Identification of Transcription Factors of GmHPL Involved in Modulating Pathogen Stresses in Soybean
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
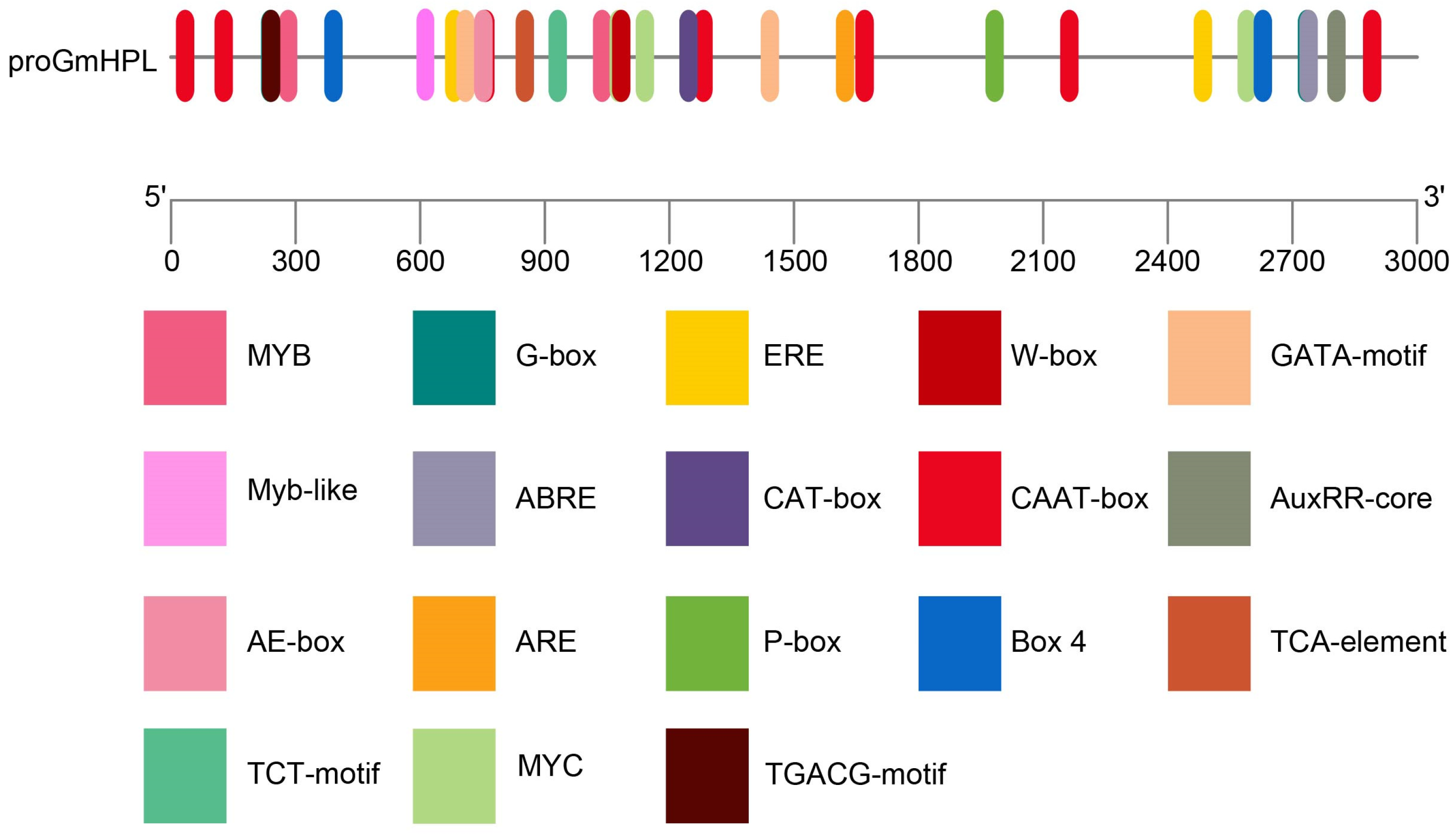
2.1. Characterization of GmHPL Promoter
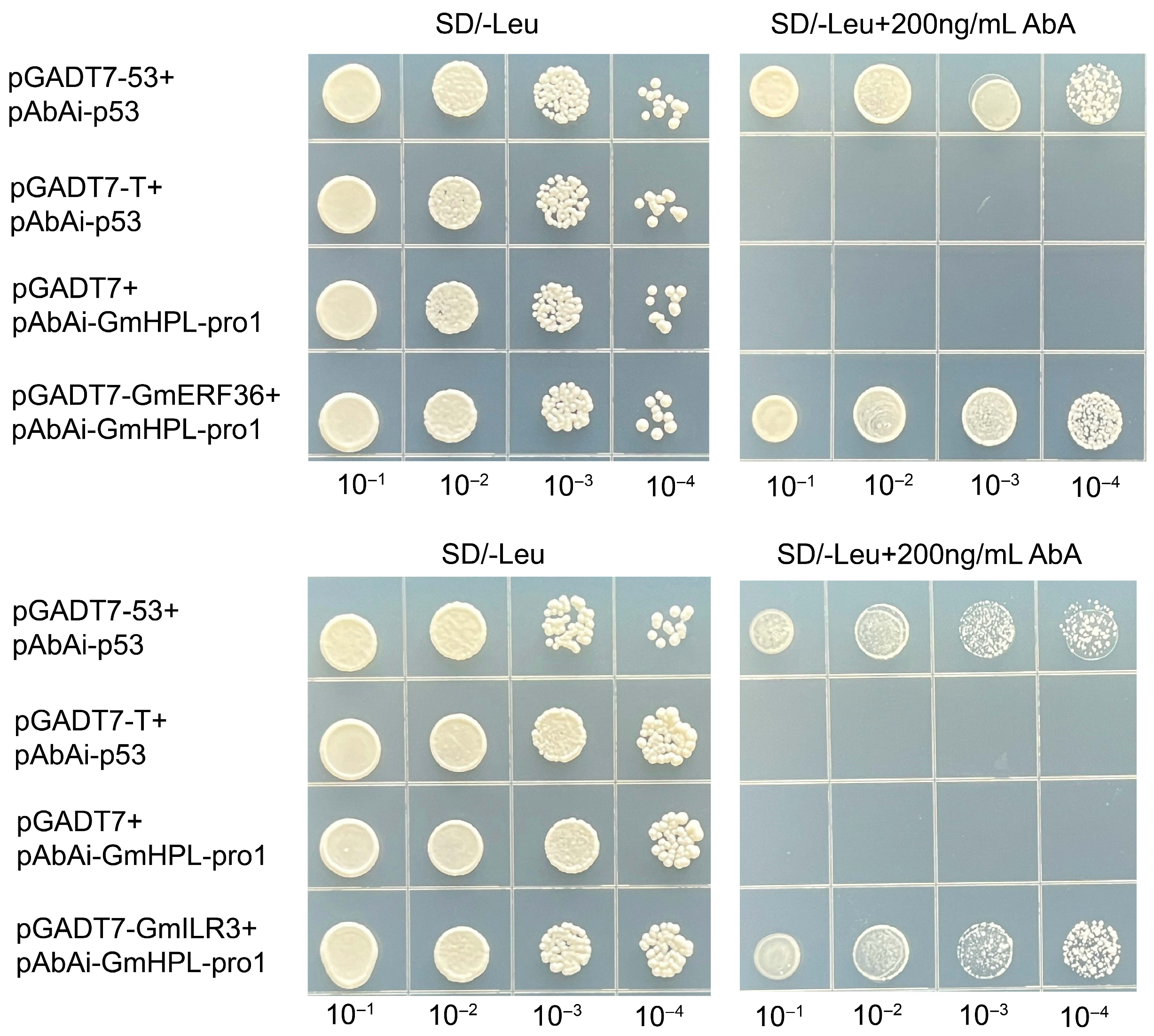
2.2. Two Transcription Factors of GmHPL Were Identified Through Yeast One-Hybrid Assay
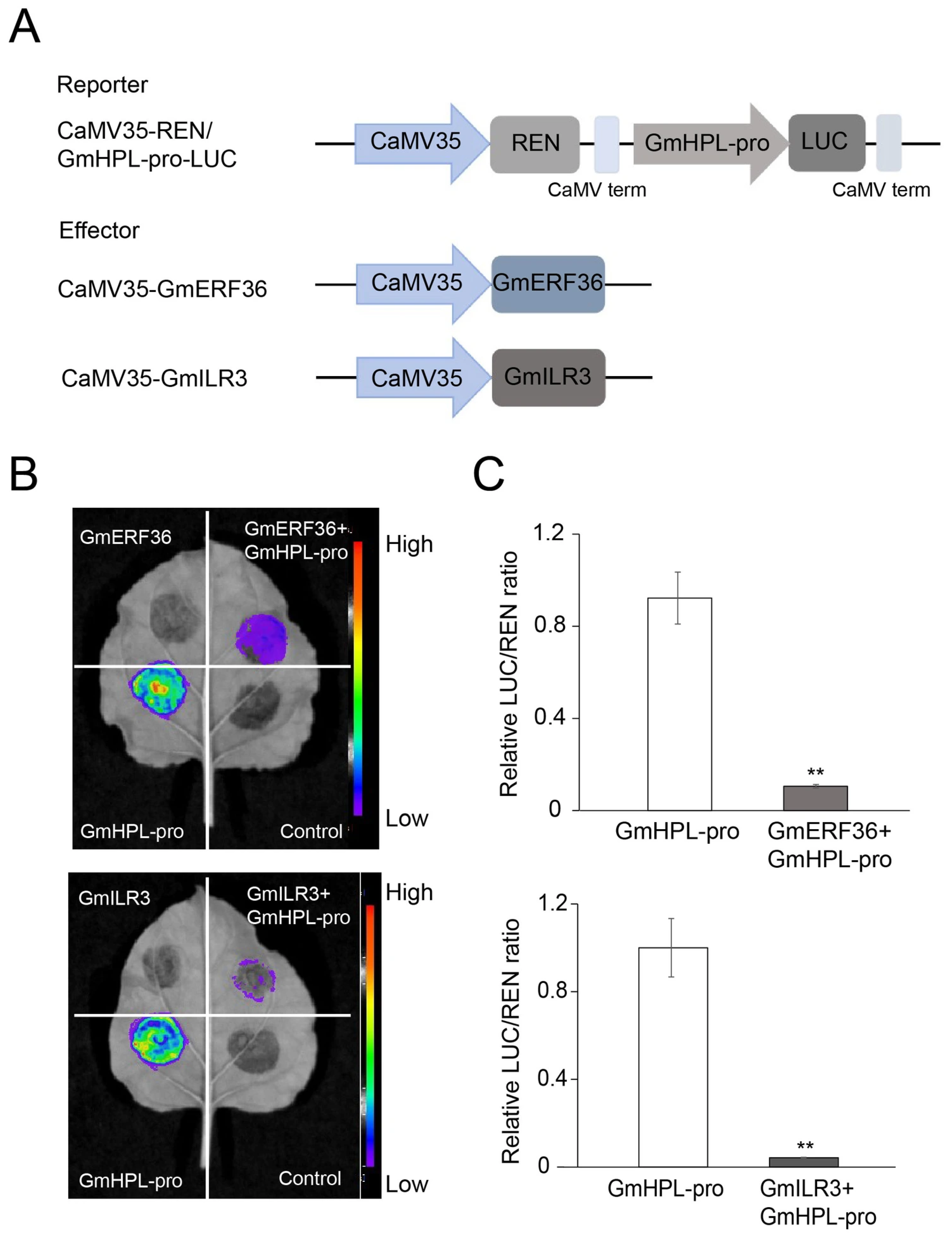
2.3. GmERF36 and GmILR3 Inhibited the Protein Levels of GmHPL
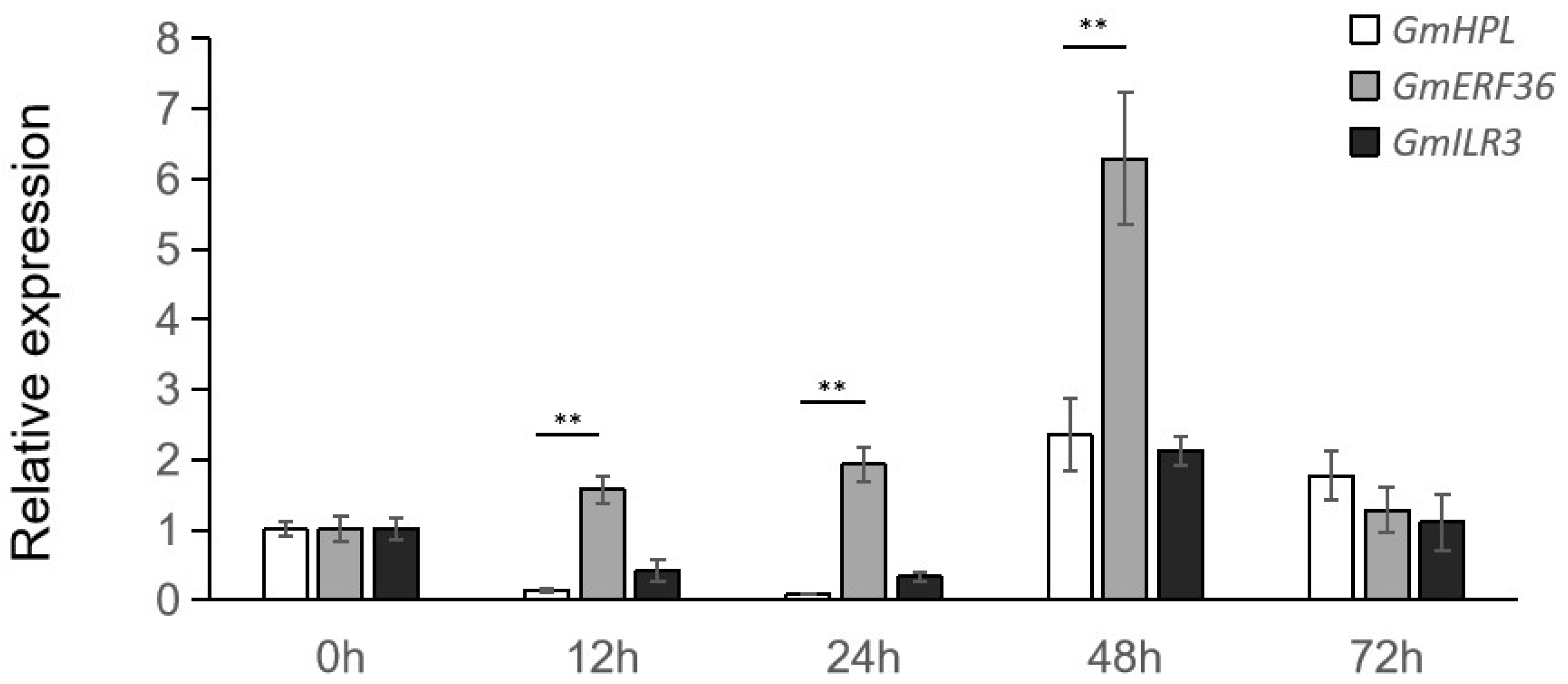
2.4. Expression Level of GmHPL Induced by C. truncatum Was Partially Dependent on GmERF36
| Primer Name | Forward Primer (5′—3′) | Reverse Primer (5′—3′) |
|---|---|---|
| GmActin-qRT | GGTGGTTCTATCTTGGCATC | CTTCGCTTCAATAACCCTA |
| GmHPL-qRT | CTTCCTCGTCGGTGGAAACT | CCGTAGGAGTTGAAGCCCAG |
| GmERF36-qRT | GACCTCCTCGAACCCGAAAT | CGATTAGCAGCGACGGTTTC |
| GmILR3-qRT | GTTGATCGACGACGACGTTAT | TTAGGCCATCAGAATCCCCA |
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
4.2. Yeast One-Hybrid Analysis
4.3. Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay
4.4. Treatment with C. truncatum
4.5. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deboever, E.; Deleu, M.; Mongrand, S.; Lin, L.; Fauconnier, M. Plant–pathogen interactions: Underestimated roles of phyto-oxylipins. Trends Plant Sci. 2020, 25, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feussner, I.; Wasternack, C. The lipoxygenase pathway. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2002, 53, 275–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creelman, R.A.; Mullet, J.E. Biosynthesis and action of jasmonates in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 1997, 48, 355–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, G.A.; Schilmiller, A.L. Oxylipin metabolism in response to stress. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2002, 5, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maynard, D.; Chibani, K.; Schmidtpott, S.; Seidel, T.; Spross, J.; Viehhauser, A.; Dietz, K.J. Biochemical characterization of 13-lipoxygenases of Arabidopsis thaliana. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelberth, J. Green leaf volatiles: A new player in the protection against abiotic stresses? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tressl, R.; Drawert, F. Biogenesis of banana volatiles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1973, 21, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vick, B.A.; Zimmerman, D.C. Lipoxygenase and hydroperoxide lyase in germinating watermelon seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1976, 57, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matoba, T.; Hidaka, H.; Kitamura, K.; Kaizuma, N.; Kito, M. Contribution of hydroperoxide lyase activity to n-Hexanal formation in soybean. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1985, 33, 856–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughn, S.F.; Gardner, H.W. Lipoxygenase-derived aldehydes inhibit fungi pathogenic on soybean. J. Chem. Ecol. 1993, 19, 2337–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heil, M.; Bueno, J.C.S. Within-plant signaling by volatiles leads to induction and priming of an indirect plant defense in nature. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 5467–5472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.J.; Yin, L.J.; Liu, Y.; Ma, J.; Zheng, J.C.; Lan, J.H.; Fu, J.D.; Chen, M.; Xu, Z.S.; Ma, Y.Z. The ABA-induced soybean ERF transcription factor gene GmERF75 plays a role in enhancing osmotic stress tolerance in Arabidopsis and soybean. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, T.; Suzuki, K.; Fujimura, T.; Shinshi, H. Genome-wide analysis of the ERF gene family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Physiol. 2006, 140, 411–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, M.D.; Yamasaki, K.; Ohme-Takagi, M.; Tateno, M.; Suzuki, M. A novel mode of DNA recognition by a β-sheet revealed by the solution structure of the GCC-box binding domain in complex with DNA. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 5484–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.H.; Lai, A.G. Genome-wide analyses of the bHLH superfamily in crustaceans: Reappraisal of higher-order groupings and evidence for lineage-specific duplications. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 172433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybel, B.D.; Möller, B.; Yoshida, S.; Grabowicz, I.; de Reuille, P.B.; Boeren, S.; Smith, R.S.; Borst, J.W.; Weijers, D. A bHLH complex controls embryonic vascular tissue establishment and indeterminate growth in Arabidopsis. Dev. Cell 2013, 24, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo-Ortiz, G.; Huq, E.; Quail, P.H. The Arabidopsis basic/helix-loop-helix transcription factor family. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 1749–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Duan, X.; Jiang, H.; Sun, Y.; Tang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Guo, J.; Liang, W.; Chen, L.; Yin, J.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of basic/helix-loop-helix transcription factor family in rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 1167–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.M.; Huang, Z.N.; Duan, W.K.; Ren, J.; Liu, T.K.; Li, Y.; Hou, X.L. Genome-wide analysis of the bHLH transcription factor family in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis). Mol. Genet. Genom. 2014, 289, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Jin, X.; Ma, Z.; Chen, H.; Liu, M. Basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) gene family in Tartary buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum): Genome-wide identification, phylogeny, evolutionary expansion and expression analyses. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 1478–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Li, L.; Wei, M.; Yang, F. Genome-wide analysis of basic helix-loop-helix superfamily members related to anthocyanin biosynthesis in eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). PeerJ 2019, 7, e7768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Xue, Y.; Fu, J.; Liu, X.; Qu, X.; Dai, X.; Dong, P.; Xu, Y.; Hong, Y.; Yao, Y.; et al. Evolution and function divergence analysis of the bHLH transcription factor family in soybean (Glycine max L.). J. Xinyang Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2019, 32, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Ge, D.; Akhter Bhat, J.; Li, Y.; Kong, J.; Liu, K.; Zhao, T. Hydroperoxide lyase modulates defense response and confers lesion-mimic leaf phenotype in soybean (Glycine max (L.) merr.). Plant J. 2020, 104, 1315–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Savchenko, T.; Baidoo, E.E.K.; Chehab, W.; Hayden, D.; Tolstikov, V.; Corwin, J.A.; Kliebenstein, D.J.; Keasling, J.D.; Dehesh, K. Retrograde signaling by the plastidial metabolite MEcPP regulates expression of nuclear stress-response genes. Cell 2012, 149, 1525–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohlmann, M.; Bachmann, A.; Weichert, H.; Kolbe, A.; Balkenhohl, T.; Wasternack, C.; Feussner, I. Formation of lipoxygenase-pathway-derived aldehydes in barley leaves upon methyl jasmonate treatment. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 260, 885–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.P.; Lu, W.J.; Mao, L.C.; Han, X.; Wei, X.; Zhao, X.; Xia, M.; Xu, C. ABF2 and MYB transcription factors regulate feruloyl transferase FHT involved in ABA-mediated wound suberization of kiwifruit. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhao, Q.C.; Zeng, D.X.; Xu, J.; Zhou, H.; Wang, F.; Ma, N.; Li, Y. RhMYB108, an R2R3-MYB transcription factor, is involved in ethylene- and JA-induced petal senescence in rose plants. Hortic. Res. 2019, 6, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.H.; Teng, S.Z.; Liu, D.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cui, X.; Wu, J.; Ai, P.; Sun, X.; Lu, T.; et al. RLM1, encoding an R2R3 MYB transcription factor, regulates the development of secondary cell wall in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 905111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Wang, F.; Wang, S.; Diao, J.; Lan, S.; Xu, Y.; Lyu, X.; Kang, H.; Yao, Y. Ethylene modulates the phenylpropanoid pathway by enhancing VvMYB14 expression via the ERF5-melatonin-ERF104 pathway in grape seeds. Hortic. Res. 2025, 12, uhaf061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Bao, Y.; Xiang, W.; Cai, X.; Zheng, Y.; Jin, P. Exogenous H2S promoted osmoregulatory capability via PpWRKY11-mediated transcriptional activation of PpGAD1 in cold-stored peach fruit. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2025, 228, 110258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feller, A.; Machemer, K.; Braun, E.L.; Grotewold, E. Evolutionary and comparative analysis of MYB and bHLH plant transcription factors. Plant J. 2011, 66, 94–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, N.A.A.; Hassan, M.N.U.; Zainal, Z.; Ismail, I. Persicaria minor F-box gene PmF-box1 indirectly affects Arabidopsis thaliana LOX-HPL pathway for green leaf volatile production. Sains Malays. 2023, 52, 1649–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, D.; Ohme-Takagi, M.; Sarai, A. Unique mode of GCC box recognition by the DNA-binding domain of ethylene-responsive element-binding factor (ERF domain) in plant. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 26857–26861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moffat, C.S.; Ingle, R.A.; Wathugala, D.L.; Saunders, N.J.; Knight, H.; Knight, M.R. ERF5 and ERF6 play redundant roles as positive regulators of JA/Et-mediated defense against Botrytis cinerea in Arabidopsis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, G.H.; Wan, J.; Kim, H.J.; Nguyen, X.C.; Chung, W.S.; Hong, J.C.; Stacey, G. Ethylene-responsive element-binding factor 5, ERF5, is involved in chitin-induced innate immunity response. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2012, 25, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröschel, C.; Iven, T.; Walper, E.; Bachmann, V.; Weiste, C.; Dröge-Laser, W. A gain-of-function screen reveals redundant ERF transcription factors providing opportunities for resistance breeding toward the vascular fungal pathogen Verticillium longisporum. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2019, 32, 1095–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akmakjian, G.Z.; Riaz, N.; Guerinot, M.L. Photoprotection during iron deficiency is mediated by the bHLH transcription factors PYE and ILR3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2024918118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samira, R.; Li, B.; Kliebenstein, D.; Li, C.; Davis, E.; Gillikin, J.W.; Long, T.A. The bHLH transcription factor ILR3 modulates multiple stress responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2018, 97, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Xu, N.; Bhandari, D.D.; Lapin, D.; Sun, X.; Luo, X.; Wang, Y.; Cao, J.; Wang, H.; Coaker, G.; et al. Bacterial effector targeting of a plant iron sensor facilitates iron acquisition and pathogen colonization. Plant Cell 2021, 33, 2015–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.; Li, Y.; Gui, X.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Qiao, Y.; Xu, N.; Liu, J. An RNA helicase coordinates with iron signal regulators to alleviate chilling stress in Arabidopsis. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Qi, J.; Zhu, X.; Mao, B.; Zeng, L.; Wang, B.; Li, Q.; Zhou, G.; Xu, X.; Lou, Y.; et al. The rice hydroperoxide lyase OsHPL3 functions in defense responses by modulating the oxylipin pathway. Plant J. 2012, 71, 763–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, H.; Huang, M.; Palacio, K.; Schuler, M.A. Variations in CYP74B2 (hydroperoxide lyase) gene expression differentially affect hexenal signaling in the Columbia and Landsberg erecta ecotypes of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2005, 139, 1529–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues Magalhães, H.C.; Alves Filho, E.G.; Rivero Meza, S.L.; Oliveira, A.; Garruti, D.S.; Purgatto, E. Effect of Methyl jasmonate on the biosynthesis of volatile compounds associated with the ripening of grape tomato fruits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 4696–4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, R.; Wei, W.; Zhang, T.; Chen, S. Cloning and expression analysis of hydroperoxide lyase gene 13-CsHPL in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Mol. Plant Breed. 2018, 16, 6907–6914, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, L.; Deng, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, P.; Jin, W.; Li, J.; Guo, H. Characterisation of the NtHPL genes and their expression pattern under TMV stress in tobacco. J. Henan Agric. Sci. 2025, 54, 47–56, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Clone ID | Gene ID | Functional Annotation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Glyma.05G049900 | AP2 domain |
| 2 | Glyma.08G297200 | Whirly transcription factor |
| 3 | Glyma.10G186800 | AP2 domain |
| 4, 25, 32 | Glyma.17G124100 | AP2 domain |
| 5 | Glyma.13G286700 | Helix–loop–helix DNA-binding domain |
| 6, 14, 18 | Glyma.05G063500 | AP2 domain |
| 7 | Glyma.09G034500 | Transcription factor bHLH148 |
| 8 | Glyma.17G035200 | Response to hydrogen peroxide, response to oxidative stress, response to salt stress |
| 9 | Glyma.07G048200 | B3 DNA-binding domain |
| 10 | Glyma.14G063400 | Myb-like DNA-binding domain |
| 11 | Glyma.19G061600 | Myb-like DNA-binding domain |
| 12 | Glyma.10G146300 | bHLH149-like |
| 13 | Glyma.19G178500 | Histone-like transcription factor (CBF/NF-Y) and archaeal histone |
| 15 | Glyma.13G290100 | Myb-like DNA-binding domain |
| 16, 17 | Glyma.06G266800 | Helix–loop–helix DNA-binding domain |
| 19 | Glyma.09G131400 | Myb-like DNA-binding domain |
| 20 | Glyma.14G020100 | AP2 domain |
| 21 | Glyma.08G142400 | WRKY DNA-binding domain |
| 22 | Glyma.04G008900 | GATA zinc finger |
| 23 | Glyma.03G127800 | VQ motif |
| 24 | Glyma.02G016100 | AP2 domain |
| 26 | Glyma.14G086500 | Myb-like DNA-binding domain |
| 27 | Glyma.18G181300 | Myb-like DNA-binding domain |
| 28, 56 | Glyma.02G012700 | bZIP transcription factor |
| 29 | Glyma.09G017400 | MYB-CC type transfactor, LHEQLE motif |
| 30 | Glyma.05G148800 | K-box region |
| 31 | Glyma.12G039900 | NAC domain |
| 33 | Glyma.15G077100 | AP2 domain |
| 34 | Glyma.04G177300 | Myb-like DNA-binding domain |
| 35 | Glyma.14G139700 | bZIP transcription factor |
| 36 | Glyma.11G142900 | Myb-like DNA-binding domain |
| 37 | Glyma.17G075200 | Helix–loop–helix DNA-binding domain |
| 38, 62 | Glyma.17G237900 | Myb-like DNA-binding domain |
| 39 | Glyma.08G215300 | bHLH25-like |
| 40 | Glyma.12G226600 | AP2 domain |
| 41 | Glyma.02G161100 | bZIP transcription factor |
| 42 | Glyma.08G325900 | GRAS domain family |
| 43 | Glyma.04G145000 | Histone-like transcription factor (CBF/NF-Y) and archaeal histone |
| 44 | Glyma.08G274200 | Helix–loop–helix DNA-binding domain |
| 45 | Glyma.07G057400 | WRKY DNA-binding domain |
| 46 | Glyma.13G189400 | Histone-like transcription factor (CBF/NF-Y) and archaeal histone |
| 47, 52 | Glyma.15G003300 | WRKY DNA-binding domain |
| 48 | Glyma.12G136300 | Helix–loop–helix DNA-binding domain |
| 49 | Glyma.03G252100 | Whirly transcription factor |
| 50 | Glyma.03G240000 | Helix–loop–helix DNA-binding domain |
| 51 | Glyma.16G023000 | Myb-like DNA-binding domain |
| 53 | Glyma.18G105800 | SRF-type transcription factor (DNA-binding and dimerization domain) |
| 54 | Glyma.10G013300 | bZIP transcription factor |
| 55 | Glyma.04G103900 | AP2 domain |
| 57 | Glyma.17G145300 | AP2 domain |
| 58 | Glyma.13G236500 | AP2 domain |
| 59 | Glyma.20G175000 | Transcription factor UPBEAT1 |
| 60 | Glyma.15G261300 | Histone-like transcription factor (CBF/NF-Y) and archaeal histone |
| 61 | Glyma.18G159900 | AP2 domain |
| 63 | Glyma.14G185800 | WRKY DNA-binding domain |
| 64 | Glyma.03G135800 | HSF-type DNA-binding domain |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Lyu, W.; Li, S.; Fu, M.; Yu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Hu, S.; Xu, H. Identification of Transcription Factors of GmHPL Involved in Modulating Pathogen Stresses in Soybean. Plants 2026, 15, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants15010054
Wang Y, Lyu W, Li S, Fu M, Yu X, Zhao Z, Hu S, Xu H. Identification of Transcription Factors of GmHPL Involved in Modulating Pathogen Stresses in Soybean. Plants. 2026; 15(1):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants15010054
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yaqi, Wenhuan Lyu, Shuguang Li, Mengmeng Fu, Xiwen Yu, Zhixin Zhao, Shanshan Hu, and Haifeng Xu. 2026. "Identification of Transcription Factors of GmHPL Involved in Modulating Pathogen Stresses in Soybean" Plants 15, no. 1: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants15010054
APA StyleWang, Y., Lyu, W., Li, S., Fu, M., Yu, X., Zhao, Z., Hu, S., & Xu, H. (2026). Identification of Transcription Factors of GmHPL Involved in Modulating Pathogen Stresses in Soybean. Plants, 15(1), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants15010054






