; PA4—The company must reduce the use of products that harm the environment; DA3—Reduces water and energy consumption; and DA4—Environmental Awareness. However, there were well analyzed variables that remained, and one specifically that verifies that their concept is more comprehensive and largely covers the objectives of the variables removed.
Our results shed significant light on the managers’ understanding and trust in applying social and environmental practices. We found evidence of a correct assessment of the relationship between those social and environmental practices on the social, environmental, and economic performance of the company, but those are not perceived strong enough to actually convince managers to, perhaps, incorporate them into their management initiatives.
6. Conclusions
The aim of the study was to understand the perspectives of Mozambican managers on the consequences of social and environmental CSR practices on company performance. To this end, hypotheses were developed on the relationship between CSR practices and economic–financial, social, and environmental performance. In general, all of them were confirmed, i.e., the data showed that managers are aware of the benefits of adhering to CSR practices, although the correlations are mostly insignificant. The data obtained confirms the results of various studies that justify the fact that social and environmental practices result in positive performance.
Our results significantly point to a low consistency in the managers’ perceptions of the full extent of the consequences of social and environmental practices on the previously mentioned aspects of performance—i.e., economic–financial, social, and environmental. Although the association between those practices and their consequences on the several aspects of performance are correctly and consistently perceived by Mozambican managers, the correlation structure implied in their answers are worryingly low, pointing to challenges in the correct framing of the incentives for managers to incorporate CSR into their business model in order to benefit from these consequences through the company’s performance. We found that managers only correlate, weakly, the implementation of social practices with achieving superior economic–financial and environmental performance and identify, weakly as well, the introduction of social practices with improvements in environmental performance. The remaining tested perceptions of the implications of the different CSR practices show an insignificant perceived impact on the different levels of performance.
We contribute to the literature in several ways. Firstly, we analyze the nexus between CSR practices and performance in a geography that is significantly understudied, Mozambique, which faces greater challenges in implementing a stakeholder view of business under the context of an underdeveloped economy. Secondly, we address these matters from the point of view of the managers’ perspectives, which have a significant impact on business decisions. Finally, we perform our analysis under structural equation modelling, which presents advantages when compared to the regression analysis that is overwhelmingly used in the previous literature. In fact, we are able to understand, with less restrictive assumptions, how the multiple interactions and perceptions of CSR practices impact the several layers of performance on the point of view of the managers.
From a practical perspective, our conclusions matter for companies, the government, academics, and society in general, and make these groups aware that the practice of CSR in Mozambique has benefits for a company’s business beyond social and environmental well-being, which will enable the formulation of appropriate strategies both to encourage adoption by companies and to make society, in general, more aware of the value of those that practice it.
As for the limitations, since this is a study on Mozambique, the results should be generalized to other locations with caution. One can also note that there is still little collaboration from companies for research of this nature, as some managers showed resistance in providing data for fear of damaging their business, which may have influenced the responses given that it is not possible to observe the facts reported.
This study also opens avenues for future research, such as analyzing the actual performance achieved by some companies that already practice social and environmental actions and examining whether there is a positive relationship over a certain period. It may also be relevant to use other variables not studied here and explore the existing relationship between CSR practices and the performance of a certain business sector.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.M. and T.C.G.; methodology, E.M. and T.G; software, E.M.; validation, E.M. and T.C.G.; formal analysis, E.M.; investigation, E.M. and T.C.G.; resources, T.C.G.; data curation, E.M.; writing—original draft preparation, E.M. and T.C.G.; writing—review and editing, T.C.G.; visualization, E.M. and T.C.G.; supervision, T.C.G.; project administration, E.M. and T.C.G.; funding acquisition, T.C.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
E.M. was funded by Camões IP under Programa de Cooperação ISEG/UL FACECO/UEM and T.C.G. was funded by FCT—Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia (Portugal), grant number UID/04521/2020, via Advance/CSG.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Interested readers may contact the corresponding author for acquiring relevant datasets generated in this research study.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to José Almeida for his assistantship.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Survey indicators factorial loadings.
Table A1.
Survey indicators factorial loadings.
| Variable Indicators | Codes | Factorial | Loadings | t-Student |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Social Responsibility Practices | Quality of life of employees | PS1 | 0.775 | 14.668 |
| Competence development of employees | PS2 | 0.813 | 26.483 | |
| Employee satisfaction | PS3 | 0.781 | 18.527 | |
| Social projects | PS4 | 0.815 | 27.272 | |
| Social Inclusion | PS5 | 0.680 | 12.844 | |
| Family support | PS6 | 0.822 | 18.742 | |
| Environmental Responsibility Practices | Energy and water savings | PA5 | 0.750 | 18.061 |
| Sorting solid waste | PA6 | 0.779 | 20.766 | |
| Environmental awareness | PA7 | 0.852 | 37.151 | |
| Environmental management system | PA8 | 0.741 | 16.973 | |
| Economic and financial performance | Low production costs | DEF1 | 0.825 | 30.633 |
| Energy and water savings | DEF2 | 0.685 | 12.858 | |
| It allows for low waste treatment rates | DFE3 | 0.813 | 31.397 | |
| Improves return on investment | DFE4 | 0.782 | 22.019 | |
| Increases the value of the company’s capital in the medium and long term | DFE5 | 0.757 | 17.487 | |
| Social Performance | Improves the well-being of stakeholders | DS1 | 0.757 | 17.222 |
| Improves the safety and health of the local community | DS2 | 0.726 | 13.564 | |
| Improve workers’ safety and health in the workplace | DS3 | 0.744 | 12.051 | |
| Improves information and reduces complaints from all stakeholders | DS4 | 0.859 | 52.538 | |
| Environmental Performance | Reduces solid waste production | DA1 | 0.871 | 36.332 |
| Decreases consumption of toxic/hazardous/harmful materials | DA2 | 0.852 | 27.941 | |
| Increases the use of renewable resources | DA5 | 0.209 | 1.886 |
Note
| 1 | The Institute for the Promotion of Small and Medium Enterprises (IPEME) is the Mozambican public institution whose mission is to encourage the establishment, consolidation and development of small enterprises in Mozambique. |
References
- Albasu, Joseph, and Jerome Nyameh. 2017. Relevance of Stakeholders Theory, Organizational Identity Theory and Social Exchange Theory to Corporate Social Responsibility and Employees Performance in the Commercial Banks in Nigeria. International Journal of Business, Economics and Management 4: 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allouche, José, and Patrice Laroche. 2005. A Meta-analytical investigation of the relationship between corporate social and financial performance. Revue de Gestion Des Ressources Humaines 57: 18. [Google Scholar]
- Arrow, Keneth J. 1997. Social Responsibility and Economic Efficiency. (A revised version of K. J. Arrow’s 1972 Carl Snyder Memorial Lecture). In Ethics in Business and Economics. Edited by Thomas Donaldson and Thomas W. Dunfee. Aldershot: Ashgate-Dartmouth, vol. 1, pp. 137–51. [Google Scholar]
- Bagur-Femenias, Llorenç, Josep Llach, and María del Mar Alonso-Almeida. 2013. Is the adoption of environmental practices a strategical decision for small service companies? An empirical approach. Management Decision 51: 41–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldarelli, Maria-Gabriella, Mara Del Baldo, and Ninel Nesheva-Kiosseva. 2017. Environmental Accounting and Reporting. Cham: Springer International Publishing AG. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, José Carlos, and Jorge Emanuel Cajazeira. 2012. Responsabilidade Social, Empresarial e Empresa Sustentável. Da Teoria à Prática, 2nd ed. São Paulo: Saraiva. [Google Scholar]
- Benkraiem, Ramzi, Sabri Boubaker, and Asif Saeed. 2021. How does corporate social responsibility engagement affect the information content of stock prices? Managerial and Decision Economics. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubaker, Sabri, Alexis Cellier, Riadh Manita, and Asif Saeed. 2020. Does corporate social responsibility reduce financial distress risk? Economic Modelling 91: 835–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubaker, Sabri, Lamia Chourou, Darlene Himick, and Samir Saadi. 2017. It’s about time! The influence of institutional investment horizon on corporate social responsibility. Thunderbird International Business Review 59: 571–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, Celia Maria Braga, and Alisson Victor Moreira Rodrigues. 2014. The determinants of Corporate Social Responsibility commitment to the internal public of companies. XVI ENGEMA. Available online: https://www.engema.org.br/XVIENGEMA/452.pdf (accessed on 13 May 2021).
- Carroll, Archie B. 2008. A History of Corporate Social Responsibility: Concepts and Practices. In The Oxford Handbook of Corporate Social Responsibility. Oxford: Oxford University Press, pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Faria, Maria José. 2015. Responsabilidade Social Empresarial—Relato e Análise Económica e Financeira. Porto: Vida Económica. [Google Scholar]
- Delautre, Guillaume, and Bruno Abriata. 2018. Corporate social responsibility: Exploring determinants and complementarities. ILO Research Department Working Paper. No. 38. Available online: http://englishbulletin.adapt.it/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/wcms_654735.pdf (accessed on 13 May 2021).
- Donaldson, Thomas, and Lee E. Preston. 1995. The Stakeholder Theory of the Corporation: Concepts, Evidence, and Implications. Academy of Management Review 20: 65–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, W. Brooke, Kevin E. Jackson, Mark E. Peecher, and Brian J. White. 2014. The Unintended Effect of Corporate Social Responsibility Performance on Investors’ Estimates of Fundamental Value. The Accounting Review 89: 275–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandes, Nuno Miguel A. 2010. A Responsabilidade Social das Empresas: A Dimensão Interna: Uma Ferramenta para a Criação de Valor [ISCAL—Instituto Superior de Contabilidade e Administração de Lisboa]. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10400.21/91 (accessed on 13 May 2021).
- Fornell, Claes, and David F. Larcker. 1981. Evaluating Structural Equation Models with Unobservable Variables and Measurement Error. Journal of Marketing Research 18: 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, R. Edward. 1984. Strategic Management: A Stakeholder Approach. Boston: Pitman. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, Milton. 1962. Capitalism and Freedom. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, Milton. 1970. The Social Responsibility of Business is to Increase Its Profits. The New York Times Magazine. September 13. Available online: https://www.nytimes.com/1970/09/13/archives/a-friedman-doctrine-the-social-responsibility-of-business-is-to.html (accessed on 13 May 2021).
- Gonçalves, Tiago, Cristina Gaio, and Eva Costa. 2020. Committed vs. opportunistic corporate and social responsibility reporting. Journal of Business Research 115: 417–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, Tiago, Cristina Gaio, and André Ferro. 2021a. Corporate social responsibility and earnings management: Moderating impact of economic cycles and financial performance. Sustainability 13: 9969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, Tiago, Diego Pimentel, and Cristina Gaio. 2021b. Risk and Performance of European Green and Conventional Funds. Sustainability 13: 4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, Rob. 2013. Back to basics: What do we mean by environmental (and social) accounting and what is it for?-A reaction to Thornton. Critical Perspectives on Accounting 24: 459–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, Rudiger, and Michael Kühnen. 2013. Determinants of sustainability reporting: A review of results, trends, theory, and opportunities in an expanding field of research. Journal of Cleaner Production 59: 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, Joseph F., William C. Black, Bill J. Babi, Rolph E. Anderson, and Ronald L. Tatham. 2009. Multivariate Data Analysis. Porto Alegre: Bookman Publisher. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, Joseph F., G. Thomas M. Hult, Christian Ringle, and Marko Sarstedt. 2014. A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM). Thousand Oaks: Sage Pub. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Harrison, Jeffrey Kubik, and Jose Scheinkman. 2012. Financial Constraints on Corporate Goodness. Cambridge: National Bureau of Economic Research. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Xiaobei B., and Luke Watson. 2015. Corporate social responsibility research in accounting. Journal of Accounting Literature 34: 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, Katrin, and Christian Schlick. 2016. The relationship between sustainability performance and sustainability disclosure—Reconciling voluntary disclosure theory and legitimacy theory. Journal of Accounting and Public Policy 35: 455–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hunjra, Ahmed I., Sabri Boubaker, Murugesh Arunachalam, and Asad Mehmood. 2021. How does CSR mediate the relationship between culture, religiosity and firm performance? Finance Research Letters 39: 101587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabolad, Natalia. 2008. The Paths and Challenges for Global Governance and Social and Environmental Responsibility as a Tool for Sustainability. In Responsabilidade Social nas Empresas: A Contribuição das Universidades. Edited by Bruno Gaspar. São Paulo: Peirópolis, vol. 6. [Google Scholar]
- Khoury, George, Janet Rostami, and Peri Lynn Turnbull. 1999. Corporate Social Responsibility: Turning Words into Action. Ottawa: The Conference Board of Canada. [Google Scholar]
- Kolk, Ans, and Jonatan Pinkse. 2008. A perspective on multinational enterprises and climate change: Learning from “an inconvenient truth”? Journal of International Business Studies 39: 1359–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Bai, Tao Ju, and Simon S. Gao. 2021. The combined effects of innovation and corporate social responsibility on firm financial risk. Journal of International Financial Management & Accounting 32: 283–310. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Yingjun, and Indra Abeysekera. 2021. Do investors and analysts value strategic corporate social responsibility disclosures? Evidence from China. Journal of International Financial Management & Accounting 32: 147–81. [Google Scholar]
- Lucato, Wagner C., Jose Carlos da Silva Santos, and Athos Paulo T. Pacchini. 2018. Measuring the sustainability of a manufacturing process: A conceptual framework. Sustainability 10: 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Margolis, Joshua D., Hillary Anger Elfenbein, and James P. Walsh. 2009. Does It Pay to Be Good...and Does It Matter? A Meta-Analysis of the Relationship between Corporate Social and Financial Performance. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=1866371 (accessed on 13 May 2021).
- Margolis, Joshua D., and James P. Walsh. 2001. Misery Loves Companies: Whither Social Initiatives by Business? Boston: Division of Research, Harvard Business School. [Google Scholar]
- Mello, Mario Fernando, and Arthur Zago Mello. 2018. An analysis of the practices of social responsibility and sustainability as strategies for industrial companies in the furniture sector: A case study. Gestao e Producao 25: 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moskowitz, Milton. 1972. Choosing socially responsible stocks. Business and Society Review 1: 71–75. [Google Scholar]
- O’Brien, Robert M. 1979. The Use of Pearson’s with Ordinal Data. American Sociological Review 44: 851–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parket, I. Robert, and Henry Eilbirt. 1975. The practice of business social responsibility: The underlying factors. Business Horizons 18: 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pava, Moses L., and Joshua Krausz. 1996. The association between corporate social-responsibility and financial performance: The paradox of social cost. Journal of Business Ethics 15: 321–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, Inês, Cristina Gaio, and Tiago Gonçalves. 2019. Corporate governance, foreign direct investment, and bank income smoothing in African countries. International Journal of Emerging Markets 15: 670–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzi, Simone, Maria Del Baldo, Fabio Caputo, and Andrea Venturelli. 2021. Voluntary disclosure of Sustainable Development Goals in mandatory non-financial reports: The moderating role of cultural dimension. Journal of International Financial Management & Accounting. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pondeville, Sophie, Valerie Swaen, and Yves De Rongé. 2013. Environmental management control systems: The role of contextual and strategic factors. Management Accounting Research 24: 317–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, Michael E., and Mark R. Kramer. 2006. The link between competitive Advantage and corporate social responsibility. Harvard Business Review 84: 78–92. [Google Scholar]
- Preston, Lee E., and Douglas P. O’Bannon. 1997. The Corporate Social-Financial Performance Relationship: A Typology and Analysis. Business & Society 36: 419–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, G. 2010. Mainstreaming an Unorganized Industry: The Case of Suguna Poultry. Vikalpa 35: 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramírez, Tulio. 2010. Cómo hacer un proyecto de investigación. Caracas: Panapo. [Google Scholar]
- Ringle, Christian M., Dirceu Da Silva, and Diogenes de Souza Bido. 2014. Modelagem de Equações Estruturais com Utilização do Smartpls. Revista Brasileira de Marketing 13: 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, Michael V., and Paul A. Fouts. 1997. A resouce-perspective on corporate environment perfomance and profitability. Academy of Management Journal 40: 534–59. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/245040725_Russo_M_V_P_A_Fouts_1997_A_Resource-Based_Perspective_on_Corporate_Environmental_Performance_and_Profitability_Academy_of_Management_Journal (accessed on 13 May 2021).
- Sarstedt, Marko, Jorg Henseler, and Christian M. Ringle. 2011. Multigroup Analysis in Partial Least Squares (PLS) Path Modeling: Alternative Methods and Empirical Results. Measurement and Research Methods in International Marketing 22: 195–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servaes, Henri, and Ane Tamayo. 2013. The Impact of Corporate Social Responsibility on Firm Value: The Role of Customer Awareness. Management Science 59: 1045–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stanaland, Andrea J. S., May O. Lwin, and Patrick E. Murphy. 2011. Consumer Perceptions of the Antecedents and Consequences of Corporate Social Responsibility. Journal of Business Ethics 102: 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabachnick, Barbara G., and Linda S. Fidell. 2007. Using Multivariate Statistics, 5th ed. Boston: Pearson/Allyn & Bacon. [Google Scholar]
- Tench, Ralph, Ryan Bowd, and Brian Jones. 2007. Perceptions and perspectives: Corporate social responsibility and the media. Journal of Communication Management 11: 348–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenório, Fernando G. 2006. Responsabilidade Social Empresarial: Teoria E Prática, 2nd ed. Rio de Janeiro: Editora FGV. [Google Scholar]
- Tsoutsoura, Margarita. 2004. Corporate Social Responsibility and Financial Performance. Berkeley: Center for Responsible Business, Available online: https://escholarship.org/uc/item/111799p2 (accessed on 13 May 2021).
- UNDP. 2015. The Sustainable Development Goals. Available online: http://www.pnud.org.br/ods.aspx (accessed on 13 May 2021).
- Van Beurden, Pieter, and Tobias Gössling. 2008. The worth of values—A literature review on the relation between corporate social and financial performance. Journal of Business Ethics 82: 407–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Velinov, Emil, and Simona Cincalova. 2021. Corporate Social Responsibility and Internationalization of Czech Transport Enterprises. Hradec Economic Days. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Ken Kwong-Kay. 2013. Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) Techniques Using SmartPLS. Marketing Bulletin 24: 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Wren, Daniel A. 2005. History of Management Thought, 5th ed. Hoboken: John Wiley and Sons, Inc. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).