Functional Analyses of a Rhodobium marinum RH-AZ Genome and Its Application for Promoting the Growth of Rice Under Saline Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of RH-AZ
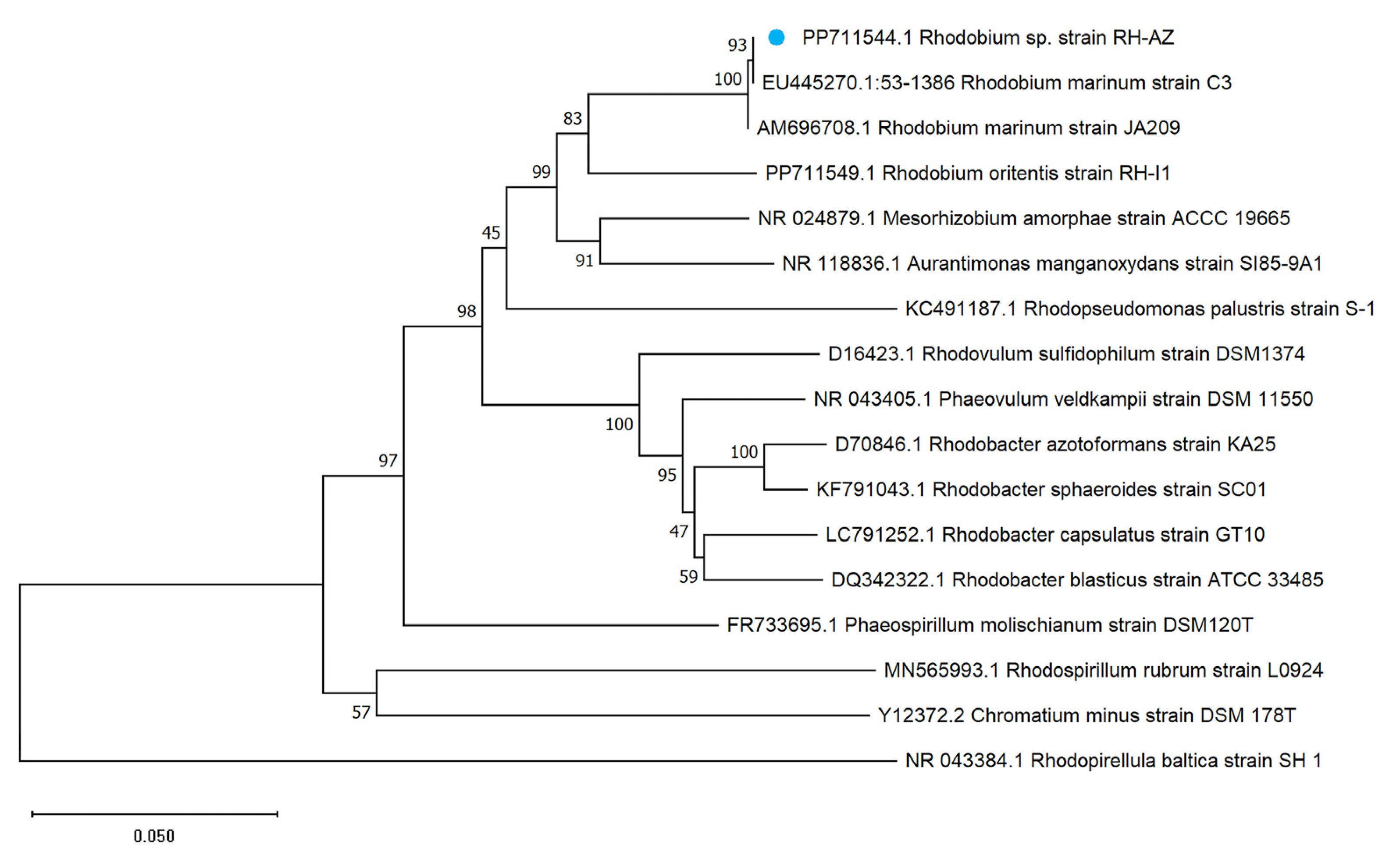
2.2. Phylogenetic Classification of RH-AZ
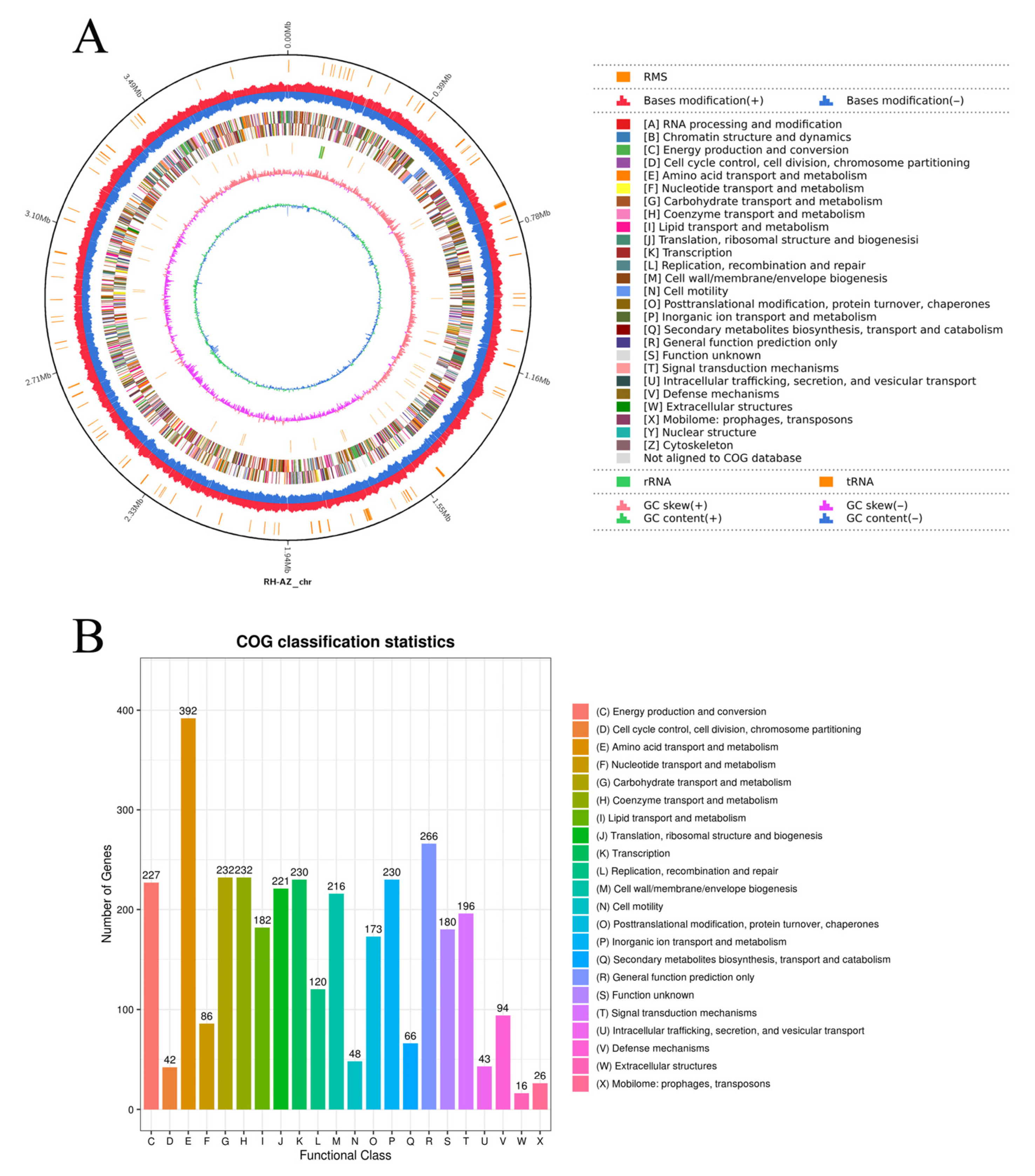
2.3. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Functional Annotation of RH-AZ
2.4. Genes Analysis of Plant Growth Promotion and Salt Stress Tolerance
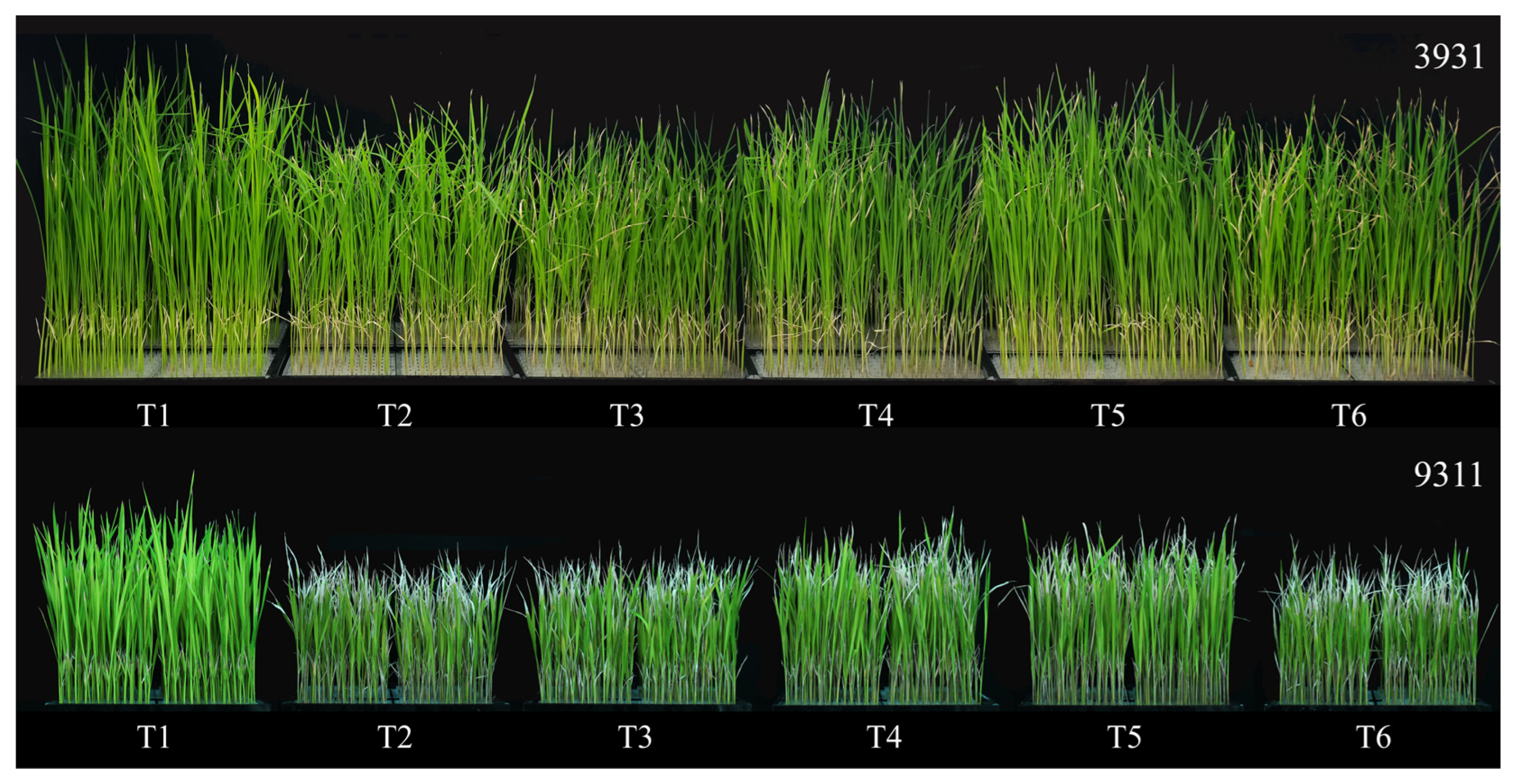
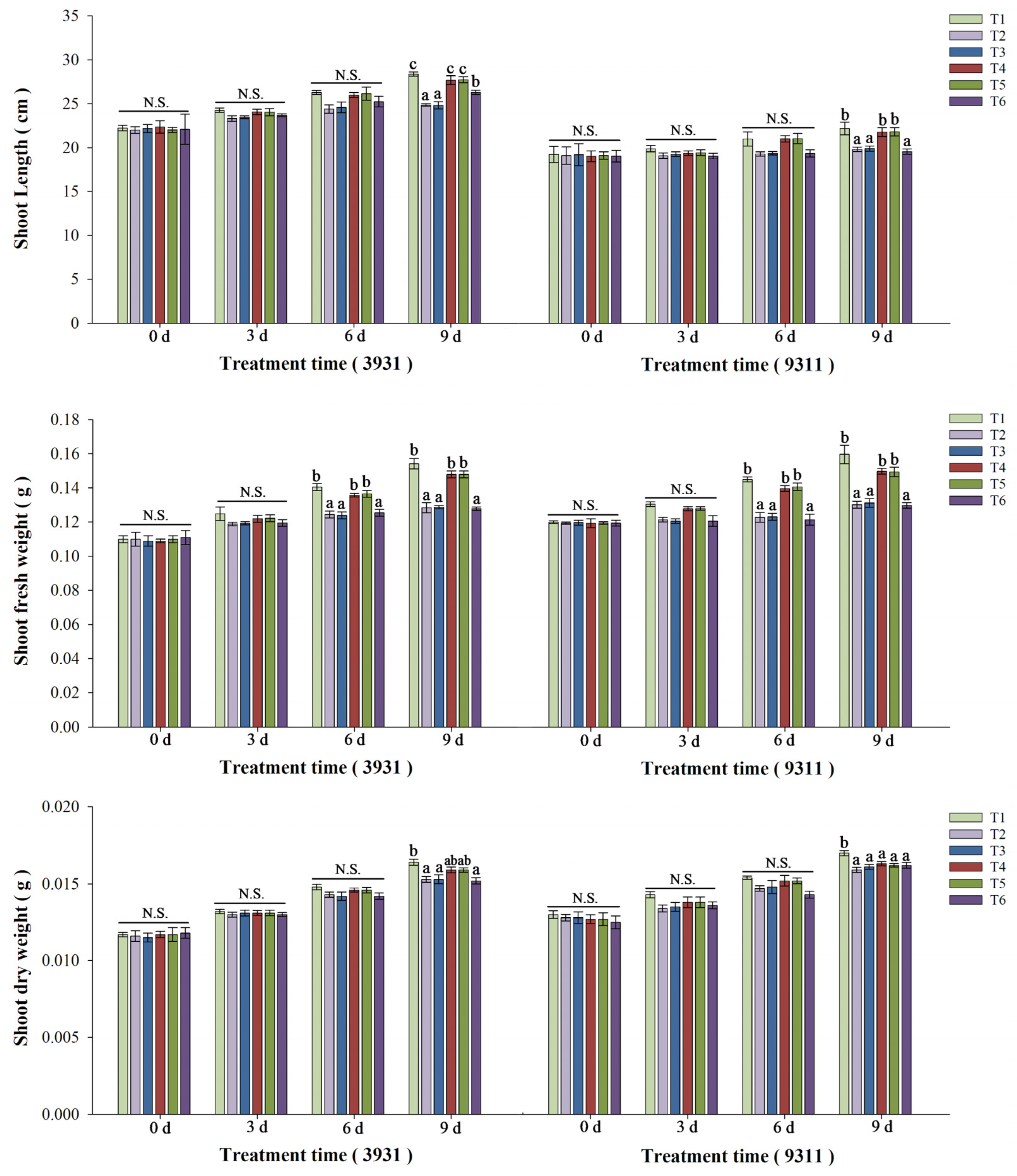
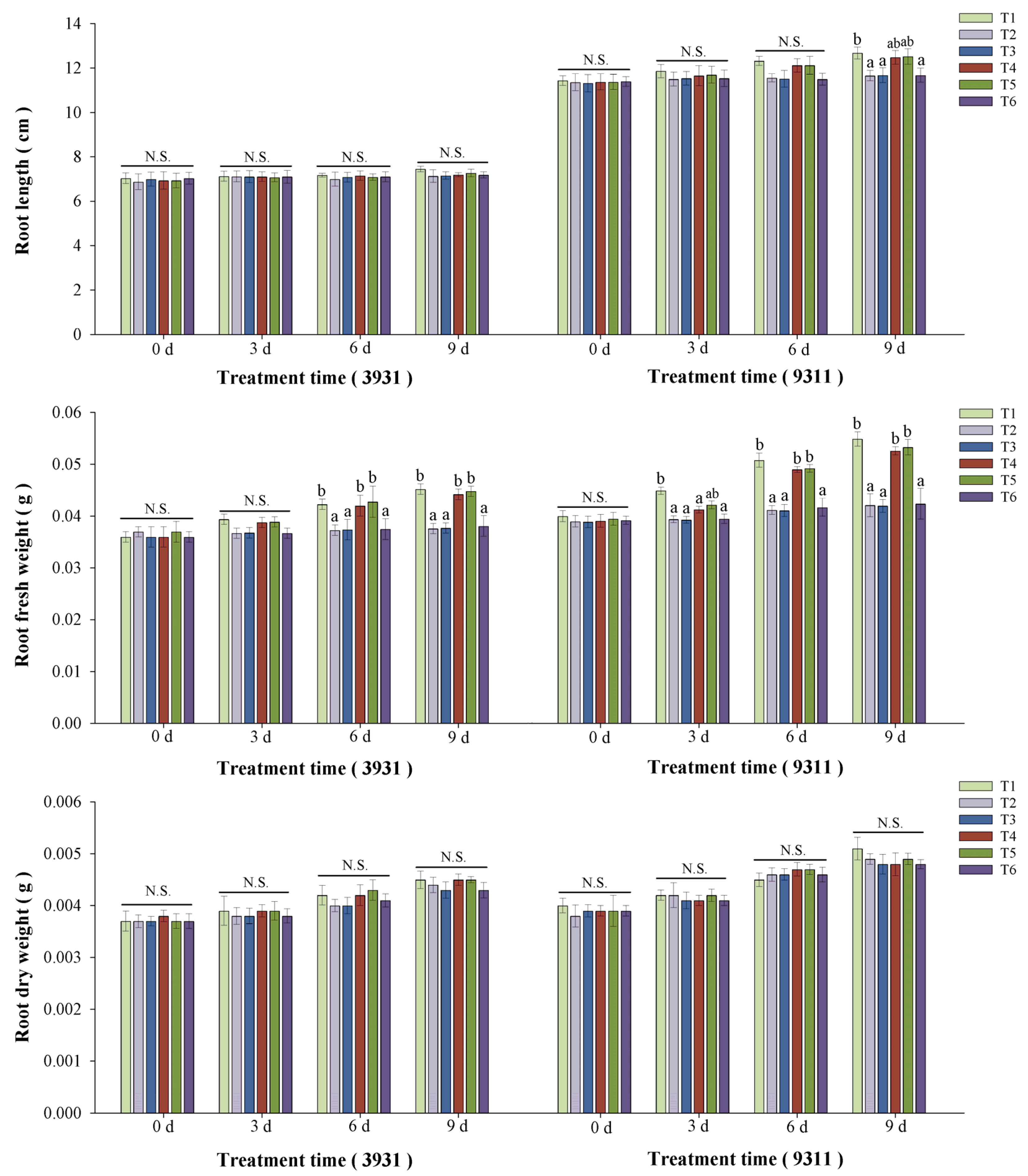
2.5. Effects of Salt Stress and Bacterial Inoculation on Plant Growth Parameters
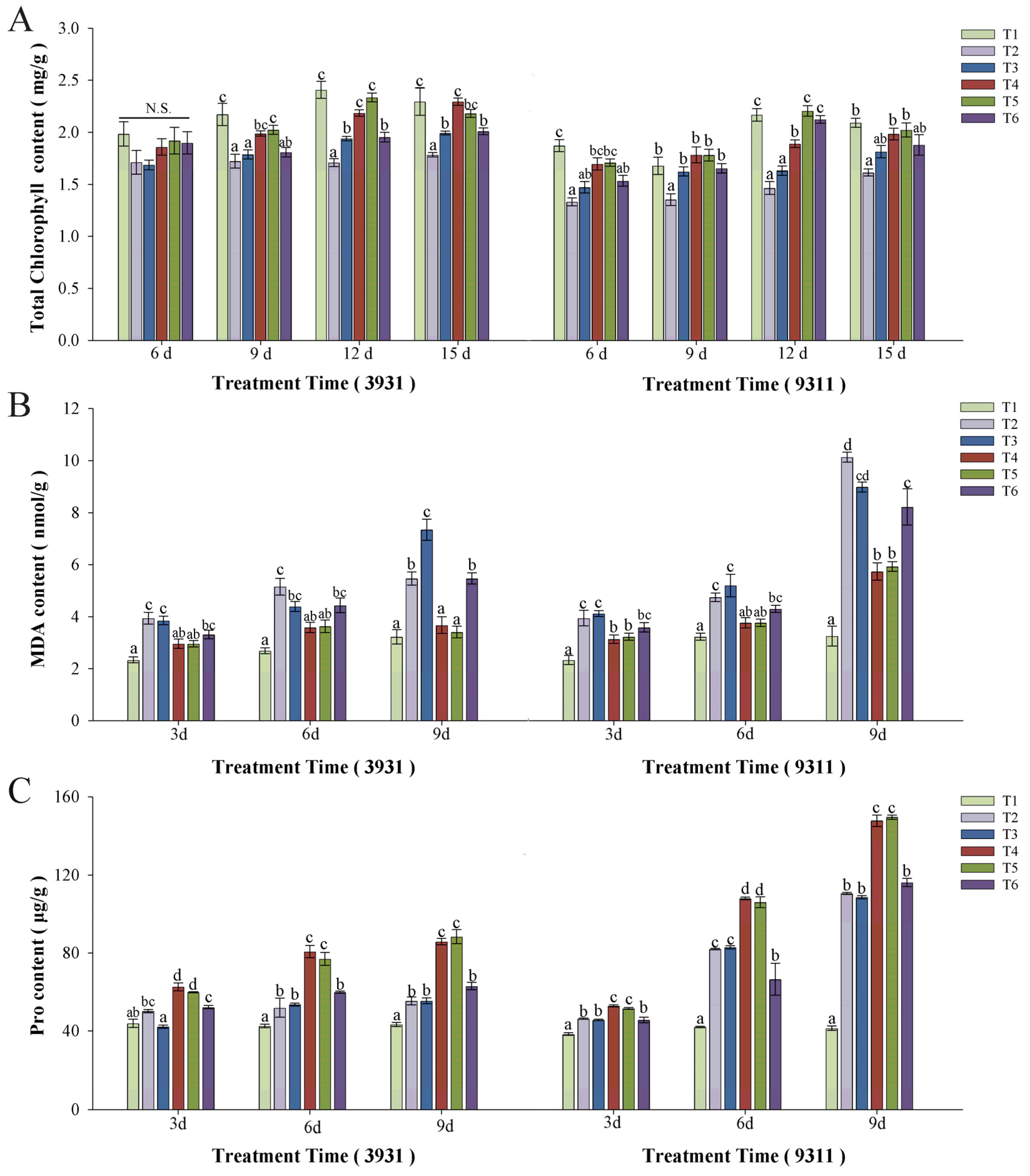
2.6. Effects of Salt Stress and Bacterial Inoculation on Chlorophyll Content, Malondialdehyde (MDA), and Proline (Pro)
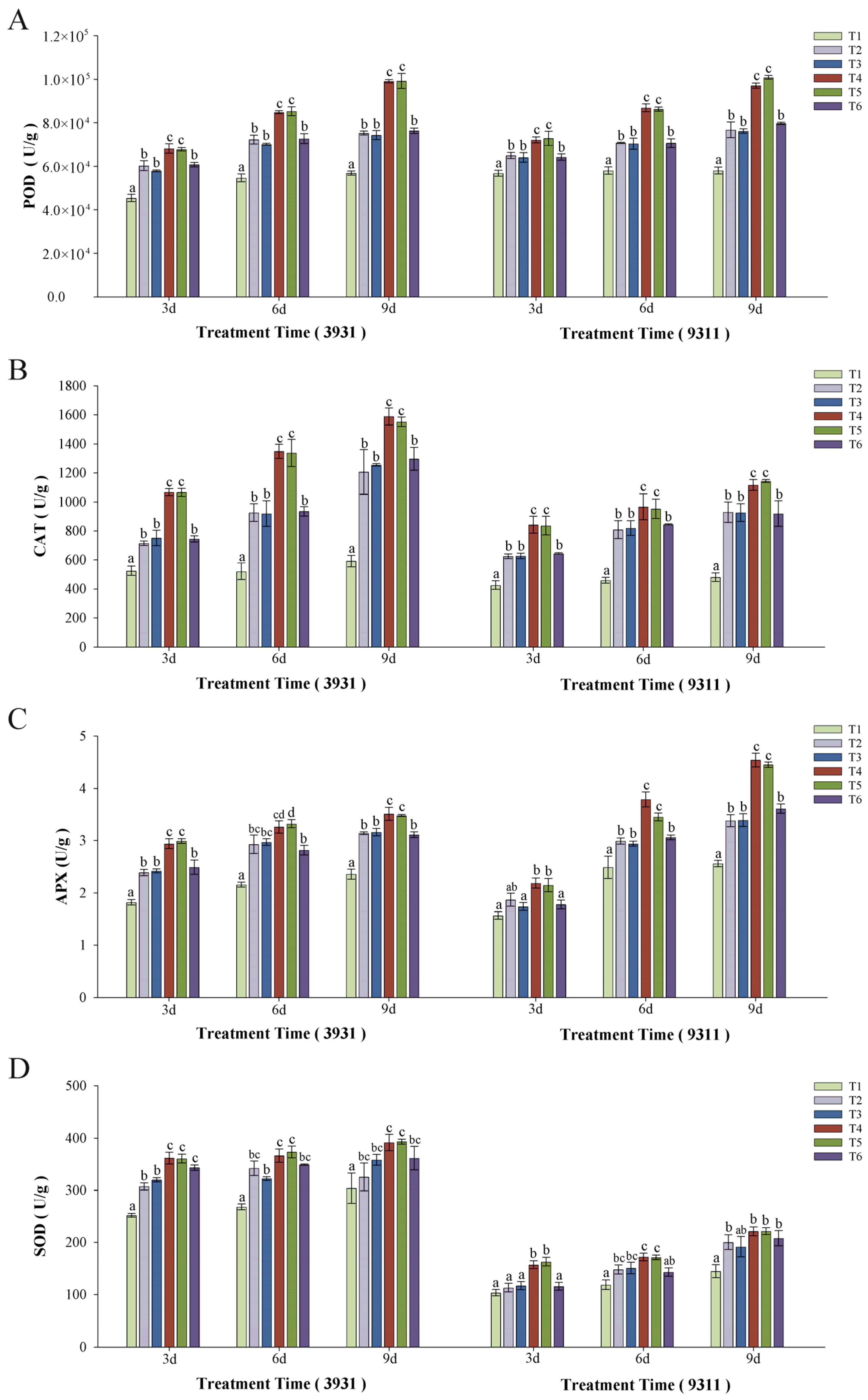
2.7. Effects of Salt Stress and Bacteria Inoculation on Antioxidant Enzyme Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Microbial Cultivation and Salt Stress Tolerance Assay
4.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
4.3. Genome Sequencing of the RH-AZ Strain
4.3.1. Genomic DNA Extraction
4.3.2. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Functional Annotation
4.4. Genome Characteristics of the RH-AZ Strain
4.5. Genomic Analysis and Functional Annotation
4.6. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
4.7. Plant Salt Stress and Treatment Applications
4.8. Effect of RH-AZ Inoculation on Rice Growth Parameters Under Salt Stress
4.9. Analysis of Chlorophyll, Malondialdehyde, Proline, and Antioxidant Enzyme Activities
4.10. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Otlewska, A.; Migliore, M.; Dybka-Stezpien, K.; Manfredini, A.; Struszczyk-Swita, K.; Napoli, R.; Białkowska, A.; Canfora, L.; Pinzari, F. When salt meddles between plant, soil, and microorganisms. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 553087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilangumaran, G.; Smith, D.L. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria in amelioration of salinity stress: A systems biology perspective. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosleh, M.K.; Hassan, Q.K.; Chowdhury, E.H. Application of remote sensors in Mapping rice area and forecasting its production: A review. Sensors 2015, 15, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.; Zhang, J.H.; Zhong, C.; Zhu, L.F.; Cao, X.C.; Yu, S.M.; James, A.B.; Hu, J.J.; Jin, Q.Y. Effects of salt stress on rice growth, development characteristics, and the regulating ways: A review. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 2357–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Gan, L.Z.; Wang, C.Y.; He, T.X. Salt-tolerant plant growth-promoting bacteria as a versatile tool for combating salt stress in crop plants. Arch. Microbiol. 2024, 206, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, J.; Prakash, J.; Arora, N.K. Role of beneficial soil microbes in sustainable agriculture and environmental management. Clim. Change Environ. Sustain. 2016, 4, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R. Comparative physiology of salt and water stress. Plant Cell Environ. 2002, 25, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimal, S.R.; Patel, V.K.; Singh, J.S. Plant growth promoting Curtobacterium albidum strain SRV4: An agriculturally important microbe to alleviate salinity stress in paddy plants. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 105, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugtenberg, B.J.; Malfanova, N.; Kamilova, F.; Berg, G. Plant growth promotion by microbes. In Molecular Microbial Ecology of the Rhizosphere, 1st ed.; Bruijn, F.J.D., Ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 559–573. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, O.M.B.; Slimene, I.B.; Zribi, O.T.; Abdelly, C.; Djébali, N. Response to salt stress is modulated by growth-promoting rhizobacteria inoculation in two contrasting barley cultivars. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2017, 39, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, S.; Paul, S.C.; Parveen, S.; Alam, S.; Rahman, N.; Jannat, B.; Hoque, S.; Rahman, M.T.; Karim, M.M. Isolation and identification of salt-tolerant plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria and their application for rice cultivation under salt stress. Can. J. Microbiol. 2020, 66, 144–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, C.; Feng, Q.; Liou, R.M.; Lin, Y.F. Biological inoculant of salt-tolerant bacteria for plant growth stimulation under different saline soil conditions. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 31, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egamberdieva, D.; Jabborova, D.; Hashem, A. Pseudomonas induces salinity tolerance in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) and resistance to Fusarium root rot through the modulation of indole-3-acetic acid. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 22, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, P.K.; Kumari, N.; Gupta, A.; Manzar, N. Rhizospheric and endophytic microorganisms and their role in alleviation of salinity stress in plants. In Plant, Soil and Microbes in Tropical Ecosystems, 1st ed.; Dubey, S.K., Verma, S.K., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2021; pp. 19–37. [Google Scholar]
- Kushwaha, P.; Kashyap, P.L.; Bhardwaj, A.K.; Kuppusamy, P.; Srivastava, A.K.; Tiwari, R.K. Bacterial endophyte mediated plant tolerance to salinity: Growth responses and mechanisms of action. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 36, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerrouk, I.Z.; Benchabane, M.; Khelifi, L.; Yokawa, K.; Ludwig-Muller, J.; Baluska, F. A Pseudomonas strain isolated from date-palm rhizospheres improves root growth and promotes root formation in maize exposed to salt and aluminum stress. J. Plant Physiol. 2016, 191, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Jha, P.N. Alleviation of salinity-induced damage on wheat plant by an ACC deaminase-producing halophilic bacterium Serratia sp. SL12 isolated from a salt lake. Symbiosis 2016, 69, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, R.H.; Song, H.G. Effects of application of Rhodopseudomonas sp. on seed germination and growth of tomato under axenic conditions. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 17, 1805–1810. [Google Scholar]
- Sakpirom, J.; Kantachote, D.; Nunkaew, T.; Khan, E. Characterizations of purple non-sulfur bacteria isolated from paddy fields, and identification of strains with potential for plant growth-promotion, greenhouse gas mitigation and heavy metal bioremediation. Res. Microbiol. 2017, 168, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantha, T.; Kantachote, D.; Klongdee, N. Potential of biofertilizers from selected Rhodopseudomonas palustris strains to assist rice (Oryza sativa L. subsp. indica) growth under salt stress and to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Ann. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 2109–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantachote, D.; Nunkaew, T.; Kantha, T.; Chaiprapat, S. Biofertilizers from Rhodopseudomonas palustris strains to enhance rice yields and reduce methane emissions. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 100, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokat, S.; Großkinsky, D.K. Tackling salinity in sustainable agriculture-what developing countries may learn from approaches of the developed world. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, J.F. Anoxygenic phototrophic bacteria. In Methods in Aquatic Bacteriology; Austin, B., Ed.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1988; pp. 207–240. [Google Scholar]
- Imhoff, J.F.; Trüper, H.G. The genus Rhodospirillum and related genera. In The Prokaryotes, 2nd ed.; Balows, A., Trüper, H.G., Dworkin, M., Harder, W., Schleifer, K.H., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 2141–2155. [Google Scholar]
- Hiraishi, A.; Urata, K.; Satoh, T. A new genus of marine budding phototrophic bacteria, Rhodobium gen. nov., which includes Rhodobium orientis sp. nov. and Rhodobium marinum comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1995, 45, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Pandey, R.; Chauhan, N.S. Unveiling wheat growth promotion potential of phosphate solubilizing Pantoea agglomerans PS1 and PS2 through genomic, physiological, and metagenomic characterizations. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1467082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Ma, J.B.; Huang, Y.; Muhammad, M.; Lian, H.T.; Shurigin, V.; Egamberdieva, D.; Li, W.J.; Li, L. Insight into endophytic microbial diversity in two halophytes and plant beneficial attributes of Bacillus swezeyi. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1447755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Estepa, R.; Argandoña, M.; Reina-Bueno, M.; Capote, N.; Iglesias-Guerra, F.; Nieto, J.J.; Vargas, C. The ectD gene, which is involved in the synthesis of the compatible solute hydroxyectoine, is essential for thermoprotection of the halophilic bacterium Chromohalobacter salexigens. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 3774–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, P.; Li, H.; Yu, Y.J.; Gu, J.D.; Liu, Y.D. Ectoine and 5-hydroxyectoine accumulation in the halophile Virgibacillus halodenitrificans PDB-F2 in response to salt stress. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 6779–6789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waditee-Sirisattha, R.; Kageyama, H. Halotolerance, stress mechanisms, and circadian clock of salt-tolerant cyanobacteria. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 1129–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csitári, B.; Bedics, A.; Felföldi, T.; Boros, E.; Nagy, H.; Máthé, I.; Székely, A.J. Anion-type modulates the effect of salt stress on saline lake bacteria. Extremophiles 2022, 26, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Yoshidome, D.; Hidaka, M.; Araki, Y.; Ito, K.; Kosono, S.; Nishiyama, M. Improvement of the nitrogenase activity in Escherichia coli that expresses the nitrogen fixation-related genes from Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2024, 728, 150345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, F.; Sun, J.K.; Ren, Y.; He, B.; Li, J.; Yang, S.; Li, W. Transcriptomic and enzymatic analysis reveals the roles of glutamate dehydrogenase in Corynebacterium glutamicum. AMB Express 2022, 12, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.J.; Luo, L.; Xie, D.T.; Li, Z.L. Dissimilatory Nitrate Reduction to Ammonium in Four Pseudomonas spp. under Aerobic Conditions. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etesami, H.; Glick, B.R. Bacterial Indole-3-Acetic Acid: A Key Regulator for Plant Growth, Plant-Microbe Interactions, and Agricultural Adaptive Resilience. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 281, 127602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.T.; Li, Y.K.; Zhang, L.L.; Mu, J.T.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Fu, H.L.; Zhang, Y.F.; Cui, H.F.; Yu, X.P.; Ye, Z.H. Biosynthetic Pathways and Functions of Indole-3-Acetic Acid in Microorganisms. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, X.Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.H.; Huang, L.F.; Luo, Y.R. Isolation and Plant Growth Promotion Effect of Endophytic Siderophore-Producing Bacteria: A Study on Halophyte Sesuvium portulacastrum. Plants 2024, 13, 2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timofeeva, A.M.; Galyamova, M.R.; Sedykh, S.E. Plant Growth-Promoting Soil Bacteria: Nitrogen Fixation, Phosphate Solubilization, Siderophore Production, and Other Biological Activities. Plants 2023, 12, 4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.L.; Zhou, F.Y.; Zhou, J.B.; Harvey, P.R.; Yu, H.Y.; Zhang, G.Z.; Zhang, X.J. Genomic analysis of Pseudomonas asiatica JP233: An efficient phosphate-solubilizing bacterium. Genes 2022, 13, 2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín, J.F.; Liras, P. Molecular mechanisms of phosphate sensing, transport and signalling in Streptomyces and related actinobacteria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrão, S.; Schmöckel, S.M.; Tester, M. Evaluating physiological responses of plants to salinity stress. Ann. Bot. 2017, 119, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karumannil, S.; Khan, T.A.; Kappachery, S.; Gururani, M.A. Impact of Exogenous Melatonin Application on Photosynthetic Machinery under Abiotic Stress Conditions. Plants 2023, 12, 2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, T.; Ali, S.; Seleiman, M.F.; Naveed, N.H.; Ali, A.; Ahmed, K.; Abid, M.; Rizwan, M.; Shahid, M.R.; Alotaibi, M.; et al. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria alleviates drought stress in potato in response to suppressive oxidative stress and antioxidant enzymes activities. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazerooni, E.A.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Al-Sadi, A.M.; Kang, S.M.; Yun, B.W.; Lee, I.J. Biocontrol potential of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens against Botrytis pelargonii and Alternaria alternata on Capsicum annuum. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavi Kishor, P.B.; Sreenivasulu, N. Is proline accumulation per se correlated with stress tolerance or is proline homeostasis a more critical issue? Plant Cell Environ. 2014, 37, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.Q.; Lei, P.; Pang, X.; Li, H.S.; Feng, X.H.; Xu, H. Exogenous application of poly-γ-glutamic acid enhances stress defense in Brassica napus L. seedlings by inducing cross-talks between Ca2+, H2O2, brassinolide, and jasmonic acid in leaves. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 118, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.T.T.; Das Bhowmik, S.; Long, H.; Cheng, Y.; Mundree, S.; Hoang, L.T.M. Rapid accumulation of proline enhances salinity tolerance in Australian wild rice Oryza australiensis domin. Plants 2021, 10, 2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofo, A.; Scopa, A.; Nuzzaci, M.; Vitti, A. Ascorbate peroxidase and catalase activities and their genetic regulation in plants subjected to drought and salinity stresses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, R.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, M.D.; Kwon, S.Y.; Cho, K.; Lee, H.S.; Kwak, S.S. Simultaneous expression of choline oxidase, superoxide dismutase and ascorbate peroxidase in potato plant chloroplasts provides synergistically enhanced protection against various abiotic stresses. Physiol. Plant. 2010, 138, 520–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuo, J.; Chen, Y.Y.; Lu, P.Z.; Liu, M.; Sun, P.; Zhang, Z.M. Roles of endophytic bacteria in Suaeda salsa grown in coastal wetlands: Plant growth characteristics and salt tolerance mechanisms. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, K. Preparation of genomic DNA from bacteria. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2001, 56, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA 11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witham, F.H.; Blaydes, D.F.; Devin, R.M. Experiments in Plant Physiology; Von Nostrand Reinhold Company: New York, NY, USA, 1971; pp. 55–58. [Google Scholar]
- Sadasivam, S.; Manickam, A. Biochemical Methods; New Age International Publishers: New Delhi, India, 1997; pp. 187–188. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Y.; Xu, C.; Tang, T.; Xie, X.; Huang, R.; Xiao, Y.; Shi, X.; Hu, H.; Liu, Y.; Peng, J.; et al. Functional Analyses of a Rhodobium marinum RH-AZ Genome and Its Application for Promoting the Growth of Rice Under Saline Stress. Plants 2025, 14, 2516. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162516
Gao Y, Xu C, Tang T, Xie X, Huang R, Xiao Y, Shi X, Hu H, Liu Y, Peng J, et al. Functional Analyses of a Rhodobium marinum RH-AZ Genome and Its Application for Promoting the Growth of Rice Under Saline Stress. Plants. 2025; 14(16):2516. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162516
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Yang, Cheng Xu, Tao Tang, Xiao Xie, Renyan Huang, Youlun Xiao, Xiaobin Shi, Huiying Hu, Yong Liu, Jing Peng, and et al. 2025. "Functional Analyses of a Rhodobium marinum RH-AZ Genome and Its Application for Promoting the Growth of Rice Under Saline Stress" Plants 14, no. 16: 2516. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162516
APA StyleGao, Y., Xu, C., Tang, T., Xie, X., Huang, R., Xiao, Y., Shi, X., Hu, H., Liu, Y., Peng, J., & Zhang, D. (2025). Functional Analyses of a Rhodobium marinum RH-AZ Genome and Its Application for Promoting the Growth of Rice Under Saline Stress. Plants, 14(16), 2516. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162516







