Identification of CP12 as a Novel Calcium-Binding Protein in Chloroplasts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Identification of Novel Chloroplast Calcium-Binding Proteins
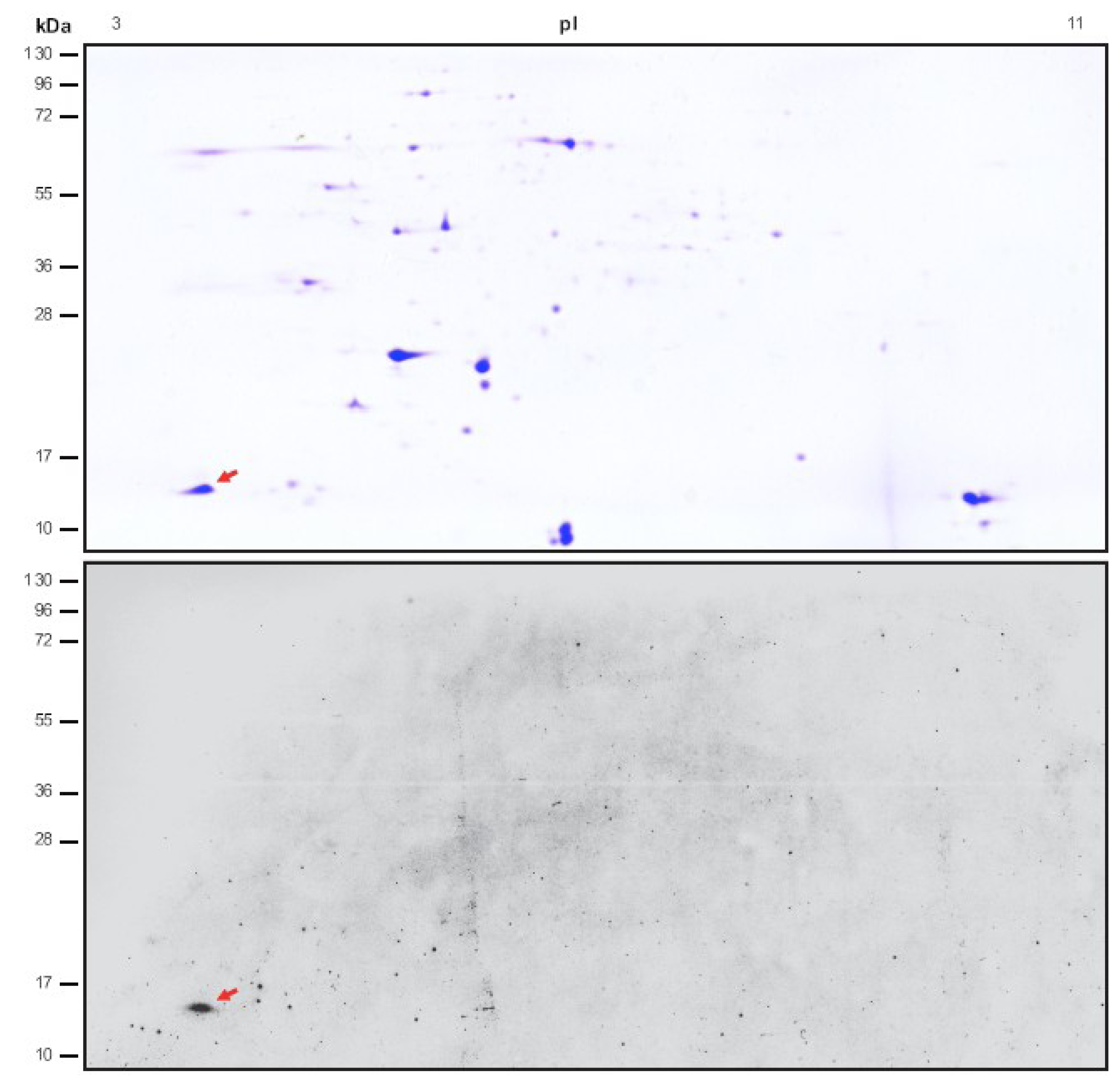

2.2. CP12 Binds Calcium with High Affinity
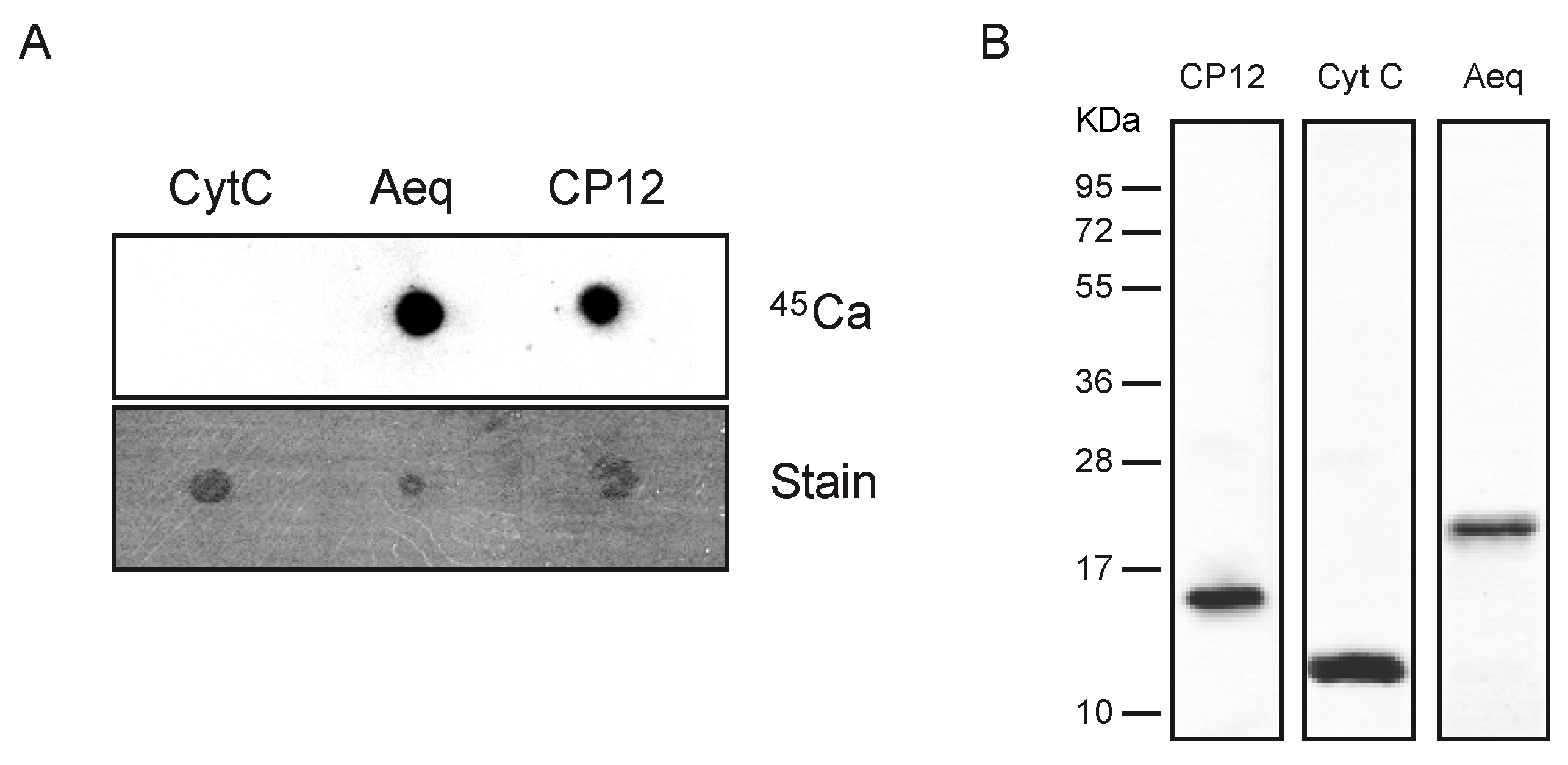
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Plant Growth and Preparation of Chloroplast Proteins
3.2. Proteins Separation by 2D IEF-SDS PAGE
3.3. Mass Spectrometry Analysis
3.4. Radioactive Calcium Overlay Assays
3.5. Expression and Purification of Recombinant CP12
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Supplementary Materials

Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berridge, M.J.; Lipp, P.; Bootman, M.D. The versatility and universality of calcium signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 1, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapham, D.E. Calcium signaling. Cell 2007, 131, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, A.G.; Vothknecht, U.C. The role of calcium in chloroplasts—An intriguing and unresolved puzzle. Protoplasma 2012, 249, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heredia, P.; de Las Rivas, J. Calcium-dependent conformational change and thermal stability of the isolated PsbO protein detected by FTIR Spectroscopy. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 11831–11838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, J.; Burda, K.; Jemiola-Rzeminska, M.; Strzalka, K. The 33 kDa protein of photosystem II is a low-affinity calcium- and lanthanide-binding protein. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 14862–14867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shutova, T.; Nikitina, J.; Deikus, G.; Andersson, B.; Klimov, V.; Samuelsson, G. Structural dynamics of the manganese-stabilizing protein-effect of pH, calcium, and manganese. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 15182–15192. [Google Scholar]
- Surek, B.; Kreimer, G.; Melkonian, M.; Latzko, E. Spinach ferredoxin is a calcium-binding protein. Planta 1987, 171, 565–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.C.; Tang, R.H.; Anderson, L.K.; Woerner, T.E.; Pei, Z.M. A cell surface receptor mediates extracellular Ca2+ sensing in guard cells. Nature 2003, 425, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, H.; Komori, T.; Kobori, M.; Nakahira, Y.; Shiina, T. Evidence for chloroplast control of external Ca2+-induced cytosolic Ca2+ transients and stomatal closure. Plant J. 2008, 53, 988–998. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, R.H.; Han, S.C.; Zheng, H.L.; Cook, C.W.; Choi, C.S.; Woerner, T.E.; Jackson, R.B.; Pei, Z.M. Coupling diurnal cytosolic Ca2+ oscillations to the CAS-IP3 pathway in Arabidopsis. Science 2007, 315, 1423–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinl, S.; Held, K.; Schlucking, K.; Steinhorst, L.; Kuhlgert, S.; Hippler, M.; Kudla, J. A plastid protein crucial for Ca2+-regulated stomatal responses. New Phytol. 2008, 179, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vainonen, J.P.; Sakuragi, Y.; Stael, S.; Tikkanen, M.; Allahverdiyeva, Y.; Paakkarinen, V.; Aro, E.; Suorsa, M.; Scheller, H.V.; Vener, A.V.; et al. Light regulation of CaS, a novel phosphoprotein in the thylakoid membrane of Arabidopsis thaliana. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 1767–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stael, S.; Rocha, A.G.; Wimberger, T.; Anrather, D.; Vothknecht, U.C.; Teige, M. Cross-talk between calcium signalling and protein phosphorylation at the thylakoid. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 1725–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, S.; Kretsinger, R.H. Evolution of the EF-hand family of proteins. Ann. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 1994, 23, 473–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.S.; Ali, G.S.; Reddy, A.S.N. Genes encoding calmodulin-binding proteins in the arabidopsis genome. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 9840–9852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Poovaiah, B.W. Arabidopsis chloroplast chaperonin 10 is a calmodulin-binding protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 275, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buaboocha, T.; Liao, B.; Zielinski, R.E. Isolation of cDNA and genomic DNA clones encoding a calmodulin-binding protein related to a family of ATPases involved in cell division and vesicle fusion. Planta 2001, 212, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussemer, J.; Chigri, F.; Vothknecht, U.C. Arabidopsis ATPase family gene 1-like protein 1 is a calmodulin-binding AAA+-ATPase with a dual localization in chloroplasts and mitochondria. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 3870–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, R.G.; Stael, S.; Csaszar, E.; Teige, M. Mining the soluble chloroplast proteome by affinity chromatography. Proteomics 2011, 11, 1287–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, M.; Salvi, D.; Brugiere, S.; Miras, S.; Kowalski, S.; Louwagie, M.; Garin, J.; Joyard, J.; Rolland, N. Proteomics of the chloroplast envelope membranes from Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2003, 2, 325–345. [Google Scholar]
- Stael, S.; Rocha, A.G.; Robinson, A.J.; Kmiecik, P.; Vothknecht, U.C.; Teige, M. Arabidopsis calcium-binding mitochondrial carrier proteins as potential facilitators of mitochondrial ATP-import and plastid SAM-import. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 3935–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozawa, Y.; Nozawa, A.; Kanno, T.; Narisawa, T.; Masuda, S.; Kasai, K.; Nanamiya, H. Calcium-activated (p)ppGpp synthetase in chloroplasts of land plants. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 35536–35545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, M.R.; Gasteiger, E.; Bairoch, A.; Sanchez, J.C.; Williams, K.L.; Appel, R.D.; Hochstrasser, D.F. Protein identification and analysis tools in the ExPASy server. Methods Mol. Biol. 1999, 112, 531–552. [Google Scholar]
- Emanuelsson, O.; Nielsen, H.; von Heijne, G. ChloroP, a neural network-based method for predicting chloroplast transit peptides and their cleavage sites. Protein Sci. 1999, 8, 978–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seigneurin-Berny, D.; Salvi, D.; Dorne, A.J.; Joyard, J.; Rolland, N. Percoll-purified and photosynthetically active chloroplasts from Arabidopsis thaliana leaves. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 46, 951–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, K.; Mikawa, T.; Ebashi, S. Detection of calcium-binding proteins by 45Ca autoradiography on nitrocellulose membrane after sodium dodecyl-sulfate gel-electrophoresis. J. Biochem. 1984, 95, 511–519. [Google Scholar]
- Wedel, N.; Soll, J.; Paap, B.K. CP12 provides a new mode of light regulation of Calvin cycle activity in higher plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 10479–10484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedel, N.; Soll, J. Evolutionary conserved light regulation of Calvin cycle activity by NADPH-mediated reversible phosphoribulokinase/CP12/glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase complex dissociation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 9699–9704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebreton, S.; Graciet, E.; Gontero, B. Modulation, via protein-protein interactions, of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase activity through redox phosphoribulokinase regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 12078–12084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, S.; Easterby, J.S.; Powls, R. Properties of a multimeric protein complex from chloroplasts possessing potential activities of NADPH-dependent glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and phosphoribulokinase. Eur. J. Biochem. 1987, 162, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obrien, M.J.; Easterby, J.S.; Powls, R. Algal glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenases conversion of NADH-linked enzyme of scenedesmus-obliquus into a form which preferentially uses NADPH as coenzyme. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1976, 449, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boggetto, N.; Gontero, B.; Maberly, S.C. Regulation of phosphoribulokinase and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase in a freshwater diatom, Asterionella formosa. J. Phycol. 2007, 43, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erales, J.; Gontero, B.; Maberly, S.C. Specificity and function of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase in a freshwater diatom, Asterionella formosa (Bacillariophyceae). J. Phycol. 2008, 44, 1455–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marri, L.; Zaffagnini, M.; Collin, V.; Issakidis-Bourguet, E.; Lemaire, S.D.; Pupillo, P.; Sparla, F.; Miginiac-Maslow, M.; Trost, P. Prompt and easy activation by specific thioredoxins of Calvin cycle enzymes of Arabidopsis thaliana associated in the GAPDH/CP12/PRK supramolecular complex. Mol. Plant 2009, 2, 259–269. [Google Scholar]
- Graciet, E.; Lebreton, S.; Camadro, J.-M.; Gontero, B. Characterization of native and recombinant A4 glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Eur. J. Biochem. 2003, 270, 129–136. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, T.P.; Fryer, M.J.; Singh, P.; Metodiev, M.; Lytovchenko, A.; Obata, T.; Fernie, A.R.; Kruger, N.J.; Quick, W.P.; Lloyd, J.C.; et al. Antisense suppression of the small chloroplast protein CP12 in tobacco alters carbon partitioning and severely restricts growth. Plant Physiol. 2011, 157, 620–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamoi, M.; Miyazaki, T.; Fukamizo, T.; Shigeoka, S. The Calvin cycle in cyanobacteria is regulated by CP12 via the NAD(H)/NADP(H) ratio under light/dark conditions. Plant J. 2005, 42, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, W.L.; Waller, J.C.; Vanderbeld, B.; Snedden, W.A. Cloning and characterization of two NAD kinases from Arabidopsis. Identification of a calmodulin binding isoform. Plant Physiol. 2004, 135, 1243–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chardot, T.; Meunier, J.-C. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate and calcium activate oxidized spinach (Spinacia oleracea) chloroplast fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. Plant Sci. 1990, 70, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadet, F.; Meunier, J.C. Spinach (Spinacia oleracea) chloroplast sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphatase. activation and deactivation, and immunological relationship to fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. Biochem. J. 1988, 253, 243–248. [Google Scholar]
- Charles, S.A.; Halliwell, B. Action of calcium-ions on spinach (Spinacia-Oleracea) chloroplast fructose bisphosphatase and other enzymes of the Calvin cycle. Biochem. J. 1980, 188, 775–779. [Google Scholar]
- Portis, A.R., Jr.; Heldt, H.W. Light-dependent changes of the Mg2+ concentration in the stroma in relation to the Mg2+ dependency of CO2 fixation in intact chloroplasts. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 1976, 449, 434–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolosiuk, R.A.; Hertig, C.M.; Nishizawa, A.N.; Buchanan, B.B. Enzyme regulation in C4 photosynthesis. Role of Ca2+ in thioredoxin-linked activation of sedoheptulose bisphosphatase from corn leaves. FEBS Lett. 1982, 140, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sai, J.; Johnson, C.H. Dark-stimulated calcium ion fluxes in the chloroplast stroma and cytosol. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 1279–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettinger, W.F.; Clear, A.M.; Fanning, K.J.; Peck, M.L. Identification of a Ca2+/H+ antiport in the plant chloroplast thylakoid membrane. Plant Physiol. 1999, 119, 1379–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Rocha, A.G.; Vothknecht, U.C. Identification of CP12 as a Novel Calcium-Binding Protein in Chloroplasts. Plants 2013, 2, 530-540. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants2030530
Rocha AG, Vothknecht UC. Identification of CP12 as a Novel Calcium-Binding Protein in Chloroplasts. Plants. 2013; 2(3):530-540. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants2030530
Chicago/Turabian StyleRocha, Agostinho Gomes, and Ute C. Vothknecht. 2013. "Identification of CP12 as a Novel Calcium-Binding Protein in Chloroplasts" Plants 2, no. 3: 530-540. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants2030530
APA StyleRocha, A. G., & Vothknecht, U. C. (2013). Identification of CP12 as a Novel Calcium-Binding Protein in Chloroplasts. Plants, 2(3), 530-540. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants2030530



