Effect of Compound Planting Mode on Nutrient Distribution in Cotton
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Sample Determination
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Composite Cropping Pattern on Soil Physicochemical Properties
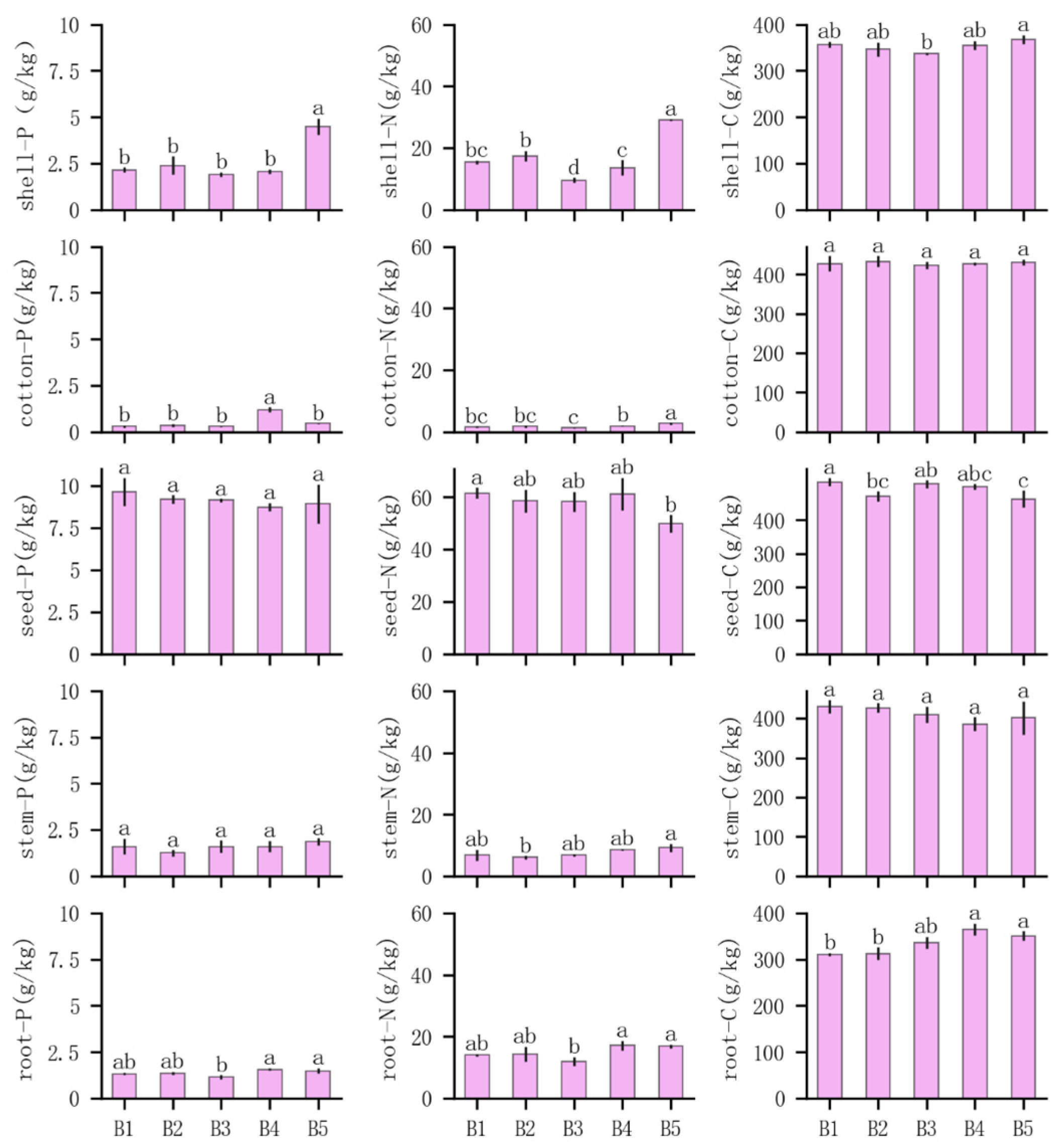
3.2. Effects of Compound Planting Pattern on Nutrient Allocation to Major Organs of Cotton
3.3. Composite Planting and Ecological Stoichiometry of Cotton Major Organs
3.4. Compound Planting Pattern and Nitrogen–Phosphorus Isokinetic Allocation
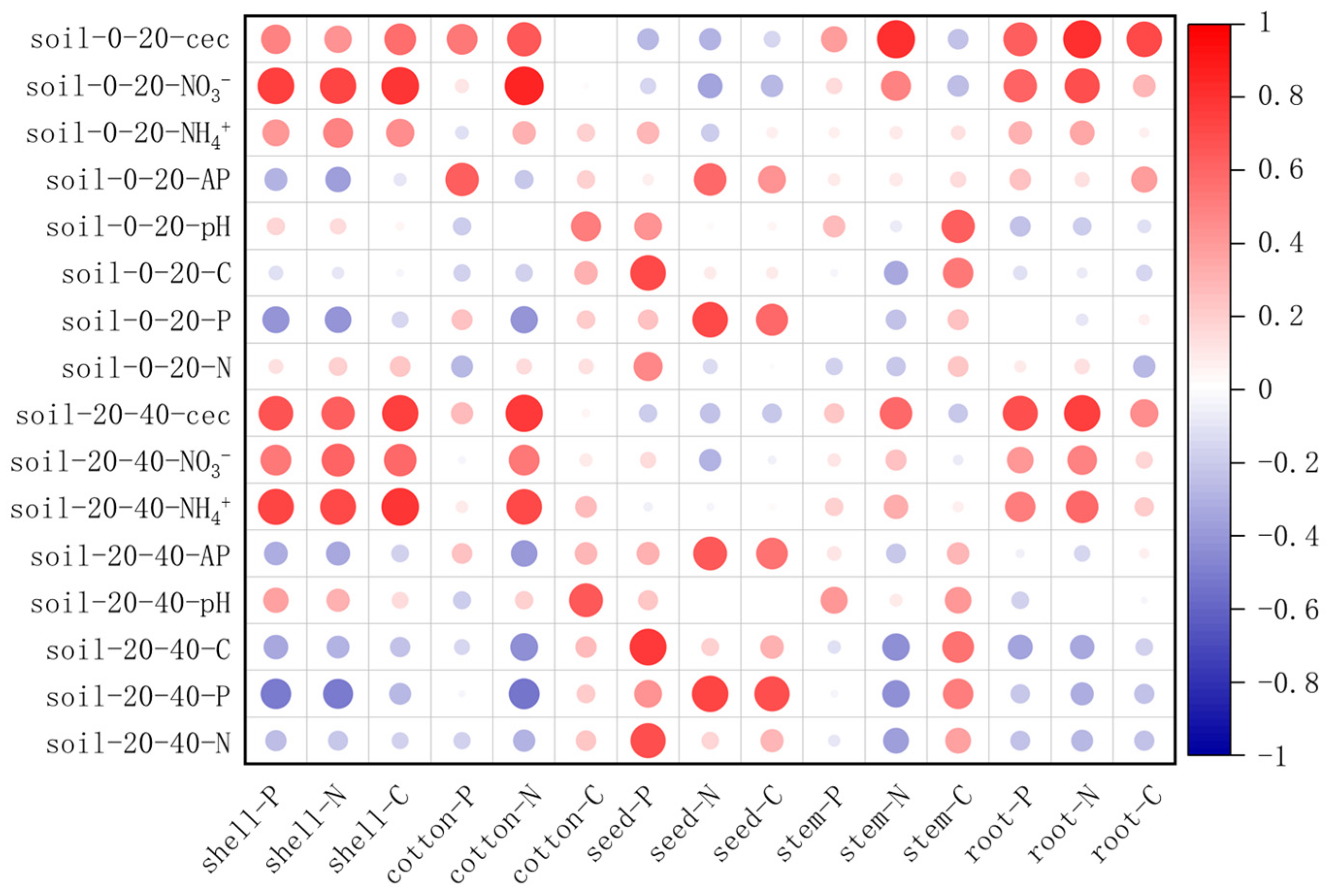
3.5. Soil–Plant Nutrient Relationship
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
SMRAT Software Setup Interface

- where I is the data source file name and O is the data output file name.
- where G, Y, X are the data headers, and T selects log Y vs. log X.
References
- Berg, G. Plant–microbe interactions promoting plant growth and health: Perspectives for controlled use of microorganisms in agriculture. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 84, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pretty, J.; Bharucha, Z.P. Sustainable intensification in agricultural systems. Ann. Bot. 2014, 114, 1571–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratnadass, A.; Fernandes, P.; Avelino, J.; Habib, R. Plant species diversity for sustainable management of crop pests and diseases in agroecosystems: A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2012, 32, 273–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Stomph, T.J.; Makowski, D.; Li, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, F.; Van der Werf, W. The productive performance of intercropping. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2201886120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, E.; Gong, W.; Xu, L.; Zhao, Z.; He, D.; Yang, F.; Wang, X.; Yong, T.; Liu, J.; et al. Soybean yield variations and the potential of intercropping to increase production in China. Field Crops Res. 2023, 291, 108771. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Jiang, F.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, G.; Gao, B.; Cao, G.; Islam, M.U.I.; Cao, Z.; Zhao, X. Potential crop yield gains under intensive soybean/maize intercropping in China. Plant Soil 2025, 506, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebede, E. Contribution, Utilization, and Improvement of Legumes-Driven Biological Nitrogen Fixation in Agricultural Systems. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 767998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Ouyang, X.; Wang, B.; Tian, D.; Xu, C.; Lin, Z.; Ge, X.; Tang, L. Understanding the effects of tree-crop intercropping systems on crop production in China by combining field experiments with a meta-analysis. Agric. Syst. 2023, 210, 103705. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, L.; Dai, J.; Tian, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, W.; Dong, H. Review of the technology for high-yielding and efficient cotton cultivation in the northwest inland cotton-growing region of China. Field Crops Res. 2017, 208, 18–26. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Li, Y.; Biswas, A.; Wang, J.; Dong, H.; Chen, J.; Liu, C.; Fan, X. Impact of climate change and crop management on cotton phenology based on statistical analysis in the main-cotton-planting areas of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 298, 126750. [Google Scholar]
- Govereh, J.; Jayne, T.S. Cash cropping and food crop productivity: Synergies or trade-offs? Agric. Econ. 2003, 28, 39–50. [Google Scholar]
- Grassini, P.; Cassman, K.G. High-yield maize with large net energy yield and small global warming intensity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1074–1079. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, B.J.; Gan, Y.W.; Duan, Z.P.; Hao, X.D.; Xu, W.L.; Li, L.H. Competitive interaction in jujube tree/cotton agroforestry system in Xinjiang province, northwestern China. Agrofor. Syst. 2019, 93, 591–605. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, T.; Zhang, N.; Wang, T.; Wang, D.; Yu, C.; Meng, W.; Fei, H.; Chen, R.; Li, Y.; Zhou, B. Simulating on the effects of irrigation on jujube tree growth, evapotranspiration and water use based on crop growth model. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 243, 106517. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, P.; Ma, Y.; Hai, Y. Influence of jujube/cotton intercropping on soil temperature and crop evapotranspiration in an arid area. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 256, 107118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Khan, A.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, Z. Improving the productivity of Xinjiang cotton in heat-limited regions under two life history strategies. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 363, 121374. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, M.A.; Farooq, M.; Hussain, M. Productivity and profitability of cotton–wheat system as influenced by relay intercropping of insect resistant transgenic cotton in bed planted wheat. Eur. J. Agron. 2016, 75, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matloob, A.; Aslam, F.; Rehman, H.U.; Khaliq, A.; Ahmad, S.; Yasmeen, A.; Hussain, N. Cotton-Based Cropping Systems and Their Impacts on Production. In Cotton Production and Uses: Agronomy, Crop Protection, and Postharvest Technologies; Ahmad, S., Hasanuzzaman, M., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 283–310. [Google Scholar]
- Peixi, S.; Tingting, X. Agroecology Research and Practice in the Oasis Region, Northwest China. In Agroecology in China; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, P. A New Theory Producing Heterosis of Crops. Open Access Libr. J. 2021, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Jia, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Hu, X.; Ye, X.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y. Growth, photosynthesis, and nutrient uptake in wheat are affected by differences in nitrogen levels and forms and potassium supply. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veresoglou, S.D.; Peñuelas, J.; Fischer, R.; Rautio, P.; Sardans, J.; Merilä, P.; Tabakovic-Tosic, M.; Rillig, M.C. Exploring continental-scale stand health—N:P ratio relationships for European forests. New Phytol. 2014, 202, 422–430. [Google Scholar]
- Ekvall, L.; Greger, M. Effects of environmental biomass-producing factors on Cd uptake in two Swedish ecotypes of Pinus sylvestris. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 121, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Veresoglou, S.D.; Peñuelas, J. Variance in biomass-allocation fractions is explained by distribution in European trees. New Phytol. 2019, 222, 1352–1363. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Xia, M.; Guan, F.; Fan, S. Spatial Distribution of Soil Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Potassium Stocks in Moso Bamboo Forests in Subtropical China. Forests 2016, 7, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Lin, Z.; Penttinen, P.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Luo, Y.; Yue, T.; Jiang, P.; Fu, W. Effects of conversion from a natural evergreen broadleaf forest to a Moso bamboo plantation on the soil nutrient pools, microbial biomass and enzyme activities in a subtropical area. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 422, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, W.; Feng, B.; Lv, W.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, X.; Dong, Q. Plant biomass partitioning in alpine meadows under different herbivores as influenced by soil bulk density and available nutrients. CATENA 2024, 240, 108017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Huang, X.; Liu, Z.; Jin, W.; Hu, W.; Meng, Y.; Zhou, Z. Phosphorus application under continuous wheat-cotton straw retention enhanced cotton root productivity and seedcotton yield by improving the carbohydrate metabolism of root. Field Crops Res. 2024, 317, 109541. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, X.; Li, H.; Ding, R.; Du, T. Hydraulic, morphological, and anatomical changes over the development of cotton bolls and pedicels leading to boll opening under well-watered and water deficit conditions. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2024, 228, 105996. [Google Scholar]
- Schad, P. World Reference Base for Soil Resources—Its fourth edition and its history. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2023, 186, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, X.; Wang, Z.; Geng, Q.; Li, X.; Chen, S. The influence of topography on the quality of cultivated land and its improvement measures in Shache County. J. Agric. Sci. 2014, 4, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S. Soil Agrochemical Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Koven, C.D.; Kueppers, L.M. Allometric relationships and trade-offs in 11 common mediterranean-climate grasses. Ecol. Appl. 2024, 34, e2976. [Google Scholar]
- Hafner, J.M.; Steinke, J.; Uckert, G.; Sieber, S.; Kimaro, A.A. Allometric equations for estimating on-farm fuel production of gliricidia sepium (gliricidia) shrubs and cajanus cajan (pigeon pea) plants in semi-arid tanzania. Energy Sustain. Soc. 2021, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wu, F.; Han, W.; Li, Q.; Han, Y.; Wang, G.; Feng, L.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Lei, Y.; et al. Carbon footprint of cotton production in China: Composition, spatiotemporal changes and driving factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 821, 153407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, F.; Xin, Q.; Li, Y.; Lin, Z. Historical variability of cotton yield and response to climate and agronomic management in Xinjiang, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, G.; Lu, W.; Lu, D. Interactive Effects of Nitrogen and Potassium on Grain Yield and Quality of Waxy Maize. Plants 2022, 11, 2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Meng, L.; Yin, T.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, Z.; Ogundeji, A.O.; Li, S. Maize/soybean intercrop over time has higher yield stability relative to matched monoculture under different nitrogen-application rates. Field Crops Res. 2023, 301, 109015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, R.; Gao, F.; Xiao, H.; Xu, H.; Wang, D. Apple and maize physiological characteristics and water-use efficiency in an alley cropping system under water and fertilizer coupling in Loess Plateau, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 221, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Wang, B.; Niu, X. Soil Erosion Reduction by Grain for Green Project in Desertification Areas of Northern China. Forests 2020, 11, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Song, L. A review of ecological mechanisms for management practices of protective forests. J. For. Res. 2021, 32, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, Y. Leaf Functional Traits and Relationships with Soil Properties of Zanthoxylum planispinum ‘dintanensis’ in Plantations of Different Ages. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Ma, Y.; Yang, T.; He, S.; Wang, D.; Jin, L.; Zhan, L.; Guo, Z.; Fan, K.; Li, J.; et al. Bacterial community composition of wheat aboveground compartments correlates with yield during the reproductive phase. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2024, 90, e01078-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akça, E.; Aydin, M.; Kapur, S.; Kume, T.; Nagano, T.; Watanabe, T.; Çilek, A.; Zorlu, K. Long-term monitoring of soil salinity in a semi-arid environment of Turkey. CATENA 2020, 193, 104614. [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro, L.C.P.; Matos, C.d.C.d.; Cândido, A.d.O.; Mendes, T.A.d.O.; Santana, M.F.; Costa, M.D. Changes in rhizosphere microbial diversity and composition due to NaCl addition to the soil modify the outcome of maize-weed interactions. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 159, 103818. [Google Scholar]
- Iseas, M.S.; Sainato, C.M.; Gómez, A.; Romay, C. Assessing salinity and sodicity of irrigated soils using apparent electrical conductivity in the Pampean region. Environ. Earth Sci. 2024, 83, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinman, P.J.A.; Sharpley, A.N.; Wolf, A.M.; Beegle, D.B.; Moore, P.A., Jr. Measuring Water-Extractable Phosphorus in Manure as an Indicator of Phosphorus in Runoff. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 2009–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, V.; Horta, C.; Dias-Ferreira, C. Evaluation of a phosphorus fertiliser produced from anaerobically digested organic fraction of municipal solid waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 238, 117911. [Google Scholar]
- Wissuwa, M.; Gonzalez, D.; Watts-Williams, S.J. The contribution of plant traits and soil microbes to phosphorus uptake from low-phosphorus soil in upland rice varieties. Plant Soil 2020, 448, 523–537. [Google Scholar]
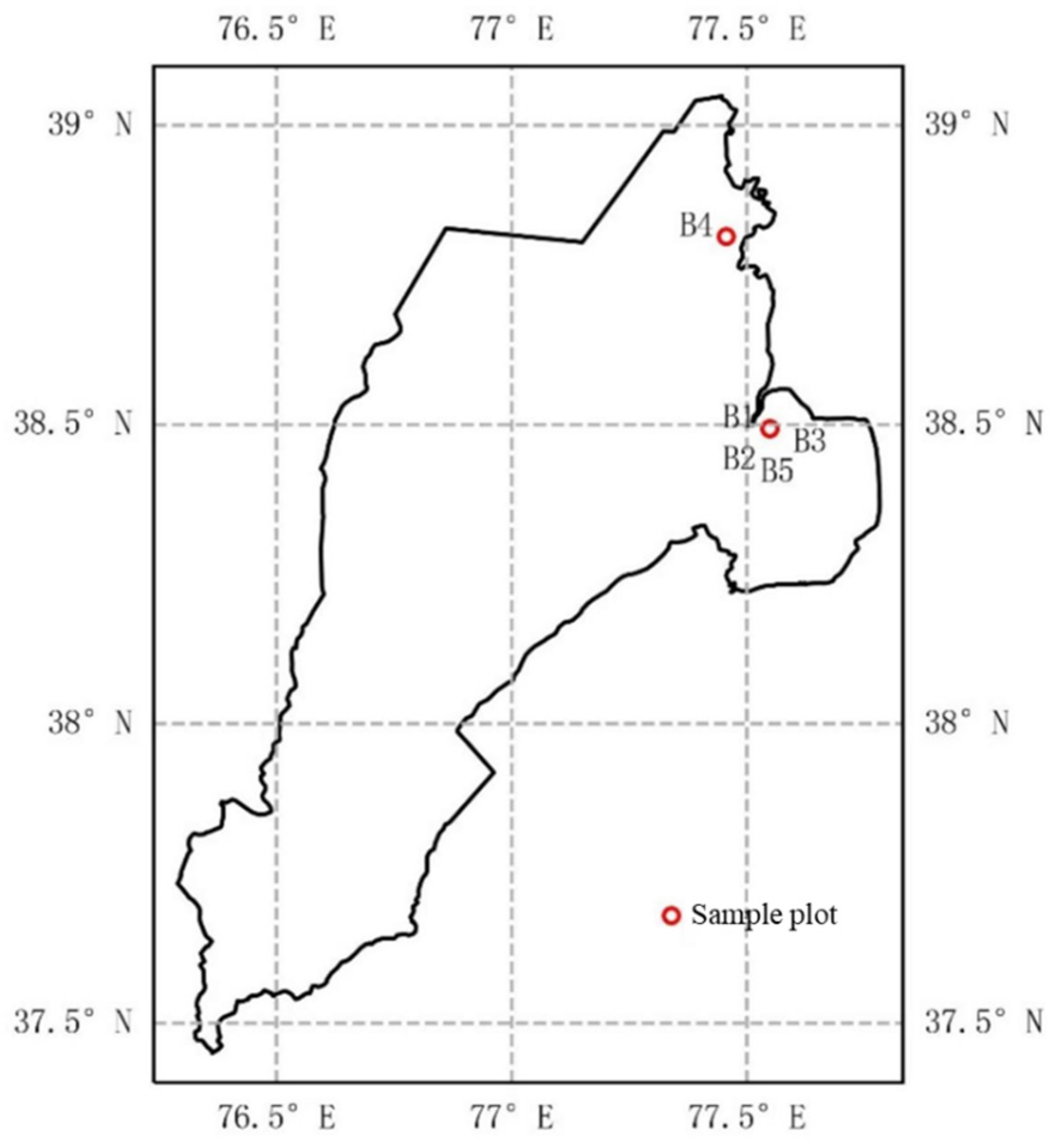


| Group | Planting Patterns | Planting Time |
|---|---|---|
| B1 | Peach trees are planted with a row spacing of 6.0 m and a plant spacing of 4.0 m, with cotton planted in between rows. | 2018 |
| B2 | Almond trees are planted with a row spacing of 6.1 m and a plant spacing of 4.8 m, with cotton planted in between rows. | 2011 |
| B3 | Peach trees are planted with a row spacing of 6.0 m and a plant spacing of 4.5 m, with cotton planted in between rows. | 2011 |
| B4 | Apple trees are planted with a row spacing of 6.0 m and a plant spacing of 4.2 m, with cotton planted in between rows. | 2018 |
| B5 | At intervals of 5.4 m, two rows of corn are planted with a row spacing of 60 cm and a plant spacing of 20 cm | 2021 |
| Indexes | Soil Layer (cm) | Compound Planting Mode | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 | B5 | ||
| EC (μs/cm) | 0–20 | 519.33 ± 62.37 b | 698.33 ± 38.78 b | 928.33 ± 100.25 b | 2078.67 ± 265.26 a | 2415.67 ± 370.62 a |
| 20–40 | 591.67 ± 87.79 d | 1099.67 ± 251.1 c | 927.33 ± 120.33 c | 1720.33 ± 263.22 b | 2682.00 ± 121.96 a | |
| NO3−-N (mg/kg) | 0–20 | 11.50 ± 1.60 c | 34.22 ± 6.79 b | 5.14 ± 1.10 c | 57.85 ± 10.54 b | 144.33 ± 25.79 a |
| 20–40 | 29.31 ± 2.04 c | 53.91 ± 8.26 b | 4.77 ± 0.36 d | 21.72 ± 9.12 c | 105.81 ± 19.46 a | |
| NH4+-N (mg/kg) | 0–20 | 1.06 ± 0.45 a | 0.91 ± 0.69 a | 0.39 ± 0.01 b | 0.56 ± 0.01 b | 1.38 ± 0.55 a |
| 20–40 | 0.57 ± 0.28 b | 1.12 ± 0.01 a | 0.50 ± 0.02 b | 1.00 ± 0.02 a | 1.61 ± 0.58 a | |
| AP (mg/kg) | 0–20 | 11.10 ± 2.07 bc | 14.43 ± 0.71 b | 9.37 ± 0.61 bc | 22.04 ± 2.23 a | 8.11 ± 1.29 c |
| 20–40 | 10.88 ± 2.70 a | 13.58 ± 1.37 a | 13.48 ± 0.88 a | 13.34 ± 3.52 a | 9.40 ± 1.49 a | |
| pH | 0–20 | 8.34 ± 0.05 a | 8.25 ± 0.09 a | 8.23 ± 0.22 a | 7.85 ± 0.03 a | 8.34 ± 0.18 a |
| 20–40 | 8.22 ± 0.26 a | 8.22 ± 0.15 a | 8.16 ± 0.14 a | 7.98 ± 0.17 a | 8.33 ± 0.16 a | |
| SOC (g/kg) | 0–20 | 6.52 ± 0.61 ab | 9.24 ± 1.31 a | 4.92 ± 0.54 b | 4.30 ± 0.12 b | 6.02 ± 0.56 ab |
| 20–40 | 7.62 ± 0.98 a | 7.20 ± 0.58 a | 6.01 ± 0.34 ab | 4.41 ± 0.46 b | 5.53 ± 0.89 ab | |
| TP (g/kg) | 0–20 | 0.91 ± 0.07 a | 0.87 ± 0.10 a | 0.82 ± 0.06 a | 0.95 ± 0.05 a | 0.75 ± 0.05 a |
| 20–40 | 1.03 ± 0.16 a | 0.93 ± 0.16 a | 0.85 ± 0.02 ab | 0.85 ± 0.03 ab | 0.70 ± 0.07 b | |
| TN (g/kg) | 0–20 | 0.73 ± 0.07 b | 0.95 ± 0.0 9a | 0.44 ± 0.01 b | 0.58 ± 0.03 b | 0.74 ± 0.11 ab |
| 20–40 | 0.88 ± 0.04 a | 0.82 ± 0.10 a | 0.59 ± 0.09 b | 0.55 ± 0.04 b | 0.67 ± 0.17 ab | |
| Group | n | R2 | Slope | LowCI | UppCI | Interc | LowCI | UppCI | Ymean | Xmean | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | 15 | 0.837 | 0.9708 | 0.7333 | 1.2853 | −0.7907 | −1.1445 | −0.4369 | 0.408 | 1.234 | ** |
| B2 | 15 | 0.862 | 0.9907 | 0.7646 | 1.2838 | −0.8332 | −1.1659 | −0.5005 | 0.39 | 1.235 | ** |
| B3 | 15 | 0.83 | 0.9726 | 0.7305 | 1.295 | −0.7567 | −1.0994 | −0.414 | 0.374 | 1.162 | ** |
| B4 | 15 | 0.853 | 0.98 | 0.7503 | 1.2799 | −0.8331 | −1.1794 | −0.4868 | 0.412 | 1.271 | ** |
| B5 | 15 | 0.791 | 1.1385 | 0.8293 | 1.5631 | −1.0136 | −1.5143 | −0.5129 | 0.509 | 1.338 | ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, L.; Shi, L.; Gao, Q.; Liu, G.; Liang, C. Effect of Compound Planting Mode on Nutrient Distribution in Cotton. Plants 2025, 14, 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14071051
He L, Shi L, Gao Q, Liu G, Liang C. Effect of Compound Planting Mode on Nutrient Distribution in Cotton. Plants. 2025; 14(7):1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14071051
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Lirong, Lei Shi, Qiaoni Gao, Guobin Liu, and Chutao Liang. 2025. "Effect of Compound Planting Mode on Nutrient Distribution in Cotton" Plants 14, no. 7: 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14071051
APA StyleHe, L., Shi, L., Gao, Q., Liu, G., & Liang, C. (2025). Effect of Compound Planting Mode on Nutrient Distribution in Cotton. Plants, 14(7), 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14071051








