Identification of the KNOX Gene Family in Salvia miltiorrhiza Revealing Its Response Characteristics to Salt Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of SmKNOX Gene Family of S. miltiorrhiza
2.2. SmKNOX Protein Sequence Alignment Analysis
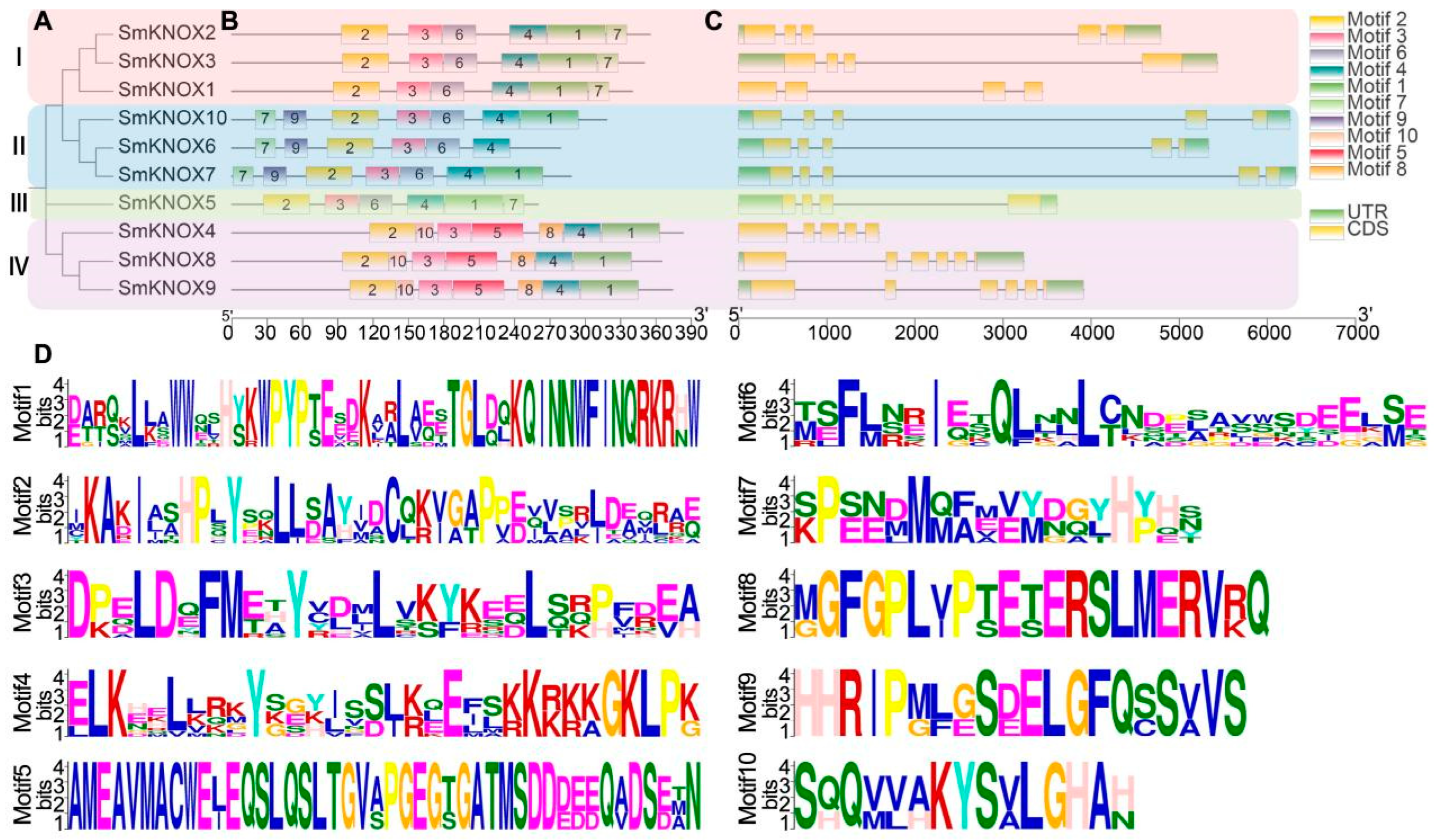
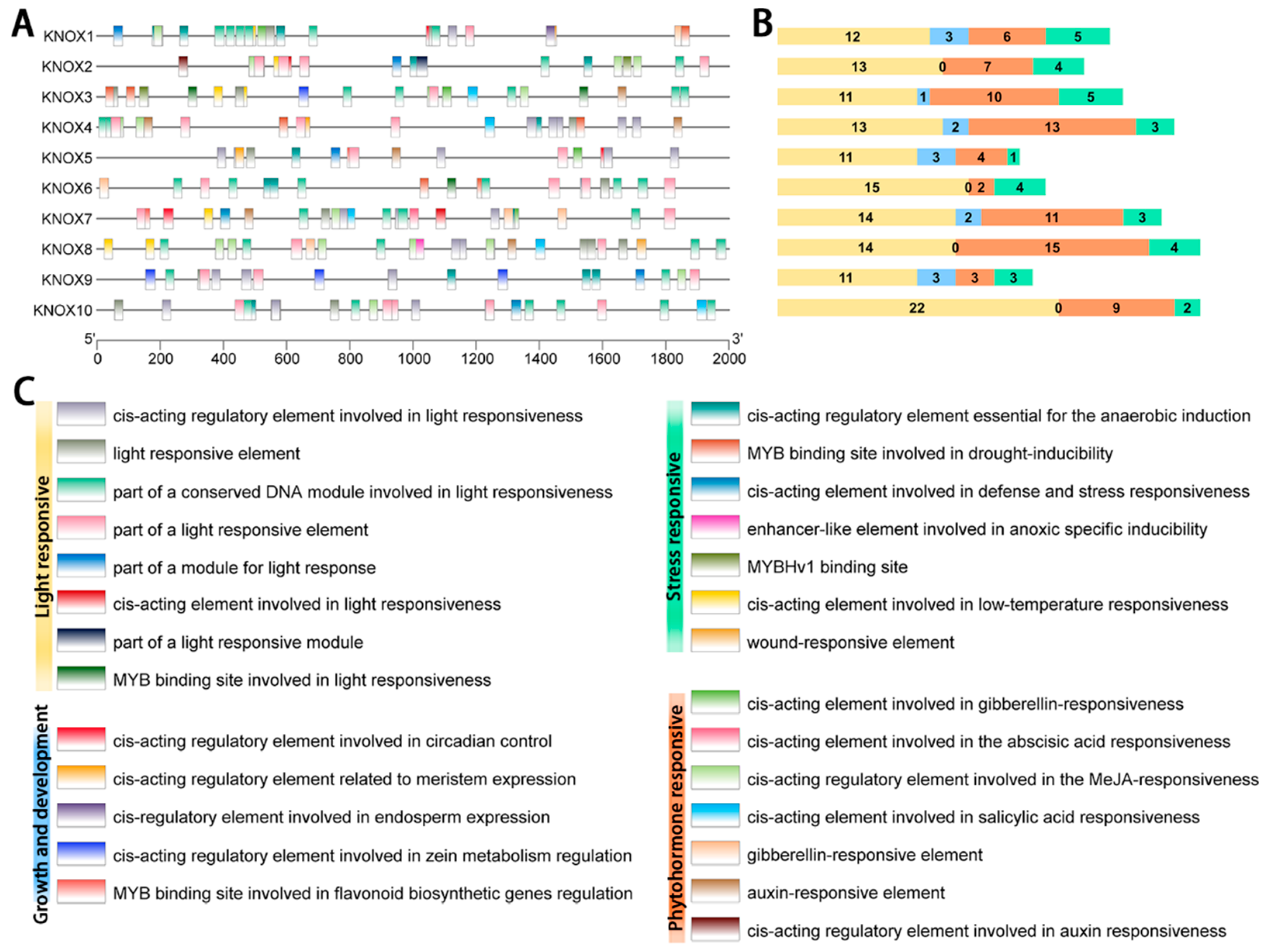
2.3. Gene Structure and Conserved Domains Analysis
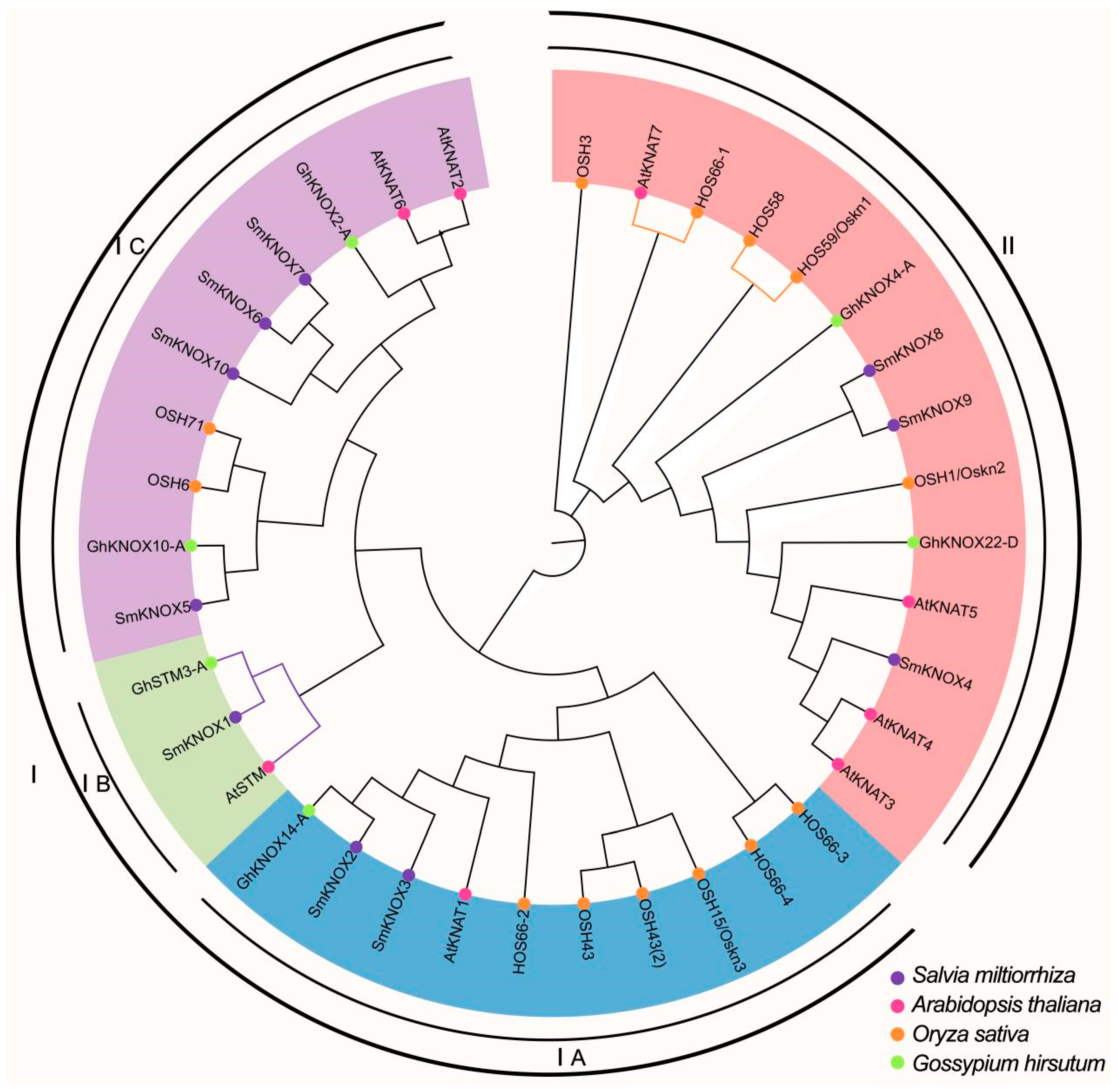
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis of SmKNOXs
2.5. Cis-Acting Element Analysis
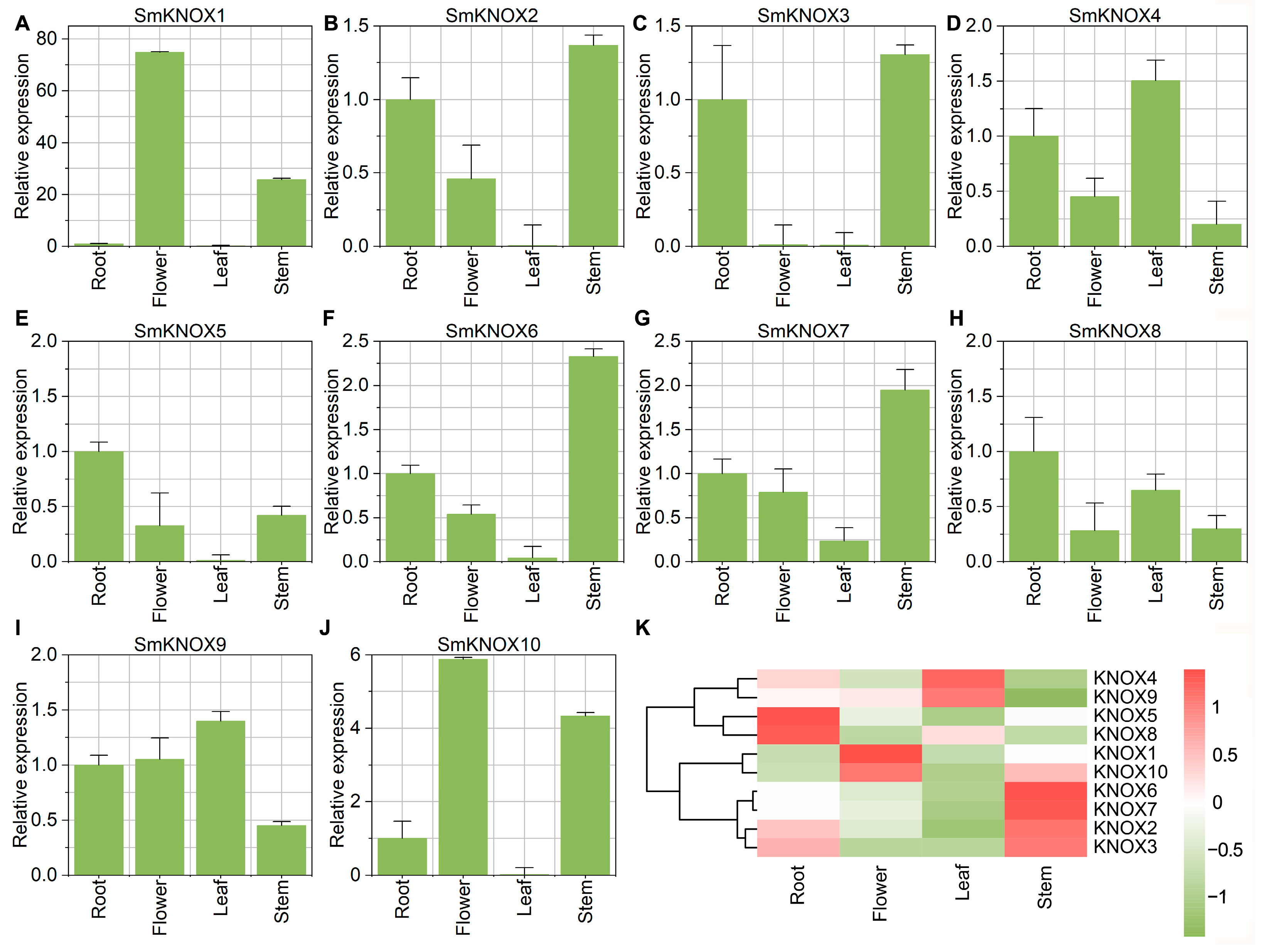
2.6. The Expression Profiling of SmKNOXs Genes Among Tissues
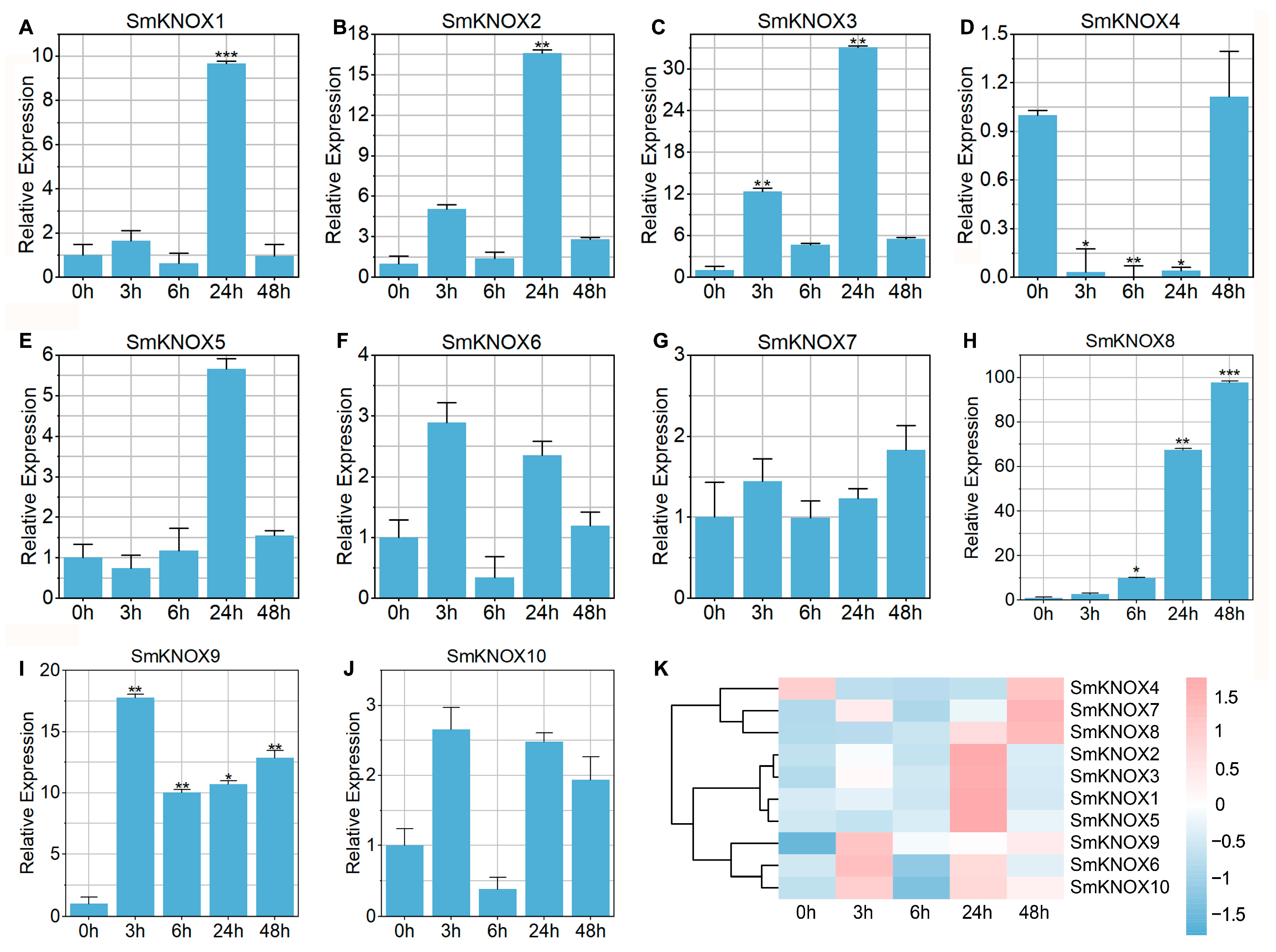
2.7. Expression Analysis of SmKNOXs Under Salt Stress
2.8. Expression Analysis of Target Genes of SmKNOXs Under Salt Stress
2.9. Gene Cloning of SmKNOXs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Gene Family Identification and Characterization
4.3. Multiple Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Relationship Analysis
4.4. Tissue Differential Expression Analysis of SmKNOX Genes
4.5. Stress Response Analysis of SmKNOX Genes
4.6. Gene Cloning Analysis of SmKNOX Genes
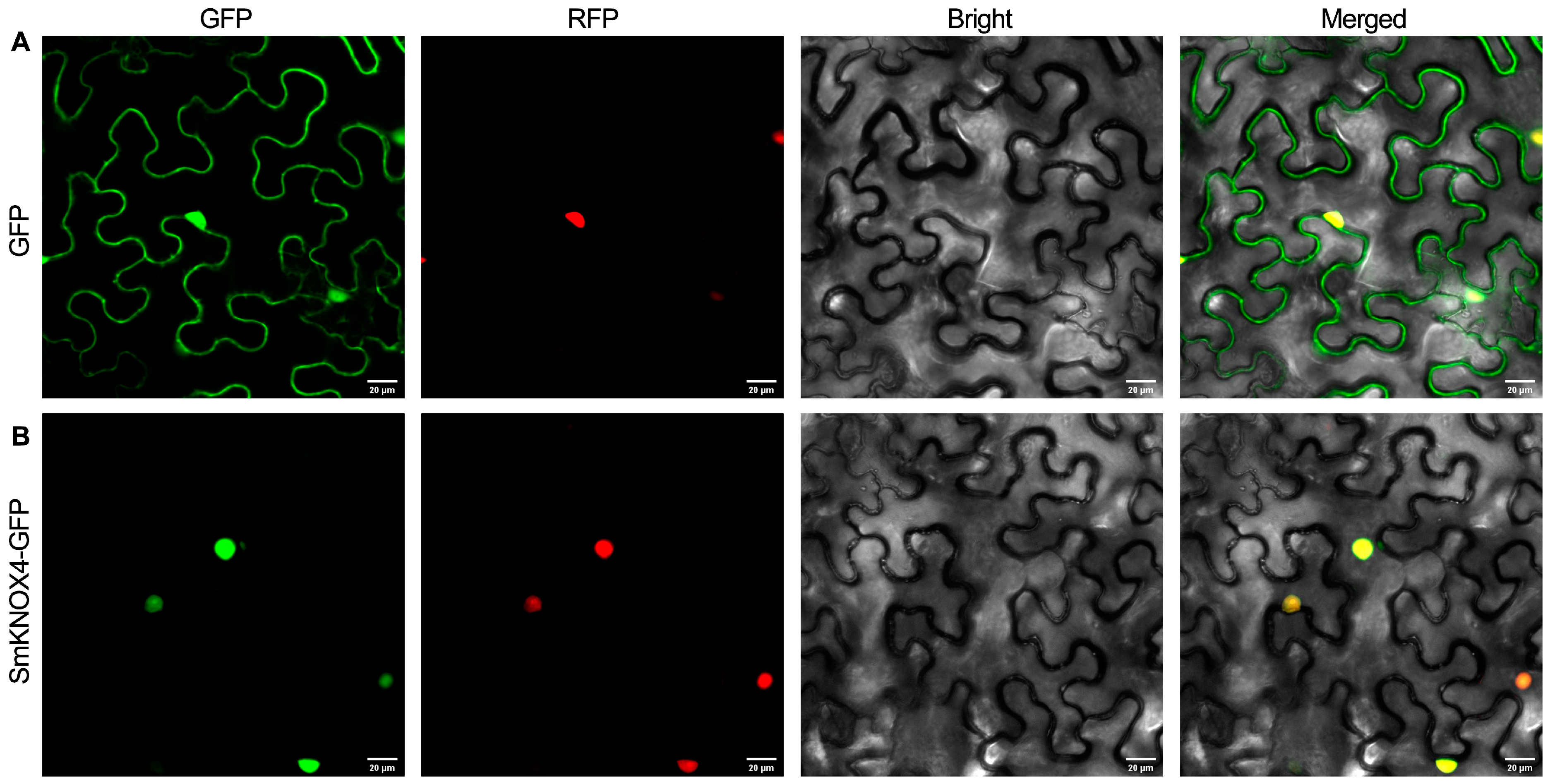
4.7. Subcellular Localization Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, L.G.; Greene, B.; Veit, B.; Hake, S.J.D. A dominant mutation in the maize homeobox gene, Knotted-1, causes its ectopic expression in leaf cells with altered fates. Development 1992, 116, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truernit, E.; Siemering, K.R.; Hodge, S.; Grbic, V.; Haseloff, J. A map of KNAT gene expression in the Arabidopsis root. Plant Mol. Biol. 2006, 60, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Yao, Y.; Ye, W.; Wang, S.; Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; Sun, F.; Xi, Y. Genome-Wide Identification of Wheat KNOX Gene Family and Functional Characterization of TaKNOX14-D in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.; Tan, J.; Guo, H.; Huang, B.; Ying, Y.; Ramakrishnan, M.; Zhang, Z. Genome-wide analysis of the KNOX gene family in Moso bamboo: Insights into their role in promoting the rapid shoot growth. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuda, K.; Ito, Y.; Sato, Y.; Kurata, N. Positive autoregulation of a KNOX gene is essential for shoot apical meristem maintenance in rice. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 4368–4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, O.; Alvarez, J.P.; Levy, M.; Bowman, J.L.; Ori, N.; Shani, E. The KNOXI Transcription Factor SHOOT MERISTEMLESS Regulates Floral Fate in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 1309–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, M.; Ma, X.; Wang, J.; Xue, T.; Li, Z.; Cao, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, W.; et al. KNOX II transcription factor HOS59 functions in regulating rice grain size. Plant J. 2022, 110, 863–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, J.; Wu, X.; Hu, G.; Fan, S.; Ma, Q. Evolutionary Relationships and Divergence of KNOTTED1-Like Family Genes Involved in Salt Tolerance and Development in Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 774161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Qin, T.; Wall, S.B.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X.; Sun, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, B. Genome-wide identification of KNOX transcription factors in cotton and the role of GhKNOX4-A and GhKNOX22-D in response to salt and drought stress. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 226, 1248–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Lu, M.Z. The transcription factor KNAT2/6b mediates changes in plant architecture in response to drought via down-regulating GA20ox1 in Populus alba × P. glandulosa. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 5625–5637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Manzoor, M.A.; Wang, G.; Chen, C.; Song, C. Comparative analysis of KNOX genes and their expression patterns under various treatments in Dendrobium huoshanense. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1258533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.C.; Yang, Z.T.; Shang, L.L.; He, S.Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Xin, G.S. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the KNOX family and its diverse roles in response to growth and abiotic tolerance in sweet potato and its two diploid relatives. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannelli, M.A.; Nicolodi, C.; Coraggio, I.; Fabriani, M.; Baldoni, E.; Frugis, G. A Novel Role of Medicago truncatula KNAT3/4/5-like Class 2 KNOX Transcription Factors in Drought Stress Tolerance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.M.; Xu, S.W.; Liu, P.Q. Salvia miltiorrhizaBurge (Danshen): A golden herbal medicine in cardiovascular therapeutics. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 802–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing-Yan, H.; Jing-Yu, F.; Yoshinori, H.; Soichiro, M.; De-Hua, C.; Hiromasa, I.; Toshifumi, H.; Hiroshi, T.; Ikuko, K.J.P.T. Ameliorating effects of compounds derived from Salvia miltiorrhiza root extract on microcirculatory disturbance and target organ injury by ischemia and reperfusion. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 117, 280–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Song, J.; Luo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Song, C.; Wang, B.; et al. Analysis of the Genome Sequence of the Medicinal Plant Salvia miltiorrhiza. Mol. Plant 2016, 9, 949–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Lin, C.; Xing, P.; Fen, Y.; Jin, H.; Zhou, C.; Gu, Y.Q.; Wang, J.; Li, X. A high-quality reference genome sequence of Salvia miltiorrhiza provides insights into tanshinone synthesis in its red rhizomes. Plant Genome 2020, 13, e20041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Chang, Y.; Li, C.; Qiu, X.; Cui, X.; Meng, F.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Lu, S. Chromosome-level genome assembly of Salvia miltiorrhiza with orange roots uncovers the role of Sm2OGD3 in catalyzing 15,16-dehydrogenation of tanshinones. Hortic. Res. 2023, 10, uhad069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasaki, H.; Sakamoto, T.; Sato, Y.; Matsuoka, M. Functional Analysis of the Conserved Domains of a Rice KNOX Homeodomain Protein, OSH15. Plant Cell 2001, 13, 2085–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, T.; Nishimura, A.; Tamaoki, M.; Kuba, M.; Tanaka, H.; Iwahori, S.; Matsuoka, M. The Conserved KNOX Domain Mediates Specificity of Tobacco KNOTTED1-Type Homeodomain Proteins. Plant Cell 1999, 11, 1419–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jasinski, S.; Piazza, P.; Craft, J.; Hay, A.; Woolley, L.; Rieu, I.; Phillips, A.; Hedden, P.; Tsiantis, M. KNOX Action in Arabidopsis Is Mediated by Coordinate Regulation of Cytokinin and Gibberellin Activities. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, 1560–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.; Wang, Y.; Sharif, R.; Dong, Q.L.; Liu, Y.; Luan, H.A.; Zhang, X.M.; Guo, S.P.; Qi, G.H. KNOTTED1-like homeobox (KNOX) transcription factors—Hubs in a plethora of networks: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; You, S.; Taylor-Teeples, M.; Li, W.L.; Schuetz, M.; Brady, S.M.; Douglas, C.J. BEL1-LIKE HOMEODOMAIN6 and KNOTTED ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA7 Interact and Regulate Secondary Cell Wall Formation via Repression of REVOLUTA. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 4843–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, S.C.; Chen, J.C.; Chang, P.Y.; Lin, H.Y. Co-option of the SHOOT MERISTEMLESS network regulates protocorm-like body development in Phalaenopsis aphrodite. Plant Physiol. 2022, 190, 127–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Cho, Y.H.; Ryu, H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, T.H.; Hwang, I. BLH1 and KNAT3 modulate ABA responses during germination and early seedling development in Arabidopsis. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 75, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Banerjee, A.K.; Hannapel, D.J. The tandem complex of BEL and KNOX partners is required for transcriptional repression of ga20ox1. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2004, 38, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Yang, X.; Zhao, W.; Lang, T.; Samuelsson, T. Evolution, diversification, and expression of KNOX proteins in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.A.; Moan, E.I.; Medford, J.I.; Barton, M.K. A member of the KNOTTED class of homeodomain proteins encoded by the STM gene of Arabidopsis. Nature 1996, 379, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, K.; Hake, S. Diverse functions of KNOX transcription factors in the diploid body plan of plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2015, 27, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hay, A.; Tsiantis, M. KNOX genes: Versatile regulators of plant development and diversity. Development 2010, 137, 3153–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.; Tabb, P.; Hepworth, S.R. BLADE-ON-PETIOLE1 and 2 regulate Arabidopsis inflorescence architecture in conjunction with homeobox genes KNAT6 and ATH1. Plant Signal. Behav. 2012, 7, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Yang, S.; Chen, C.Y.; Li, C.; Shan, W.; Lu, W.; Cui, Y.; Liu, X.; Wu, K. Arabidopsis BREVIPEDICELLUS interacts with the SWI2/SNF2 chromatin remodeling ATPase BRAHMA to regulate KNAT2 and KNAT6 expression in control of inflorescence architecture. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Yin, Q.; Chen, J.; Zhao, X.; Yue, F.; He, J.; Yang, L.; Liu, L.; Zeng, Q.; Lu, F.; et al. The class II KNOX transcription factors KNAT3 and KNAT7 synergistically regulate monolignol biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 5469–5483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yamaguchi, M.; Grienenberger, E.; Martone, P.T.; Samuels, A.L.; Mansfield, S.D. The Class II KNOX genes KNAT3 and KNAT7 work cooperatively to influence deposition of secondary cell walls that provide mechanical support to Arabidopsis stems. Plant J. 2020, 101, 293–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Morales, S.; Solís-Gaona, S.; Valdés-Caballero, M.V.; Juárez-Maldonado, A.; Loredo-Treviño, A.; Benavides-Mendoza, A. Transcriptomics of Biostimulation of Plants Under Abiotic Stress. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 583888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yang, X.; Gao, Y.; Yang, S. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of TALE Superfamily Genes in Soybean (Glycine max L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, Z.; Yao, W.; Li, R.; Jiang, T.; Zhou, B. Comprehensive analysis of the three-amino-acid-loop-extension gene family and its tissue-differential expression in response to salt stress in poplar. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 136, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, J.; Chuguransky, S.; Williams, L.; Qureshi, M.; Salazar, G.A.; Sonnhammer, E.L.L.; Tosatto, S.C.E.; Paladin, L.; Raj, S.; Richardson, L.J.; et al. Pfam: The protein families database in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D412–D419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consortium, T.U. UniProt: The Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 51, D523–D531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, T.L.; Johnson, J.; Grant, C.E.; Noble, W.S. The MEME Suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W39–W49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodstein, D.M.; Shu, S.; Howson, R.; Neupane, R.; Hayes, R.D.; Fazo, J.; Mitros, T.; Dirks, W.; Hellsten, U.; Putnam, N.; et al. Phytozome: A comparative platform for green plant genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D1178–D1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Chen, Y.; Cai, G.; Cai, R.; Hu, Z.; Wang, H. Tree Visualization By One Table (tvBOT): A web application for visualizing, modifying and annotating phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W587–W592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Hou, S.; Cui, G.; Chen, S.; Wei, J.; Huang, L. Characterization of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR analysis in various tissues of Salvia miltiorrhiza. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2010, 37, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Gene Name | Number of Amino Acids | Molecular Weight | pI | Instability Index | Grand Average of Hydropathicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SmKNOX1 | 340 | 38,093.08 | 5.73 | 57.33 | −0.56 |
| SmKNOX2 | 355 | 40,606.38 | 5.86 | 45.66 | −0.849 |
| SmKNOX3 | 350 | 40,538.12 | 6.22 | 55.54 | −1.065 |
| SmKNOX4 | 383 | 43,083.98 | 6.15 | 59.2 | −0.72 |
| SmKNOX5 | 260 | 30,056.95 | 6.50 | 52.1 | −0.717 |
| SmKNOX6 | 279 | 32,165.15 | 4.91 | 42.07 | −0.71 |
| SmKNOX7 | 288 | 33,516.71 | 5.50 | 45.65 | −0.863 |
| SmKNOX8 | 365 | 41,819.66 | 6.25 | 61.99 | −0.924 |
| SmKNOX9 | 374 | 42,534.07 | 6.03 | 53.65 | −0.941 |
| SmKNOX10 | 318 | 36,265.81 | 4.99 | 39.75 | −0.671 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, S.; Ma, W.; Cui, C.; Wang, S.; Jiang, M. Identification of the KNOX Gene Family in Salvia miltiorrhiza Revealing Its Response Characteristics to Salt Stress. Plants 2025, 14, 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14030348
Deng S, Ma W, Cui C, Wang S, Jiang M. Identification of the KNOX Gene Family in Salvia miltiorrhiza Revealing Its Response Characteristics to Salt Stress. Plants. 2025; 14(3):348. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14030348
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Siqi, Wenjing Ma, Chunxu Cui, Shiqian Wang, and Mei Jiang. 2025. "Identification of the KNOX Gene Family in Salvia miltiorrhiza Revealing Its Response Characteristics to Salt Stress" Plants 14, no. 3: 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14030348
APA StyleDeng, S., Ma, W., Cui, C., Wang, S., & Jiang, M. (2025). Identification of the KNOX Gene Family in Salvia miltiorrhiza Revealing Its Response Characteristics to Salt Stress. Plants, 14(3), 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14030348






