Effects of Water-Nitrogen Management on the Growth and Nitrogen Uptake and Utilization of Intercropped Alfalfa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
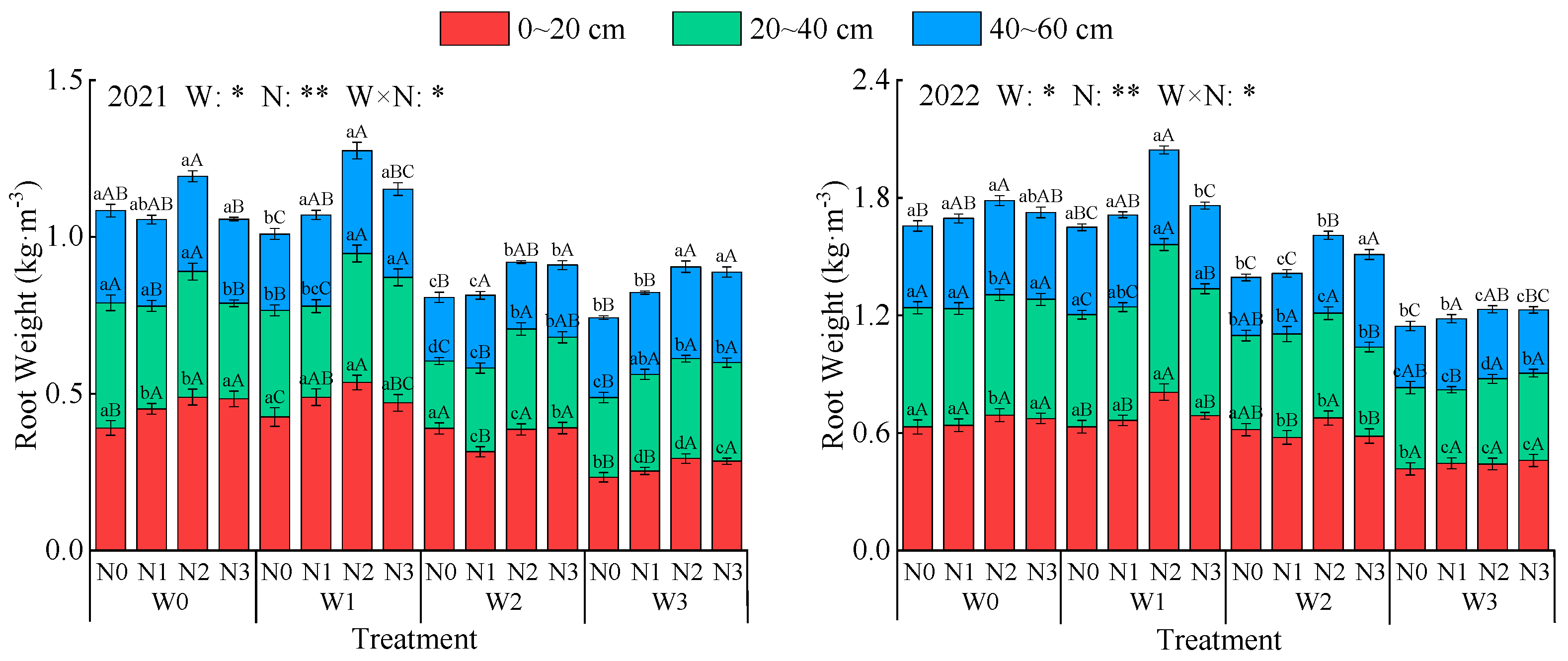
2.1. Effects of Water and Nitrogen Management on Biomass Allocation in Intercropped Alfalfa
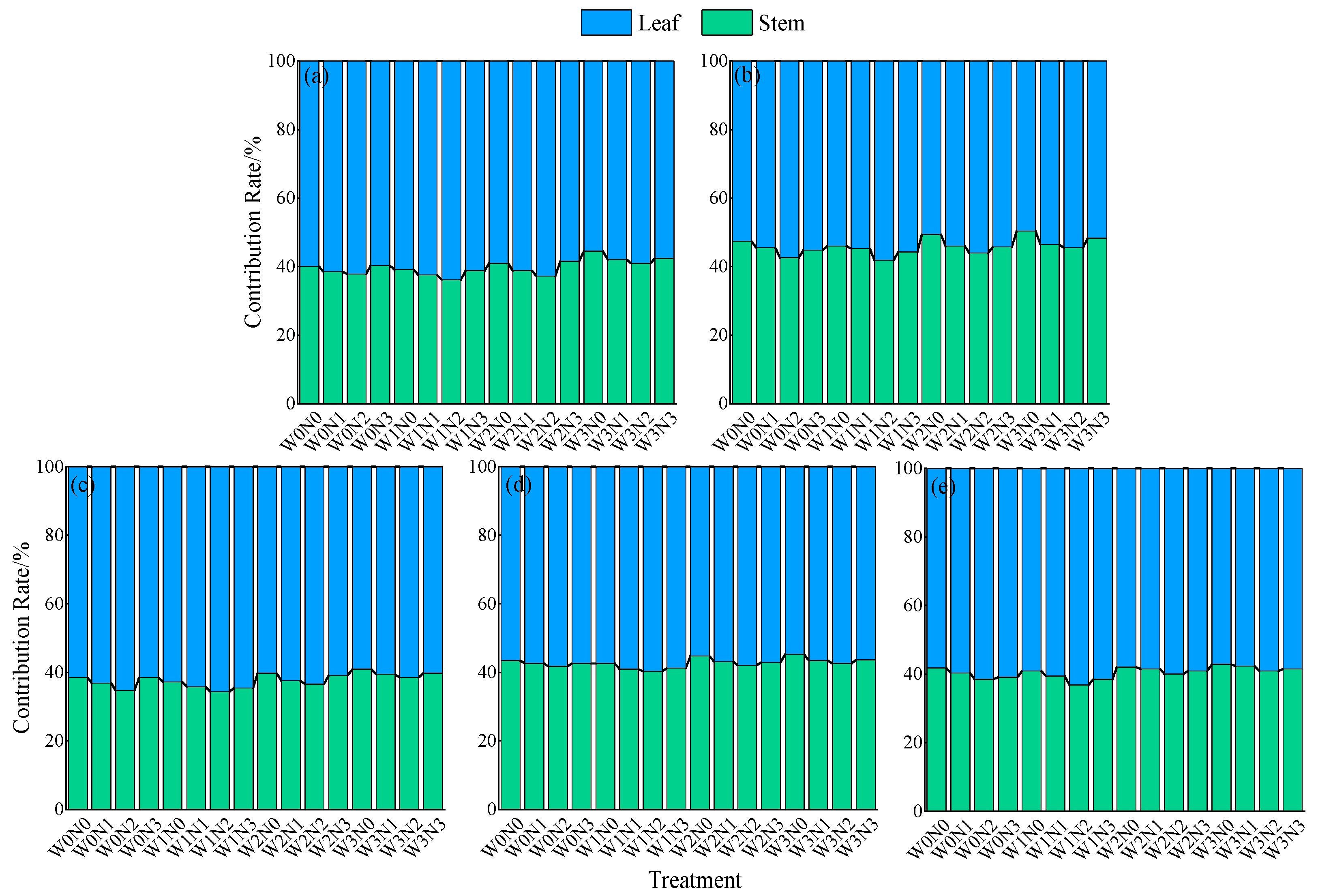
2.1.1. Stem-to-Leaf Allocation
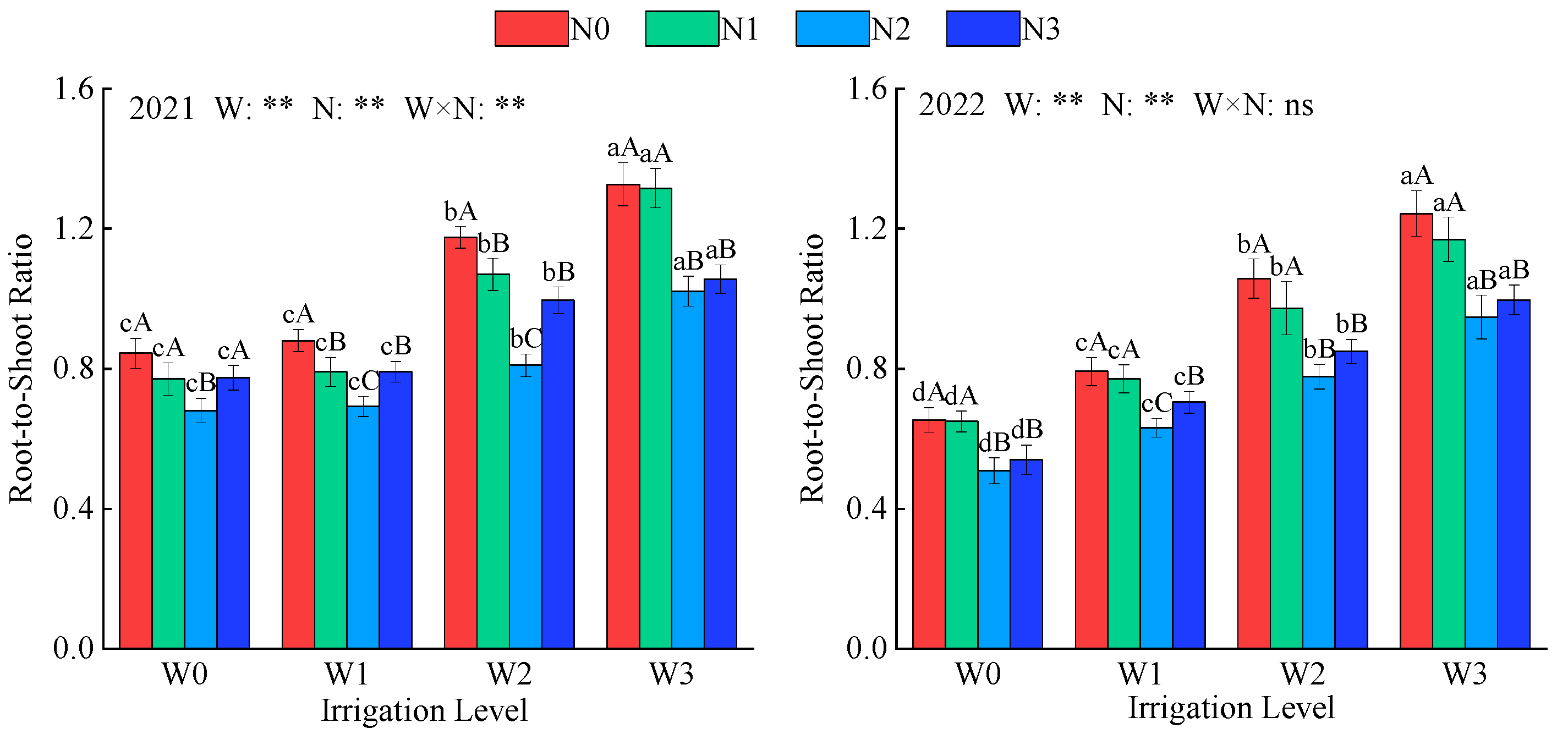
2.1.2. Root-Shoot Ratio
2.2. The Effect of Water and Nitrogen Regulation on Nitrogen Turnover in Intercropped Alfalfa
2.2.1. Alfalfa Nitrogen Accumulation
2.2.2. Stem and Leaf Nitrogen Transport
2.2.3. Soil Nitrogen Balance
2.3. The Effect of Water and Nitrogen Regulation on the Production of Intercropped Alfalfa
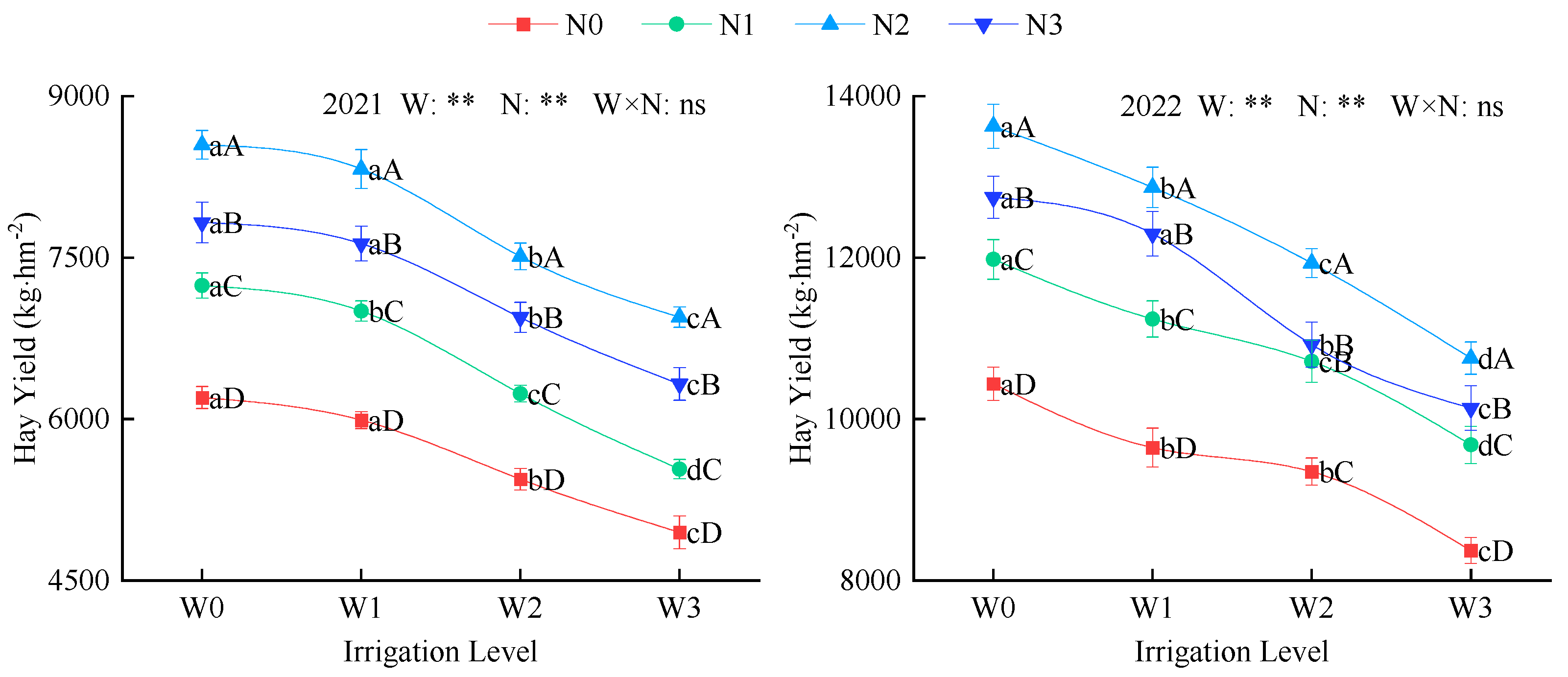
2.3.1. Hay Yield
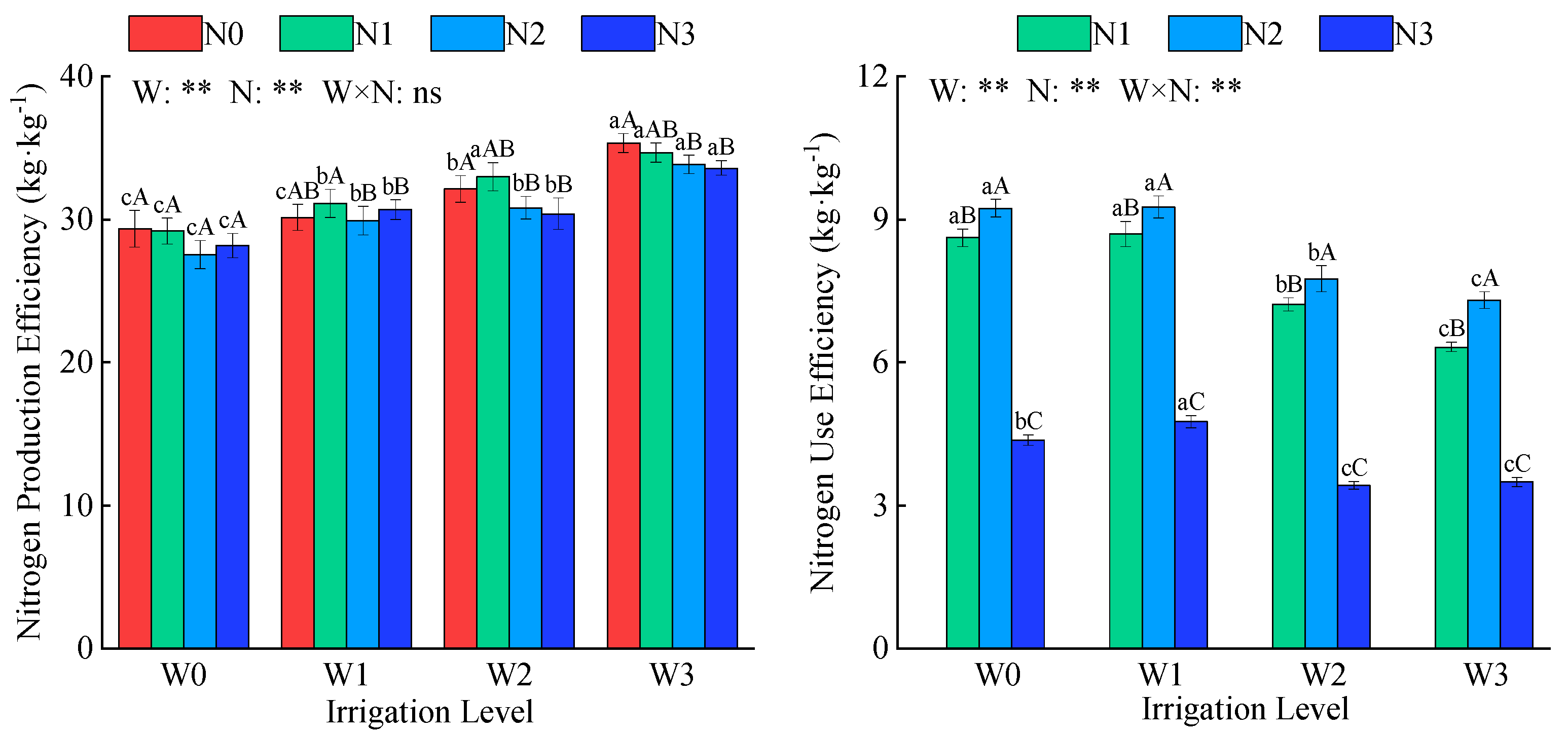
2.3.2. Nitrogen Use Efficiency
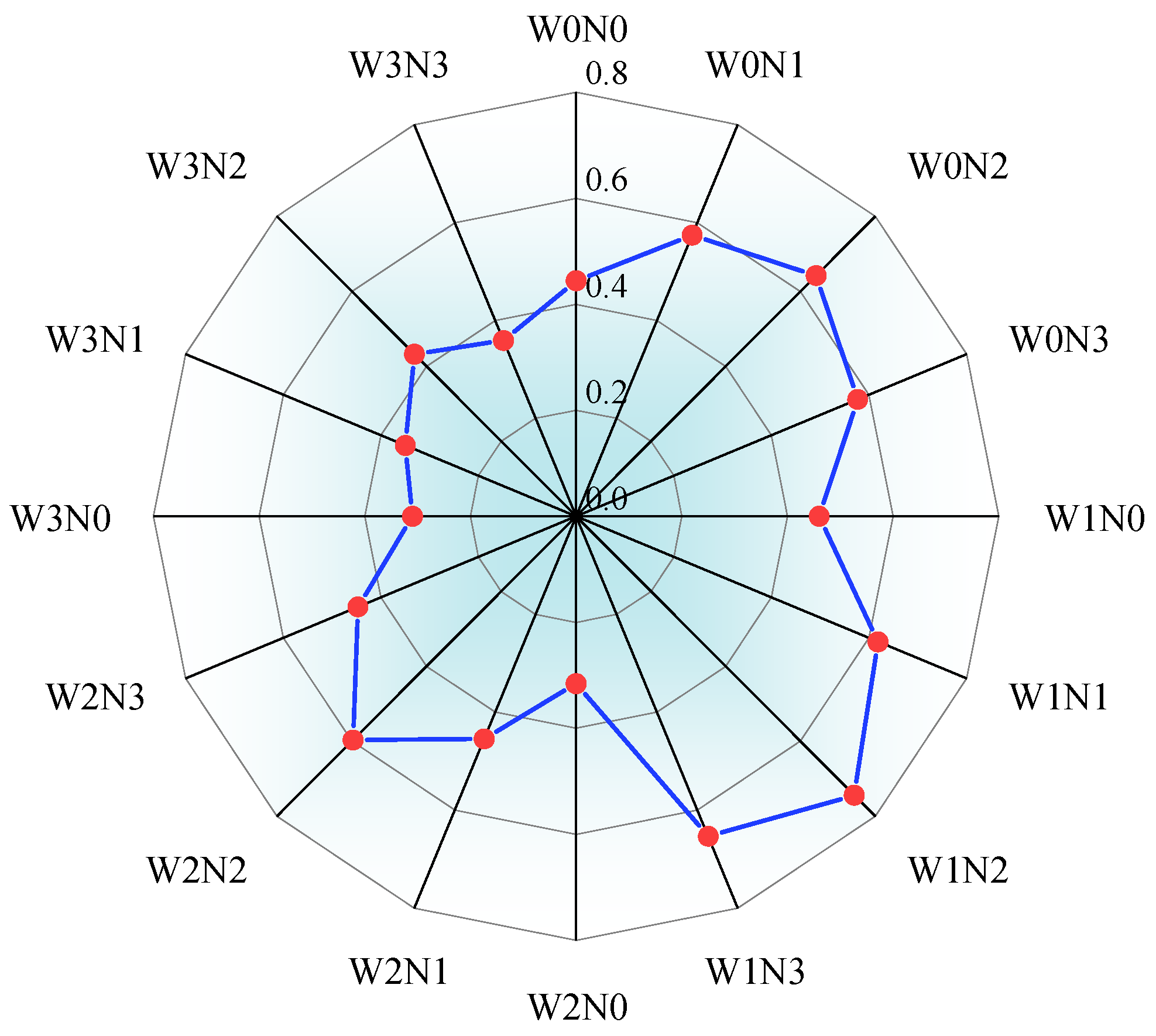
2.4. Comprehensive Evaluation of the Effects of Water and Nitrogen Regulation on Intercropped Alfalfa
3. Discussion
3.1. The Effect of Water and Nitrogen Regulation on Alfalfa Growth and Yield
3.2. The Effect of Water and Nitrogen Regulation on Nitrogen Allocation in Alfalfa Plants
3.3. The Effect of Water and Nitrogen Regulation on Nitrogen Absorption and Utilization in Alfalfa
4. Materials and Methods
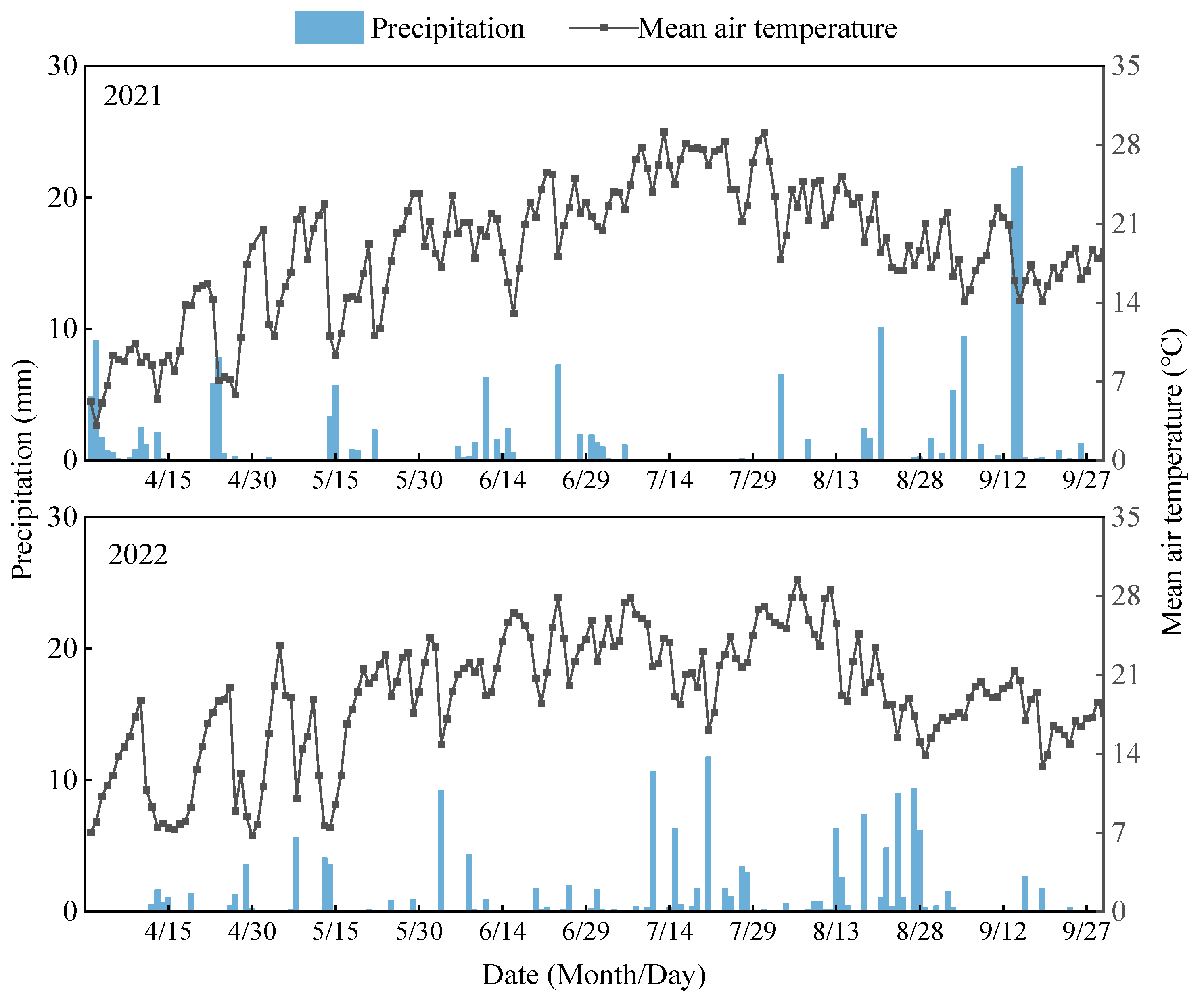
4.1. Description of the Experimental Site
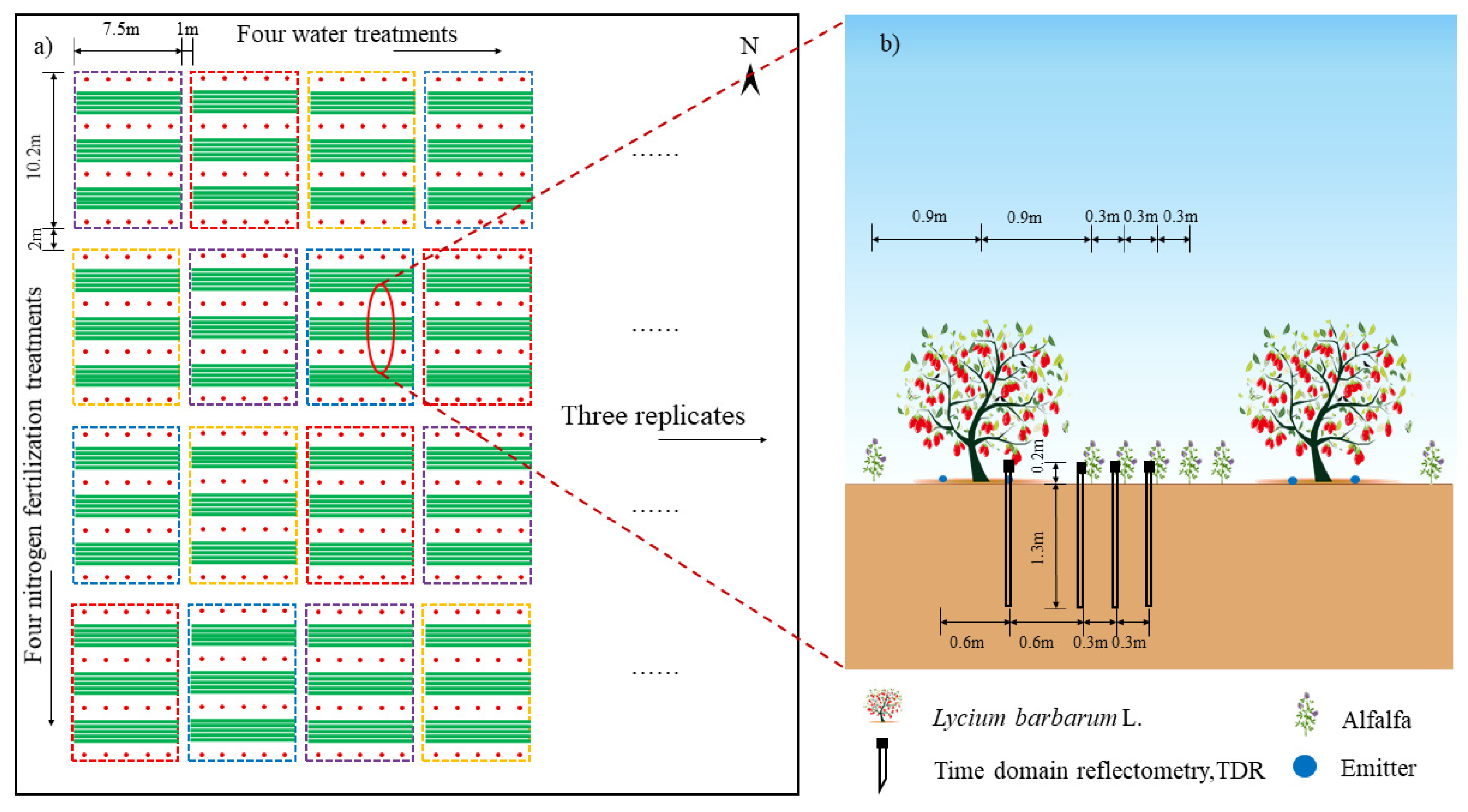
4.2. Experimental Design
4.3. Sample Collection and Analysis Methods
4.3.1. Biomass
4.3.2. Yield
4.3.3. Nitrogen-Related Indicators
4.4. Entropy Weight-TOPSIS Model
4.4.1. Determining the Weights of Indicators Using the Entropy Weight Method
4.4.2. Comprehensive Evaluation Using the TOPSIS Method
- (1)
- Construction of the weighted normalized matrix
- (2)
- Determination of the positive ideal solution R+ and the negative ideal solution R−
- (3)
- Optimal solution distance D+ and worst solution distance D−
- (4)
- Relative Closeness Ci
4.5. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mo, X.G.; Liu, W.; Meng, C.C.; Hu, S.; Liu, S.X.; Lin, Z.H. Variations of forage yield and forage-livestock balance in grass-lands over the Tibetan Plateau, China. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 32, 2415–2425. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.L.; Cheng, W.Y. The Feeding Value and High-yield Cultivation Technology of Alfalfa. Tillage Cultiv. 2023, 43, 104–107. [Google Scholar]
- Silitonga, A.S.; Riayatsyah, T.M.; Kalam, M.A.; Sarifudin, A.; Fattah, I.M.; Muraza, O.; Putra, N.S.; Sebayang, A.R.; Sebayang, A.H.; Hermawan, H. Status, developments, and sustainability of biowaste feedstock: A review of current progress. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2025, 217, 115769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danishta, A.; Summira, R.; Pawan, S.; Ishtiyaq, A.; Basanagouda, G.; Sheikh, A.R.; Shafiya, R.; Pooja, S.; Gulab, K.R.; Khursheed, A.; et al. Remote sensing and artificial intelligence: Revolutionizing pest management in agriculture. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2025, 9, 1551460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahima, C.; Sarita, K.; Prem, K.; Muthukumaran, P.; Bandana, K.S.; Kamaljit, K.; Parul, S.; Raman, K.; Abishek, K.; Vijayakumar, S. Rational fertilizer application dream: Ammonia gas sensor for monitoring urea loss from crops. Microchem. J. 2025, 214, 114064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, S.J.; Shi, J.L.; Tian, X.H.; Ye, X.X. Integrated mulching and nitrogen management strategies influence carbon footprint and sustainability of wheat production on the Loess Plateau of China. Field Crops Res. 2023, 297, 108928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, P.F.; Lu, C.; Huang, T.T.; Zhang, M.M.; Yang, N.; Han, X.Q.; Xu, C.H.; Wang, S.G.; Wan, C.X.; Qin, X.L.; et al. Enhancing intercropping sustainability: Manipulating soybean rhizosphere microbiome through cropping patterns. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 931, 172714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poloko, M.; Moeketsi, N.; Tumelo, N.; Palo, L. The Role of Intercropping Selected Maize Cultivars and Forage Legumes on Yield, Weed Dynamics, and Soil Chemical Properties. Int. J. Agron. 2025, 2025, 9989566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnese, B.; Gergely, U.; Matteo, D.; Filippo, R.; Claudia, B.; Roberta, P.; Giacomo, B.; Carlo, V. The impact of alfalfa inter-cropping and conventional tillage on N-cycling microbes: A Tuscan vineyard case study. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2025, 213, 106240. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.J.; Zhong, M.H.; Zhao, X.X.; Zhang, X.L.; Hu, Y.B.; Zhang, H.H. Intercropping Forage Mulberry Benefits Nodulation and Growth of Soybeans. Agronomy 2025, 15, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Z.; Wei, Y.W.; Yin, Y.; Zhu, W.X.; Bai, X.J.; Zhou, Y.B. Characteristics of Soil Physicochemical Properties and Microbial Community of Mulberry (Morus alba L.) and Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Intercropping System in Northwest Liaoning. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.G.; Dong, S.T.; Yang, Z.B. Production performance of alfalfa + maize intercropping systems and evaluation of interspecies competition. Acta Pratacult. Sin. 2011, 20, 22–30. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Cao, B.; Wang, X.J.; Feng, L.X. Intercropping ryegrass with ‘LingwuChangzao’ (Ziziphus jujuba Mill. cv. Lingwu-Changzao) enhances crop yield and quality in the arid regions of Northern China. Agroforest. Syst. 2025, 99, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.J.; Finn, D.R.; Wang, H.T.; Joachim, B.; Tebbe, C.C. Seasonal dynamics of prokaryotic nitrogen cycling genes in cropland soils: Effects of soil texture, tillage, and environmental factors. Soil Tillage Res. 2025, 253, 106694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.L.; Liu, S.B.; Guo, M.J.; Cheng, Y.H.; Shi, L.F.; Li, J.P.; Yu, Y.J.; Wu, S.Y.; Dong, Q.G.; Ge, J.K.; et al. Optimizing Nitrogen Fertilization and Irrigation Practices for Enhanced Winter Wheat Productivity in the North China Plain: A Meta-Analysis. Plants 2025, 14, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.X.; Qi, G.P.; Jia, Q.; Wang, A.X.; Yin, M.H.; Ma, Y.L.; Wang, J.H.; Jiang, Y.B.; Tang, Z.X. Appropriate Water-Nitrogen Regulation Mode to Improve Productivity of Mixed-Sowing Grassland of Bromus inermis and Alfalfa. Water 2023, 15, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.X.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, X.J.; Jiang, P. Effects of subsurface drip irrigation and nitrogen fertilizer management on N2O emissions and forage yield in alfalfa production. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1598110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, M.H.; Jiang, Y.B.; Ling, Y.; Ma, Y.L.; Qi, G.P.; Kang, Y.X.; Wang, Y.Y.; Lu, Q.; Shang, Y.J.; Fan, X.R.; et al. Optimizing Lucerne Productivity and Resource Efficiency in China’s Yellow River Irrigated Region: Synergistic Effects of Ridge-Film Mulching and Controlled-Release Nitrogen Fertilization. Agriculture 2025, 15, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Lu, W.H.; Li, B.; Duan, Z.P.; Shen, L.; Teng, Y.X.; Liu, T.T.; Tian, Y.Q.; Zhang, W.; Li, L.H. Root distribution characteristics and productivity in a poplar-alfalfa silvopastoral system. Agric. Res. Arid Areas 2020, 38, 116–124+134. [Google Scholar]
- Zunker, S.M.J.H.; Knappe, H. (De)politicizing water: Justice in times of water crisis. Front. Polit. Sci. 2024, 6, 1409630. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Qi, G.P.; Ma, Y.L.; Yin, M.H.; Wang, J.H.; Kang, Y.X.; Jia, Q.; Gao, Y.L.; Tian, R.R.; Zhang, R.; et al. Effects of Water and Nitrogen Control on the Growth Physiology, Yields, and Economic Benefits of Lycium barbarum Plants in a Lycium barbarum + Alfalfa System. Plants 2024, 13, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Li, Y.S.; Li, W.H.; Yuan, G.D.; Wu, J.H.; Han, F.X.; Chen, M.H. Co-applications of Biochar and Reduced Fertilizer Improved Soil Fertility, Nitrogen Use Efficiency, and Yield of Lycium chinense Mill: A Two-Year Field Trial. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2025, 25, 4371–4384. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Shang, J.X.; Wang, X.L.; Ye, R.Q.; Zhao, D.; Li, X.Y.; Yang, Y.D.; Zhang, H.Y.; Gong, X.W.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Soil Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Nitrogen Dynamics: Effects of Maize Straw Incorporation Under Contrasting Nitrogen Fertilization Levels. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.L.; Laubach, J.; Hunt, J.E.; Mudge, P.L.; Nuñez, J.; Rogers, G.N.D.; Buxton, R.P.; Carrick, S.; Whitehead, D. Irrigation and grazing management affect leaching losses and soil nitrogen balance of Lucerne. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 259, 107233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.D.; Zhang, Q.C.; Ju, M.X.; Gao, K.; Han, L.L.; Li, X.F.; He, J.; Su, D.R. Alfalfa Photosynthesis Under Partial Root-Zone Drying: Diurnal Patterns and Its Non-Stomatal Limitations. Plants 2025, 14, 1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crookston, S.B.; Boren, D.; Yost, M.; Sullivan, T.; Creech, E.; Barker, B.; Reid, C. Irrigation technology, irrigation dose, and crop genetic impacts on alfalfa yield and quality. Agric. Water Manag. 2025, 311, 109366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.D.; Zhang, Q.C.; Gao, K.; Han, L.L.; Li, X.F.; He, J.; Su, D.R. Deficit Irrigation Provides a Trade-Off Between Water Use and Alfalfa Quality. Agronomy 2025, 15, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qi, G.P.; Kang, Y.X.; Ma, Y.L.; Yin, M.H.; Li, X.M.; Li, Z. Photosynthetic Characteristics, Chlorophyll Fluorescence Parameters and Biomass of Alfalfa under Different Irrigation Treatments. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2019, 27, 1569–1576. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.Q.; Bian, C.Y.; Liu, X.H.; Ma, C.J.; Liu, Q.R. Winter wheat grain yield and water use efficiency in wide-precision planting pattern under deficit irrigation in North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 153, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, P.W.; Xu, M.G.; Ma, H.Y.; Yang, X.Y.; Zhang, S.L. Effects of soil fertility and N application rates on soil organic N components and N mineralization. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Sha, B.P.; Xie, Y.Z.; Gao, X.Q.; Cai, W.; Fu, B.Z. Effects of coupling of drip irrigation water and fertilizer on yield and quality of alfalfa in the yellow river irrigation district. Acta Pratacult. Sin. 2021, 30, 102–114. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Wang, Y.D.; Cui, P.F.; Su, D.R. Effects of Different Irrigation Limits on Growth and Photosynthetic Characteristics of Alfalfa in Arid Region of Northwest China. Chin. J. Grassl. 2021, 43, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, H.P.; Ning, S.R.; Yan, A.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Li, N.; Huo, T.T. Response of Alfalfa Yield to Rates and Ratios of N, P, and K Fertilizer in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions of China Based on Meta-Analysis. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.G.; Wang, Z.K.; Mu, L.; Xu, R.; Yang, H.M. Effect of regulated deficit irrigation on alfalfa performance under two irrigation systems in the inland arid area of midwestern China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 248, 106764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, G.Y.; Jiang, Y.B.; Li, H.Y.; Wei, S.N.; Qi, G.P.; Kang, Y.X.; Yin, M.H.; Ma, Y.L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.B.; et al. Water–Fertilizer Synergistic Effects and Resource Optimization for Alfalfa Production: A Central Composite Design and Response Surface Methodology Approach. Plants 2025, 14, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Brooks, E.; Mohamed, A.Z.; Kelley, J. Deep Infiltration Model to Quantify Water Use Efficiency of Center-Pivot Irrigated Alfalfa. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2024, 150, 04024021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgharably, A.; Benes, S. Alfalfa Biomass Yield and Nitrogen Fixation in Response to Applied Mineral Nitrogen Under Saline Soil Conditions. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 744–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Q.; Liu, J.Y.; Liu, W.K. Enhancing growth, quality, and metabolism of nitrogen of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) by high red–blue light intensity. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2023, 186, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.H.; Lu, J.; Zhao, H.; Velthof, G.L.; Oenema, O.; Chadwick, D.; Williams, J.R.; Jin, S.Q.; Liu, H.B.; Wang, M.R.; et al. Designing Vulnerable Zones of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Transfers To Control Water Pollution in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 8987–8988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, F.H.; Yu, X.X.; Tang, X.K.; Liu, X.D.; Tang, W.; Zhao, Y.H.; Yang, C.; Xu, Y.F.; Yang, G.F.; Sun, J. The Responses of Stem and Leaf Functional Traits of Medicago sativa and Bromus inermis to Different Mixed Planting Patterns. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.D.; Liu, C.; Cui, P.F.; Su, D.R. Effects of partial root-zone drying on alfalfa growth, yield and quality under sub-surface drip irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 245, 106608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Y.; Zhang, J.R.; Liu, F.; Yao, B. A review of ecological benefits of silvopasture systems. Pratacult. Sci. 2014, 31, 1789–1797. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, B.; Teng, Y.; Wang, X.; Lv, W.; Wu, X.Z.; Wang, Z.T. Response of soil moisture to rainfall in alfalfa fields under severe soil drying condition. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2025, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Imène, B.S.; Alfonso, A.; Cristina, M.A.; Rabiaa, H.; Nehla, L.; Fethia, Z.; Vicente, M.; Francisco, P.A.; Chedly, A. Response of nitrogen fixation in relation to nodule carbohydrate metabolism in Medicago ciliaris lines subjected to salt stress. J. Plant Physiol. 2008, 166, 477–488. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Z.Q.; Zheng, C.C.; Postma, J.A.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, J.J. More N fertilizer, more maize, and less alfalfa: Maize benefits from its higher N uptake per unit root length. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1338521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karan, T.; Moran, B. Alfalfa (Medicago sativa) Leaves Mediated Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Assessment of Their Cytotoxic Effects on Various Cancer Cell Lines. Biol. Bull. 2025, 52, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.F.; Zhang, X.C.; Liu, Y.N.; Zhang, A.Q.; Song, W.S.; Li, L.X.; Zhao, J.W.; Pang, Q.Y. Salt-alkali-tolerant growth-promoting Streptomyces sp. Jrh8-9 enhances alfalfa growth and resilience under saline-alkali stress through integrated modulation of photosynthesis, antioxidant defense, and hormone signaling. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 296, 128158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Qi, G.P.; Yin, M.H.; Kang, Y.X.; Ma, Y.L.; Jia, Q.; Wang, J.H.; Jiang, Y.B.; Wang, C.; Gao, Y.L.; et al. Alfalfa Cultivation Patterns in the Yellow River Irrigation Area on Soil Water and Nitrogen Use Efficiency. Agronomy 2024, 14, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, K.Q.; Mu, L.; Zhou, T.; Kamran, M.; Yang, H.M. Intercropped alfalfa and spring wheat reduces soil alkali-salinity in the arid area of northwestern China. Plant Soil 2022, 499, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurélie, Q.; Patricia, B.; Lydie, D.; Jacques, W.; Christian, D. Effects of walnut trees on biological nitrogen fixation and yield of intercropped alfalfa in a Mediterranean agroforestry system. Eur. J. Agron. 2017, 84, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.M.; Wang, N.; Hu, Y.B.; Sun, G.Y. Changes in soil physicochemical properties and soil bacterial community in mulberry (Morus alba L.)/alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) intercropping system. Microbiol. Open 2018, 7, e00555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Y.R.; Wang, J.H.; Yin, M.H.; Kang, Y.X.; Ma, Y.L.; Jia, Q.; Qi, G.P.; Jiang, Y.B.; Lu, Q.; Chen, X.L. Effects of Planting and Nitrogen Application Patterns on Alfalfa Yield, Quality, Water–Nitrogen Use Efficiency, and Economic Benefits in the Yellow River Irrigation Region of Gansu Province, China. Water 2023, 15, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.F.; Nan, Z.B.; Tang, Z.; Wang, L.J. Comparison of economic benefit of alfalfa, wheat and maize—A case study in Gansu Province. Pratacult. Sci. 2016, 33, 990–995. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, S.D.; Jiang, H.S.; Dong, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Guo, T.W.; Han, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yan, Q.Y. Effects of Reduced Application of Slow/Controlled Release Ammonium Sulfate on Maize Growth and Soil Nitrogen Balance. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci. 2024, 38, 1772–1781. [Google Scholar]

| Treatment | Stem Dry Weight (g) | Leaf Dry Weight (g) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Harvest | 2nd Harvest | 1st Harvest | 1st Harvest | 2nd Harvest | 1st Harvest | |
| W0N0 | 17.2 ± 0.75 aA | 18.3 ± 0.75 aC | 14.9 ± 0.85 aC | 21.2 ± 1.03 aC | 18.5 ± 0.54 aC | 16.8 ± 1.23 aC |
| W0N1 | 17.5 ± 0.85 aA | 19.6 ± 0.85aBC | 17.2 ± 0.45aB | 23.7 ± 0.84aAB | 21.1 ± 1.27aB | 19.8 ± 0.81aB |
| W0N2 | 18.2 ± 0.55 aA | 21.7 ± 0.91 aA | 19.8 ± 0.79 aA | 25.6 ± 1.42 aA | 24.3 ± 0.95 aA | 24.2 ± 0.72 aA |
| W0N3 | 18.1 ± 0.84 aA | 20.9 ± 0.84 aAB | 19.4 ± 0.42 aA | 22.9 ± 0.98 aBC | 22.8 ± 1.25 aAB | 22.9 ± 1.35 aA |
| W1N0 | 15.5 ± 0.67 bAB | 16.8 ± 1.40 aB | 13.3 ± 0.55 bC | 21.2 ± 0.80 aB | 18.4 ± 0.77 aC | 15.7 ± 0.76 aC |
| W1N1 | 16.4 ± 0.65 aA | 17.8 ± 0.55 bAB | 14.8 ± 0.71 bB | 23.7 ± 0.73 aA | 20.9 ± 1.32 aB | 18.5 ± 1.12 aB |
| W1N2 | 16.8 ± 0.65 bA | 19.6 ± 1.35 bA | 16.5 ± 0.65 bA | 25.9 ± 1.84 aA | 23.6 ± 1.35 aA | 22.9 ± 0.63 aA |
| W1N3 | 14.5 ± 0.75 bB | 17.8 ± 0.70 bAB | 16.8 ± 0.87 bA | 21.3 ± 1.21 aB | 20.7 ± 0.82 aB | 21.9 ± 0.92 aA |
| W2N0 | 12.8 ± 0.37 cA | 14.8 ± 0.38 bB | 11.7 ± 0.75 cB | 16.7 ± 1.03 bB | 15.7 ± 0.36 bB | 13.3 ± 0.67 bB |
| W2N1 | 13.4 ± 0.9 bA | 16.0 ± 0.56 cAB | 13.3 ± 0.95 cA | 18.8 ± 1.04 bAB | 17.6 ± 1.41 bAB | 16.1 ± 0.99 bA |
| W2N2 | 13.5 ± 0.6 cA | 17.0 ± 1.25 cA | 13.5 ± 0.65 cA | 20.5 ± 0.96 bA | 19.3 ± 0.59 bA | 17.6 ± 0.9 bA |
| W2N3 | 13.7 ± 0.71 bA | 15.8 ± 0.74 cAB | 13.6 ± 0.45 cA | 17.8 ± 1.66 bB | 17.3 ± 1.28 bAB | 17.2 ± 0.66 bA |
| W3N0 | 11.7 ± 0.82 cB | 14.1 ± 0.49 bB | 11.3 ± 0.4 cC | 13.8 ± 0.74 cC | 13.9 ± 0.83 cB | 12.2 ± 0.9 bC |
| W3N1 | 13.3 ± 0.63 bA | 15.1 ± 0.45 cAB | 13.3 ± 0.35 cB | 16.6 ± 0.79 cB | 16.1 ± 1.14 bA | 14.8 ± 0.45 bB |
| W3N2 | 14.6 ± 0.7 cA | 16.0 ± 0.45 cA | 14.4 ± 0.83 cA | 18.9 ± 0.67 bA | 17.6 ± 0.71 bA | 16.9 ± 1.26 bA |
| W3N3 | 13.9 ± 0.75 bA | 15.4 ± 1.13 cAB | 13.6 ± 0.45 cAB | 17.2 ± 0.95 bB | 16.2 ± 1.02 bA | 15.7 ± 1.17 bAB |
| ANOVA | ||||||
| W | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| N | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| W × N | * | ns | ** | ns | ns | * |
| Treatment | 2021 | 2022 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Harvest | 2nd Harvest | 1st Harvest | 2nd Harvest | 3rd Harvest | |
| W0N0 | 0.853 ± 0.032 bA | 1.192 ± 0.028 aA | 0.811 ± 0.044 abA | 0.989 ± 0.041 abA | 0.887 ± 0.045 aA |
| W0N1 | 0.779 ± 0.043 bB | 1.041 ± 0.046 aB | 0.738 ± 0.029 abBC | 0.929 ± 0.048 aAB | 0.869 ± 0.027 bA |
| W0N2 | 0.731 ± 0.031 bB | 0.963 ± 0.021 abB | 0.711 ± 0.041 abC | 0.893 ± 0.046 aB | 0.818 ± 0.036 abA |
| W0N3 | 0.872 ± 0.035 aA | 1.029 ± 0.062 bB | 0.79 ± 0.032 aAB | 0.917 ± 0.039 abAB | 0.847 ± 0.031 abA |
| W1N0 | 0.795 ± 0.044 bA | 1.035 ± 0.026 bA | 0.731 ± 0.035 cA | 0.913 ± 0.034 bA | 0.847 ± 0.041 aA |
| W1N1 | 0.743 ± 0.04 bAB | 1.011 ± 0.023 aA | 0.692 ± 0.026 bAB | 0.852 ± 0.053 aA | 0.8 ± 0.033 abAB |
| W1N2 | 0.704 ± 0.036 bB | 0.883 ± 0.025 cB | 0.649 ± 0.032 bB | 0.831 ± 0.031 aA | 0.721 ± 0.044 cC |
| W1N3 | 0.782 ± 0.031 bA | 0.972 ± 0.053 bA | 0.681 ± 0.027 bAB | 0.86 ± 0.042 bA | 0.767 ± 0.037 cBC |
| W2N0 | 0.819 ± 0.047 bAB | 1.073 ± 0.022 bA | 0.766 ± 0.029 bcA | 0.943 ± 0.042 abA | 0.88 ± 0.042 aA |
| W2N1 | 0.765 ± 0.032 bAB | 1.021 ± 0.05 aAB | 0.718 ± 0.036 bA | 0.909 ± 0.036 aA | 0.831 ± 0.047 abAB |
| W2N2 | 0.747 ± 0.034 bB | 0.914 ± 0.02 bcC | 0.659 ± 0.023 bB | 0.881 ± 0.054 aA | 0.767 ± 0.032 bcB |
| W2N3 | 0.834 ± 0.039 abA | 0.985 ± 0.049 bBC | 0.77 ± 0.033 aA | 0.913 ± 0.043 abA | 0.791 ± 0.028 bcB |
| W3N0 | 0.983 ± 0.038 aA | 1.243 ± 0.044 aA | 0.848 ± 0.038 aA | 1.014 ± 0.062 aA | 0.926 ± 0.055 aA |
| W3N1 | 0.891 ± 0.037 aB | 1.064 ± 0.028 aBC | 0.801 ± 0.042 aAB | 0.938 ± 0.037 aAB | 0.899 ± 0.034 aA |
| W3N2 | 0.852 ± 0.045 aB | 1.022 ± 0.055 aC | 0.772 ± 0.034 aB | 0.909 ± 0.035 aB | 0.852 ± 0.033 aA |
| W3N3 | 0.903 ± 0.037 aB | 1.137 ± 0.029 aB | 0.808 ± 0.031 aAB | 0.951 ± 0.037 aAB | 0.866 ± 0.043 aA |
| ANOVA | |||||
| W | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| N | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| W × N | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Treatment | Transshipment Volume in 2021/(kg·hm−2) | Transshipment Volume in 2022/(kg·hm−2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Harvest | 2nd Harvest | 1st Harvest | 2nd Harvest | 1st Harvest | |
| W0N0 | 34.6 ± 2.26 abA | 28.2 ± 2.25 abB | 60.7 ± 6.53 aB | 50.6 ± 5.07 aB | 35.9 ± 2.50 abB |
| W0N1 | 37.4 ± 1.36 abA | 32.7 ± 2.07 abA | 72.1 ± 6.70 aAB | 58.6 ± 5.65 aAB | 43.7 ± 3.31 aA |
| W0N2 | 38.1 ± 3.19 aA | 33.7 ± 2.19 abA | 75.4 ± 7.41 abA | 63.8 ± 5.89 aA | 46.3 ± 3.52 aA |
| W0N3 | 36.5 ± 1.36 aA | 31.9 ± 2.07 abAB | 70.5 ± 6.74 aAB | 56.5 ± 5.68 aAB | 40.4 ± 2.88 abAB |
| W1N0 | 36.8 ± 2.22 aA | 31.7 ± 2.24 aA | 62.4 ± 6.45 aB | 49.5 ± 4.39 aB | 37.8 ± 2.40 aB |
| W1N1 | 39.1 ± 3.09 aA | 35.3 ± 3.21 aA | 75.1 ± 6.90 aAB | 63.1 ± 5.82 aA | 45.8 ± 3.16 aA |
| W1N2 | 40.0 ± 3.38 aA | 35.5 ± 3.47 aA | 80.9 ± 7.82 aA | 66.1 ± 5.76 aA | 48.8 ± 3.08 aA |
| W1N3 | 38.2 ± 2.57 aA | 33.9 ± 3.31 aA | 69.9 ± 7.13 aAB | 58.1 ± 6.01 aAB | 44.4 ± 2.75 aA |
| W2N0 | 33.9 ± 2.15 abA | 26.1 ± 1.77 bcB | 55.7 ± 5.21 abB | 45.1 ± 4.17 aC | 33.3 ± 1.94 bB |
| W2N1 | 35.2 ± 2.62 abA | 29.5 ± 1.79 bAB | 69.4 ± 6.97 aA | 56.0 ± 5.88 aAB | 35.0 ± 1.94 bAB |
| W2N2 | 35.9 ± 4.13 aA | 30.4 ± 1.88 bcA | 72.0 ± 6.47 abA | 59.3 ± 5.46 aA | 38.8 ± 3.24 bA |
| W2N3 | 35.4 ± 3.13 aA | 28.5 ± 2.07 bcAB | 63.5 ± 6.78 bcAB | 49.0 ± 4.72 aBC | 35.8 ± 2.21 bcAB |
| W3N0 | 31.6 ± 1.83 bA | 23.0 ± 2.17 cA | 49.1 ± 4.76 bB | 42.5 ± 3.68 aB | 28.9 ± 2.15 cB |
| W3N1 | 33.9 ± 1.63 bA | 25.0 ± 2.13 cA | 61.9 ± 7.17 aA | 52.9 ± 6.05 aA | 29.7 ± 2.39 cB |
| W3N2 | 35.5 ± 2.91 aA | 25.8 ± 1.98 cA | 62.8 ± 6.97 bA | 56.9 ± 5.88 aA | 34.9 ± 2.25 bA |
| W3N3 | 33.5 ± 2.05 aA | 24.7 ± 2.21 cA | 56.1 ± 5.08 cAB | 50.1 ± 5.13 aAB | 33.1 ± 2.54 cAB |
| ANOVA | |||||
| W | ** | * | * | ** | ** |
| N | * | * | ** | ** | ** |
| W × N | * | ** | * | ** | ** |
| Treatment | Nitrogen Application Rate (kg·hm−2) | Alfalfa Nitrogen Fixation (kg·hm−2) | Total Nitrogen Input (kg·hm−2) | Gas Losses (kg·hm−2) | Nitrogen Uptake by Alfalfa (kg·hm−2) | Nitrogen Uptake of Goji Berries (kg·hm−2) | Soil Nitrogen Change (kg·hm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W0N0 | 0 | 200 | 200 | 40 | 80 | 100 | −20 |
| W0N1 | 150 | 200 | 350 | 70 | 90 | 150 | 40 |
| W0N2 | 300 | 200 | 500 | 100 | 100 | 250 | 50 |
| W0N3 | 450 | 200 | 650 | 130 | 100 | 350 | 70 |
| W1N0 | 0 | 200 | 200 | 30 | 80 | 100 | −10 |
| W1N1 | 150 | 200 | 350 | 52.5 | 90 | 150 | 57.5 |
| W1N2 | 300 | 200 | 500 | 75 | 100 | 250 | 75 |
| W1N3 | 450 | 200 | 650 | 97.5 | 100 | 350 | 102.5 |
| W2N0 | 0 | 200 | 200 | 20 | 80 | 100 | 0 |
| W2N1 | 150 | 200 | 350 | 35 | 90 | 150 | 75 |
| W2N2 | 300 | 200 | 500 | 50 | 100 | 250 | 100 |
| W2N3 | 450 | 200 | 650 | 65 | 100 | 350 | 135 |
| W3N0 | 0 | 200 | 200 | 10 | 80 | 100 | 10 |
| W3N1 | 150 | 200 | 350 | 17.5 | 90 | 150 | 92.5 |
| W3N2 | 300 | 200 | 500 | 25 | 100 | 250 | 125 |
| W3N3 | 450 | 200 | 650 | 32.5 | 100 | 350 | 167.5 |
| Indicator | Information Entropy | Information Utility Valued | Weighting (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SLR | 0.951 | 0.049 | 9.6 |
| RW | 0.913 | 0.087 | 17.2 |
| RSR | 0.938 | 0.062 | 12.2 |
| NAC | 0.936 | 0.064 | 12.6 |
| NLCR | 0.947 | 0.053 | 10.4 |
| NT | 0.943 | 0.057 | 11.3 |
| HY | 0.939 | 0.061 | 12.0 |
| NPE | 0.925 | 0.075 | 14.7 |
| Bulk Density (g·cm−3) | Organic Matter Content (g·kg−1) | Total N Content (g·kg−1) | Total P Content (g·kg−1) | Total K Content (g·kg−1) | Available N Content (mg·kg−1) | Available P Content (mg·kg−1) | Available K Content (mg·kg−1) | Field Capacity (%) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.63 | 6.09 | 1.62 | 1.32 | 34.0 | 74.5 | 26.3 | 173 | 24.1% | 8.11 |
| Year | Harvest | Moving Date | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Branching Stage | Budding Stage | Initial Flowering Stage | ||
| 2021 | 1st harvest | 06-13 | 07-04 | 07-20 |
| 2nd harvest | 08-19 | 09-07 | 09-19 | |
| 2022 | 1st harvest | 04-26 | 05-15 | 05-28 |
| 2nd harvest | 06-17 | 07-07 | 07-15 | |
| 3rd harvest | 08-15 | 09-06 | 09-20 | |
| Treatment | Nitrogen Application Rate (kg·hm−2) | Irrigation Lever | The Lower Irrigation Limits | The Higher Irrigation Limits | Irrigation Water Volume (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 2022 | |||||
| W0N0 | 0 | Full irrigation | 75% θfc | 85% θfc | 393 | 471 |
| W0N1 | 150 | 403 | 491 | |||
| W0N2 | 300 | 402 | 482 | |||
| W0N3 | 450 | 404 | 481 | |||
| W1N0 | 0 | Mild water deficit | 65% θfc | 75% θfc | 333 | 383 |
| W1N1 | 150 | 341 | 408 | |||
| W1N2 | 300 | 307 | 381 | |||
| W1N3 | 450 | 314 | 367 | |||
| W2N0 | 0 | Moderate water deficit | 55% θfc | 65% θfc | 282 | 327 |
| W2N1 | 150 | 287 | 346 | |||
| W2N2 | 300 | 293 | 344 | |||
| W2N3 | 450 | 260 | 304 | |||
| W3N0 | 0 | Severe water deficit | 45% θfc | 55% θfc | 223 | 262 |
| W3N1 | 150 | 194 | 254 | |||
| W3N2 | 300 | 217 | 264 | |||
| W3N3 | 450 | 184 | 262 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, H.; Jiang, Y.; Qi, G.; Yin, M.; Kang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, F.; Peng, J.; Li, H.; et al. Effects of Water-Nitrogen Management on the Growth and Nitrogen Uptake and Utilization of Intercropped Alfalfa. Plants 2025, 14, 2572. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162572
Lv H, Jiang Y, Qi G, Yin M, Kang Y, Ma Y, Wang Y, Xiao F, Peng J, Li H, et al. Effects of Water-Nitrogen Management on the Growth and Nitrogen Uptake and Utilization of Intercropped Alfalfa. Plants. 2025; 14(16):2572. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162572
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Huile, Yuanbo Jiang, Guangping Qi, Minhua Yin, Yanxia Kang, Yanlin Ma, Yayu Wang, Feng Xiao, Jianqing Peng, Haiyan Li, and et al. 2025. "Effects of Water-Nitrogen Management on the Growth and Nitrogen Uptake and Utilization of Intercropped Alfalfa" Plants 14, no. 16: 2572. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162572
APA StyleLv, H., Jiang, Y., Qi, G., Yin, M., Kang, Y., Ma, Y., Wang, Y., Xiao, F., Peng, J., Li, H., Luo, C., Chen, J., Wang, Y., & Wang, M. (2025). Effects of Water-Nitrogen Management on the Growth and Nitrogen Uptake and Utilization of Intercropped Alfalfa. Plants, 14(16), 2572. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162572









