Maize Crops Under Rising Temperatures: Bacterial Influence on Biochemical and Lipidomic Changes Induced by Heat
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
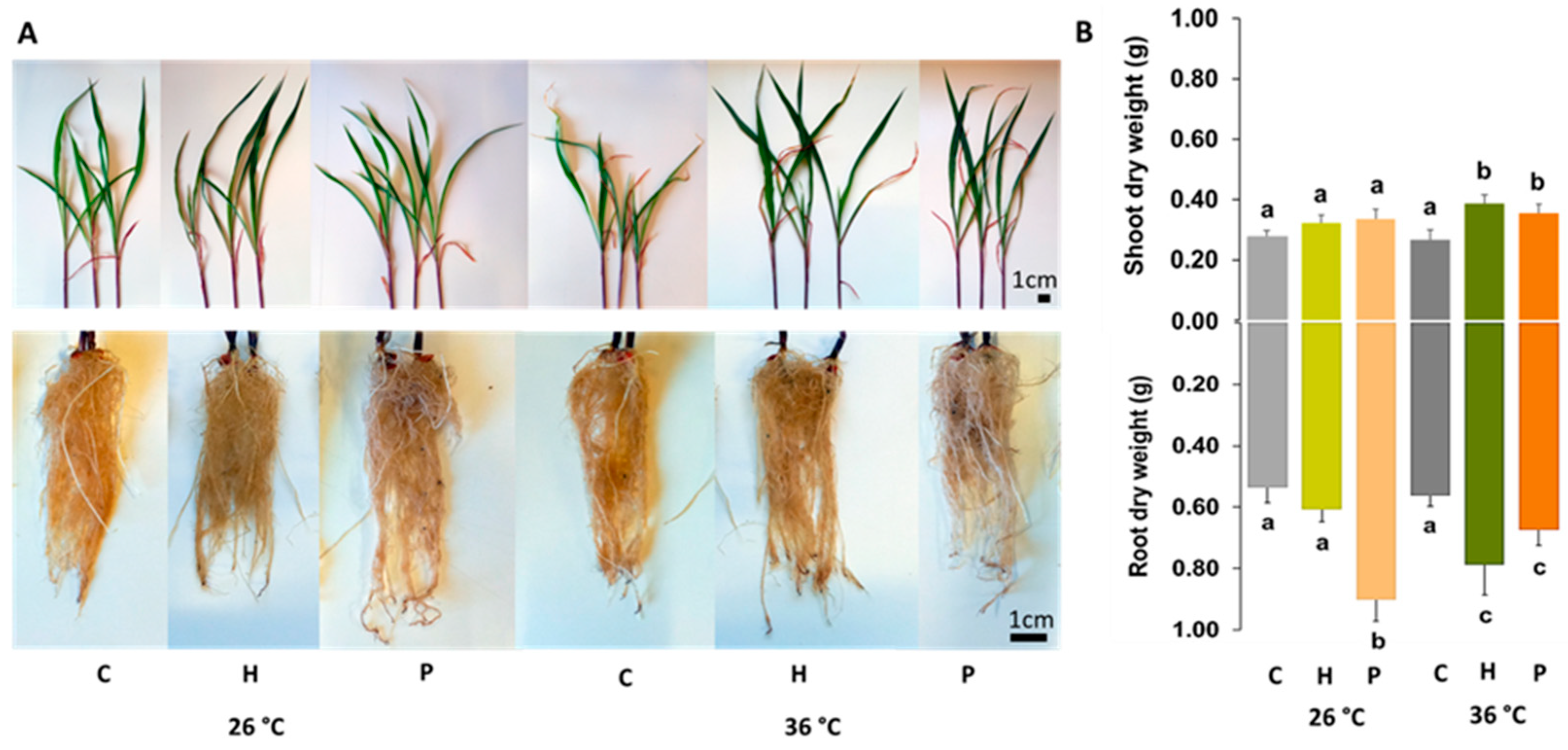
2.1. Seed Germination and Plant Growth
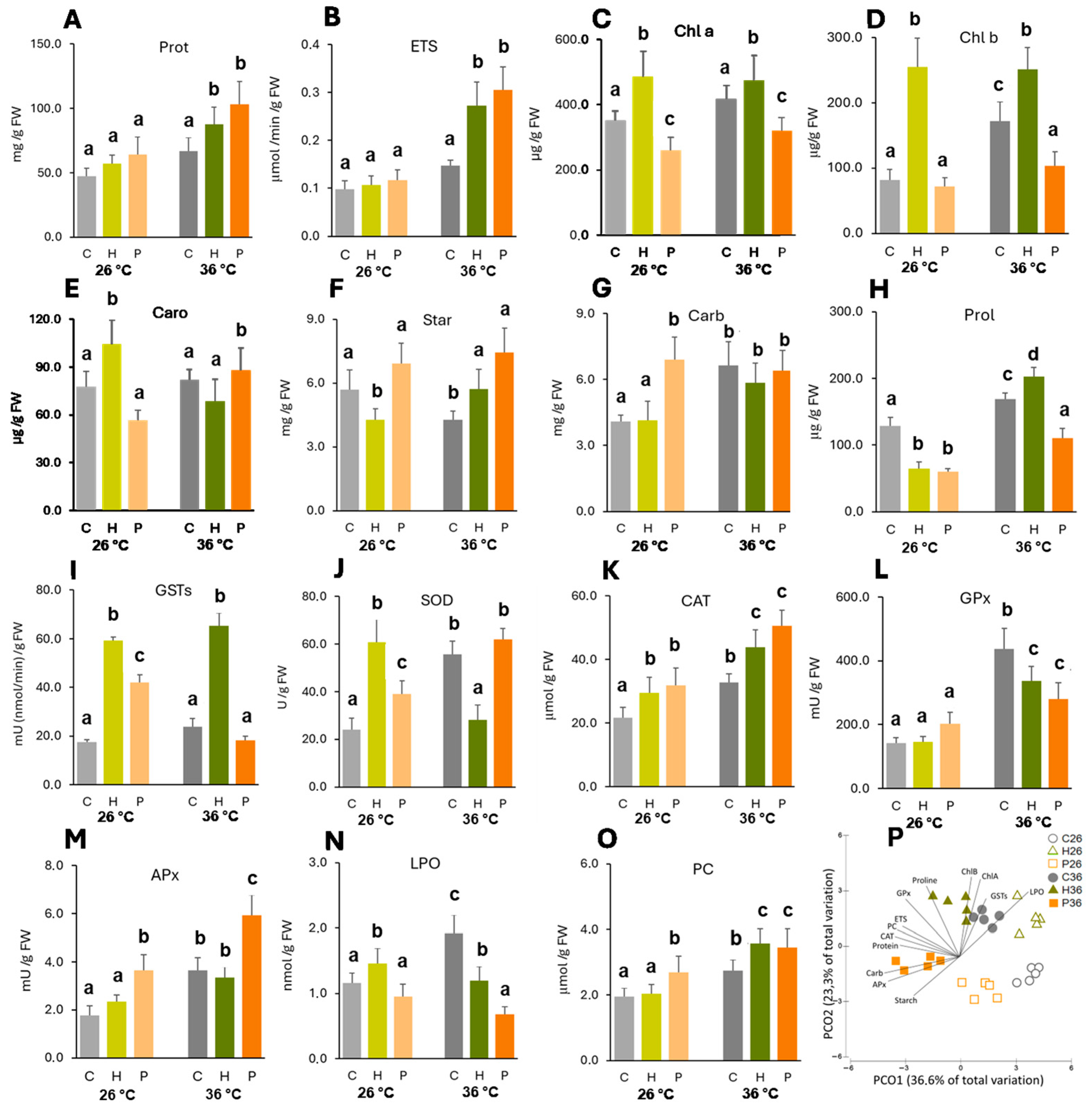
2.2. Biochemical Analysis
2.2.1. Cell Functioning
2.2.2. Osmolytes
2.2.3. Activity of Antioxidant Enzymes
2.2.4. Cell Damage
2.3. Multivariate Analysis of the Biochemical Parameters
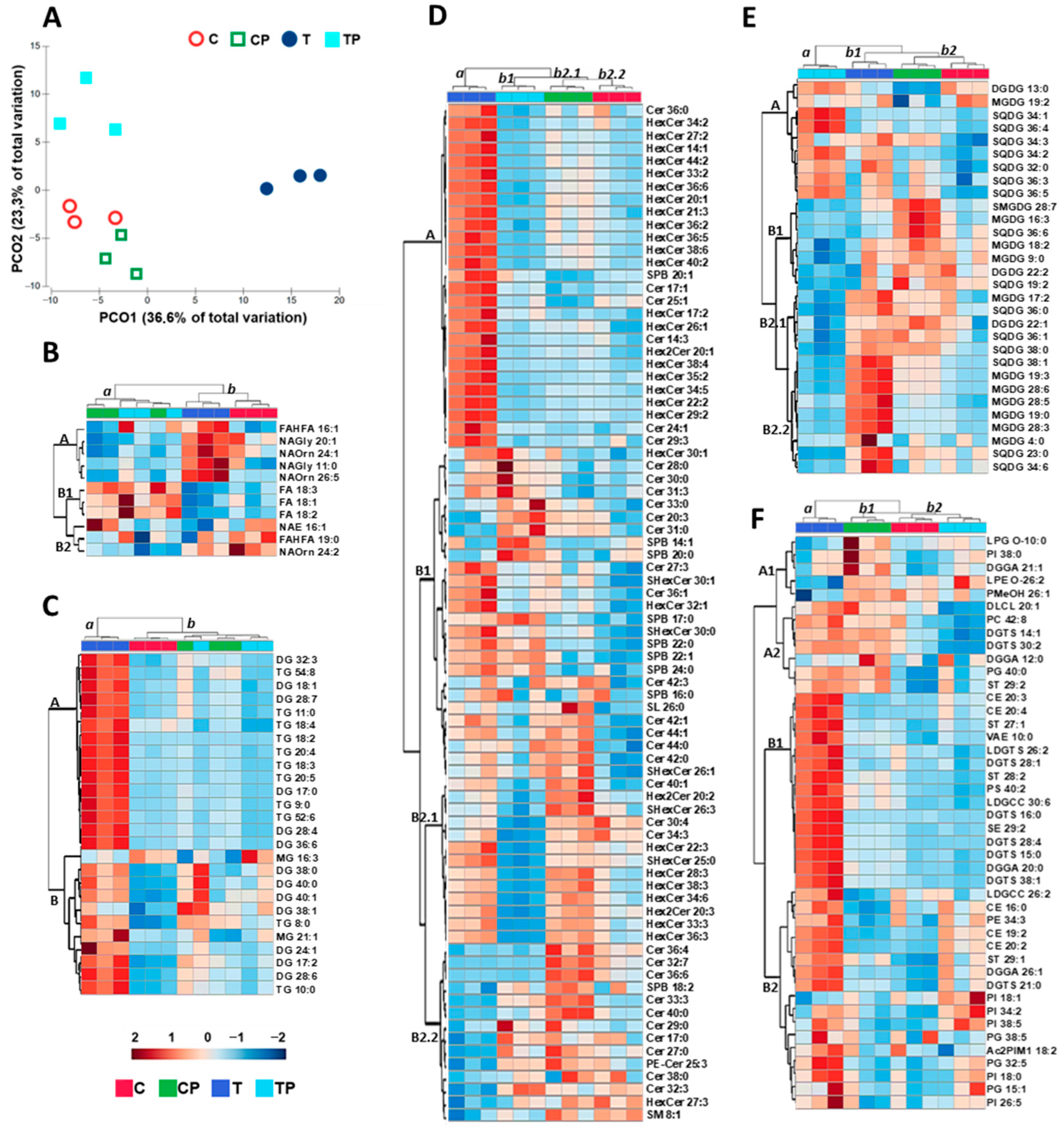
2.4. Lipids
2.4.1. Multivariate Analysis of Lipids
2.4.2. Fatty Acids
2.4.3. Glycerolipids
2.4.4. Sphingolipids
2.4.5. Galactolipids
2.4.6. Glycerophospholipids and Other Lipids
3. Discussion
3.1. Plant Emergence and Growth
3.2. Biochemical Response
3.2.1. Heat Stress Effect
3.2.2. Inoculation Effects at Control Temperature
3.2.3. Inoculation Effect Under Heat Stress
3.3. Lipid Profiles
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains
4.2. Experimental Conditions
4.3. Photosynthetic Pigments
4.4. Soluble and Insoluble Carbohydrates
4.5. Proline
4.6. Lipid Peroxidation
4.7. Protein, Protein Carbonylation, Electron Transport System, and Antioxidant Enzymes
4.8. Statistical Analysis
4.9. Lipidomics Analysis
4.9.1. Extraction Procedure
4.9.2. Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (UPLC-MS)
4.9.3. Untargeted Lipidomic Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shiferaw, B.; Smale, M.; Braun, H.; Duveiller, E.; Reynolds, M.; Muricho, G. Crops that feed the world 10. Past successes and future challenges to the role played by wheat in global food security. Food Secur. 2013, 5, 291–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Agricultural production statistics 2000–2021. In FAOSTAT Analytical Briefs, No. 60; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Climate Change 2021—The Physical Science Basis: Working Group I Contribution to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2023; pp. 1513–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djalovic, I.; Kundu, S.; Bahuguna, R.N.; Pareek, A.; Raza, A.; Singla-Pareek, S.L.; Prasad, P.V.V.; Varshney, R.K. Maize and heat stress: Physiological, genetic, and molecular insights. Plant Genome 2024, 17, 20378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Wang, L.; Yue, Y.; Wang, L.; Yang, N.X. The effects of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria on plants under temperature stress: A meta-analysis. Rhizosphere 2023, 28, 100788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Lim, J.A.; Harikrishna, J.A.; Islam, T.; Rahim, M.H.A.; Yaacob, J.S. Regulation of plant responses to temperature stress: A key factor in food security and for mitigating effects of climate change. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2024, 18, 141–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulut, M.; Karakas, E.; Fernie, A.R. Metabolic responses to multi-stress: An update. Plant Stress 2025, 15, 100729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibler, C.L.; Trugman, A.T.; Roberts, D.A.; Still, C.J.; Scott, R.L.; Caylor, K.K.; Stella, J.C.; Singer, M.B. Evapotranspiration regulates leaf temperature and respiration in dryland vegetation. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 339, 109560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, N.; Jiang, C.; Chen, L.; Paul, A.; Chatterjee, A.; Shen, G. Achieving abiotic stress tolerance in plants through antioxidative defense mechanisms. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1110622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oubohssaine, M.; Hnini, M.; Rabeh, K. Exploring lipid signaling in plant physiology: From cellular membranes to environmental adaptation. J. Plant Physiol. 2024, 300, 154295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrero-Sicilia, C.; Silvestre, S.; Haslam, R.P.; Michaelson, L.V. Lipid remodelling: Unravelling the response to cold stress in Arabidopsis and its extremophile relative Eutrema salsugineum. Plant Sci. 2017, 263, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, B.; Carreiras, J.A.; Cruz-Silva, A.; Mateos-Naranjo, E.; Rodríguez-Llorente, I.D.; Pajuelo, E.; Redondo-Gómez, S.; Mesa-Marín, J.; Figueiredo, A. Marine Plant Growth Promoting Bacteria (PGPB) inoculation technology: Testing the effectiveness of different application methods to improve tomato plants tolerance against acute heat wave stress. Plant Stress 2024, 11, 100434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, C.; Cardoso, P.; Santos, J.; Matos, D.; Figueira, E. Bioprospecting Soil Bacteria from Arid Zones to Increase Plant Tolerance to Drought: Growth and Biochemical Status of Maize Inoculated with Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria Isolated from Sal Island, Cape Verde. Plants 2022, 11, 2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timofeeva, A.M.; Galyamova, M.R.; Sedykh, S.E. How do Plant Growth-Promoting bacteria use plant hormones to regulate stress reactions? Plants 2024, 13, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goszcz, A.; Furtak, K.; Stasiuk, R.; Wójtowicz, J.; Musiałowski, M.; Schiavon, M.; Dębiec-Andrzejewska, K. Bacterial osmoprotectants—A way to survive in saline conditions and potential crop allies. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2025, 49, fuaf020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, M.; Borromeo, I.; Capo, C.; Glick, B.R.; Del Gallo, M.; Pietrini, F.; Forni, C. PGPB Improve Photosynthetic Activity and Tolerance to Oxidative Stress in Brassica napus Grown on Salinized Soils. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macabuhay, A.; Arsova, B.; Walker, R.; Johnson, A.; Watt, M.; Roessner, U. Modulators or facilitators? Roles of lipids in plant root–microbe interactions. Trends Plant Sci. 2021, 27, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Iqbal, A.; Hussain, A.; Hussain, A.; Shah, F.; Yun, B.; Mun, B. Exploring Plant–Bacterial symbiosis for Eco-Friendly agriculture and enhanced resilience. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.J.; Duan, M.; Zhou, C.; Jiao, J.; Cheng, P.; Yang, L.; Wei, W.; Shen, Q.; Ji, P.; Yang, Y.; et al. Antioxidant defense system in plants: Reactive oxygen species production, signaling, and scavenging during abiotic Stress-Induced oxidative damage. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breedt, G.; Labuschagne, N.; Coutinho, T. Seed treatment with selected plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria increases maize yield in the field. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2017, 171, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notununu, I.; Moleleki, L.; Roopnarain, A.; Adeleke, R. Enhancing maize drought and heat tolerance: Single vs combined plant growth promoting rhizobacterial inoculation. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1480718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaeim, H.; Kende, Z.; Jolánkai, M.; Kovács, G.P.; Gyuricza, C.; Tarnawa, Á. Impact of Temperature and Water on Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Maize (Zea mays L.). Agronomy 2022, 12, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, I.B.D.; De Araújo Pereira, A.P.; De Souza, A.J.; Cardoso, E.J.B.N.; Da Silva, F.G.; Oliveira, J.T.C.; Verdi, M.C.Q.; Sobral, J.K. Selection and Characterization of Burkholderia spp. for Their Plant-Growth Promoting Effects and Influence on Maize Seed Germination. Front. Soil Sci. 2022, 1, 805094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houida, S.; Yakkou, L.; Kaya, L.; Bilen, S.; Fadil, M.; Raouane, M.; Harti, A.E.; Amghar, S. Biopriming of maize seeds with plant growth-promoting bacteria isolated from the earthworm Aporrectodea molleri: Effect on seed germination and seedling growth. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 75, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisskopf, L.; Schulz, S.; Garbeva, P. Microbial volatile organic compounds in intra-kingdom and inter-kingdom interactions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, A.; Rana, A.; Dhaka, R.K.; Singh, A.P.; Chahar, M.; Singh, S.; Nain, L.; Singh, K.P.; Minz, D. Bacterial volatile organic compounds as biopesticides, growth promoters and plant-defense elicitors: Current understanding and future scope. Biotechnol. Adv. 2022, 63, 108078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moloi, M.J.; Tóth, C.; Hafeez, A.; Tóth, B. Insights into the Photosynthetic Efficiency and Chloroplast Ultrastructure of Heat-Stressed Edamame Cultivars During the Reproductive Stages. Agronomy 2025, 15, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brestic, M.; Zivcak, M.; Kunderlikova, K.; Allakhverdiev, S.I. High temperature specifically affects the photoprotective responses of chlorophyll b-deficient wheat mutant lines. Photosynth. Res. 2016, 130, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landman, W.A.; Engelbrecht, F.; Hewitson, B.; Malherbe, J.; Van Der Merwe, J. Towards bridging the gap between climate change projections and maize producers in South Africa. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2017, 132, 1153–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfiqar, F.; Ashraf, M. Proline alleviates abiotic stress induced oxidative stress in plants. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2022, 42, 4629–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqas, M.A.; Wang, X.; Zafar, S.A.; Noor, M.A.; Hussain, H.A.; Nawaz, M.A.; Farooq, M. Thermal Stresses in Maize: Effects and Management Strategies. Plants 2021, 10, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Cao, B.; Chen, Z.; Xu, K. Response of growth, photosynthetic electron transfer, and chloroplast ultrastructure to different LED light combination in green onion (Allium fistulosum L.). Physiol. Plant 2021, 172, 1662–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, I.; Munné-Bosch, S. Linking phosphorus availability with photo-oxidative stress in plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 2889–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Tariq, A.; Zeng, F.; Chai, X.; Graciano, C. Involvement of soluble proteins in growth and metabolic adjustments of drought-stressed Calligonum mongolicum seedlings under nitrogen addition. Plant Biol. 2020, 23, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.; Roychoudhury, A. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and response of antioxidants as ROS-scavengers during environmental stress in plants. Front. Environ. Sci. 2014, 2, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustakas, M.; Sperdouli, I.; Adamakis, I.S. Editorial: Reactive oxygen species in chloroplasts and chloroplast antioxidants under abiotic stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1208247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, E.; Kim, S.; Yun, M.; Choi, W. Recapitulation of the function and role of ROS generated in response to heat stress in plants. Plants 2021, 10, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tola, A.J.; Missihoun, T.D. Iron Availability Influences Protein Carbonylation in Arabidopsis thaliana Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarzábal, L.A.; Monserrate, L.; Buela, L.; Chica, E. Antarctic Pseudomonas spp. promote wheat germination and growth at low temperatures. Polar Biol. 2018, 41, 2343–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latef, A.a.H.A.; Alhmad, M.F.A.; Kordrostami, M.; Abo–Baker, A.A.; Zakir, A. Inoculation with Azospirillum lipoferum or Azotobacter chroococcum Reinforces Maize Growth by Improving Physiological Activities Under Saline Conditions. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2020, 39, 1293–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, P.; Kim, K.; Krishnamoorthy, R.; Mageswari, A.; Selvakumar, G.; Sa, T. Cold Stress Tolerance in Psychrotolerant Soil Bacteria and Their Conferred Chilling Resistance in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum Mill.) under Low Temperatures. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiryaki, D.; Aydın, İ.; Atıcı, Ö. Psychrotolerant bacteria isolated from the leaf apoplast of cold-adapted wild plants improve the cold resistance of bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) under low temperature. Cryobiology 2018, 86, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacheron, J.; Péchy-Tarr, M.; Brochet, S.; Heiman, C.M.; Stojiljkovic, M.; Maurhofer, M.; Keel, C. T6SS contributes to gut microbiome invasion and killing of an herbivorous pest insect by plant-beneficial Pseudomonas protegens. ISME J. 2019, 13, 1318–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas-Tapias, D.; Moreno-Galván, A.; Pardo-Díaz, S.; Obando, M.; Rivera, D.; Bonilla, R. Effect of inoculation with plant growth-promoting bacteria (PGPB) on amelioration of saline stress in maize (Zea mays). Appl. Soil Ecol. 2012, 61, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Guo, S.; Tian, W.; Chen, Y.; Han, H.; Chen, E.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z. Effects of Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria (PGPB) Inoculation on the Growth, Antioxidant Activity, Cu Uptake, and Bacterial Community Structure of Rape (Brassica napus L.) Grown in Cu-Contaminated Agricultural Soil. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, M.; Roitsch, T.; Pandey, C. Antioxidant responses and redox regulation within Plant-Beneficial microbe interaction. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Asaf, S.; Khan, A.L.; Jan, R.; Kang, S.; Kim, K.; Lee, I. Thermotolerance effect of plant growth-promoting Bacillus cereus SA1 on soybean during heat stress. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.; Lee, H.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.; Choi, K. Membrane fluidity-related adaptive response mechanisms of foodborne bacterial pathogens under environmental stresses. Food Res. Int. 2015, 72, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasertthai, P.; Paethaisong, W.; Theerakulpisut, P.; Dongsansuk, A. High Temperature Alters Leaf Lipid Membrane Composition Associated with Photochemistry of PSII and Membrane Thermostability in Rice Seedlings. Plants 2022, 11, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vayghan, H.S.; Tavalaei, S.; Grillon, A.; Meyer, L.; Ballabani, G.; Glauser, G.; Longoni, P. Growth Temperature Influence on Lipids and Photosynthesis in Lepidium sativum. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiva, S.; Samarakoon, T.; Lowe, K.A.; Roach, C.; Vu, H.S.; Colter, M.; Porras, H.; Hwang, C.; Roth, M.R.; Tamura, P.; et al. Leaf Lipid Alterations in Response to Heat Stress of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plants 2020, 9, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kränzlein, M.; Schmöckel, S.M.; Geilfus, C.; Schulze, W.X.; Altenbuchinger, M.; Hrenn, H.; Roessner, U.; Zörb, C. Lipid remodeling of contrasting maize (Zea mays L.) hybrids under repeated drought. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1050079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Qin, C.; Wang, X.; Ding, N. Plant Unsaturated fatty Acids: Biosynthesis and regulation. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Ding, N. Plant unsaturated fatty acids: Multiple roles in stress response. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 562785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graça, J. Suberin: The biopolyester at the frontier of plants. Front. Chem. 2015, 3, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castanheira, N.L.; Dourado, A.C.; Pais, I.; Semedo, J.; Scotti-Campos, P.; Borges, N.; Carvalho, G.; Crespo, M.T.B.; Fareleira, P. Colonization and beneficial effects on annual ryegrass by mixed inoculation with plant growth promoting bacteria. Microbiol. Res. 2017, 198, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, A. Lipid Metabolism in Plants Under Low-Temperature Stress: A Review; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 409–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Islam, Z.; Das, S.; Barman, A.; Chowdhury, M.; Mondal, B.P.; Ajnabi, J.; Manna, D. Harmonizing plant resilience: Unveiling the symphony of membrane lipid dynamics in response to abiotic stresses: A review. Discov. Plants. 2025, 2, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, U.; Ullah, S.; Tang, Z.; Elateeq, A.A.; Khan, Y.; Khan, J.; Khan, A.; Ali, S. Plant Metabolomics: An Overview of the Role of Primary and Secondary Metabolites against Different Environmental Stress Factors. Life 2023, 13, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N. Decoding Phytohormone signaling in Plant Stress Physiology: Insights, challenges, and future directions. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2025, 231, 106099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiade, S.R.G.; Zand-Silakhoor, A.; Fathi, A.; Rahimi, R.; Minkina, T.; Rajput, V.D.; Zulfiqar, U.; Chaudhary, T. Plant metabolites and signaling pathways in response to biotic and abiotic stresses: Exploring bio stimulant applications. Plant Stress 2024, 12, 100454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reszczyńska, E.; Hanaka, A. Lipids composition in plant membranes. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 78, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oubohssaine, M.; Hnini, M.; Rabeh, K. Phospholipid signaling in Plant Growth and Development: Insights, biotechnological implications and future directions. J. Plant Physiol. 2025, 307, 154454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashi, Y.; Saito, K. Lipidomic studies of membrane glycerolipids in plant leaves under heat stress. Prog. Lipid Res. 2019, 75, 100990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurchenko, O.; Kimberlin, A.; Mehling, M.; Koo, A.J.; Chapman, K.D.; Mullen, R.T.; Dyer, J.M. Response of high leaf-oil Arabidopsis thaliana plant lines to biotic or abiotic stress. Plant Signal. Behav. 2018, 13, e1464361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, S.P.; Krause, D.M.; Mueller, M.J.; Fekete, A. Accumulation of extra-chloroplastic triacylglycerols in Arabidopsis seedlings during heat acclimation. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 4517–4526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, N.; Mitra, R.; Dasgupta, D.; Ganguly, R.; Acharya, K.; Minkina, T.; Popova, V.; Churyukina, E.; Keswani, C. Unraveling lipid peroxidation-mediated regulation of redox homeostasis for sustaining plant health. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 206, 108272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xu, W.; Burke, J.J.; Xin, Z. Role of phosphatidic acid in high temperature tolerance in maize. Crop Sci. 2010, 50, 2506–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhou, C.; Fan, J.; Shanklin, J.; Xu, C. Mechanisms and functions of membrane lipid remodeling in plants. Plant J. 2021, 107, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshihara, A.; Kobayashi, K. Lipids in photosynthetic protein complexes in the thylakoid membrane of plants, algae, and cyanobacteria. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 73, 2735–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Miao, X. Monoglucosyldiacylglycerol participates in phosphate stress adaptation in Synechococcus sp. PCC 7942. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 522, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaduri, S.; Zhang, H.; Erramilli, S.; Cramer, W.A. Structural and functional contributions of lipids to the stability and activity of the photosynthetic cytochrome b6f lipoprotein complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 17758–17767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahaka, M.; Amara, S.; Wattanakul, J.; Gedi, M.A.; Aldai, N. The digestion of galactolipids and its ubiquitous function in nature for the uptake of the essential linolenic acid. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 6710–6744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Lin, Y.; Li, H. Increased ratio of galactolipid MGDG: DGDG induces jasmonic acid overproduction and changes chloroplast shape. New Phytol. 2020, 228, 1327–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Q.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Sui, P. Yield penalty of maize (Zea mays L.) under heat stress in different growth stages: A review. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 2465–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Cheng, B.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, G.; Han, L.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, X. Metabolic regulation and lipidomic remodeling in relation to spermidine-induced stress tolerance to high temperature in plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangla, S.; Ahlawat, Y.K.; Pathak, G.; Sharma, N.; Samani, M.; Bhan, V.; Essemine, J.; Sampasivam, Y.; Brar, N.S.; Malik, A.; et al. Metabolic engineering of lipids for crop resilience and nutritional improvements towards sustainable agriculture. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2025, 25, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueira, E.; Matos, D.; Cardoso, P.; Sá, C.; Fernandes, C.; Tauler, R.; Bedia, C. An underground strategy to increase mercury tolerance in the salt marsh halophyte Juncus maritimus Lam.: Lipid remodelling and Hg restriction. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2021, 191, 104619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueira, E.; Matos, D.; Cardoso, P.; Pires, A.; Fernandes, C.; Tauler, R.; Bedia, C. A biochemical and lipidomic approach to perceive Halimione portulacoides (L.) response to mercury: An environmental perspective. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 186, 114393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spicher, L.; Glauser, G.; Kessler, F. Lipid Antioxidant and Galactolipid Remodeling under Temperature Stress in Tomato Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munnik, T. Plant cell monographs. In Lipid Signaling in Plants; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 16, pp. 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harwood, J.L.; Okanenko, A.A. Sulphoquinovosyl Diacylglycerol (SQDG)—The Sulpholipid of Higher Plants; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 189–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batsale, M.; Bahammou, D.; Fouillen, L.; Mongrand, S.; Joubès, J.; Domergue, F. Biosynthesis and functions of Very-Long-Chain fatty acids in the responses of plants to abiotic and biotic stresses. Cells 2021, 10, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, U.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Guo, L. Emerging roles of sphingolipid signaling in plant response to biotic and abiotic stresses. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 1328–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordyum, E.L.; Artemenko, O.A.; Hasenstein, K.H. Lipid rafts and plant gravisensitivity. Life 2022, 12, 1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huby, E.; Napier, J.A.; Baillieul, F.; Michaelson, L.V.; Dhondt-Cordelier, S. Sphingolipids: Towards an integrated view of metabolism during the plant stress response. New Phytol. 2019, 225, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groux, R.; Fouillen, L.; Mongrand, S.; Reymond, P. Sphingolipids are involved in insect egg-induced cell death in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2022, 189, 2535–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Lai, Y.; Yao, N. Plant sphingolipids: Subcellular distributions and functions. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2025, 85, 102704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Lakra, N.; Goyal, A.; Ahlawat, Y.K.; Zaid, A.; Siddique, K.H.M. Drought and heat stress mediated activation of lipid signaling in plants: A critical review. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1216835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroppa, N.; Onelli, E.; Moreau, P.; Maneta-Peyret, L.; Berno, V.; Cammarota, E.; Ambrosini, R.; Caccianiga, M.; Scali, M.; Moscatelli, A. Sterols and Sphingolipids as New Players in Cell Wall Building and Apical Growth of Nicotiana tabacum L. Pollen Tubes. Plants 2022, 12, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, L.; Herrfurth, C.; Feussner, I.; Ehlers, K.; Haslam, T.M. Complex sphingolipids are essential for cell division and plasmodesmal development in the moss Physcomitrium patens. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, B.E.; Yu, D.; Martinez-Seidel, F.; Ho, W.W.H.; Rupasinghe, T.W.T.; Dolferus, R.; Roessner, U. The Effect of Cold Stress on the Root-Specific Lipidome of Two Wheat Varieties with Contrasting Cold Tolerance. Plants 2022, 11, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, H.E.; Rotsch, A.H.; Herrfurth, C.; Scholz, P.; Shomroni, O.; Salinas-Riester, G.; Feussner, I.; Ischebeck, T. Heat stress leads to rapid lipid remodeling and transcriptional adaptations in Nicotiana tabacum pollen tubes. Plant Physiol. 2022, 189, 490–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukov, A.; Vereshchagin, M. Polar glycerolipids and membrane lipid rafts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djanaguiraman, M.; Narayanan, S.; Erdayani, E.; Prasad, P.V.V. Effects of high temperature stress during anthesis and grain filling periods on photosynthesis, lipids and grain yield in wheat. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhong, C.; Deng, X.; Wang, X. Plant Sterol Clustering Correlates with Membrane Microdomains as Revealed by Optical and Computational Microscopy. Membranes 2021, 11, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colin, L.A.; Jaillais, Y. Phospholipids across scales: Lipid patterns and plant development. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2019, 53, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zheng, Q.; Shen, W.; Cram, D.; Fowler, D.B.; Wei, Y.; Zou, J. Understanding the biochemical basis of Temperature-Induced lipid pathway adjustments in plants. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 86–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J. Phospholipase D and phosphatidic acid in plant defence response: From protein–protein and lipid–protein interactions to hormone signalling. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 1721–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, K.; Li, M. Functions and interaction of plant lipid signalling under abiotic stresses. Plant Biol. 2023, 25, 361–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foka, I.C.K.; Ketehouli, T.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, F.; Li, H. The emerging roles of diacylglycerol kinase (DGK) in plant stress tolerance, growth, and development. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Singh, B.; Joshi, R.; Jaju, P.; Pati, P.K. Changes in the leaf proteome profile of Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal in response to Alternaria alternata infection. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, P.; Alves, A.; Silveira, P.; Sá, C.; Fidalgo, C.; Freitas, R.; Figueira, E. Bacteria from nodules of wild legume species: Phylogenetic diversity, plant growth promotion abilities and osmotolerance. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 1094–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellburn, A.R.; Lichtenthaler, H. Formulae and Program to Determine Total Carotenoids and Chlorophylls A and B of Leaf Extracts in Different Solvents. In Advances in Photosynthesis Research; Advances in Agricultural Biotechnology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1984; Volume 2, pp. 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuBois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric Method for Determination of Sugars and Related Substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, L.S.; Waldren, R.P.; Teare, I.D. Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 1973, 39, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buege, J.A.; Aust, S.D. Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol. CD-ROM/Methods Enzymol. 1978, 52, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, H.W.; Hogden, C.G. The biuret reaction in the determination of serum proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1940, 135, 707–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, C.S.; Oliveira, R.; Bento, F.; Geraldo, D.; Rodrigues, J.V.; Marcos, J.C. Simplified 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine spectrophotometric assay for quantification of carbonyls in oxidized proteins. Anal. Biochem. 2014, 458, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udenigwe, C.C.; Udechukwu, M.C.; Yiridoe, C.; Gibson, A.; Gong, M. Antioxidant mechanism of potato protein hydrolysates against in vitro oxidation of reduced glutathione. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 20, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, F.D.; Packard, T.T. Respiration and the activity of the respiratory electron transport system in marine zooplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1975, 20, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchamp, C.; Fridovich, I. Superoxide dismutase: Improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal. Biochem. 1971, 44, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, L.H.; Borg, L.H. A spectrophotometric method for determination of catalase activity in small tissue samples. Anal. Biochem. 1988, 174, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habig, W.H.; Pabst, M.J.; Jakoby, W.B. Glutathione S-Transferases. J. Biol. Chem. 1974, 249, 7130–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paglia, D.E.; Valentine, W.N. Studies on the Quantitative and Qualitative Characterization of Erythrocyte Glutathione Peroxidase. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1967, 70, 158–169. [Google Scholar]
- Nakano, Y.; Asada, K. Hydrogen Peroxide is Scavenged by Ascorbate-specific Peroxidase in Spinach Chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol. 1981, 22, 867–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorrochategui, E.; Jaumot, J.; Tauler, R. ROIMCR: A powerful analysis strategy for LC-MS metabolomic datasets. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrato, A.; Bedia, C.; Capriotti, A.L.; Cavaliere, C.; Gentile, V.; Maggi, M.; Montone, C.M.; Piovesana, S.; Sciarra, A.; Tauler, R.; et al. Untargeted metabolomics of prostate cancer zwitterionic and positively charged compounds in urine. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1158, 338381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Cova, M.; Bedia, C.; Stoll, D.R.; Tauler, R.; Jaumot, J. MSroi: A pre-processing tool for mass spectrometry-based studies. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2021, 215, 104333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wold, S.; Sjöström, M.; Eriksson, L. PLS-regression: A basic tool of chemometrics. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2001, 58, 109–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Our Results | Previous Results | Previous Studies |
|---|---|---|
| The strains were able to increase the dry weight of inoculated Zea mays plants in control and heat stress conditions. | Increased yield in temperature-stressed maize plants inoculated with Paenibacillus alvei, Bacillus safensis, Bacillus pumilus, and Brevundimonas vesicularis. | Breedt et al. [20] |
| At 26 °C, only Herbaspirillum sp. increased germination, but at 36 °C, both strains increased the germination rate and were able to increase shoot and root growth in Zea mays. | Increase in seed germination rate and early development in maize inoculated with strains of Burkholderia cepacian and Burkholderia graminis. | Dos Santos et al. [23] |
| Both Pantoea sp. and Herbaspirillum sp. were able to produce IAA at high temperature, and also increased the germination rate, root elongation, and plant weight in Zea mays. | Aeromonas encheleia and Pseudomonas azotoformans significantly increased maize germination rate, root elongation, and seedling weight due their strong ability to produce indole-3-acetic acid (IAA). | Houida et al. [24] |
| Herbaspirillum sp. inoculation significantly increased photosynthetic pigments, while Pantoea sp. did not have a significant effect. This effect was enhanced at high temperature. | PGPB inoculation resulted in increased chlorophyll content. | Rojas et al. [44] and Ren et al. [45] |
| Herbaspirillum sp. significantly increased GSTs and CAT and Pantoea sp. significantly increased CAT and APx in heat-stressed plants compared to heat-stressed non-inoculated ones, leading to lower LPO levels. | Bacillus safensis, Ochrobactrium pseudogrignonense, and Bacillus cereus were reported to activate antioxidant signaling in plants under heat stress, leading to a reduction in LPO. | Khan et al. [47] |
| Herbaspirillum sp. was able to significantly increase GST, SOD, and CAT activity and Pantoea sp. significantly induced the activity of GSTs, SOD, CAT, and APx at the control temperature. | Some beneficial microorganisms such as Pseudomonas strains can enhance the activity of antioxidant enzymes (APX, CAT, SOD) in plants. | González et al. [46] |
| Neither an increase in saturated fatty acids nor a decrease in unsaturated fatty acids at 36 °C was observed. | Bacteria inoculation on ryegrass increased FA biosynthesis by 65%. | Castanheira et al. [56] |
| Tocopherols did not change significantly among the conditions tested. | There were reported increases in tocopherols in Solanum lycopersicum grown at high temperature. | Spicher et al. [80] |
| Higher temperature increased sphingolipid (SPB and HexCer) concentration. | It was reported that heat stress led to an additional increase in all sphingolipid subclasses, especially the levels of SPB phosphates and HexCer in tobacco. | Krawkczyk et al. [93] |
| PI, PC, and PE increased with temperature. Pantoea sp. inoculation further increased PI, PC, and PE content. | It was found that PC and PE contents generally decreased in wheat under high temperature stress. | Narayanan et al. [95] |
| Heat stress increased PC content with no change in PE levels in leaves of Atriplex lentiformis. | Li et al. [98] | |
| No significant changes were observed in PA levels. | Reported an increase in PA levels with temperature in Zea mays. | Chen et al. [68] |
| There was an increase in sterols with temperature. Pantoea sp. inoculation further increased sterol content. | Reported increases in sterol levels in Arabidopsis thaliana in response to heat stress. | Shiva et al. [51] |
| Reported increases in sterol levels in Withania somnifera in response to heat stress. | Singh et al. [102] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pinto, R.; Cardoso, P.; Carneiro, B.; Pinto, G.; Bedia, C.; Figueira, E. Maize Crops Under Rising Temperatures: Bacterial Influence on Biochemical and Lipidomic Changes Induced by Heat. Plants 2025, 14, 2593. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162593
Pinto R, Cardoso P, Carneiro B, Pinto G, Bedia C, Figueira E. Maize Crops Under Rising Temperatures: Bacterial Influence on Biochemical and Lipidomic Changes Induced by Heat. Plants. 2025; 14(16):2593. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162593
Chicago/Turabian StylePinto, Ricardo, Paulo Cardoso, Bruno Carneiro, Glória Pinto, Carmen Bedia, and Etelvina Figueira. 2025. "Maize Crops Under Rising Temperatures: Bacterial Influence on Biochemical and Lipidomic Changes Induced by Heat" Plants 14, no. 16: 2593. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162593
APA StylePinto, R., Cardoso, P., Carneiro, B., Pinto, G., Bedia, C., & Figueira, E. (2025). Maize Crops Under Rising Temperatures: Bacterial Influence on Biochemical and Lipidomic Changes Induced by Heat. Plants, 14(16), 2593. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162593








