The Effect of Aspergillus flavus on Seedling Development in Maize
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
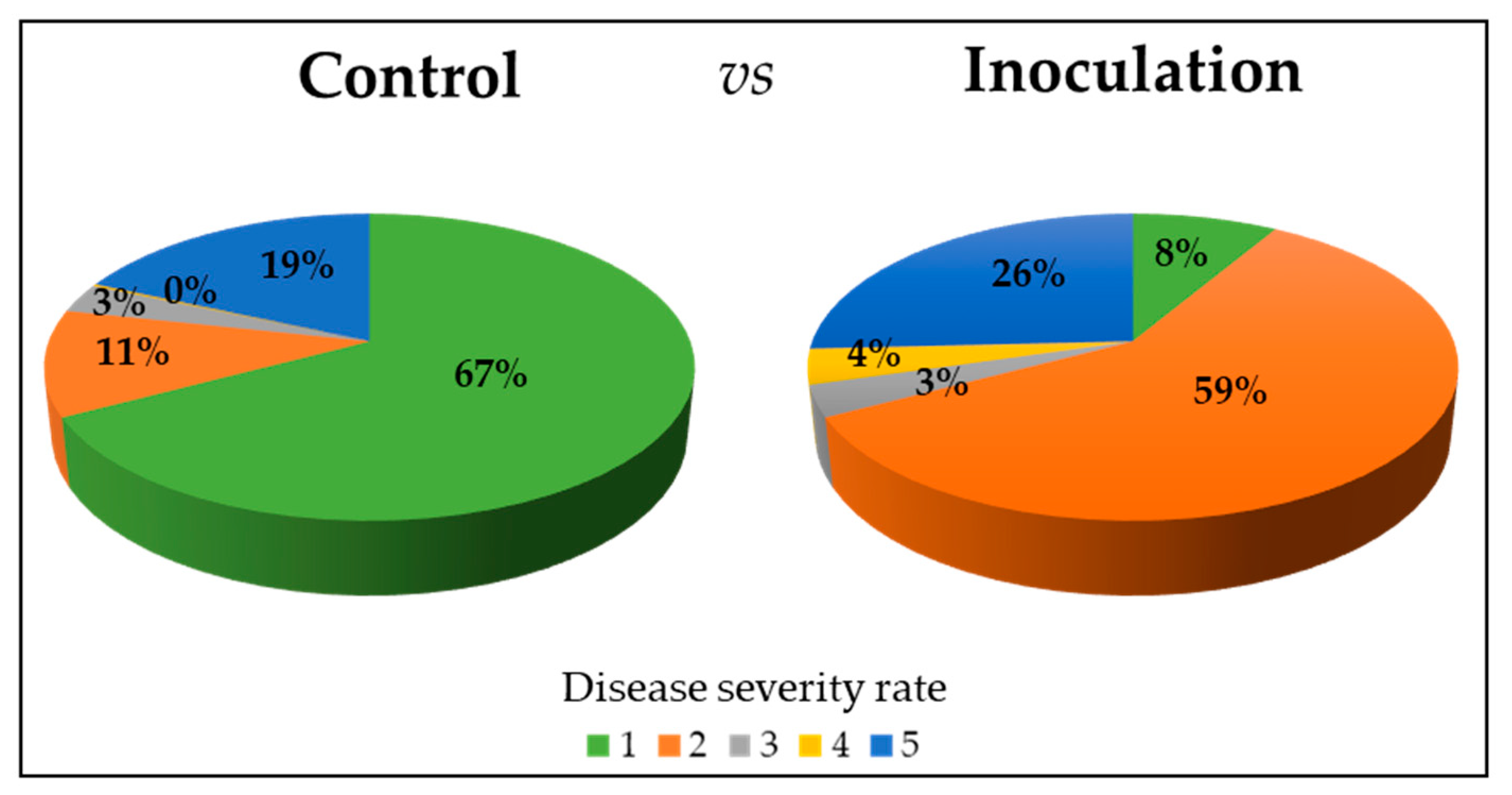
2.1. Germination Scores and Disease Severity
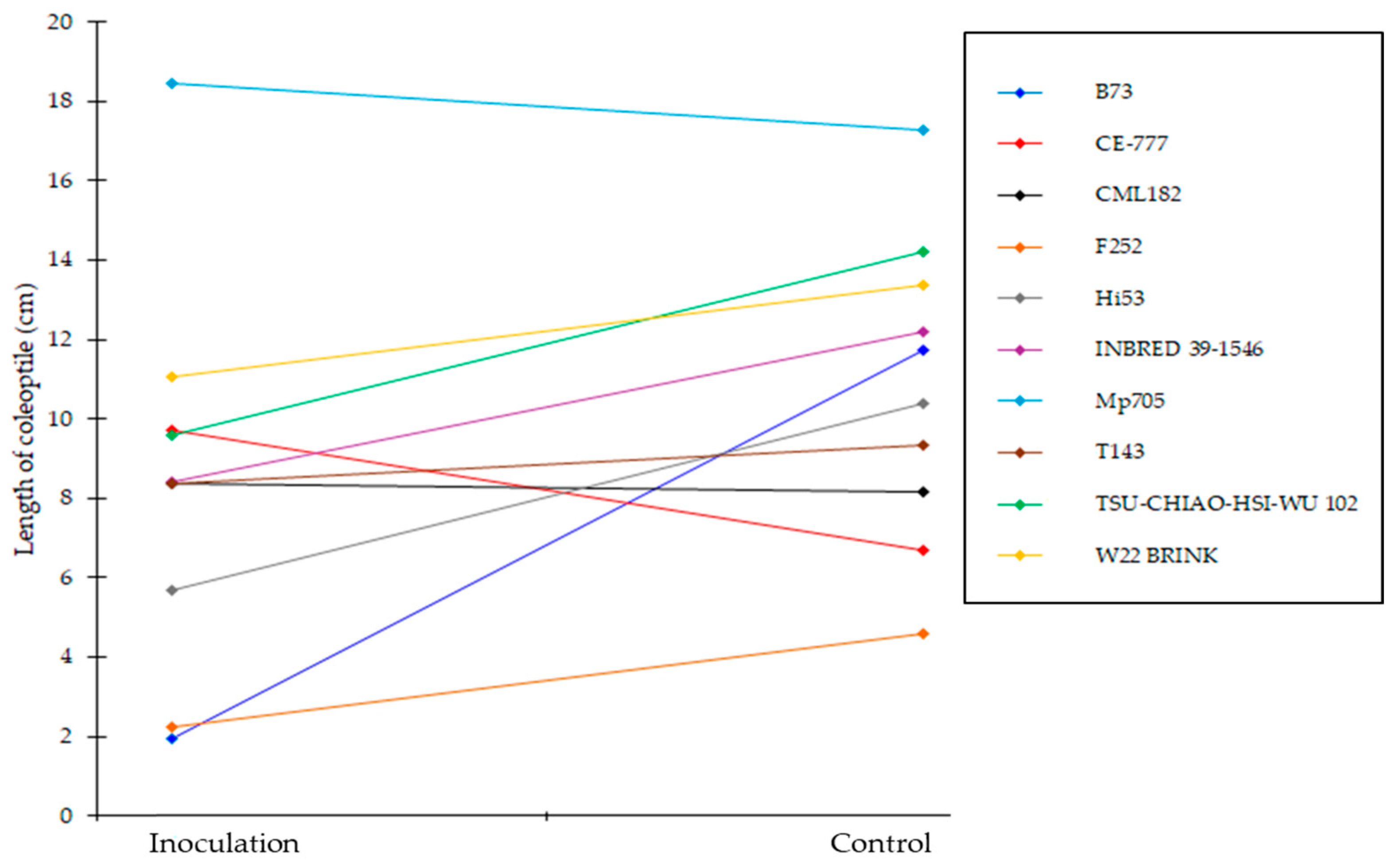
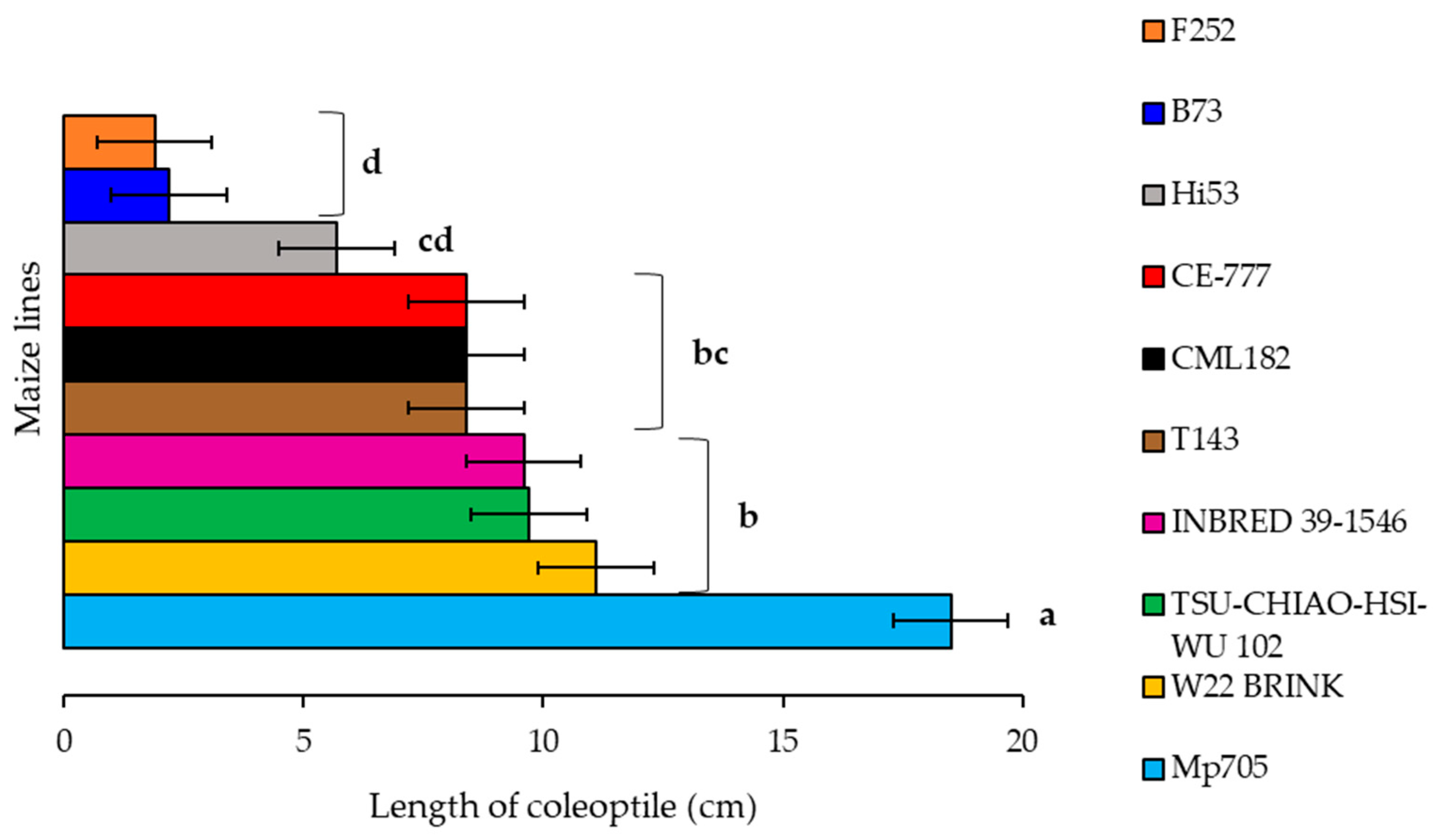
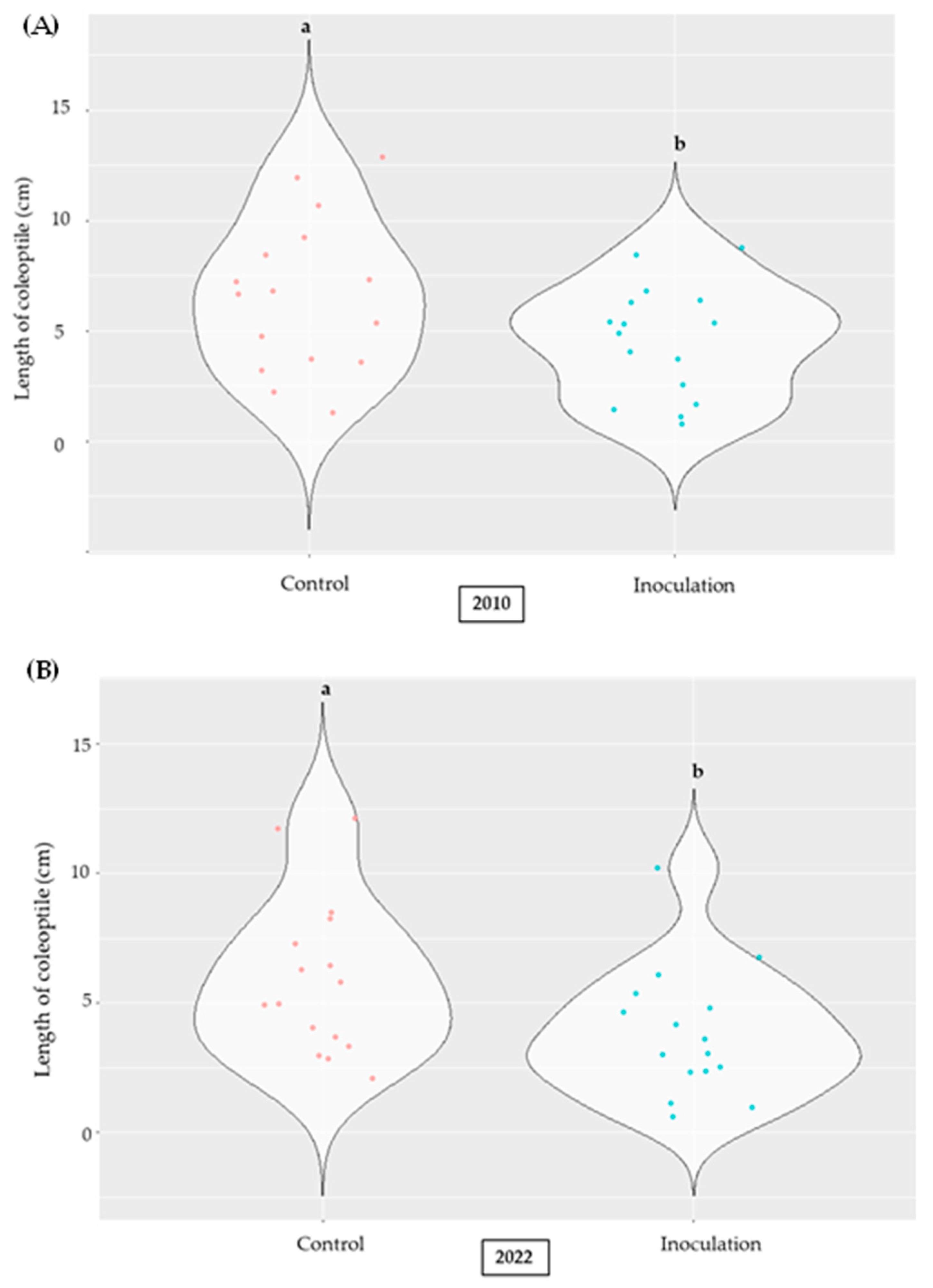
2.2. Effect of A. flavus Inoculation on the Length of Coleoptile in Selected Inbred Maize Lines of the Panel
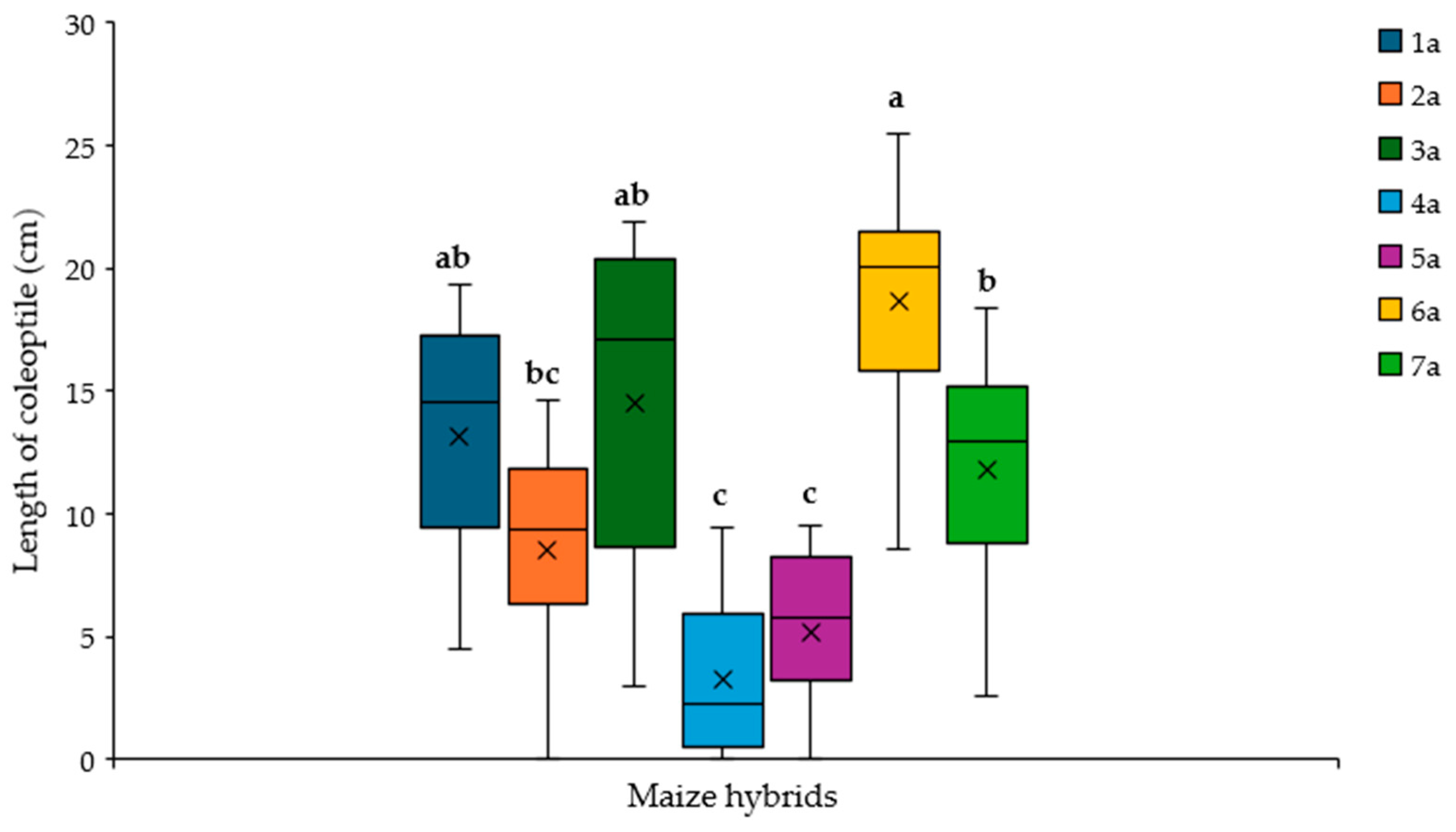
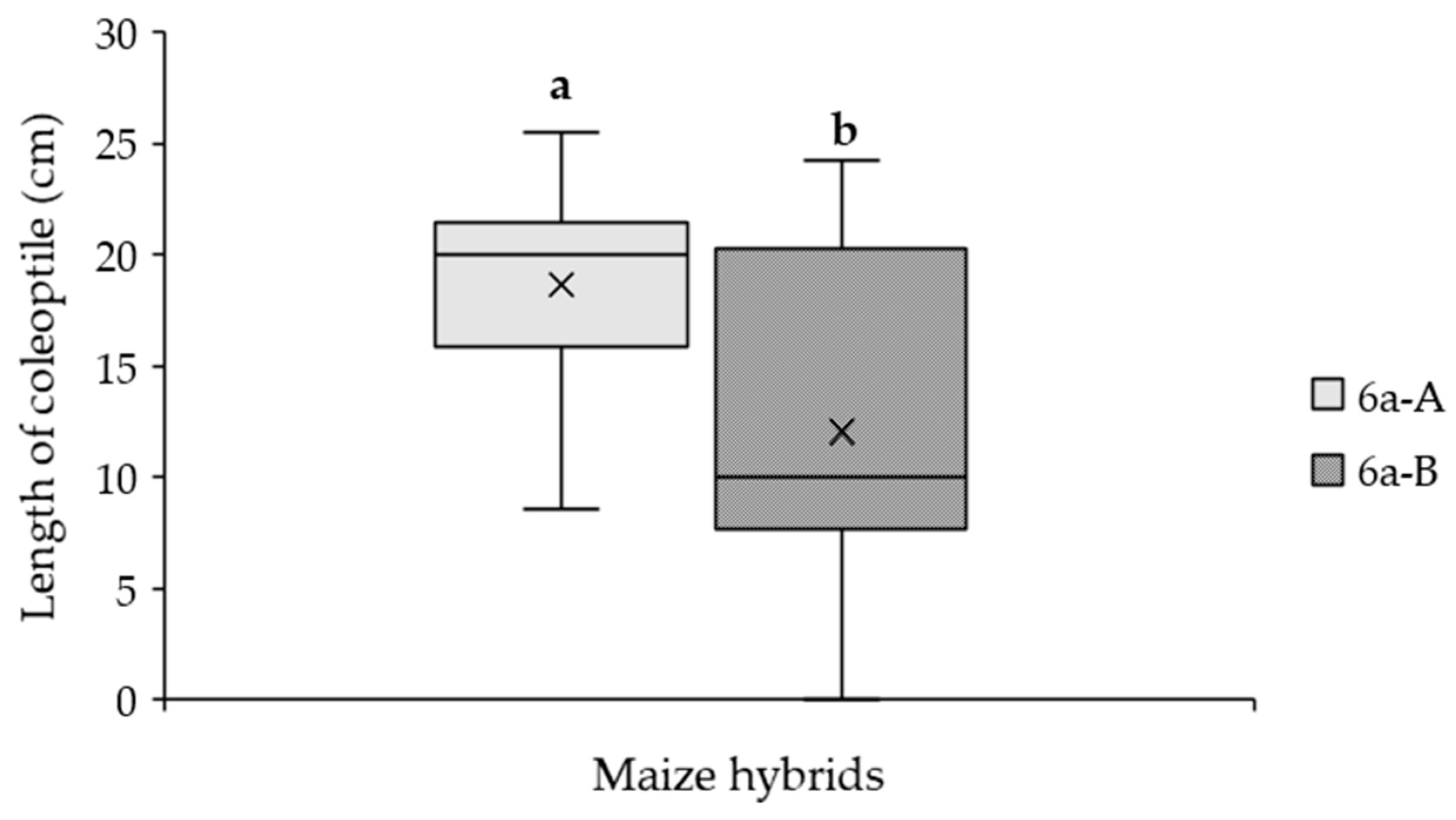
2.3. Effect of A. flavus Inoculation on the Length of Coleoptile in Maize Hybrids
2.4. Effect of Parental Line on the Susceptibility to A. flavus in Maize Hybrid
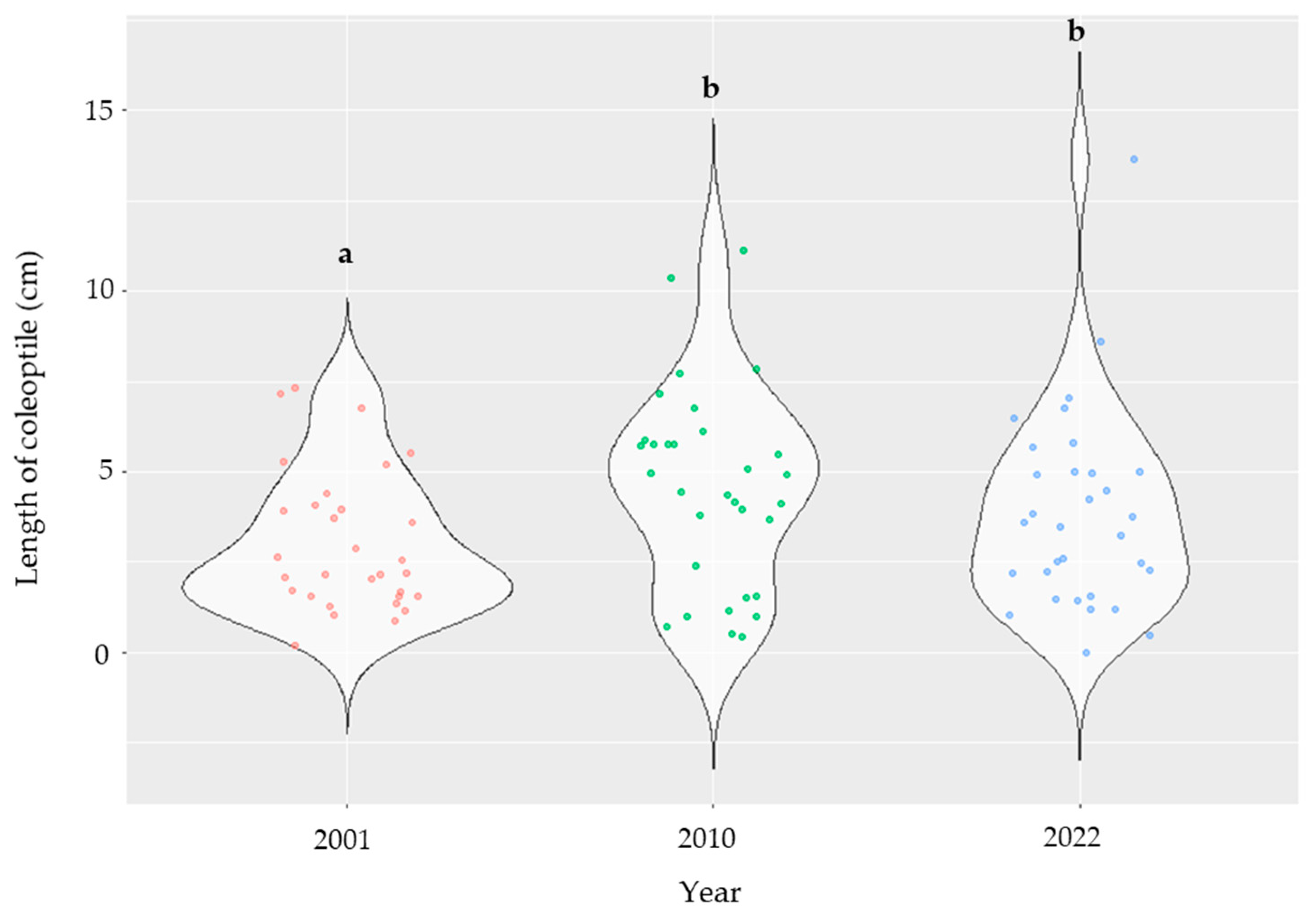
2.5. Variations in the Inoculated Maize Lines According to the Year
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Maize Genotypes
4.2. Fungal Strain
4.3. Experimental Procedure
4.4. Disease Severity Evaluation After Inoculation
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Strable, J.; Scanlon, M.J. Maize (Zea mays): A Model Organism for Basic and Applied Research in Plant Biology. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2009, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andorf, C.; Beavis, W.D.; Hufford, M.; Smith, S.; Suza, W.P.; Wang, K.; Woodhouse, M.; Yu, J.; Lübberstedt, T. Technological advances in maize breeding: Past, present and future. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2019, 132, 817–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erenstein, O.; Jaleta, M.; Sonder, K.; Mottaleb, K.; Prasanna, B.M. Global maize production, consumption and trade: Trends and R&D implications. Food Secur. 2022, 14, 1295–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOStat. FAO Stat. FAO, Rome. 2022. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat (accessed on 18 February 2025).
- Barug, D.; van Egmond, H.; López Garzia, R.; van Osenbruggen, T.; Visconti, A. Meeting the Mycotoxin Menace; Wageningen Academic Publisher: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2004; p. 319. [Google Scholar]
- Shabeer, S.; Asad, S.; Jamal, A.; Ali, A. Aflatoxins contamination, its impact and management strategies: An update review. Toxins 2022, 14, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahlali, R.; Taoussi, M.; Laasli, S.E.; Gachara, G.; Ezzouggari, R.; Belabess, Z.; Aberkami, K.; Assouguem, A.; Meddich, A.; El Jarroudi, M.; et al. Effects of climate change on plant pathogens and host-pathogen interactions. Crop Environ. 2024, 3, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskola, M.; Kos, G.; Elliott, C.T.; Hajšlová, J.; Mayar, S.; Krska, R. Worldwide contamination of food-crops with mycotoxins: Validity of the widely cited ‘FAO estimate’ of 25%. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2773–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stutt, R.O.J.H.; Castle, M.D.; Markwell, P.; Baker, R.; Gilligan, C.A. An integrated model for pre- and post-harvest aflatoxin contamination in maize. Sci. Food 2023, 7, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.M.; Ahmad, M.; Ali, A.; Hamid, R.; Javed, S.; Abdin, M.Z. Detection of Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus from aflatoxin-contamined peanuts and their differentiation using PCR-RFLP. Ann. Microbiol 2014, 64, 1597–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northolt, M.D.; van Egmond, H.P. Limits of water activity and temperature for the production of some mycotoxins. In Proceedings of the 4th Meeting Mycotoxins in Animal Disease, Weybridge, UK, 1–3 April 1981; pp. 106–108. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, P.M.; Lawrence, J.W.; Van Walbeek, W. Detection of mycotoxins by thin layer chromatography: Application to screening of fungal extracts. Appl. Microbiol. 1970, 20, 839–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchis, V.; Magan, N. Environmental conditions affecting mycotoxins. In Mycotoxins in Food: Detection and Control; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2004; pp. 174–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaye, M.A.; Gemeda, N.; Weledesemayat, G.T. Aspergillus species and aflatoxins contamination of pre and post-harvest maize grain in West Gojam, Ethiopia. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 2, 013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiser, D.M.; Dorner, J.W.; Horn, B.W.; Taylor, J.W. The phylogenetics of Mycotoxin and Sclerotium production in Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus oryzae. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2000, 31, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, I.; Jakobek, Y.L.; Ramirez-Prado, J.H.; Horn, B.W. Recombination, balancing selection and adaptative evolution in the aflatoxin gene cluster of Aspergillus parasiticus. Mol. Ecol. 2007, 16, 4401–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweany, R.R.; Damann Jr, K.E.; Kaller, M.D. Comparison of soil and corn kernel Aspergillus flavus populations: Evidence for niche specialization. Phytopathology 2011, 101, 952–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, B.W. Ecology and population biology of aflatoxigenic fungi in soil. J. Toxicol. 2003, 22, 351–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, B.W.; Gell, R.M.; Singh, R.; Sorensen, R.B.; Carbone, I. Sexual reproduction in Aspergillus flavus sclerotia: Acquisition of novel alleles from soil populations and uniparental mitochondrial inheritance. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gell, R.M.; Horn, B.W.; Carbone, I. Genetic map and heritability of Aspergillus flavus. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2020, 144, 103478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, R.A.; Blankenship, P.D.; Cole, R.J.; Sanders, T.H. Effects of soil moisture and temperature on preharvest invasion of peanuts by the Aspergillus flavus group and subsequent aflatoxins development. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1983, 45, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.K.; Duncan, H.E.; Payne, G.A.; Leonard, K.J. Factors influencing infection by Aspergillus flavus in silk-inoculated corn. Plant Dis. 1980, 64, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolezal, A.L.; Obrian, G.R.; Nielsen, D.M.; Woloshuk, C.P.; Boston, R.S.; Payne, G.A. Localization, morphology and transcriptional profile of Aspergillus flavus during seed colonization. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2013, 14, 898–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolezal, A.L.; Shu, X.; Obrian, G.R.; Nielsen, D.M.; Woloshuk, C.P.; Boston, R.S.; Payne, G.A. Aspergillus flavus infection induces transcriptional and physical changes in developing maize kernels. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Livingston, D.P.; Franks, R.G.; Boston, R.S.; Woloshuk, C.P.; Payne, G.A. Tissue-specific gene expression in maize seeds during colonization by Aspergillus flavus and Fusarium verticillioides. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2015, 16, 662–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.L.; Cleveland, T.E.; Payne, G.A.; Woloshuk, C.P.; Campbell, K.W.; White, D.G. Determination of resistance to aflatoxin production in maize kernels and detection of fungal colonization using an Aspergillus flavus transformant expressing Escherichia coli β-glucuronidase. Phytopathology 1995, 85, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windham, G.L.; Williams, W.P.; Mylroie, J.E.; Reid, C.X.; Womack, E.D. A histological study of Aspergillus flavus colonization of wound inoculated maize kernels of resistant and susceptible maize hybrids in the field. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Wang, X.; Hao, J.; Yan, J.; Ding, J. Genome-wide association implicates candidate genes conferring resistance to maize rough dwarf disease in maize. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casacuberta, J.M.; Puigdomenech, P.; San Segundo, B. A gene coding for a basic pathogenesis-related (PR-like) protein from Zea mays. Molecular cloning and induction by a fungus (Fusarium moniliforme) in germination maize seeds. Plant Mol. Biol. 1991, 16, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casacuberta, J.M.; Raventos, D.; Puigdomenech, P.; San Segundo, B. Expression of the gene encoding the PR-like protein PRms in germination maize embryos. Mol. Genet. Genom. 1992, 234, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.Z.; Cleveland, T.E.; Brown, R.L.; Widstrom, N.W.; Lynch, R.E.; Russin, J.S. Distribution of antifungal proteins in maize kernel tissue using immunochemistry. J. Food Prot. 1999, 87, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cary, J.W.; Rajasekaran, K.; Brown, R.L.; Luo, M.; Chen, Z.Y.; Bhatnagar, D. Developing Resistance to aflatoxins in maize and cottonseed. Toxins 2011, 3, 678–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busboom, K.N.; White, D.G. Inheritance of resistance to aflatoxin production and aspergillus ear rot of corn from the cross of inbreds B73 and Oh516. Phytopathology 2004, 10, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, T.D.; Williams, W.P.; Windham, G.L.; Willcox, M.C.; Abbas, H.K. Quantitative trait loci contributing resistance to aflatoxin accumulation in the maize inbred Mp313E. Crop Sci. 2005, 1, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maupin, L.M.; Clements, M.J.; White, D.G. Evaluation of the M182 corn line as a source of resistance to aflatoxin in grain and use of BGYF as a selection tool. Plant Dis. 2003, 87, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mideros, S.X.; Warburton, M.L.; Jamann, T.M.; Windham, G.L.; Williams, W.P.; Nelson, R.J. Quantitative trait loci influencing mycotoxin contamination of maize: Analysis by linkage mapping, characterization of near-isogenic lines and met-analysis. Crop Sci. 2014, 54, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, C.; Naidoo, G.; Forbes, A.; Mikkilineni, V.; White, D.; Rocheford, T. Quantitative trait loci for low aflatoxin production in two related maize populations. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 107, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widstrom, N.W.; Burton, A.; Guo, B.Z.; Wilson, D.M.; Snook, M.E.; Cleveland, T.E.; Lynch, R.E. Control of preharvest aflatoxin contamination in maize by pyramiding QTL involved in resistance to ear-feeding insects and invasion by Aspergillus spp. Eur. J. Agron. 2003, 19, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwala, S.; Kimbeng, C.A.; Williams, W.P.; Kang, M.S. Molecular markers associated with resistance to Aspergillus flavus in maize grain: QTL and discriminant analyses. J. New Seeds 2008, 9, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburton, M.L.; Brooks, T.D.; Krakowsky, M.D.; Shan, X.; Windham, G.L.; Williams, W.P. Identification and mapping of new sources of resistance to aflatoxin accumulation in maize. Crop Sci. 2009, 49, 1403–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayfield, K.L.; Murray, S.C.; Rooney, W.L.; Isakeit, T.; Odvody, G.A. Confirmation of QTL reducing aflatoxin in maize testcrosses. Crop Sci. 2011, 51, 2489–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburton, M.L.; Brooks, T.D.; Windham, G.L.; Williams, W.P. Identification of novel QTL contributing resistance to aflatoxin accumulation in maize. Mol. Breed. 2011, 27, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willcox, M.C.; Davis, G.L.; Warburton, M.L.; Windham, G.L.; Abbas, H.K.; Betran, J.; Holland, J.B.; Williams, W.P. Confirming quantitative trait loci for aflatoxin resistance from Mp313E in different genetic backgrounds. Mol. Breed. 2013, 32, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wu, F.; Gu, X.; Bian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Deng, D. Quantitative trait locus mapping of resistance to Aspergillus flavus infection using a recombinant inbred line population in maize. Mol. Breed. 2014, 33, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, R.; Windham, G.L.; Williams, W.P.; Subudhi, P.K. Quantitative trait loci (QTL) for reducing aflatoxin accumulation in corn. Mol. Breed. 2016, 36, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cui, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, C.; Kan, X. Confirmation and fine mapping of a major QTL for aflatoxin resistance in maize using a combination of linkage and association mapping. Toxins 2016, 8, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Womack, E.D.; William, W.P.; Windham, G.L.; Xu, W. Mapping quantitative trait loci associated with resistance to aflatoxin accumulation in maize inbred Mp719. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baisakh, N.; Da Silva, E.A.; Pradhan, A.K.; Rajasekaran, K. Comprehensive meta-analysis of QTL and gene expression studies identify candidate genes associated with Aspergillus flavus resistance in maize. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1214907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wu, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, S.; Yin, Z. Comparative transcriptome profiling and co-expression network analysis uncover the key genes associated withearly-stage resistance to Aspergillus flavus in maize. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, M.L.; Broders, K.D.; Paul, P.A.; Dorrance, A.E. Infection of soyabean seed by Fusarium graminearum and effect of seed treatments on disease under controlled conditions. Plant Dis. 2011, 95, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanubile, A.; Muppiral, U.K.; Severin, A.J.; Marocco, A.; Munkvold, G.P. Transcriptome profiling of soyabean (Glycine max) roots challenged with pathogenic and non-pathogenic isolates of Fusarium oxysporum. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, J.; Stagnati, L.; Lucini, L.; Rocchetti, G.; Lanubile, A.; Cortellini, C.; De Poli, G.; Busconi, M.; Marocco, A. Phenolic profile and susceptibility to Fusarium infection of pigmentated maize cultivars. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stagnati, L.; Lanubile, A.; Samayoa, L.F.; Bragalanti, M.; Giorni, P.; Busconi, M.; Holland, J.B.; Marocco, A. A genome wide association study reveals markers and genes associated with resistance to Fusarium verticilloides infection of seedlings in maize diversity panel. G3 2019, 9, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M.; Long, Y.; Wang, Q.; Tian, X.; Fan, S.; Zhang, C.; Huang, W. Physiological alterations and nondestructive test methods of crop seed vigor: A comprehensive review. Agriculture 2023, 13, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munkvold, G.P.; Desjardins, A.E. Fumonisins in maize: Can we reduce their occurrence? Plant Dis. 1997, 81, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, I.E.; Bacon, C.W.; Hinton, D.M. Effects of endophytic infection by Fusarium moniliforme on corn growth and cellular morphology. Plant Dis. 1997, 81, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stagnati, L.; Rahjoo, V.; Samayoa, L.F.; Holland, J.B.; Borrelli, V.M.G.; Busconi, M.; Lanubile, A.; Marocco, A. A genome wide association study to understand the effect of Fusarium verticilloides infection on seedling of a maize diversity panel. G3 2020, 10, 1685–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, K.W.; White, D.G. Evaluation of corn genotypes for resistance to Aspergillus ear rot, kernel infection, and aflatoxin production. Plant Dis. 1995, 79, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalivendra, S.; Huang, F.; Busman, M.; Williams, W.P.; Ham, J.H. Low aflatoxin levels in aspergillus flavus-resistant maize are correlated with increased corn earworm damage and enhanced seed fumonisin. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 565323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mideros, S.X.; Windham, G.L.; Williams, W.P.; Nelson, R.J. Tissue-specific components of resistance to Aspergillus ear rot of maize. Phytopathology 2012, 102, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorman, D.P.; Kang, M.S. Preharvest Aflatoxin Contamination in Maize: Resistance and Genetics. Plant Breed. 1991, 107, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gembeh, S.V.; Brown, R.L.; Grimm, C.; Cleveland, T. Identification of chemical components of corn kernel pericarp wax associated with resistance to Aspergillus flavus infection and aflatoxin production. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 4635–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Xin, X.; Song, C.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, S.; Li, R.; Liu, X.; Lu, X. Activity levels and expression of antioxidant enzymes in the ascorbate-glutathione cycle in artificially aged rice seed. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 80, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.H.; Zhang, Y.D.; Kang, M.S.; Chen, H.; Li, L.; Yu, L.J.; Fan, X. Diallel analysis models: A comparison of certain genetic statistics. Crop Sci. 2013, 53, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.M.; Zhang, Y.D.; Yao, W.H.; Bi, Y.Q.; Liu, L.; Chen, H.M.; Kang, M.S. Reciprocal diallel crosses impact combining ability, variance estimation, and heterotic group classification. Crop Sci. 2014, 54, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.M.; Bi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jeffers, D.; Yin, X.F.; Kang, M. Improving breeding efficiency of a hybrid maize program using a three heterotic-group classification. J. Agron. 2018, 110, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosho, B.M.; Ifie, B.E.; Asante, I.K.; Danquah, E.Y.; Zelekhe, H. Combining ability of quality protein maize inbred lines under low and optimum soil nitrogen environments in Ethiopia. Afr. J. Plant Sci. 2021, 15, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonipas, A.J.; Rajashekhar, M.K.; Gopalakrishna, N.; Sidramappa, C.T.; Zerka, R.; Bindiganavile, S.V.; Nagesh, P.; Shiddappa, R.S.; Prema, G.U. Maternal effects, reciprocal differences and combining ability study for yield and its component traits in maize (Zea mays L.) through modified diallel analysis. PeerJ 2024, 12, 17600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheridan, W.F.; Clark, J.K. Fertilization and Embryogeny in Maize. In The Maize Handbook; Freeling, M., Walbot, V., Eds.; Springer Lab Manuals; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walbot, V.; Evans, M.M.S. Unique features of the plant life cycle and their consequences. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2003, 4, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, M.M.S.; Kermicle, J.L. Interaction between maternal effect and zygotic effect mutations during maize seed development. Genetics 2001, 159, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutieérrez-Marcos, J.F.; Costa, L.M.; Biderre-Petit, C.; Khbaya, B.; O’Sullivan, D.M.; Wormald, M.; Perez, P.; Dickinson, H.G. Maternally expressed gene1 is a novel maize endosperm transfer cell-specific gene with a maternal parent-of-origin pattern of expression. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 1288–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.L.; Yuan, J.; Rouster, J.; Paul, W.; Dickinson, H.; Gutiérrez-Marcos, J.F. Maternal control of nutrient allocation in plant seeds by genomic imprinting. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, F.; Daliberti, M.; Bagadion, A.; Xu, M.; Li, Y.; Baier, J.; Tseung, C.-W.; Evans, M.M.S.; Settles, A.M. Parent-of-origin-effect rough endosperm mutants in maize. Genetics 2016, 204, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.D.; Lee, S.B.; Taylor, J.W. Amplification and Direct Sequencing of Fungal Ribosomal RNA Genes for Phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Innis, M.A., Gelfand, D.H., Sninsky, J.J., White, T.J., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Septiani, P.; Lanubile, A.; Stagnati, L.; Busconi, M.; Nelissen, H.; Pè, M.E.; Dell’Acqua, M.; Marocco, A. Unravelling the genetic basis of Fusarium seedling rot resistance in the MAGIC maize population: Novel targets for breeding. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| CLASS | T | MT | MS | S |
| CLUSTER | a | b | c | d |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mazzoleni, I.; Novarina, E.; Zerlottin, Y.M.; Bardelli, T.; Dal Prà, M.; Zuffada, M.; Cremonesi, M.; Antonietti, L.; Bravi, R.; Bianchi, P.G.; et al. The Effect of Aspergillus flavus on Seedling Development in Maize. Plants 2025, 14, 1109. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14071109
Mazzoleni I, Novarina E, Zerlottin YM, Bardelli T, Dal Prà M, Zuffada M, Cremonesi M, Antonietti L, Bravi R, Bianchi PG, et al. The Effect of Aspergillus flavus on Seedling Development in Maize. Plants. 2025; 14(7):1109. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14071109
Chicago/Turabian StyleMazzoleni, Isabella, Elena Novarina, Yuki Michelangelo Zerlottin, Tommaso Bardelli, Mauro Dal Prà, Mattia Zuffada, Matteo Cremonesi, Luca Antonietti, Romana Bravi, Pier Giacomo Bianchi, and et al. 2025. "The Effect of Aspergillus flavus on Seedling Development in Maize" Plants 14, no. 7: 1109. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14071109
APA StyleMazzoleni, I., Novarina, E., Zerlottin, Y. M., Bardelli, T., Dal Prà, M., Zuffada, M., Cremonesi, M., Antonietti, L., Bravi, R., Bianchi, P. G., & Giulini, A. P. M. (2025). The Effect of Aspergillus flavus on Seedling Development in Maize. Plants, 14(7), 1109. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14071109






